Development of Life Course Exposure Estimates Using Geospatial Data and Residence History
Abstract
1. Introduction
Importance and Applications of Geospatial Data
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Collection of Residential History Data
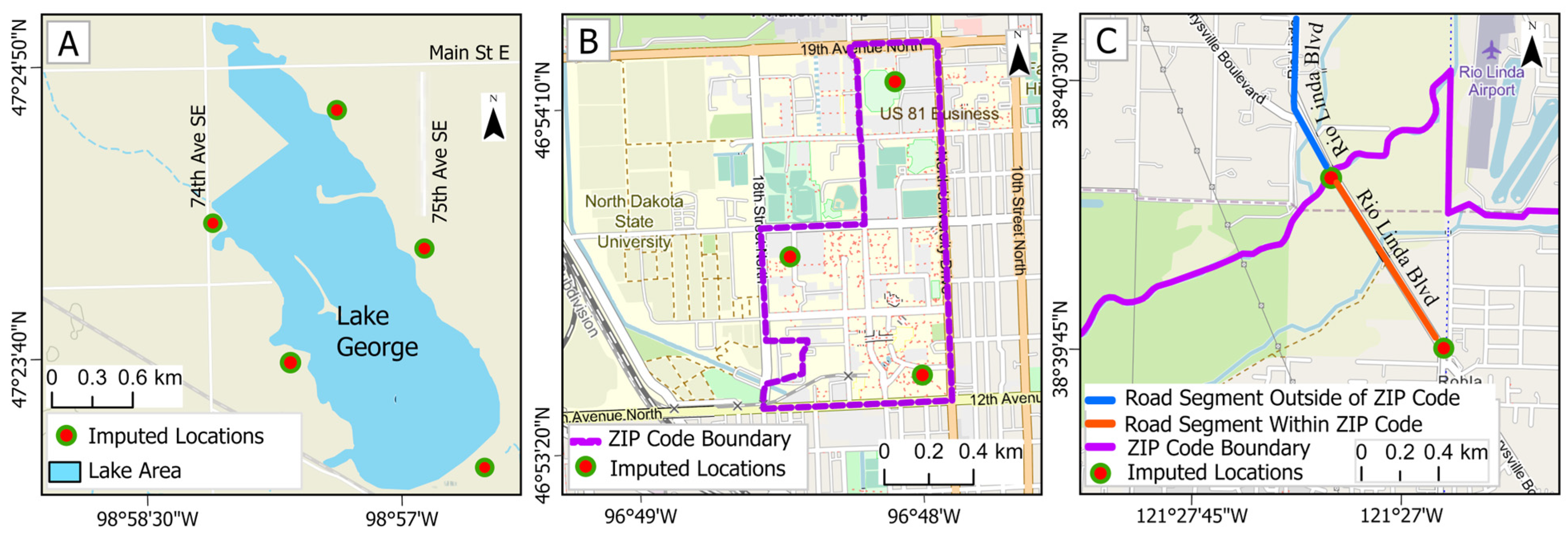
2.3. Geocoding and Spatial Imputation
2.4. Exposure Datasets
2.5. Spatial Linking, Interpolation, and Correlation
3. Results
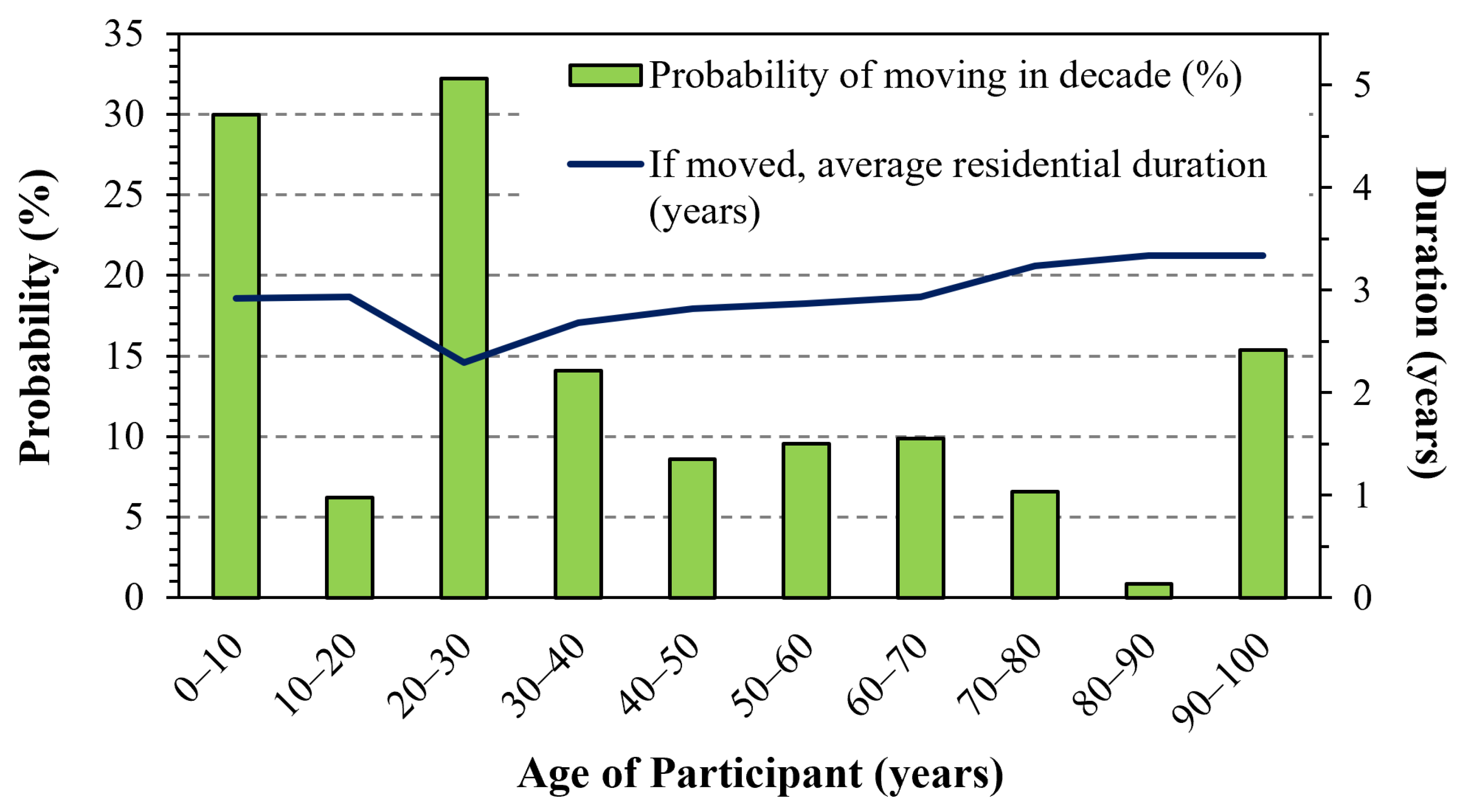
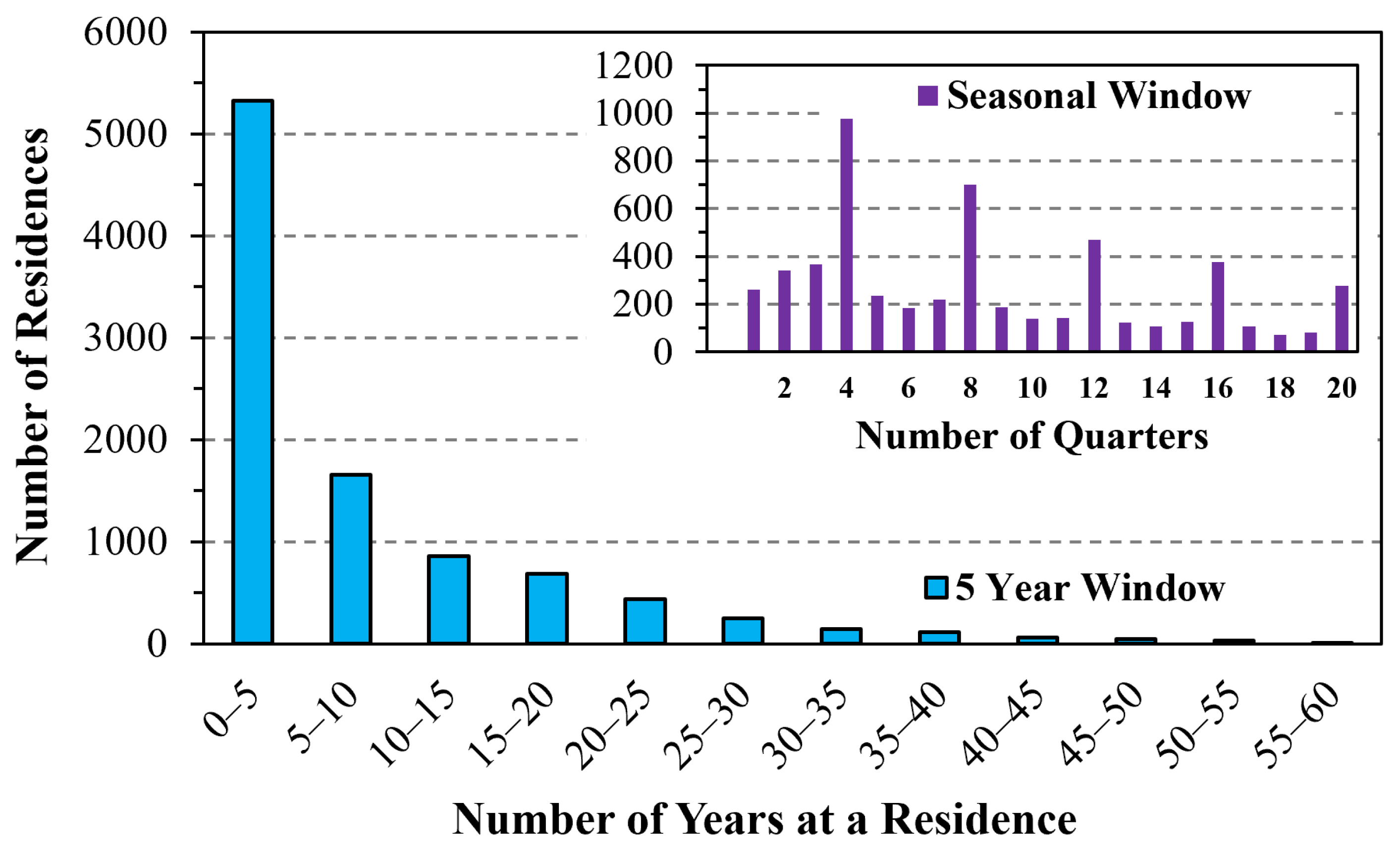
3.1. Residential Dates
3.2. Residence Locations
3.3. Geocoding
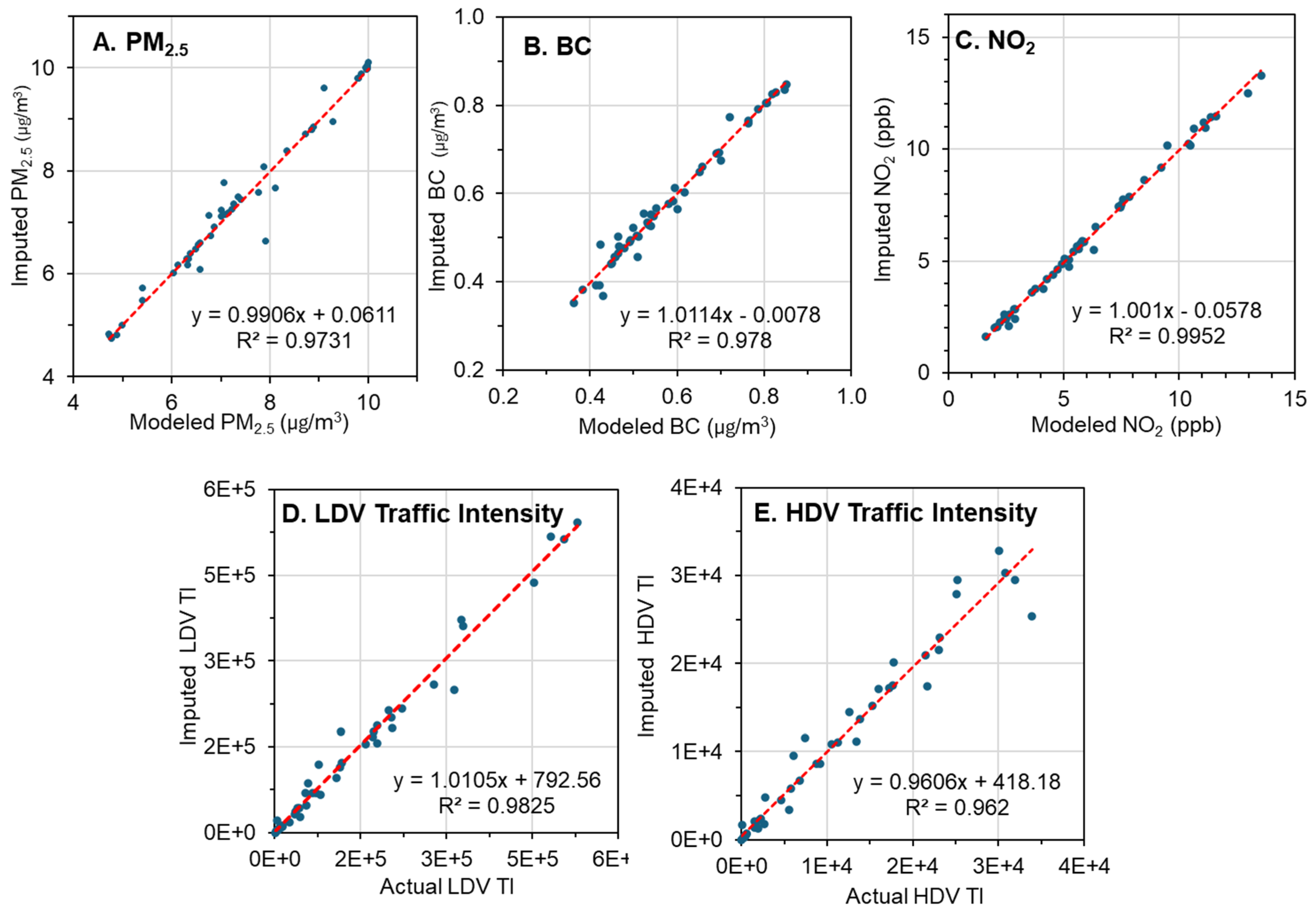
3.4. Spatial Imputation
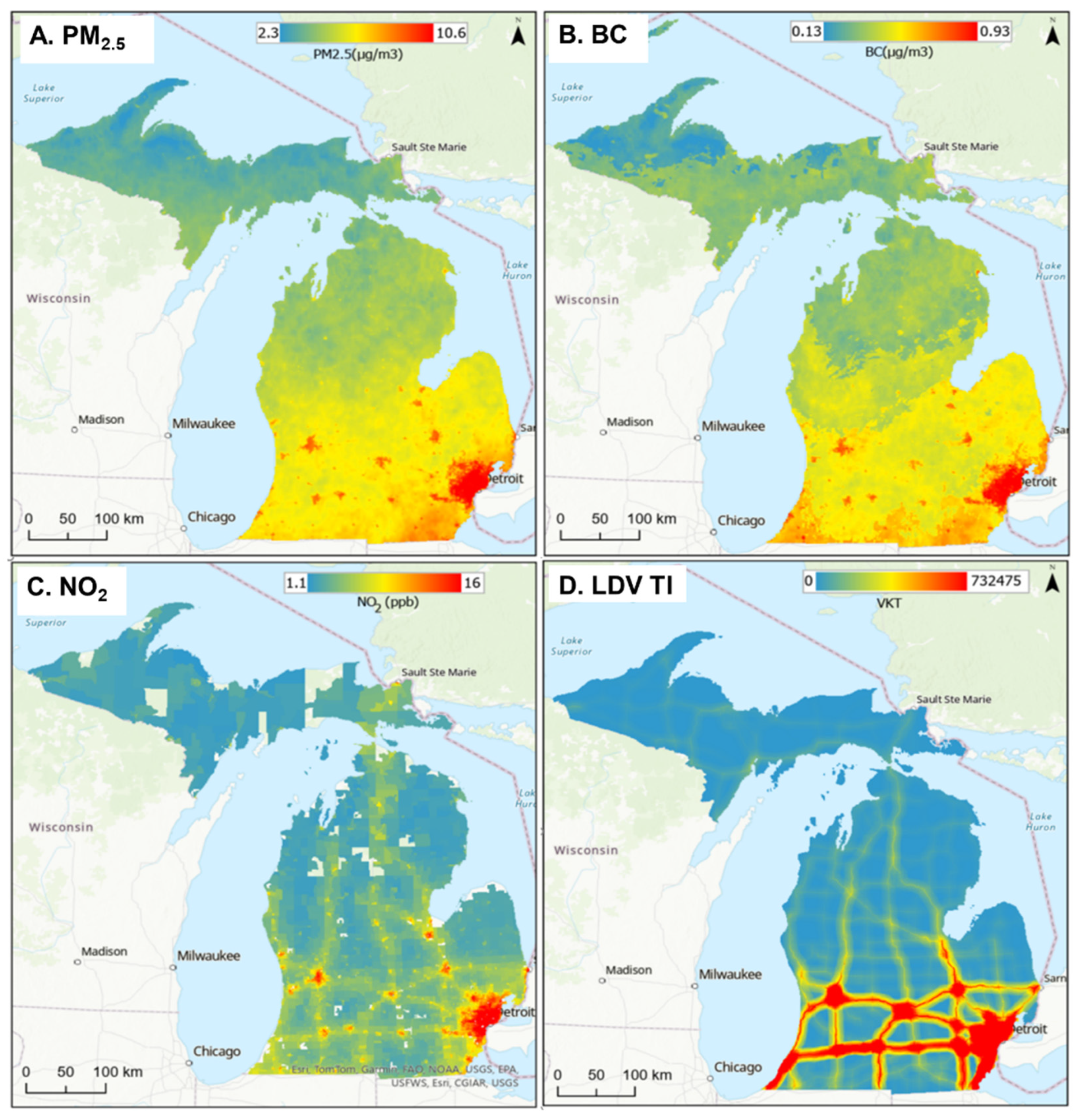
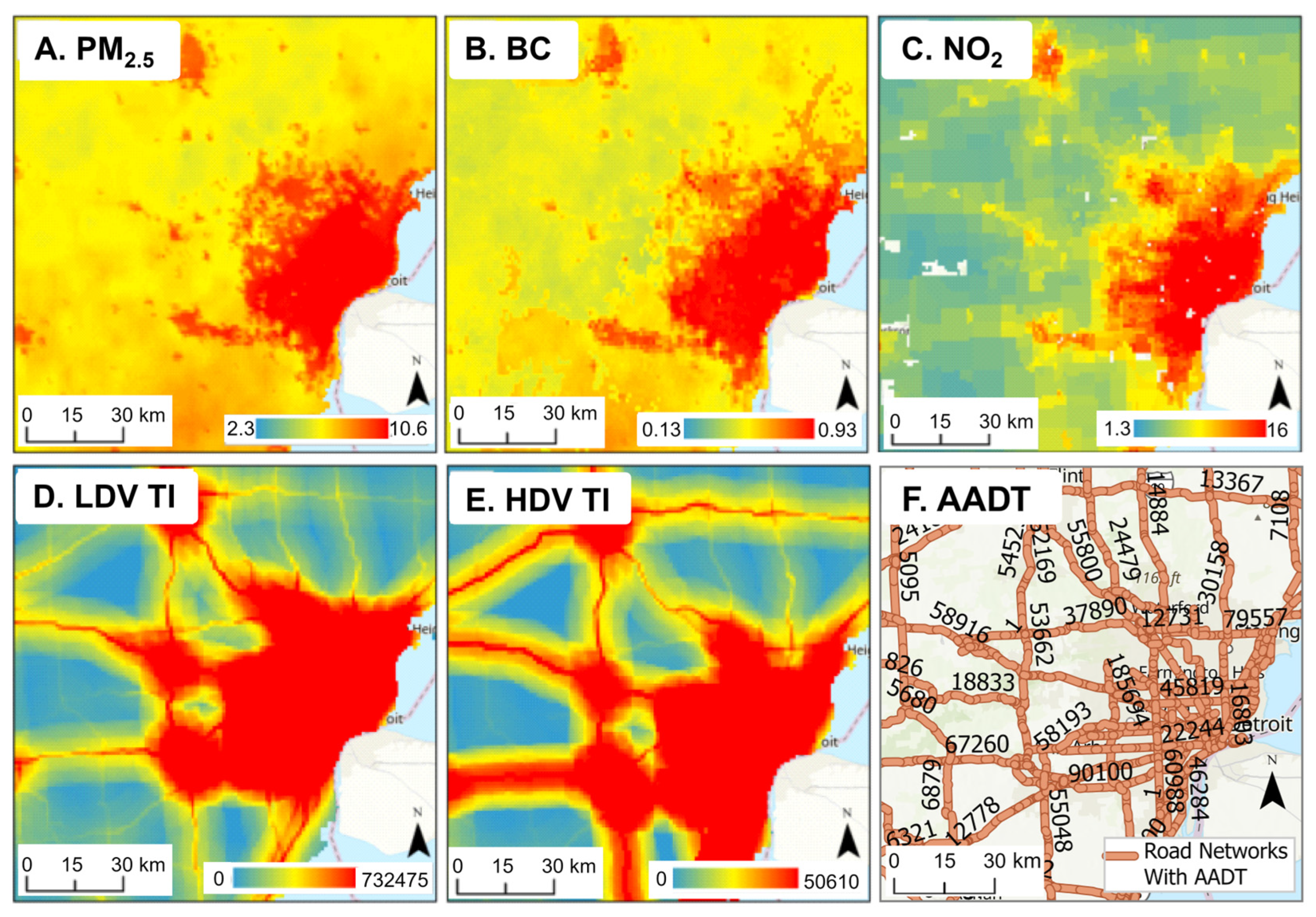
3.5. Comparison of the Geospatial Datasets
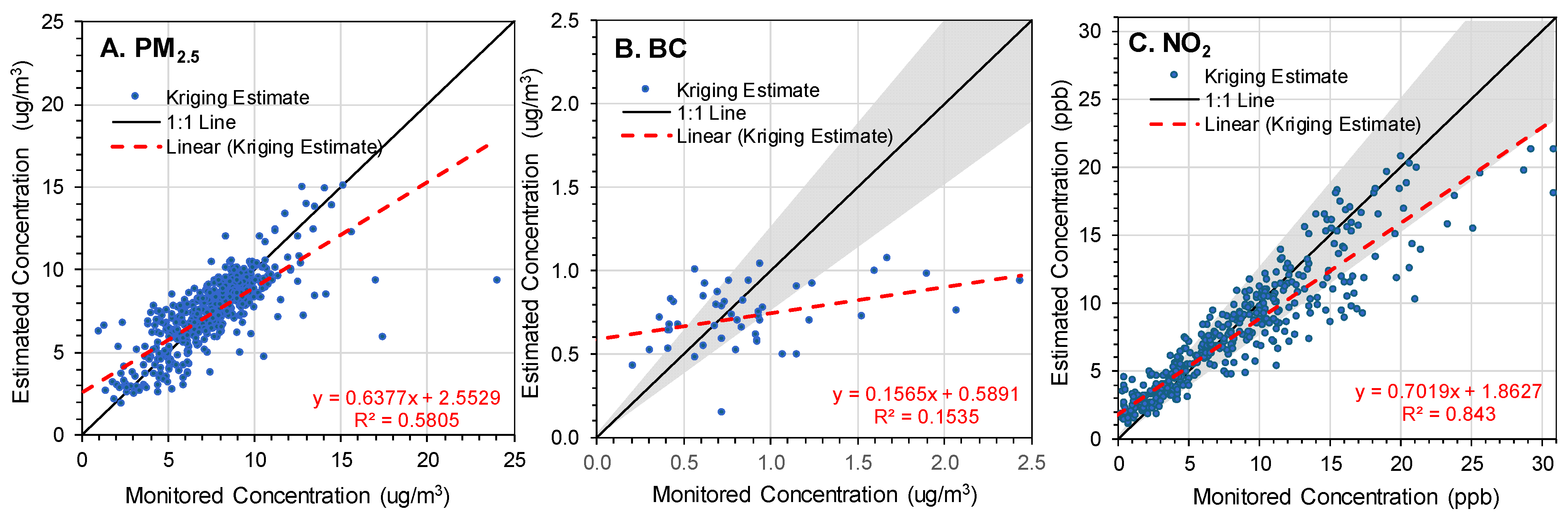
3.6. Comparison of Geospatial and Monitoring Data
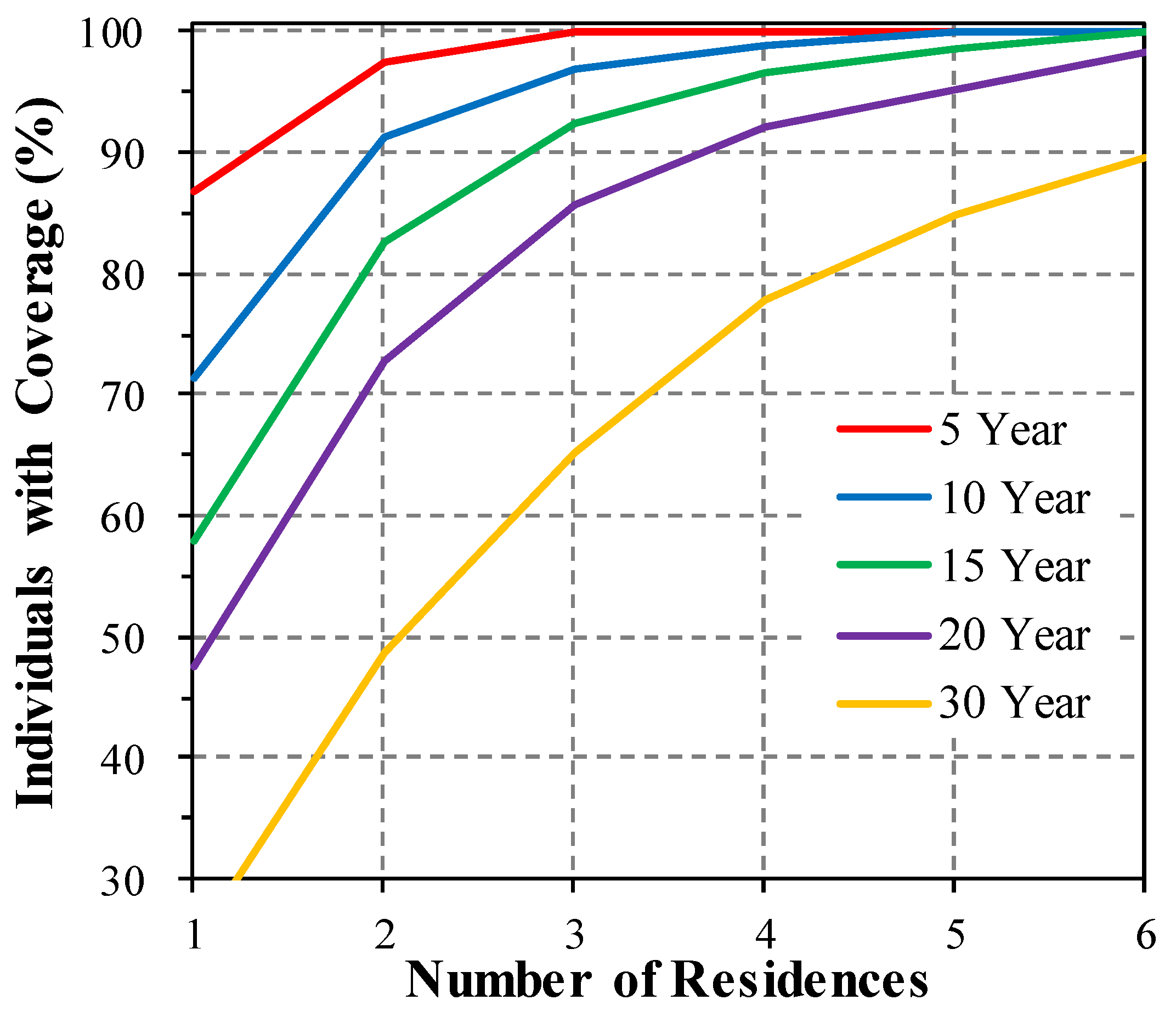
3.7. Interpolation and Linking
4. Discussion
4.1. Residential Mobility of an Older Cohort
4.2. Resolving Incomplete Residential Histories
4.3. Geospatial Datasets
4.4. Spatial Linkage, Interpolations and Resolution
4.5. Limitations and Evaluation of Geospatial Exposure Estimates
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AADT | annual average daily traffic |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BC | black carbon |
| CAADT | commercial annual average daily traffic |
| COV | coefficient of variation |
| CVKT | commercial vehicle kilometers traveled |
| HDV | heavy duty vehicle, e.g., truck |
| IDW | inverse distance weighting |
| KS | Kolmogorov–Smirnov |
| LDV | light duty vehicle, e.g., car |
| LUR | land use regression |
| MAE | mean average error |
| MAPE | mean absolute percentage error |
| MI | multiple imputation |
| NAAQS | National Ambient Air Quality Standard |
| NO2 | nitrogen dioxide |
| PM2.5 | particulate matter under 2.5 micron in diameter |
| RBF | radial basis function |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| SES | socioeconomic status |
| TI | traffic intensity |
| VKT | vehicle kilometers traveled |
References
- Brender, J.D.; Maantay, J.A.; Chakraborty, J. Residential Proximity to Environmental Hazards and Adverse Health Outcomes. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101, S37–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokamp, C.; LeMasters, G.K.; Ryan, P.H. Residential Mobility Impacts Exposure Assessment and Community Socioeconomic Characteristics in Longitudinal Epidemiology Studies. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-L.; Batterman, S. Residence Location as a Measure of Environmental Exposure: A Review of Air Pollution Epidemiology Studies. