Research on the Effect of Manufacturing Agglomeration on Green Use Efficiency of Industrial Land
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Empirical Methodology
2.2. Variable Setting
- (1)
- Explained variable: green use efficiency of industrial land
- (2)
- Core explanatory variable: manufacturing agglomeration
- (3)
- Control variables
2.3. Data Sources
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of MA and GUEIL
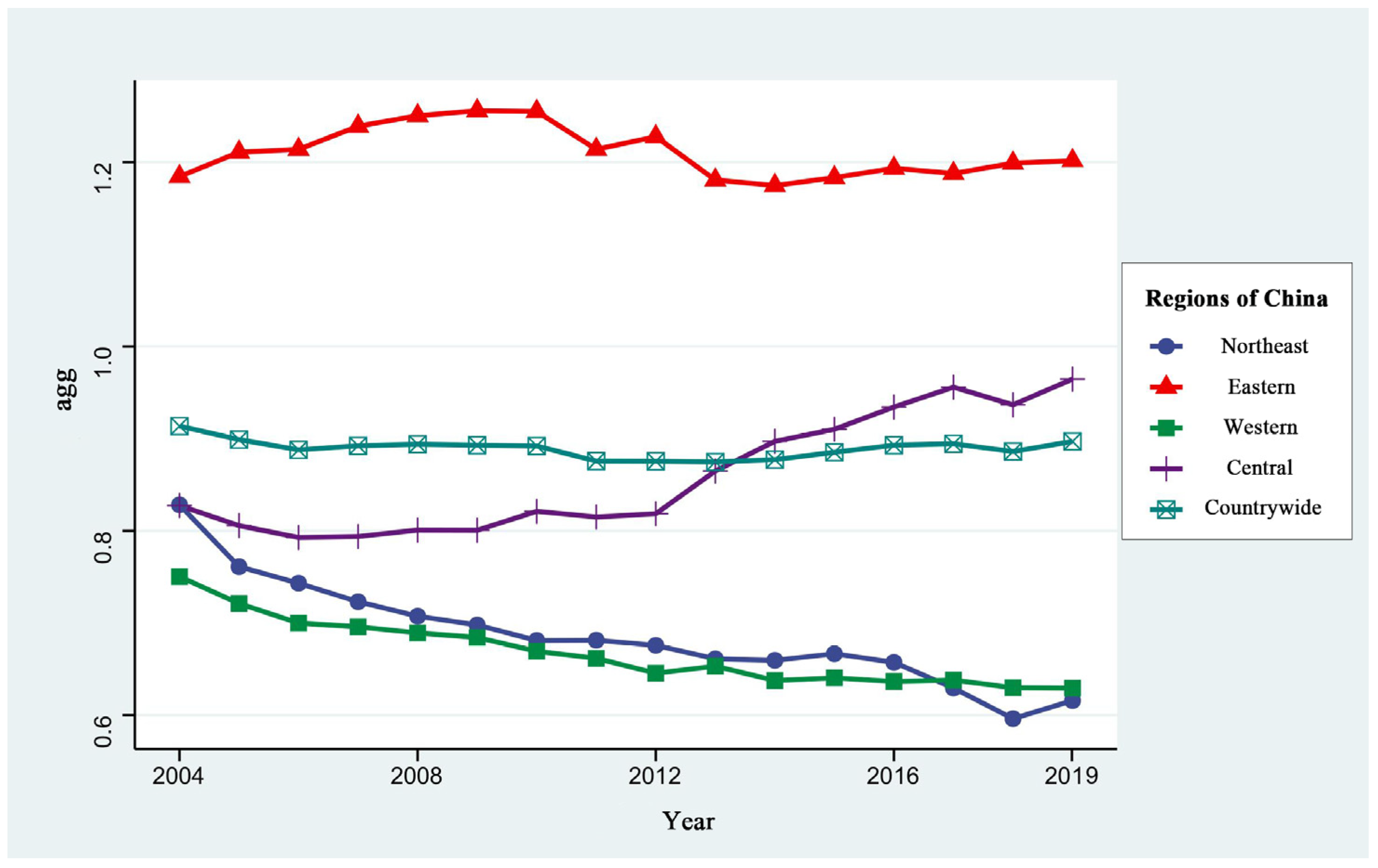
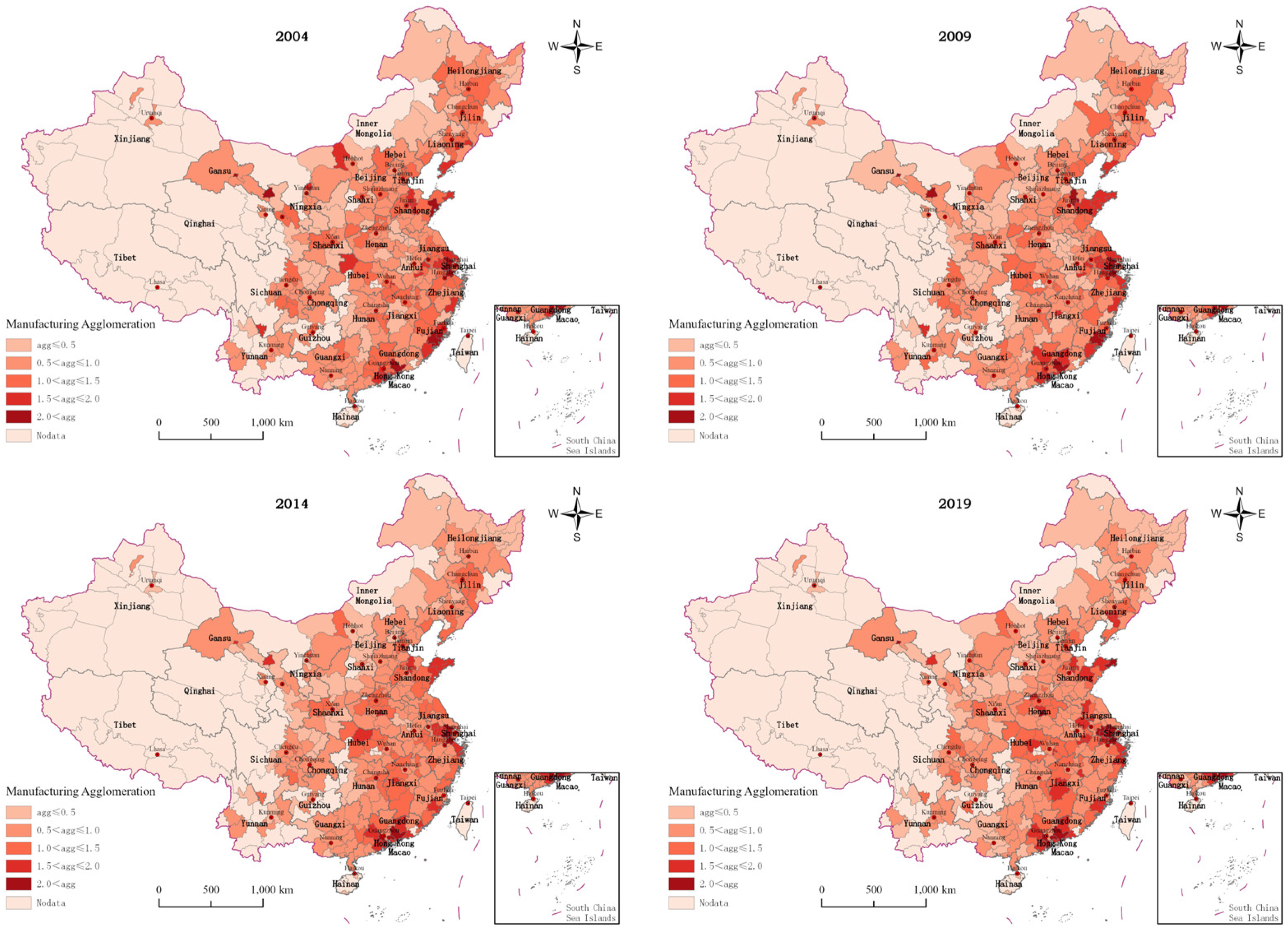
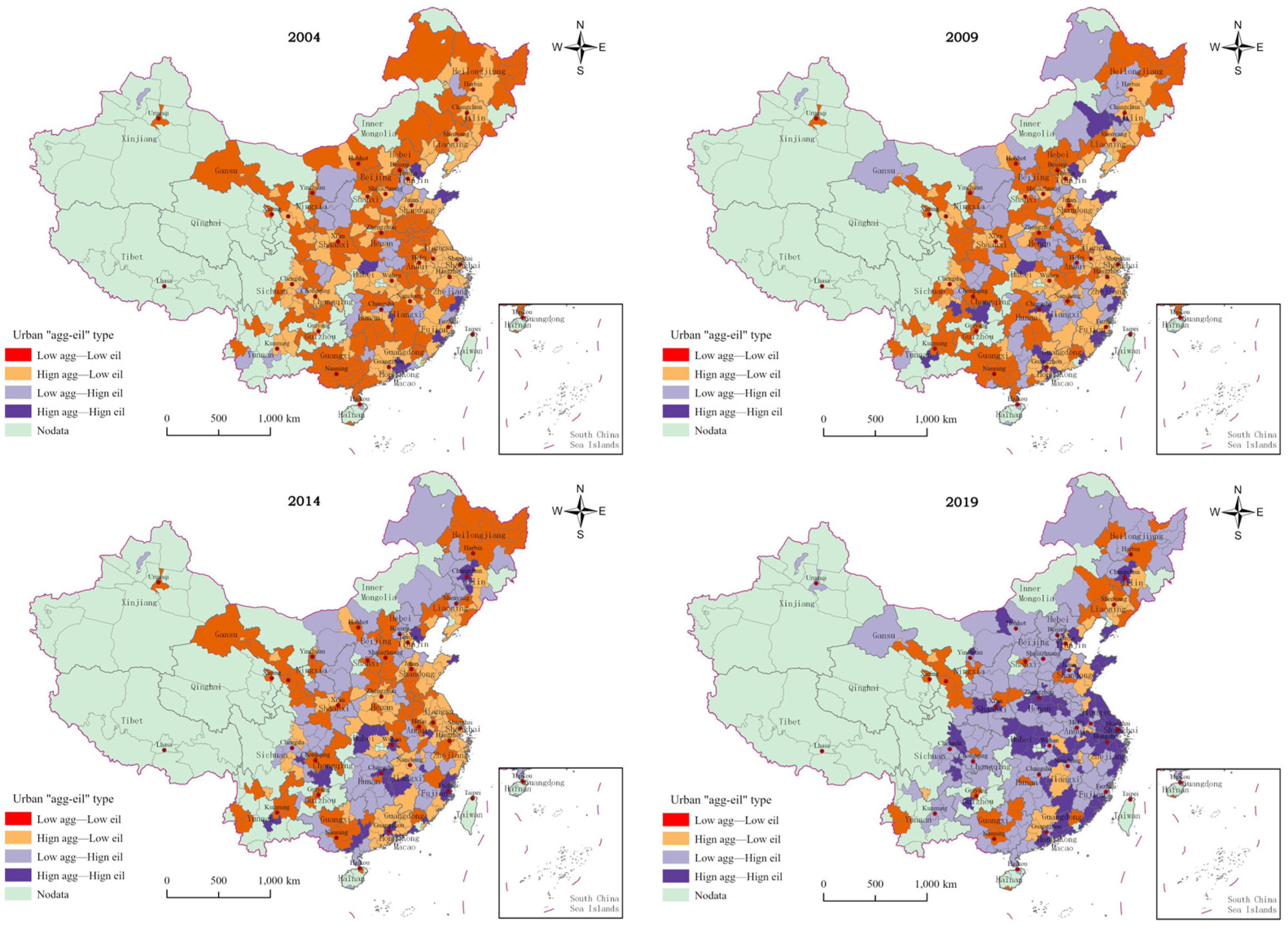
3.1.1. Measurement Results and Spatio-Temporal Analysis of MA
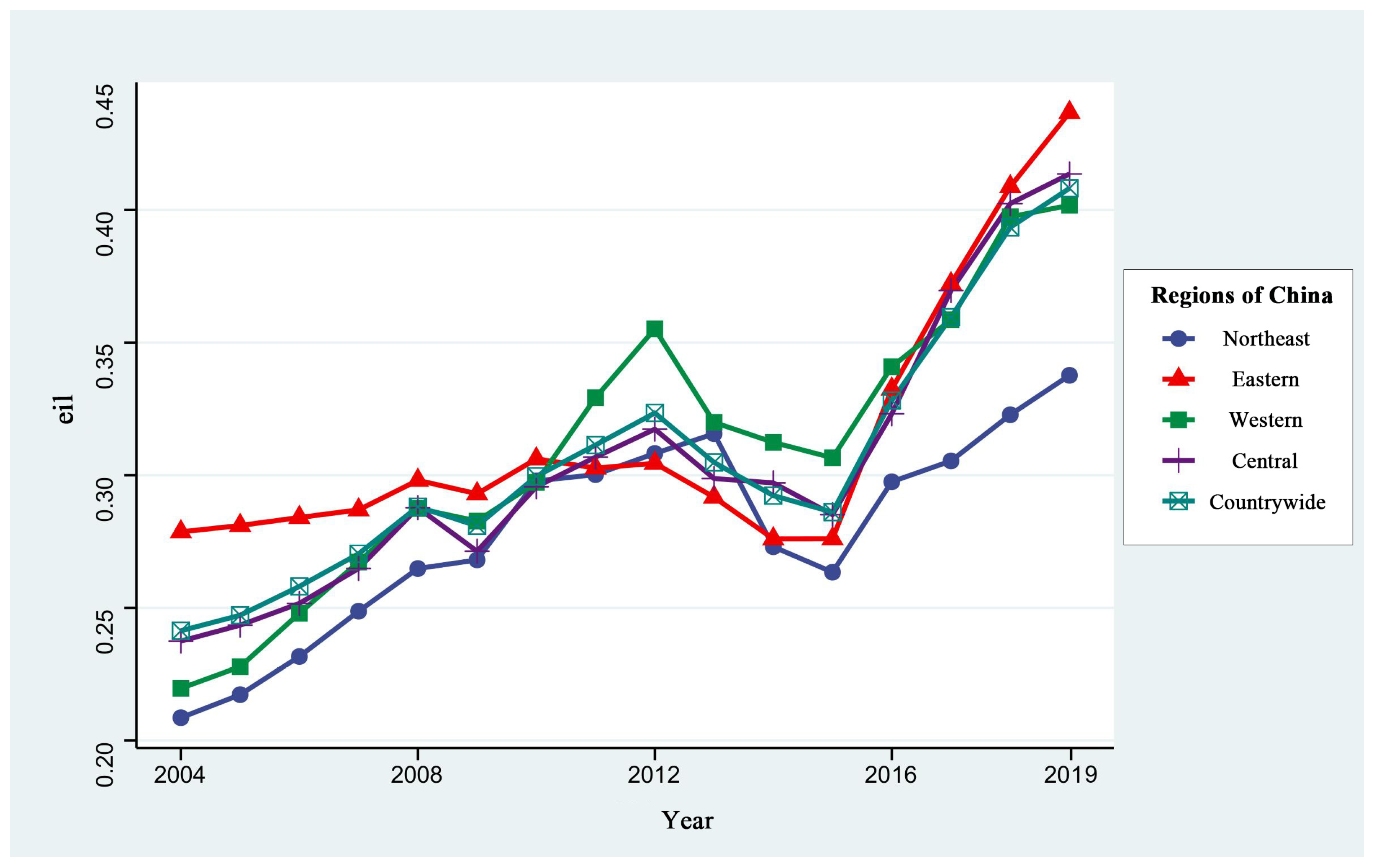
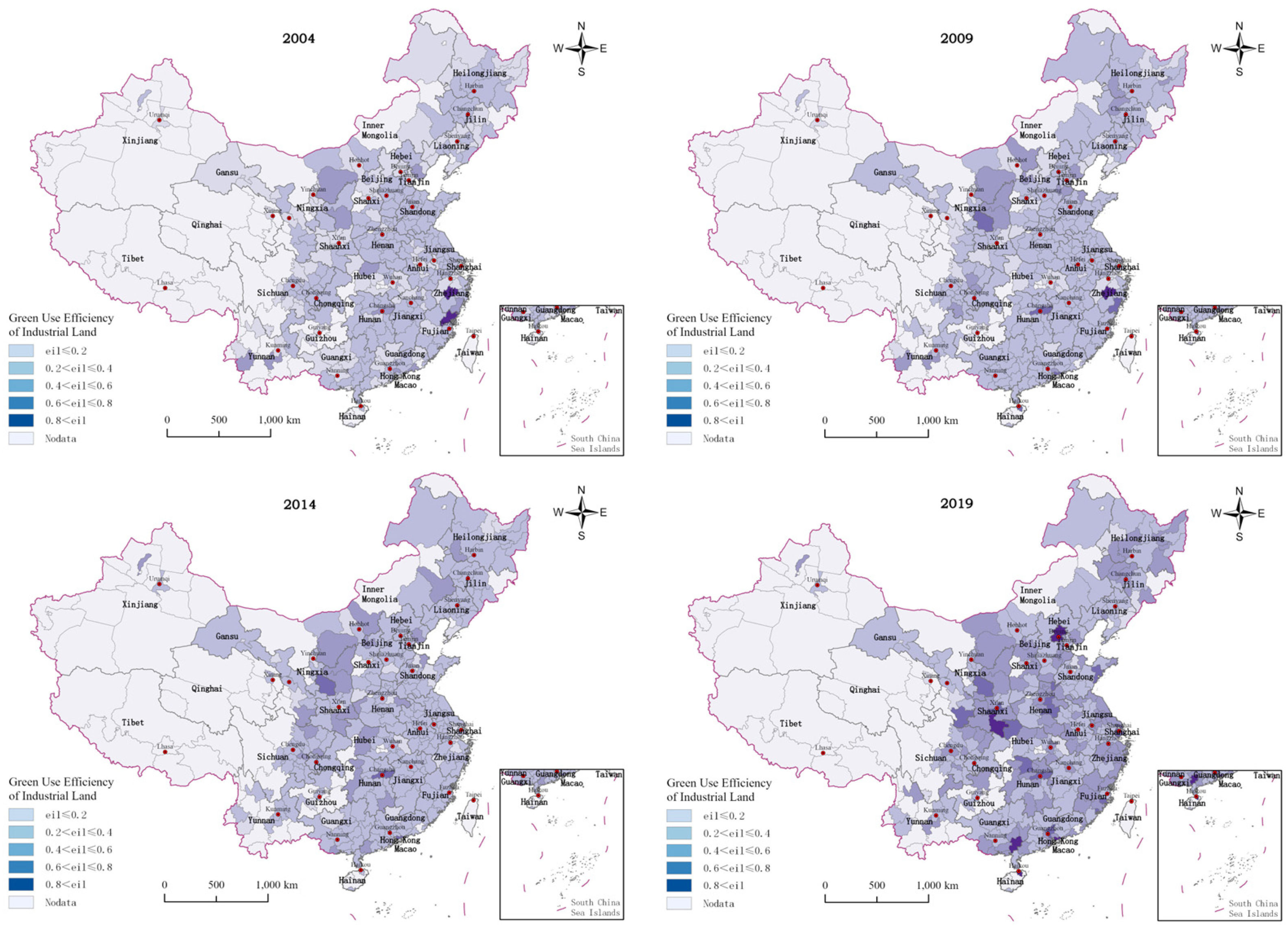
3.1.2. Measurement Results and Spatio-Temporal Analysis of GUEIL
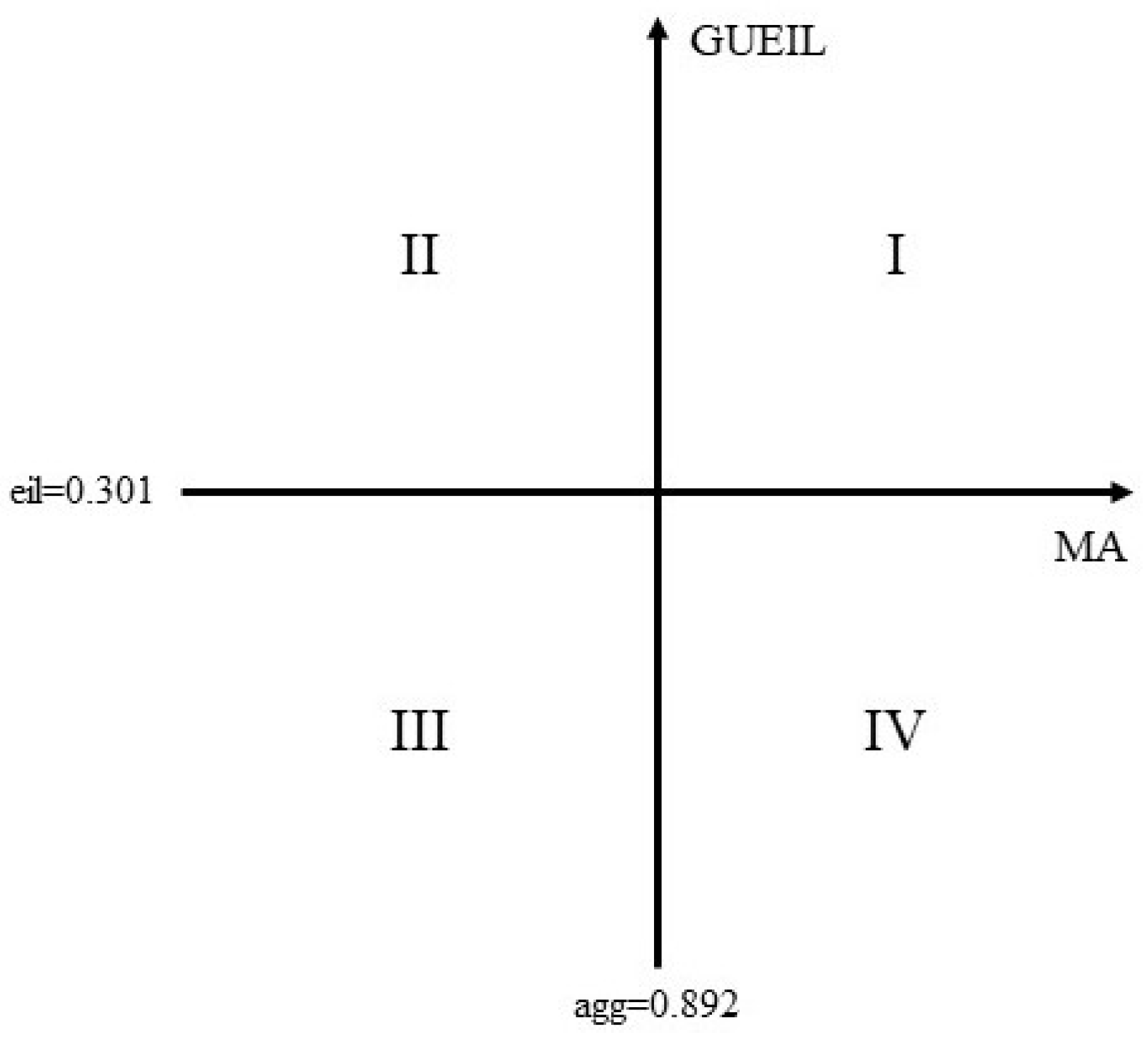
3.1.3. Comprehensive Analysis of MA and GUEIL
3.2. The Effect of MA on GUEIL
3.2.1. Model Testing and Identification
3.2.2. Analysis of National-Scale Regression Results
3.2.3. Regional Heterogeneity Analysis
3.2.4. Robustness Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, P.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal responses between urban regeneration and policy change of stock industrial land: A case study of Tianjin downtown area. City Plan. Rev. 2020, 44, 43–52+105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Glendinning, A.; Xu, Y. Land-Use Changes and Land Policies Evolution in China’s Urbanization Processes. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Interjurisdictional Competition for FDI: The Case of China’s “Development Zone Fever”. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2011, 41, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertaud, A. Government intervention and urban land markets: The case of China. J. Archit. Plan. Res. 2012, 29, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Tang, D.; Da, D.; Chen, W.; Kong, L.; Boamah, V. Research on China’s Manufacturing Industry Moving towards the Middle and High-End of the GVC Driven by Digital Economy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, G. Quantifying Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Urban Expansion in Beijing during 1985–2013 with Rural-Urban Development Transformation. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Ma, E. Does Urban Industrial Agglomeration Lead to the Improvement of Land Use Efficiency in China? An Empirical Study from a Spatial Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Li, J. Regional Difference Decomposition and Policy Implications of China’s Urban Land Use Efficiency under the Environmental Restriction. Habitat Int. 2018, 77, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S. Agglomeration, Productivity, and Spatial Spillovers across Chinese Cities. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2009, 45, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Gong, J.; Zhao, X. FDI and Environmental Regulation: Pollution Haven or a Race to the Top? J. Regul. Econ. 2011, 41, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Tang, X.; Xie, R.; Han, F. The Effect of Manufacturing Agglomerations on Smog Pollution. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2020, 54, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z. The Spatial Correlation and Interaction between Manufacturing Agglomeration and Environmental Pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Peng, H. Can Industrial Agglomeration Achieve the Emission-Reduction Effect? Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 75, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Does Industrial Agglomeration Facilitate Environmental Performance: New Evidence from Urban China? J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Cen, Y. How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Econ. 2020, 92, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Managi, S. Industrial agglomeration effect for energy efficiency in Japanese production plants. Energy Policy 2021, 156, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, C. Investigating the mechanisms among industrial agglomeration, environmental pollution and sustainable industrial efficiency: A case study in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 12467–12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Chen, Q.; Lu, F.; Wang, W.; Yao, G.; Yu, J. Spatial-Temporal Disparities and Influencing Factors of Total-Factor Green Use Efficiency of Industrial Land in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Hu, B.; Kuang, B.; Zhou, M. Regional Differences and Dynamic Evolution of Urban Land Green Use Efficiency within the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. Dynamic DEA: A Slacks-Based Measure Approach. Omega 2010, 38, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zeng, G.; Dai, S.; Wang, F. Research on the effects of different policy tools on China’s emissions reduction innovation: Based on the panel data of 285 prefectural-level municipalities. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 115–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Lindley, S.; Meng, F.; Niu, M. Change, mechanism, and response of pollutant discharge pattern resulting from manufacturing industrial transfer: A case study of the Pan-Yangtze River Delta, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, H. High Energy-Consuming Industrial Transfers and Environmental Pollution in China: A Perspective Based on Environmental Regulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ning, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, E.-n.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Industrial Land Green Efficiency in China: Evidence from Prefecture-Level Cities. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46 (Suppl. S1), 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Cao, H. Environmental Decentralization, Heterogeneous Environmental Regulation, and Green Total Factor Productivity—Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Wei, Y.D. How Does Industrial Agglomeration Affect Urban Land Use Efficiency? A Spatial Analysis of Chinese Cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Ma, Z.; Ni, B.; Peng, J.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Q. Research on the spatial differences of pollution-intensive industry transfer under the environmental regulation in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L. The Driving Mechanism of Urban Land Green Use Efficiency in China Based on the EBM Model with Undesirable Outputs and the Spatial Dubin Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zou, L.; Feng, Y.; Huang, L. Does manufacturing agglomeration promote or hinder green development efficiency? Evidence from Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Xie, Z.; Li, C.; Ji, F. The influence of the manufacturing agglomeration heterogeneity on the green economic efficiency in China. Electron. Commer. Res. 2022, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indicator Type | Element Name | Indicator Name |
