Seasonal Dynamics of Bacterial Community Structure in Diesel Oil-Contaminated Soil Cultivated with Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Instrumental Analysis
2.4. Bacterial Community Structure Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seasonal Degradation Performance of TPH in Diesel-Contaminated Soil
3.2. Seasonal Dynamics of the Bacterial Community Structure
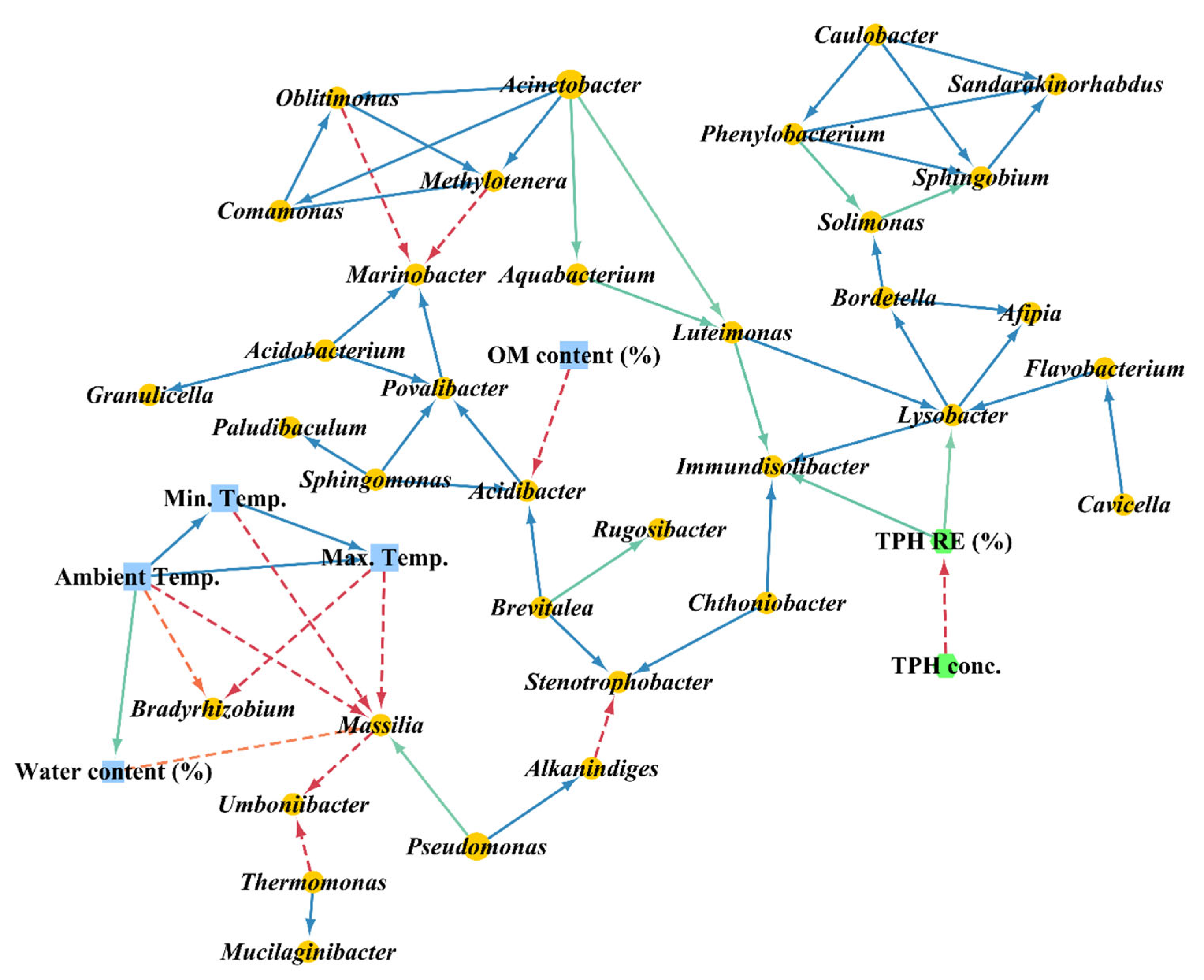
3.3. Extended Local Similarity Analysis (eLSA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ugochukwu, U.C.; Ochonogor, A.; Jidere, C.M.; Agu, C.; Nkoloagu, F.; Ewoh, J.; Okwu-Delunzu, V.U. Exposure risks to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by humans and livestock (cattle) due to hydrocarbon spill from petroleum products in Niger-delta wetland. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Mendelssohn, I.A. Potential of restoration and phytoremediation with Juncus roemerianus for diesel-contaminated coastal wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGenity, T.J. Hydrocarbon biodegradation in intertidal wetland sediments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruley, J.A.; Amoding, A.; Tumuhairwe, J.B.; Basamba, T.A.; Opolot, E.; Oryem-Origa, H. Enhancing the phytoremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils in the Sudd wetlands, South Sudan, using organic manure. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2020, 2020, 4614286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baldawi, I.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Anuar, N.; Suja, F.; Mushrifah, I. Phytodegradation of total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) in diesel-contaminated water using Scirpus grossus. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.C.; Wang, R.G.; Niu, X.W.; Wang, M.; Chu, H.R.; Zhou, Q.X. Characterisation of the rhizoremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil: Effect of different influencing factors. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 3961–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, R.C.; Powell, J.B.; Frakes, R.V. Historical development. In Tall Fescue, 1st ed.; Buckner, R.C., Bush, L.P., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Maidison, WI, USA, 1979; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, S.M.; Brewer, T.G.; Steiner, J.J. Thermal dependence of the apparent Km of glutathione reductase from three wetland grasses and maize. Ann. Bot. 2001, 87, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.