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2000, 10, 66–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stingone, J.A.; Geller, A.M.; Hood, D.B.; Makris, K.C.; Mouton, C.P.; States, J.C.; Sumner, S.J.; Wu, K.L.; Rajasekar, A.K. Members of the Exposomics Consortium Community-Level Exposomics: A Population-Centered Approach to Address Public Health Concerns. Exposome 2023, 3, osad009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.P.; Zilber, D.; Schmitt, C.; Fargo, D.C.; Reif, D.M.; Motsinger-Reif, A.A.; Messier, K.P. A Review of Geospatial Exposure Models and Approaches for Health Data Integration. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2024, 35, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Eccles, K.M.; Kwok, R.K.; Joubert, B.R.; Messier, K.P.; Balshaw, D.M. Integrating Multiscale Geospatial Environmental Data into Large Population Health Studies: Challenges and Opportunities. Toxics 2022, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, T.; Miller, D.; Anenberg, S.; Diao, M.; Duncan, B.; Fiore, A.M.; Henze, D.K.; Hess, J.; Kinney, P.L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Satellite Monitoring for Air Quality and Health. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2021, 4, 417–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed Al Ahad, M.; Demšar, U.; Sullivan, F.; Kulu, H. The Spatial–Temporal Effect of Air Pollution on Individuals’ Reported Health and Its Variation by Ethnic Groups in the United Kingdom: A Multilevel Longitudinal Analysis. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKone, T.E.; Ryan, P.B.; Özkaynak, H. Exposure Information in Environmental Health Research: Current Opportunities and Future Directions for Particulate Matter, Ozone, and Toxic Air Pollutants. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, P.; Wartenberg, D. Spatial Epidemiology: Current Approaches and Future Challenges. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P. Spatial Lifecourse Epidemiology. Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, e57–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliker, J.R.; Sloan, C.D. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiology: Principles and Opportunities. Spat. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2011, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Simpkin, A.J.; Suderman, M.J.; Lussier, A.A.; Walton, E.; Dunn, E.C.; Smith, A.D.A.C. A Structured Approach to Evaluating Life-Course Hypotheses: Moving Beyond Analyses of Exposed Versus Unexposed in the -Omics Context. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, T.C.; Cherrie, M.P.C.; Dibben, C.; Tomlinson, S.; Reis, S.; Dragosits, U.; Vieno, M.; Beck, R.; Carnell, E.; Shortt, N.K.; et al. Life Course Air Pollution Exposure and Cognitive Decline: Modelled Historical Air Pollution Data and the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936. JAD 2021, 79, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalley, L.J.; Dick, F.D.; McNeill, G. A Life-Course Approach to the Aetiology of Late-Onset Dementias. