Therapeutic Effects of Metaverse Rehabilitation for Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ethical Assumptions
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.3.1. GMFM 66
2.3.2. Cardiopulmonary Function
2.3.3. FIM
2.3.4. Pediatric QOL
2.3.5. Perceived Risk of COVID-19 Transmission
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Patients (N = 26)
3.2. Clinical Outcome Measurements
3.2.1. GMFM
3.2.2. Cardiopulmonary Function
3.2.3. FIM and QOL
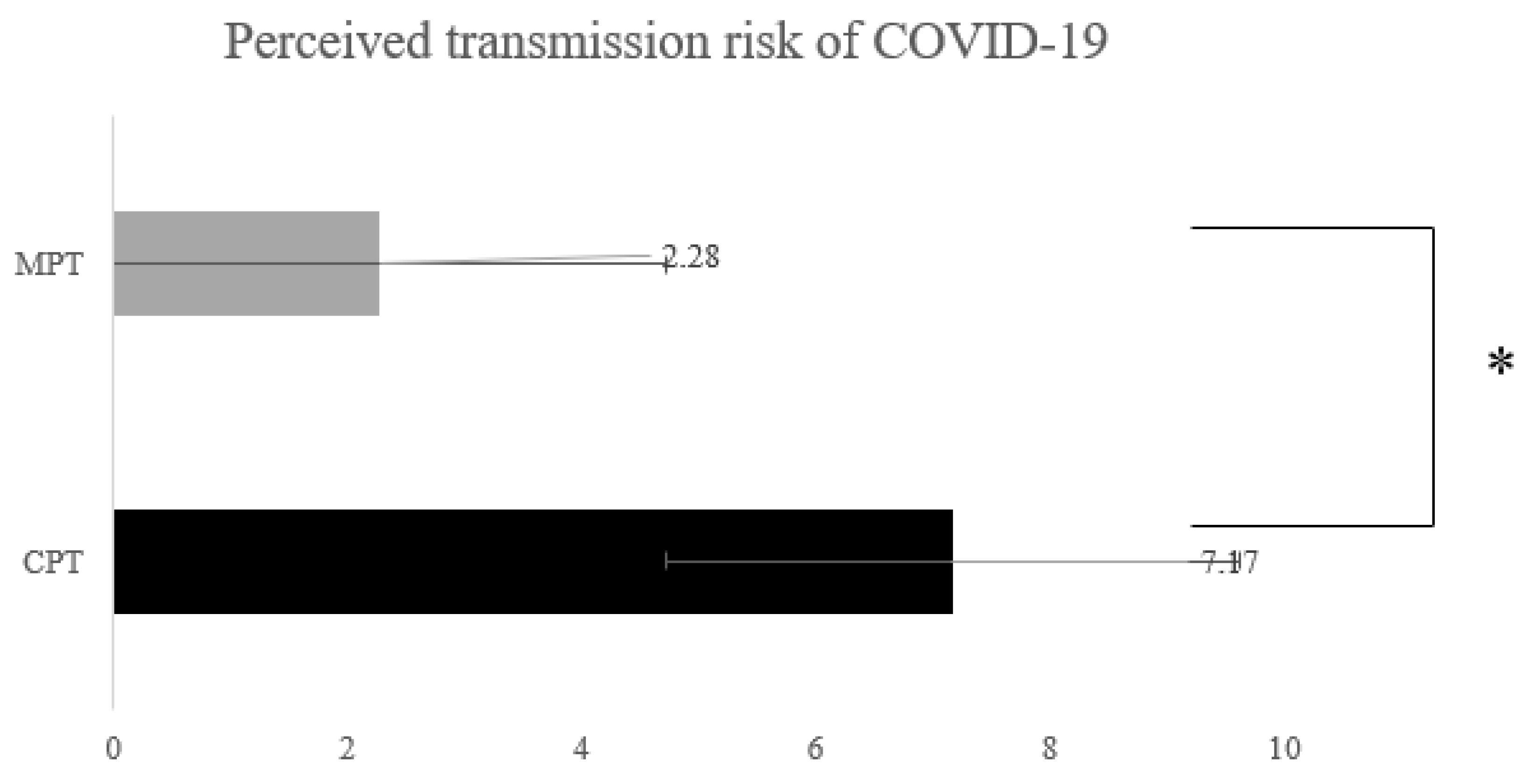
3.3. Perceived Risk of COVID-19 Transmission
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blair, E.; Cans, C. The definition of cerebral palsy. In Cerebral Palsy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Eggink, H.; Kremer, D.; Brouwer, O.F.; Contarino, M.F.; van Egmond, M.E.; Elema, A.; Folmer, K.; van Hoorn, J.F.; van de Pol, L.A.; Roelfsema, V. Spasticity, dyskinesia and ataxia in cerebral palsy: Are we sure we can differentiate them? Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2017, 21, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, S.; Decoulon, G.; Bonnefoy-Mazure, A. Gait analysis in children with cerebral palsy. EFORT Open Rev. 2016, 1, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.; Sakzewski, L.; Whittingham, K.; Wotherspoon, J.; Chatfield, M.D.; Ware, R.S.; Boyd, R.N. Development of social functioning in children with cerebral palsy: A longitudinal study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, S.; Ziviani, J.; Boyd, R. A systematic review of activities of daily living measures for children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, D.; Rabatin, A.E.; Shea, J.E.; Parmeter, B.; Shore, B.J.; Stracciolini, A. Attitudes and Behaviors of Physical Activity in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Findings from PLAY Questionnaire. Children 2022, 9, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.B.; Grether, J.K. Causes of cerebral palsy. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 1999, 11, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanon, M.A.; Pacheco, R.L.; Latorraca, C.d.O.C.; Martimbianco, A.L.C.; Pachito, D.V.; Riera, R. Neurodevelopmental treatment (Bobath) for children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 34, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-W.; Zhang, C.; Fan, X.; Meng, F.-P.; Xu, Z.; Xia, P.; Cao, W.-J.; Yang, T.; Dai, X.-P.; Wang, S.-Y. Immunological and inflammatory profiles in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, L.O.; Barreto, R.P.G.; Ferreira, C.H.J. Digital physical therapy in the COVID-19 pandemic. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2020, 24, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crebbin, K.; Grisbrook, T.; Elliott, C.; Thornton, A. The Use of Serious Gaming to Improve Sensorimotor Function and Motivation in People with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Games Health J. 2022, 11. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.J.; Lee, B.-H. The effects of flipped learning on learning motivation and attitudes in a class of college physical therapy students. J. Probl. Based Learn. 2018, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarzynski, T.; Miles, O.; Cowie, A.; Ridge, D. Acceptability of artificial intelligence (AI)-led chatbot services in healthcare: A mixed-methods study. Digit. Health 2019, 5, 2055207619871808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Velde, A.; Morgan, C. Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM-66 & GMFM-88) User’s Manual, Book Review. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2022, 34, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Su-Juan, W.; Yuan-Gui, L.; Hong, Y.; Xiu-Juan, X.; Xiao-Mei, S. Reliability and validity of the GMFM-66 in 0-to 3-year-old children with cerebral palsy. