Impact of Different Occupational Noises on Static and Dynamic Postural Stability in Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
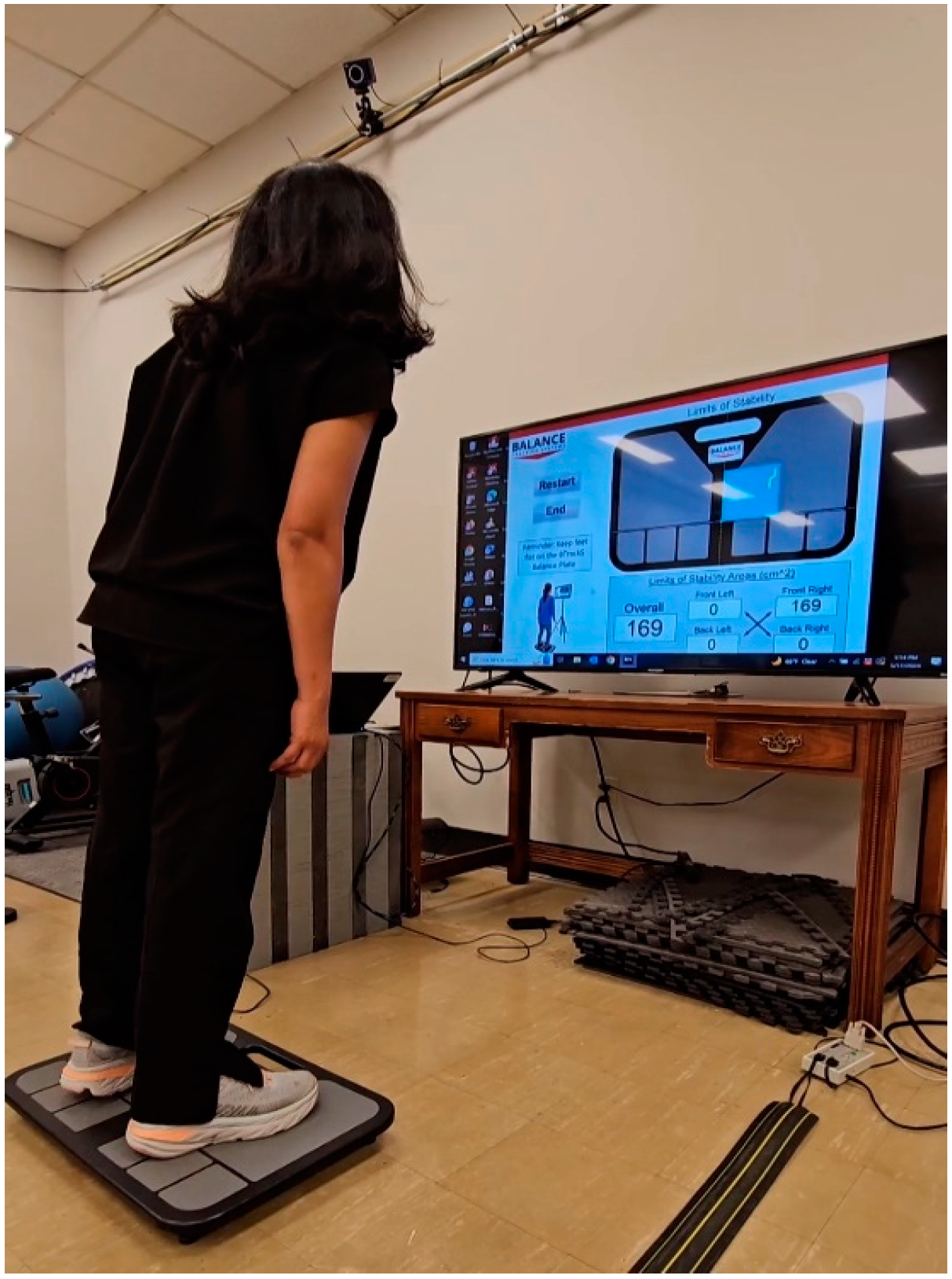
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Assessments
2.4. Experimental Procedures
2.5. Data and Statistical Analysis
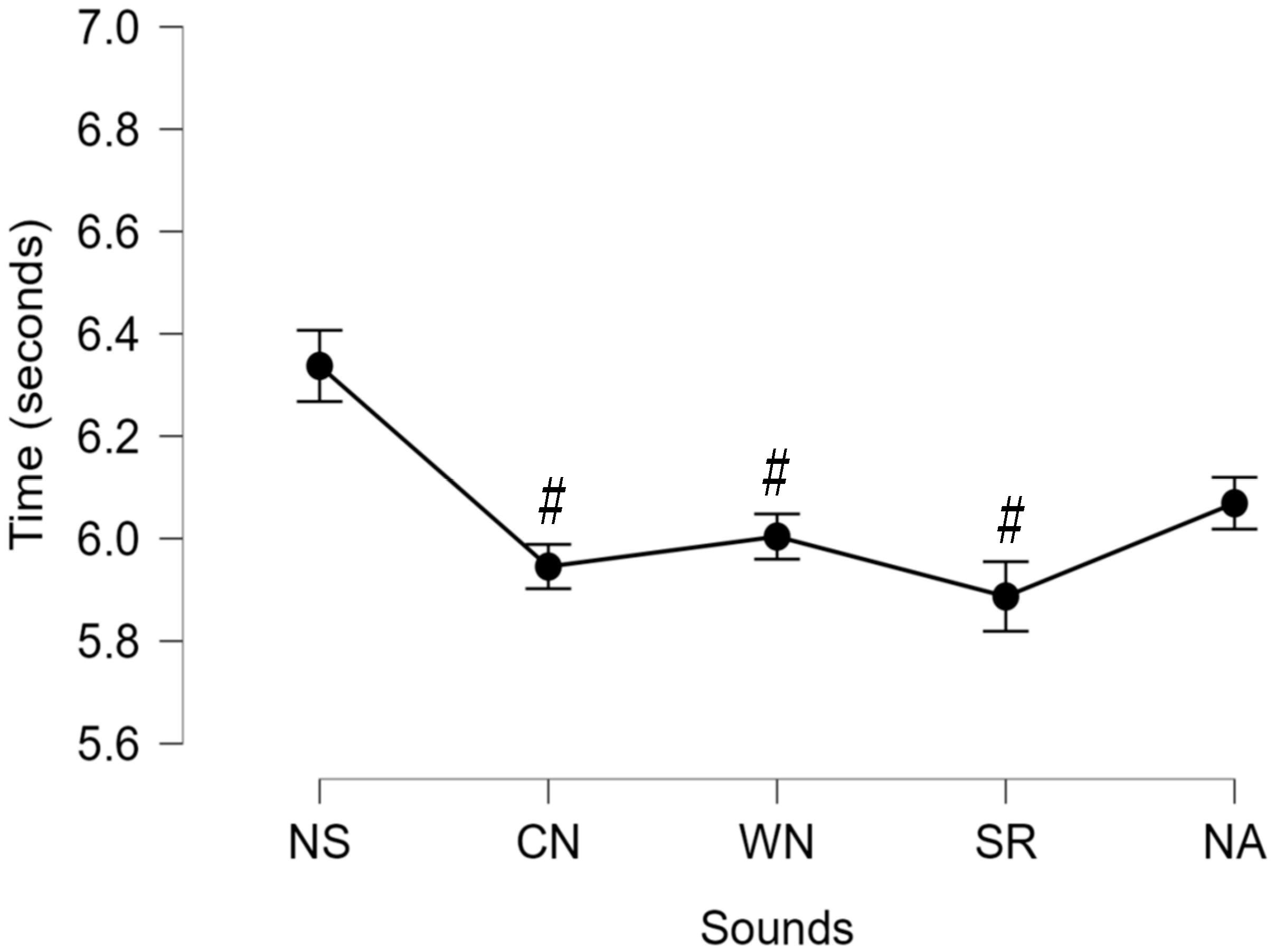
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Practical Implications
4.2. Limitations and Recommendations for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NSC. Work Injury Costs-Injury Facts 2022; National Safety Council: Itasca, IL, USA, 2022; Available online: https://injuryfacts.nsc.org/work/costs/work-injury-costs/ (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- BLS. Employer-Reported Workplace Injuries and Illnesses—2021–2022; US Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/news.release/archives/osh_11082023.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- BLS. National Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries in 2022; US Department of Labor, Bureau of Labor Statistics: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/news.release/archives/cfoi_12192023.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Akdogan, O.; Selcuk, A.; Take, G.; Erdoğan, D.; Dere, H. Continuous or intermittent noise exposure, does it cause vestibular damage?: An experimental study. Auris Nasus Larynx 2009, 36, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad-Sardrudi, H.; Dormohammadi, A.; Golmohammadi, R.; Poorolajal, J. Effect of Noise Exposure on Occupational Injuries: A Cross-sectional Study. J. Res. Health Sci. 2012, 12, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barkokébas, B., Jr.; Vasconcelos, B.M.; Lago, E.M.G.; Alcoforador, A.F.P. Analysis of noise on construction sites of high-rise buildings. Work 2012, 41, 2982–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, L.F.; Galusha, D.; Cullen, M.R.; Dixon-Ernst, C.; Rabinowitz, P.M.; Neitzel, R.L. Association between ambient noise exposure, hearing acuity, and risk of acute occupational injury. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 2015, 41, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra Prashanth, K.; Venugopalachar, S. The possible influence of noise frequency components on the health of exposed industrial workers—A review. Noise Health 2011, 13, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, M.; Lanciani, R.; Bruno, E.; Napolitano, B.; Di Girolamo, S. Posturography frequency analysis of sound-evoked body sway in normal subjects. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 263, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarsson, J.J.; Wiens, S.; Nilsson, M.E. Stress Recovery during Exposure to Nature Sound and Environmental Noise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Qu, X. Influence of affective auditory stimuli on balance control during static stance. Ergonomics 2016, 60, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainenti, M.R.; De Oliveira, L.F.; De Melo Tavares De Lima, M.A.; Nadal, J. Stabilometric signal analysis in tests with sound stimuli. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 181, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, K.; Lockhart, T.; Kim, S. Effects of Sound on Postural Stability during Quiet Standing. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2011, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, B.; Sobera, M.; Sikora, A.; Drzewowska, I. The influence of sounds on posture control. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2015, 17, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, T.; Woodward, J.; Wu, M.; Jackson, B.; Souza, P.; Siegel, J.; Dhar, S.; Gordon, K.E. Walking With Ears: Altered Auditory Feedback Impacts Gait Step Length in Older Adults. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamacher, D.; Schley, F.; Hollander, K.; Zech, A. Effects of manipulated auditory information on local dynamic gait stability. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, K.M.; Voth, J.; Munce, S.E.; Straus, S.E.; Jaglal, S.B. Chronic disease and falls in community-dwelling Canadians over 65 years old: A population-based study exploring associations with number and pattern of chronic conditions. BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.M.; Will, O.J.; McGann, Z.; Balasubramaniam, R. Auditory white noise reduces age-related fluctuations in balance. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 630, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuehr, M.; Nusser, E.; Krafczyk, S.; Straube, A.; Brandt, T.; Jahn, K.; Schniepp, R. Noise-Enhanced Vestibular Input Improves Dynamic Walking Stability in Healthy Subjects. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażkiewicz, M.; Gulatowska, M.; Hadamus, A.; Kędziorek, J. Effect of Annoying Sounds on Postural Control. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, O.P.; Gvozdeva, A.P.; Shamantseva, N.D.; Moshonkina, T.R.; Andreeva, I.G. Destabilization of Human Vertical Posture by Affective Auditory Stimuli. Hum. Physiol. 2023, 49, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, J.; Goble, D.; Pile, M.; Kendall, B. BTrackS limits of stability test is a reliable assessment of volitional dynamic postural control. Gait Posture 2020, 80, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchet, O.; Fantino, B.; Allali, G.; Muir, S.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Annweiler, C. Timed up and go test and risk of falls in older adults: A systematic review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The timed “Up & Go”: A test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, S.L.; Marchetti, G.F.; Pritcher, M.; Furman, J.M. Gaze stabilization and gait performance in vestibular dysfunction. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumann, K.; Gärling, T.; Stormark, K.M. Selective attention and heart rate responses to natural and urban environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 2003, 23, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.S.; Simons, R.F.; Losito, B.D.; Fiorito, E.; Miles, M.A.; Zelson, M. Stress recovery during exposure to natural and urban environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 1991, 11, 201–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, M.W.; Derakshan, N.; Santos, R.; Calvo, M.G. Anxiety and cognitive performance: Attentional control theory. Emotion 2007, 7, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturnieks, D.L.; Delbaere, K.; Brodie, M.A.; Lord, S.R. The influence of age, anxiety and concern about falling on postural sway when standing at an elevated level. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2016, 49, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stins, J.; Michielsen, M.; Roerdink, M.; Beek, P. Sway regularity reflects attentional involvement in postural control: Effects of expertise, vision and cognition. Gait Posture 2009, 30, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.; Teixeira, N.; Abade, E.; Carvalho, A. Effects of noise on postural stability when in the standing position. Work 2016, 54, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateni, H.; Vaizasatya, A.; Blaschak, M.J. The effect of 80 dB environmental noise on control of posture in healthy young adults. Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf. Serv. Ind. 2013, 23, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandemer, L.; Parseihian, G.; Kronland-Martinet, R.; Bourdin, C. Spatial cues provided by sound improve postural stabilization: Evidence of a spatial auditory map? Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, K.; Ernst, A.; Basta, D. A static sound source can improve postural stability during walking. J. Vestib. Res. 2021, 31, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gourley, K.; Chander, H.; Beam, A.S.; Knight, A.C. Impact of Different Occupational Noises on Static and Dynamic Postural Stability in Healthy Young Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050679
Gourley K, Chander H, Beam AS, Knight AC. Impact of Different Occupational Noises on Static and Dynamic Postural Stability in Healthy Young Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(5):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050679
Chicago/Turabian StyleGourley, Kristy, Harish Chander, Asher Street Beam, and Adam C. Knight. 2025. "Impact of Different Occupational Noises on Static and Dynamic Postural Stability in Healthy Young Adults" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 5: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050679
APA StyleGourley, K., Chander, H., Beam, A. S., & Knight, A. C. (2025). Impact of Different Occupational Noises on Static and Dynamic Postural Stability in Healthy Young Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(5), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050679






