Abstract
In recent years, mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) have been widely applied in competition sports with respect to athletic performance and mental health promotion, whereas evidence of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) has not been well summarized. Therefore, this study aimed to systematically review and meta-analyze the existing evidence on the effects of MBIs on improving athletic performance, mindfulness level, mindfulness-related psychological components (e.g., acceptance, self-compassion, flow), and mental health (e.g., burnout, stress, psychological well-being) among athletes. Following the PRISMA guidelines, a literature search was implemented on five electronic databases (Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, ProQuest, and ScienceDirect) and relevant review papers. The article selection, risk of bias assessment, and data extraction were performed by two investigators independently. The standardized mean difference (SMD) was calculated to evaluate the effects of interventions using the random effect model. Among the 1897 original hits, thirty-two eligible RCT studies were included in the systematic review, of which seven were involved in the meta-analysis. The results showed that MBIs were effective in promoting athletes’ athletic performances (by narrative synthesis), mindfulness-level (n = 3; SMD = 0.50, 95% CI = [0.17, 0.83]; I2 = 45%, p = 0.16), and mindfulness-related psychological components (n = 5; SMD = 0.81, 95% CI = [0.53, 1.10], I2 = 77%, p =0.001), while no significant intervention effects were found on the mental health of athletes (n = 4; SMD = −0.03, 95% CI = [−0.35, 0.29], I2 = 89%, p < 0.001). Our findings preliminarily support the potential effectiveness of MBIs, whereas more high-quality RCTs were needed in the future.
1. Introduction
In competitive sports, pursuing optimal athletic performance is the ultimate goal for athletes [1]. During past decades, sport psychologists have developed diverse psychological training approaches, endeavoring to help athletes promote their competitive performance [2]. As a traditional stream of psychological training, cognitive behavioral therapies (CBTs) have been widely applied and shown effectiveness in the promotion of athletic performance among athletes [3]. CBT emphasizes the self-control of internal states through the training of psychological skills, with a view of improving motor performance [3,4]. However, an increasing group of evidence has shown that negative effects might be caused by controlling, eliminating, or suppressing athletes’ internal states [5]. Some studies have also indicated that goal-oriented behaviors might be replaced by excessive cognitive activities [5].
To address the limitations of traditional CBTs, mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) have raised increasing concerns, which have shown a great potential for promoting athletes’ competitive performances as an alternative of traditional psychological training approaches [6]. The term of mindfulness is derived from Eastern Zen [7], which is defined as non-judgmental, conscious, purposeful focus, understanding, and acceptance of the things around one in the present moment [8]. In contrast to the traditional behavioral therapies, mindfulness emphasized that individuals should be aware of and experience the internal and external thoughts and feelings without any judgments [9]. In the sports domain, mindfulness has been used to cultivate athletes’ abilities to accept and realize, to inspire athletes to effectively control their attention and improve their body perception ability [8,9,10]. Mindfulness underlines the process from perceiving to experiencing the constant changes of current things and one’s own emotions without the inhibition and control of undesirable responses in order to remove the emotional state of pervious worries, avoid performance failure under pressure, and adjust the mental state of athletes [11]. Mindfulness provides a potential not only to improve performance but also to decrease the risks of mental health problems [11].
With increasing understandings of the mechanisms of mindfulness with different outcomes, a series of mindfulness training approaches have been developed, such as Mindfulness-Acceptance-Commitment (MAC) training, Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) training, and Mindfulness-based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) [12,13,14,15]. Mindfulness has shown to be positively associated with a wide range of indicators among athletes, including greater athletic performance, better mindfulness, and related psychological components (e.g., acceptance, flow, and psychological flexibility) and lower risks of mental health problems (e.g., stress, anxiety, depression, and burnout) [9,11,12,13,14,15]. Two previous review and meta-analysis studies compiling evidence from diverse types of studies (e.g., RCT, case study, and observational) provided preliminary support for the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) on improving athletes’ sports performance [9,12,16]. Furthermore, previous review papers have also examined the effects of MBIs on the mindfulness-related psychological components (i.e., flow) and mental health among specific athlete samples (e.g., elite athletes and long-distance runners) [17,18,19]. However, none of previous review studies focused only on the evidence from RCTs (the rigorous study design), which may be due to the limited numbers of studies. In addition, the above review studies did not provide a comprehensive overview of the effectiveness of MBIs on a wide range of outcomes (i.e., performance, psychological components, and mental health) targeting all types of athletes (e.g., elite, collegiate, and retired).
Therefore, the present study aimed to systemically review and meta-analyze existing RCT evidence on the effects of MBIs in improving athletic performance, mindfulness, and mindfulness-related psychological components and mental health among athletes. It is expected that the research findings may contribute to future mindfulness research, interventions, and policymaking, with the aim of promoting sport performance and health among athletes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
The current systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Supplementary Materials); the review protocol has been prospectively registered on PROSPERO (CRD42022299940). Based on a predefined literature search strategy, the following five electronic databases were searched using Boolean logic’s multi-filed search format with no limit to the date range: Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, ProQuest, and ScienceDirect. In addition, the reference lists of relevant review papers were also checked. We combined three groups of keywords in the search: (1) mindfulness; (2) sport* OR athlete* OR player* OR athletic* OR exercise* OR training; and (3) performance OR achievement. The literature search was limited to human participants and the publication language was limited to English.
