Mental Health Is a Family Affair—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Associations between Mental Health Problems in Parents and Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Are parental mental health problems prior to the COVID-19 pandemic associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- (2)
- Are current parental mental health symptoms associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- (3)
- Are parents’ general stress levels associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic?
- (4)
- Is parenting stress associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic?
2. Methods
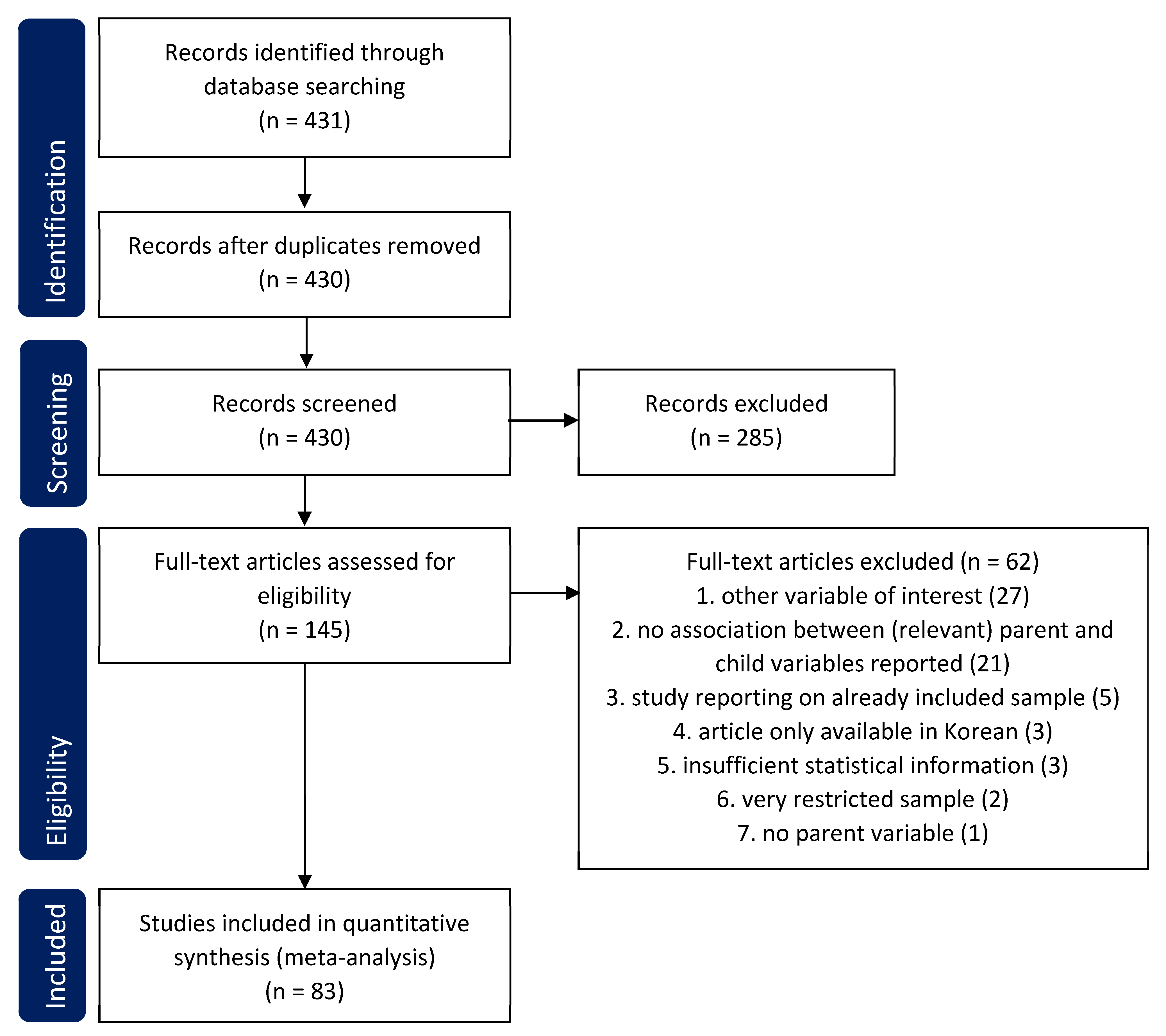
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias
2.5. Systematic Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Research Question 1: Are Parental Mental Health Problems Prior to the COVID-19 Pandemic Associated with Child Mental Health Outcomes during the COVID-19 Pandemic?
3.2. Research Question 2: Are Current Parental Mental Health Symptoms Associated with Child Mental Health Outcomes during the COVID-19 Pandemic?
3.3. Research Question 3: Are Parents’ General Stress Levels Associated with Child Mental Health Outcomes during the COVID-19 Pandemic?
