Factors Associated with Undertaking Health-Promoting Activities by Older Women at High Risk of Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Participants
2.4. Measurement
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
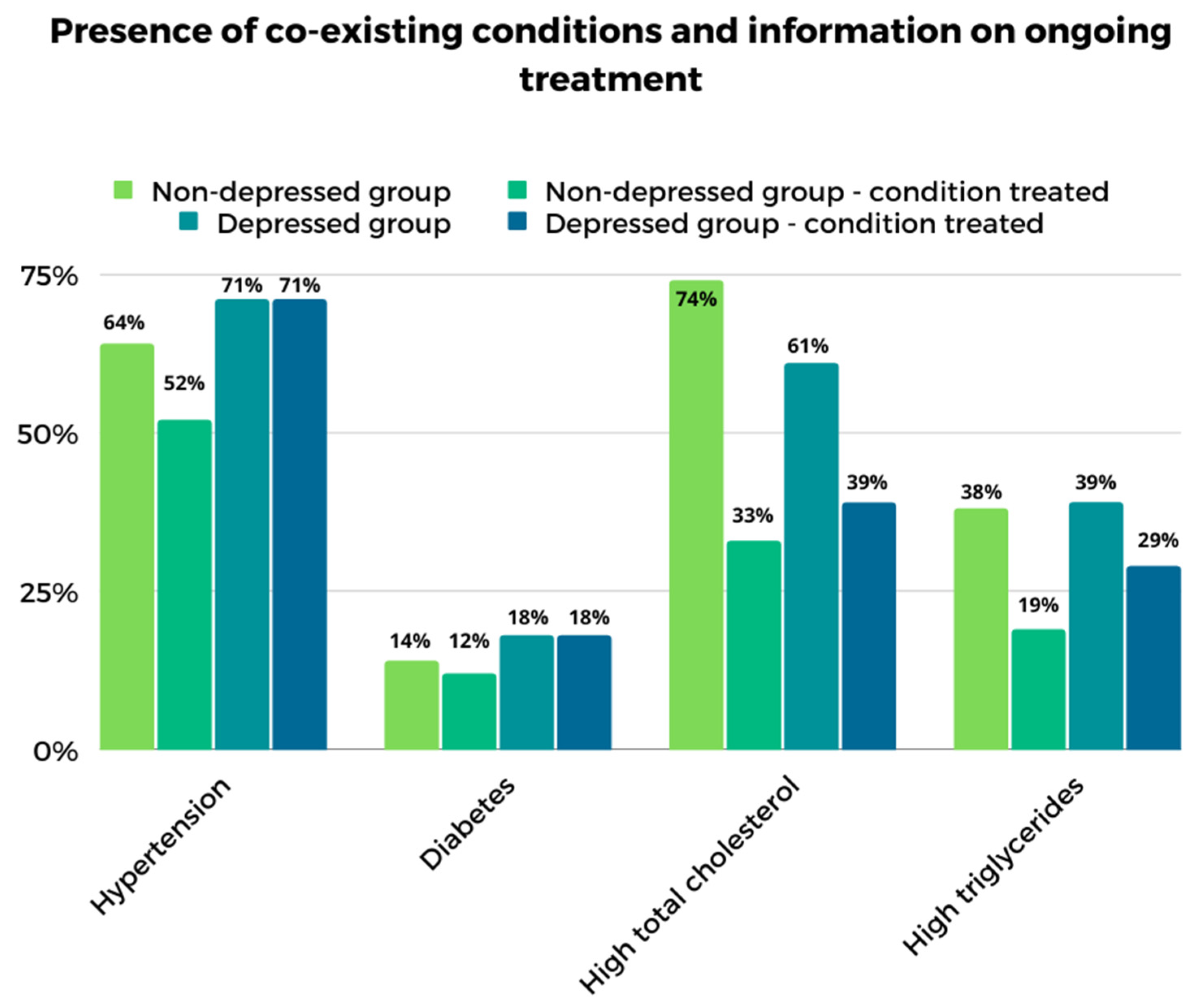
3.1. Sociodemographic and Clinical Data
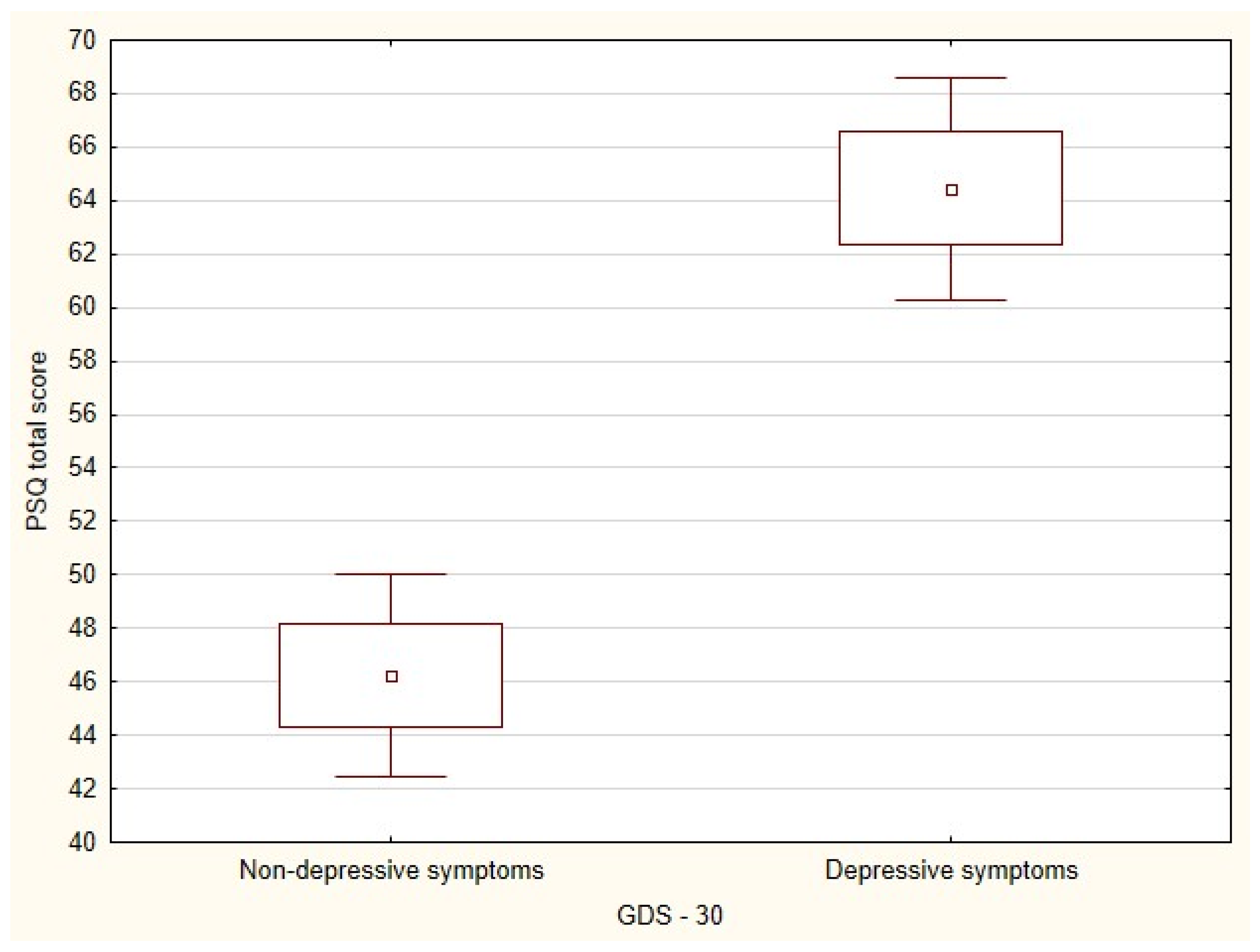
3.2. GDS-30 and PSQ
3.3. Analysis of Groups with and without Depressive Symptoms
3.4. Motivations and Problems Related to Maintaining Good Health and Physical in the D and ND Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kunkel, S.; Brown, J.S.; Whittington, F.J.; Chahal, J. (Eds.) Global Aging: Comparative Perspectives on Aging and the Life Course; Springer Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Ageing and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- World Health Organization; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; National Institute on Aging; National Institutes of Health. Global Health and Aging; 2011; pp. 1–32. Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/sites/default/files/2017-06/global_health_aging.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- Murray, C.J.L.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Zheng, P.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; et al. Global Burden of 87 Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abolhassani, H.; Abreu, L.G.; Abrigo, M.R.M.; et al. Global Age-Sex-Specific Fertility, Mortality, Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE), and Population Estimates in 204 Countries and Territories, 1950–2019: A Comprehensive Demographic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1160–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, S.; Paneni, F.; Cosentino, F. Ageing, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Ageing. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadini, G.P.; Ceolotto, G.; Pagnin, E.; de Kreutzenberg, S.; Avogaro, A. At the Crossroads of Longevity and Metabolism: The Metabolic Syndrome and Lifespan Determinant Pathways: Longevity Pathways and Metabolic Syndrome. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, M.R.A.; Nawi, A.M.; Tauhid, N.M.; Othman, H.; Rahman, M.R.A.; Yusoff, H.M.; Safian, N.; Ng, P.Y.; Manaf, Z.A.; Kadir, N.B.A.; et al. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Associated Risk Factors among Staffs in a Malaysian Public University. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.Z. Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Provisional Report of a WHO Consultation. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornier, M.-A.; Dabelea, D.; Hernandez, T.L.; Lindstrom, R.C.; Steig, A.J.; Stob, N.R.; Van Pelt, R.E.; Wang, H.; Eckel, R.H. The Metabolic Syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 777–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sygnowska, E.; Piwońska, A.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Broda, G. Socioeconomic Factors and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in the Adult Polish Population: The WOBASZ Study. Kardiol. Pol. 2012, 70, 718–727. [Google Scholar]