Following the Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, and Study design (PICOS) principles, the study selection criteria included:
Population: any types of athletes without limits to the demographics and sports levels (e.g., collegiate, recreational/amateur, professional, elite, retired, or handicapped) were included.
Intervention: any types of mindfulness-based interventions (MBI) without limits to the training types and components (e.g., traditional Mindfulness-Acceptance-Commitment intervention, Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction intervention, mindfulness-based yoga, or mindfulness-based cognitive therapy), frequency, and duration were included.
Comparison: any control conditions without mindfulness components (e.g., non-treatment control, waiting-list control, and active control using CBT) were eligible.
Outcome: objectively or subjectively measured athletic performance was the primary outcome and secondary outcomes included the mindfulness level, mindfulness-related psychological components (e.g., acceptance, self-compassion, psychological flexibility, flow, and ruminative response) and mental health indicators (e.g., anxiety, stress, and depression).
Study design: due to the large number of studies found in the literature search after protocol submission, we decided to limit our analysis to randomized controlled trials (RCTs) as this type of study provided the highest standard of evidence. All the RCT designs were included, while quasi-experimental, observational, and case studies were excluded.
In addition, book chapters, editorial letters, commentaries, conference proceedings, qualitative articles, and review articles were not eligible for inclusion.
All the initially searched articles were exported into the Mendeley to remove the duplications. Two investigators (W.Y. and F.J.J.) independently screened the titles and abstracts of all the remaining articles, where all clearly irrelevant articles were deleted. Afterwards, the full texts of all the identified articles were checked for eligibility by two investigators independently according to the aforementioned inclusion criteria. During the review process, any disagreements were addressed by consensus or by involving a third investigator (SML).
2.2. Data Extraction
A standardized form was used to extract data from the full texts of eligible articles by one investigator (WY). A second investigator (FJJ) checked the accuracy of the data extraction. All the information including authors, publication year, study design, participants, sample size, mean age, intervention duration, frequency, measures, and main findings were extracted to the Excel sheet for the following narrative synthesis and meta-analysis.
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
The study quality of included studies was evaluated using the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool in Review Manager software (RevMan, version 5.4, Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK). Seven aspects of biases, including random sequence generation (selection bias), concealment of allocation sequence (selection bias), blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias), blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective outcome reporting (reporting bias), and others, were assessed. The overall quality of the study was categorized as low risk (“low risk” in all aspects), unclear risk (at least one aspect with “some concerns of biases”), and high risk (at least one aspect with “high risk” or several aspects with “some concerns”). The study quality was evaluated by two investigators (W.Y. and F.J.J.) independently and any discrepancies were resolved by consensus or confirmation of a third investigator (SML).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The meta-analyses were implemented using RevMan 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK) if at least three studies presented the same exposure with adequate information for the effect size estimates [20,21,22]. The standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) was extracted from the pre- and post-intervention. For studies that reported other effect sizes (e.g., odds ratio and Cohen’s f2), the SMDs were calculated using a conversion spreadsheet [22,23]. Pooled effect sizes were estimated using a random effects model and were presented in forest plots. The heterogeneity was assessed using the I2, with I2 values of 25%, 50%, and 75% indicating low, medium, and high heterogeneity, respectively [24]. The publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots and Egger’s regression tests [25,26]. The subgroup analyses were implemented on study quality and demographics in case the number of included samples is no less than 10 [22,27,28]. The statistical significance level was set as p < 0.05 for effect sizes estimation and p < 0.10 for heterogeneity and publication bias assessments [27,28].
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
Figure 1 shows the PRISMA flow diagram. Initially, we retrieved 3072 records from the databases search and identified an additional five articles from other sources. After the duplicates were removed, 1897 articles were screened by two investigators at the title and abstract level and the full texts of 66 potential articles were assessed. Finally, we included 32 articles after removing ineligible articles.
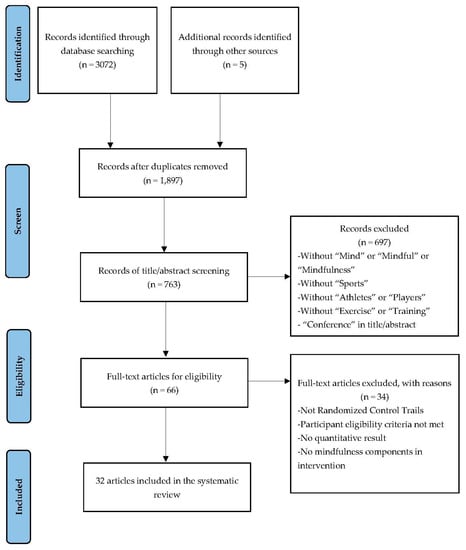
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow chart was used to identify of the include studies.