3.4. Research Question 4: Is Parenting Stress Associated with Child Mental Health Outcomes during the COVID-19 Pandemic?
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Implications for Research and Practice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fegert, J.M.; Vitiello, B.; Plener, P.L.; Clemens, V. Challenges and burden of the Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic for child and adolescent mental health: A narrative review to highlight clinical and research needs in the acute phase and the long return to normality. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2020, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashbord. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Wirkner, J.; Christiansen, H.; Knaevelsrud, C.; Lüken, U.; Wurm, S.; Schneider, S.; Brakemeier, E.-L. Mental Health in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Eur. Psychol. 2021, 26, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakemeier, E.-L.; Wirkner, J.; Knaevelsrud, C.; Wurm, S.; Christiansen, H.; Lueken, U.; Schneider, S. Die COVID-19-Pandemie als Herausforderung für die psychische Gesundheit. Z. Für Klin. Psychol. Und Psychother. 2020, 49, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.; Prinstein, M.J.; Clark, L.A.; Rottenberg, J.; Abramowitz, J.S.; Albano, A.M.; Aldao, A.; Borelli, J.L.; Chung, T.; Davila, J.; et al. Mental health and clinical psychological science in the time of COVID-19: Challenges, opportunities, and a call to action. Am. Psychol. 2021, 76, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, R.S.; Folkman, S. Stress, Appraisal, and Coping; Springer Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Wittchen, H.-U.; Hoyer, J. Klinische Psychologie & Psychotherapie; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, E.A.; O’Connor, R.C.; Perry, V.H.; Tracey, I.; Wessely, S.; Arseneault, L.; Ballard, C.; Christensen, H.; Cohen Silver, R.; Everall, I.; et al. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: A call for action for mental health science. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhanom Ghebreyesus, T. Addressing mental health needs: An integral part of COVID-19 response. World Psychiatry Off. J. World Psychiatr. Assoc. (WPA) 2020, 19, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, K.; Duddu, V.; Anyim, N.; Neelam, J.; Lewis, S. Pandemics and pre-existing mental illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2021, 10, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, U.; Salazar de Pablo, G.; Franco, M.; Moreno, C.; Parellada, M.; Arango, C.; Fusar-Poli, P. The impact of COVID-19 lockdown on child and adolescent mental health: Systematic review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.J.S.; Lewis, C.; Roberts, A.; Richards, N.A.; Evison, C.; Pearce, H.A.; Lloyd, K.; Meudell, A.; Edwards, B.M.; Robinson, C.A.; et al. The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in individuals with pre-existing mental illness. BJPsych Open 2022, 8, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cénat, J.M.; Blais-Rochette, C.; Kokou-Kpolou, C.K.; Noorishad, P.-G.; Mukunzi, J.N.; McIntee, S.-E.; Dalexis, R.D.; Goulet, M.-A.; Labelle, P.R. Prevalence of symptoms of depression, anxiety, insomnia, posttraumatic stress disorder, and psychological distress among populations affected by the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 295, 113599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomauro, D.F.; Mantilla Herrera, A.M.; Shadid, J.; Zheng, P.; Ashbaugh, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Abbafati, C.; Adolph, C.; Amlag, J.O.; Aravkin, A.Y.; et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Jia, X.; Shi, H.; Niu, J.; Yin, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, X. Prevalence of mental health problems during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 281, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Lipsitz, O.; Nasri, F.; Lui, L.M.W.; Gill, H.; Phan, L.; Chen-Li, D.; Iacobucci, M.; Ho, R.; Majeed, A.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.A.K.; Mitra, A.K.; Bhuiyan, A.R. Impact of COVID-19 on Mental Health in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meherali, S.; Punjani, N.; Louie-Poon, S.; Abdul Rahim, K.; Das, J.K.; Salam, R.A.; Lassi, Z.S. Mental Health of Children and Adolescents Amidst COVID-19 and Past Pandemics: A Rapid Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K.; Gupta, J.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Kumar, R.; Meena, A.K.; Madaan, P.; Sharawat, I.K.; Gulati, S. Psychological and Behavioral Impact of Lockdown and Quarantine Measures for COVID-19 Pandemic on Children, Adolescents and Caregivers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67, fmaa122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, N.; McArthur, B.A.; Cooke, J.E.; Eirich, R.; Zhu, J.; Madigan, S. Global Prevalence of Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Children and Adolescents During COVID-19: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Z. Public mental health problems during COVID-19 pandemic: A large-scale meta-analysis of the evidence. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeisler, M.É.; Rohan, E.A.; Melillo, S.; Matjasko, J.L.; DePadilla, L.; Patel, C.G.; Weaver, M.D.; Drane, A.; Winnay, S.S.; Capodilupo, E.R.; et al. Mental Health Among Parents of Children Aged <18 Years and Unpaid Caregivers of Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, December 2020 and February–March 2021. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, R.R. The Determinants of Parenting Behavior. J. Clin. Child Psychol. 1992, 21, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, L.G.; Anthony, B.J.; Glanville, D.N.; Naiman, D.Q.; Waanders, C.; Shaffer, S. The relationships between parenting stress, parenting behaviour and preschoolers’ social competence and behaviour problems in the classroom. Infant Child Dev. Int. J. Res. Pract. 2005, 14, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.M.; Weems, C.F.; Pellerin, K.; Dalton, R. Parenting Stress and Childhood Psychopathology: An Examination of Specificity to Internalizing and Externalizing Symptoms. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2006, 28, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.M. Association Between Independent Reports of Maternal Parenting Stress and Children’s Internalizing Symptomatology. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2011, 20, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillmann, J.; Sensoy, Ö.; Schwarzer, G. Parental perceived stress and its consequences on early social-emotional child development during COVID-19 pandemic. J. Early Child. Res. 2022, 20, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babore, A.; Trumello, C.; Lombardi, L.; Candelori, C.; Chirumbolo, A.; Cattelino, E.; Baiocco, R.; Bramanti, S.M.; Viceconti, M.L.; Pignataro, S.; et al. Mothers’ and Children’s Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown: The Mediating Role of Parenting Stress. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2021, 54, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.H.; Rouse, M.H.; Connell, A.M.; Broth, M.R.; Hall, C.M.; Heyward, D. Maternal depression and child psychopathology: A meta-analytic review. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, A.M.; Goodman, S.H. The association between psychopathology in fathers versus mothers and children’s internalizing and externalizing behavior problems: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 128, 746–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, P.; Garber, J. The relations among depression in fathers, children’s psychopathology, and father-child conflict: A meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 24, 339–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasic, D.; Hajek, T.; Alda, M.; Uher, R. Risk of mental illness in offspring of parents with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis of family high-risk studies. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Santvoort, F.; Hosman, C.; Janssens, J.; van Doesum, K.; Reupert, A.; van Loon, L. The Impact of Various Parental Mental Disorders on Children’s Diagnoses: A Systematic Review. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2015, 18, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorup, A.A.E.; Laursen, T.M.; Munk-Olsen, T.; Ranning, A.; Mortensen, P.B.; Plessen, K.J.; Nordentoft, M. Incidence of child and adolescent mental disorders in children aged 0–17 with familial high risk for severe mental illness—A Danish register study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 197, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosman, C.; van Doesum, K.; van Santvoort, F. Prevention of emotional problems and psychiatric risks in children of parents with a mental illness in the Netherlands: I. The scientific basis to a comprehensive approach. Aust. e-J. Adv. Ment. Health 2009, 8, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prime, H.; Wade, M.; Browne, D.T. Risk and resilience in family well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am. Psychol. 2020, 75, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.H.; Call, T.A.; Wolford, S.N.; McWey, L.M. Parental Stress and Child Outcomes: The Mediating Role of Family Conflict. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2021, 30, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Chen, W.; Liu, X.; Wu, T.; Wen, L.; Yang, X.; Hou, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; et al. Children of parents with mental illness in the COVID-19pandemic: A cross-sectional survey in China. Asian J. Psychiatry 2021, 64, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022). Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupinski, M.T.; Dunlap, W.P. Approximating Pearson Product-Moment Correlations from Kendall’s Tau and Spearman’s Rho. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1996, 56, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.J.; Brennan, M.L.; Williams, H.C.; Dean, R.S. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhne, E.; van der Meer, A.S.; Kamp-Becker, I.; Christiansen, H. A systematic review of risk and protective factors of mental health in unaccompanied minor refugees. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Haidich, A.B. Meta-analysis in medical research. Hippokratia 2010, 14, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Beheshti, A. Meta-Mar: Free Online Meta-Analysis Calculator. Available online: https://www.meta-mar.com/ (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Beheshti, A.; Chavanon, M.-L.; Christiansen, H. Emotion dysregulation in adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, G.; Hartung, J. Improved tests for a random effects meta-regression with a single covariate. Stat. Med. 2003, 22, 2693–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IntHout, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Borm, G.F. The Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard DerSimonian-Laird method. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, R. The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.R.; Evans, M.L.; Aaron, L.; Brabham, D.R.; Kaplan, R.M. Covariance Between Parent and Child Symptoms Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2021, 46, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, S.N.; Ding, M.; Burniston, A.B.; Smiley, P.A.; Chow, C.M.; Liu, C.H. Changes in Maternal Depression and Children’s Behavior Problems: Investigating the Role of COVID-19-Related Stressors, Hair Cortisol, and Dehydroepiandrosterone. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2022, 10, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feurer, C.; Granros, M.; Calentino, A.E.; Suor, J.H.; Patel, K.; Burkhouse, K.L. The interplay of stress and electrocortical reactivity to reward in the prospective prediction of depression symptoms during COVID-19. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, A.; Brown, S.; Gartland, D.; Mensah, F.; Seymour, M.; Savopoulos, P.; FitzPatrick, K.; Papadopoullos, S.; Giallo, R. Psychosocial factors associated with adolescent depressive and anxiety symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 2022, 46, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosco, G.M.; Sloan, C.J.; Fang, S.; Feinberg, M.E. Family vulnerability and disruption during the COVID-19 pandemic: Prospective pathways to child maladjustment. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2022, 63, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenstein, T.; Colasante, T.; Lougheed, J.P. Adolescent and Maternal Anxiety Symptoms Decreased but Depressive Symptoms Increased before to during COVID-19 Lockdown. J. Res. Adolesc. Off. J. Soc. Res. Adolesc. 2021, 31, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler-Dauner, F.; Buchheim, A.; Hildebrand, K.; Mayer, I.; Clemens, V.; Ziegenhain, U.; Fegert, J.M. Maternal attachment representation, the risk of increased depressive symptoms and the influence on children’s mental health during the SARS-CoV-2-pandemic. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2022, 31, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengua, L.J.; Thompson, S.F.; Kim, S.G.; Rosen, M.L.; Rodman, A.; Kasparek, S.; Mayes, M.; Zalewski, M.; Meltzoff, A.; McLaughlin, K.A. Maternal mental health mediates the effects of pandemic-related stressors on adolescent psychopathology during COVID-19. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2022, 63, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achterberg, M.; Dobbelaar, S.; Boer, O.D.; Crone, E.A. Perceived stress as mediator for longitudinal effects of the COVID-19 lockdown on wellbeing of parents and children. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgül, G.; Atalan Ergin, D. Adolescents’ and parents’ anxiety during COVID-19: Is there a role of cyberchondriasis and emotion regulation through the internet? Curr. Psychol. 2021, 40, 4750–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Levante, A.; Petrocchi, S.; Lecciso, F.; Castelli, I. Maternal Psychological Distress and Children’s Internalizing/Externalizing Problems during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Moderating Role Played by Hypermentalization. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbás, R.; Fehlbaum, L.V.; Dimanova, P.; Negri, A.; Arudchelvam, J.; Schnider, C.B.; Raschle, N.M. Mental well-being during the first months of COVID-19 in adults and children: Behavioral evidence and neural precursors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, D.T.; Wade, M.; May, S.S.; Jenkins, J.M.; Prime, H. COVID-19 disruption gets inside the family: A two-month multilevel study of family stress during the pandemic. Dev. Psychol. 2021, 57, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechel, C.; Nehring, I.; Seifert, C.; Eber, S.; Behrends, U.; Mall, V.; Friedmann, A. A cross-sectional investigation of psychosocial stress factors in German families with children aged 0–3 years during the COVID-19 pandemic: Initial results of the CoronabaBY study. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2022, 16, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescentini, C.; Feruglio, S.; Matiz, A.; Paschetto, A.; Vidal, E.; Cogo, P.; Fabbro, F. Stuck Outside and Inside: An Exploratory Study on the Effects of the COVID-19 Outbreak on Italian Parents and Children’s Internalizing Symptoms. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 586074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daks, J.S.; Peltz, J.S.; Rogge, R.D. Psychological flexibility and inflexibility as sources of resiliency and risk during a pandemic: Modeling the cascade of COVID-19 stress on family systems with a contextual behavioral science lens. J. Context. Behav. Sci. 2020, 18, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollberg, D.G.; Hanetz-Gamliel, K. Mediation-Moderation Links Between Mothers’ ACEs, Mothers’ and Children’s Psychopathology Symptoms, and Maternal Mentalization During COVID-19. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 837423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois-Comtois, K.; Suffren, S.; St-Laurent, D.; Milot, T.; Lemelin, J.-P. Child Psychological Functioning During the COVID-19 Lockdown: An Ecological, Family-Centered Approach. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2021, 42, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, M.E.; Mogle, J.A.; Lee, J.-K.; Tornello, S.L.; Hostetler, M.L.; Cifelli, J.A.; Bai, S.; Hotez, E. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Parent, Child, and Family Functioning. Fam. Process 2022, 61, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, L.; La Cascia, C.; Daino, M.; Tripoli, G.; Maniaci, G.; Santorio, C.; Seminerio, F.; Lo Baido, R.; La Barbera, D. Children and Families’ mental health during the first COVID-19 lockdown in Italy. Mediterr. J. Clin. Psychol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, S.; Badinlou, F.; Brocki, K.C.; Frick, M.A.; Ronchi, L.; Hughes, C. Family Function and Child Adjustment Difficulties in the COVID-19 Pandemic: An International Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.X.; Cornish, K.; Kirk, H.; Ilias, K.; Shaikh, M.F.; Golden, K.J. Impact of the COVID-19 Lockdown in Malaysia: An Examination of the Psychological Well-Being of Parent-Child Dyads and Child Behavior in Families With Children on the Autism Spectrum. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 733905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, A.; Nettuno, F.; Nazzari, S. Maternal mood moderates the trajectory of emotional and behavioural problems from pre- to during the COVID-19 lockdown in preschool children. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, L.M.; Davis, E.P.; Luby, J.L.; Baram, T.Z.; Sandman, C.A. A predictable home environment may protect child mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 14, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hails, K.A.; Petts, R.A.; Hostutler, C.A.; Simoni, M.; Greene, R.; Snider, T.C.; Riley, A.R. COVID-19 distress, negative parenting, and child behavioral problems: The moderating role of parent adverse childhood experiences. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 130, 105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.E.; Kaur, H.; Gonzalez, A. Parental Mental Health and Hostility Are Associated With Longitudinal Increases in Child Internalizing and Externalizing Problems During COVID-19. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 706168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.; Han, H.; Jung, J.; Yang, S.J.; Shin, Y. Parental Mental Health and Children’s Behaviors and Media Usage during COVID-19-Related School Closures. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Ward, K.P.; Chang, O.D.; Downing, K.M. Parenting activities and the transition to home-based education during the COVID-19 pandemic. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2021, 122, 105585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, L.; Wu, F.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Zou, J.; Guo, Z.; Kong, L. Perceived family adaptability and cohesion and depressive symptoms: A comparison of adolescents and parents during COVID-19 pandemic. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 287, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, N.; Mounts, N.S. Economic stress, parenting, and adolescents’ adjustment during the COVID-19 pandemic. Fam. Relat. 