-H.; Ji, K.-J.; An, Y.; Ro, H.-M. Soil salinity and vegetation distribution at four tidal reclamation project areas. Korean J. Environ. Agric. 2003, 22, 79–86, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.K.; Jung, Y.S.; Joo, Y.K.; Jung, H.G.; Chun, S.U.; Lee, S.H. Vegetation distribution and soil salinity on Daeho reclaimed tidal land of Kyonggi-bay in the mid-west coast of Korea. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2009, 42, 447–453, (In Korean with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Gong, H.; Guo, X. Rhizosphere bacterial community of Typha angustifolia L. and water quality in a river wetland supplied with reclaimed water. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, C.; Luo, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Nover, D. Effects of phytoremediation treatment on bacterial community structure and diversity in different petroleum-contaminated soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Franks, A.E. PGPR enhanced phytoremediation of petroleum contaminated soil and rhizosphere microbial community response. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Gong, Z.; Miao, R.; Su, D.; Li, X.; Jia, C.; Zhuang, J. The influence of root exudates of maize and soybean on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation and soil bacterial community structure. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-Y.; Seo, Y.; Ha, M.; Lee, J.; Yang, H.; Cho, K.-S. Evaluation of rhizoremediation and methane emission in diesel-contaminated soil cultivated with tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea). Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Ministry of Environment Korean Standard Soil Analysis Method, Revised in 2018. Available online: http://me.go.kr/home/web/law/read.do?pagerOffset=0&maxPageItems=10&maxIndexPages=10&searchKey=lawTitle&searchValue=%ED%86%A0%EC%96%91&menuId=71&orgCd=&condition.typeCode=admrul&typeCode=admrul&lawSeq=586 (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Korean Ministry of Environment Korean Standard Wastes Analysis Method, Revised in 2017. Available online: http://me.go.kr/home/web/law/read.do?pagerOffset=0&maxPageItems=10&maxIndexPages=10&searchKey=lawTitle&searchValue=%ED%8F%90%EA%B8%B0%EB%AC%BC&menuId=71&orgCd=&condition.typeCode=admrul&typeCode=admrul&lawSeq=1296 (accessed on 21 January 2022).