The feature coding results show that the studies included in this review came from a wide range of countries and territories: seven studies reported data from Iran; five from the USA; three each from Switzerland, Brazil, and Sweden; two each from Portugal, India, Australia, China, and Germany; and one from Norway.
The characteristics of studies included in this review are presented in Table 1. All these 32 studies were RCT studies. A total sample of 1788 athletes from a variety of sports were included, with an average age of 23.67 years. The athletes were involved in basketball, football, shooting, volleyball, wushu, cycling, track and field, and other sports. There was also a range of athletic experience from amateur to elite international athletes, with most studies including athletes competing at university level or higher. All the included trails were published after 2009, ranging from 2010 to 2022. The average intervention period was 6.3 weeks and the intervention training period was different in different programs. The intervention programs mainly include MAC, MBCT, MBSR, brief mindfulness training, and other mindfulness-based intervention types.

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies (n = 32).
For the risk of bias assessment, 71% of the included studies had a low risk of bias, while six studies (29%) were rated as a high risk of bias. Most studies showed a high risk of bias with respect to the allocation concealment (22%), blinding of participants and personnel (29%), incomplete outcome data (29%), and selective reporting (19%) (Figure 2).
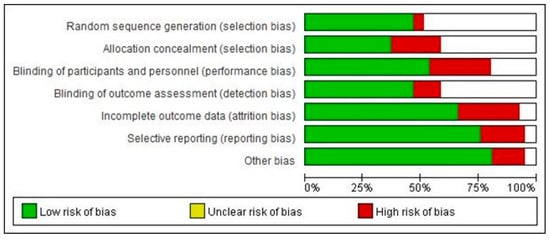
Figure 2.
Risk of bias assessment for the included studies.
3.2. Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Athletic Performance among Athletes
Consistent results were observed in the included studies, showing significant improvements in sport performance following MBIs. Specifically, a randomized controlled trial [29] examined the effects of a 15 min mindfulness intervention on basketball players’ athletic performance under pressure. The results showed that 15 min mindfulness intervention was effective in promoting participants’ first free-throw performance under a stressful setting compared to the control condition. In another study [30], the results found that participants in the intervention group (n = 18) receiving a 15 min mindfulness treatment had a small-to-moderate increase (Cohen’s d = 0.48) in free-throw performance compared with the control group (n = 18). Another RCT study [31] which examined the effectiveness of an eight-session MAC method on improving performance and sports competition anxiety in athletes found that MAC was effective in improving athletic performance compared to the control group. An American research group investigated the effectiveness of the MAC approach compared to traditional psychological skills training (PST) for mental health and sport performance [13]. The results indicated that the MAC group outperformed the PST group on the outcomes. There was also a significant within-group effect, where the MAC participants experienced significant increases in sport performance from pre-intervention to post-intervention (p = 0.04). In another study [32], compared with the PST group (n = 33), the MAC group (n = 36) reported higher levels of training performance (β = −0.10, 95% CI = [−0.14, −0.08] among elite athletes. In addition, a pilot study of MBSoccerP [39] explored the potential role of mindfulness and other psychological factors on flow and elite performance in soccer athletes. The results showed that after receiving eight 1.5–2 h weekly sessions of MBSoccerP, mindfulness mediated the peak performance of elite soccer players. In a Swiss study [33], researchers tested elite athletes (n = 133) from twenty-three different sports and the results indicated that the trait mindfulness was related to fewer performance worries and prevented the remaining worries from influencing athletes’ behavior, thereby helping them to perform better. As for the two studies of MMT, one of them estimated the effect of MMT on shooting performance in elite shooters (n = 96) and was assessed using a pre-and-post-test approach [34]. Compared to the control, the results of the experimental group showed that MMT intervention decreased pre-competition stress and enhanced shooting performance. Another one also examined the effect of MMT on 110 shooters [35]. The duration of intervention lasted for 4 weeks and the results indicated that MMT enhanced sports performance (p < 0.001) compared to the control group. In another study of fifty-two university athletes, the participants who received a six-week mindful sport performance enhancement (MSPE) intervention (90 min each week) significantly increased the self-rated sport performance compared to the control condition [36]. In a Portuguese study of twenty-eight elite soccer athletes [38], the results indicated that MBSoccerP was effective in enhancing elite soccer athletes’ performance compared to the control group. In addition, one study used the ACT method to intervene on 34 junior elite ice hockey players and found that ACT had significant effects on both objective performance outcomes (goals, assists, and taken shots) and blinded coach ratings of players performance in comparison with the control condition [57]. Another study with 24 collegiate students found that after the MBI, the participants reported greater sport enjoyment, less negative internal states of current sport performance, and greater improvements in satisfaction with sport performance compared to the PST group [58].