- Tune, J.D.; Goodwill, A.G.; Sassoon, D.J.; Mather, K.J. Cardiovascular Consequences of Metabolic Syndrome. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.; Azevedo, I. Chronic Inflammation in Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, L.S.; Mechanick, J.I.; Neeland, I.J.; Herrick, C.J.; Després, J.-P.; Ndumele, C.E.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Handelsman, Y.; Puckrein, G.A.; Araneta, M.R.G.; et al. The CardioMetabolic Health Alliance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1050–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliga, E.; Cieśla, E.; Rębak, D.; Kozieł, D.; Głuszek, S. Relationship Between Sitting Time, Physical Activity, and Metabolic Syndrome Among Adults Depending on Body Mass Index (BMI). Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 7633–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świątkiewicz, I.; Woźniak, A.; Taub, P.R. Time-Restricted Eating and Metabolic Syndrome: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Nutrients 2021, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; So, W.-Y. Lifestyle-Related Factors and Their Association with Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults: A Population-Based Study. J. Phys. Sci. 2015, 27, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slanovic-Kuzmanović, Z.; Kos, I.; Domijan, A.-M. Endocrine, Lifestyle, and Genetic Factors in the Development of Metabolic Syndrome. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martínez, P.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Athyros, V.G.; Bullo, M.; Couture, P.; Covas, M.I.; de Koning, L.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Drevon, C.A.; et al. Lifestyle Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Syndrome: An International Panel Recommendation. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliga, E.; Kozieł, D.; Cieśla, E.; Rębak, D.; Głuszek, S. Dietary Patterns in Relation to Metabolic Syndrome among Adults in Poland: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, B.; Dashti, H.S.; Gómez-Abellán, P.; Hernández-Martínez, A.M.; Esteban, A.; Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Saxena, R.; Garaulet, M. Modifiable Lifestyle Behaviors, but Not a Genetic Risk Score, Associate with Metabolic Syndrome in Evening Chronotypes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.; Kokkinos, P.; Nyelin, E. Physical Activity, Cardiorespiratory Fitness, and the Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability for 301 Acute and Chronic Diseases and Injuries in 188 Countries, 1990–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzechowska, A.; Zajączkowska, M.; Talarowska, M.; Gałecki, P. Depression and Ways of Coping with Stress: A Preliminary Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2013, 19, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.; Steffens, D.C. What Are the Causes of Late-Life Depression? Psychiatr. Clin. North. Am. 2013, 36, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, C.A.; Reynolds-III, C.F. Late-Life Depression in the Primary Care Setting: Challenges, Collaborative Care, and Prevention. Maturitas 2014, 79, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszyńska, M.; Jaworska-Burzyńska, L.; Szczepańska-Gieracha, J. Severity of depressive symptoms in women over 60 who undertake regular physical exercise and health-seeking activities. Contemp. Gerontol. 