The Effect of Two Types of Back Pillow Support on Transversus Abdominis and Internal Oblique Muscle Fatigue, Patient Satisfaction, and Discomfort Score during Prolonged Sitting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Population Recruitment
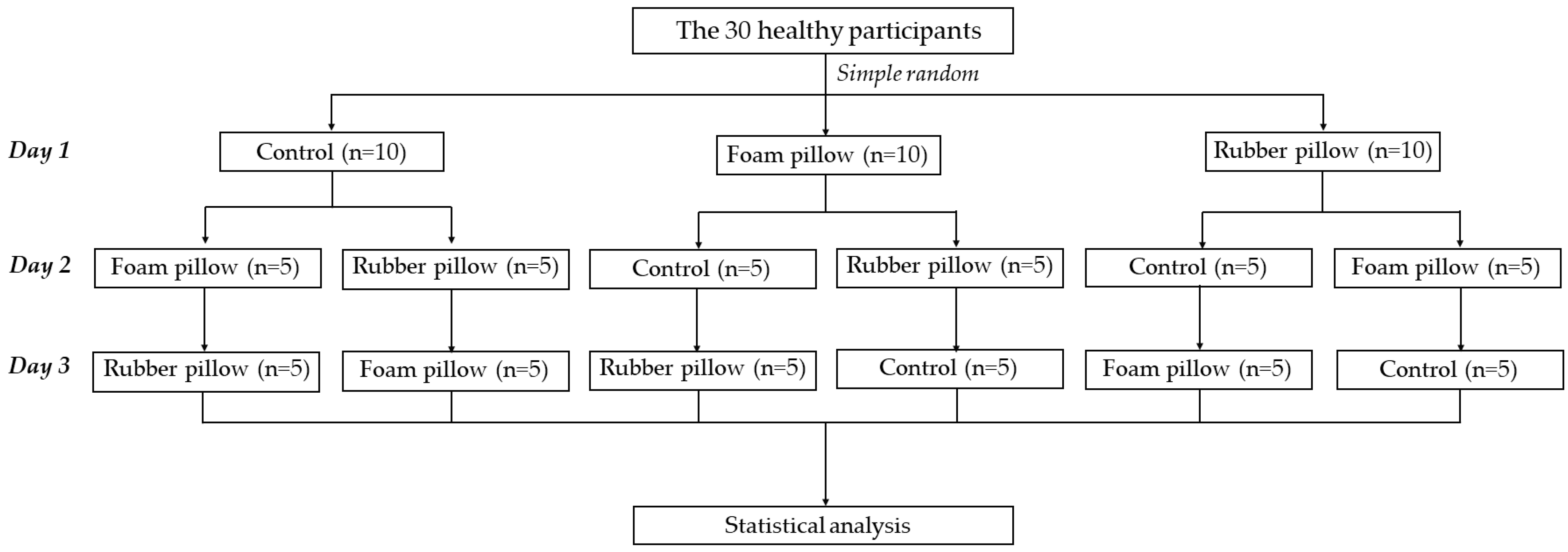
2.3. Procedure
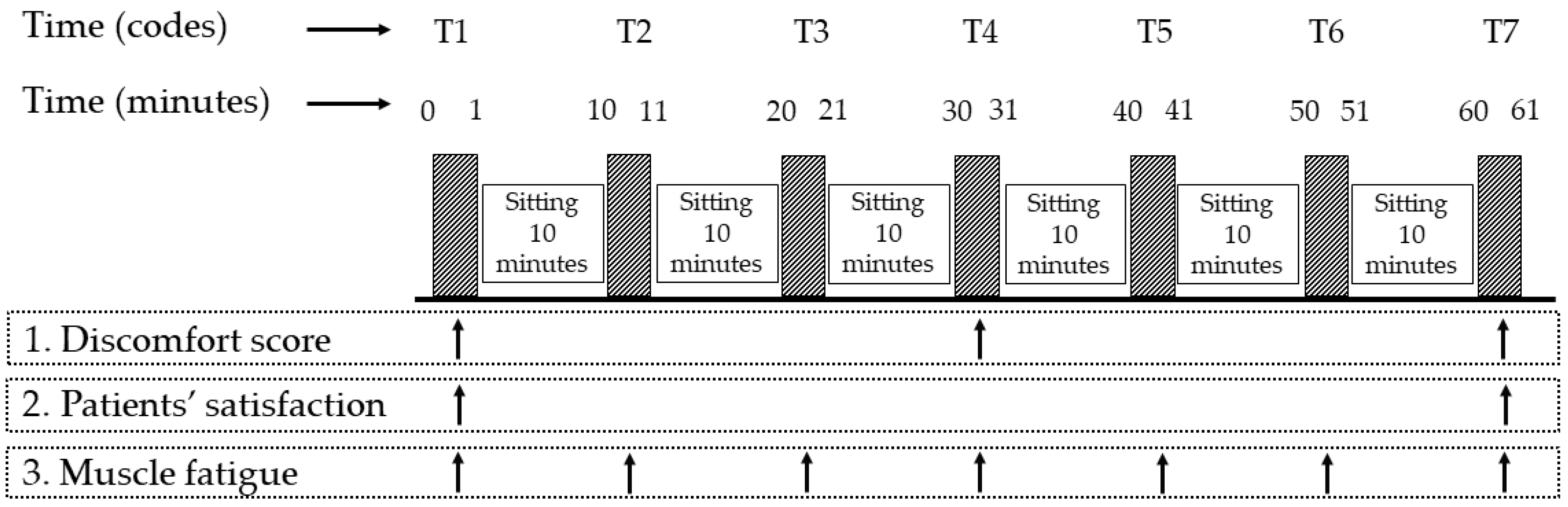
2.4. Outcome Measurement
2.4.1. Discomfort Scores
2.4.2. Patients’ Satisfaction
2.4.3. Trunk Muscle Fatigue
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Discomfort Score
3.2. Participants’ Satisfaction
3.3. Trunk Muscle Fatigue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hadgraft, N.T.; Healy, G.N.; Owen, N.; Winkler, E.A.; Lynch, B.M.; Sethi, P.; Eakin, E.G.; Moodie, M.; Lamontagne, A.D.; Wiesner, G.; et al. Office workers’ objectively assessed total and prolonged sitting time: Individual-level correlates and worksite variations. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 4, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, S.; Straker, L. The contribution of office work to sedentary behaviour associated risk. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 296. Available online: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2458/13/296 (accessed on 22 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Montakarn, C.; Nuttika, N. Physical activity levels and prevalence of low back pain in Thai call-center operators. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 20, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, F.; Daas, R.N.; El-Shareif, T.J.; Al-Marridi, H.H.; Al-Rojoub, Z.M.; Adegboye, O.A. The relationship between sedentary behavior, back pain, and psychosocial correlates among university employees. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Cook, J.; Bass, S.; Lo, S.K. Sedentary lifestyle as a risk factor for low back pain: A systematic review. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2009, 82, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsson, G.; Jonsson, E.; Fritzell, P.; Hägg, O.; Borgström, F. A health economic lifetime treatment pathway model for low back pain in Sweden. J. Med. Econ. 2017, 20, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Pellisé, F.; Cedraschi, C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2012, 379, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjabi, M.M. Clinical spinal instability and low back pain. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faries, M.D.; Greenwood, M. Core Training: Stabilizing the confusion. Strength Cond. J. 2007, 29, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmark, A. Stability of the lumbar spine: A study in mechanical engineering. Acta Orthop. 1989, 60, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, S.M.; Grenier, S.; Kavcic, N.; Cholewicki, J. Coordination of muscle activity to assure stability of the lumbar spine. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, P.W.; Eriksson, A.E.; Shirley, D.; Gandevia, S.C. Intra-abdominal pressure increases stiffness of the lumbar spine. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiklang, P.; Puntumetakul, R.; Swangnetr, N.M.; Boucaut, R. The immediate effect of the abdominal drawing-in maneuver technique on stature change in seated sedentary workers with chronic low back pain. Ergonomics 2020, 64, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredericson, M.; Moore, T. Core stabilization training for middle and long-distance runners. New Stud. Athl. 2005, 20, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, P.W.; Richardson, C.A. Inefficient muscular stabilization of lumbar spine associated with low back pain: A motor evaluation of transversus abdominis. Spine 1996, 21, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, P.; Cresswell, A.; Thorstensson, A. Preparatory trunk motion accompanies rapid upper limb movement. Exp. Brain Res. 1999, 124, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waongenngarm, P.; Rajaratnam, B.S.; Janwantanakul, P. Internal oblique and transversus abdominis muscle fatigue induced by slumped sitting posture after 1 hour of sitting in office workers. Saf. Health Work. 2016, 7, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergroesen, P.P.A.; Van Der Veen, A.J.; Emanuel, K.S.; Van Dieën, J.H.; Smit, T.H. The poro-elastic behaviour of the intervertebral disc: A new perspective on diurnal fluid flow. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, R.; Guarnieri, G.; Guglielmi, G.; Muto, M. Biomechanics of the spine. Part II: Spinal instability. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiklang, P.; Puntumetakul, R.; Selfe, J.; Yeowell, G. An evaluation of an innovative exercise to relieve chronic low back pain in sedentary workers. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2020, 64, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kobara, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Osaka, H.; Ishida, H. Influence of trunk muscle co-contraction on spinal curvature during sitting. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabilit. 2014, 27, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryer, J.C.J.; Quon, J.A.; Smith, F.W. Magnetic resonance imaging and stadiometric assessment of the lumbar discs after sitting and chair-care decompression exercise: A pilot study. Spine J. 2010, 10, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.W.R.; Carvalho, D.E.D.; Karakolis, T.; Callaghan, J.P. Evaluating abdominal and lower back muscle activity while performing core exercises on a stability ball and a dynamic office chair. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2015, 57, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, D.E.; Dunk, M.N.; Callaghan, J.P. Stability ball versus office chair: Comparisonof muscle activation and lumbar spine posture during prolonged sitting. Hum. Factors J. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. 2006, 48, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolin, S.M. McKenzie diagnosis and therapy in the evaluation and management of a lumbar disc derangement syndrome: A case study. J. Chiropr. Med. 2003, 2, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prommanon, B.; Puntumetakul, R.; Puengsuwan, P.; Chatchawan, U.; Kamolrat, T.; Rittitod, T.; Yamauchi, Y. Effectiveness of a back care pillow as an adjuvant physical therapy for chronic non-specific low back pain treatment: A randomized controlled trial. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompayak, S.; Puntumetakul, R.; Karukunchit, U.; Peungsuwan, P.; Kamonrat, T. A comparative study of the effectiveness of the use of a back care pillow and a lumbar support, as an adjuvant physical therapy in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain. J. Med. Technol. Phys. Ther. 2016, 28, 116–176. Available online: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ams/article/view/67959 (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Chuayprakong, S.; Chuchat, J.; Poruksa, T.; Soccio, M. Feasibility of using natural rubber (NR) Latex foam as a soft robotic finger: Role of foaming agent in morphology and dynamic properties of NR latex foam. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 14, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatchawan, U.; Jupamatangb, U.; Chanchitc, S.; Puntumetakul, R.; Donpunha, W.; Yamauchi, J. Immediate effects of dynamic sitting exercise on the lower back mobility of sedentary young adults. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 3359–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PuntumetaKul, R.; Hiruntrakul, P.; Premchaisawat, W.; Puntumetakul, M.; Thavornpitak, Y. The measurement of lumbar spinal curvature in normal Thai population aged 20–69 years using flexible ruler. J. Med. Technol. Phy. Ther. 2012, 24, 308–317. Available online: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ams/article/view/66292 (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Hertzog, M.A. Considerations in determining sample size for pilot studies. Res. Nurs. Health 2008, 31, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Valente, M.A.; Pais-Ribeiro, J.L.; Jensen, M.P. Validity of four pain intensity rating scales. Pain 2011, 152, 2399–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotle, M.; Brox, J.I.; Vøllestad, N.K. Concurrent comparison of responsiveness in pain and functional status measurements used for patients with low back pain. Spine 2004, 29, E492–E501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, A.F.; Junge, A.; Fairbank, J.C.; Dvorak, J.; Grob, D. Development of a german version of the oswestry disability index. Part i: Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability and validity. Eur. Spine J. 2005, 15, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamper, S.J.; Ostelo, R.W.; Knol, D.L.; Maher, C.G.; de Vet, H.C.; Hancock, M.J. Global perceived effect scales provided reliable assessments of health transition in people with musculoskeletal disorders, but ratings are strongly influenced by current status. J. Clin. Epidemiology 2010, 63, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshell, P.W.; Murphy, B.A. The validity and reliability of surface EMG to assess the neuromuscular response of the abdominal muscles to rapid limb movement. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, A.; Kaneoka, K.; Okubo, Y.; Shiina, I.; Tatsumura, M.; Izumi, S.; Shiraki, H. Trunk muscle activity during lumbar stabilization exercises on both a stable and unstable surface. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 40, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntumetakul, R.; Areeudomwong, P.; Emasithi, A.; Yamauchi, J. Effect of 10-week core stabilization exercise training and detraining on pain-related outcomes in patients with clinical lumbar instability. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2013, 7, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Areeudomwong, P.; Puntumetakul, R.; Jirarattanaphochai, K.; Wanpen, S.; Kanpittaya, J.; Chatchawan, U.; Yamauchi, J. Core stabilization exercise improves pain intensity, functional disability and trunk muscle activity of patients with clinical lumbar instability: A pilot randomized controlled study. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2012, 24, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.K.; Parnianpour, M.; Kippers, V.; Richardson, C.A. Reliability of electromyographic and torque measures during isometric axial rotation exertions of the trunk. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkarakittichoke, N.; Janwantanakul, P. Seat pressure distributioncharacteristics during 1 hour sitting in office workers with andwithout chronic low back pain. Saf. Health Work. 2017, 8, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.; Coenen, P.; Howie, E.; Williamson, A.; Straker, L. The short term musculoskeletal and cognitive effects of prolonged sitting during office computer work. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldstad, J.C.; Sherman, B.R. The effects of a back belt on posture, strength, and spinal compressive force during static lift exertions. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 1998, 22, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.K.; Chainm, D.B.; Herrin, G.D. A study of lumbosacral orientation under varied static loads. Spine 1986, 11, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.A.; May, S.; Freeman, B.J.; Morrison, H.P.; Dolan, P. Effects of backward bending on lumbar intervertebral discs. Relevance to physical therapy treatments for low back pain. Spine 2000, 25, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirikulchaikij, S.; Kokoo, R.; Khangkhanmano, M. Natural rubber latex foam production using air microbubbles: Microstructure and physical properties. Mater. Lett. 2020, 260, 126916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, R.J. Mechanical Properties of Rubber in Harris Shock and Vibration Handbook; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 33.1–33.18. [Google Scholar]
- Areeudomwong, P.; Puntumetakul, R.; Kaber, D.B.; Wanpen, S.; Leelayuwat, N.; Chatchawan, U. Effects of handicraft sitting postures on lower trunk muscle fatigue. Ergonomics 2012, 55, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, H.; Druitt, T.R.; Schollum, T.M.; Hodges, P.W. Motor training of the lumbar paraspinal muscles induces immediate changes in motor coordination in patients with recurrent low back pain. J. Pain 2010, 11, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimphasak, C.; Swangnetr, M.; Puntumetakul, R.; Chatchawan, U.; Boucaut, R. Effects of seated lumbar extension postures on spinal height and lumbar range of motion during prolonged sitting. Ergonomics 2016, 59, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Frequency (%) | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 40.97 ± 13.77 | |
