Clinical Usefulness of a Short Version of the Internet Addiction Test to Screen for Probable Internet Addiction in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Internet Addiction Test (IAT)
2.3. A Short Version of the Internet Addiction Test (s-IAT)
2.4. Clinical Diagnosis of IA
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic of the Subjects
3.2. Clinical Diagnosis of IA
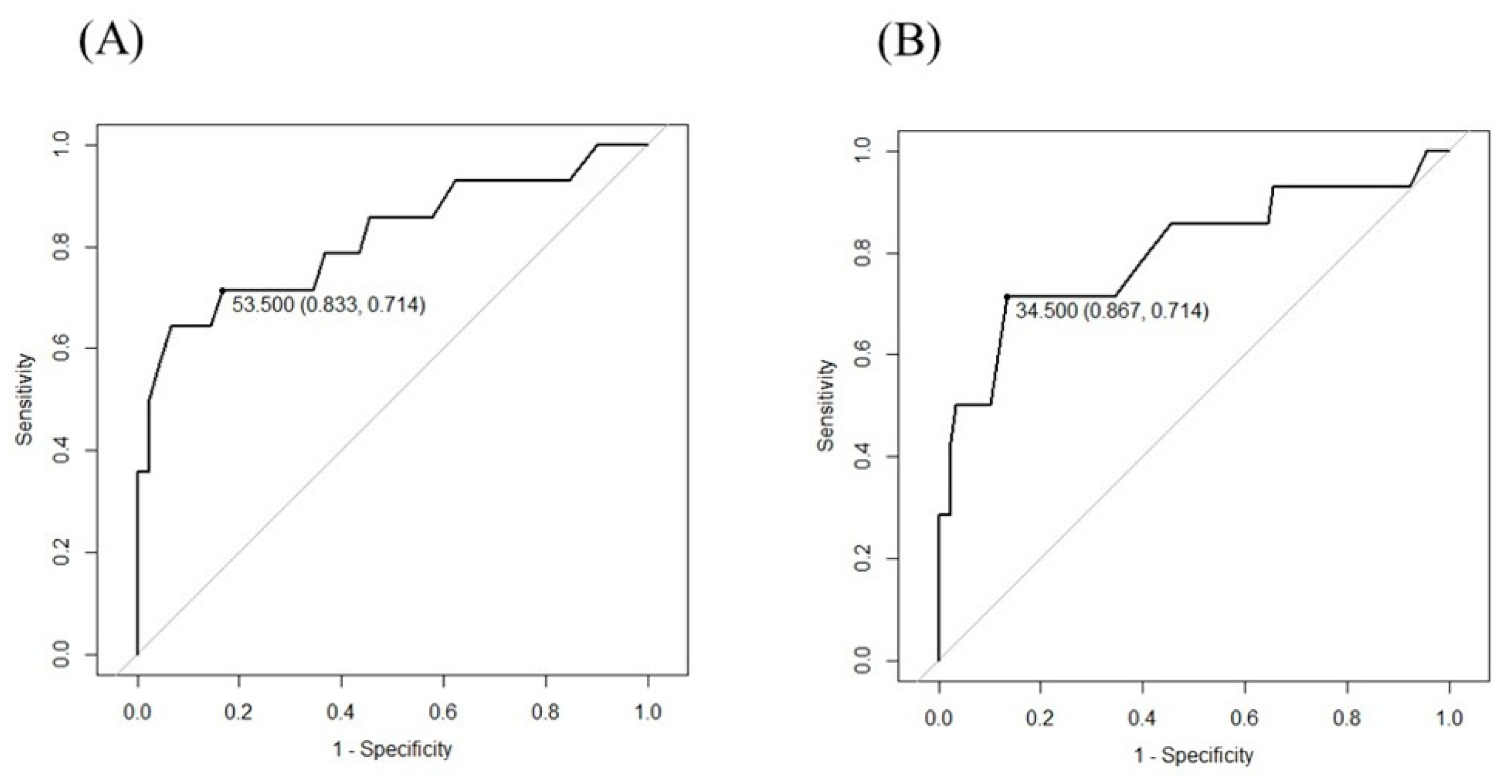
3.3. Cut-Off Points for IAT and s-IAT
3.4. Results of the IAT and s-IAT for Screening IA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aboujaoude, E. Problematic Internet use: An overview. World Psychiatry Off. J. World Psychiatr. Assoc. 2010, 9, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, M.G.; Nunez, X.; de Almeida, R.M.M. Internet Addiction and Attention in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2021, 24, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabe, K.; Horiuchi, F.; Miyama, T.; Jogamoto, T.; Aibara, K.; Ishii, E.; Ueno, S.I. Internet addiction and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 89, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, R.; Makino, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Hirota, T.; Ohcho, K.; Ikeda, S.; Tsubouchi, S.; Inagaki, M. The Prevalence of Internet Addiction among a Japanese Adolescent Psychiatric Clinic Sample with Autism Spectrum Disorder and/or Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Autism. Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Q.; Yao, N.Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z.T. The association between attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and internet addiction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Wen, M.; Huang, H.; Zheng, R.; Wang, W.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, J.; Han, S.; et al. Structural and Functional Brain Abnormalities in Internet Gaming Disorder and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Comparative Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 679437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Yen, J.Y.; Chen, C.S.; Yeh, Y.C.; Yen, C.F. Predictive values of psychiatric symptoms for internet addiction in adolescents: A 2-year prospective study. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2009, 163, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateno, M.; Matsuzaki, T.; Takano, A.; Higuchi, S. Increasing important roles of child and adolescent psychiatrists in the treatment of gaming disorder: Current status in Japan. Front. Psych. 2022, 13, 995665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullur, P.; Krishnan, V.; Diaz, A.M. A systematic review on the intersection of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and gaming disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 133, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.; Koronczai, B.; Király, O.; Griffiths, M.D.; Mannion, A.; Leader, G.; Demetrovics, Z. Autism, Problematic Internet Use and Gaming Disorder: A Systematic Review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2022, 9, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane-Simpson, C.; Brooks, P.J.; Obeid, R.; Denton, E.; Gillespie-Lynch, K. Associations between compulsive internet use and the autism spectrum. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2016, 23, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, S.H.; Gau, S.S. ADHD and autistic traits, family function, parenting style, and social adjustment for Internet addiction among children and adolescents in Taiwan: A longitudinal study. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, M.V.; Chakrabarti, B.; Bullmore, E.T.; Sadek, S.A.; Pasco, G.; Wheelwright, S.J.; Suckling, J.; Consortium, M.A.; Baron-Cohen, S. Atypical neural self-representation in autism. Brain 2010, 133, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.C.; Lombardo, M.V.; Baron-Cohen, S. Autism. Lancet 2014, 383, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.L.