Pharmaceuticals and Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Pathways and Distribution, Toxicological and Ecological Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sources and Distribution of Pharmaceuticals and Microplastics
2.1. Wastewater Discharge and WWTP Effluents
2.1.1. Pharmaceuticals
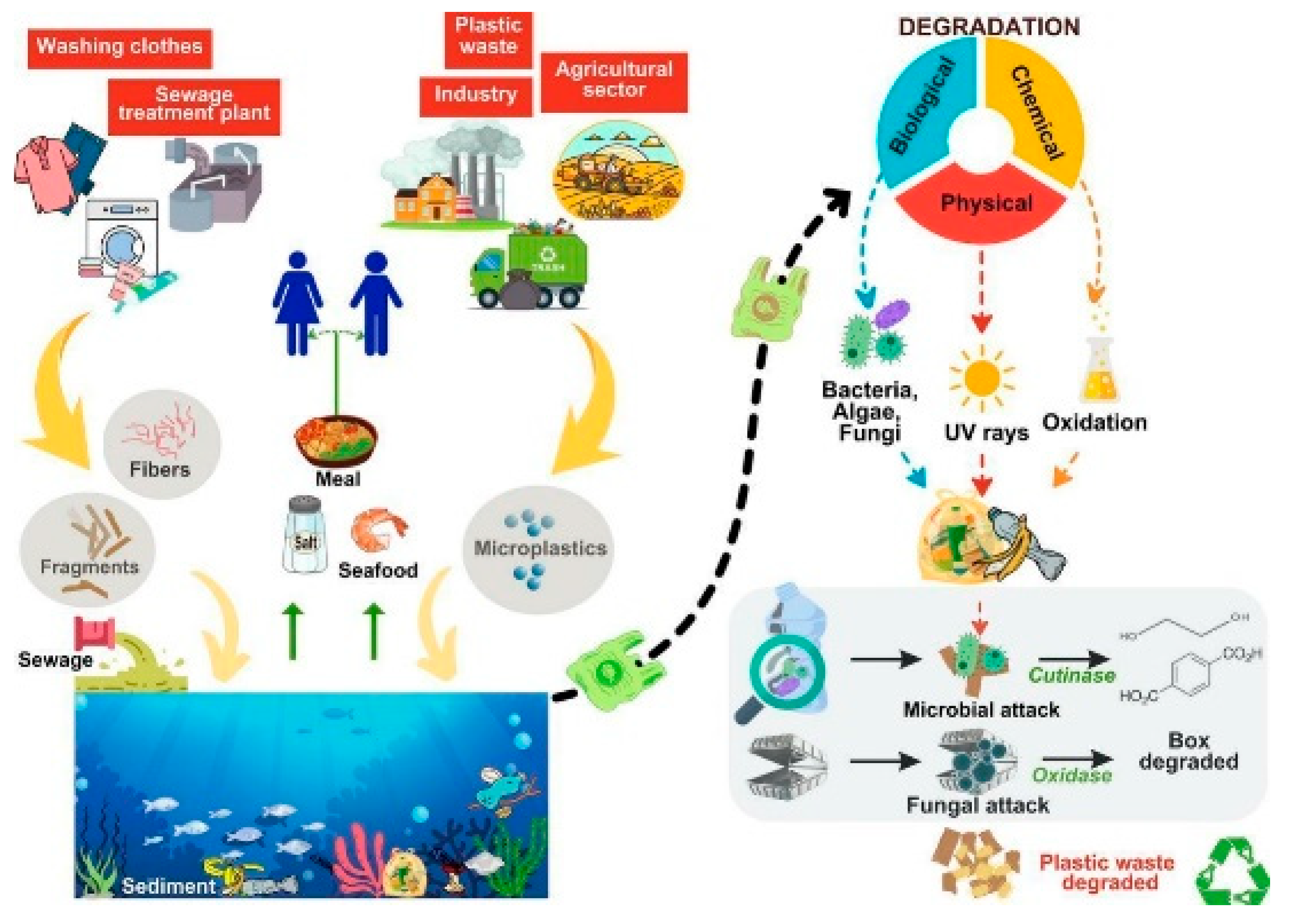
2.1.2. Microplastics
2.2. Agricultural Runoff
2.2.1. Pharmaceuticals
2.2.2. Microplastics
2.3. Aquaculture Operations
2.3.1. Pharmaceuticals
2.3.2. Microplastics
2.4. Land Application of Biosolids
2.4.1. Pharmaceuticals
2.4.2. Microplastics
2.5. Atmospheric Deposition
2.5.1. Pharmaceuticals
2.5.2. Microplastics
2.6. The Origins and Persistence of Microplastics and Pharmaceuticals in Aquatic Environments
2.7. Environmental and Toxicological Effects: Disadvantages
3. Effects on Freshwater Fish
3.1. The Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification of Pharmaceuticals Within Freshwater Food Chains
3.2. Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification of Microplastics in Aquatic Food Chain
4. Physiological Effects on Fish, Encompassing Effects on Growth, Reproduction, Immune System Performance, and Behavioral Modifications
4.1. Pharmaceuticals
4.1.1. Immune System and Toxicity Effects
4.1.2. Growth and Behavior
4.1.3. Reproduction
4.1.4. Hospital Wastewater and DNA Damage
4.2. Microplastics
4.2.1. Physiological Disorders in Fish Due to Microplastics (MPs)
4.2.2. Health Impacts of MPs on Fish
4.2.3. Specific Impact on Freshwater Fish
4.2.4. Accumulation of MPs and Organ Dysfunction
4.2.5. Broader Impact of MPs on Fish Health
5. Impacts on Fish
5.1. Ecological Effects of Pharmaceuticals on Fish Populations
5.2. Ecological Effects of Microplastics on Fish Populations
6. Impact on Human Health
7. Conclusions
8. Recommendations
8.1. Improving Wastewater Treatment Technologies
- Advanced Filtration Systems: Conventional wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are not fully effective in removing pharmaceutical residues and microplastics. Investing in membrane bioreactors (MBRs), advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) (e.g., ozonation, photocatalysis), and nanofiltration techniques have shown promising results in removing micropollutants [51].
- Biodegradation Strategies: Some micro-organisms, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus species, have demonstrated potential in breaking down pharmaceutical compounds, while enzymatic treatments could enhance MP degradation [270]. Scaling up these biological approaches could improve treatment efficiency.
- Regulatory Measures on Industrial and Hospital Effluents: Stricter discharge limits for pharmaceutical manufacturing plants and healthcare facilities can reduce the entry of active pharmaceutical ingredients into waterways. In Switzerland, for example, a nationwide program mandates WWTP upgrades to reduce micropollutants [271].
8.2. Strengthening Public Health Policies
- Risk-Based Monitoring of Water Supplies: Many regions lack systematic surveillance of pharmaceuticals and microplastics in drinking water. Countries like Germany and Sweden have implemented priority substance monitoring programs, which should be expanded globally to ensure public health safety.
- Universal Standards for Water Safety: There is no universal guideline for pharmaceutical contamination in water. The World Health Organization (WHO) and national agencies should collaborate on setting maximum allowable concentrations for pharmaceuticals, similar to existing standards for heavy metals.
8.3. Raising Public Awareness and Education
- Pharmaceutical Take-Back Programs: Many pharmaceuticals enter water systems due to improper disposal. Expanding drug take-back initiatives, like those in the United States (DEA National Prescription Drug Take-Back Day), can significantly reduce household pharmaceutical waste [272].
