At-Home Orthodontic Treatment for Severe Teeth Arch Malalignment and Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in a Child with Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
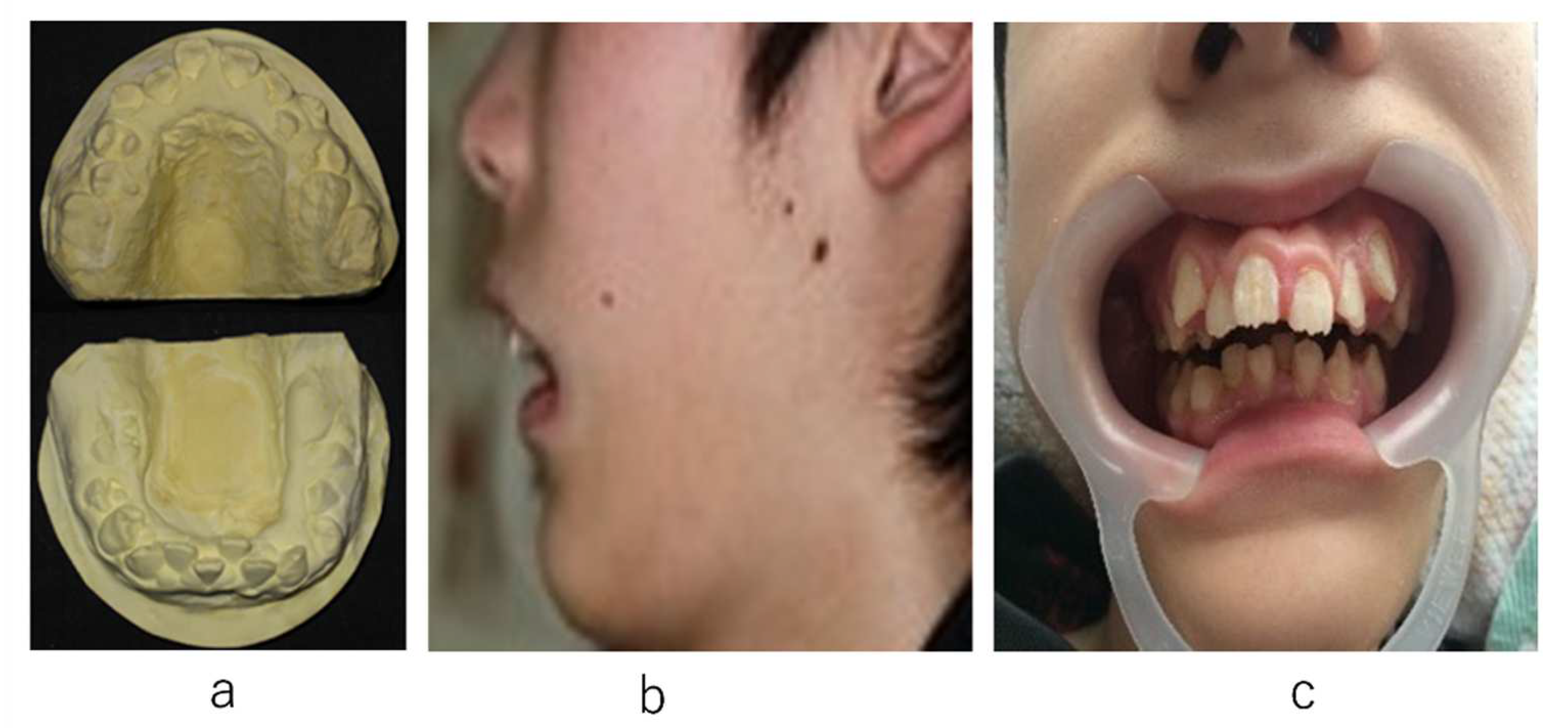
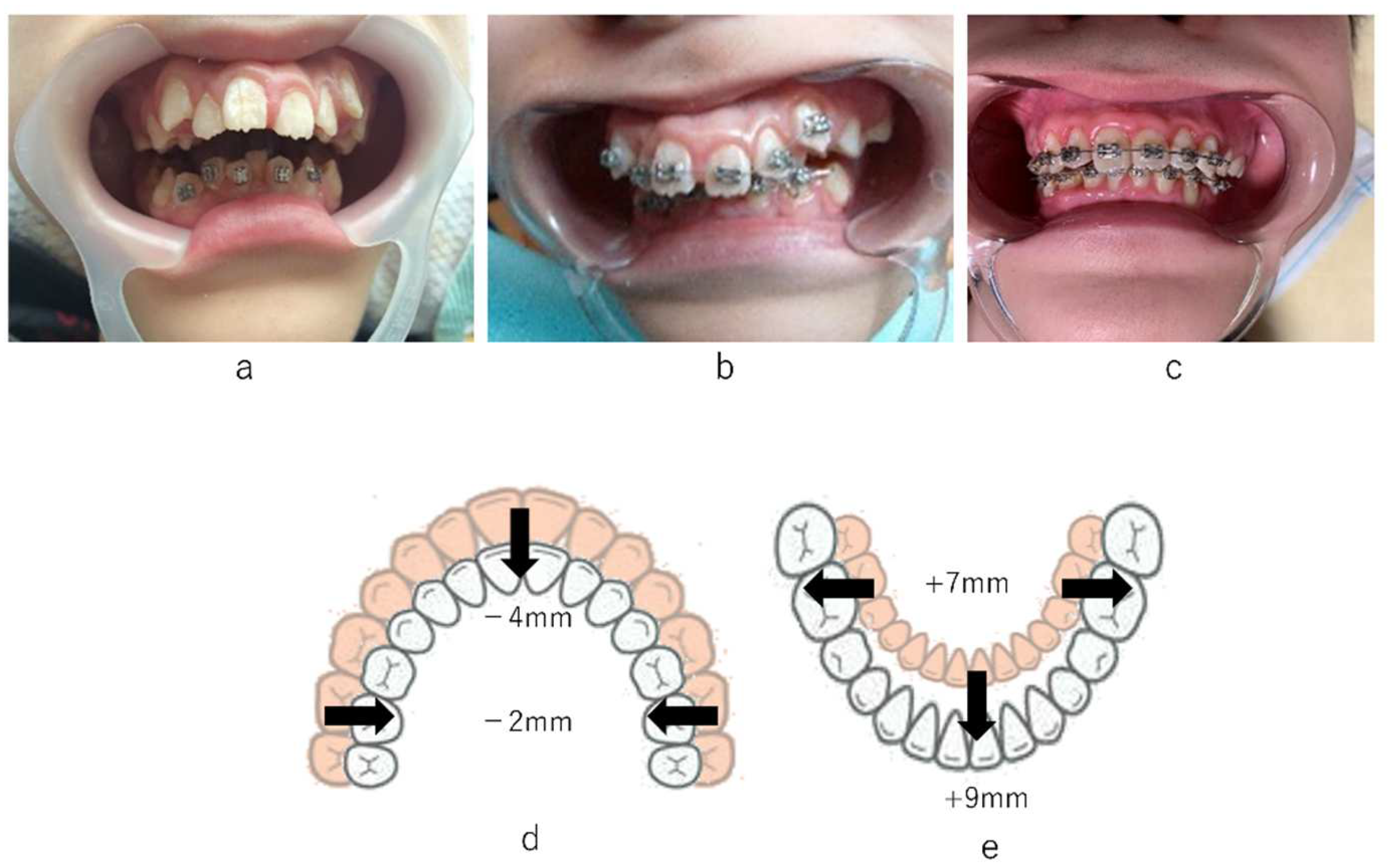
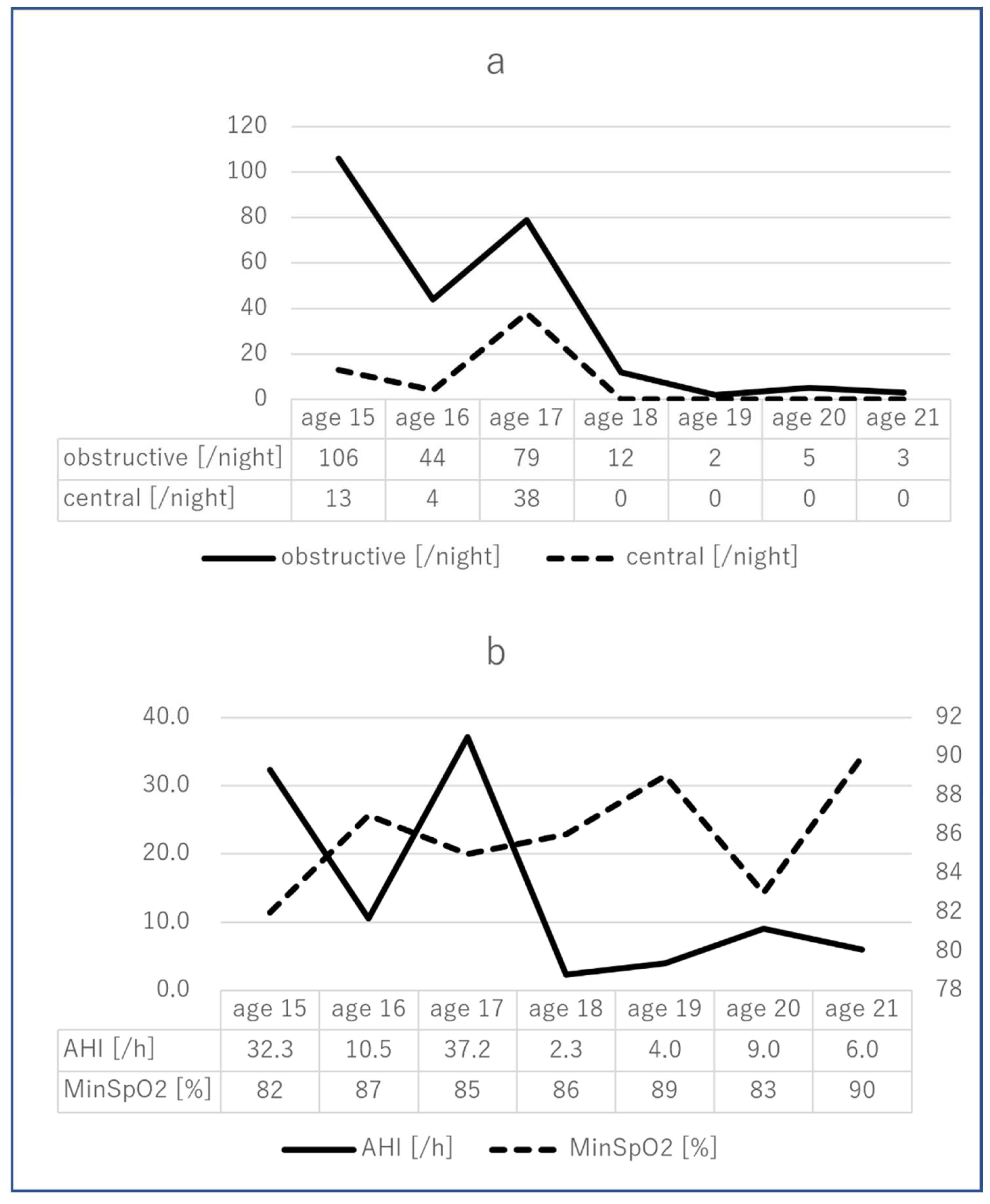
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bax, M.; Goldstein, M.; Rosenbaum, P.; Leviton, A.; Paneth, N.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B.; Damiano, D. Executive Committee for the Definition of Cerebral Palsy. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2005, 47, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavcic, A.; Vodusek, D.B. The definition of cerebral palsy, April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008, 50, 240. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, J.; Ito, M. Incidence patterns of cerebral palsy in Shiga Prefecture, Japan, 1977–1991. Brain Dev. 2002, 24, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztürk, A.; Demirci, F.; Yavuz, T.; Yildiz, S.; Değirmenci, Y.; Döşoğlu, M.; Avşar, Y. Antenatal and delivery risk factors and prevalence of cerebral palsy in Duzce (Turkey). Brain Dev. 2007, 29, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petridou, E.; Koussouri, M.; Toupadaki, N.; Papavassiliou, A.; Youroukos, S.; Katsarou, E.; Trichopoulos, D. Risk factors for cerebral palsy: A case-control study in Greece. Scand. J. Soc. Med. 1996, 24, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukojević, M.; Soldo, I.; Granić, D. Risk factors associated with cerebral palsy in newborns. Coll. Antropol. 2009, 33 (Suppl. 2), 199–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.W.; Colford, J.M., Jr. Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2000, 284, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Riet, J.E.; Vandenbussche, F.P.; Le Cessie, S.; Keirse, M.J. Newborn assessment and long-term adverse outcome: A systematic review. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 180, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, B.; Hagberg, G.; Hagberg, B.; Ladfors, L.; Niklasson, A.; Hagberg, H. Cerebral palsy in preterm infants: A population-based case-control study of antenatal and intrapartal risk factors. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmach, T.; Pisarev, H.; Talvik, T. Ante- and perinatal factors for cerebral palsy: Case-control study in Estonia. J. Child Neurol. 