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M. Contemporary Issues in Exposure Assessment Using Biomonitoring. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2016, 3, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheepers, P.T.J.; Bos, P.M.J.; Konings, J.; Janssen, N.A.H.; Grievink, L. Application of Biological Monitoring for Exposure Assessment Following Chemical Incidents: A Procedure for Decision Making. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirby, R.S.; Delmelle, E.; Eberth, J.M. Advances in Spatial Epidemiology and Geographic Information Systems. Ann. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayo, M.R.; Talbot, T.O. Positional Error in Automated Geocoding of Residential Addresses. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2003, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.R. Complexity and Uncertainty in Geography of Health Research: Incorporating Life-Course Perspectives. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2018, 108, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.L.; Banerjee, G.; Pereira, G. Residential Mobility of Pregnant Women and Implications for Assessment of Spatially-Varying Environmental Exposures. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, S.; Rushton, G.; Smith, B.J.; Zimmerman, D.L.; Donham, K.J. Geocoding Accuracy and the Recovery of Relationships between Environmental Exposures and Health. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2008, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H.; Nuckols, J.R.; Giglierano, J.; Bonner, M.R.; Wolter, C.; Airola, M.; Mix, W.; Colt, J.S.; Hartge, P. Positional Accuracy of Two Methods of Geocoding. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandbergen, P.A. A Comparison of Address Point, Parcel and Street Geocoding Techniques. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2008, 32, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnee, E.J.; Tripathy, S.; Schinasi, L.; Shmool, J.L.C.; Sheffield, P.E.; Holguin, F.; Clougherty, J.E. Geocoding Error, Spatial Uncertainty, and Implications for Exposure Assessment and Environmental Epidemiology. IJERPH 2020, 17, 5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harden, S.R.; Schuurman, N. Geospatial Science and Health: Overview. In Understanding Cancer Prevention Through Geospatial Science: Putting Cancer in its Place; Springer: London, UK, 2024; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, J.; Maantay, J.A.; Brender, J.D. Disproportionate Proximity to Environmental Health Hazards: Methods, Models, and Measurement. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101, S27–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner-Frolick, R.; Boyd, D.; Giang, A. Selecting Data Analytic and Modeling Methods to Support Air Pollution and Environmental Justice Investigations: A Critical Review and Guidance Framework. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2843–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, T.; Domínguez-Castillo, A.; de Larrea-Baz, N.F.; Lucas, P.; Sierra, M.Á.; Maeso, S.; Llobet, R.; Pino, M.N.; Martínez-Cortés, M.; Pérez-Gómez, B. Mammographic Density and Exposure to Air Pollutants in Premenopausal Women: A Cross-Sectional Study. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2024, 29, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Sarma, K. Mapping Spatial Distribution of Traffic Induced Criteria Pollutants and Associated Health Risks Using Kriging Interpolation Tool in Delhi. J. Transp. Health 2020, 18, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Shorshani, M.; Hatzopoulou, M.; Ross, N.A.; Patterson, Z.; Weichenthal, S. Evaluating the Impact of Neighborhood Characteristics on Differences between Residential and Mobility-Based Exposures to Outdoor Air Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10777–10786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutman, S.A.; Boss, J.; Godwin, C.; Mukherjee, B.; Feldman, E.L.; Batterman, S.A. Associations of Self-Reported Occupational Exposures and Settings to ALS: A Case–Control Study. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2022, 95, 1567–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutman, S.A.; Boss, J.; Godwin, C.; Mukherjee, B.; Feldman, E.L.; Batterman, S.A. Occupational History Associates with ALS Survival and Onset Segment. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2023, 24, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Huber, J.C., Jr. Evaluation of Multiple Imputation with Large Proportions of Missing Data: How Much Is Too Much? Iran. J. Public Health 2021, 50, 1372. [Google Scholar]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Li, C.; Burnett, R.T. Regional Estimates of Chemical Composition of Fine Particulate Matter Using a Combined Geoscience-Statistical Method with Information from Satellites, Models, and Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2595–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Air, Climate & Energy Solutions. Available online: https://www.caces.us/data (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Lu, T.; Kim, S.-Y.; Marshall, J. High-Resolution Geospatial Database: National Criteria-Air-Pollutant Concentrations in the Contiguous US, 2016–2020; Center for Air. Climate & Energy Solutions (CACES): Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Liu, C.; Meng, X.; Wang, W.; Niu, C.; Kan, L.; Schikowski, T. Application of Land Use Regression to Assess Exposure and Identify Potential Sources in PM2. 