2022, 71, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, M.G.; Stagnitti, M.C.; Calatozzo, P.; Cannavò, A.; Bruschetta, D.; Foti Cuzzola, M.; Manuli, A.; Pioggia, G.; Calabrò, R.S. What about the Consequences of the Use of Distance Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic? A Survey on the Psychological Effects in Both Children and Parents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, D.; Fontanesi, L.; Di Giandomenico, S.; Mazza, C.; Roma, P.; Verrocchio, M.C. The Effect of Parent Psychological Distress on Child Hyperactivity/Inattention During the COVID-19 Lockdown: Testing the Mediation of Parent Verbal Hostility and Child Emotional Symptoms. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 567052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzilli, E.; Cerniglia, L.; Tambelli, R.; Trombini, E.; de Pascalis, L.; Babore, A.; Trumello, C.; Cimino, S. The COVID-19 Pandemic and Its Impact on Families’ Mental Health: The Role Played by Parenting Stress, Parents’ Past Trauma, and Resilience. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, B.A.; Racine, N.; McDonald, S.; Tough, S.; Madigan, S. Child and family factors associated with child mental health and well-being during COVID-19. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 32, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, J.; Gallagher, E.A.; Walsh, E.H.; O’Connor, C. Experiences of remote education during COVID-19 and its relationship to the mental health of primary school children. Ir. Educ. Stud. 2021, 40, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morban, H.; Demian, A.; Massiel Méndez, J.; Sosa, C. Efecto Spillover en los cuidadores de infantes de 1.5 a 5 años durante la pandemia del COVID-19. Pediatría (Asunción) 2020, 47, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, F.; El-Aarbaoui, T.; Bustamante, J.J.H.; Héron, M.; Mary-Krause, M.; Rouquette, A.; Galéra, C.; Melchior, M. Risk and protective factors related to children’s symptoms of emotional difficulties and hyperactivity/inattention during the COVID-19-related lockdown in France: Results from a community sample. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penner, F.; Elzaki, Y.; Contreras, H.T.; Santos, R.P.; Sarver, D.E. Behavioral, Affective, and Cognitive Parenting Mechanisms of Child Internalizing and Externalizing Problems during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Res. Child Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2022, 50, 1121–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polónyiová, K.; Belica, I.; Celušáková, H.; Janšáková, K.; Kopčíková, M.; Szapuová, Ž.; Ostatníková, D. Comparing the impact of the first and second wave of COVID-19 lockdown on Slovak families with typically developing children and children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Int. J. Res. Pract. 2022, 26, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radanović, A.; Micić, I.; Pavlović, S.; Krstić, K. Don’t Think That Kids Aren’t Noticing: Indirect Pathways to Children’s Fear of COVID-19. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 635952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizeq, J.; Korczak, D.J.; Cost, K.T.; Anagnostou, E.; Charach, A.; Monga, S.; Birken, C.S.; Kelley, E.; Nicolson, R.; Burton, C.L.; et al. Vulnerability pathways to mental health outcomes in children and parents during COVID-19. Curr. Psychol. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, E.L.; Piscitello, J.; Schmidt, E.; Mallar, C.; Davidson, B.; Natale, R. Longitudinal transactional relationships between caregiver and child mental health during the COVID-19 global pandemic. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2021, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, E.; López-Romero, L.; Domínguez-Álvarez, B.; Villar, P.; Gómez-Fraguela, J.A. Testing the Effects of COVID-19 Confinement in Spanish Children: The Role of Parents’ Distress, Emotional Problems and Specific Parenting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.S.; Hutchison, M.; Tambling, R.; Tomkunas, A.J.; Horton, A.L. Initial Challenges of Caregiving During COVID-19: Caregiver Burden, Mental Health, and the Parent-Child Relationship. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2020, 51, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddik, B.; Hussein, A.; Albanna, A.; Elbarazi, I.; Al-Shujairi, A.; Temsah, M.-H.; Saheb Sharif-Askari, F.; Stip, E.; Hamid, Q.; Halwani, R. The psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on adults and children in the United Arab Emirates: A nationwide cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelleby, E.C.; Pittman, L.D.; Bridgett, D.J.; Keane, J.; Zolinski, S.; Caradec, J. Associations between local COVID-19 case rates, pandemic-related financial stress and parent and child functioning. J. Fam. Psychol. 2022, 36, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, A.E.; Oblath, R.; Dayal, R.; Loubeau, J.K.; Lejeune, J.; Sikov, J.; Savage, M.; Posse, C.; Jain, S.; Zolli, N.; et al. Changes in psychosocial functioning among urban, school-age children during the COVID-19 pandemic. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2021, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Singletary, B.; Jiang, H.; Justice, L.M.; Lin, T.-J.; Purtell, K.M. Child behavior problems during COVID-19: Associations with parent distress and child social-emotional skills. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2022, 78, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.E.; Khan, N.M.; Ahmed, H.U. Emotional and Behavioural Changes in Children and Adolescents and Their Association With Parental Depression During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Pilot Study in Bangladesh. East Asian Arch. Psychiatry Off. J. Hong Kong Coll. Psychiatr. 2022, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cheong, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Havewala, M.; Ye, Y. Parent work-life conflict and adolescent adjustment during COVID-19: Mental health and parenting as mediators. J. Fam. Psychol. 2022, 36, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Household Chaos and Caregivers’ and Young Children’s Mental Health during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mediation Model. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2022, 31, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, N.; Zou, J.; Xie, D.; Liu, M.; Geng, F. The transmission of psychological distress and lifestyles from parents to children during COVID-19. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 303, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Bian, X.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, S.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; Finan, J. Maternal Anxiety Symptoms and Chinese Adolescents’ Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Protective Role of Adolescents’ Self-Compassion. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 837846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shein, B.W.; Khalil, A.; Duncan, R.J. Parent and child adjustment dual trajectories at the beginning of the COVID-19 syndemic. Fam. Process 2022. [CrossRef]