2005, 20, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstab, J.E.; Bell, R.J.; Reddihough, D.S.; Brennecke, S.P.; Bessell, C.K.; Beischer, N.A. Factors identified during the neonatal period associated with risk of cerebral palsy. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2004, 44, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, U.; Gray, P.H.; O’Callaghan, M.J. Neonatal antecedents for cerebral palsy in extremely preterm babies and interaction with maternal factors. Early Hum. Dev. 2005, 81, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grether, J.K.; Nelson, K.B.; Emery, E.S., 3rd; Cummins, S.K. Prenatal and perinatal factors and cerebral palsy in very low birth weight infants. J. Pediatr. 1996, 128, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvanand, S.; Kapoor, S.K.; Reddaiah, V.P.; Singh, U.; Sundaram, K.R. Risk factors for cerebral palsy. Indian J. Pediatr. 1997, 64, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, B.; Hagberg, G. Antenatal risk factors for cerebral palsy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2004, 18, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.W. Review of cerebral palsy. Part 1: Description, incidence, and etiology. Neonatal Netw. 1997, 16, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg, B.; Hagberg, G.; Beckung, E.; Uvebrant, P. The changing panorama of cerebral palsy in Sweden. VIII. Prevalence and origin in the birth-year period 1991–1994. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelman, K.; Hagberg, G.; Beckung, E.; Hagberg, B.; Uvebrant, P. The changing panorama of cerebral palsy in Sweden. IX. Prevalence and origin in the birth-year period 1995–1998. Acta Paediatr. 2005, 94, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelmann, K.; McManus, V.; Hagberg, G.; Uvebrant, P.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Cans, C. SCPE Collaboration. Dyskinetic cerebral palsy in Europe: Trends in prevalence and severity. Arch. Dis. Child 2009, 94, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krägeloh-Mann, I. Imaging of early brain injury and cortical plasticity. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 190, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Hagberg, G.; Meisner, C.; Haas, G.; Eeg-Olofsson, K.E.; Selbmann, H.K.; Hagberg, B.; Michaelis, R. Bilateral spastic cerebral palsy—A collaborative study between southwest Germany and western Sweden. III: Aetiology. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1995, 37, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.; Rosenbaum, P. The gross motor function classification system for cerebral palsy: A study of reliability and stability over time. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2000, 42, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorter, J.W.; Rosenbaum, P.L.; Hanna, S.E.; Palisano, R.J.; Bartlett, D.J.; Russell, D.J.; Walter, S.D.; Raina, P.; Galuppi, B.E.; Wood, E. Limb distribution, motor impairment, and functional classification of cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2004, 46, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Novak, I.; Hines, M.; Goldsmith, S.; Barclay, R. Clinical prognostic messages from a systematic review on cerebral palsy. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1285–e1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin Foo, R.; Guppy, M.; Johnston, L.M. Intelligence assessments for children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehrawat, N.; Marwaha, M.; Bansal, K.; Chopra, R. Cerebral palsy: A dental update. Int. J. Chin. Pediatr. Dent. 2014, 7, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, A.O.L.; Guimarães, A.S.; Ciamponi, A.L.; Marie, S.K.N. Frequency of parafunctional oral habits in patients with cerebral palsy. J. Oral Rehabil. 2007, 34, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.E.; Avery, D.R.; Dean, J.A. (Eds.) McDonald and Avery’s Dentistry for the Child and Adolescent, 9th ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.P.; Schodel, D.R. A review of controlled surveys of dental disease in handicapped persons. ASDC J. Dent. Child 1976, 43, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ariya, C.; Totoki, H.; Tohara, H. Dysphagia in a persistently vegetative patient improved by orthodontic treatment of severe dental misalignment. Spec. Care Dent. 2021, 41, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modha, B. Global Developmental Delay and Its Considerations in Paediatric Dental Care—A Case Report. Oral 2021, 1, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotagal, S.; Gibbons, V.P.; Stith, J.A. Sleep abnormalities in patients with severe cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1994, 36, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Management of the developing dentition and occlusion in pediatric dentistry. In The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry; American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry: Chicago, IL, USA, 2021; pp. 408–425. [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Policy on obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry; American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry: Chicago, IL, USA, 2021; pp. 