- Wu, L.; Wen, C.; Qin, Y.; Yin, H.; Tu, Q.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J. Phasing amplicon sequencing on Illumina Miseq for robust environmental microbial community analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the Miseq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R. UniFrac-an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.C.; Steele, J.A.; Cram, J.A.; Cardon, Z.G.; Simmons, S.L.; Vallino, J.J.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Sun, F. Extended local similarity analysis (eLSA) of microbial community and other time series data with replicates. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, S.M.; Smoot, M.; Cerami, E.; Kuchinsky, A.; Landys, N.; Workman, C.; Christmas, R.; Avila-campilo, I.; Creech, M.; Gross, B.; et al. Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2366–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baldawi, I.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Suja, F.; Anuar, N.; Mushrifah, I. Effect of aeration on hydrocarbon phytoremediation capability in pilot sub-surface flow constructed wetland operation. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 61, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberai, M.; Khanna, V. Rhizoremediation-Plant microbe interactions in the removal of pollutants. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.J.; Upasani, V.N. A new look on factors affecting microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 120, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, P.Y.; Johnson, R.L.; Xu, J.G. Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil as affected by heating and forced aeration. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steliga, T.; Kluk, D. Application of Festuca arundinacea in phytoremediation of soils contaminated with Pb, Ni, Cd and petroleum hydrocarbons. