Prevalence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Populations: Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategies
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Recorded Variables
2.4. Meta-Analytic Approach
3. Results
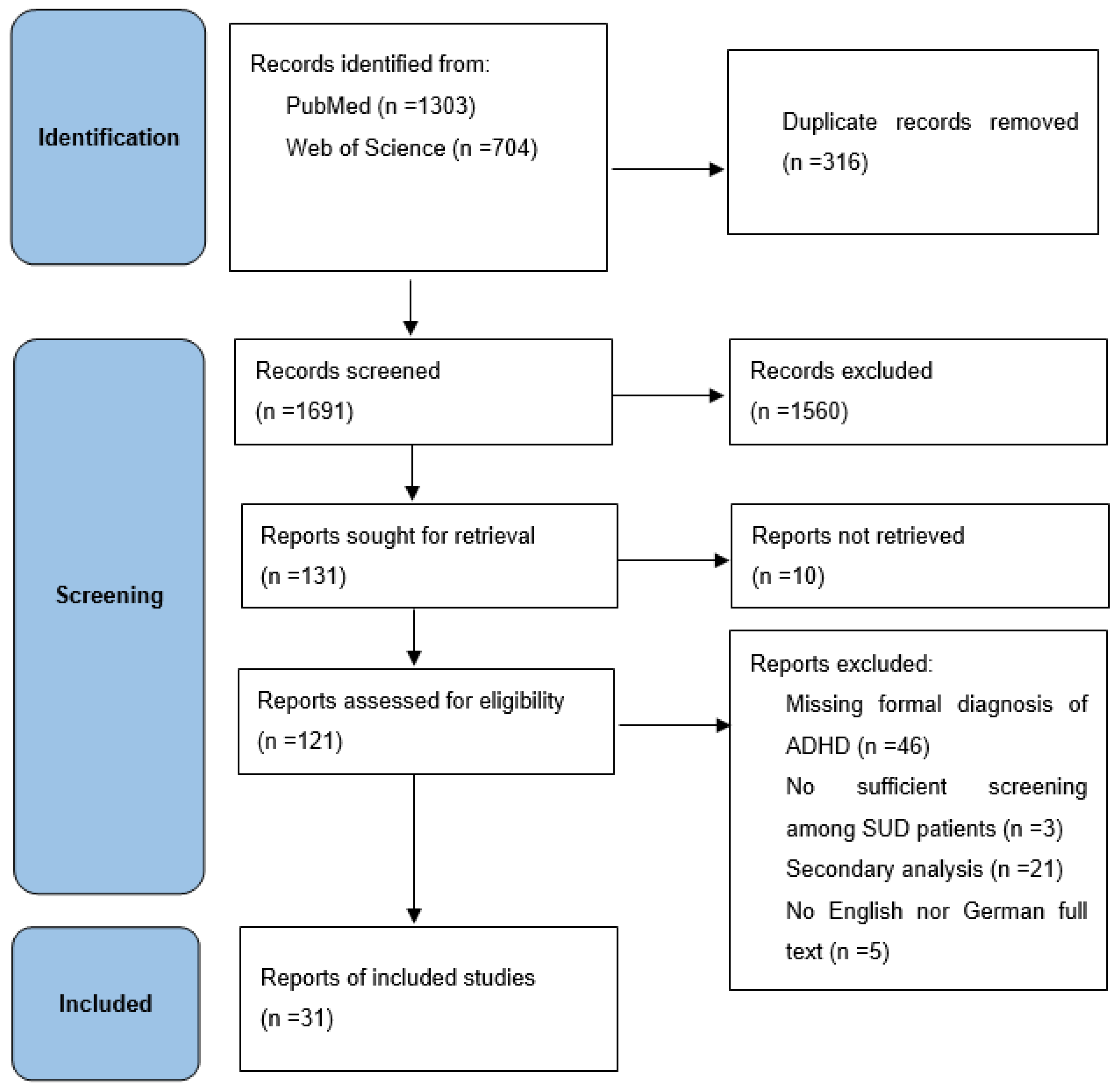
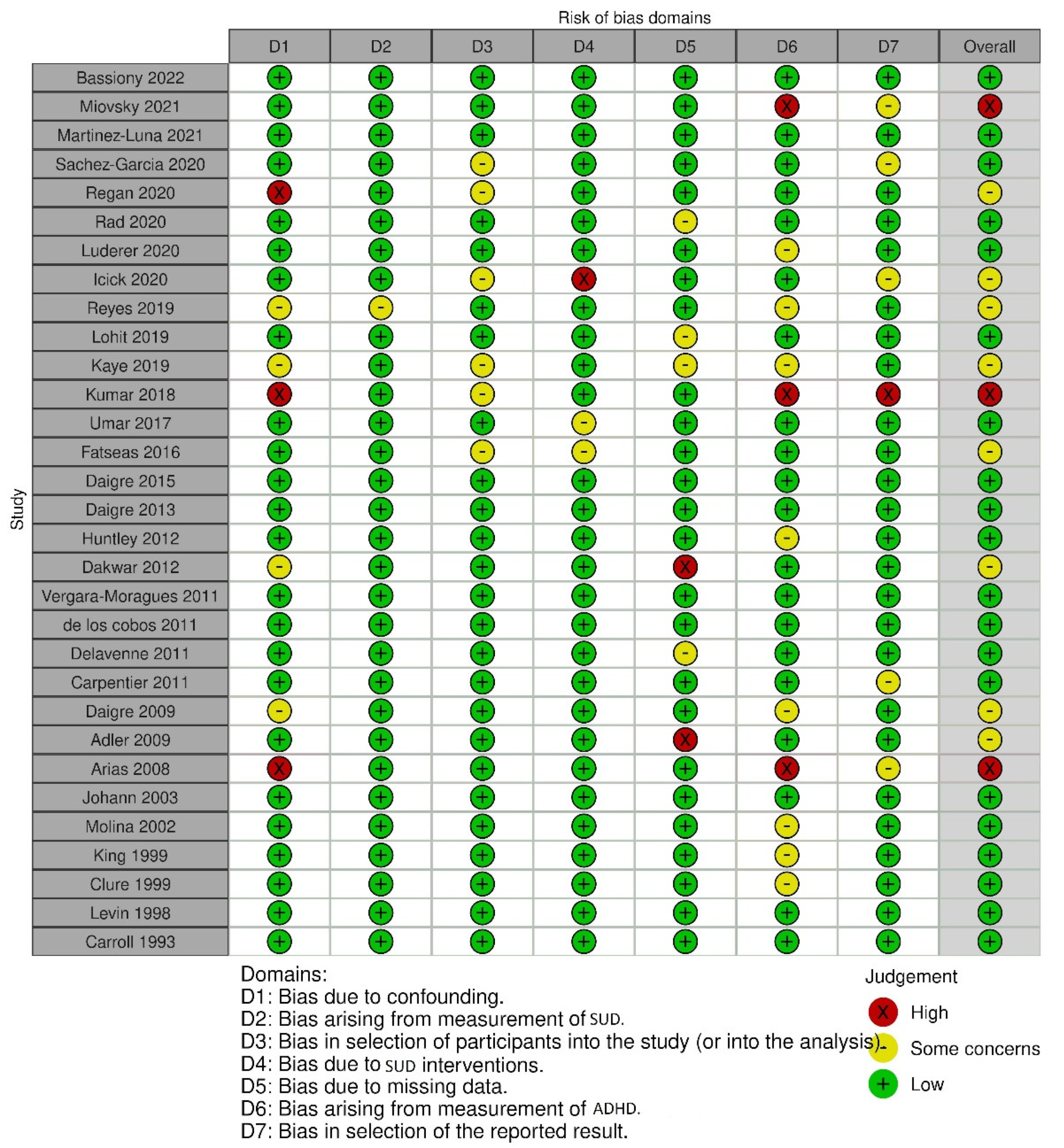
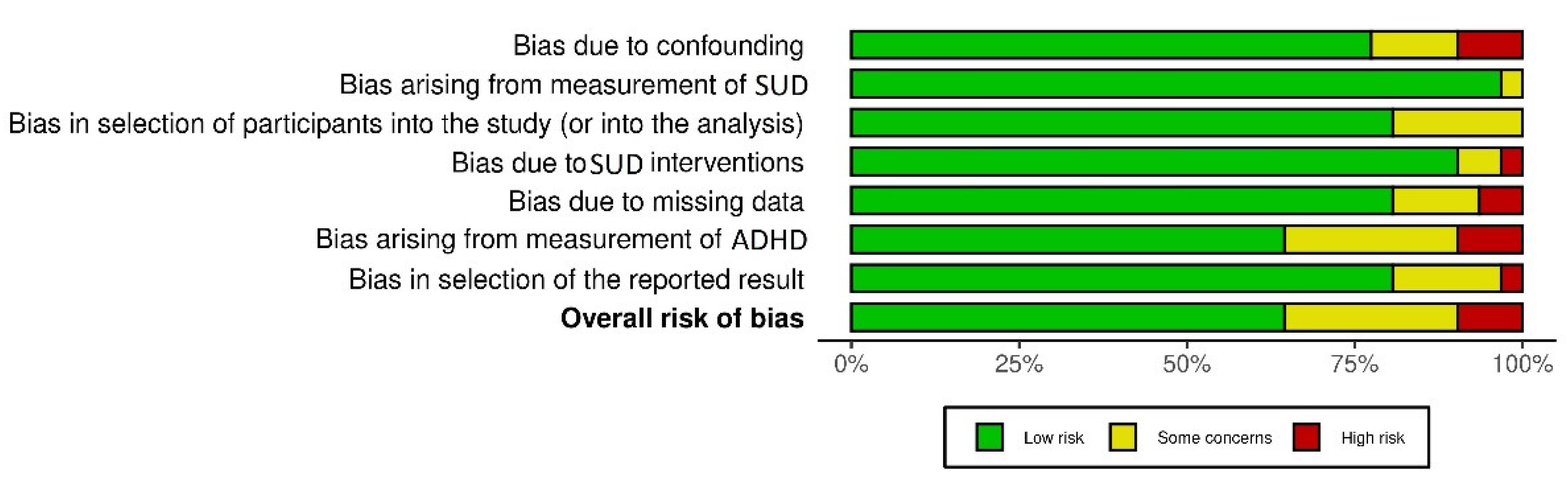
3.1. Included Studies and Sample Characteristics
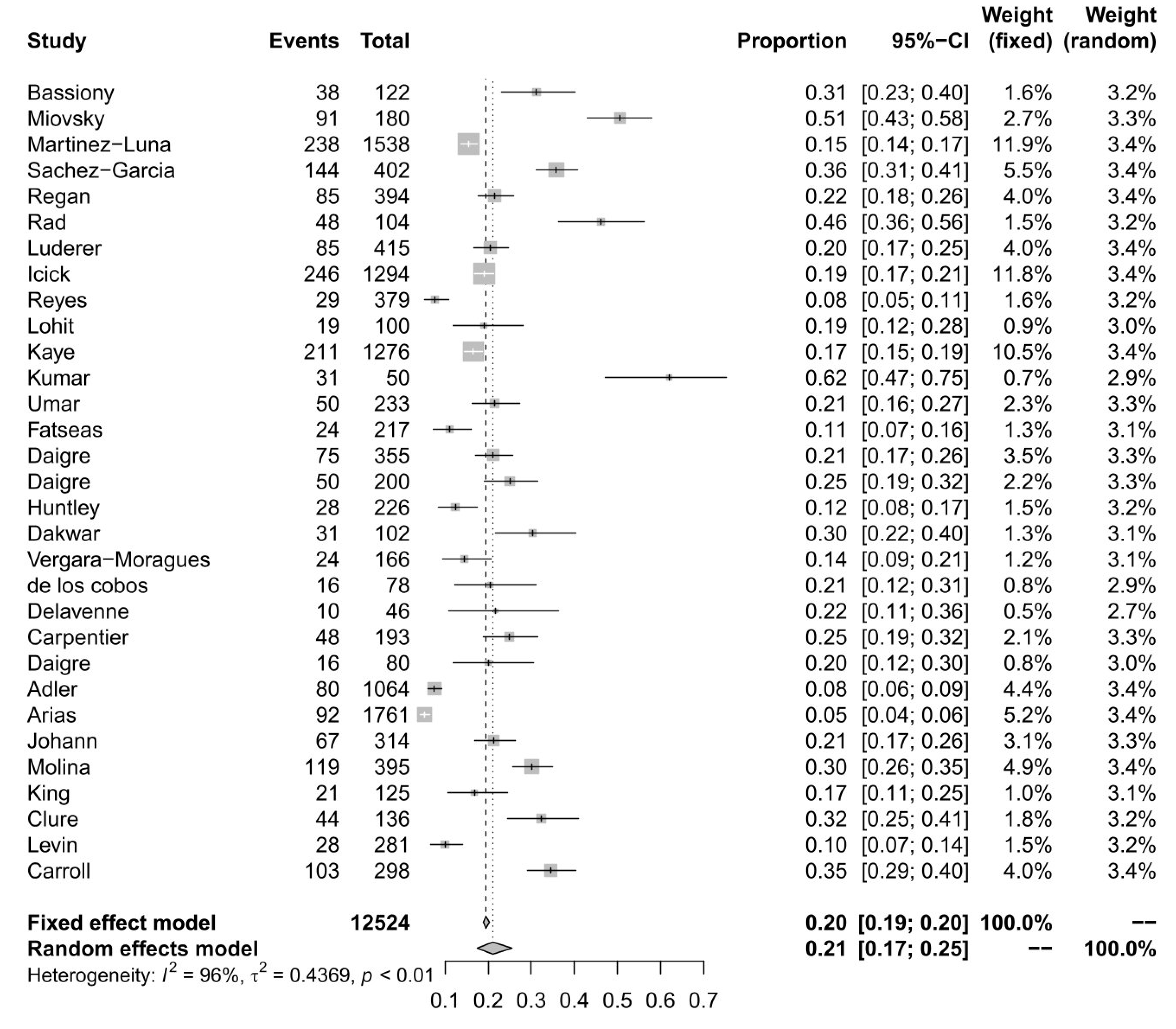
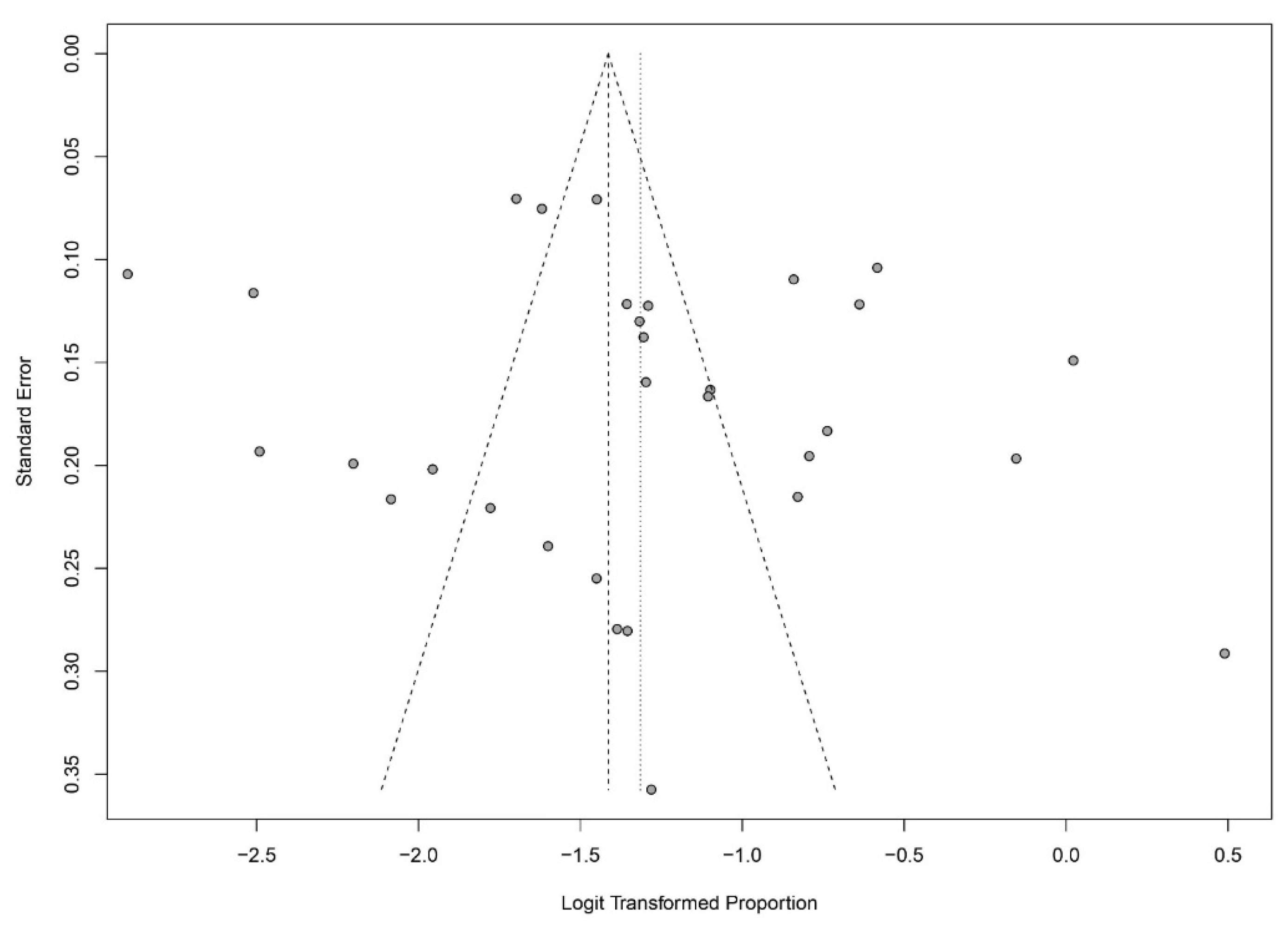
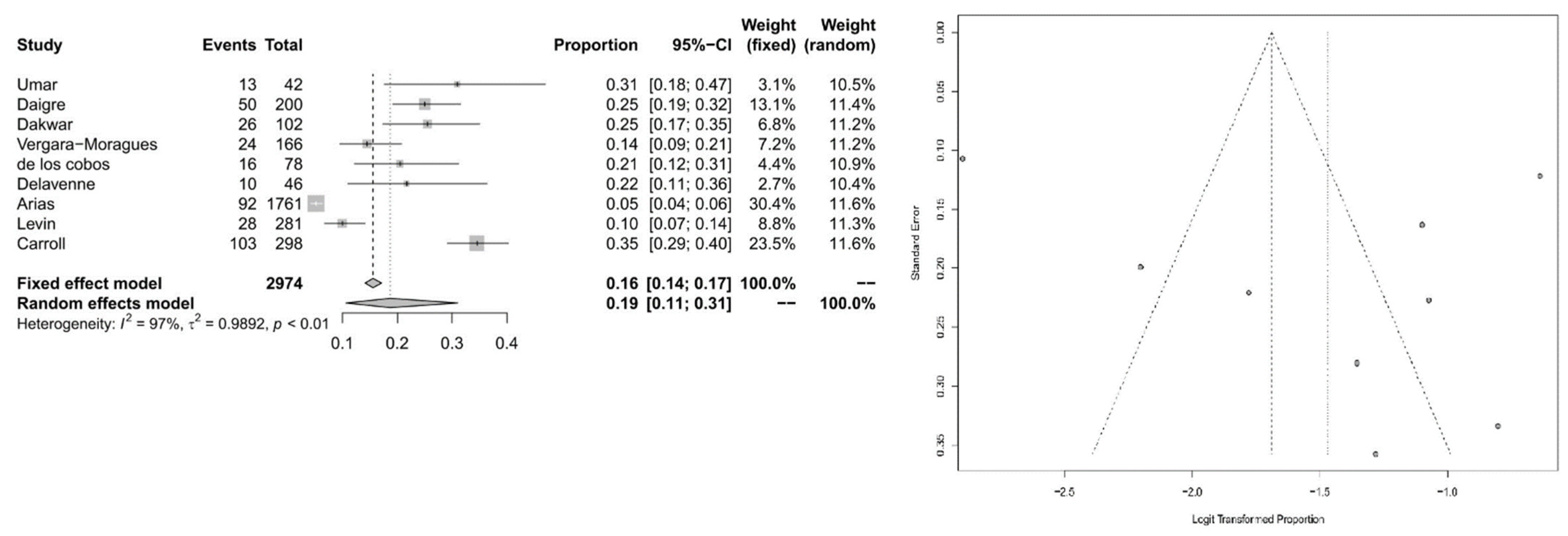
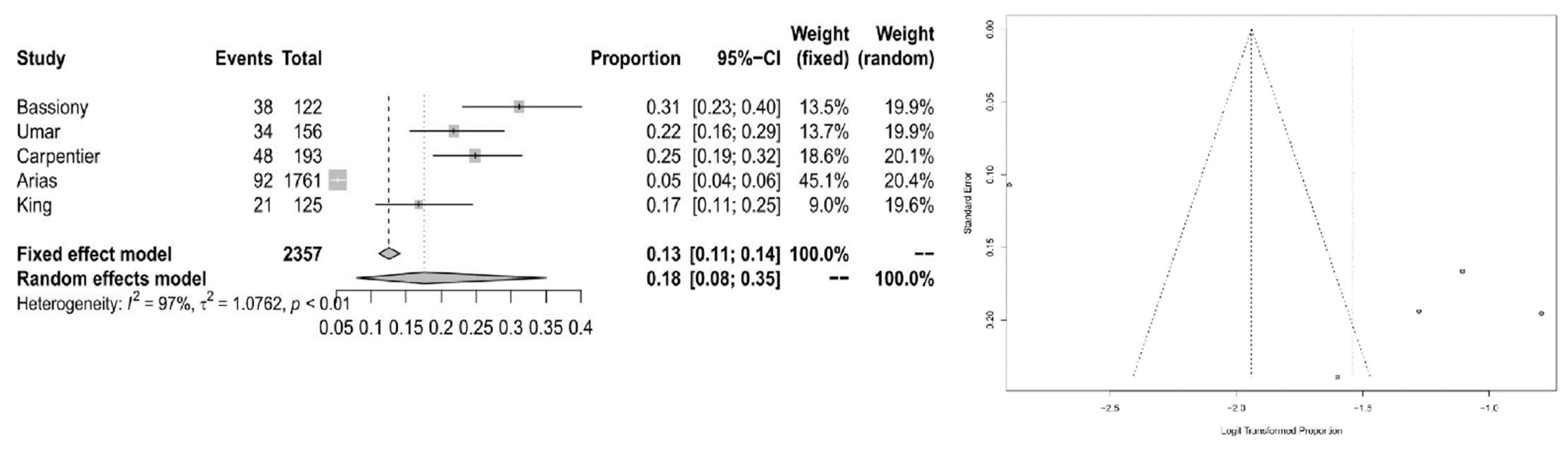
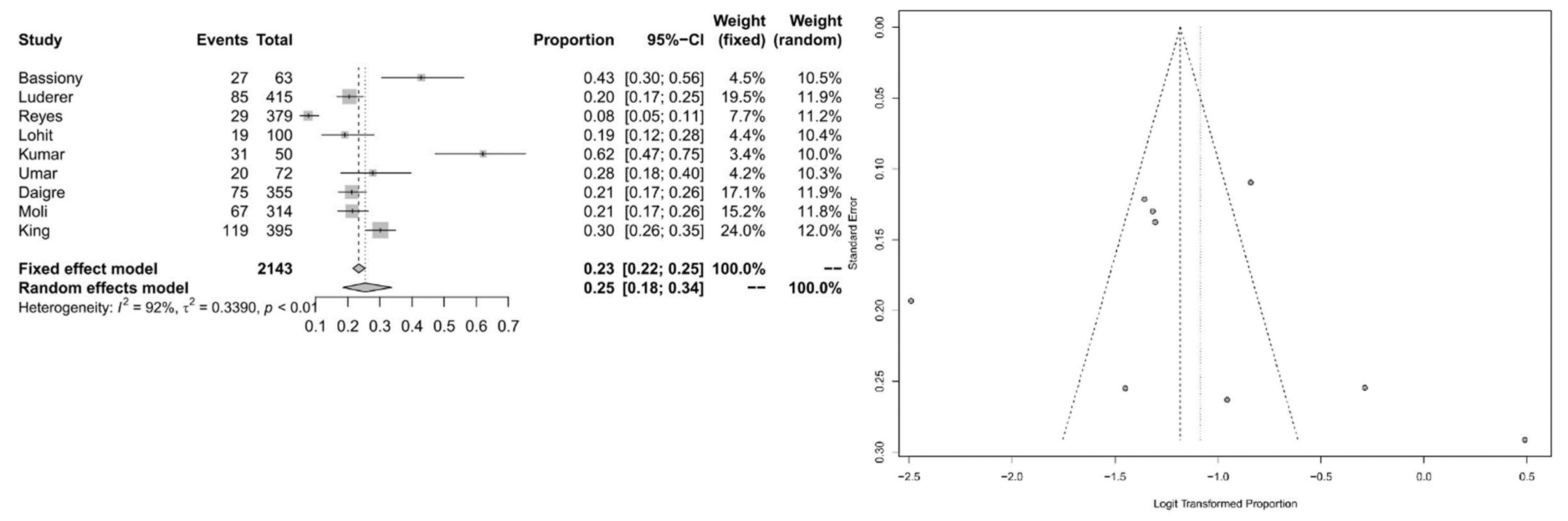
3.2. Meta-Analytic Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suen, L.W.; Makam, A.N.; Snyder, H.R.; Repplinger, D.; Kushel, M.B.; Martin, M.; Nguyen, O.K. National Prevalence of Alcohol and Other Substance Use Disorders Among Emergency Department Visits and Hospitalizations: NHAMCS 2014–2018. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 2420–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkanen, T.; Kaskela, T.; Levola, J. Mortality of treatment-seeking men and women with alcohol, opioid or other substance use disorders—A register-based follow-up study. Addict Behav. 