|---|---|---|
| Input Indicators | Capital Investment | Total assets of industrial enterprises above average per land(Million Yuan/km2) |
| Labor input | Number of manufacturing workers per land (million people/km2) | |
| Land input | Industrial land area (km2) | |
| Output Indicators | Expected output | industrial value added per land (billion yuan/km2) |
| Non-desired outputs | industrial sulfur dioxide emissions per land (tons/km2) | |
| industrial wastewater discharge per land (million tons/km2) | ||
| industrial smoke (dust) emissions per land (tons/km2) |
| Variables | Variable Name | Measurements | Mean | Min | Max | Sample Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lneil | green use efficiency of industrial land | Super-SBM model | −1.252 | −3.135 | 0.286 | 4464 |
| agg | manufacturing agglomeration | location entropy | 0.889 | 0.022 | 3.189 | 4464 |
| lnep | environmental regulation | index of “industrial waste” | −3.062 | −14.526 | 3.558 | 4464 |
| lnpgdp | economic development level | GDP per capita | 10.076 | 7.603 | 13.245 | 4464 |
| is | Industrialization degree | share of secondary industry in GDP | 0.473 | 0.107 | 0.910 | 4464 |
| od | opening degree | Total import and export trade/ regional GDP | 0.204 | 0.000 | 8.134 | 4464 |
| si | technology input level | science and technology expenditure/public finance expenditure | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.131 | 4464 |
| gil | government intervention level | public finance expenditure/GDP | 0.171 | 0.040 | 1.027 | 4464 |
| ifi | Informationalized level | number of international Internet users/year-end population | 0.160 | 0.001 | 1.987 | 4464 |