3.3. Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Mindfulness among Athletes
The use of MBIs has yielded significant improvements in mindfulness levels in most studies. For example, two studies of MBSoccerP found that mindfulness intervention was effective in improving the mindfulness level of Portuguese football players [38,39]. One study of BATL found that the MBI was effective in increasing mindfulness in athletes [48]. A Switzerland research group investigated the effectiveness of the MI approach and traditional psychological skills training (PST) in promoting functional athletic behavior in athletes [33]. Elite athletes from 23 different sports were selected (n = 133) and the results indicated that the MI approach could effectively improve the mindfulness level of athletes. In a study of 22 Iranian athletes, the intervention group who received a weekly, seven-session MAC intervention had significantly higher post-test mindfulness scores than pre-test scores. The study also found that increased mindfulness levels were associated with both reduced injury and enhanced performance [40]. In another study of 30 amateur basketball players in Iran, the result found that the experimental group (n =15) had significant higher mindfulness scores than the control group (p < 0.05) [51]. In addition, in a study of eight-week MBSR, researchers found that athletes’ pain levels decreased as their level of mindfulness increased, suggesting that mindfulness practice could be an effective adjunct to exercise therapy [53]. Additionally, applying mindfulness exercises in athletes’ daily training could not only increase their mindfulness levels but also decrease the risk of injury [54].
Three studies were included in the meta-analysis and a significant moderate effect size was yielded (d = 0.50, 95% CI = [0.17, 0.83], p = 0.003). There was a from low to moderate heterogeneity among the included studies (I² = 45%, p = 0.16). (Figure 3).
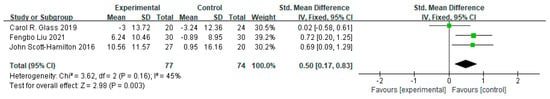
Figure 3.
Pooled effect sizes of mindfulness-based interventions on mindfulness among athletes.
3.4. Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Mindfulness-Related Psychological Components among Athletes
For mindfulness-related psychological components, in a Portuguese study, researchers found that MBSoccerP was effective in increasing the attributes of compassion, psychological flexibility, and in which terms that mediates dispositional flow on elite soccer players [39]. MSPE was evident to increase flow and satisfaction with life [38]. Mindfulness-based intervention might be associated with diminished psychological stress responses to competition [37]. In one study of twenty-eight elite soccer athletes, an 8-week MBSoccerP intervention found that the intervention was effective in enhancing participants’ self-compassion, psychological flexibility, and flow [39]. Thirty-two of them improved the performance-relevant psychological factors, especially concerning the handing of emotions and attention control [41]. In Australia, researchers found that MBI tailored to specific athletic pursuits was effective in facilitating flow experiences [42]. A study of 40 elite football players found that the mindfulness meditation sustained the levels of mindfulness skills and attentional control, whereas the control reported decreases in these outcomes during the period of four months [43]. In another MAC intervention, athletes reported that brief mindfulness training could significantly improve athletes flow and resilience and that resilience partly mediated the effect of brief mindfulness training flow [44]. Furthermore, one study showed that 6-week mindfulness training was effective in helping athletes achieve a flow state [47]. In China, one study indicated that reducing pre-sleep arousal and promoting the sleep quality of athletes after night training may be influenced by brief mindfulness induction [50]. Of the last two studies, one of them found that MAC improved dimensions of self-compassion and grit among female adult athletes [55]. Another one suggested that BATL improved both sustained and selective attention in young athletes and that more training in the same amount of time resulted in higher scores in the assessment [56].
Five studies were included in the meta-analysis, showing a large effect size of mindfulness interventions on the psychological components of athletes (d = 0.81, 95% CI = [0.53, 1.10], p < 0.001). There was high heterogeneity among included studies (I² = 77%, p = 0.001) (Figure 4).
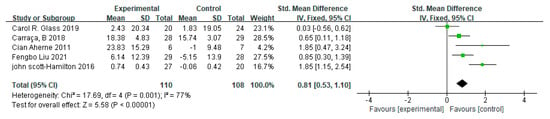
Figure 4.
Pooled effect sizes of mindfulness-based interventions on mindfulness-related psychological components among athletes.
3.5. Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Mental Health Indicators among Athletes
Eleven studies examined the effects of MBI on promoting athletes’ mental health. A study of NCAA women’s basketball in USA found that the MAC was an effective intervention for the mental health of female collegiate athletes [13]. A study of retired football players in Iran found that MBSR intervention has the potential to increase their psychological well-being [45]. A RCT study found that elite volleyball athletes who received the MBI significantly reduced their mental fatigue caused by competition compared to the control group [46]. A Norwegian study found that the mindfulness intervention was effective in improving athletes’ burnout [49]. In a USA study, 16 recreational basketball players showed significant reductions in anxiety after a brief mindfulness intervention [29]. Another study from USA found that a brief mindfulness intervention mitigated the effects of ego depletion in a basketball free-throw task [30]. In Iran, one study suggested that a MAC intervention was effective in decreasing athlete’s experiential avoidance and exercise anxiety [31]. Another study using the MAC showed that the MAC approach was a more effective intervention condition in reducing emotion regulation difficulties, as well as enhancing sport-relevant mindfulness skills and perceived athletic training performance in elite sport [32]. Two studies of MMT in India both found that the intervention was effective in decreasing pre-competition stress [34,35]. In addition, one study found that MSPE could significantly reduce worry [36]. In Brazil, after eight gun and pistol shooters underwent MBI intervention, the results showed that mindfulness was effective in reducing pre-competition stress [52].