2020, 105, 106330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertzen, C.A.; Ross, F.E. Strength of drug habits: For heroin, morphine, methadone, alcohol, barbiturates, pentobarbital, benzedrine, cocaine, and marijuana. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1980, 5, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigre, C.; Roncero, C.; Grau-López, L.; Martínez-Luna, N.; Prat, G.; Valero, S.; Tejedor, R.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Casas, M. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in cocaine-dependent adults: A psychiatric comorbidity analysis. Am. J. Addict. 2013, 22, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, H.F.; Faller, S.; Benzano, D.; Szobot, C.; von Diemen, L.; Stolf, A.R.; Souza-Formigoni, M.L.; Cruz, M.S.; Brasiliano, S.; Pechansky, F.; et al. The Effects of Adhd in Adult Substance Abusers. J. Addict. Dis. 2013, 32, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austerman, J. ADHD and behavioral disorders: Assessment, management, and an update from DSM-5. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2015, 82, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkley, R.A.; Fischer, M.; Smallish, L.; Fletcher, K. Young adult outcome of hyperactive children: Adaptive functioning in major life activities. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2006, 45, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, M.H.; Mitchell, J.T.; Becker, S.P. Method of adult diagnosis influences estimated persistence of childhood ADHD: A systematic review of longitudinal studies. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, G.V.; Willcutt, E.G.; Salum, G.A.; Kieling, C.; Rohde, L.A. ADHD prevalence estimates across three decades: An updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, V.; Czobor, P.; Bálint, S.; Mészáros, A.; Bitter, I. Prevalence and correlates of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: Meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2009, 194, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Humphreys, K.L.; Flory, K.; Liu, R.; Glass, K. Prospective association of childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and substance use and abuse/dependence: A meta-analytic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 31, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassiony, M.M.; Salah El-Deen, G.M.; Ameen, N.; Mahdy, R.S. Prevalence, correlates, and consequences of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a clinical sample of adults with tramadol use in Egypt. Am. J. Addict. 