5, BC, NO2 Concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Du, S.; Bai, Z.; Shao-fei, K.; Yan, Y.; Bin, H.; Dao-wen, H.; Li, Z. Application of Land Use Regression for Estimating Concentrations of Major Outdoor Air Pollutants in Jinan, China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2010, 11, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Beelen, R.; Bellander, T.; Birk, M.; Cesaroni, G.; Cirach, M.; Cyrys, J.; De Hoogh, K.; Declercq, C.; Dimakopoulou, K.; et al. Performance of Multi-City Land Use Regression Models for Nitrogen Dioxide and Fine Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.G.; Jerrett, M.; Beckerman, B.; Wilhelm, M.; Ghosh, J.K.; Ritz, B. Predicting Traffic-Related Air Pollution in Los Angeles Using a Distance Decay Regression Selection Strategy. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, A.M.; Arena, V.C.; Song, R.; Whitsel, E.A.; Rager, J.R.; Stewart, J.; Yanosky, J.D.; Liao, D.; Talbott, E.O. Long-Term Air Pollution and Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Mortality in the Women’s Health Initiative Cohort. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, R.M.; Nunez, Y.; Balalian, A.A.; Gibson, E.A.; Hansen, J.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Ketzel, M.; Khan, J.; Brandt, J.; Vermeulen, R. Long-Term Traffic-Related Air Pollutant Exposure and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Diagnosis in Denmark: A Bayesian Hierarchical Analysis. Epidemiology 2022, 33, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.A.; Islam, M.K.; Jang, D.G.; Feldman, E.L.; Goutman, S.A. Life Course Exposure to Cyanobacteria and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Survival. IJERPH 2025, 22, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakowski, S.A.; Koubek, E.J.; Chen, K.S.; Goutman, S.A.; Feldman, E.L. Role of the Exposome in Neurodegenerative Disease: Recent Insights and Future Directions. Ann. Neurol. 2024, 95, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelleyman, T.; Spencer, N. Residential Mobility in Childhood and Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2008, 62, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwak, E.; Longino, C.F. Migration Patterns Among the Elderly: A Developmental Perspective. Gerontol. 1987, 27, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, B.J.; Fokkema, T. Life Events, Social Conditions and Residential Mobility among Older Adults. Popul. Space Place 2024, 30, e2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerns-D’Amore, K.; McKenzie, B.; Locklear, L.S. Migration in the United States: 2006 to 2019; ACS-53; US Census Bureau: Suitland, MD, USA, 2023.