- Reducing Microplastic Pollution: Public awareness campaigns should highlight the impact of synthetic textiles and cosmetic products containing microplastics. Incentivizing the adoption of microplastic-free personal care products and promoting sustainable fashion choices can reduce MP emissions. The European Union’s Microplastic Restriction Initiative is an example of proactive policy action.
8.4. Investing in Research and Innovation
- Long-Term Toxicological Studies: More research is needed to understand the chronic health impacts of exposure to pharmaceuticals and microplastics. Ongoing studies on nanoplastics and endocrine-disrupting compounds should be expanded to assess long-term risks to aquatic life and human health [273].
- Eco-Friendly Material Development: Alternatives to microplastics, such as biodegradable biopolymers (e.g., polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs)), should be promoted for use in consumer products and medical applications. Investments in green chemistry approaches can lead to the development of less persistent pharmaceuticals with minimal environmental impact [274].
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaudry, M.H. Evaluating Non-Point Source Microplastic Pollution and Its Impact on Biota in the Huron River. Master’s Thesis, Eastern Michigan University, Ypsilanti, MI, USA, 2023. Available online: https://commons.emich.edu/theses (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Naidu, R.; Espana, V.A.A.; Liu, Y.; Jit, J. Emerging contaminants in the environment: Risk-based analysis for better management. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrull, J.; Colom, A.; Fabregas, J.; Pocurull, E.; Borrull, F. A simple, fast method for the analysis of 20 contaminants of emerging concern in river water using large-volume direct injection liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Česen, M.; Ahel, M.; Terzić, S.; Heath, D.J.; Heath, E. The occurrence of contaminants of emerging concern in Slovenian and Croatian wastewaters and receiving Sava river. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2446–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obimakinde, S.; Fatoki, O.; Opeolu, B.; Olatunji, O. Veterinary pharmaceuticals in aqueous systems and associated effects: An update. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3274–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Li, Y.; Song, B.; Zhou, C.; Gong, J.; Zeng, G. Smoked cigarette butts: Unignorable source for environmental microplastic fibers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, J.; Söderström, H.; Lindberg, R.H.; Phan, C.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.G.J. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes, M.D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OCED. Pharmaceutical Residues in Freshwater; OCED Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEachran, A.D.; Shea, D.; Bodnar, W.; Nichols, E.G. Pharmaceutical Occurrence in Groundwater and Surface Waters in Forests Land-Applied with Municipal Wastewater. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2015, 35, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Tenorio, R.; González-Juárez, E.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L.; Hernández-Ramírez, A. Review of occurrence of pharmaceuticals worldwide for estimating concentration ranges in aquatic environments at the end of the last decade. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 8, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aus der Beek, T.; Weber, A.; Bergmann, A.; Grüttner, G.; Carius, A. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Global Occurrence and Potential Cooperative Action under the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM); Umweltbundesamt Texte: Dessau-Roßlau, Germany, 2016; Volume 67, pp. 1862–4804. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330934183_Pharmaceuticals_in_the_environment_Global_occurrence_and_potential_cooperative_action_under_the_Strategic_Approach_to_International_Chemicals_Management_SAICM/figures?lo=1&utm_source=google&utm_medium=organic (accessed on 19 October 2024).
- Clara, M.; Strenn, B.; Gans, O.; Martinez, E.; Kreuzinger, N.; Kroiss, H. Removal of selected pharmaceuticals, fragrances and endocrine disrupting compounds in a membrane bioreactor and conventional wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4797–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charuaud, L.; Jardé, E.; Jaffrézic, A.; Liotaud, M.; Goyat, Q.; Mercier, F.; Le Bot, B. Veterinary pharmaceutical residues in water resources and tap water in an intensive husbandry area in France. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 664, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Gaur, A.; Suravajhala, R.; Chauhan, U.; Pant, M.; Tripathi, V.; Pant, G. Microplastic pollution: Understanding microbial degradation and strategies for pollutant reduction. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 905, 167098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarano, L.; Suarez, E.G.P.; Maggio, C.; La Marca, A.; Iovine, R.; Lofrano, G.; Guida, M.; Vaiano, V.; Carotenuto, M.; Libralato, G. Assessment of ecological risks posed by veterinary antibiotics in European aquatic environments: A comprehensive review and analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 954, 176280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Pascarella, L.; Parrella, A. Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Rani, L.; Grewal, A.S.; Srivastav, A.L. Impact of pharmaceuticals and antibiotics waste on the river ecosystem: A growing threat. In Ecological Significance of River Ecosystems: Challenges and Management Strategies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanand, A.C.; Mohapatra, S.; Tyagi, V.K. Microplastics in aquatic environment: Challenges and perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.S.; Singh, S. Microplastic Pollution: Threats and Impacts on Global Marine Ecosystems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sinha, J.K.; Ghosh, S.; Vashisth, K.; Han, S.; Bhaskar, R. Microplastics as an Emerging Threat to the Global Environment and Human Health. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roursgaard, M.; Rothmann, M.H.; Schulte, J.; Karadimou, I.; Marinelli, E.; Møller, P. Genotoxicity of Particles From Grinded Plastic Items in Caco-2 and HepG2 Cells. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 906430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniappan, S.; Sadacharan, C.M.; Rostama, B. Polystyrene and Polyethylene Microplastics Decrease Cell Viability and Dysregulate Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers of MDCK and L929 Cells In Vitro. Expo. Health 2022, 14, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputi, S.; Diomede, F.; Lanuti, P.; Marconi, G.D.; Di Carlo, P.; Sinjari, B.; Trubiani, O. Microplastics Affect the Inflammation Pathway in Human Gingival Fibroblasts: A Study in the Adriatic Sea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Araújo, A.N.; Fachini, A.; Pena, A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 45–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Chemicals Outlook II (GCO-II): From Legacies to Innovative Solutions | UNEP-UN Environment Programme. 2019. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/global-chemicals-outlook-ii-legacies-innovative-solutions (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Gevao, B.; Uddin, S.; Krishnan, D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Habibi, N. Antibiotics in Wastewater: Baseline of the Influent and Effluent Streams in Kuwait. Toxics 2022, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzhelele, E.P.; Ayinde, W.B.; Gitari, W.M.; Pindihama, G.K.; Mudzielwana, R. Occurrence of efavirenz, levonorgestrel, ibuprofen, and diclofenac in wastewaters of limpopo province, South Africa. Heliyon 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Björn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: Effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerranti, C.; Martellini, T.; Perra, G.; Scopetani, C.; Cincinelli, A. Microplastics in cosmetics: Environmental issues and needs for global bans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Muñoz, D.; Rodríguez, M.S.; Maulvault, A.; Tediosi, A.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Heuvel, F.V.D.; Kotterman, M.; Marques, A.; Barceló, D. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in macroalgaes, bivalves, and fish from coastal areas in Europe. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samal, K.; Mahapatra, S.; Ali, M.H. Pharmaceutical Wastewater as Emerging Contaminants (EC): Treatment Technologies, Impact on Environment and Human Health. Energy Nexus 2022, 6, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, A.B.A.; Rudd, M.A.; Brooks, B.W.; Caldwell, D.J.; Choi, K.; Hickmann, S.; Innes, E.; Ostapyk, K.; Staveley, J.P.; Verslycke, T.; et al. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in the Environment: What Are the Big Questions? Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakova, J.; Villar-Navarro, M.; Ramos-Payán, M.; Aranda-Merino, N.; Román-Hidalgo, C.; Bello-López, M.