Effects of Policy for Controlling Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China: From a Perspective of Regional and Policy Measures Differences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Source
2.1. Data for Calculation of ANPS Pollution Emissions
2.2. Data for Calculation of Policy Strength
3. Methods
3.1. Calculation Equations of ANPS Pollution Emissions
3.2. Calculation of Policy Strength
3.3. Empirical Model and Variable Definitions
4. Results
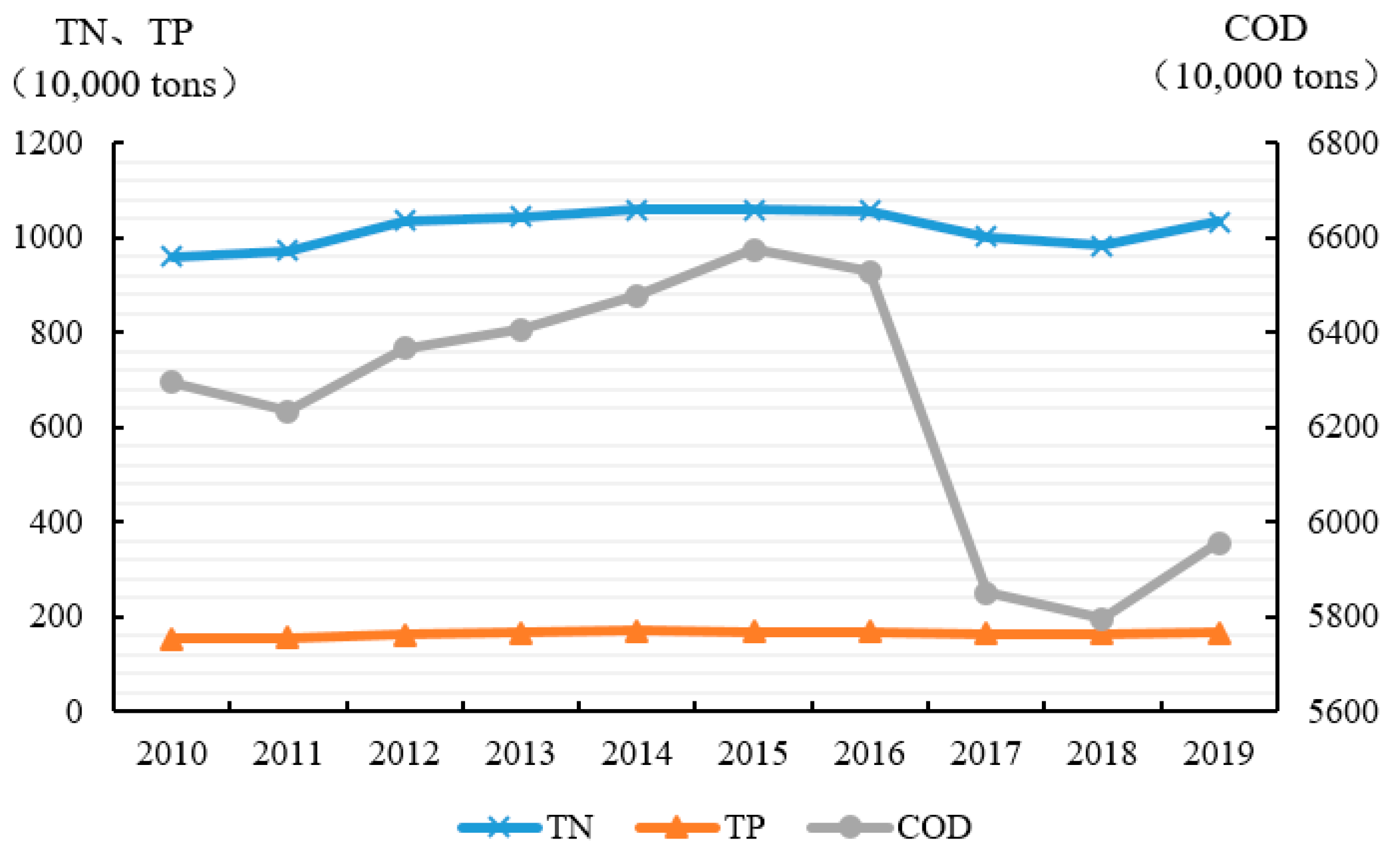
4.1. Construction of TN, TP, and COD Emissions
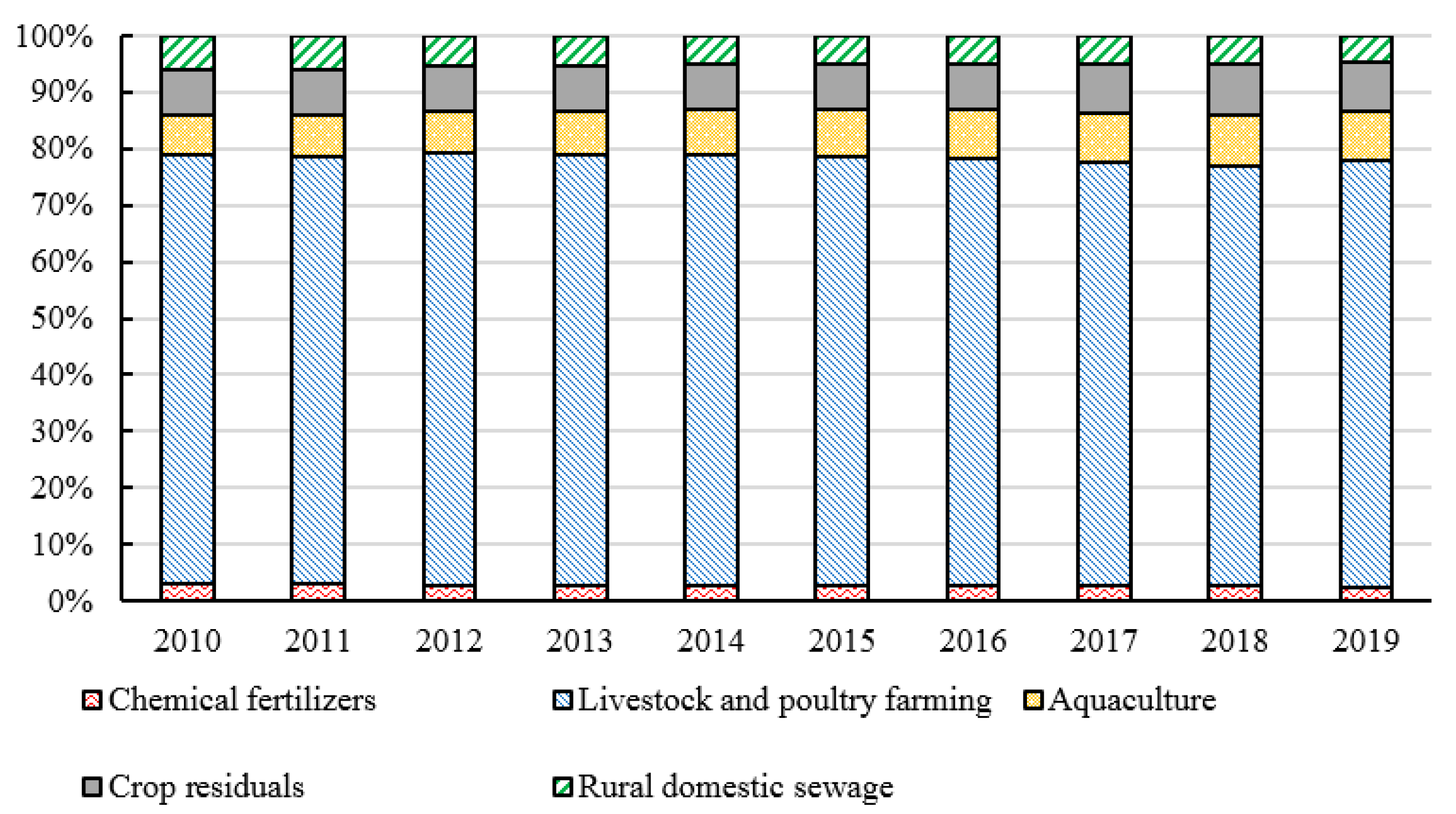
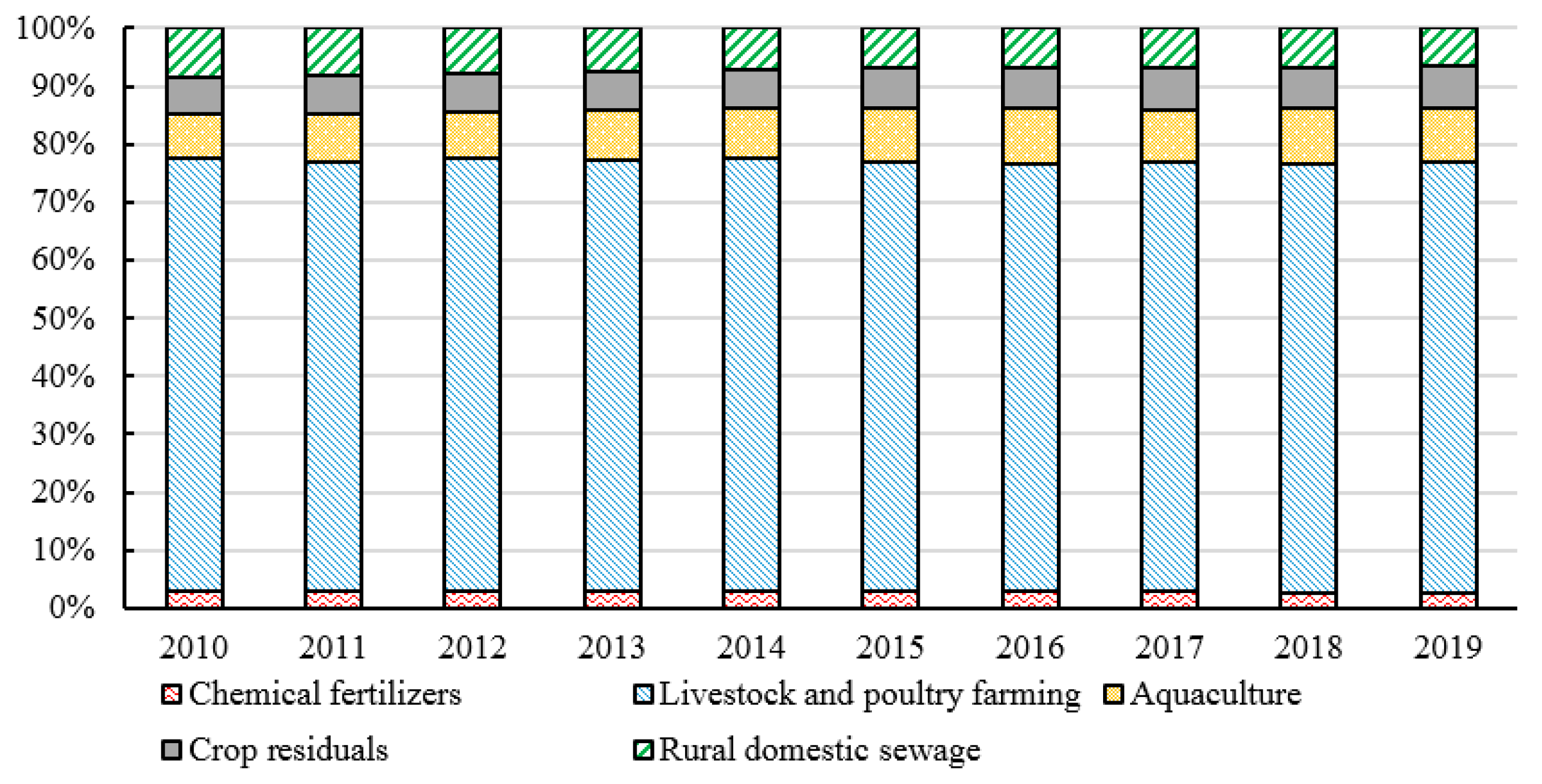
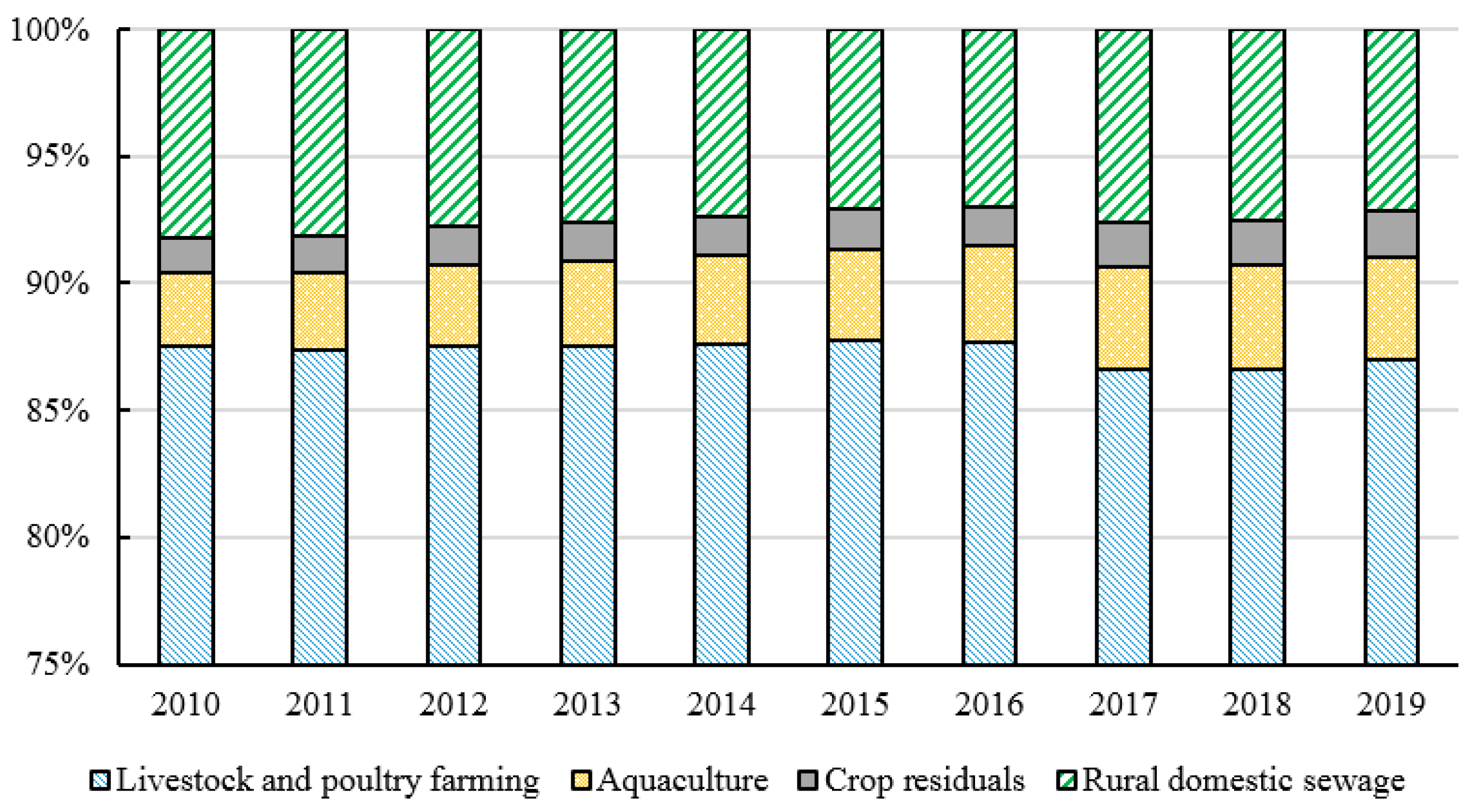