- Delmelle, E.M.; Desjardins, M.R.; Jung, P.; Owusu, C.; Lan, Y.; Hohl, A.; Dony, C. Uncertainty in Geospatial Health: Challenges and Opportunities Ahead. Ann. Epidemiol. 2022, 65, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, D.L. Estimating the Intensity of a Spatial Point Process from Locations Coarsened by Incomplete Geocoding. Biometrics 2008, 64, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquez, G.M.; Slotnick, M.J.; Meliker, J.R.; AvRuskin, G.; Copeland, G.; Nriagu, J. Accuracy of Commercially Available Residential Histories for Epidemiologic Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudeville, J.; Regrain, C.; Tognet, F.; Bonnard, R.; Guedda, M.; Brochot, C.; Beauchamp, M.; Letinois, L.; Malherbe, L.; Marliere, F.; et al. Characterizing Environmental Geographic Inequalities Using an Integrated Exposure Assessment. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VoPham, T.; White, A.J.; Jones, R.R. Geospatial Science for the Environmental Epidemiology of Cancer in the Exposome Era. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2024, 33, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Ganguly, R.; Harbin, P. High Resolution Spatial and Temporal Mapping of Traffic-Related Air Pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3646–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, V.; Arunachalam, S.; Batterman, S.; Bereznicki, S.; Burke, J.; Dionisio, K.; Garcia, V.; Heist, D.; Perry, S.; Snyder, M. Air Quality Modeling in Support of the Near-Road Exposures and Effects of Urban Air Pollutants Study (NEXUS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8777–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anondo, M.; Ryder, O.; McCarthy, M.; Brown, S.; Eisinger, D. Near-Road Particulate Pollution: PM2.5, Black Carbon, and Ultrafine Particles at U.S. Near-Road Monitoring Sites; Texas Department of Transportation: Austin, TX, USA, 2019; p. 56.
- Mukherjee, A.; McCarthy, M.C.; Brown, S.G.; Huang, S.; Landsberg, K.; Eisinger, D.S. Influence of Roadway Emissions on Near-Road PM2.5: Monitoring Data Analysis and Implications. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 86, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.G.; Penfold, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Landsberg, K.; Eisinger, D.S. Conditions Leading to Elevated PM2.5 at Near-Road Monitoring Sites: Case Studies in Denver and Indianapolis. IJERPH 2019, 16, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perveen, S.; Allan James, L. Changes in Correlation Coefficients with Spatial Scale and Implications for Water Resources and Vulnerability Data. Prof. Geogr. 2012, 64, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, H.; Danesh-Yazdi, M.; Di, Q.; Requia, W.; Wei, Y.; AbuAwad, Y.; Shi, L.; Franklin, M.; Kang, C.; Wolfson, M.J.; et al. Annual Mean PM2.5 Components (EC, NH4, NO3, OC, SO4) 50m Urban and 1km Non-Urban Area Grids for Contiguous U.S., 2000-2019 V1; CIESIN: Palisades, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Chao, Y.; Chen, H. A Novel Prediction Framework for Estimating High Spatial Resolution Near-Ground PM2.5 and O3 Concentrations at Street-Level in Urban Areas. Build. Environ. 2025, 267, 112141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.A.; Fuentes, M.; Zhang, Y.; Burr, M.J.; Bell, M.L. Comparison of Exposure Estimation Methods for Air Pollutants: Ambient Monitoring Data and Regional Air Quality Simulation. Environ. Res. 2012, 116, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenailleau, Q.; Lanier, C.; Prud’homme, J.; Cuny, D.; Deram, A.; Occelli, F. Distance-Based Indicators for Evaluating Environmental Multi-Contamination and Related Exposure: How Far Should We Go? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 50642–50653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandbergen, P.A.; Chakraborty, J. Improving Environmental Exposure Analysis Using Cumulative Distribution Functions and Individual Geocoding. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2006, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Joyce, B.T.; Nannini, D.R.; Zheng, Y.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Shikany, J.M.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Hu, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Vaughan, D.E.; et al. Inequalities in Urban Greenness and Epigenetic Aging: Different Associations by Race and Neighborhood Socioeconomic Status. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, D.; Pavlik, C.; Ruggles, A.; Armstrong, M.P. An Experimental Comparison of Ordinary and Universal Kriging and Inverse Distance Weighting. Math. Geol. 1999, 31, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezyk, Y.; Sówka, I.; Górka, M.; Blachowski, J. Gis-Based Approach to Spatio-Temporal Interpolation of Atmospheric Co2 Concentrations in Limited Monitoring Dataset. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A.D. Spatial Interpolation Methods Applied in the Environmental Sciences: A Review. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 53, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, M.; Courbin, F.; Meylan, G. Interpolating Point Spread Function Anisotropy. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 549, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtkar, M.; Heidari, H.; Moazzeni, N.; Azadi, H. Analysis of Changes in Air Pollution Quality and Impact of COVID-19 on Environmental Health in Iran: Application of Interpolation Models and Spatial Autocorrelation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 38505–38526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Sheppard, L.; Kim, H. Health Effects of Long-Term Air Pollution: Influence of Exposure Prediction Methods. Epidemiology 2009, 20, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, K.; Sisodiya, S.; Mathur, A.K.; Zare, A.; Verma, P. Assessment and Spatial Distribution Mapping of Criteria Pollutants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, A.; Ghasemi, S.M. Determination of the Best Interpolation Method in Estimating the Concentration of Environmental Air Pollutants in Tehran City in 2015. J. Air Pollut. Health 2018, 3, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, R.; Batterman, S.; Isakov, V.; Snyder, M.; Breen, M.; Brakefield-Caldwell, W. Effect of Geocoding Errors on Traffic-Related Air Pollutant Exposure and Concentration Estimates. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippmann, M. Pathways and Measuring Exposure to Toxic Substances. In Encyclopedia of Agrochemicals; Plimmer, J.R., Gammon, D.W., Ragsdale, N.A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-471-26363-0. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Guidance on the Development, Evaluation, and Application of Environmental Models; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. 99.
- Models in Environmental Regulatory Decision Making; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 11972. ISBN 978-0-309-11000-6.