Á.; Fernández-Torres, R. Monitoring of pharmaceuticals in aquatic biota (Procambarus clarkii) of the Doñana National Park (Spain). J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Stumpf, M.; Mueller, J.; Haberer, K.; Wilken, R.-D.; Servos, M. Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence and risk assessment of pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater treatment plants. A case study: Seville city (Spain). Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Melis, M.; Fanelli, R. Source, occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Italian aquatic environment. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 179, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei, R.; Dzingelevičienė, R.; Abbasi, S.; Szultka-Młyńska, M.; Buszewski, B. Determination of the pharmaceuticals–nano/microplastics in aquatic systems by analytical and instrumental methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, P.; Reda, D.; Aida, B.; Alireza, L.; Malgorzata, M.; Nerijus, D.; Saulius, R.; Artūras, R.; Sajjad, A.; Robert, M.; et al. Pharmaceutical and Microplastic Pollution before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Surface Water, Wastewater, and Groundwater. Water 2022, 14, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, J.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (CAS) and advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlicchi, P.; Galletti, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Hospital effluents as a source of emerging pollutants: An overview of micropollutants and sustainable treatment options. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, D.; Horan, N. Handbook of Water and Wastewater Microbiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291139679 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Meric, S.; Nikolaou, A. Pharmaceutical residues in environmental waters and wastewater: Current state of knowledge and future research. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.L.; Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, A.N.; Bohnert, T.; Williams, D.A.; Gan, L.L.; Leduc, B.W. Mechanism of Drug-Drug Interactions between Warfarin and Statins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, A.N.; Grater, R.; Lulla, M.; Williams, D.A.; Gan, L.L.; Bohnert, T.; LeDuc, B.W. Comparison of enzyme kinetics of warfarin analyzed by LC–MS/MS QTrap and differential mobility spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1008, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblonde, T.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Hartemann, P. Emerging pollutants in wastewater: A review of the literature. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.J.S.; Naveed, S.A.; Tiwari, N.K.; Shashikumar, D.; Muzeeb, S.; Kumar, T.R.; Kumar, N.V.; Rao, N.P.; Srinivas, N.; Mullangi, R.; et al. Concurrent determination of ezetimibe and its phase-I and II metabolites by HPLC with UV detection: Quantitative application to various in vitro metabolic stability studies and for qualitative estimation in bile. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 853, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, J.; Dominic, J.A.; Achari, G.; Langford, C.H.; Tay, J.H. Effect of UV dose on degradation of venlafaxine using UV/H2O2: Perspective of augmenting UV units in wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojkovic, Z.; Lindberg, R.H.; Tysklind, M.; Funk, C. Northern green algae have the capacity to remove active pharmaceutical ingredients. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feier, B.; Ionel, I.; Cristea, C.; Sǎndulescu, R. Electrochemical behaviour of several penicillins at high potential. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12947–12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C. Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Gin, K.Y.H.; Lin, A.Y.C.; Reinhard, M. Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: Review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6062–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, J.B.; Gunther, F.A.; Gunther, J.D. (Eds.) Antibiotics in sediments and run-off waters from feedlots. In Residue Reviews; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984; Volume 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalling, K.L.; Kuivila, K.M.; Orlando, J.L.; Phillips, B.M.; Anderson, B.S.; Siegler, K.; Hunt, J.W.; Hamilton, M. Environmental fate of fungicides and other current-use pesticides in a central California estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M. An assessment of microplastic inputs into the aquatic environment from wastewater streams. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, A.; Assad, I.; Sofi, M.S.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Bhat, S.U. A global review of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Understanding their occurrence, fate and impact. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, M.; Hedström, A.; Kvarnström, E.; Österlund, H.; Nordqvist, K.; Herrmann, I. Treatment of greywater and presence of microplastics in on-site systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.L.; Jeong, J.; Eo, S.; Hong, S.H.; Shim, W.J. Occurrence and characteristics of microplastics in greywater from a research vessel. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, Á.T.; Navarro, S.; García-De-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Browne, M.A.; Halpern, B.S.; Hentschel, B.T.; Hoh, E.; Karapanagioti, H.K.; Rios-Mendoza, L.M.; Takada, H.; Teh, S.; Thompson, R.C. Classify plastic waste as hazardous. Nature 2013, 494, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GESAMP. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment (Part 1)|GESAMP. Available online: http://www.gesamp.org/publications/reports-and-studies-no-90 (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution–Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, D.P.; Lydy, M.J. Urban and agricultural sources of pyrethroid insecticides to the sacramento-san joaquin delta of California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Gros, M.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pena, A.; Barceló, D.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. Contribution of hospital effluents to the load of pharmaceuticals in urban wastewaters: Identification of ecologically relevant pharmaceuticals. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; de Pedro, C.; Paxeus, N. Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Coetsier, C.; Causserand, C.; Serrano, K.G. An experimental and modelling study of the electrochemical oxidation of pharmaceuticals using a boron-doped diamond anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, G.; Scheers, T.; Van Eyck, K.; Van Schepdael, A.; Adams, E.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Cabooter, D.; Dewil, R. Electrochemical oxidation of key pharmaceuticals using a boron doped diamond electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Lee, J.T.; Cho, J.Y. Fate, occurrence, and toxicity of veterinary antibiotics in environment. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2012, 55, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, I.E.; Bair, D.A.; Tate, K.W.; Parikh, S.J. Sorption, Leaching, and Surface Runoff of Beef Cattle Veterinary Pharmaceuticals under Simulated Irrigated Pasture Conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez-Couso, A.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Álvarez-Enjo, M.A.; Simal-Gándara, J.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M. Pollution of surface waters by metalaxyl and nitrate from non-point sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxall, A.B.A.; Johnson, P.; Smith, E.J.; Sinclair, C.J.; Stutt, E.; Levy, L.S. Uptake of veterinary medicines from soils into plants. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2006, 54, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeke, E.S.; Okoye, C.O.; Atakpa, E.O.; Ita, R.E.; Nyaruaba, R.; Mgbechidinma, C.L.; Akan, O.D. Microplastics in agroecosystems-impacts on ecosystem functions and food chain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santisteban, L.M.; Casalí, J.; López, J.J. Assessing soil erosion rates in cultivated areas of Navarre (Spain). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.; Wu, W. Use of Plastic Mulch in Agriculture and Strategies to Mitigate the Associated Environmental Concerns, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, R.; Zeyer, T.; Schmidt, A.; Fiener, P. Soil erosion as transport pathway of microplastic from agriculture soils to aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, H.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shu, S.; Zhang, J. Removal of polystyrene and polyethylene microplastics using PAC and FeCl3 coagulation: Performance and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; He, W.Q.; Yan, C.R. ‘White revolution’ to ‘white pollution’—Agricultural plastic film mulch in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 091001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, Z.; Wollmann, C.; Schaefer, M.; Buchmann, C.; David, J.; Tröger, J.; Muñoz, K.; Frör, O.; Schaumann, G.E. Plastic mulching in agriculture. Trading short-term agronomic benefits for long-term soil degradation? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.P. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahney, J.; Hallerud, M.; Heim, E.; Hahnenberger, M.; Sukumaran, S. Plastic rain in protected areas of the United States. Science 2020, 368, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradini, F.; Meza, P.; Eguiluz, R.; Casado, F.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Geissen, V. Geissen Evidence of microplastic accumulation in agricultural soils from sewage sludge disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico, A.; Satapornvanit, K.; Haque, M.M.; Min, J.; Nguyen, P.T.; Telfer, T.C.; Van den Brink, P.J. Use of chemicals and biological products in Asian aquaculture and their potential environmental risks: A critical review. Rev. Aquac. 2012, 4, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.; Elliott, J.; Lees, P. (Eds.) Comparative and Veterinary Pharmacology. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sorensen, B.; Nielsen, S.N.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Liitzhofl, H.C.H.; Jorgensen, S.E. Occurrence, Fate and Effects of Pharmaceutical Substances in the Environment-A Review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboubakr, M.; Soliman, A. Pharmacokinetics of danofloxacin in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) after intravenous and intramuscular administrations. Acta Vet. Hung. 2019, 67, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, J.S. Aquaculture production and biodiversity conservation. Bioscience 2009, 59, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xie, S.; Feng, K.; Wang, Q. Occurrence of microplastics in a pond-river-lake connection water system: How does the aquaculture process affect microplastics in natural water bodies. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 352, 131632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skirtun, M.; Sandra, M.; Strietman, W.J.; van den Burg, S.W.K.; De Raedemaecker, F.; Devriese, L.I. Plastic pollution pathways from marine aquaculture practices and potential solutions for the North-East Atlantic region. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T. Marine Litter and Aquaculture Gear: White Paper; Report Produced by Poseidon Aquatic Resources Management Ltd. for the Aquaculture Stewardship Council; Aquaculture Stewardship Council: London, UK, 2019; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Sandra, M.; Devriese, L.; De Raedemaecker, F.; Lonneville, B.; Lukic, I.; Altvater, S.; Compa, M.; Deudero, S.; Alomar, C.; Gin, I. Knowledge Wave on Marine Litter from Aquaculture Sources. D2.2 Aqua-Lit Project. Oostende, Belgium. 2020, p. 136. Available online: http://www.ba.ieo.es/es/investigacion/grupos-de-investigacion/impactsea/publicaciones/2466-knowledge-wave-on-marine-litter-from-aquaculture-sources (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Ni, F.; Cizdziel, J.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Y. Characterization of microplastics in environment by thermal gravimetric analysis coupled with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolandhasamy, P.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Qu, X.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Adherence of microplastics to soft tissue of mussels: A novel way to uptake microplastics beyond ingestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantoro, I.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Widianarko, B.; Ragas, A.M.J. Microplastics in coastal areas and seafood: Implications for food safety. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 674–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E.; Halling-Sørensen, B. Drugs in the environment. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; De Alda, M.J.L.; Barceló, D. Environmental behavior and analysis of veterinary and human drugs in soils, sediments and sludge. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2003, 22, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Ward, R.S. Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: A review of sources, fate and occurrence. Environmental Pollution. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of pharmaceutical compounds in wastewater and sludge from wastewater treatment plants: Removal and ecotoxicological impact of wastewater discharges and sludge disposal. J. Hazard Mater. 2012, 239–240, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.S.; Ullah, H.; Faruk, O.; Simon, E.; Czédli, H. Role of Microplastics in Global Warming and Climate Change: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Ai, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Meta-analysis of the effects of microplastic on fish: Insights into growth, survival, reproduction, oxidative stress, and gut microbiota diversity. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; Van Der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Emmerik, T.; Schwarz, A. Plastic debris in rivers. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2020, 7, e1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tern, T.A. Occurrence of drugs in German sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Res. 1988, 32, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D.; Cho, J.; Kim, I.S.; Vanderford, B.J.; Snyder, S.A. Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in South Korean surface, drinking, and waste waters. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The occurrence of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs in surface water in South Wales, UK. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3498–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrey, M.L.; Hamilton, M.C.; Backe, W.J.; Anderson, K.E. Pharmaceuticals and other anthropogenic chemicals in atmospheric particulates and precipitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, S.; Schrlau, J.; Butler, J.; Jia, Y.; Harper, B.; Harris, S.; Bramer, L.M.; Waters, K.M.; Harding, A.; Simonich, S.L.M. Relative Influence of Trans-Pacific and Regional Atmospheric Transport of PAHs in the Pacific Northwest, U.S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13807–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, D.H.; Simonich, S.M.; Jaffe, D.; Geiser, L.; Campbell, D.H.; Schwindt, A.; Schreck, C.; Kent, M.; Hafner, W.; Taylor, H.E.; et al. The Western airborne contaminant assessment project (WACAP): An interdisciplinary evaluation of the impacts of airborne contaminants in Western U.S. national parks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiffmeyer, T.K.; Kube, C.; Opiolka, S.; Schmidt, K.G.; Schöppe, G.; Sessink, P.J.M. Vapour pressures, evaporation behaviour and airborne concentrations of hazardous drugs: Implications for occupational safety. Pharm. J. 2002, 268, 331–337. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/5477028/Vapour_pressures_evaporation_behaviour_and_airborne_concentrations_of_hazardous_drugs_implications_for_occupational_safety (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Mechanisms of Atmospheric Wet Deposition of Chemical Contaminants|Health & Environmental Research Online (HERO)|US EPA. Available online: https://hero.epa.gov/hero/index.cfm/reference/details/reference_id/2181464 (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- Huang, Y.; Qing, X.; Wang, W.; Han, G.; Wang, J. Mini-review on current studies of airborne microplastics: Analytical methods, occurrence, sources, fate and potential risk to human beings. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 125, 115821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Sun, C.; He, C.; Zheng, L.; Dai, D.; Li, F. Atmospheric microplastics in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean: Distribution, source, and deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, S.; Alirezazadeh, M.; Razeghi, N.; Rezaei, M.; Pourmahmood, H.; Dehbandi, R.; Mehr, M.R.; Ashayeri, S.Y.; Oleszczuk, P.; Turner, A. Microplastics captured by snowfall: A study in Northern Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewc, K.; Graca, B.; Dołęga, A. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the coastal zone: Characteristics and relationship with meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, Z.R.; Fu, W.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.J. The atmospheric microplastics deposition contributes to microplastic pollution in urban waters. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Ulke, J.; Font, A.; Chan, K.L.A.; Kelly, F.J. Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groskreutz, S.R.; Horner, A.R.; Varner, E.L.; Yin, B.; Michael, A.C.; Weber, S.G. A selective report on topics at Pittcon 2015. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 68, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater Treatment Works (WwTW) as a Source of Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Gao, T.; Sillanpää, M. Atmospheric microplastics: A review on current status and perspectives. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 203, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. The presence of pharmaceuticals in the environment due to human use–present knowledge and future challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Shim, W.J. Nanoplastics in the aquatic environment. Critical review. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesson, A.; Fahlman, J.; Brodin, T.; Fick, J.; Jonsson, M.; Byström, P.; Klaminder, J. Bioaccumulation of five pharmaceuticals at multiple trophic levels in an aquatic food web-Insights from a field experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.E.; Hamann, M.; Kroon, F.J. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification of microplastics in marine organisms: A review and meta-analysis of current data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, J.F.; Bond, A.L.; Avery-Gomm, S.; Borrelle, S.B.; Rebolledo, E.L.B.; Hammer, S.; Kühn, S.; Lavers, J.L.; Mallory, M.L.; Trevail, A.; et al. Quantifying ingested debris in marine megafauna: A review and recommendations for standardization. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1454–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, J.F.; Ammendolia, J.; Rochman, C.M.; Mallory, M.L. Assessing plastic debris in aquatic food webs: What we know and don’t know about uptake and trophic transfer. Environ. Rev. 2019, 27, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maack, G.; Williams, M.; Backhaus, T.; Carter, L.; Kullik, S.; Leverett, D.; Nostro, F.L.L.; Sallach, J.B.; Staveley, J.; Eede, C.V.D. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Just One Stressor Among Others or Indicators for the Global Human Influence on Ecosystems? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical pollution of the world’s rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumpter, J.P.; Johnson, A.C.; Runnalls, T.J. Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment: No Answers Yet to the Major Questions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, J. Rationale and procedures for using the tissue-residue approach for toxicity assessment and determination of tissue, water, and sediment quality guidelines for aquatic organisms. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal. 2006, 12, 1018–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tan, Z.; Peng, J.; Qiu, Q.; Li, M. The behaviors of microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 113, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumpter, J.P.; Margiotta-Casaluci, L. Environmental Occurrence and Predicted Pharmacological Risk to Freshwater Fish of over 200 Neuroactive Pharmaceuticals in Widespread Use. Toxics 2022, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W.; Chambliss, C.K.; Stanley, J.K.; Ramirez, A.; Banks, K.E.; Johnson, R.D.; Lewis, R.J. Determination of Select Antidepressants in Fish from an Effluent-Dominated Stream. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, C.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Lyu, C.; Sun, L.; Zhong, S. Occurrence, Bioaccumulation, Metabolism and Ecotoxicity of Fluoroquinolones in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenker, M.; Harush, D.; Ben-Ari, J.; Chefe, B. tz Uptake of carbamazepine by cucumber plants-A case study related to irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lu, G.; Yan, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of pharmaceuticals in food webs from a large freshwater lake. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W.; Riley, T.M.; Taylor, R.D. Water quality of effluent-dominated ecosystems: Ecotoxicological, hydrological, and management considerations. Hydrobiologia 2006, 556, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boethling, R.S.; Mackay, D. Boethling Property Estimation Methods for Chemicals Property Estimation Methods for Chemicals Property Estimation Methods for Chemicals. In Handbook of Property Estimation Methods for Chemicals: Environmental and Health Sciences; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Wegner, A.; Foekema, E.M. Plastic as a carrier of POPs to aquatic organisms: A model analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7812–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, S.; Shen, L.; Li, S.; Cui, J.; Liu, Y. Bioaccumulation, trophic transfer, and human health risk of quinolones antibiotics in the benthic food web from a macrophyte-dominated shallow lake, North. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, P.; Meena, R.A.A.; Palanisami, T.; Ashokkumar, V.; Palvannan, T.; Gu, F.L. Occurrence, interactive effects and ecological risk of diclofenac in environmental compartments and biota-a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z.; Ma, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W. Occurrence, bioaccumulation, and trophic magnification of pharmaceutically active compounds in Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelodun, B.; Anand, U.; Cabreros, C.; Kumar, P.; Suresh, S.; Dey, A.; Ballesteros, F.; Bontempi, E. Occurrence, transformation, bioaccumulation, risk and analysis of pharmaceutical and personal care products from wastewater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3883–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, D.; Simmons, D.; Wang, X.; Peart, T.; Villella, M.; Miller, J.; Sherry, J. Bioaccumulation of pharmaceuticals and personal care product chemicals in fish exposed to wastewater effluent in an urban wetland. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gong, Z.; Kelly, B.C. Bioaccumulation Behavior of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Influence of Physical-Chemical Properties and Biotransformation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11085–11095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnnok, P.; Singh, R.R.; Burakham, R.; Pérez-Fuentetaja, A.; Aga, D.S. Selective Uptake and Bioaccumulation of Antidepressants in Fish from Effluent-Impacted Niagara River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10652–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Haddad, S.P.; Luek, A.; Scott, W.C.; Saari, G.N.; Kristofco, L.A.; Connors, K.A.; Rash, C.; Rasmussen, J.B.; Chambliss, C.K.; et al. Bioaccumulation and trophic dilution of human pharmaceuticals across trophic positions of an effluent-dependent wadeable stream. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20140058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.P.; Luek, A.; Scott, W.C.; Saari, G.N.; Burket, S.R.; Kristofco, L.A.; Corrales, J.; Rasmussen, J.B.; Chambliss, C.K.; Luers, M.; et al. Spatio-temporal bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of ionizable pharmaceuticals in a semi-arid urban river influenced by snowmelt. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heynen, M.; Fick, J.; Jonsson, M.; Klaminder, J.; Brodiny, T. Effect of bioconcentration and trophic transfer on realized exposure to oxazepam in 2 predators, the dragonfly larvae (Aeshna grandis) and the Eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, E.K.; Rosi, E.J.; Walters, D.M.; Fick, J.; Hamilton, S.K.; Brodin, T.; Sundelin, A.; Grace, M.R. A diverse suite of pharmaceuticals contaminates stream and riparian food webs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, A.; Mordec, M.; Caban, M.; Øverjordet, I.B.; Wielogórska, E.; Włodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Balazy, P.; Chełchowski, M.; Lepoint, G. Bioaccumulation of pharmaceuticals and stimulants in macrobenthic food web in the European Arctic as determined using stable isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, M.I.; Lambrianides, A.; Schneider, M.; Kümmerer, K.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Environmental side effects of pharmaceutical cocktails: What we know and what we should know. J Hazard Mater. 2014, 279, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frédéric, O.; Yves, P. Pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater: Their ecotoxicity and contribution to the environmental hazard of the effluent. Chemosphere 2014, 115, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Zhu, R.; Cai, Y.; Xu, N.; Yap, P.-S.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. Environmental fate and impacts of microplastics in aquatic ecosystems: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15762–15784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Z.; Lu, J.; Fu, G. The bio–accumulation and–magnification of microplastics under predator–prey isotopic relationships. J Hazard Mater 2024, 480, 135896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, M.E.; Sheehan, K.L. Bioaccumulation, transfer, and impacts of microplastics in aquatic food chains. J. Environ. Expo. Assess. 2024, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, B.; Reddy, P.B. Impacts of human pharmaceuticals on fish health. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2021, 12, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Bell, A.M.; Johnson, J.C.; Ziemba, R.E. Behavioral Syndromes: An Integrative Overview. Q. Rev. Biol. 2004, 79, 241–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Festa-Bianchet, M. Predator-induced natural selection on temperament in bighorn ewes. Anim. Behav. 2003, 65, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.R.; Blumstein, D.T. Fitness consequences of personality: A meta-analysis. Behav. Ecol. 2008, 19, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G. Biodiversity, ecosystem functioning and food webs in fresh waters: Assembling the jigsaw puzzle. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 2171–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudin, P.; Augé, C.; Just, N.; Mhaouty-Kodja, S.; Mortaud, S.; Pillon, D. When pharmaceutical drugs become environmental pollutants: Potential neural effects and underlying mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtake, F.; Takeyama, K.-I.; Matsumoto, T.; Kitagawa, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nohara, K.; Tohyama, C.; Krust, A.; Mimura, J.; Chambon, P.; et al. Modulation of oestrogen receptor signalling by association with the activated dioxin receptor. Nature 2003, 423, 6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meston, C.M.; Frohlich, P.F. The Neurobiology of Sexual Function. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, M.; Watts, C.; Boucard, T. Chronic aquatic environmental risks from exposure to human pharmaceuticals. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.; Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. An investigation into the acute and chronic toxicity of eleven pharmaceuticals (and their solvents) found in wastewater effluent on the cnidarian, Hydra attenuata. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.; Fogarty, S.; Weinersmith, K.; Brodin, T.; Sih, A. Personality traits and dispersal tendency in the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.; Antunes, S.C.; Gomes, R.; Campos, J.C.; Braga, M.R.; Ramos, A.S.; Correia, A.T. Acute Effects of Tetracycline Exposure in the Freshwater Fish Gambusia holbrooki: Antioxidant Effects, Neurotoxicity and Histological Alterations. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Gao, J.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Q. DNA damage and biochemical toxicity of antibiotics in soil on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snavely, S.R.; Hodges, G.R. The neurotoxicity of antibacterial agents. Ann. Intern. Med. 1984, 101, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.J. Neurotoxicity of antibacterial therapy. South. Med. J. 1994, 87, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milla, S.; Depiereux, S.; Kestemont, P. The effects of estrogenic and androgenic endocrine disruptors on the immune system of fish: A review. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Yan, S.; Chen, R.; Hong, X.; Zha, J. 3-(4-Methylbenzylidene) camphor induced reproduction toxicity and antiandrogenicity in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinert, C.; Lacaze, E.; Mounier, M.; De Guise, S.; Fournier, M. Immunotoxic effects of single and combined pharmaceuticals exposure on a harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) B lymphoma cell line. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehberger, K.; von Siebenthal, E.W.; Bailey, C.; Bregy, P.; Fasel, M.; Herzog, E.L.; Neumann, S.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Segner, H. Long-term exposure to low 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) concentrations disrupts both the reproductive and the immune system of juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, W.; Adamovsky, O.; Martyniuk, C.J. Elucidating mechanisms of immunotoxicity by benzotriazole ultraviolet stabilizers in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Implication of the AHR-IL17/IL22 immune pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Paul, T.; Prasad, K.P.; Shukla, S.P.; Kumar, K. Triclosan induces immunosuppression and reduces survivability of striped catfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus during the challenge to a fish pathogenic bacterium Edwardsiella tarda. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Aziz, H.A.; Khan, N.A.; Hasan, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Farooqi, I.H.; Dhingra, A.; Vambol, V.; Changani, F.; Yousefi, M.; et al. Impact, disease outbreak and the eco-hazards associated with pharmaceutical residues: A Critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.R.; Sloman, K.A. The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: Integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 68, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, S.D.; Wilson, S.P. The utility of behavioral studies for aquatic toxicology testing: A meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelangeli, M.; Smith, C.R.; Wong, B.B.M.; Chapple, D.G. Aggression mediates dispersal tendency in an invasive lizard. Anim. Behav. 2017, 133, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, T.; Piovano, S.; Fick, J.; Klaminder, J.; Heynen, M.; Jonsson, M. Ecological effects of pharmaceuticals in aquatic systems—Impacts through behavioural alterations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodin, T.; Fick, J.; Jonsson, M.; Klaminder, J. Dilute concentrations of a psychiatric drug alter behavior of fish from natural populations. Science 2013, 339, 814–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomati, F.; Castiglioni, S.; Zuccato, E.; Fanelli, R.; Vigetti, D.; Rossetti, C.; Calamari, D. Effects of a complex mixture of therapeutic drugs at environmental levels on human embryonic cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesiuk, M.; Spijkerman, E.; Lachmann, S.C.; Wacker, A. Environmental concentrations of pharmaceuticals directly affect phytoplankton and effects propagate through trophic interactions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legradi, J.B.; Di Paolo, C.; Kraak, M.H.S.; van der Geest, H.G.; Schymanski, E.L.; Williams, A.J.; Dingemans, M.M.L.; Massei, R.; Brack, W.; Cousin, X.; et al. An ecotoxicological view on neurotoxicity assessment. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollmann, T. The Effects of a Series of Poisons on Adult and Embryonic Funduli. Amerian Journal of Physiol.-Leg. Content 1906, 16, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelford, V. An Experimental Study of the Effects of Gas Waste Upon Fishes, with Especial Reference to Stream Pollution. Ill. Nat. Hist. Surv. Bull. 1918, 11, 381–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaristo, M.; Brodin, T.; Balshine, S.; Bertram, M.G.; Brooks, B.W.; Ehlman, S.M.; McCallum, E.S.; Sih, A.; Sundin, J.; Wong, B.B.M.; et al. Direct and indirect effects of chemical contaminants on the behaviour, ecology and evolution of wildlife. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20181297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.G.; Iwama, G.K.; Pickering, A.D.; Sumpter, J.P.; Schreck, C.B. Fish stress and health in aquaculture. Estuaries 1998, 21, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Der Kraak, G. observations of endocrine effects in wildlife with evidence of their causation. Pure Appl. Chem. 1998, 70, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kime, D.; Ebrahimi, M.; Nysten, K.; Roelants, I.; Rurangwa, E.; Moore, H.; Ollevier, F. Use of computer assisted sperm analysis (CASA) for monitoring the effects of pollution on sperm quality of fish; application to the effects of heavy metals. Aquat. Toxicol. 1996, 36, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, C.R.; Jobling, S.; Sumpter, J.P.; Tyler, C. Endocrine Disruption in Wildlife: A Critical Review of the Evidence. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1998, 28, 319–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillette, L.J.; Gunderson, M.P. Alterations in development of reproductive and endocrine systems of wildlife populations exposed to endocrine-disrupting contaminants. Reproduction 2001, 122, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.P.; Kime, D.E.; Van der Ven, L.T.M.; Wester, P.W.; Brion, F.; Maack, G.; Stahlschmidt-Allner, P.; Tyler, C.R. Long-term exposure to environmental concentrations of the pharmaceutical ethynylestradiol causes reproductive failure in fish. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, C.A.; Penland, T.N.; Kwak, T.J.; Cope, W.G.; Heise, R.J.; Mac Law, J.; Shea, D.; Aday, D.D.; Rice, J.A.; Kullman, S.W. Relation of contaminants to fish intersex in riverine sport fishes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Williams, R.J. A model to estimate influent and effluent concentrations of estradiol, estrone, and ethinylestradiol at sewage treatment works. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3649–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.M.; Bertram, M.G.; Saaristo, M.; Ecker, T.E.; Hannington, S.L.; Tanner, J.L.; Michelangeli, M.; O’Bryan, M.K.; Wong, B.B. Impact of the widespread pharmaceutical pollutant fluoxetine on behaviour and sperm traits in a freshwater fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubruge, E.; Petit, F.; Gage, M.J.G. Reduced sperm counts in guppies (Poecilia reticulata) following exposure to low levels of tributyltin and bisphenol A. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colborn, T. Chemically Induced Alterations in Sexual and Functional Development: The Wildlife/Human Connection; Princeton Scientific Publishing: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1992; Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=Bern+HA+1992.+The+fragile+fetus.+In%3A+Chemically-Induced+Alterations+in+Sexual+and+Functional+Development%3A+The+Wildlife+Human+Connection+%28Colborn+T%2C+Clement+C%2C+eds%29.+Princeton%2C+NJ%3APrinceton+Scientific+Publishing%2C+9%E2%80%9315 (accessed on 9 May 2024).