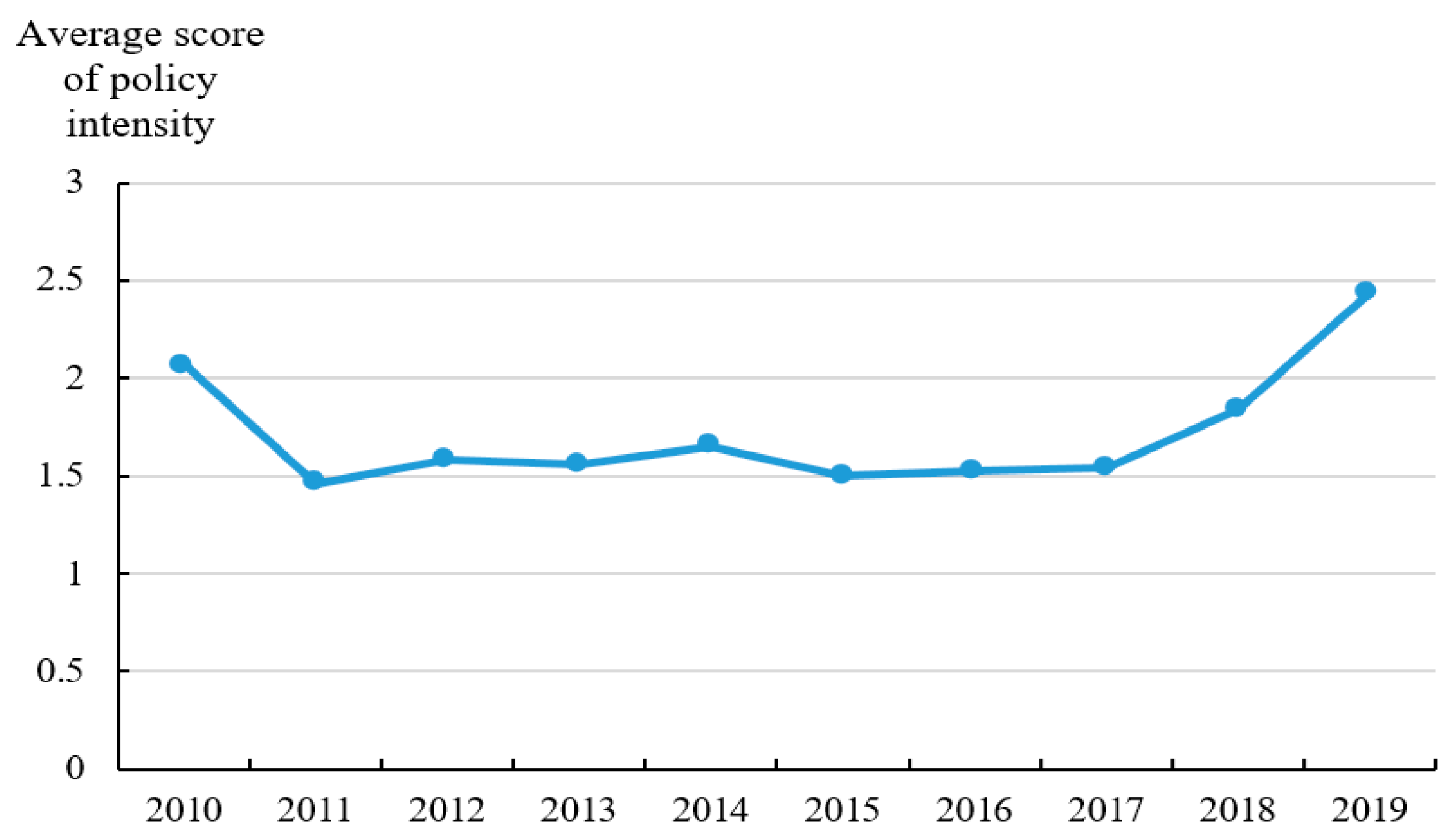
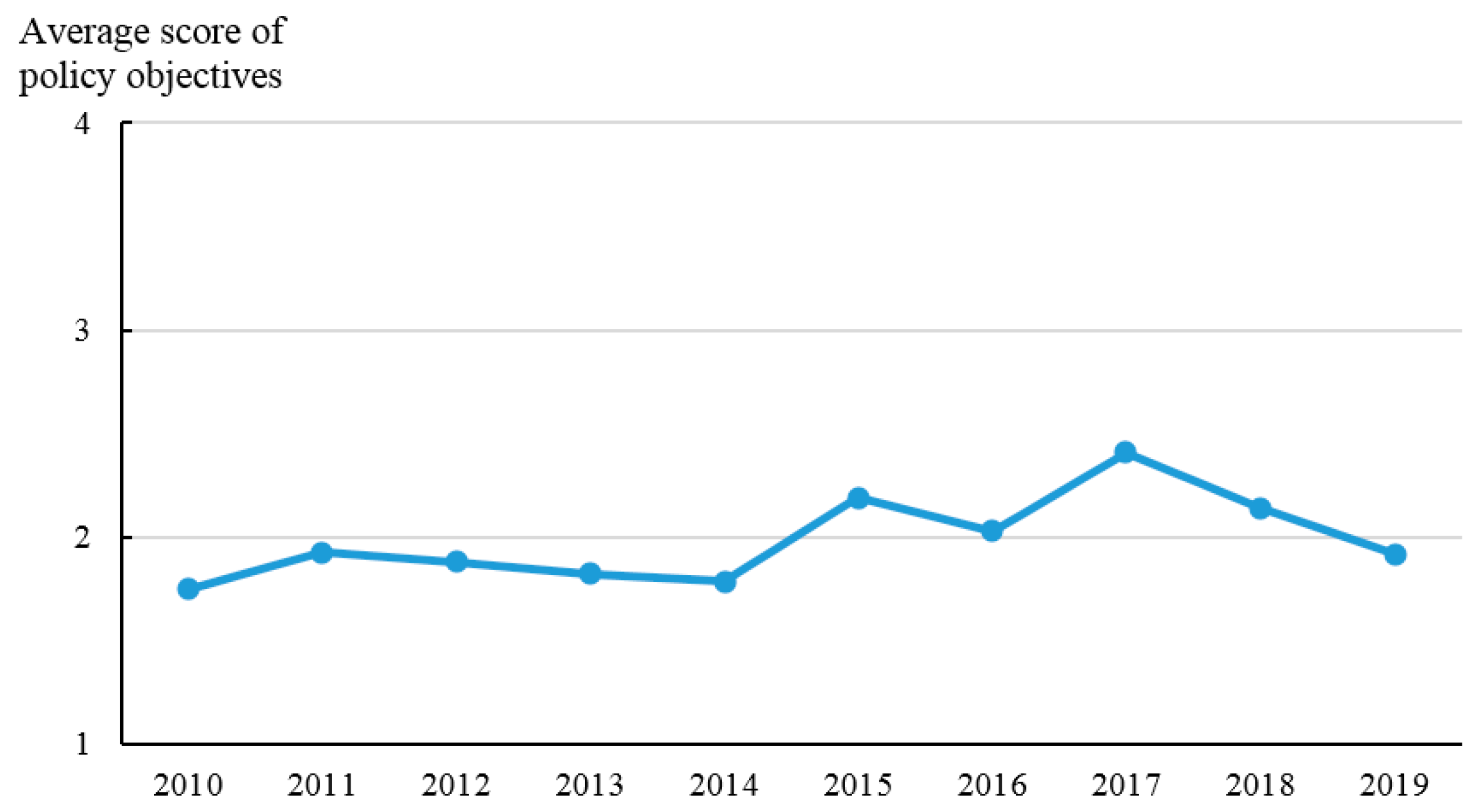
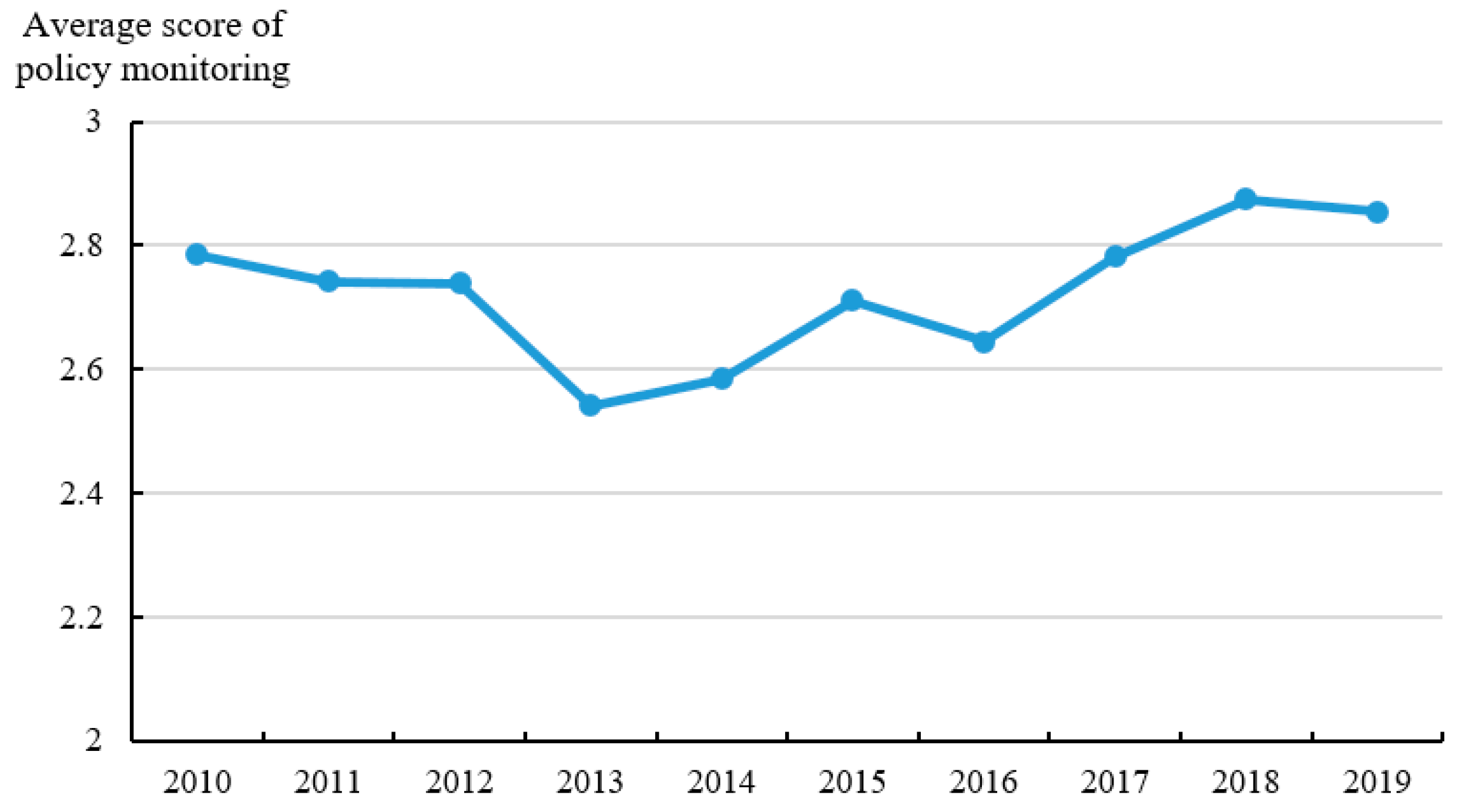
4.2. Calculation Results of Policy Intensity, Objectives, Monitoring, and Measures
4.3. The ANPS Pollution and Policy Strength
4.4. Regression Results for Effects of Policy Strength
4.5. Regression Results for Effects of Policy with Different Measures
4.6. Robustness Check
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribaudo, M.O.; Heimlich, R.; Peters, M. Nitrogen sources and Gulf hypoxia: Potential for environmental credit trading. J. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 52, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortle, J.S.; Horan, R.D. Nutrient