Examining the Link Between Problematic Smartphone Use and Substance Use Disorders Among College Students: Association Patterns Using Network Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Type and Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Data Analysis
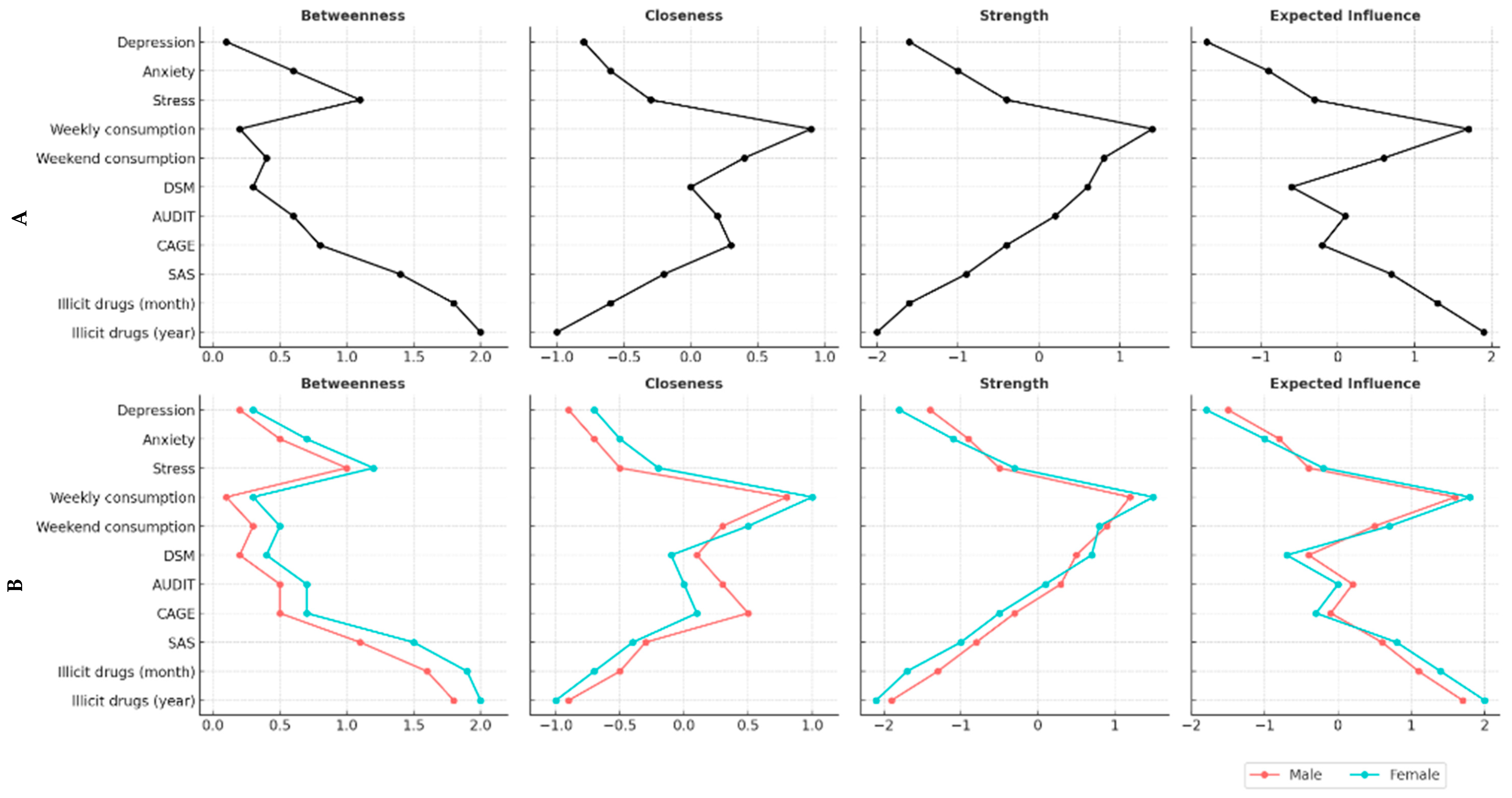
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reichert, R.A.; Andrade, A.L.M.; De Micheli, D. (Eds.) Neuropsychology and Substance Use Disorders: Assessment and Treatment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Darcq, E.; Kieffer, B.L. Neuroscience and Addiction Research: Current Advances and Perspectives. J. Neural Transm. 2024, 131, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nall, R.W.; Heinsbroek, J.A.; Nentwig, T.B.; Kalivas, P.W.; Bobadilla, A.C. Circuit Selectivity in Drug versus Natural Reward Seeking Behaviors. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 1450–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, J.; Munding, C.; Schmitgen, M.M.; Wolf, N.D.; Sambataro, F.; Hirjak, D.; Kubera, K.M.; Koenig, J.; Wolf, R.C. Structural and Functional Correlations of Smartphone Addiction. Addict. Behav. 2020, 105, 106334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, H.; Wiers, R.W.; Su, S.; Cousijn, J. Excessive Smartphone Use and Addiction: When Harms Start Outweighing Benefits. Addiction 2023, 118, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León Méndez, M.; Padrón, I.; Fumero, A.; Marrero, R.J. Effects of Internet and Smartphone Addiction on Cognitive Control in Adolescents and Young Adults: A Systematic Review of fMRI Studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 159, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Kuhn, A.; Puga, J.L.; Flores, P.; Ruiz-Ruano, A.M. From non-problematic smartphone use to smartphone addiction: Impulsivity-based profiles. Del uso no problemático a la adicción al móvil: Perfiles de impulsividad. Adicciones 2024, 36, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.L.M.; Passos, M.A.Z.; Vellozo, E.P.; Schoen, T.H.; Kulik, M.A.; Niskier, S.R.; de Souza Vitalle, M.S. The Contextual Factors Associated with Co-occurring Substance and Problematic Internet Use in Adolescence: A Network Approach. Trends Psychol. 2022, 32, 1252–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, H.; Itani, O.; Osaki, Y.; Higuchi, S.; Jike, M.; Kaneita, Y.; Kanda, H.; Nakagome, S.; Ohida, T. The Association between Alcohol Use and Problematic Internet Use: A Large-Scale Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study of Adolescents in Japan. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, J.; Akre, C.; Berchtold, A.; Suris, J.C. Problematic Internet Use Is Associated with Substance Use in Young Adolescents. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, J.J.; Forbes, M.K.; Almquist, Z.W.; Menk, J.S.; Thuras, P.; Unruh, A.S.; Kushner, M.G. A network approach to modeling comorbid internalizing and alcohol use disorders. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2017, 126, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, S.; Gainsbury, S.M.; Starcevic, V.; Richard, J.B.; Beck, F.; Billieux, J. Gender differences in gambling preferences and problem gambling: A network-level analysis. Int. Gambl. Stud. 2018, 18, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sârbu, E.A.; Marici, M.; Bostan, S.; Gavrila-Ardelean, L. Physical and Recreational Activities, Sedentary Screen Time, Time Spent with Parents and Drug Use in Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, P.K.; Li, J.B.; Jiang, H.; Lau, J.T.F. Problematic Internet Use and Smoking among Chinese Junior Secondary Students: The Mediating Role of Depressive Symptomatology and Family Support. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustiniani, J.; Nicolier, M.; Diwoux, A.; Chabin, T.; Pazart, L.; Haffen, E.; Gabriel, D. Impact of Online Poker Gambling on Behavioural and Neurophysiological Responses to a Virtual Gambling Task. Addict. Biol. 2024, 29, e13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.; Marian, M.; Drăgoi, A.M.; Costea, R.V. Understanding the Genetics and Neurobiological Pathways Behind Addiction (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Timmeren, T.; van Holst, R.J.; Goudriaan, A.E. Striatal Ups or Downs? Neural Correlates of Monetary Reward Anticipation, Cue Reactivity and Their Interaction in Alcohol Use Disorder and Gambling Disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 2023, 12, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Lim, C.C.W.; Rutherford, B.N.; Huang, S.; Ashley, D.P.; Johnson, B.; Chung, J.; Chan, G.C.K.; Coates, J.M.; Gullo, M.J.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Youth Drinking, Self-Posting of Alcohol Use and Other Social Media Engagement (2012–21). Addiction 2024, 119, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qeadan, F.; Egbert, J.; English, K. Associations Between Problematic Internet Use and Substance Misuse Among US College Students. Comput. Human Behav. 2022, 134, 107327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessor, R. Problem-Behavior Theory, Psychosocial Development, and Adolescent Problem Drinking. Br. J. Addict. 1987, 82, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.C.; Obong’o, C.O.; Chavan, P.; Vander Weg, M.W.; Ward, K.D. Applying the Problem Behavior Theory to Adolescent Drug Use Among a Cross-Sectional Sample of Boys Participating in a Community-Based Youth Organization. Subst. Use Misuse 2018, 53, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón-Arbués, E.; Granada-López, J.M.; Martínez-Abadía, B.; Echániz-Serrano, E.; Antón-Solanas, I.; Nash, M. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Problematic Internet Use in a Population of Spanish University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahjehan, A.; Shah, S.I.; Qureshi, J.A.; Wajid, A. A Meta-Analysis of Smartphone Addiction and Behavioral Outcomes. Int. J. Manag. Stud. 2021, 28, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Chen, J.S.; Huang, S.W.; Potenza, M.N.; Su, J.A.; Chang, K.C.; Pakpour, A.H.; Lin, C.Y. Problematic Smartphone Use and Two Types of Problematic Use of the Internet and Self-Stigma among People with Substance Use Disorders. Addict. Behav. 