Four studies were included in the meta-analysis (Figure 5), which showed that there was no significant effect of MBI on mental health among athletes (d = −0.03, 95% CI = [−0.35, 0.29], p = 0.85). There was high heterogeneity among the studies (I² = 89%, p < 0.001).
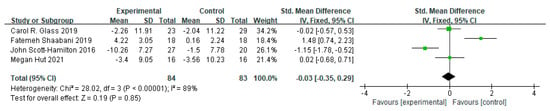
Figure 5.
Pooled effect sizes of mindfulness-based interventions on mental health indicators among athletes.
3.6. Publication Bias Assessment, Subgroup Analysis, and Sensitivity Tests
The results of the funnel plots and Egger’s regression tests showed that there was no evidence supporting a significant publication bias of included studies (all p > 0.1). For the subgroup analysis, as there was no adequate number of studies (i.e., n < 10) to be included, a further subgroup analysis for the potential moderators was not available. In addition, a sensitivity test was conducted by excluding the studies with a high risk of bias. The results were consistent with primary analyses that included all the studies.
4. Discussion
This is the first study that systematically reviewed and meta-analyzed the RCT evidence regarding the effectiveness of MBIs on athletic performance, mindfulness levels, mindfulness-related psychological components, and mental health outcomes among athletes. Thirty-two eligible studies were included in the narrative synthesis, of which nineteen were included in the quantitative analysis. Narratively, the MBIs were effective in promoting athletes’ sports performance. The results of the meta-analysis found that MBIs showed effectiveness on improving the mindfulness and mindfulness-based psychological components, yet no significant effects were found for mental health outcomes among athletes.
For athletic performance, from the narrative synthesis, we found that all the included studies indicated a significant improvement in the performance indicators after receiving the MBI. Our finding is consistent with the previous review papers supporting for the effectiveness of MBIs on athletes’ sport performance [9,12]. However, due to the limited evidence and considerable variety in the outcome measures, a quantitative synthesis is not available. More studies using an RCT design to examine the effects of using MBIs in athletes’ sports performance are needed in the future.
For mindfulness levels, in accordance with previous evidence [59,60], our study found that MBIs could significantly improve the athletes’ mindfulness levels. For the mindfulness-related psychological components (e.g., acceptance, flow, psychological flexibility, and ruminative response), we found a significant effect of MBIs on improving these indicators, which is in line with previous evidence among different types of athletes and general populations [10,61,62]. During the games, it is easy for athletes to experience negative emotions, such as nervousness and worries [63,64]. On game day, players may experience dissatisfaction with their performance, negative thinking, reality avoidance, and immersion in unpleasant emotions due to off-court circumstances, such as the unfavorable response of the crowd or losing points [65,66]. Mindfulness may play a crucial role in addressing these problems for athletes. Our research findings preliminarily supported the effects of MBIs on improving these mindfulness-related psychological components, implying that, in future practice, MBI could be applied in relevant sports domains to achieve specific training targets (e.g., enhancement of emotion control, prevention of performance failure under pressure, and improvement of flow and commitment).
For the mental health outcomes, our findings were inconsistent with the previous evidence that showed that MBIs were effective in improving mental health symptoms [19,62]. The potential reasons for the discrepancy may be multifaceted. For example, our review targeted all types of athletes, while previous studies focused on the elite athletes or general populations. Another reason MBIs may have not demonstrated improvements in mental health symptoms of athletes is because the athletes in the studies that were selected for our review are not clinical populations. It may have been that athletes’ mental health symptoms were already low; therefore, changes in mental health outcomes may have been inconsequential. In addition, we only included studies using an RCT design, while the previous evidence did not limit the study types for qualitative and quantitative syntheses. Although, in our narrative analysis, most studies supported a significant effect of MBI on athletes’ mental health indicators, the meta-analysis results did not yield a significant effect size. Considering the limited number of studies in the analysis as well as the high heterogeneity, we are not able to provide convincing evidence on the MBI intervention effects on improving the mental health outcomes among athletes, which to some extent emphasize the importance and requirements of more high quality RCTs on this domain.
Several limitations of this review should be noted. First, despite our efforts to implement a thorough literature search in the limited databases, we might omit some studies due to the settings of search strategies (e.g., only limited to English language). Moreover, due to the limited number of studies, we were not able to conduct a subgroup analysis to further identify the moderators (e.g., participants characteristics, MBI types, and outcome measures) that could explain the high degree of heterogeneity. The small number of studies could also result in the cautious interpretation of the research findings. In addition, we did not examine the potential mediators in the MBI programs due to the lack of relevant data such that a further understanding of the underlying mechanisms could not be identified.