Pollution: A Wicked Challenge for Economic Instruments. Water Econ. Policy 2017, 3, 1650033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaehringer, J.G.; Wambugu, G.; Kiteme, B.; Eckert, S. How do large-scale agricultural investments affect land use and the environment on the western slopes of Mount Kenya? Empirical evidence based on small-scale farmers’ perceptions and remote sensing. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsagris, M.; Tzouvelekas, V. Nitrate Pollution and Efficiency Measurement in Intensive Farming Systems: A Parametric By-Production Technology Approach; Working Papers. 2021. Available online: https://9b9ec758578b3ee0d46b-305404f9eb35eaf4130aa2d106c6a91c.ssl.cf3.rackcdn.com/597/market/publications/995/files/p1era7u63qktbm4qqpv16n31ddvj.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Li, L. Legal and policy tools to prevent and control agricultural non-point source pollution in the United States. Theory Reform 2015, 3, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.T.; Lu, L.X.; Hua, C.L. Construction of agricultural non-point source pollution control mechanism from the perspective of circular economy. Rural. Econ. 2016, 11, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.Q. Characteristics and treatment of agricultural non-point source pollution. Reform 2017, 11, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, T. Research on multi-subject cooperative management model of agricultural non-point source pollution under the background of rural revitalization. Rural. Econ. 2019, 1, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.F.; Yan, P.F.; Wang, Z.W.; Wen, J.D.; Feng, J.H.; Liu, F.L.; Yang, Y.S.; Wu, H.H.; Guo, Q.Y. Western Economics (Part 1); Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2016; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China.Notice of Publication. “Zero Growth Action Plan for Fertilizer Use by 2020” and the “Zero Growth Action Plan for Pesticide Use by 2020”. Available online: http//www.moa.gov.cn/nybgb/2015/san/201711/t20171129_5923401.htm (accessed on 29 November 2017).