| gc | eco-environmental endowment | greening coverage of built-up areas | 0.376 | 0.004 | 0.696 | 4464 |
| ri | regional Innovation Level | number of invention patents granted/total population at the end of the year | 0.914 | 0.000 | 48.132 | 4464 |
| Year | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 |
| Moran’s I | 0.078 *** | 0.078 *** | 0.062 *** | 0.044 ** | 0.051 *** | 0.043 ** | 0.040 ** | 0.023 |
| sd statistics | 4.403 | 4.367 | 3.509 | 2.542 | 2.930 | 2.502 | 2.353 | 1.448 |
| Year | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
| Moran’s I | 0.033 * | 0.028 * | 0.067 *** | 0.060 *** | 0.057 *** | 0.066 *** | 0.092 *** | 0.107 *** |
| sd statistics | 1.953 | 1.725 | 3.774 | 3.429 | 3.296 | 3.766 | 5.160 | 5.921 |
| Test Method | Test Statistic Results | p Value | Test Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM-Lag | 81.106 | 0.0000 | Can choose SEM model |
| Robust LM-Lag | 3.858 | 0.0490 | |
| LM-Error | 1047.219 | 0.0000 | Can choose SAR model |
| Robust LM-Erro | 969.971 | 0.0000 | |
| LR-SDM-SEM | 244.98 | 0.0000 | Compared with SEM and SAR models, choosing SDM models is better |
| LR-SDM-SAR | 201.23 | 0.0000 | |
| Wald-SAR | 73.14 | 0.0000 | |
| Wald-SEM | 70.98 | 0.0000 | |
| Hausman | −208.80 | - | Choosing the SDM model, the fixed effect model is better |
| Time Effect | 4392.19 | 0.0000 | Choosing the SDM model, the dual fixed model of time and space is better |
| Spatial effects | 160.87 | 0.0000 |
| Variables | eil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Countrywide | Eastern | Central | Western | Northeast | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| agg | −0.4963 *** | −0.2461 ** | −0.4176 *** | −0.9803 *** | −0.7956 *** |