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ji, W.; Kang, D.M.; Kim, M.S. Effect of soil water content on heavy mineral oil biodegradation in soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghollahi, A.; Fazaelipoor, M.H.; Schaffie, M. The effect of soil type on the bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogbara, R.B.; Ayotamuno, J.M.; Worlu, D.C.; Fubara-Manuel, I. A case study of petroleum degradation in different soil textural classes. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2015, 9, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Park, W. Acinetobacter species as model microorganisms in environmental microbiology: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2533–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Baik, K.S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, S.C.; Kim, S.S.; Rhee, M.S.; Kwak, Y.S.; Seong, C.N. Acinetobacter soli sp. nov., isolated from forest soil. J. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizova, L.; Maixnerova, M.; Sedo, O.; Nemec, A. Acinetobacter bohemicus sp. nov. widespread in natural soil and water ecosystems in the Czech Republic. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, P.T.; Zhang, K.Y.; Ding, F.R. Isolation of biosurfactant producers, optimization and properties of biosurfactant produced by Acinetobacter sp. from petroleum-contaminated soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corteselli, E.M.; Aitken, M.D.; Singleton, D.R. Description of Immundisolibacter cernigliae gen. Nov., sp. nov., a high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium within the class Gammaproteobacteria, and proposal of Immundisolibacterales ord. nov. and Immundisolibacteraceae fam. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shaoping, K.; Zhiwei, D.; Bingchen, W.; Huihui, W.; Jialiang, L.; Hongbo, S. Changes of sensitive microbial community in oil polluted soil in the coastal area in Shandong, China for ecorestoration. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeszcz, J.; Kapusta, P.; Steliga, T. Hydrocarbon removal by two differently developed microbial inoculants and comparing their actions with biostimulation treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, S.; Xu, H. Abundance and diversity of Sphingomonas in Shenfu petroleum-wastewater irrigation zone, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Xu, H. Sphingomonas from petroleum-contaminated soils in Shenfu, China and their PAHs degradation abilities. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-de-Mora, A.; Engel, M.; Schloter, M. Abundance and diversity of n-alkane-degrading bacteria in a forest soil co-contaminated with hydrocarbons and metals: A molecular study on alkB homologous genes. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, S.; Yamamura, S.; Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Iwasaki, K. Diversity of alkane hydroxylase genes on the rhizoplane of grasses planted in petroleum-contaminated soils. Springerplus 2015, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Jagannadham, M.V.; Ray, M.K. Low-temperature-induced changes in composition and fluidity of lipopolysaccharides in the antarctic psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas syringae. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 6746–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Jing, L. Nitrate removal from low C/N wastewater at low temperature by immobilized Pseudomonas sp. Y39-6 with versatile nitrate metabolism pathways. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallwood, B.; Shears, J.; Williams, P.A.; Hughes, K.A. Low temperature bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil using biostimulation and bioaugmentation with a Pseudomonas sp. from maritime Antarctica. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xu, L.; Jia, L. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Pseudomonas sp. JM2 isolated from active sewage sludge of chemical plant. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, Z. Pseudomonas, the dominant polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from Antarctic soils and the role of large plasmids in horizontal gene transfer. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouseoud, M.; Maachi, R.; Amrane, A. Biosurfactant production from olive oil by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Commun. Curr. Res. Educ. Top. Trends Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 1, 340–347. [Google Scholar]
- Malavenda, R.; Rizzo, C.; Michaud, L.; Gerçe, B.; Bruni, V.; Syldatk, C.; Hausmann, R.; Giudice, A.L. Biosurfactant production by Arctic and Antarctic bacteria growing on hydrocarbons. Polar Biol. 2015, 38, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avontuur, J.R.; Palmer, M.; Beukes, C.W.; Chan, W.Y.; Coetzee, M.P.A.; Blom, J.; Stępkowski, T.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Woyke, T.; Shapiro, N.; et al. Genome-informed Bradyrhizobium taxonomy: Where to from here? Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 42, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Adhikari, D.; Itoh, K.; Suyama, K. Effects of temperature on competition and relative dominance of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium elkanii in the process of soybean nodulation. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Prithiviraj, B.; Charles, T.C.; Driscoll, B.T.; Smith, D.L. Low temperature tolerant Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains allowing improved nodulation and nitrogen fixation of soybean in a short season (cool spring) area. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lou, J.; Gu, H.; Luo, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Efficient biodegradation of phenanthrene by a novel strain Massilia sp. WF1 isolated from a PAH-contaminated soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13378–13388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.U.; Ka, J.O. Massilia aromaticivorans sp. nov., a BTEX degrading bacterium isolated from Arctic soil. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Shen, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, N.; Xing, T.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J. Massilia psychrophila sp. nov., isolated from an ice core. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4088–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescia, F.; Pertot, I.; Puopolo, G. Lysobacter. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology, 1st ed.; Amaresan, N., Kumar, M.S., Annapurna, K., Kumar, K., Sankaranarayanan, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 313–338. [Google Scholar]
- De La Cueva, S.C.; Rodríguez, C.H.; Cruz, N.O.S.; Contreras, J.A.R.; Miranda, J.L. Changes in bacterial populations during bioremediation of soil contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilaningsih, D.; Okazaki, F.; Yopi, Y.; Widyastuti, Y.; Harayama, S. Isolation and screening of surfactant-producing bacteria from Indonesian marine environments and its application on bioremediation. Ann. Bogor. 2013, 17, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
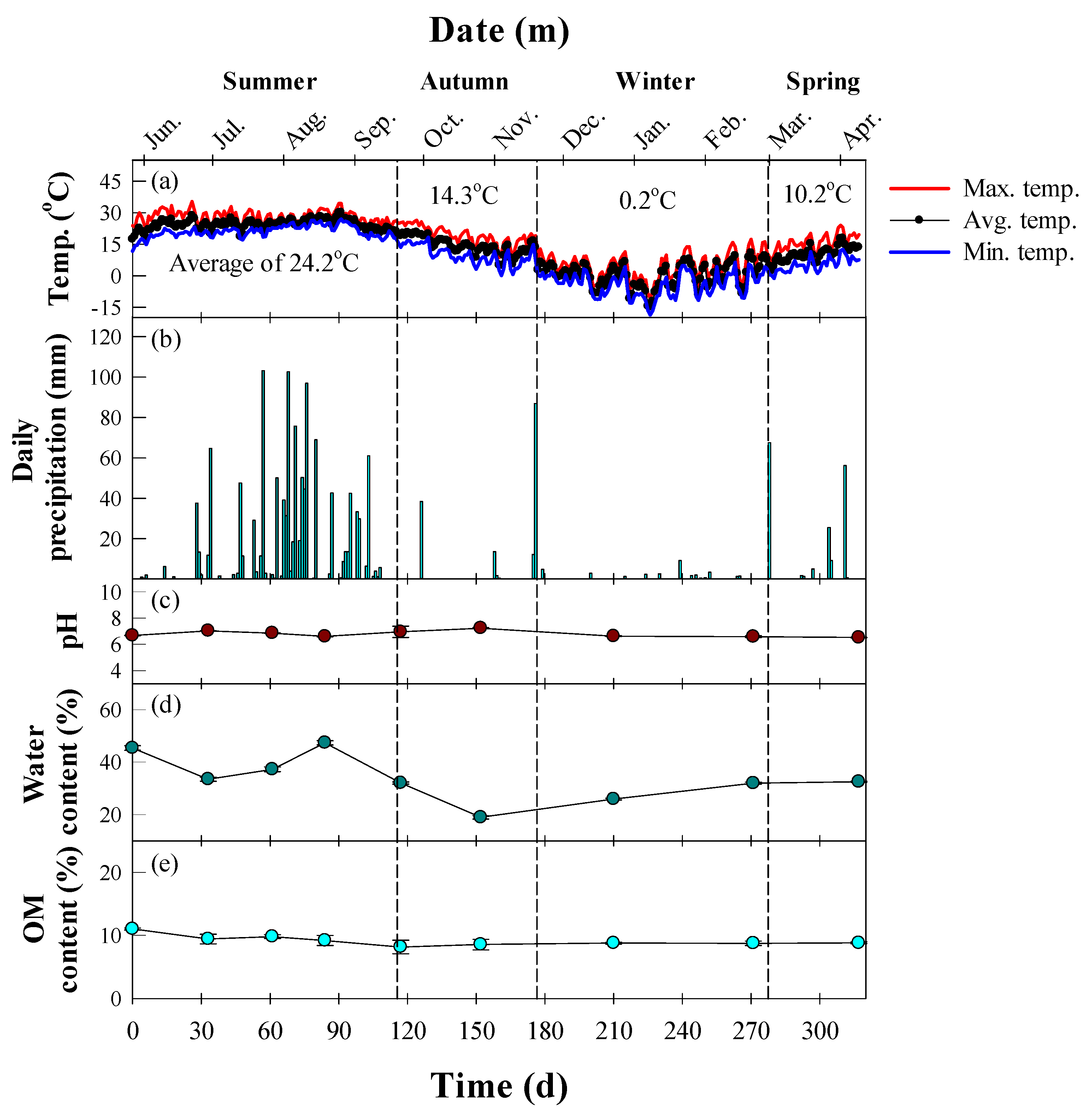
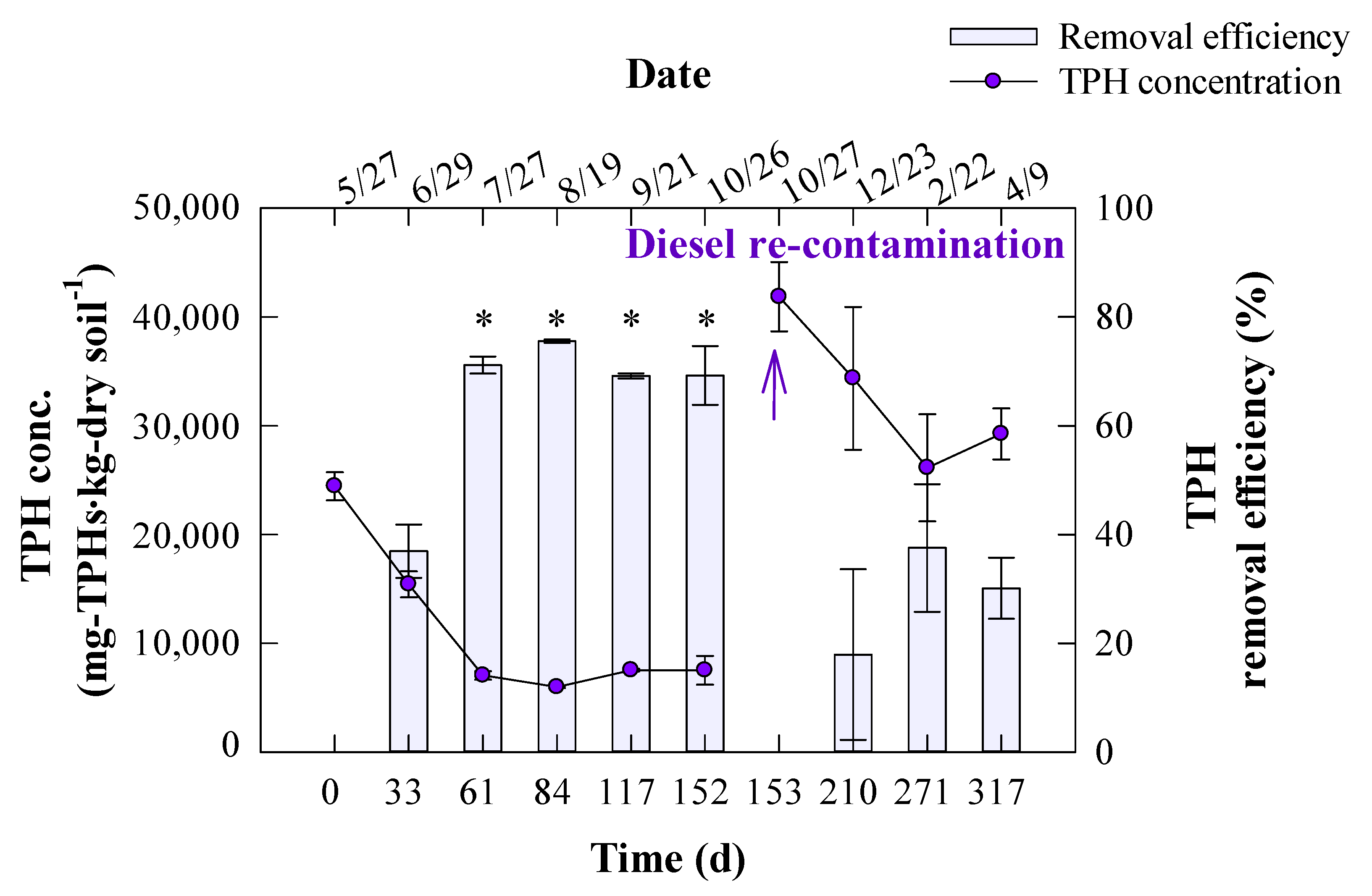
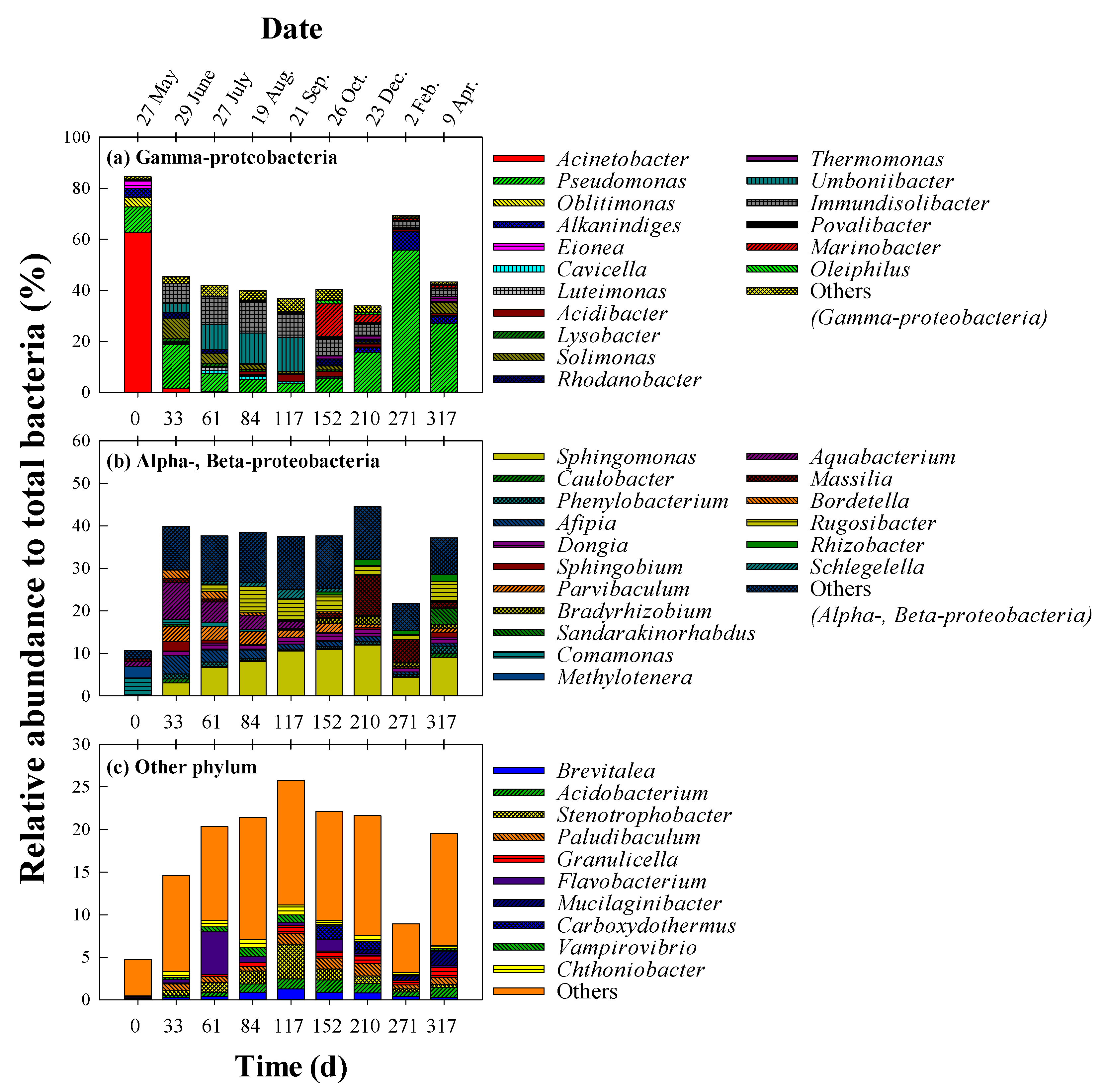