Despite these limitations, our research findings add values to future research and interventions on MBIs among athletes. Our findings suggest that MBIs may be a potentially effective approach for improving athletes’ sport performance; however, more strict empirical studies (e.g., RCT and cluster-RCT) should be undertaken to further identify the effectiveness of MBIs and its dose–response effect with athletic performance. Furthermore, MBIs had moderate-to-large effect sizes on enhancing athletes’ mindfulness and mindfulness-related psychological components (e.g., flow, acceptance, and self-compassion), implying that future studies could use MBIs to achieve specific training targets (e.g., enhancement of emotional control and improvement of flow and commitment). In addition, our findings could not provide convincing quantitative evidence for the effectiveness of MBIs on athletes’ mental health outcomes due to the limited number of included studies. More RCT studies focusing on the mental health aspects among athletes are warranted in the future.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our systematic review and meta-analysis provided preliminary support for the effectiveness of MBIs in promoting athletic performance, mindfulness level, and mindfulness-related psychological components among athletes. The research findings also suggest that more high-quality studies using a rigorous empirical design (e.g., RCT) are warranted in the future, especially with respect to the mental health domains of athletes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijerph20032038/s1. Table S1: PRISMA 2020 Checklist.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and S.-M.L.; methodology, Y.W. and S.-M.L.; software, Y.W.; validation, J.F. and S.-M.L.; formal analysis, Y.W.; investigation, Y.W. and J.F.; resources, Y.W. and J.F.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, S.-M.L.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, S.-M.L.; project administration, S.-M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available by contacting the corresponding or first authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Su, N.; Si, G.; Zhang, C.Q. Mindfulness and acceptance-based training for Chinese athletes: The mindfulness-acceptance-insight-commitment (MAIC) program. J. Sport. Psychol. Action 2019, 10, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekańska, M.; Bondár, R.Z.; di Fronso, S.; Blecharz, J.; Bertollo, M. Integrating technology in psychological skills training for performance optimization in elite athletes: A systematic review. Psychol. Sport. Exerc. 2021, 57, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrer, D.; Röthlin, P.; Morgan, G. Mindfulness to enhance athletic performance: Theoretical considerations and possible impact mechanisms. Mindfulness 2012, 3, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, M.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Tod, D.; Dellal, A.; Hue, O.; Cheour, F.; Taylor, L.; Chamari, K. Do cognitive training strategies improve motor and positive psychological skills development in soccer players? Insights from a systematic review. J. Sport. Sci. 2016, 34, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, K.; Hansen, J.; Larsen, C.H. Mindfulness and Acceptance in Sport: How to Help Athletes Perform and Thrive under Pressure; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, R.A.; Krietemeyer, J. Overview of mindfulness-and acceptance-based treatment approaches. In Mindfulness-Based Treatment Approaches: Clinician’s Guide to Evidence Base and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kabat-Zinn, J. Mindfulness-based interventions in context: Past, present, and future. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 2003, 10, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, M.; Thienot, E.; Codron, R.; Fournier, J.F. Mindfulness and acceptance approaches in sport performance. J. Clin. Sport Psychol. 2009, 3, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappington, R.; Longshore, K. Systematically reviewing the efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions for enhanced athletic performance. J. Clin. Sport Psychol. 2015, 9, 232–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feruglio, S.; Matiz, A.; Grecucci, A.; Pascut, S.; Fabbro, F.; Crescentini, C. Differential effects of mindfulness meditation conditions on repetitive negative thinking and subjective time perspective: A randomized active-controlled study. Psychol. Health 2021, 36, 1275–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannsen, M.; Nissen, E.R.; Lundorff, M.; O’Toole, M.S. Mediators of acceptance and mindfulness-based therapies for anxiety and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2022, 94, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühlmayer, L.; Birrer, D.; Röthlin, P.; Faude, O.; Donath, L. Effects of mindfulness practice on performance-relevant parameters and performance outcomes in sports: A meta-analytical review. Sport. Med. 2017, 47, 2309–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Moore, Z.E.; Gardner, F.L.; Wolanin, A.T.; Pess, R.; Marks, D.R. An empirical examination comparing the mindfulness-acceptance-commitment approach and psychological skills training for the mental health and sport performance of female student athletes. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2018, 16, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, D.D.; Shang, B.R.; Zhang, C.Q.; Duan, Y.P.; Si, G.Y. Further examination of the psychometric properties of the Brief Self-Control Scale: Evidence from Chinese athletes and students. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2022, 20, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadkhosh, S.M.; Zandi, H.G.; Ghorbannejad, M. The effects of Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) on cognitive skills in young soccer players. Exerc. Qual. Life 2019, 11, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbally, L.; Wilkinson, M.; Fothergill, M.A. Effects of mindfulness practice on performance and factors related to performance in long-distance running: A systematic review. J. Clin. Sport Psychol. 