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Carragher, N.; Billieux, J.; Stein, D.; Mueller, K.; Potenza, M.N.; Rumpf, H.J.; Saunders, J.; Starcevic, V.; et al. Screening and assessment tools for gaming disorder: A comprehensive systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 77, 101831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerkerk, G.J.; Van Den Eijnden, R.; Vermulst, A.A.; Garretsen, H.F.L. The Compulsive Internet Use Scale (CIUS): Some psychometric properties. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2009, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.H.; Yen, J.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Yang, M.J.; Lin, H.C.; Yen, C.F. Proposed diagnostic criteria and the screening and diagnosing tool of Internet addiction in college students. Compr. Psychiatry 2009, 50, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.S. Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyber. Psychol. Behav. 1998, 1, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction—And a Winning Strategy for Recovery; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaal, Y.; Billieux, J.; Thorens, G.; Khan, R.; Louati, Y.; Scarlatti, E.; Theintz, F.; Lederrey, J.; Van Der Linden, M.; Zullino, D. French validation of the internet addiction test. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Impact Internet Multimed. Virtual Real. Behav. Soc. 2008, 11, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.; Laier, C.; Pawlikowski, M.; Schachtle, U.; Scholer, T.; Altstotter-Gleich, C. Watching pornographic pictures on the Internet: Role of sexual arousal ratings and psychological-psychiatric symptoms for using Internet sex sites excessively. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2011, 14, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Villa, T.; Molina, A.J.; Garcia-Martin, M.; Llorca, J.; Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Martin, V. Validation and psychometric analysis of the Internet Addiction Test in Spanish among college students. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, G.; Caci, B.; D’Amico, A.; Di Blasi, M. Internet addiction disorder: An Italian study. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Impact Internet Multimed. Virtual Real. Behav. Soc. 2007, 10, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siomos, K.E.; Dafouli, E.D.; Braimiotis, D.A.; Mouzas, O.D.; Angelopoulos, N.V. Internet addiction among Greek adolescent students. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Impact Internet Multimed. Virtual Real. Behav. Soc. 2008, 11, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, F.; Delen, E.; Young, K.S. Psychometric properties of the Internet Addiction Test in Turkish. J. Behav. Addict. 2016, 5, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernja, I.; Vejmelka, L.; Rajter, M. Internet addiction test: Croatian preliminary study. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.T.; Peng, Z.W.; Mai, J.C.; Jing, J. Factors associated with Internet addiction among adolescents. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Impact Internet Multimed. Virtual Real. Behav. Soc. 2009, 12, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, A.L.; Bae, S.M.; Kim, J.W. Psychometric Properties of the Internet Addiction Test: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2018, 21, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelapaijit, A.; Pinyopornpanish, M.; Simcharoen, S.; Kuntawong, P.; Wongpakaran, N.; Wongpakaran, T. Psychometric properties of a Thai version internet addiction test. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siste, K.; Suwartono, C.; Nasrun, M.W.; Bardosono, S.; Sekartini, R.; Pandelaki, J.; Sarasvita, R.; Murtani, B.J.; Damayanti, R.; Wiguna, T. Validation study of the Indonesian internet addiction test among adolescents. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateno, M.; Teo, A.R.; Shiraishi, M.; Tayama, M.; Kawanishi, C.; Kato, T.A. Prevalence rate of Internet addiction among Japanese college students: Two cross-sectional studies and reconsideration of cut-off points of Young’s Internet Addiction Test in Japan. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yeo, K.J.; Guo, F.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, O. Psychometric property and measurement invariance of internet addiction test: The effect of socio-demographic and internet use variables. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlikowskia, M.; Altstötter-Gleichb, C.; Brandac, M. Validation and psychometric properties of a short version of Young’s Internet Addiction Test. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafur-Mendoza, A.A.; Acosta-Prado, J.C.; Zarate-Torres, R.A.; Ramirez-Ospina, D.E. Assessing the Psychometric Properties of the Internet Addiction Test in Peruvian University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tateno, M.; Teo, A.R.; Kato, T.A. Does LINE addiction exist? Potential concerns about Japan’s most popular form of social media on smartphones. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 540–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, M.; Brunelle, N.; Tremblay, J.; Leclerc, D.; Cousineau, M.M.; Khazaal, Y.; Legare, A.A.; Rousseau, M.; Berbiche, D. Gender Difference in Internet Use and Internet Problems among Quebec High School Students. Can. J. Psychiatry 2016, 61, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.M.; Mak, K.K.; Cheng, C.; Watanabe, H.; Nomachi, S.; Bahar, N.; Young, K.S.; Ko, H.C.; Kim, D.; Griffiths, M.D. Measurement Invariance of the Internet Addiction Test among Hong Kong, Japanese, and Malaysian Adolescents. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.K.; Lai, C.M.; Watanabe, H.; Kim, D.I.; Bahar, N.; Ramos, M.; Young, K.S.; Ho, R.C.; Aum, N.R.; Cheng, C. Epidemiology of internet behaviors and addiction among adolescents in six Asian countries. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wery, A.; Burnay, J.; Karila, L.; Billieux, J. The Short French Internet Addiction Test Adapted to Online Sexual Activities: Validation and Links With Online Sexual Preferences and Addiction Symptoms. J. Sex Res. 2016, 53, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, E.; Oberst, U.; Stodt, B.; Brand, M. Online-specific fear of missing out and Internet-use expectancies contribute to symptoms of Internet-communication disorder. Addict. Behav. Rep. 2017, 5, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, E.; Stodt, B.; Brand, M. Addictive use of social networking sites can be explained by the interaction of Internet use expectancies, Internet literacy, and psychopathological symptoms. J. Behav. Addict. 2015, 4, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.M.; Wegmann, E.; Garcia Arias, M.; Bernabeu Brotons, E.; Marchena Giraldez, C.; Brand, M. Deficits in executive functions but not in decision making under risk in individuals with problematic social-network use. Compr. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 152228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, B.X.; Mai, H.T.; Nguyen, L.H.; Nguyen, C.T.; Latkin, C.A.; Zhang, M.W.B.; Ho, R.C.M. Vietnamese validation of the short version of Internet Addiction Test. Addict. Behav. Rep. 2017, 6, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision (ICD-11); World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, S.; Osaki, Y.; Kinjo, A.; Mihara, S.; Maezono, M.; Kitayuguchi, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nakayama, H.; Rumpf, H.J.; Saunders, J.B. Development and validation of a nine-item short screening test for ICD-11 gaming disorder (GAMES test) and estimation of the prevalence in the general young population. J. Behav. Addict. 