- Berry, A.; Burke, T.; Carr, A. The impact of the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic on parents of children with externalising difficulties in ireland: A longitudinal cohort study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackwell, C.K.; Mansolf, M.; Sherlock, P.; Ganiban, J.; Hofheimer, J.A.; Barone, C.J.; Bekelman, T.A.; Blair, C.; Cella, D.; Collazo, S.; et al. Youth Well-being During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pediatrics 2022, 149, e2021054754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büber, A.; Aktaş Terzioğlu, M. Caregiver’s reports of their children’s psychological symptoms after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic and caregiver’s perceived stress in Turkey. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2022, 76, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.C.H. Dyadic associations between COVID-19-related stress and mental well-being among parents and children in Hong Kong: An actor–partner interdependence model approach. Fam. Process 2022, 61, 1730–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, S.; Delhalle, M.; Baiverlin, A.; Blavier, A. Parental peritraumatic distress and feelings of parental competence in relation to COVID-19 lockdown measures: What is the impact on children’s peritraumatic distress? Eur. J. Trauma Dissociation 2021, 5, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohodes, E.M.; McCauley, S.; Gee, D.G. Parental Buffering of Stress in the Time of COVID-19: Family-Level Factors May Moderate the Association Between Pandemic-Related Stress and Youth Symptomatology. Res. Child Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2021, 49, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, B.A.; Muscatello, R.A.; Klemencic, M.E.; Schwartzman, J.M. The impact of COVID-19 on stress, anxiety, and coping in youth with and without autism and their parents. Autism Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Autism Res. 2021, 14, 1496–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.; Schmidt, E.; Mallar, C.; Mahmoud, F.; Rothenberg, W.; Hernandez, J.; Berkovits, M.; Jent, J.; Delamater, A.; Natale, R. Risk and resilience of well-being in caregivers of young children in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Transl. Behav. Med. 2021, 11, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vet, S.M.; Vrijhof, C.I.; van der Veek, S.M.C.; Pieplenbosch, J.M.; van Bakel, H.J.A.; Vermeer, H.J. Child Care in Times of COVID-19: Predictors of Distress in Dutch Children and Parents When Re-entering Center-Based Child Care After a 2-Month Lockdown. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 718898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donker, M.H.; Mastrotheodoros, S.; Branje, S. Development of parent-adolescent relationships during the COVID-19 pandemic: The role of stress and coping. Dev. Psychol. 2021, 57, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essler, S.; Christner, N.; Paulus, M. Longitudinal Relations Between Parental Strain, Parent-Child Relationship Quality, and Child Well-Being During the Unfolding COVID-19 Pandemic. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2021, 52, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Mazzeschi, C.; Delvecchio, E. The Impact of Parental Stress on Italian Adolescents’ Internalizing Symptoms during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgilés, M.; Espada, J.P.; Delvecchio, E.; Francisco, R.; Mazzeschi, C.; Pedro, M.; Morales, A. Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms in Children and Adolescents during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Transcultural Approach. Psicothema 2021, 33, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, B.S.; Tomkunas, A.J.; Hutchison, M.; Tambling, R.R.; Horton, A.L. The Protective Role of Parent Resilience on Mental Health and the Parent-Child Relationship During COVID-19. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2022, 53, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singletary, B.; Schmeer, K.K.; Purtell, K.M.; Sayers, R.C.; Justice, L.M.; Lin, T.-J.; Jiang, H. Understanding family life during the COVID-19 shutdown. Fam. Relat. 2022, 71, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, M.; Lionetti, F.; Pastore, M.; Fasolo, M. Parents’ Stress and Children’s Psychological Problems in Families Facing the COVID-19 Outbreak in Italy. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeau-Nielsen, R.B.; Palermo, F.; White, R.E.; Wilson, A.; Dier, S. Child Adjustment During COVID-19: The Role of Economic Hardship, Caregiver Stress, and Pandemic Play. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 716651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tso, W.W.Y.; Wong, R.S.; Tung, K.T.S.; Rao, N.; Fu, K.W.; Yam, J.C.S.; Chua, G.T.; Chen, E.Y.H.; Lee, T.M.C.; Chan, S.K.W.; et al. Vulnerability and resilience in children during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 31, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrupp, E.M.; Bennett, C.; Berkowitz, T.; Youssef, G.J.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Tucker, R.; Andrews, F.J.; Evans, S.; Teague, S.J.; Karantzas, G.C.; et al. Child, parent, and family mental health and functioning in Australia during COVID-19: Comparison to pre-pandemic data. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 32, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakşi, N.; Eroğlu, M.; Özdemir, M. COVID-19: Predictors of Depression and Anxiety Among High School Students. Cyprus Turk. J. Psychiatry Psychol. 2021, 3, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, Z.; Sasser, J.; Carvalho, C.; Oshri, A. Family stress during the pandemic worsens the effect of adverse parenting on adolescent sleep quality. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 123, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés-Romero, M.P.; Flujas-Contreras, J.M.; Fernández-Torres, M.; Gómez-Becerra, I.; Sánchez-López, P. Analysis of Psychosocial Adjustment in the Family During Confinement: Problems and Habits of Children and Youth and Parental Stress and Resilience. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 647645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusinato, M.; Iannattone, S.; Spoto, A.; Poli, M.; Moretti, C.; Gatta, M.; Miscioscia, M. Stress, Resilience, and Well-Being in Italian Children and Their Parents during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannotti, M.; Mazzoni, N.; Bentenuto, A.; Venuti, P.; de Falco, S. Family adjustment to COVID-19 lockdown in Italy: Parental stress, coparenting, and child externalizing behavior. Fam. Process 2021, 61, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannotti, M.; Mazzoni, N.; Facchini, M.; de Falco, S.; Venuti, P.; Iandolo, G. Determinants of maternal stress during COVID-19 outbreak in Italy and Spain: A cross-cultural investigation. J. Fam. Psychol. 2022, 36, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionetti, F.; Spinelli, M.; Moscardino, U.; Ponzetti, S.; Garito, M.C.; Dellagiulia, A.; Aureli, T.; Fasolo, M.; Pluess, M. The interplay between parenting and environmental sensitivity in the prediction of children’s externalizing and internalizing behaviors during COVID-19. Dev. Psychopathol. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensi, M.M.; Capone, L.; Rogantini, C.; Orlandi, M.; Ballante, E.; Borgatti, R. COVID-19-related psychiatric impact on Italian adolescent population: A cross-sectional cohort study. J. Commun. Psychol. 2021, 49, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrana, K.A.; Hart, K.C. Riesgo Y Resiliencia: Exploring the Role of Parenting Stress and Self-efficacy on Young Latino Children’s Well-being and Home Learning Experiences during COVID-19. J. Lat. Educ. 2022, 21, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, S.V.; Biederman, J. Depression: A family affair. Lancet 1998, 351, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.; Robinson, C.; Seddon, D. Invisible Children: Young Carers of Parents with Mental Health Problems—The Perspectives of Professionals. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2008, 13, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.; Lanier, P.; Wong, P.Y.J. Mediating Effects of Parental Stress on Harsh Parenting and Parent-Child Relationship during Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic in Singapore. J. Fam. Violence 2022, 37, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daundasekara, S.S.; Beauchamp, J.E.S.; Hernandez, D.C. Parenting stress mediates the longitudinal effect of maternal depression on child anxiety/depressive symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 295, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loon, L.M.A.; van de Ven, M.O.M.; van Doesum, K.T.M.; Witteman, C.L.M.; Hosman, C.M.H. The Relation Between Parental Mental Illness and Adolescent Mental Health: The Role of Family Factors. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2014, 23, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, J.A.; Solantaus, T.S.; Punamäki, R.-L. Parental mental health and children’s adjustment: The quality of marital interaction and parenting as mediating factors. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2003, 44, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroes, G.; Veerman, J.W.; de Bruyn, E.E. Bias in Parental Reports? Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2003, 19, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.J. Outcome in psychotherapy: The past and important advances. Psychotherapy 2013, 50, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compas, B.E.; Champion, J.E.; Forehand, R.; Cole, D.A.; Reeslund, K.L.; Fear, J.; Hardcastle, E.J.; Keller, G.; Rakow, A.; Garai, E.; et al. Coping and parenting: Mediators of 12-month outcomes of a family group cognitive-behavioral preventive intervention with families of depressed parents. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2010, 78, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compas, B.E.; Forehand, R.; Keller, G.; Champion, J.E.; Rakow, A.; Reeslund, K.L.; McKee, L.; Fear, J.M.; Colletti, C.J.M.; Hardcastle, E.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of a family cognitive-behavioral preventive intervention for children of depressed parents. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2009, 77, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, M.; Gilbert, K.; Kieser, M.; Klose, C.; Krisam, J.; Ebert, D.D.; Buntrock, C.; Christiansen, H. COMPARE Family (Children of Mentally Ill Parents at Risk Evaluation): A Study Protocol for a Preventive Intervention for Children of Mentally Ill Parents (Triple P, Evidence-Based Program That Enhances Parentings Skills, in Addition to Gold-Standard CBT With the Mentally Ill Parent) in a Multicenter RCT-Part II. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.D.; Gjøde, I.C.T.; Eigil, M.S.; Busck, H.; Bonne, M.; Nordentoft, M.; Thorup, A.A.E. VIA Family-a family-based early intervention versus treatment as usual for familial high-risk children: A study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. Trials 2019, 20, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluver, L.; Lachman, J.M.; Sherr, L.; Wessels, I.; Krug, E.; Rakotomalala, S.; Blight, S.; Hillis, S.; Bachman, G.; Green, O.; et al. Parenting in a time of COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maudsley Charity. Families Under Pressure. Available online: https://maudsleycharity.org/familiesunderpressure/ (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Schneider, S.; Christiansen, H.; Büttner, M. Familien Unter Druck. Available online: https://www.familienunterdruck.de/ (accessed on 10 January 2023).
| Research Question | Parental Variable | Child Outcome | Meta-Analytic Results | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | o | r | 95% CI | z | p-Value | Q | I2 | T2 | Fail-Safe N | |||
| 1. Are parental mental health problems prior to the COVID-19 pandemic associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic? | Psy-pathol | Psy-pathol | 2 | 351 | 0.23 | (−0.85; 0.94) | 1.96 | 0.30 | 4.65, p = 0.03 | 78.5% | 0.022 | |
| Psy-pathol | Int symp | 4 | 754 | 0.18 | (−0.07; 0.40) | 2.28 | 0.11 | 13.30, p < 0.01 | 77.4% | 0.019 | ||
| Psy-pathol | Dep symp | 2 | 403 | 0.16 | (−0.29; 0.56) | 4.53 | 0.14 | 0.53, p = 0.47 | 0.0% | 0 | ||
| Psy-pathol | Anx symp | 2 | 403 | 0.09 | (−0.03; 0.21) | 9.61 | 0.07 | 0.04, p = 0.85 | 0.0% | 0 | ||