2020, 14, 376–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noetel, M.; Ciarrochi, J.; Van Zanden, B.; Lonsdale, C. Mindfulness and acceptance approaches to sporting performance enhancement: A systematic review. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2019, 12, 139–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.B.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Qiu, F.B.; Li, A.Q.; Liu, S.Q. Effect of Mindfulness on Psychological Rehabilitation of Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chin. J. Rehabil. Theory Pract. 2020, 26, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Myall, K.; Montero-Marin, J.; Gorczynski, P.; Kajee, N.; Sheriff, R.S.; Bernard, R.; Harriss, E.; Kuyken, W. Effect of mindfulness-based programmes on elite athlete mental health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2023, 57, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Hamm, M.P.; Shulhan, J.; Vandermeer, B.; Hartling, L. Social media interventions for diet and exercise behaviours: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e003926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liang, W.; Rhodes, R.E.; Duan, Y.; Wang, X.; Shang, B.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Yang, M.; Supriya, R.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the preventive behaviors in response to the COVID-19 pandemic among children and adolescents. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Duan, Y.; Li, F.; Rhodes, R.E.; Wang, X.; Peiris, D.L.I.H.K.; Zhou, L.; Shang, B.; Yang, Y.; Baker, J.S.; et al. Psychosocial Determinants of Hand Hygiene, Facemask Wearing, and Physical Distancing During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Behav. Med. 2022, 56, 1174–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Shang, B.; Liang, W.; Du, G.; Yang, M.; Rhodes, R.E. Effects of eHealth-based multiple health behavior change interventions on physical activity, healthy diet, and weight in people with noncommunicable diseases: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e23786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, D.L.I.H.K.; Duan, Y.; Vandelanotte, C.; Liang, W.; Yang, M.; Baker, J.S. Effects of In-Classroom Physical Activity Breaks on Children’s Academic Performance, Cognition, Health Behaviours and Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Duan, Y.; Liang, W.; Peiris, D.L.I.H.K.; Baker, J.S. Effects of Face-to-Face and eHealth Blended Interventions on Physical Activity, Diet, and Weight-Related Outcomes among Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, M.; Garner, P.; Donegan, S. Interpretation of subgroup analyses in systematic reviews: A tutorial. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 7, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolch, N.J.; Arthur-Cameselle, J.N.; Keeler, L.A.; Suprak, D.N. The effects of a brief mindfulness intervention on basketball free-throw shooting performance under pressure. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2021, 33, 510–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, F.; Naderi, A.; Borella, E.; Calmeiro, L. Does a brief mindfulness intervention counteract the detrimental effects of ego depletion in basketball free throw under pressure? Sport Exerc. Perform. Psychol. 2020, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Saf, A.D.; Vosoughi, A.; Tebbenouri, G.; Zarnagh, H.G. Effectiveness of the mindfulness-acceptance-commitment-based approach on athletic performance and sports competition anxiety: A randomized clinical trial. Electron. Phys. 2018, 10, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefsson, T.; Ivarsson, A.; Gustafsson, H.; Stenling, A.; Lindwall, M.; Tornberg, R.; Böröy, J. Effects of mindfulness-acceptance-commitment (MAC) on sport-specific dispositional mindfulness, emotion regulation, and self-rated athletic performance in a multiple-sport population: An RCT study. Mindfulness 2019, 10, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röthlin, P.; Horvath, S.; Birrer, D. Mindfulness promotes the ability to deliver performance in highly demanding situations. Mindfulness 2016, 7, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Verma, S.K.; Khanna, G.L. The effect of mindfulness meditation on HPA-Axis in pre-competition stress in sports performance of elite shooters. Natl. J. Integr. Res. Med. 2011, 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kachanathu, S.J.; Verma, S.K.; Khanna, G.L. Effect of music therapy on heart rate variability: A reliable marker to pre-competition stress in sports performance. J. Med. Sciences. 2013, 13, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.R.; Spears, C.A.; Perskaudas, R.; Kaufman, K.A. Mindful sport performance enhancement: Randomized controlled trial of a mental training program with collegiate athletes. J. Clin. Sport Psychol. 2019, 13, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrsafar, A.H.; Strahler, J.; Gazerani, P.; Khabiri, M.; Sánchez, J.C.J.; Moosakhani, A.; Zadeh, A.M. The effects of mindfulness training on competition-induced anxiety and salivary stress markers in elite Wushu athletes: A pilot study. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 210, 112655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrança, B.; Serpa, S.; Rosado, A.; Guerrero, J.P. A pilot study of a mindfulness-based program (MBSoccerP): The potential role of mindfulness, self-compassion and psychological flexibility on flow and elite performance in soccer athletes. Rev. Iberoam. Psicol. Ejerc. Deporte 2019, 14, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Carraça, B.; Serpa, S.; Guerrero, J.P.; Rosado, A. Enhance Sport performance of elite athletes: The mindfulness-based interventions. Cuad. Psicol. Del Deporte 2018, 18, 79–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mozafari Zadeh, M.; Heidari, F.; Khabiri, M. Effectiveness of Mindfulness and Acceptance Training on Reducing Sport Injury Anxiety and Improving Performance of Soccer Players. Sci. J. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 8, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Röthlin, P.; Horvath, S.; Trösch, S.; Birrer, D. Differential and shared effects of psychological skills training and mindfulness training on performance-relevant psychological factors in sport: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Psychol. 