2021, 10, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R_Core_Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fay, M.P. Two-sided Exact Tests and Matching Confidence Intervals for Discrete Data. R J. 2010, 2, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.C.; Muller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, S.; Osaki, Y.; Kinjo, A.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nakayama, H.; Kitayuguchi, T.; Harada, T.; Higuchi, S. Validation of the Ten-Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10) based on the clinical diagnosis of IGD in Japan. J. Behav. Addict. 2022, 11, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overall | Non-Addicted | Addicted | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 104 | n = 90 | n = 14 | (Welch’s t-Test or $ Fisher’s Exact Test) | |
| Age (Age range) Early/Late teens | 14.4 ± 2.4 (10–18) 57/47 | 14.4 ± 2.5 (10–18) 47/43 | 14.1 ± 1.9 (11–18) 10/4 | p = 0.5446 p = 0.2507 $ |
| Gender (M/F) | 80/24 | 71/19 | 9/5 | p = 0.3042 $ |
| IQ | 82.8 ± 14.0 | 82.8 ± 14.1 | 82.2 ± 14.0 | p = 0.8798 |
| IAT (20 items) | 43.7 ± 12.4 | 41.6 ± 11.0 | 56.8 ± 13.1 | p = 0.0012 |
| s-IAT (12 items) | 27.4 ± 7.9 | 26.2 ± 6.9 | 35.5 ± 9.0 | p = 0.0023 |
| Overall | Non-Addicted | Addicted | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 104 | n = 90 | n = 14 | (Fisher’s Exact Test) | |
| s-IAT ≥ 35 | 22 | 12 | 10 | p = 0.07986 |
| IAT ≥ 50 | 35 | 25 | 10 | |
| IAT ≥ 70 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Sensitivity | Specificity | FPR | FNR | PPV | NPV | PLR | NLR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s-IAT (CO35) | 0.714 | 0.867 | 0.133 | 0.286 | 0.455 | 0.951 | 5.357 | 0.330 |
| IAT (CO50) | 0.714 | 0.722 | 0.278 | 0.286 | 0.286 | 0.942 | 2.571 | 0.396 |
| IAT (CO70) | 0.143 | 1.00 | 0 | 0.857 | 1.00 | 0.882 | - | 0.857 |
| (A) s-IAT (CO35) and IAT (CO50) | ||||
| s-IAT ≥ 35 | s-IAT < 35 | Sum | p-Value (McNemar) | |
| IAT ≥ 50 | 21 | 14 | 35 | p = 0.00098 |
| IAT < 50 | 1 | 68 | 69 | |
| Sum | 22 | 82 | 104 | |
| (B) s-IAT (CO35) and IAT (CO70) | ||||
| s-IAT ≥ 35 | s-IAT < 35 | Sum | p-Value (McNemar) | |
| IAT ≥ 70 | 2 | 0 | 2 | p < 0.00001 |
| IAT < 70 | 20 | 82 | 102 | |
| Sum | 22 | 82 | 104 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tateno, M.; Horie, K.; Shirasaka, T.; Nanba, K.; Shiraishi, E.; Tateno, Y.; Kato, T.A. Clinical Usefulness of a Short Version of the Internet Addiction Test to Screen for Probable Internet Addiction in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054670
Tateno M, Horie K, Shirasaka T, Nanba K, Shiraishi E, Tateno Y, Kato TA. Clinical Usefulness of a Short Version of the Internet Addiction Test to Screen for Probable Internet Addiction in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(5):4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054670
Chicago/Turabian StyleTateno, Masaru, Kazumasa Horie, Tomohiro Shirasaka, Kotaro Nanba, Eri Shiraishi, Yukie Tateno, and Takahiro A. Kato. 2023. "Clinical Usefulness of a Short Version of the Internet Addiction Test to Screen for Probable Internet Addiction in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 5: 4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054670
APA StyleTateno, M., Horie, K., Shirasaka, T., Nanba, K., Shiraishi, E., Tateno, Y., & Kato, T. A. (2023). Clinical Usefulness of a Short Version of the Internet Addiction Test to Screen for Probable Internet Addiction in Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054670