2023, 147, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.A.; de Oliveira, L.G.; da Silva, G.T.; Scatena, A.; Kim, H.S.; Andrade, A.L.M. Validation of Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) in Brazilian Colleges: Network Analysis, Measurement Invariance and Screening Efficiency. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M.A.; Furlanetto, L.M. Validity of the CAGE Questionnaire for Screening Alcohol-Dependent Inpatients on Hospital Wards. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2005, 27, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobell, L.C.; Sobell, M.B. Timeline follow-back: A technique for assessing self-reported alcohol consumption. In Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychosocial and Biological Methods; Litten, R.Z., Allen, J.P., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar]
- House of Commons; Science and Technology Committee. Alcohol Guidelines: Eleventh Report of Session 102. 2011. Available online: https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201012/cmselect/cmsctech/1536/1536.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the Development of Medicinal Products for the Treatment of Alcohol Dependence. EMEA/CHMP/EWP/20097/2008. 2010. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-development-medicinal-products-treatment-alcohol-dependence_en.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- De Micheli, D.; Formigoni, M.L. Screening of Drug Use in a Teenage Brazilian Sample Using the Drug Use Screening Inventory (DUSI). Addict. Behav. 2000, 25, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.L.M.; Kim, D.J.; Caricati, V.V.; Martins, G.D.G.; Kirihara, I.K.; Barbugli, B.C.; De Micheli, D. Validity and Reliability of the Brazilian Version of the Smartphone Addiction Scale-Short Version for University Students and Adult Population. Estud. Psicol. 2020, 37, e190117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patias, N.D.; Machado, W.D.L.; Bandeira, D.R.; Dell’Aglio, D.D. Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS-21)—Short Form: Adaptation and Validation for Brazilian Adolescents. Psico-USF 2016, 21, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.G.; Marti, C.N.; Choi, B.Y. Perceived Risk of Binge Drinking among Older Alcohol Users: Associations with Alcohol Use Frequency, Binge Drinking, Alcohol Use Disorder, and Alcohol Treatment Use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Götestam, K.G. Internet addiction: Characteristics of a questionnaire and prevalence in Norwegian youth (12–18 years). Scand. J. Psychol. 2004, 45, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Son, H.; Park, M.; Han, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, B.; Gwak, H. Internet Overuse and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Adolescents. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 63, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Johnson, C.A.; Palmer, P.; Arpawong, T.E.; Unger, J.B.; Xie, B.; Rohrbach, L.A.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; Sussman, S. Concurrent and Predictive Relationships Between Compulsive Internet Use and Substance Use: Findings from Vocational High School Students in China and the USA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| PSU | nPSU | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | χ2 | p | Effect | |