- Pan, D.; Chen, H.; Kong, F.B. Research on the evolution characteristics and rules of China’s forestry policy since 1949—Based on the quantitative analysis of 283 normative documents related to forest. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2019, 7, 89–108. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.J.; Jin, S.Q.; Feng, S. General mode for environmental policy evaluation. Environ. Pollut. Control. 2011, 33, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.N. Public Policy Analysis: An Introduction; China Renmin University Press: Beijing, China, 2011; p. 249. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.Q.; Xing, X.X. Trend analysis, policy review and countermeasures of agricultural non-point source pollution. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 593–600. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. The Utilization Rate of Fertilizers and Pesticides for the Three Major Food Crops in My Country Both Exceeds 40%. Available online: http//www.kjs.moa.gov.cn/gzdt/202101/t20210119_6360102.htm (accessed on 9 January 2021).
- Cao, H.H.; Wang, R.C.; Li, L. Research on the policy effects of ecological agriculture in Erhai Basin by DID model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2014, 24, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Ma, C.W.; Feng, J.C.; Xue, S. Emission reduction effects and its spatial heterogeneity of rural water environmental policy based on discrete grey model. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2017, 25, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, C.C.; Liu, M.C.; Li, W.H. Evaluation on the policies of non-point pollution control of chemical fertilizer in China. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2015, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, P.; Zhu, L.Z. Agricultural pollution prevention and control in China, environmental regulation defects and adverse selection of stakeholders. Issues Agric. Econ. 2015, 36, 73–80+112. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.Q.; Han, D.M.; Wu, N.W. Evaluation on prevention policies for livestock and poultry pollution in China. Issues Agric. Econ. 2018, 39, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liu, Y. Evaluation And Policy Prospect of Zero Growth Action of Chemical Fertilizer in the 13th Five-year Plan. Environ. Prot. 2022, 5, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.F.; Liu, M.C.; Hong, C.C.; Li, W.H.; Min, Q. Preliminary evaluation on the policies for control of nonpoint pollution from agriculture in China. Environ. Pollut. Control. 2015, 37, 90–95+109. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.W. Agriculture surface source prevention and control of pollution’s system mechanism discusses in China. Rural. Econ. 2008, 24, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, J.; Xu, X.Y.; Ji, X.T. Research on the current situation, mechanism and countermeasures of agricultural non-point source pollution in China. Issues Agric. Econ. 2011, 32, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.H.; Shang, J.; Yang, G. Review and improvement strategies of non-point source pollution control policies from the perspective of farmers. Issues Agric. Econ. 2020, 3, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jin, S.Q. Agricultural non-point source pollution situation and policy orientation of the 14th Five-Year Plan, A comparative analysis based on two national pollution source census bulletins. Environ. Prot. 2021, 49, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, W.W.; Zhong, C.B.; Li, Z.L.; Pan, Y.Q. Spatial and temporal characteristics of agricultural non-point source pollution emission patterns in China. China Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2019, 40, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.H.; Xue, L. Agricultural industrial agglomeration and agricultural non-point source pollution, based on spatial heterogeneity. Sci. Financ. Econ. 2019, 8, 82–96. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.J.; Zhao, R.Y. Evolution and frontiers of international agricultural diffused pollution research—Quantitative analysis based on CiteSpace. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, T.; Qi, Y. Food security and agricultural non-point source pollution, A case study of the impact of farmland endowment on fertilizer input intensity. Res. Financ. Econ. 2015, 41, 132–144. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, X.N.; Shan, J.J. Research on fertilizer and pesticide reduction and soil pollution control in agricultural land. Jianghuai Forum 2019, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.Y. Investigation and Evaluation Method of Non-Point Source Pollution and Its Application; Tsinghua University: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.X.; Cai, H.Z.; Fu, P.; Liu, A. Analysis on resource disposal of agricultural solid waste straw in China. J. Eco-Environ. 2016, 25, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, H.B.; Shen, Y.J.; Meng, H.B.; Yao, Z.L.; Feng, J.; Hou, L.; Yuan, Y.; Dai, M.; Wu, Y.; Sheng, C. Classification of agricultural solid waste and its pollution risk identification and treatment path. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.X. The current situation of China’s rural environmental pollution and its protection countermeasures. Rural. Econ. 2004, 9, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.F.; Hu, X.Y. Necessity of treatment and utilization of livestock and poultry manure and suggestions for sustainable development. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2021, 41, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.F.; Xu, R.; Wu, T.; Xu, Z.-H.; Xu, G.-C. Current situation and future development of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in aquaculture environment in China. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 34, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.Y.; Zhu, N.; Li, Y.X.; Xu, L. Analysis of payment behavior of farmers benefiting from rural domestic sewage treatment, Based on the survey of farmers in the Dongjiang River water source area. Agric. Resour. Reg. China 2022, 6, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.Y.; Du, P.F.; Chen, J.N. Investigation and evaluation of non-point source pollution based on unit analysis. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2004, 9, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.P.; Chen, J.N.; Lai, S.Y. Inventory analysis and spatial characteristics identification of agricultural and rural pollution in China. China Environ. Sci. 2006, 6, 751–755. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.S.; Yang, S.S. Measurement and control of agricultural non-point source pollution, a case study of Hunan province. Syst. Eng. 2015, 33, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.M.; An, J.W.; Han, C. Application of entropy method in urban sustainable development evaluation. Res. Quant. Econ. Technol. Econ. 2003, 6, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Sun, Z.C. The Development of Western New type Urbanization Level Evaluation Based on Entropy Method. Econ. Issuess 2015, 3, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.S.; Zhong, W.G.; Sun, W.X. Policy measurement, policy co-evolution and Economic Performance, An empirical study based on innovation policy. Manag. World 2008, 9, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.X.; Gao, X.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Guo, J.E. Research on the effectiveness of synergy of energy conservation and Emission Reduction policies in China, 1997–2011. Manag. Rev. 2015, 27, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.F.; Wu, Q. Research on Policy efficiency evaluation of urban Land Intensive Use based on policy Quantification, A Case study of Nanjing City. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 2193–2201. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Bao, X.Z.; Zhang, R.; Shen, X.Y. Analysis on the effectiveness of technology and finance policies in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on policy quantification. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2018, 38, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.L.; Zhang, C.H. Evaluation of the effect of China’s urban mineral policy from the perspective of policy tools. Urban Issues 2018, 11, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.J.; Zhu, R. Evaluation of policy effectiveness and effect of industry-university-research collaborative innovation, Based on quantitative analysis of China’s policy texts from 2006 to 2016. Soft Sci. 2019, 33, 30–35+44. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.Q. Innovation Ability of Agricultural Science and Technology in China, Spatial Differences, Influencing Factors and Promotion Strategies; Huazhong Agricultural University: Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, S. Whether Moderate scale Operation can inhibit agricultural Non-point source Pollution, An empirical study based on dynamic threshold panel model. J. Agric. Tech. Econ. 2021, 7, 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Li, J.R. Research on the evaluation index system of rural residents’ life affluence—Based on the perspective of building a well-off society in an all-round way. Res. World 2020, 1, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.Y.; Wang, Y. Research on the Influencing Factors of New Urbanization Quality—Based on the Comparison between the Eastern and Western Regions. Forcasting 2021, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.Z.; Yin, L.J.; He, B. Logistics Industry Aggregation, Space Spillover Effects, and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity—Based on Empirical Analysis of the Provincial Data. China Bus. Mark. 2022, 9, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, J. Empirical analysis of the influencing factors of farmers’ fertilization decision—Based on the survey data of Hubei Province. Agric. Econ. Issues 2008, 10, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg, E.; Smith-Ramírez, R. Slippage in Conservation Cost Sharing. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2011, 93, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Wu, L.S. Rural environmental pollution and innovation of regulation tools in the low-carbon era—An analysis based on regulation economics. Financ. Theory Pract. 2012, 33, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.; Jia, X.P.; Huang, J.K.; Hu, R.F.; Zhang, F.S.; Cui, Z.L. The impact of agricultural technology training on farmers’ nitrogen fertilizer application behavior, an empirical study based on corn production in Shouguang City, Shandong Province. Agric. Technol. Econ. 2012, 9, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Keiser, A.D.; Shapiro, S.J. Consequences of the Clean Water Act and the demand for water quality. Q. J. Econ. 2019, 134, 349–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortle, J.S.; Horan, R.D. Policy Instruments for Water Quality Protection. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2013, 5, 111–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Ye, Y.Q.; Guan, X.; Yin, J.H.; Lv, X.L. Difference and collaboration in Jing-Jin-Ji’s energy saving and emission reduction policy measurers. J. Manag. Sci. China 2018, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.K.; Ren, S.G.; Li, X.L. The Effects of Different Types of Environmental Policies on Regional Carbon Emissions in China. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. (Soc. Sci.) 2018, 2, 55–64. [Google Scholar]


| Source | Category | Unit | Key Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planting | Chemical fertilizer | Nitrogen fertilizer, Phosphate fertilizer, Compound fertilizer | Total input amount of kth fertilizer (k = 1, 2, 3) |
| Crop residue | Crop residue of rice, wheat, corn, beans, potatoes, oilseeds, and vegetables | Total amount of mth crop yield (m = 1, 2, …, 7) | |
| Animal breeding industry | Livestock and poultry farming | Pig, cattle, poultry | Slaughter quantity of pigs (z1) and poultry (z2), Stock quantity of cattle (z3) |
| Aquaculture | Marine and freshwater aquaculture | production of rth aquaculture (r = 1, 2) | |
| Rural community | Rural domestic sewage | Rural population (pop) |
| Chemical Fertilizer | Crop Residue | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TN | TN | ||
| TP | TP | ||
| COD | — | COD | |
| Livestock and poultry farming | Rural domestic sewage | ||
| TN | TN | ||
| TP | TP | ||
| COD | COD | ||
| Aquaculture | |||
| TN | |||
| TP | |||
| COD | |||
| Indicator | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Policy intensity (IN) | The administrative influence of policy documents | 1–4 |
| Policy objectives (OB) | The goals, requirements, and effects expected to be achieved by the implementation of a policy | 1–4 |