2017, 5, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, G.L. The Clinical Application of the Biopsychosocial Model. AJP 1980, 137, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepańska-Gieracha, J.; Mazurek, J.; Serweta, A.; Boroń-Krupińska, K.; Kowalska, J.; Skrzek, A. Effectiveness Assessment of a Therapeutic Programme for Women with Overweight and Obesity: A Biopsychosocial Perspective. Fmpcr 2019, 21, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnanto, H.; Agustian, D.; Hilmanto, D. Biopsychosocial Model of Illnesses in Primary Care: A Hermeneutic Literature Review. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2018, 7, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchegoyen, M.; Nobile, M.H.; Baez, F.; Posesorski, B.; González, J.; Lago, N.; Milei, J.; Otero-Losada, M. Metabolic Syndrome and Neuroprotection. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.P.; Ramadas, A.; Fatt, Q.K.; Shin, H.L.; Onn, W.Y.; Kadir, K.A. Relationship of Sociodemographic and Lifestyle Factors and Diet Habits with Metabolic Syndrome (MetS) among Three Ethnic Groups of the Malaysian Population. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0224054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, Y.; Rajaa, S.; Murali, S.; Sahoo, J.; Kar, S.S. Association between Behavioural Risk Factors and Metabolic Syndrome among Adult Population in India: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Moura, A.R.; da Paz, S.M.R.S.; de Macêdo Gonçalves Frota, K.; de Carvalho, C.M.R.G. Lifestyle Associated with Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults and the Elderly. Nutrition 2022, 99–100, 111647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasens, E.R.; Imes, C.C.; Kariuki, J.K.; Luyster, F.S.; Morris, J.L.; DiNardo, M.M.; Godzik, C.M.; Jeon, B.; Yang, K. Sleep and Metabolic Syndrome. Nurs. Clin. North Am. 2021, 56, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morga, P.; Cieślik, B.; Sekułowicz, M.; Bujnowska-Fedak, M.; Drower, I.; Szczepańska-Gieracha, J. Low-Intensity Exercise as a Modifier of Depressive Symptoms and Self-Perceived Stress Level in Women with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2021, 20, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusowicz, J.; Serweta, A.; Idzikowski, W.; Szczepańska-Gieracha, J. Multimodal Therapeutic Approach in Women with High Risk of Metabolic Syndrome—A Single Group One Center Pre-Post Study. JCM 2021, 10, 4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszko, K.; Serweta, A.; Cieślik, B.; Idzikowski, W.; Szczepańska-Gieracha, J.; Gajda, R. Remote Support of Elderly Women Participating in Mental Health Promotion Programme during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Single-Group Longitudinal Intervention. IJERPH 2022, 19, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic Syndrome-a New World-Wide Definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. The IDF Consensus Worldwide Definition of the Metabolic Syndrome; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Folstein, M.F. The Mini-Mental State Examination. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1983, 40, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykarski, A.