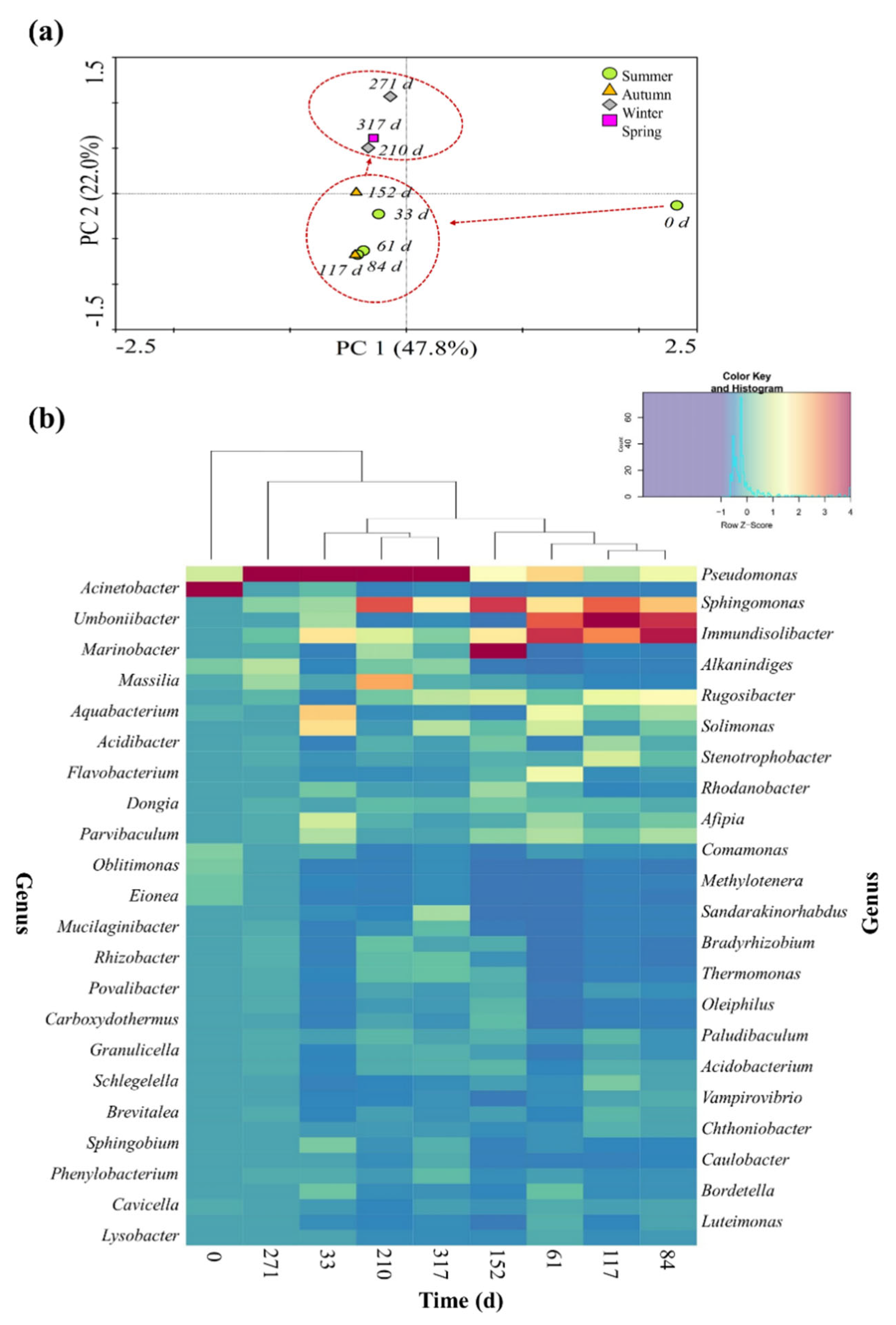
| Date | Sampling Time (d) | OTUs | Chao1 a | Shannon b | Inverse Simpson c | Good’s Coverage d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 May | 0 | 565 | 756.4 | 3.41 | 0.71 | 0.995 |
| 29 June | 33 | 970 | 1380.7 | 6.39 | 0.96 | 0.987 |
| 27 July | 61 | 538 | 830.3 | 5.20 | 0.89 | 0.972 |
| 19 August | 84 | 1383 | 1698.5 | 7.02 | 0.97 | 0.993 |
| 21 September | 117 | 901 | 1163.3 | 5.62 | 0.94 | 0.995 |
| 26 October | 152 | 788 | 794.9 | 7.58 | 0.98 | 1.000 |
| 23 December | 210 | 729 | 740.8 | 6.62 | 0.96 | 0.999 |
| 22 February | 271 | 744 | 752.1 | 6.71 | 0.95 | 0.999 |
| 9 April | 317 | 749 | 757.0 | 7.01 | 0.97 | 0.999 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.D.; Cho, K.-S. Seasonal Dynamics of Bacterial Community Structure in Diesel Oil-Contaminated Soil Cultivated with Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084629
Lee Y-Y, Lee SY, Lee SD, Cho K-S. Seasonal Dynamics of Bacterial Community Structure in Diesel Oil-Contaminated Soil Cultivated with Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(8):4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084629
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yun-Yeong, Soo Yeon Lee, Sang Don Lee, and Kyung-Suk Cho. 2022. "Seasonal Dynamics of Bacterial Community Structure in Diesel Oil-Contaminated Soil Cultivated with Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 8: 4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084629
APA StyleLee, Y.-Y., Lee, S. Y., Lee, S. D., & Cho, K.-S. (2022). Seasonal Dynamics of Bacterial Community Structure in Diesel Oil-Contaminated Soil Cultivated with Tall Fescue (Festuca arundinacea). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(8), 4629. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19084629