- Dawson, A. Comparative reproductive physiology of non-mammalian species. Pure Appl. Chem. 1998, 70, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strüssmann, C.A.; Nakamura, M. Morphology, endocrinology, and environmental modulation of gonadal sex differentiation in teleost fishes. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 26, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Länge, R.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Croudace, C.P.; Siegmund, F.; Schweinfurth, H.; Hampe, P.; Panter, G.H.; Sumpter, J.P. Effects of the synthetic estrogen 17α-ethinylestradiol on the life-cycle of the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, L.; Jauhiainen, A.; Kristiansson, E.; Nerman, O.; Larsson, D.G.J. Evolutionary conservation of human drug targets in organisms used for environmental risk assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreke, N.; Dietrich, D.R. Physiological Endpoints for Potential SSRI Interactions in Fish. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 38, 215–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesaar, C. The serotonergic system in fish. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.D. An AOP analysis of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 197, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fursdon, J.B.; Martin, J.M.; Bertram, M.G.; Lehtonen, T.K.; Wong, B.B.M. The pharmaceutical pollutant fluoxetine alters reproductive behaviour in a fish independent of predation risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, B.B.; Hulthén, K.; Blomqvist, D.R.; Hansson, L.; Nilsson, J.; Brodersen, J.; Nilsson, P.A.; Skov, C.; Brönmark, C. To boldly go: Individual differences in boldness influence migratory tendency. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.K.; Ramirez, A.J.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W. Enantiospecific sublethal effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine to a model aquatic vertebrate and invertebrate. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaworecki, K.M.; Klaine, S.J. Behavioral and biochemical responses of hybrid striped bass during and after fluoxetine exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 88, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nentwig, G. Effects of pharmaceuticals on aquatic invertebrates. Part II: The antidepressant drug fluoxetine. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 52, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraz, S.; Lee, A.H.; Pollard, S.; Srinivasan, K.; Vermani, A.; David, E.; Wilson, J.Y. Paternal Exposure to Carbamazepine Impacts Zebrafish Offspring Reproduction over Multiple Generations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12734–12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palace, V.P.; Wautier, K.G.; Evans, R.E.; Blanchfield, P.; Mills, K.; Chalanchuk, S.; Godard, D.; McMaster, M.; Tetrault, G.; Peters, L.E.; et al. Biochemical and Histopathological Effects of Ethynylestradiol in Pearl Dace (Semotilus margarita) Exposed to the Synthetic Estrogen in a Whole Lake. 2006. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?hl=en&volume=25&publication_year=2006&pages=1114-1125&journal=Environ.+Toxicol.+Chem.&author=VP+Palace&title=Biochemical+and+histopathological+effects+of+ethynylestradiol+in+pearl+dace+%28Semotilus+margarita%29+exposed+to+the+synthetic+estrogen+in+a+whole+lake+experiment (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- Palace, V.P.; Evans, R.E.; Wautier, K.G.; Mills, K.H.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Park, B.J.; Baron, C.L.; Kidd, K.A. Interspecies differences in biochemical, histopathological, and population responses in four wild fish species exposed to ethynylestradiol added to a whole lake. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 66, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnalls, T.J.; Hala, D.N.; Sumpter, J.P. Preliminary studies into the effects of the human pharmaceutical Clofibric acid on sperm parameters in adult Fathead minnow. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, W.; Sremski, W.; Piccini, B.; Palluel, O.; Maillot-Maréchal, E.; Betoulle, S.; Jaffal, A.; Aït-Aïssa, S.; Brion, F.; Thybaud, E.; et al. Adverse effects in wild fish living downstream from pharmaceutical manufacture discharges. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.; Ogawa, S.; Parhar, I.S. Role of serotonin in fish reproduction. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 141586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, L.A.; Green, J.W.; Schneider, S.Z. Ibuprofen: Fish Short-Term Reproduction Assay with Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Based on an Extended OECD 229 Protocol. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.G.; Muñoz-Peñuela, M.; Gomes, A.D.O.; Tolussi, C.E.; Brambila-Souza, G.; Branco, G.S.; Nostro, F.L.L.; Moreira, R.G. Endocrine disruptive action of diclofenac and caffeine on Astyanax altiparanae males (Teleostei: Characiformes: Characidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 231, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, F.; Li, K.; Nie, X.; Fang, H. Effects of norfloxacin nicotinate on the early life stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio): Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 96, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, S.A.; Pedreira, A.C.d.O.; de Freitas, J.M.A.; Dalmaso, A.C.S.; Chiella, R.J.; Meurer, F.; Romão, S.; Bombardelli, R.A. Diets containing purified nucleotides reduce oxidative stress, interfere with reproduction, and promote growth in Nile tilapia females. Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, A.; Cicero, M.R.; Prestinaci, F.; Bottoni, P.; Carere, M. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of pharmaceuticals with a focus to the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallik, A.; Xavier, K.A.M.; Naidu, B.C.; Nayak, B.B. Ecotoxicological and physiological risks of microplastics on fish and their possible mitigation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.K.M.M.; Hamed, M.; Hasan, J.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Niyogi, S.; Chivers, D.P. A review of the neurobehavioural, physiological, and reproductive toxicity of microplastics in fishes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 282, 116712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, I.; Huy, D.T.N.; Alsaikhan, F.; Opulencia, M.J.C.; Van Tuan, P.; Nurmatova, K.C.; Majdi, A.; Shoukat, S.; Yasin, G.; Margiana, R.; et al. Toxic effects on enzymatic activity, gene expression and histopathological biomarkers in organisms exposed to microplastics and nanoplastics: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, E.; Hussain, S.M.; Ali, S.; Sarker, P.K.; Farah, M.A. Investigating the toxicity of polylactic acid microplastics on the health and physiology of freshwater fish, Cirrhinus mrigala. Ecotoxicology 2024, 33, 1210–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; The Impacts of Microplastics on Health. Protect Henderson Inlet. Available online: https://protecthendersoninlet.org/the-impacts-of-microplastics-on-health/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z. Growth inhibition, toxin production and oxidative stress caused by three microplastics in Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, K.A.; Paterson, M.J.; Rennie, M.D.; Podemski, C.L.; Findlay, D.L.; Blanchfield, P.J.; Liber, K. Direct and indirect responses of a freshwater food web to a potent synthetic oestrogen. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, I.; Aherne, J.; Wentworth, G.R. Impacts and Effects Indicators of Atmospheric Deposition of Major Pollutants to Various Ecosystems-A Review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1953–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.M.; Padilla, I.Y.; Romanok, K.M.; Smalling, K.L.; Focazio, M.J.; Breitmeyer, S.E.; Cardon, M.C.; Conley, J.M.; Evans, N.; Givens, C.E.; et al. Pilot-scale expanded assessment of inorganic and organic tapwater exposures and predicted effects in Puerto Rico, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L.; Merriam, G. Conservation of Fragmented Populations (Conservación de poblaciones fragmentadas). Conserv. Biol. 1994, 8, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.L.; Dodson, S.I. Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 1965, 150, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvanera, P.; Pfisterer, A.B.; Buchmann, N.; He, J.; Nakashizuka, T.; Raffaelli, D.; Schmid, B. Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and services. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD). Pharmaceutical Residues in Freshwater Hazards and Policy Responses Pharmaceutical Residues in Freshwater Hazards and Policy Responses Contents; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2020; Available online: https://dokumen.pub/pharmaceutical-residues-in-freshwater-hazards-and-policy-responses-9264776338-9789264776333.html (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Ballinger, A.; Lake, P.S. Energy and nutrient fluxes from rivers and streams into terrestrial food webs. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2006, 57, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.; Ruesink, J.L.; Pruitt, C.; Trimble, A.C.; Donoghue, C. Temporal variation in intertidal habitat use by nekton at seasonal and diel scales. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2019, 516, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, F.; Xia, Z.; Qin, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Changes in fish assemblages following the implementation of a complete fishing closure in the Chishui River. Fish Res. 2021, 243, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.E.; Brown, A.R.; Brown, A.R.; Ankley, G.T.; Sumpter, J.P. Medicating the environment: Assessing risks of pharmaceuticals to wildlife and ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, T.G.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Lane, J.; Herborn, K.A.; Pietravalle, S.; Arnold, K.E. Behavioural and physiological responses of birds to environmentally relevant concentrations of an antidepressant. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajima, M.N.O.; Pandey, P.K. Effects of Pharmaceutical Waste in Aquatic Life. In Advances in Fisheries Biotechnology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ge, J.; Yu, X. Bioavailability and toxicity of microplastics to fish species: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.R.; Olden, J.D. Global meta-analysis reveals diverse effects of microplastics on freshwater and marine fishes. Fish Fish. 2022, 23, 1439–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A. Microplastics in Fisheries and Aquaculture; Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper 61; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper. No. 615; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A.; Hashem, M.; Mostafa, Y.S.; Alhaithloul, H.A.S.; Alghanem, S.M. Linking effects of microplastics to ecological impacts in marine environments. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, Q.; Wang, Z. From natural environment to animal tissues: A review of microplastics(nanoplastics) translocation and hazards studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aib, H.; Czédli, H.; Baranyai, E.; Sajtos, Z.; Döncző, B.; Parvez, M.S.; Berta, C.; Varga, Z.; Benhizia, R.; Nyeste, K. Fish Scales as a Non-Invasive Method for Monitoring Trace and Macroelement Pollution. Biology 2025, 14, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanni, S.; Cammalleri, V.; D’agostino, L.; Protano, C.; Vitali, M. Occurrence of pharmaceutical residues in drinking water: A systematic review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicole, W. Microplastics in seafood: How much are people eating? Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M.; Sillanpää, M. Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margot, J.; Kienle, C.; Magnet, A.; Weil, M.; Rossi, L.; de Alencastro, L.F.; Abegglen, C.; Thonney, D.; Chèvre, N.; Schärer, M.; et al. Treatment of micropollutants in municipal wastewater: Ozone or powdered activated carbon? Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughton, C.C. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Overarching issues and overview. ACS Symp. Ser. 2001, 791, 2–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Bletsou, A.A.; Damalas, D.E.; Aalizadeh, R.; Alygizakis, N.A.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J.; Thomaidis, N.S. Wide-scope target screening of >2000 emerging contaminants in wastewater samples with UPLC-Q-ToF-HRMS/MS and smart evaluation of its performance through the validation of 195 selected representative analytes. J. Hazard Mater 2020, 387, 121712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, L.; Dierkes, G.; Ternes, T.A.; Völker, C.; Wagner, M. Benchmarking the in Vitro Toxicity and Chemical Composition of Plastic Consumer Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11467–11477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pharmaceutical Class. | Examples | Concentration Range (ng/L–μg/L) | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Ciprofloxacin | 24.53–1491.8 ng/L | WWTP influents and effluents | [31] |
| Amoxicillin | Not specified, commonly detected | WWTP effluents, hospital wastewater | ||
| Painkillers | Ibuprofen | Below LOD–114,000 ng/L (influent) | Household wastewater, industrial discharge | [32] |
| Below LOD–59,900 ng/L (effluent) | ||||
| Diclofenac | 2210–25,000 ng/L (influent) | Household wastewater, industrial discharge | ||
| 360–5000 ng/L (effluent) | ||||
| Hormones | Estradiol, progesterone | Typically detected at ng/L levels | Human and veterinary drugs | [32] |
| Type of Microplastic | Examples | Particle Size Range (μm–mm) | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragments | Polystyrene, polyethylene | Oct-00 | Plastic waste degradation | [33,34] |
| Fibers | Polyester, nylon | 10–1000 | Textile fibers, wastewater | [35,36] |
| Beads | Polypropylene, acrylic | 1–500 | Personal care products | [37] |
| Contaminant | Species | Bioaccumulation Level | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | |||
| Diphenhydramine | Perca fluviatilis (European Perch) | Detected | [137] |
| Oxazepam | Perca fluviatilis (European Perch) | Detected | |
| Trimethoprim | Perca fluviatilis (European Perch) | Not detected | |
| Diclofenac | Perca fluviatilis (European Perch) | Not detected | |
| Hydroxyzine | Perca fluviatilis (European Perch) | Detected | |
| Microplastics | |||
| Various microplastics | Oncorhynchus tshawytscha (Chinook Salmon) | 1.15 particles/individual | [138,139,140] |
| Various microplastics | Siganus luridus (Dusky Spinefoot) | 3.13 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Liza aurata (Golden Grey Mullet) | 3.26 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Mullus barbatus (Red Mullet) | 1.39 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Sardina pilchardus (European Pilchard) | 2.14 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Scomber japonicus (Atlantic Chub Mackerel) | 6.71 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Mytilus edulis (Blue Mussel) | 1.23 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Copepoda spp. (Copepods) | 0.33 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Cerastoderma edule (Common Cockle) | 4.30 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Hediste diversicolor (Ragworm) | 2.70 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Pelecyora isocardia (Bivalve Mollusk) | 1.50 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Scolelepis squamata (Polychaete Worm) | 0.60 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Scrobicularia plana (Peppery Furrow Shell) | 3.30 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Senilia senilis (Bivalve Mollusk) | 1.00 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Diopatra neapolitana (Polychaete Worm) | 1.00 particles/individual | |
| Various microplastics | Glycera alba (Polychaete Worm) | 3.00 particles/individual |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aib, H.; Parvez, M.S.; Czédli, H.M. Pharmaceuticals and Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Pathways and Distribution, Toxicological and Ecological Effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050799
Aib H, Parvez MS, Czédli HM. Pharmaceuticals and Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Pathways and Distribution, Toxicological and Ecological Effects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(5):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050799
Chicago/Turabian StyleAib, Haithem, Md. Sohel Parvez, and Herta Mária Czédli. 2025. "Pharmaceuticals and Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Pathways and Distribution, Toxicological and Ecological Effects" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 5: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050799
APA StyleAib, H., Parvez, M. S., & Czédli, H. M. (2025). Pharmaceuticals and Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Pathways and Distribution, Toxicological and Ecological Effects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(5), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050799