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, D.; Hao, R. Understanding the Patterns and Drivers of Air Pollution on Multiple Time Scales: The Case of Northern China. Environ. Manag. 2018, 61, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, T.; Liu, C.; Qian, H.; Li, J. Seasonal and Diurnal Patterns of Outdoor Formaldehyde and Impacts on Indoor Environments and Health. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Islam, M.K.; Xia, T.; Batterman, S. Apportionment of PM2.5 Sources across Sites and Time Periods: An Application and Update for Detroit, Michigan. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hasheminassab, S. Long-Term Source Apportionment of PM2.5 across the Contiguous United States (2000-2019) Using a Multilinear Engine Model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

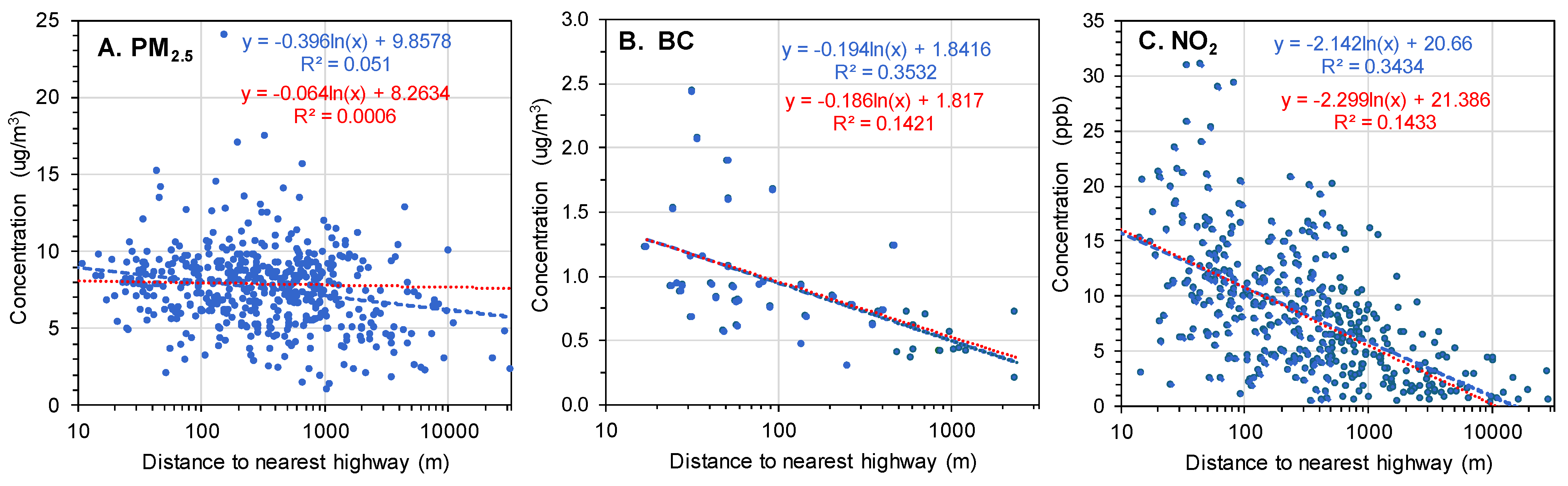
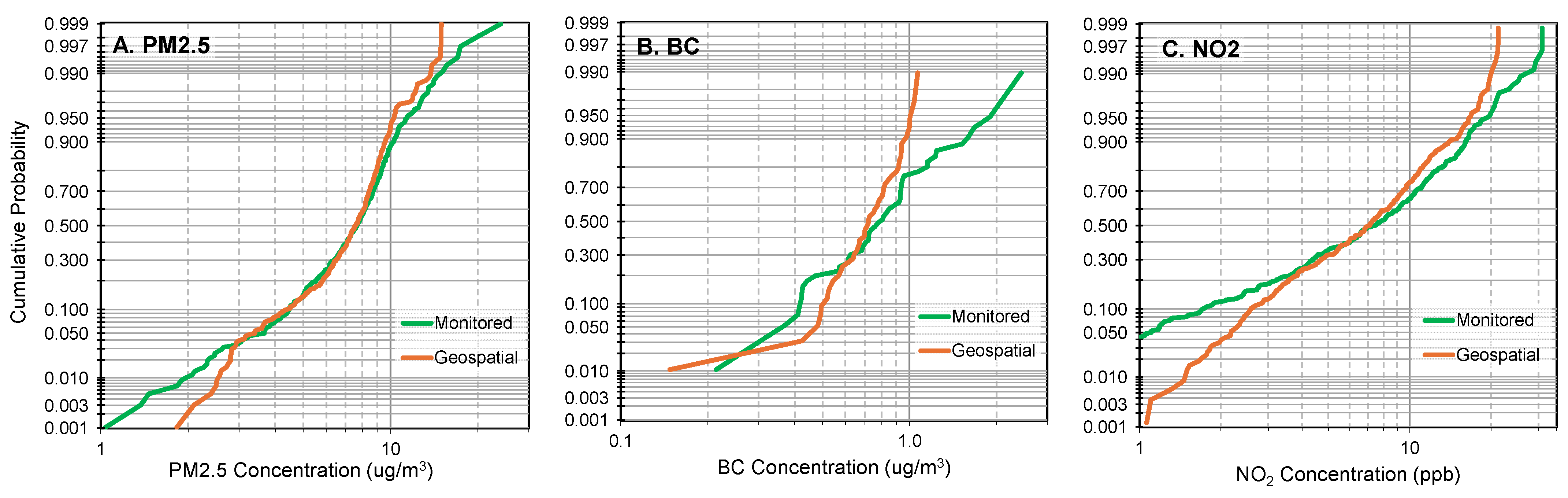
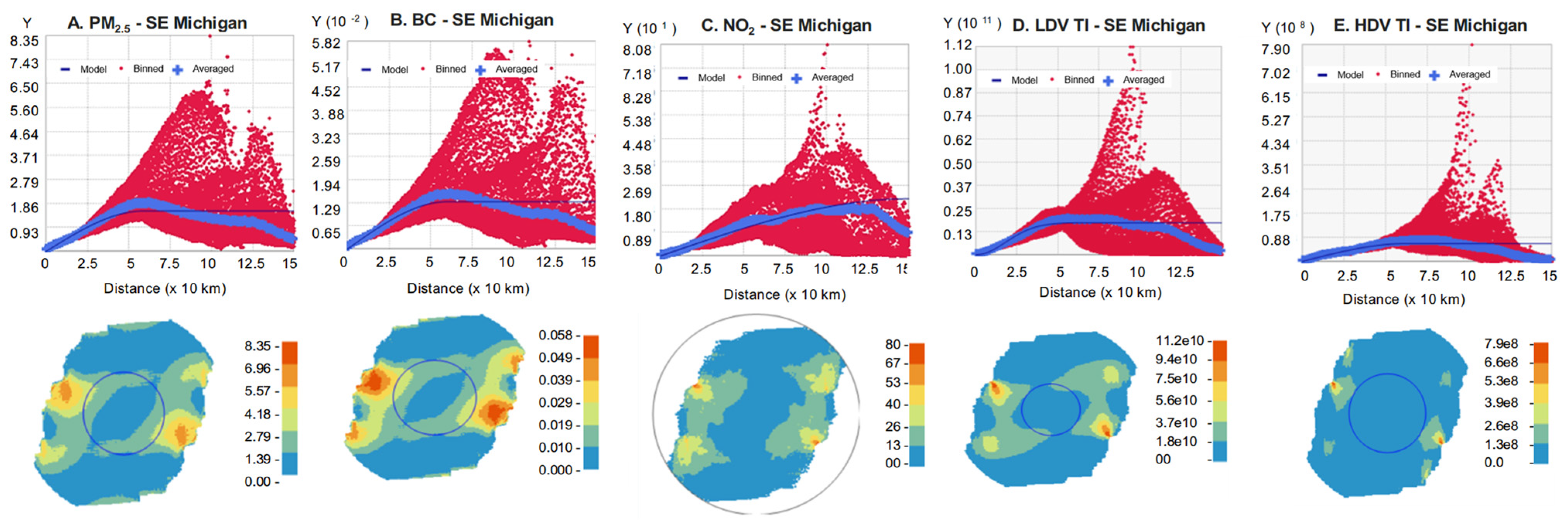

| Seq. | Year Move-In Hierarchy | N | (%) | Seq. | Year Move-Out Hierarchy | N | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Move-in year | 8731 | (88.5) | 1 | Move-out year | 7565 | (76.7) |
| 2 | Age at move-in + year of birth | 806 | (8.2) | 2 | Age at move-out + year of birth | 845 | (8.6) |
| 3 | Prior move-out year | 16 | (0.2) | 3 | Following move-in year | 68 | (0.7) |
| 4 | Prior move-out age + year of birth | 3 | (0.0) | 4 | Following move-in age + year of birth | 5 | (0.1) |
| For first (childhood) residence, birth year | 171 | (1.7) | 5 | For last residence, year of death | 466 | (4.7) | |
| 5 | Missing | 134 | (1.4) | 6 | For last residence, current year (living) | 779 | (7.9) |
| Total | 9861 | (100.0) | 7 | Missing | 133 | (1.3) | |
| Total | 9861 | (100.0) | |||||
| Seq. | Month Move-In Hierarchy | N | (%) | Seq. | Month Move-Out Hierarchy | N | (%) |
| 1 | Move-in month | 7572 | (76.8) | 1 | Move-out month | 6472 | (65.6) |
| 2 | Prior move-out month | 68 | (0.7) | 2 | Following move-in month | 223 | (2.3) |
| 3 | Initial default (8 = Aug) | 2221 | (22.5) | 3 | For latest residence, month of death | 475 | (4.8) |
| Total | 9861 | (100.0) | 4 | For latest residence, current month (living) | 780 | (7.9) | |
| 5 | Initial default (7 = July) | 1911 | (19.4) | ||||
| Total | 9861 | (100.0) |
| Relationship Status | Males | Females | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life | 20 Years | N | Life | 20 Years | N | Life | 20 Years | N | |
| Married, Partner | 7.50 | 2.00 | 575 | 7.69 | 1.98 | 390 | 7.58 | 1.99 | 965 |
| Divorced, Separated | 7.00 | 2.71 | 76 | 7.52 | 2.71 | 95 | 7.29 | 2.71 | 171 |
| Widowed | 7.44 | 1.56 | 16 | 7.09 | 2.18 | 57 | 7.16 | 2.04 | 73 |
| Never married | 7.66 | 3.07 | 44 | 8.20 | 2.93 | 44 | 7.93 | 3.00 | 88 |
| NA | 8.17 | 3.00 | 6 | 6.75 | 1.50 | 4 | 8.40 | 2.40 | 10 |
| All | 7.46 | 2.14 | 717 | 7.64 | 2.18 | 590 | 7.55 | 2.16 | 1307 |
| Information Category | Coordinate Extraction | Length (km) or Area (km2) | Residence Location | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Michigan | Elsewhere US | |||||
| 1: Sufficient Information | Geocoded | NA | 2391 | 557 | 2948 | |
| 2: Partial Information | ||||||
| 2A: Info. Corrected | Geocoded | NA | 40 | 9 | 49 | |
| 2B: Info. Corrected (Small Street/Area) | Approximated | Length/Area< 1 | 17 | 8 | 25 | |
| 2C: Small Street/Area | Approximated | Length/Area< 1 | 258 | 100 | 358 | |
| 2D: Addresses with Street Information | 1≤ Length< 2 | 79 | 42 | 121 | ||
| Multiple | 2≤ Length< 5 | 122 | 35 | 157 | ||
| Imputation | 5≤ Length< 10 | 53 | 14 | 67 | ||
| 10≤ Length≤ 20 | 53 | 7 | 60 | |||
| Length >20 | 0 | 2 | 2 | |||
| 2E: Addresses with Area Information | 1≤ Area< 2 | 7 | 11 | 18 | ||
| Multiple | 2≤ Area< 5 | 22 | 26 | 48 | ||
| Imputation | 5≤ Area< 10 | 27 | 22 | 49 | ||
| 10≤ Area≤ 20 | 43 | 45 | 88 | |||
| Area >20 | 11 | 11 | 22 | |||
| 3: Inadequate Information | NA | NA | 148 | 217 | 365 | |
| Total | NA | NA | 3271 | 1106 | 4377 | |
| Exposure Metric | Type | Summary Statistics | Spearman | Distribution Tests | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | St. Dev. | Minimum | Max | R | M-W | K-S | ||
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | Actual | 7.49 | 1.63 | 4.72 | 10.01 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1.00 |
| Imputed | 7.48 | 1.64 | 4.74 | 10.10 | ||||