Gender, n (%)
| 13 (44.33) 17 (56.67) | |
| BMI (kilogram/meter2) | 18.1 ± 2.14 | |
| Education level | ||
| 14 (46.67) 8 (26.67) 8 (26.67) | |
Smoking
| 6 (20) 24 (80) | |
Underlying disease
| 8 (26.68) 22 (73.33) | |
Exercise status
| 16 (53.33) 14 (46.67) |
| Groups | Discomfort Score | p-Value within Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T4 | T7 | ||
| Control | 0 (0–0) a,b,* | 1 (0–3) c,* | 3 (1.75–6) | 0.0001 * |
| Foam pillow | 0 (0–0) d,e,* | 0 (0–2) f,* | 2 (0–4.25) k,m,* | 0.0001 * |
| Rubber pillow | 0 (0–0) g,h,* | 0 (0–1) i,j,* | 0 (0–2.25) l,* | 0.0001 * |
| p-value between group | 0.223 | 0.007 * | 0.0001 * | |
| Groups | Patients’ Satisfaction | p-Value within Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T7 | ||
| Control | 0 (0–0) a*b* | (−2) (−4–0) d*e* | 0.002 * |
| Foam pillow | 1 (0–3.25) c* | 2 (0–4) f* | 0.389 |
| Rubber pillow | 2.5 (0–4) | 3 (1.75–5) | 0.006 * |
| p-value between group | 0.0001 * | 0.0001 * | |
| Muscle | Groups | Time | p-Value within Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | |||
| TrA & IO (Hz) | Control | 97.61 a* (74.69–127.00) | 94.5 (69.92–119.28) | 93.2 (68.57–112.46) | 91.91 (70.98–142.62) | 88.53 (65.52–130.34) | 87 (64.22–130.34) | 80.8 (67.07–122.65) | 0.038 * |
| Foam pillow | 84.5 (72.96–130.99) | 87 (64.16–123.45) | 90.35 (74.88–123.54) | 92.44 (54.44–119.05) | 93.71 (70.33–131.51) | 87.82 (70.27–121.81) | 81.56 (70.56–127.78) | 0.392 | |
| Rubber pillow | 106.32 (82.85–142.25) | 97.7 (84.11–132.65) | 89.36 (77.80–111.17) | 84.49 (69.87–130.75) | 86.96 (77.13–131.17) | 84.08 (71.73–128.94) | 82.15 (64.65–128.13) | 0.088 | |
| p-value between group | 0.136 | 0.67 | 0.648 | 0.733 | 0.587 | 0.648 | 0.421 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puntumetakul, R.; Chatprem, T.; Saiklang, P.; Leungbootnak, A. The Effect of Two Types of Back Pillow Support on Transversus Abdominis and Internal Oblique Muscle Fatigue, Patient Satisfaction, and Discomfort Score during Prolonged Sitting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043742
Puntumetakul R, Chatprem T, Saiklang P, Leungbootnak A. The Effect of Two Types of Back Pillow Support on Transversus Abdominis and Internal Oblique Muscle Fatigue, Patient Satisfaction, and Discomfort Score during Prolonged Sitting. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043742
Chicago/Turabian StylePuntumetakul, Rungthip, Thiwaphon Chatprem, Pongsatorn Saiklang, and Arisa Leungbootnak. 2023. "The Effect of Two Types of Back Pillow Support on Transversus Abdominis and Internal Oblique Muscle Fatigue, Patient Satisfaction, and Discomfort Score during Prolonged Sitting" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043742
APA StylePuntumetakul, R., Chatprem, T., Saiklang, P., & Leungbootnak, A. (2023). The Effect of Two Types of Back Pillow Support on Transversus Abdominis and Internal Oblique Muscle Fatigue, Patient Satisfaction, and Discomfort Score during Prolonged Sitting. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043742