| (0.0384) | (0.0765) | (0.0830) | (0.0781) | (0.1411) | |
| agg2 | 0.1046 *** | 0.0113 | 0.0756 * | 0.4039 *** | 0.3242 *** |
| (0.0145) | (0.0239) | (0.0393) | (0.0388) | (0.0792) | |
| lnep | −0.0418 *** | −0.0640 *** | −0.0398 *** | −0.0267 *** | −0.0525 *** |
| (0.0030) | (0.0061) | (0.0054) | (0.0055) | (0.0080) | |
| lnpgdp | 0.1693 *** | −0.1566 | 0.0714 | 0.3369 *** | 0.3869 ** |
| (0.0405) | (0.1099) | (0.0751) | (0.0630) | (0.1192) | |
| is | 1.1312 *** | 0.8055 *** | 0.8245 *** | 1.3369 *** | 0.6410 *** |
| (0.0678) | (0.1868) | (0.1283) | (0.1058) | (0.1836) | |
| od | 0.0534 *** | 0.0678 *** | −0.1644 * | −0.0062 | 0.0893 * |
| (0.0142) | (0.0153) | (0.0920) | (0.0532) | (0.0529) | |
| si | 1.9923 *** | 2.2173 ** | −1.5584 ** | 3.5111 ** | 2.5782 |
| (0.4505) | (0.7086) | (0.7104) | (1.5000) | (1.7332) | |
| gil | −0.6275 *** | −0.9827 *** | −1.0132 *** | −0.4445 *** | −1.7832 *** |
| (0.0816) | (0.2709) | (0.2431) | (0.1111) | (0.1904) | |
| ifi | 0.0687 ** | 0.0205 | 0.6316 *** | 0.0590 | 0.2553 ** |
| (0.0335) | (0.0427) | (0.1249) | (0.0713) | (0.1211) | |
| gc | −0.0014 | −0.1583 | −0.1901 ** | 0.0003 | 0.3994 ** |
| (0.0495) | (0.1009) | (0.0829) | (0.0861) | (0.1499) | |
| ri | 0.0184 *** | 0.0164 *** | 0.0071 | 0.0633 *** | −0.0303 * |
| (0.0019) | (0.0022) | (0.0081) | (0.0119) | (0.0180) | |
| City Fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 4464 | 1360 | 1264 | 1312 | 528 |
| Variables | 2004–2009 | 2010–2014 | 2015–2019 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| lneil | lneil | lneil | |
| agg | −0.6371 *** | −0.5239 *** | −0.9552 *** |
| (0.0900) | (0.0570) | (0.0883) | |
| agg2 | 0.1482 *** | 0.1078 *** | 0.2451 *** |