| BC (μg/m3) | Actual | 0.58 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Imputed | 0.58 | 0.14 | 0.35 | 0.85 | ||||
| NO2 (ppb) | Actual | 5.99 | 3.31 | 1.61 | 13.54 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
| Imputed | 5.94 | 3.33 | 1.60 | 13.28 | ||||
| LDV TI | Actual | 126,376 | 144,107 | 221 | 529,330 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 |
| Imputed | 128,497 | 146,910 | 130 | 542,061 | ||||
| HDV TI | Actual | 9956 | 10,242 | 11 | 33,915 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Imputed | 9982 | 10,030 | 7 | 32,799 | ||||
| Michigan (N = 141,065) | Southeast Michigan (N = 24,630) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | BC (μg/m3) | NO2 (ppb) | LDV TI | HDV TI | PM2.5 (μg/m3) | BC (μg/m3) | NO2 (ppb) | LDV TI | HDV TI | Color Scale | ||
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 1.00 | PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 1.00 | 0.00 | ||||||||
| BC (μg/m3) | 0.93 | 1.00 | BC (μg/m3) | 0.80 | 1.00 | 0.25 | ||||||
| NO2 (ppb) | 0.70 | 0.66 | 1.00 | NO2 (ppb) | 0.58 | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0.50 | ||||
| LDV TI | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 1.00 | LDV TI | 0.39 | 0.23 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.75 | ||
| HDV TI | 0.64 | 0.58 | 0.71 | 0.96 | 1.00 | HDV TI | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Exposure | Parameter | Southeast Michigan | Michigan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | Spherical | Exponential | Gaussian | Spherical | Exponential | Gaussian | |
| PM2.5 | Range (km) | 59 | 78 | 35 | 150 | 150 | 39 |
| Partial Sill | 1.56 | 1.64 | 1.50 | 0.49 | 0.45 | 0.37 | |
| Model Fit | Good | Fair | Fair | Good | Fair | Poor | |
| Symmetry | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | |
| RMSE | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | |
| BC | Range (km) | 60 | 81 | 34 | 71 | 131 | 19 |
| Partial Sill | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.002 | |
| Model Fit | Good | Poor | Poor | Fair | Good | Very Poor | |
| Symmetry | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | |
| RMSE | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.024 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.016 | |
| NO2 | Range (km) | 150 | 150 | 43 | 77 | 140 | 40 |
| Partial Sill | 22 | 15 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 10 | |
| Model Fit | Good | Fair | Poor | Good | Fair | Fair | |
| Symmetry | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | |
| RMSE | 0.42 | 0.42 | 1.94 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 1.92 | |
| LDV | Range (km) | 64 | 93 | 45 | 78 | 116 | 46 |
| TI | Sill (×106) | 17,391 | 18,839 | 17,190 | 1912 | 2058 | 1843 |
| Model Fit | Fair | Fair | Good | Very Good | Good | Fair | |
| Symmetry | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Asymmetric | Symmetric | Symmetric | Symmetric | |
| RMSE | 10,465 | 10,467 | 15 | 3432 | 3432 | 2562 | |
| HDV | Range (km) | 62 | 84 | 32 | 55 | 85 | 27 |
| TI | Sill (×106) | 65 | 68 | 58 | 8 | 9 | 8 |
| Model Fit | Good | Good | Fair | Good | Very Good | Fair | |
| Symmetry | Symmetric | Symmetric | Symmetric | Symmetric | Symmetric | Symmetric | |
| RMSE | 872 | 872 | 1346 | 330 | 330 | 400 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batterman, S.; Islam, M.K.; Goutman, S. Development of Life Course Exposure Estimates Using Geospatial Data and Residence History. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22111629
Batterman S, Islam MK, Goutman S. Development of Life Course Exposure Estimates Using Geospatial Data and Residence History. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(11):1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22111629
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatterman, Stuart, Md Kamrul Islam, and Stephen Goutman. 2025. "Development of Life Course Exposure Estimates Using Geospatial Data and Residence History" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 11: 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22111629
APA StyleBatterman, S., Islam, M. K., & Goutman, S. (2025). Development of Life Course Exposure Estimates Using Geospatial Data and Residence History. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(11), 1629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22111629