| Policy monitoring (MO) | The response from farmers or other policy audiences to policy implementation in practice. | 1–3 |
| Indicators of Policy measures | ||
| The official regulations include a maximum number of chemical inputs, standards for chemical inputs use, constraints, and restrictions on polluting behavior. | 1–5 | |
| The awards, fines, taxes, and subsidies encourage farmers’ environmentally friendly behavior. | 1–5 | |
| The methods or technologies can be used in the process of agricultural activities for reducing ANPS pollution | 1–5 | |
| The information on agricultural technical training courses, technical guidance on agricultural production, methods of using chemical inputs and agricultural tools, and so on. | 1–5 | |
| Variable | Mean | Std. Dev |
|---|---|---|
| ANPS pollution emissions (ANPS, scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.2188 | 0.1641 |
| Policy strength (PS, scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.2166 | 0.1789 |
| Strength of Administrative regulation measures (AMD scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.2155 | 0.1785 |
| Strength of economic incentive measures (ECO, scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.2202 | 0.1791 |
| Strength of technical support measures (TEC, scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.2121 | 0.1757 |
| Strength of education measures (EDU, scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.2123 | 0.1775 |
| Economic scale in the agricultural sector (log of GDP in hundred million yuan) | 7.4630 | 1.0789 |
| Agricultural structure (AS, scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.5244 | 0.0844 |
| Urbanization rate (URB, scale: 0.0–1.0) | 0.5609 | 0.1339 |
| Wealth of rural residents (log of INC in yuan per person) | 8.9034 | 0.3097 |
| Variable | Fixed Effect Model | Fixed Effect Model (With Lagged Policy Strength) | Dynamic Panel Model (With Lagged Policy Strength) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lag ANPS | 0.7767 *** (0.0882) | ||
| Policy Strength | −0.0017 (0.0051) | ||
| Lag Policy Strength | −0.0101 * (0.0058) | −0.0136 ** (0.0063) | |
| GDP | 0.0774 ** (0.0295) | 0.0775 ** (0.0305) | 0.0378 * (0.0196) |
| Agricultural Scale | −0.1561 ** (0.0680) | −0.1357 ** (0.0661) | −0.0308 (0.0725) |
| Urbanization rate | −0.2416 (0.2039) | −0.2921 (0.2250) | −0.2583 *** (0.0895) |
| Wealth of rural residents | 0.0082 (0.0635) | 0.0308 (0.0755) | 0.0581 (0.0545) |
| Constant | −0.2137 (0.5843) | −0.3964 (0.6778) | −0.5841 (0.4117) |
| N | 310 | 310 | 279 |
| F | 2.41 | 3.23 | |
| R2 | 0.5856 | 0.5891 | |
| AR (1) | 0.0756 | ||
| AR (2) | 0.0549 | ||
| Sargan | 0.1436 |
| Variable | Eastern | Central | Western | Northeastern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lag ANPS | 0.9455 *** (0.0797) | 1.0092 *** (0.0588) | 0.9401 *** (0.1428) | 0.6384 *** (0.0788) |
| Lag Policy Strength | −0.0015 (0.0081) | 0.0086 (0.0181) | −0.0056 (0.0134) | −0.0861 ** (0.0409) |
| GDP | 0.0013 (0.0217) | −0.1334 (0.0969) | 0.0028 (0.0423) | −0.0048 (0.0561) |
| Agricultural Scale | −0.1409 (0.1501) | 0.8095 (0.5766) | 0.0336 (0.0613) | 0.1333 (0.1298) |
| Urbanization rate | −0.1943 (0.1774) | −0.6382 * (0.3757) | −0.2472 * (0.1438) | 0.2504 (0.4007) |
| Wealth of rural residents | −0.0004 (0.1174) | 0.6570 (0.4483) | 0.1166 (0.0954) | 0.0384 (0.0424) |
| Constant | 0.2077 (1.1029) | −4.8441 (3.2669) | −0.9121 (0.6274) | −0.1870 (0.3719) |
| N | 90 | 54 | 108 | 27 |
| AR (1) | 0.0634 | 0.1514 | 0.1579 | 0.0929 |
| AR (2) | 0.4396 | 0.3467 | 0.7953 | 0.2585 |
| Sargan | 0.9971 | 0.1074 | 0.9608 | 0.7232 |
| Variables | Admin. Measures | Economic Measures | Technical Support | Educational Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L.ANPS | 0.7796 *** (0.0908) | 0.7786 *** (0.0901) | 0.7791 *** (0.0905) | 0.7776 *** (0.0902) |
| Lagged Admin. Measures strength | −0.0120 * (0.0067) | |||
| Lagged Economic Measures strength | −0.0125 ** (0.0062) | |||
| Lagged Technical Support strength | −0.0127 * (0.0066) | |||
| Lagged Educational Policies strength | −0.0126 * (0.0066) | |||
| GDP | 0.0362 * (0.0189) | 0.0368 * (0.0193) | 0.0365 * (0.0191) | 0.0367 * (0.0190) |
| Agricultural Scale | −0.0299 (0.0713) | −0.0292 (0.0707) | −0.0289 (0.0701) | −0.0297 (0.0721) |
| Urbanization rate | −0.2568 *** (0.0927) | −0.2594 *** (0.0920) | −0.2578 *** (0.0924) | −0.2583 *** (0.0924) |
| Wealth of rural residents | 0.0566 (0.0522) | 0.0577 (0.0523) | 0.0573 (0.0525) | 0.0576 (0.0518) |
| Constant | −0.5602 (0.4043) | −0.5740 (0.4013) | −0.5689 (0.4053) | −0.5724 (0.4001) |
| N | 279 | 279 | 279 | 279 |
| AR (1) | 0.0769 | 0.0769 | 0.0768 | 0.0778 |
| AR (2) | 0.0549 | 0.0501 | 0.0555 | 0.0533 |
| Sargan | 0.1513 | 0.1490 | 0.1505 | 0.1505 |
| Variables | ANPS Pollution by Entropy Method | Policy Strength by Principal Component Analysis | Differential GMM Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lag. ANPS | 1.0262 *** (0.0474) | 0.7766 *** (0.0880) | 0.5352 *** (0.0463) |
| Lag. Policy Stringency | −0.0087 * (0.0046) | −0.0010 ** (0.0004) | −0.0146 ** (0.0067) |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES |
| Constant | −0.1967 (0.3338) | −0.5875 (0.4142) | −1.0864 ** (0.5248) |
| N | 279 | 279 | 279 |
| AR (1) | 0.0367 | 0.0753 | 0.0666 |
| AR (2) | 0.5177 | 0.0557 | 0.0573 |
| Sargan | 0.2493 | 0.1428 | 0.0981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, C.; Zhang, J.; Long, Z.; Woodward, R.T. Effects of Policy for Controlling Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China: From a Perspective of Regional and Policy Measures Differences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043741
Hua C, Zhang J, Long Z, Woodward RT. Effects of Policy for Controlling Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China: From a Perspective of Regional and Policy Measures Differences. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043741
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Chunlin, Jiuhong Zhang, Zhiru Long, and Richard T. Woodward. 2023. "Effects of Policy for Controlling Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China: From a Perspective of Regional and Policy Measures Differences" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043741
APA StyleHua, C., Zhang, J., Long, Z., & Woodward, R. T. (2023). Effects of Policy for Controlling Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China: From a Perspective of Regional and Policy Measures Differences. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043741