| Gender | 8.03 | *** | 0.05 | ||||
| Male | 360 | 24.5 | 483 | 29.0 | |||
| Female | 1107 | 75.5 | 1180 | 71.0 | |||
| Ethnic origin | 1.57 | 0.45 | 0.02 | ||||
| Caucasian | 954 | 68.3 | 1059 | 66.6 | |||
| Brown | 342 | 24.5 | 421 | 26.5 | |||
| Black | 101 | 7.2 | 110 | 6.9 | |||
| Marital Status | 2.55 | 0.11 | 0.03 | ||||
| Single | 1191 | 81.2 | 1312 | 78.9 | |||
| Married | 276 | 18.8 | 351 | 21.1 | |||
| Have a religion? | 12.23 | *** | 0.06 | ||||
| Yes | 890 | 60.7 | 1109 | 66.7 | |||
| No | 577 | 39.3 | 554 | 33.3 | |||
| Who you live with | 10.6 | * | 0.06 | ||||
| Family members | 869 | 59.2 | 946 | 56.9 | |||
| Parents | 383 | 26.1 | 505 | 30.4 | |||
| Roommates | 90 | 6.1 | 72 | 4.3 | |||
| Alone | 125 | 8.5 | 140 | 8.4 | |||
| Employment status | 10.01 | ** | 0.06 | ||||
| Employed | 544 | 37.1 | 709 | 42.6 | |||
| Unemployed | 410 | 27.9 | 426 | 25.6 | |||
| Never employed | 513 | 35.0 | 528 | 31.7 | |||
| University type | 1.55 | 0.21 | 0.02 | ||||
| Private | 1143 | 77.9 | 1326 | 79.7 | |||
| Public | 324 | 22.1 | 337 | 20.3 | |||
| PSU | PSU | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | χ2 | p | Effect | |
| Illicit drugs | 15.61 | *** | 0.07 | ||||
| Yes | 205 | 14.0 | 157 | 9.4 | |||
| No | 1262 | 86.0 | 1506 | 90.6 | |||
| Alcohol | 32.6 | *** | 0.10 | ||||
| Yes | 831 | 56.6 | 772 | 46.4 | |||
| No | 636 | 43.4 | 891 | 53.6 | |||
| Cigarettes | 3.13 | 0.07 | 0.03 | ||||
| Yes | 184 | 12.5 | 175 | 10.5 | |||
| No | 1283 | 87.5 | 1488 | 89.5 | |||
| E-cigarettes | 7.44 | ** | 0.05 | ||||
| Yes | 99 | 6.7 | 75 | 4.5 | |||
| No | 1368 | 93.3 | 1588 | 95.5 | |||
| Hookah | 4.08 | * | 0.03 | ||||
| Yes | 98 | 6.7 | 83 | 5.0 | |||
| No | 1369 | 93.3 | 1580 | 95.0 | |||
| Marijuana | 13.97 | *** | 0.07 | ||||
| Yes | 198 | 13.5 | 154 | 9.3 | |||
| No | 1269 | 86.5 | 1508 | 90.7 | |||
| Cocaine | 0.10 | 0.74 | 0.00 | ||||
| Yes | 10 | 0.7 | 13 | 0.8 | |||
| No | 1457 | 99.3 | 1649 | 99.2 | |||
| Amphetamines | 9.03 | ** | 0.05 | ||||
| Yes | 27 | 1.8 | 11 | 0.7 | |||
| No | 1440 | 98.2 | 1652 | 99.3 | |||
| Benzodiazepines | 7.91 | ** | 0.05 | ||||
| Yes | 58 | 4.0 | 37 | 2.2 | |||
| No | 1409 | 96.0 | 1626 | 97.8 | |||
| UPS | nUPS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | χ2 | p | Effect | |
| Illicit drugs | 31.7 | *** | 0.10 | ||||
| Yes | 375 | 25.6 | 288 | 17.3 | |||
| No | 1092 | 74.4 | 1375 | 82.4 | |||
| Alcohol | 55.7 | *** | 0.13 | ||||
| Yes | 1107 | 75.5 | 1049 | 63.1 | |||
| No | 360 | 24.5 | 614 | 36.9 | |||
| Cigarettes | 6.93 | ** | 0.05 | ||||
| Yes | 316 | 21.5 | 296 | 17.8 | |||
| No | 1151 | 78.5 | 1367 | 82.2 | |||
| E-cigarettes | 23.2 | *** | 0.09 | ||||
| Yes | 222 | 15.1 | 158 | 9.5 | |||
| No | 1245 | 84.9 | 1505 | 90.5 | |||
| Hookah | 20.4 | *** | 0.08 | ||||
| Yes | 245 | 16.7 | 185 | 11.1 | |||
| No | 1222 | 83.3 | 1478 | 88.9 | |||
| Marijuana | 29.3 | *** | 0.10 | ||||
| Yes | 367 | 25.0 | 285 | 17.1 | |||
| No | 1100 | 75.0 | 1378 | 82.9 | |||
| Cocaine | 1.65 | 0.20 | 0.02 | ||||
| Yes | 31 | 2.1 | 25 | 1.5 | |||
| No | 1436 | 97.9 | 1638 | 98.5 | |||
| Amphetamines | 17.5 | *** | 0.07 | ||||