2022, 31, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capusan, A.J.; Bendtsen, P.; Marteinsdottir, I.; Larsson, H. Comorbidity of Adult ADHD and Its Subtypes With Substance Use Disorder in a Large Population-Based Epidemiological Study. J. Atten. Disord. 2019, 23, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, J.J.; Levin, F.R. Treatment strategies for co-occurring ADHD and substance use disorders. Am. J. Addict. 2007, 16 (Suppl. S1), 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulauf, C.A.; Sprich, S.E.; Safren, S.A.; Wilens, T.E. The complicated relationship between attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and substance use disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2014, 16, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, T.; Tubman, J. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Subtypes, Co-Occurring Psychiatric Symptoms and Sexual Risk Behaviors among Adolescents Receiving Substance Abuse Treatment. Subst. Use Misuse 2020, 55, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.J.; Gelernter, J.; Chan, G.; Weiss, R.D.; Brady, K.T.; Farrer, L.; Kranzler, H.R. Correlates of co-occurring ADHD in drug-dependent subjects: Prevalence and features of substance dependence and psychiatric disorders. Addict. Behav. 2008, 33, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Chate, S.; Patil, N.; Tekalaki, B.; Patil, S. Prevalence of undiagnosed and untreated attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in men with alcohol dependence: A case-control study. Arch. Psychiatry Psychother. 2018, 20, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Moragues, E.; González-Saiz, F.; Lozano Rojas, O.; Bilbao Acedos, I.; Fernández Calderón, F.; Betanzos Espinosa, P.; Verdejo García, A.; Pérez García, M. Diagnosing Adult Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Patients with Cocaine Dependence: Discriminant Validity of Barkley Executive Dysfunction Symptoms. Eur. Addict. Res. 2011, 17, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Cobos, J.P.; Siñol, N.; Puerta, C.; Cantillano, V.; López Zurita, C.; Trujols, J. Features and prevalence of patients with probable adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder who request treatment for cocaine use disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 185, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, M.M.; Schneekloth, T.D.; Hitschfeld, M.J.; Geske, J.R.; Atkinson, D.L.; Karpyak, V.M. The Clinical Utility of ASRS-v1.1 for Identifying ADHD in Alcoholics Using PRISM as the Reference Standard. J. Atten. Disord. 2019, 23, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, V.L.; Brooner, R.K.; Kidorf, M.S.; Stoller, K.B.; Mirsky, A.F. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and treatment outcome in opioid abusers entering treatment. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1999, 187, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Emmerik-van Oortmerssen, K.; van de Glind, G.; van den Brink, W.; Smit, F.; Crunelle, C.L.; Swets, M.; Schoevers, R.A. Prevalence of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in substance use disorder patients: A meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012, 122, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; Mckenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- ICD-10-GM Version 2020, Systematisches Verzeichnis, Internationale statistische Klassifikation der Krankheiten und verwandter Gesundheitsprobleme, 10. Revision, Stand: 20. September 2019; Deutsches Institut für Medizinische Dokumentation und Information (DIMDI) im Auftrag des Bundesministeriums für Gesundheit (BMG) unter Beteiligung der Arbeitsgruppe ICD des Kuratoriums für Fragen der Klassifikation im Gesundheitswesen (KKG): Köln, Germany, 2019.