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K.; Kokoszka-Paszkot, J.; Kusz-Rynkun, A.; Rymaszewska, J.; Bujnowska-Fedak, M.; Neumann-Podczaska, A.; Bień, B.; Siebert, J.; et al. REcomMEndations for DIAgnostics and maNagemenT of arterial hypertension in adults aged 65 years and older for General Practitioners—REMEDIA NT 65 + GP. Arter. Hypertens. 2018, 22, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesavage, J.A. Geriatric Depression Scale. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 1988, 24, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albiński, R.; Kleszczewska-Albińska, A.; Bedyńska, S. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS). Validity and reliability of different versions of the scale--review. Psychiatr. Pol. 2011, 45, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yesavage, J.A.; Sheikh, J.I. 9/Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS): Recent Evidence and Development of a Shorter Version. Clin. Gerontol. 1986, 5, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plopa, M.; Makarowski, R. Perceived Stress Questionnaire: Handbook; Vizja Press & IT: Warszawa, Poland, 2010; ISBN 978-83-61086-79-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yarmohammadi, S.; Mozafar Saadati, H.; Ghaffari, M.; Ramezankhani, A. A Systematic Review of Barriers and Motivators to Physical Activity in Elderly Adults in Iran and Worldwide. Epidemiol. Health 2019, 41, e2019049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosma, M.; Buchanan, D.; Hondzinski, J. Complexity of Exercise Behavior Among Older African American Women. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2017, 25, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Rosenbaum, S.; Stubbs, B.; Gorczynski, P.; Yung, A.R.; Vancampfort, D. Motivating Factors and Barriers towards Exercise in Severe Mental Illness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2016, 46, 2869–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, A.E.; Laditka, S.B.; Laditka, J.N.; Wilcox, S.; Corwin, S.J.; Liu, R.; Friedman, D.B.; Hunter, R.; Tseng, W.; Logsdon, R.G. Older Adults’ Perceived Physical Activity Enablers and Barriers: A Multicultural Perspective. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2010, 18, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Park, K.-Y.; Hwang, H.-S.; Park, H.-K. Association between Type and Intensity of Physical Activity and Depression. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2022, 43, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, A.; Ashdown-Franks, G.; Hendrikse, J.; Sabiston, C.M.; Stubbs, B. Physical Activity and Depression: Towards Understanding the Antidepressant Mechanisms of Physical Activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, R.M.; Reynolds, C.F. Management of Depression in Older Adults: A Review. JAMA 2017, 317, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumba, M.N.; Nacarrow, A.F.; Cody, S.; Key, B.A.; Wang, H.; Robb, M.; Jurczyk, A.; Ford, C.; Kelley, M.A.; Allen, R.S. Intensity and Type of Physical Activity Predicts Depression in Older Adults. Aging Ment. Health 2021, 25, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teychenne, M.; Ball, K.; Salmon, J. Physical Activity and Likelihood of Depression in Adults: A Review. Prev. Med. 2008, 46, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Mooney, S.J.; Kennedy, G.J.; Benjamin, E.O.; Ompad, D.; Rundle, A.G.; Beard, J.R.; Cerdá, M. Beyond METs: Types of Physical Activity and Depression among Older Adults. Age Ageing 2016, 45, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Daniele, N.; Noce, A.; Vidiri, M.F.; Moriconi, E.; Marrone, G.