| (0.0400) | (0.0212) | (0.0348) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES |
| City Fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 1674 | 1395 | 1395 |
| Variables | lneil | |
|---|---|---|
| (9) | (10) | |
| FE | SYS-GMM | |
| L.lneil | - | 0.6397 *** |
| - | (0.0426) | |
| L.lnec | - | - |
| - | - | |
| L.lntc | - | - |
| - | - | |
| agg | −0.5394 *** | −0.3300 *** |
| (0.1223) | (0.0877) | |
| agg2 | 0.1110 * | 0.0723 ** |
| (0.0604) | (0.0331) | |
| _cons | −3.1822 *** | 0.2163 |
| (0.7464) | (0.75) | |
| Control variables | YES | YES |
| City Fixed | YES | - |
| Time fixed | YES | - |
| R2 | 0.515 | - |
| N | 4464 | 4185 |
| AR(1) | - | 0.000 |
| AR(2) | - | 0.527 |
| Hansen | - | 0.191 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Min, M.; Zhao, K.; Hu, W.; Qin, F. Research on the Effect of Manufacturing Agglomeration on Green Use Efficiency of Industrial Land. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021575
Wang Y, Zhang A, Min M, Zhao K, Hu W, Qin F. Research on the Effect of Manufacturing Agglomeration on Green Use Efficiency of Industrial Land. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021575
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuan, Anlu Zhang, Min Min, Ke Zhao, Weiyan Hu, and Fude Qin. 2023. "Research on the Effect of Manufacturing Agglomeration on Green Use Efficiency of Industrial Land" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021575
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, A., Min, M., Zhao, K., Hu, W., & Qin, F. (2023). Research on the Effect of Manufacturing Agglomeration on Green Use Efficiency of Industrial Land. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021575