2020, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott-Hamilton, J.; Schutte, N.S.; Brown, R.F. Effects of a mindfulness intervention on sports-anxiety, pessimism, and flow in competitive cyclists. Appl. Psychol. Health Well-Being 2016, 8, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltar, Y.C.; Filgueiras, A. The effects of mindfulness meditation on attentional control during off-season among football players. SAGE Open 2018, 8, 2158244018781896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N. Examining the effects of brief mindfulness training on athletes’ flow: The mediating role of resilience. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6633658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, E.; Gerber, M.; Masrour, F.F.; Vaezmosavi, M.; Puehse, U.; Brand, S. Implementation of a mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) program to reduce stress, anxiety, and depression and to improve psychological well-being among retired Iranian football players. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2020, 47, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, D.R.; Bevilacqua, G.G.; Pereira, F.S.; Andrade, A. Effect of mindfulness training on fatigue and recovery in elite volleyball athletes: A randomized controlled follow-up study. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2021, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aherne, C.; Moran, A.P.; Lonsdale, C. The effect of mindfulness training on athletes’ flow: An initial investigation. Sport Psychol. 2011, 25, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekauc, D.; Kittler, C.; Schlagheck, M. Effectiveness of a mindfulness-based intervention for athletes. Psychology 2016, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, F.; Federici, R.A.; Abrahamsen, F. Examining possible Relationships between mindfulness, stress, school-and sport performances and athlete burnout. Int. J. Coach. Sci. 2015, 9, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Kee, Y.H.; Lam, L.S. Effect of brief mindfulness induction on university athletes’ sleep quality following night training. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajilchi, B.; Amini, H.R.; Ardakani, Z.P.; Zadeh, M.M.; Kisely, S. Applying mindfulness training to enhance the mental toughness and emotional intelligence of amateur basketball players. Australas. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, H.; Ayatizadeh, F.; Axt, G.; Machado, S. Comparison between mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral psychological interventions on the reduction of pre-competitive stress of elite shooters: A follow-up of 2 months. Cuad. Psicol. Deporte 2021, 21, 192–203. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, S.; Naderi, A.; Mirali, S.; Calmeiro, L.; Brewer, B.W. Adding mindfulness practice to exercise therapy for female recreational runners with patellofemoral pain: A randomized controlled trial. J. Athl. Train. 2021, 56, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivarsson, A.; Johnson, U.; Andersen, M.B.; Fallby, J.; Altemyr, M. It pays to pay attention: A mindfulness-based program for injury prevention with soccer players. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2015, 27, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebi, M.; Sadeghi-Bahmani, D.; Zarei, S.; Gharayagh Zandi, H.; Brand, S. Examining the Effects of Mindfulness–Acceptance–Commitment Training on Self-Compassion and Grit among Elite Female Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittler, C.; Arnold, M.; Jekauc, D. Effects of a Mindfulness-Based Intervention on Sustained and Selective Attention in Young Top-Level Athletes in a School Training Setting: A Randomized Control Trial Study. Sport Psychol. 2022, 1, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, O.; Garvin, P.; Nilsson, L.; Tornerefelt, V.; Andersson, G.; Kristenson, M.; Jonasson, L. Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction for Coronary Artery Disease Patients: Potential Improvements in Mastery and Depressive Symptoms. J. Clin. Psychol. Med. Settings 2022, 29, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hut, M.; Minkler, T.O.; Glass, C.R.; Weppner, C.H.; Thomas, H.M.; Flannery, C.B. A randomized controlled study of mindful sport performance enhancement and psychological skills training with collegiate track and field athletes. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, F.; Li, C.; Chow, D.H.K. Acute effects of brief mindfulness intervention coupled with carbohydrate ingestion to re-energize soccer players: A randomized crossover trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.A.; Haraldsdottir, K.; Watson, D. Mindfulness in Athletes. Curr. Sport. Med. Rep. 2021, 20, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.; Luo, L.; Hu, M. The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for ruminative thinking: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 321, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Strauss, C.; Bond, R.; Cavanagh, K. How do mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction improve mental health and wellbeing? A systematic review and meta-analysis of mediation studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2015, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.R.; Knight, C.J.; Mellalieu, S.D. Emotional experiences in youth tennis. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2017, 29, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottyn, J.; De Clercq, D.; Pannier, J.L.; Crombez, G.; Lenoir, M. The measurement of competitive anxiety during balance beam performance in gymnasts. J. Sport. Sci. 2006, 24, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivarsson, A.; Stambulova, N.; Johnson, U. Injury as a career transition: Experiences of a Swedish elite handball player. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2018, 16, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasker, S.M. Evaluation of the Mindfulness-Acceptance-Commitment (MAC) Approach for Enhancing Athletic Performance. Ph.D. Dissertation, Indiana University of Pennsylvania, Indiana, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).