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 85, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G.A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, C. Rating of perceived exertion (RPE). J. Physiother. 2012, 58, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linacre, J.M.; Heinemann, A.W.; Wright, B.D.; Granger, C.V.; Hamilton, B.B. The structure and stability of the Functional Independence Measure. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1994, 75, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, D.; Stewart, G.; Baldry, J.; Johnson, J.; Rossiter, D.; Petruckevitch, A.; Thompson, A. The Functional Independence Measure: A comparative validity and reliability study. Disabil. Rehabil. 1995, 17, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Seid, M.; Rode, C.A. The PedsQL™: Measurement model for the pediatric quality of life inventory. Med. Care 1999, 37, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Burwinkle, T.M.; Seid, M.; Skarr, D. The PedsQL™* 4.0 as a pediatric population health measure: Feasibility, reliability, and validity. Ambul. Pediatr. 2003, 3, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.D.; Zhou, C.; Stanford, S.; Haaland, W.; Varni, J.W.; Mangione-Smith, R.M. Validity and responsiveness of the pediatric quality of life inventory (PedsQL) 4.0 generic core scales in the pediatric inpatient setting. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.H.; Park, C.; You, J.H. Minimal Contact Robotic Stroke Rehabilitation on Risk of COVID-19, Work Efficiency and Sensorimotor Function. Healthcare 2022, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezas-López, M.; Bernabéu-Brotóns, E. The effects of Bobath therapy on children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Int. J. Ther. Rehabil. 2022, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbada, C.E.; Olaoye, M.I.; Dada, O.O.; Ayanniyi, O.; Johnson, O.E.; Odole, A.C.; Ishaya, G.P.; Omole, O.J.; Makinde, M.O. Comparative efficacy of clinic-based and telerehabilitation application of Mckenzie therapy in chronic low-back pain. Int. J. Telerehabilitation 2019, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, D.L. Home Program Instruction Sheets for Infants and Young Children; Therapy Skill Builders: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Cao, S. Real-time human motion behavior detection via CNN using mmWave radar. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2018, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Peng, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, K.; Wu, X.; Fan, W.; Li, F.; Chen, M. Studies on different CNN algorithms for face skin disease classification based on clinical images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 66505–66511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidziński, Ł.; Yang, B.; Hicks, J.L.; Rajagopal, A.; Delp, S.L.; Schwartz, M.H. Deep neural networks enable quantitative movement analysis using single-camera videos. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.; An, Y.; Min, S.; Park, C. Comparative Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence-Based Interactive Home Exercise Applications in Adolescents with Obesity. Sensors 2022, 22, 7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoni, J.L.B.; Pavao, S.L.; dos Santos Silva, F.P.; Rocha, N.A.C.F. Effects of virtual reality in body oscillation and motor performance of children with cerebral palsy: A preliminary randomized controlled clinical trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2019, 35, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.G.; Chang, H.J.; Jo, E.S.; Kim, D.H. The Effect of a Horse-Riding Simulator with Virtual Reality on Gross Motor Function and Body Composition of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Preliminary Study. Sensors 2022, 22, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Oliva, L.; Ortiz-Gutiérrez, R.M.; Cano-de la Cuerda, R.; Piédrola, R.M.; Alguacil-Diego, I.M.; Sánchez-Camarero, C.; Martínez Culebras Mdel, C. Kinect Xbox 360 as a therapeutic modality for children with cerebral palsy in a school environment: A preliminary study. NeuroRehabilitation 2013, 33, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.Y.; Sung, W.H.; Chang, H.A.; Wang, R.Y. Effect of a virtual reality-enhanced exercise protocol after coronary artery bypass grafting. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacau, L.d.A.P.; Oliveira, G.U.; Maynard, L.G.; Araújo Filho, A.A.d.; Silva, W.M.d., Jr.; Cerqueria Neto, M.L.; Antoniolli, A.R.; Santana-Filho, V.J. The use of the virtual reality as intervention tool in the postoperative of cardiac surgery. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 28, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-F.; Tsai, P.-Y.; Sung, W.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chuang, T.-Y. The comparisons of heart rate variability and perceived exertion during simulated cycling with various viewing devices. Presence 2008, 17, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrady, A.; McGinnis, R.; Badenhop, D.; Bentle, M.; Rajput, M. Effects of depression and anxiety on adherence to cardiac rehabilitation. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2009, 29, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Kikuchi, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Osuda, K.; Iwashiro, Y.; Arihara, A.; Okawa, A. Virtual Reality Simulation for Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting With Aortic No-Touch Total Arterial Grafting Technique. Innovations 2022, 17, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CPT a Group (n = 13) | MPT b Group (n = 13) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 6/7 | 6/7 | 1.00 |
| Age (years) | 16.15 ± 3.16 | 17.43 ± 2.88 | 0.36 |
| Body height (cm) | 133.17 ± 21.41 | 140.21 ± 18.11 | 0.14 |
| Body mass (kg) | 38.44 ± 16.08 | 42.56 ± 20.37 | 0.10 |
| c CP classification | |||
| Spastic/ataxic | 10/3 | 11/2 | 0.64 |
| CPT b | MPT c | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre Test | Post Test | Pre Test | Post Test | Time Effect | Between Groups | Time × Group Interaction | |
| GMFM a | 68.13 ± 18.27 | 72.66 ± 20.17 | 70.16 ± 11.37 | 75.01 ± 18.16 | 0.001 * | 0.21 | 0.48 |
| CPT c | MPT d | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre Test | Post Test | Pre Test | Post Test | Time Effect | Between Groups | Time × Group Interaction | |
| HR a | 78.16 ± 4.88 | 79.14 ± 3.17 | 74.84 ± 5.12 | 81.44 ± 4.11 | 0.03 * | 0.17 | 0.001 * |
| BRPE b | 11.14 ±0.88 | 10.88 ±1.43 | 12.26 ±1.10 | 10.13 ±0.75 | 0.001 * | 0.03 * | 0.02 * |
| CPT c | MPT d | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre Test | Post Test | Pre Test | Post Test | Time Effect | Between Groups | Time × Group Interaction | |
| FIM a | 17.88 ± 8.33 | 18.21 ± 6.42 | 16.79 ± 9.77 | 18.33 ± 11.21 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.18 |
| QOL b | 56.21 ± 17.44 | 53.19 ± 14.66 | 54.88 ± 16.71 | 52.67 ± 15.85 | 0.09 | 0.51 | 0.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, I.; An, Y.; Min, S.; Park, C. Therapeutic Effects of Metaverse Rehabilitation for Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021578
Moon I, An Y, Min S, Park C. Therapeutic Effects of Metaverse Rehabilitation for Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021578
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Ilyoung, Yeongsang An, Seunghwa Min, and Chanhee Park. 2023. "Therapeutic Effects of Metaverse Rehabilitation for Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021578
APA StyleMoon, I., An, Y., Min, S., & Park, C. (2023). Therapeutic Effects of Metaverse Rehabilitation for Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021578