| Yes | 60 | 4.1 | 27 | 1.6 | |||
| No | 1407 | 95.9 | 1636 | 98.4 | |||
| Benzodiazepines | 16.6 | *** | 0.07 | ||||
| Yes | 113 | 7.7 | 71 | 4.3 | |||
| No | 1354 | 92.3 | 1592 | 95.7 | |||
| UPS | nUPS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | χ2 | p | |
| Consumption Criteria | ||||||
| WHO | 2.39 | 0.12 | ||||
| At risk | 226 | 19.6 | 188 | 17.1 | ||
| No risk | 926 | 80.4 | 912 | 82.9 | ||
| UK | 1.73 | 0.21 | ||||
| At risk | 250 | 21.7 | 214 | 19.5 | ||
| No risk | 902 | 78.3 | 886 | 80.5 | ||
| 100 g or more of alcohol | 2.58 | 0.10 | ||||
| 0 g | 774 | 66.9 | 767 | 70.0 | ||
| ≥100 g | 383 | 33.1 | 328 | 30.0 | ||
| DSM-5 | 37.9 | *** | ||||
| No addiction | 683 | 59.0 | 780 | 71.2 | ||
| Mild addiction | 246 | 21.3 | 175 | 16.0 | ||
| Moderate addiction | 117 | 10.1 | 75 | 6.8 | ||
| Severe addiction | 111 | 9.6 | 65 | 5.9 | ||
| M | SD | M | SD | F | p | |
| AUDIT | ||||||
| Total score | 6.31 | 5.52 | 5.20 | 4.70 | 26.3 | *** |
| Alcohol consumption | 3.79 | 2.42 | 3.53 | 2.34 | 7.14 | ** |
| Drinking behavior | 0.55 | 1.37 | 0.31 | 1.05 | 20.8 | *** |
| Alcohol-related problems | 1.96 | 2.83 | 1.36 | 2.33 | 30.45 | *** |
| DSM-5 (Total symptoms) | 1.93 | 2.40 | 1.35 | 2.04 | 38.23 | *** |
| CAGE | ||||||
| Total score | 0.65 | 0.87 | 0.50 | 0.76 | 16.67 | *** |
| Weekend alcohol use | 3.31 | 4.34 | 2.88 | 4.13 | 5.73 | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vitta, A.S.L.; Oliveira, W.A.d.; Oliveira, L.G.d.; Silva, L.S.d.; Freires, É.M.; Semolini, F.F.; Baptista, M.N.; Romualdo, C.; Kim, H.S.; de Micheli, D.; et al. Examining the Link Between Problematic Smartphone Use and Substance Use Disorders Among College Students: Association Patterns Using Network Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22070973
Vitta ASL, Oliveira WAd, Oliveira LGd, Silva LSd, Freires ÉM, Semolini FF, Baptista MN, Romualdo C, Kim HS, de Micheli D, et al. Examining the Link Between Problematic Smartphone Use and Substance Use Disorders Among College Students: Association Patterns Using Network Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(7):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22070973
Chicago/Turabian StyleVitta, Amanda Severo Lins, Wanderlei Abadio de Oliveira, Lucio Garcia de Oliveira, Laura Soares da Silva, Évelin Moreira Freires, Fernando Ferreira Semolini, Makilim Nunes Baptista, Claudio Romualdo, Hyoun S. Kim, Denise de Micheli, and et al. 2025. "Examining the Link Between Problematic Smartphone Use and Substance Use Disorders Among College Students: Association Patterns Using Network Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 7: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22070973
APA StyleVitta, A. S. L., Oliveira, W. A. d., Oliveira, L. G. d., Silva, L. S. d., Freires, É. M., Semolini, F. F., Baptista, M. N., Romualdo, C., Kim, H. S., de Micheli, D., Scatena, A., & Andrade, A. L. M. (2025). Examining the Link Between Problematic Smartphone Use and Substance Use Disorders Among College Students: Association Patterns Using Network Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(7), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22070973