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Appleton, R.E.; Gupta, R. Cerebral palsy: Not always what it seems. Arch. Dis. Child 2019, 85, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santilli, M.; Manciocchi, E.; D’Addazio, G.; Di Maria, E.; D’Attilio, M.; Femminella, B.; Sinjari, B. Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolkove, N.; Baltzan, M.; Kamel, H.; Dabrusin, R.; Palayew, M. Long-term compliance with continuous positive airway pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Can. Respir. J. 2008, 15, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zozula, R.; Rosen, R. Compliance with continuous positive airway pressure therapy: Assessing and improving treatment outcomes. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2001, 7, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, K.; Phillips, C.L.; Cistulli, P.A. Efficacy versus effectiveness in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: CPAP and oral appliances. J. Dent. Sleep Med. 2015, 2, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Huang, Y.S.; Quo, S.; Monteyrol, P.J.; Lin, C.H. Teenage sleep-disordered breathing: Recurrence of syndrome. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Huang, Y.S.; Monteyrol, P.J.; Sato, R.; Quo, S.; Lin, C.H. Critical role of myofascial reeducation in pediatric sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeleira, M.T.; Outumuro, M.; Diniz, M.; Lucía García-Caballero, L.; Diz, P.; Limeres, J. Orthodontic Treatment in Children with Cerebral Palsy. In Cerebral Palsy-Current Steps; Gunel, M.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Napoli, J.A.; Drew, S.; Jaeger, T.C. Management of Skeletal Facial Deformation and Malocclusion in Cerebral Palsy. In Cerebral Palsy; Miller, F., Bachrach, S., Lennon, N., O’Neil, M.E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1105–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, R.; Guilleminault, C.; Herran, J.; Powell, N. Cephalometric analyses and flow-volume loop in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep 1983, 6, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A.Y.; Turkkahraman, H.; Yilmaz, H.H.; Yariktas, M. Cephalometric comparison of obstructive sleep apnea patients and healthy controls. Eur. J. Dent. 2013, 7, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Takada, T.; Matsuyama, N.; Sakai, K.; Yoshizawa, H.; Nakamata, M.; Satoh, M.; Akazawa, K.; Suzuki, E.; et al. Facial axis angle as a risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea. Intern. Med. 2005, 44, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pae, E.K.; Lowe, A.A.; Sasaki, K.; Price, C.; Tsuchiya, M.; Fleetham, J.A. A cephalometric and electromyographic study of upper airway structures in the upright and supine positions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1994, 106, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Higurashi, N.; Miyazaki, S.; Itasaka, Y. Facial patterns of obstructive sleep apnea patients using Ricketts’ method. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 54, 336–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamura, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yanagida, R.; Miyata, R.; Tohara, H. At-Home Orthodontic Treatment for Severe Teeth Arch Malalignment and Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in a Child with Cerebral Palsy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095333
Tamura A, Yamaguchi K, Yanagida R, Miyata R, Tohara H. At-Home Orthodontic Treatment for Severe Teeth Arch Malalignment and Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in a Child with Cerebral Palsy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(9):5333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095333
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamura, Atsuko, Kohei Yamaguchi, Ryosuke Yanagida, Rie Miyata, and Haruka Tohara. 2022. "At-Home Orthodontic Treatment for Severe Teeth Arch Malalignment and Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in a Child with Cerebral Palsy" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 9: 5333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095333
APA StyleTamura, A., Yamaguchi, K., Yanagida, R., Miyata, R., & Tohara, H. (2022). At-Home Orthodontic Treatment for Severe Teeth Arch Malalignment and Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in a Child with Cerebral Palsy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(9), 5333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095333