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Bias and Efficiency of Meta-Analytic Variance Estimators in the Random-Effects Model. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2005, 30, 261–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huedo-Medina, T.B.; Sánchez-Meca, J.; Marín-Martínez, F.; Botella, J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol. Methods 2006, 11, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miovsky, M.; Lukavská, K.; Rubášová, E.; Šťastná, L.; Šefránek, M.; Gabrhelík, R. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder among Clients Diagnosed with a Substance Use Disorder in the Therapeutic Communities: Prevalence and Psychiatric Comorbidity. Eur. Addict. Res. 2021, 27, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Luna, N.; Daigre, C.; Palma-Álvarez, F.; Perea-Ortueta, M.; Grau-López, L.; Roncero, C.; Castell-Panisello, E.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A. Psychiatric Comorbidity and Addiction Severity Differences in Patients With ADHD Seeking Treatment for Cannabis or Cocaine Use Disorders. J. Atten. Disord. 2021, 25, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Garcia, N.C.; González, R.A.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Van Den Brink, W.; Luderer, M.; Blankers, M.; Grau-Lopez, L.; Levin, F.R.; Kaye, S.; Demetrovics, Z.; et al. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Increases Nicotine Addiction Severity in Adults Seeking Treatment for Substance Use Disorders: The Role of Personality Disorders. Eur. Addict. Res. 2020, 26, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, F.; Buică, A.; Stancu, M.; Irimie-ana, A.; Andrei, E.; Roşca, D.; Dobrescu, I. Adult ADHD symptoms in a group of patients with substance abuse. Riv. Di Psichiatr. 2020, 55, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luderer, M.; Sick, C.; Kaplan-Wickel, N.; Reinhard, I.; Richter, A.; Kiefer, F.; Weber, T. Prevalence Estimates of ADHD in a Sample of Inpatients With Alcohol Dependence. J. Atten. Disord. 2020, 24, 2072–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icick, R.; Moggi, F.; Slobodin, O.; Dom, G.; Mathys, F.; Van Den Brink, W.; Levin, F.R.; Blankers, M.; Kaye, S.; Demetrovics, Z.; et al. Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Global Severity Profiles in Treatment-Seeking Patients with Substance Use Disorders. Eur. Addict. Res. 2020, 26, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohit, S.R.; Babu, G.N.; Sharma, S.; Rao, S.; Sachin, B.S.; Matkar, A.V. Prevalence of Adult ADHD Co-morbidity in Alcohol Use Disorders in a General Hospital Setup. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2019, 41, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, S.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Van De Glind, G.; Levin, F.R.; Faraone, S.V.; Allsop, S.; Degenhardt, L.; Moggi, F.; Barta, C.; Konstenius, M.; et al. Persistence and Subtype Stability of ADHD Among Substance Use Disorder Treatment Seekers. J. Atten. Disord. 2019, 23, 1438–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.U.; Salihu, A.S.; Owolabi, S.D. Prevalence and correlates of ADHD in individuals with substance use disorder in Nigeria. ADHD Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2017, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatseas, M.; Hurmic, H.; Serre, F.; Debrabant, R.; Daulouède, J.P.; Denis, C.; Auriacombe, M. Addiction severity pattern associated with adult and childhood Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in patients with addictions. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 246, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigre, C.; Roncero, C.; Rodríguez-Cintas, L.; Ortega, L.; Lligoña, A.; Fuentes, S.; Pérez-Pazos, J.; Martínez-Luna, N.; Casas, M. Adult ADHD Screening in Alcohol-Dependent Patients Using the Wender-Utah Rating Scale and the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale. J. Atten. Disord. 2015, 19, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, Z.; Maltezos, S.; Williams, C.; Morinan, A.; Hammon, A.; Ball, D.; Marshall, E.J.; Keaney, F.; Young, S.; Bolton, P.; et al. Rates of undiagnosed attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in London drug and alcohol detoxification units. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakwar, E.; Mahony, A.; Pavlicova, M.; Glass, A.; Brooks, D.; Mariani, J.J.; Grabowski, J.; Levin, F.R. The utility of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder screening instruments in individuals seeking treatment for substance use disorders. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2012, 73, 22036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delavenne, H.; Ballon, N.; Charles-Nicolas, A.; Garcia, F.D.; Thibaut, F.; Lacoste, J. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Is Associated With a More Severe Pattern of Cocaine Consumption in Cocaine Users From French West Indies. J. Addict. Med. 2011, 5, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, P.J.; Van Gogh, M.T.; Knapen, L.J.M.; Buitelaar, J.K.; De Jong, C.A.J. Influence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and conduct disorder on opioid dependence severity and psychiatric comorbidity in chronic methadone-maintained patients. Eur. Addict. Res. 2011, 17, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigre, C.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Valero, S.; Bosch, R.; Roncero, C.; Gonzalvo, B.; Nogueira, M.; Casas, M. Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS-v1.1) symptom checklist in patients with substance use disorders. Actas Esp. De Psiquiatr. 2009, 37, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, L.A.; Guida, F.; Irons, S.; Rotrosen, J.; O’Donnell, K. Screening and Imputed Prevalence of ADHD in Adult Patients with Comorbid Substance Use Disorder at a Residential Treatment Facility. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 121, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johann, M.; Bobbe, G.; Putzhammer, A.; Wodarz, N. Comorbidity of alcohol dependence with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: Differences in phenotype with increased severity of the substance disorder, but not in genotype (serotonin transporter and 5-hydroxytryptamine-2c receptor). Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2003, 27, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, B.S.; Bukstein, O.G.; Lynch, K.G. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and conduct disorder symptomatology in adolescents with alcohol use disorder. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2002, 16, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clure, C.; Brady, K.T.; Saladin, M.E.; Johnson, D.; Waid, R.; Rittenbury, M. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and substance use: Symptom pattern and drug choice. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 1999, 25, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, F.R.; Evans, S.M.; Kleber, H.D. Prevalence of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder among cocaine abusers seeking treatment. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1998, 52, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, K.M.; Rounsaville, B.J. History and significance of childhood attention deficit disorder in treatment-seeking cocaine abusers. Compr. Psychiatry 1993, 34, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retz-Junginger, P.; Retz, W.; Blocher, D.; Weijers, H.-G.; Trott, G.-E.; Wender, P.H.; Rössler, M. Wender Utah rating scale. The short-version for the assessment of the attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults. Nervenarzt 2002, 73, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosler, M.; Retz, W.; Retz-Junginger, P.; Thome, J.; Supprian, T.; Nissen, T.; Stieglitz, R.D.; Blocher, D.; Hengesch, G.; Trott, G.E. Tools for the diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults. Self-rating behaviour questionnaire and diagnostic checklist. Nervenarzt 2004, 75, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paucke, M.; Stark, T.; Exner, C.; Kallweit, C.; Hegerl, U.; Strauß, M. Attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and comorbid mental disorders: ADHD-specific self-rating scales in differential diagnostics. Nervenarzt 2018, 89, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conners, C.K.; Erhardt, D.; Sparrow, E. Conners Adult ADHD Rating Scales (CAARS): Technical manual; Multi-Health Systems: North Tonawanda, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, J.L.; King, T.S.; Curry, W.J. The adult ADHD self-report scale for screening for adult attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2012, 25, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.; Woodhouse, E. Assessment and treatment of substance use in adults with ADHD: A psychological approach. J. Neural Transm. 2021, 128, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year | Sex (male) | Mean Age | Age SD | ADHD Prevalence | n | Substance | Country of Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bassiony et al. [12] | 2022 | 83.6% | 31.28 | 7.24 | 31% | 122 | opioid | Egypt |
| Miovsky et al. [31] | 2021 | 76.7% | 28.1 | 6.11 | 50.6% | 180 | various | Czech Republic |
| Martinez-Luna et al. [32] | 2021 | 80% | 32.9 | 10 | 15.5% | 1538 | various | Spain |
| Sanchez-Garcia et al. [33] | 2020 | 79.6% | 36.91 | 11.87 | 35.75% | 402 | various | International |
| Regan et al. [16] | 2020 | 71.1% | 16.33 | 1.15 | 21.5% | 394 | various | U.S.A. |
| Rad et al. [34] | 2020 | 60.58% | na | na | 46% | 104 | various | Romania |
| Luderer et al. [35] | 2020 | 72.02% | 45.35 | 10.2 | 20.5% | 415 | alcohol | Germany |
| Icick et al. [36] | 2020 | 74% | 40 | 11 | 19% | 1294 | various | International |
| Reyes et al. [21] | 2019 | 65.4% | 41.9 | 11.7 | 7.7% | 379 | alcohol | International |
| Lohit et al. [37] | 2019 | 100% | 40.68 | na | 19% | 100 | alcohol | India |
| Kaye et al. [38] | 2019 | na | na | na | 16.53% | 1276 | various | International |
| Kumar et al. [18] | 2018 | 100% | 32.06 | 7.22 | 62% | 50 | alcohol | India |
| Umar et al. [39] | 2017 | 82.8% | 26.31 | 6.53 | 21.5% | 233 | various | Nigeria |
| Fatseas et al. [40] | 2016 | 66.4% | 37.7 | 10.6 | 11.1% | 217 | various | France |
| Daigre et al. [41] | 2015 | 78.3% | 36.15 | 10.43 | 21.12% | 355 | alcohol | Spain |
| Daigre et al. [4] | 2013 | 87% | 33.28 | 7.4 | 25% | 200 | cocaine | Spain |
| Huntley et al. [42] | 2012 | 76.5% | 39 | 10.3 | 12.2% | 226 | various | United Kingdom |
| Dakwar et al. [43] | 2012 | na | na | na | 25 | 102 | cocaine | U.S.A. |
| Vergara-Moragues et al. [19] | 2011 | 91% | 34.84 | 7.4 | 14.5% | 166 | cocaine | Spain |
| De los cobos et al. [20] | 2011 | 81% | 32.2 | 7.3 | 20.5% | 78 | cocaine | Spain |
| Delavenne et al. [44] | 2011 | 95.65% | na | na | 21.7% | 46 | cocaine | France |
| Carpentier et al. [45] | 2011 | 83.42% | 40.59 | 6.84 | 25.9% | 193 | opioid | Netherlands |
| Daigre et al. [46] | 2009 | 80% | 36.15 | 10.43 | 20% | 80 | various | Spain |
| Adler et al. [47] | 2009 | na | na | na | 7.5% | 1064 | various | U.S.A. |
| Arias et al. [17] | 2008 | 51.9% | 38.37 | 7.67 | 5.22% | 1761 | various | U.S.A. |
| Johann et al. [48] | 2003 | 83% | 43.1 | 8.77 | 21.3% | 314 | alcohol | Germany |
| Molina et al. [49] | 2002 | 63% | 16.75 | 1.22 | 30% | 395 | alcohol | U.S.A. |
| King et al. [22] | 1999 | 46% | 37 | 7.75 | 16.8% | 125 | opiod | U.S.A. |
| Clure et al. [50] | 1999 | 75.59% | 34.3 | 0.78 | 32% | 136 | various | U.S.A. |
| Levin et al. [51] | 1998 | 82% | 33.7 | 0.4 | 10% | 281 | cocaine | U.S.A. |
| Carroll et al. [52] | 1993 | 69% | 27.7 | 6.06 | 34.6% | 298 | cocaine | U.S.A. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rohner, H.; Gaspar, N.; Philipsen, A.; Schulze, M. Prevalence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Populations: Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021275
Rohner H, Gaspar N, Philipsen A, Schulze M. Prevalence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Populations: Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(2):1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021275
Chicago/Turabian StyleRohner, Henrik, Nikolas Gaspar, Alexandra Philipsen, and Marcel Schulze. 2023. "Prevalence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Populations: Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 2: 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021275
APA StyleRohner, H., Gaspar, N., Philipsen, A., & Schulze, M. (2023). Prevalence of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among Substance Use Disorder (SUD) Populations: Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(2), 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021275