| Psy-pathol | Ext symp | 2 | 351 | 0.23 | (−0.49; 0.76) | 3.87 | 0.16 | 1.25, p = 0.26 | 20.2% | 0.002 | ||
| Dep symp | Psy-pathol | 2 | 188 | 0.29 | (−0.73; 0.91) | 3.04 | 0.20 | 1.65, p = 0.20 | 39.5% | 0.007 | ||
| Dep symp | Int symp | 3 | 334 | 0.19 | (0.11; 0.28) | 9.65 | 0.01 | 0.27, p = 0.87 | 0.0% | 0 | 12 | |
| Dep symp | Dep symp | 3 | 582 | 0.23 | (−0.10; 0.51) | 3.03 | 0.09 | 4.51, p = 0.10 | 55.6% | 0.009 | ||
| Dep symp | Ext symp | 2 | 188 | 0.20 | (−0.37; 0.67) | 4.38 | 0.14 | 0.40, p = 0.53 | 0.0% | 0 | ||
| 2. Are current parental mental health symptoms associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic? | Psy-pathol | Psy-pathol | 25 | 11,883 | 0.36 | (0.31; 0.42) | 12.26 | <0.001 | 226.39, p < 0.001 | 89.4% | 0.020 | 12,464 |
| Psy-pathol | Int symp | 23 | 14,348 | 0.36 | (0.30; 0.42) | 10.90 | <0.001 | 213.80, p < 0.001 | 89.7% | 0.023 | 11,478 | |
| Psy-pathol | Dep symp | 8 | 6540 | 0.27 | (0.16; 0.37) | 5.93 | <0.001 | 57.00, p < 0.001 | 87.7% | 0.014 | 1076 | |
| Psy-pathol | Anx symp | 7 | 6018 | 0.27 | (0.19; 0.34) | 8.26 | <0.001 | 25.15, p < 0.001 | 76.1% | 0.006 | 823 | |
| Psy-pathol | Ext symp | 18 | 9103 | 0.32 | (0.24; 0.38) | 8.84 | <0.001 | 151.49, p < 0.001 | 88.8% | 0.021 | 5140 | |
| Psy-pathol | Gen stress | 5 | 1214 | 0.31 | (−0.01; 0.57) | 2.71 | 0.053 | 67.76, p < 0.001 | 94.1% | 0.065 | ||
| Dep symp | Psy-pathol | 18 | 5692 | 0.39 | (0.32; 0.44) | 12.26 | <0.001 | 100.62, p < 0.001 | 83.1% | 0.015 | 4935 | |
| Dep symp | Int symp | 16 | 8357 | 0.28 | (0.24; 0.33) | 12.89 | <0.001 | 35.01, p < 0.01 | 57.2% | 0.004 | 2751 | |
| Dep symp | Dep symp | 11 | 14,958 | 0.27 | (0.17; 0.37) | 5.75 | <0.001 | 196.72, p < 0.001 | 94.9% | 0.023 | 2075 | |
| Dep symp | Anx symp | 8 | 6275 | 0.25 | (0.21; 0.30) | 11.96 | <0.001 | 14.33, p < 0.05 | 51.1% | 0.002 | 856 | |
| Dep symp | Ext symp | 13 | 4018 | 0.27 | (0.22; 0.33) | 10.62 | <0.001 | 22.26, p = 0.03 | 46.1% | 0.003 | 1194 | |
| Dep symp | Gen stress | 3 | 923 | 0.39 | (−0.47; 0.87) | 1.90 | 0.20 | 71.37, p < 0.001 | 97.2% | 0.130 | ||
| Anx symp | Psy-pathol | 12 | 4110 | 0.31 | (0.25; 0.38) | 9.89 | <0.001 | 43.49, p < 0.001 | 74.7% | 0.008 | 1535 | |
| Anx symp | Int symp | 15 | 14,571 | 0.30 | (0.23; 0.36) | 9.85 | <0.001 | 152.43, p < 0.001 | 90.8% | 0.010 | 5098 | |
| Anx symp | Dep symp | 6 | 5613 | 0.22 | (0.08; 0.35) | 4.07 | <0.01 | 41.34, p < 0.001 | 87.9% | 0.015 | 481 | |
| Anx symp | Anx symp | 9 | 6549 | 0.26 | (0.20; 0.33) | 8.91 | <0.001 | 36.32, p < 0.001 | 78.0% | 0.006 | 1138 | |
| Anx symp | Ext symp | 9 | 3517 | 0.23 | (0.17; 0.28) | 8.80 | <0.001 | 18.32, p = 0.02 | 56.3% | 0.004 | 510 | |
| Anx symp | Gen stress | 3 | 923 | 0.33 | (−0.41; 0.81) | 1.91 | 0.20 | 34.72, p < 0.001 | 94.2% | 0.088 | ||
| 3. Are parents’ general stress levels associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic? | Gen stress | Psy-pathol | 20 | 38,991 | 0.34 | (0.29, 0.39) | 13.24 | <0.001 | 433.74, p < 0.001 | 95.6% | 0.012 | 18,997 |
| Gen stress | Int symp | 21 | 40,084 | 0.31 | (0.27, 0.35) | 14.37 | <0.001 | 87.39, p < 0.001 | 77.1% | 0.007 | 12,548 | |
| Gen stress | Dep symp | 10 | 5243 | 0.30 | (0.21; 0.39) | 7.39 | <0.001 | 50.19, p < 0.001 | 82.1% | 0.014 | 1510 | |
| Gen stress | Anx symp | 8 | 4913 | 0.32 | (0.22; 0.41) | 7.33 | <0.001 | 29.68, p < 0.001 | 76.4% | 0.012 | 1124 | |
| Gen stress | Ext symp | 17 | 36,844 | 0.31 | (0.27, 0.35) | 17.37 | <0.001 | 161.94, p < 0.001 | 90.1% | 0.004 | 10,637 | |
| Gen stress | Gen stress | 13 | 4110 | 0.29 | (0.18, 0.39) | 5.49 | <0.001 | 139.59, p < 0.001 | 91.4% | 0.033 | 1659 | |
| 4. Is parenting stress associated with child mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic? | Par stress | Psy-pathol | 9 | 4213 | 0.44 | (0.33, 0.54) | 8.32 | <0.001 | 43.82, p < 0.001 | 81.7% | 0.020 | 2387 |
| Par stress | Int symp | 7 | 3307 | 0.46 | (0.26, 0.63) | 5.18 | <0.01 | 95.89, p < 0.001 | 93.7% | 0.059 | 1315 | |
| Par stress | Dep symp | 2 | 251 | 0.36 | (−0.95; 0.99) | 2.16 | 0.28 | 4.30, p = 0.04 | 76.7% | 0.047 | ||
| Par stress | Ext symp | 8 | 4079 | 0.45 | (0.39, 0.50) | 16.37 | <0.001 | 15.83, p = 0.03 | 55.8% | 0.002 | 2354 | |
| Par stress | Gen stress | 2 | 1682 | 0.51 | (−0.12, 0.85) | 10.38 | 0.06 | 3.67, p = 0.06 | 72.8% | 0.004 | ||
| Child Variables (all during the COVID-19 pandemic) | |||||||
| Psychopathology | Internalizing symptoms | Depressive symptoms | Anxiety symptoms | Externalizing symptoms | General stress | ||
| Parental variables | (1) Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic | ||||||
| Depressive symptoms | 0.19 | ||||||
| (2) During the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||
| Psychopathology | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.32 | ||
| Depressive symptoms | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.27 | ||
| Anxiety symptoms | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.23 | ||
| General stress | 0.34 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.29 | |
| Parenting stress | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.45 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stracke, M.; Heinzl, M.; Müller, A.D.; Gilbert, K.; Thorup, A.A.E.; Paul, J.L.; Christiansen, H. Mental Health Is a Family Affair—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Associations between Mental Health Problems in Parents and Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054485
Stracke M, Heinzl M, Müller AD, Gilbert K, Thorup AAE, Paul JL, Christiansen H. Mental Health Is a Family Affair—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Associations between Mental Health Problems in Parents and Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(5):4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054485
Chicago/Turabian StyleStracke, Markus, Miriam Heinzl, Anne Dorothee Müller, Kristin Gilbert, Anne Amalie Elgaard Thorup, Jean Lillian Paul, and Hanna Christiansen. 2023. "Mental Health Is a Family Affair—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Associations between Mental Health Problems in Parents and Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 5: 4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054485
APA StyleStracke, M., Heinzl, M., Müller, A. D., Gilbert, K., Thorup, A. A. E., Paul, J. L., & Christiansen, H. (2023). Mental Health Is a Family Affair—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Associations between Mental Health Problems in Parents and Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054485