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; D’Urso, G.; Tesauro, M.; Rovella, V.; De Lorenzo, A. Impact of Mediterranean Diet on Metabolic Syndrome, Cancer and Longevity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8947–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.K.; Zinman, B.; Retnakaran, R. Are Metabolically Healthy Overweight and Obesity Benign Conditions?: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, K.; Radziłłowicz, P.; Zdrojewski, T.; Pakalska-Korcala, A.; Chwojnicki, K.; Piwoński, J.; Ignaszewska-Wyrzykowska, A.; Załuga, L.; Mielczarek, M.; Landowski, J.; et al. Relationship between the Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms and Metabolic Syndrome. Results of the SOPKARD Project. Kardiol. Pol. 2006, 64, 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Malmir, H.; Mirzababaei, A.; Moradi, S.; Rezaei, S.; Mirzaei, K.; Dadfarma, A. Metabolically Healthy Status and BMI in Relation to Depression: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Simmons, W.K.; van Rossum, E.F.C.; Penninx, B.W. Depression and Obesity: Evidence of Shared Biological Mechanisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheshlagh, R.G.; Parizad, N.; Sayehmiri, K. The Relationship between Depression and Metabolic Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2016, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repousi, N.; Masana, M.F.; Sanchez-Niubo, A.; Haro, J.M.; Tyrovolas, S. Depression and Metabolic Syndrome in the Older Population: A Review of Evidence. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 237, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Agarwal, M.; Garg, K.; Dalal, P.; Trivedi, J.; Srivastava, J. Metabolic Syndrome and Central Obesity in Depression: A Cross-Sectional Study. Indian J. Psychiatry 2016, 58, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzami, K.; Lima, B.B.; Sullivan, S.; Shah, A.; Bremner, J.D.; Vaccarino, V. Independent and Joint Association of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome with Depression and Inflammation. Health Psychol. 2019, 38, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, Y.; Albatineh, A.N.; Mahmoodi, H.; Gheshlagh, R.G. The Relationship between Depression and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-analysis of Observational Studies. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, A.; Hashemi, M.; Hosseini, S.R.; Omidvar, S.; Bijani, A.; Khairkhah, F. The Relationship between Depression and Metabolic Syndrome in the Elderly Population: The Cohort Aging Study. Iran. J. Psychiatry 2018, 13, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rochlani, Y.; Pothineni, N.V.; Kovelamudi, S.; Mehta, J.L. Metabolic Syndrome: Pathophysiology, Management, and Modulation by Natural Compounds. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuk, J.L.; Ardern, C.I. Age and Sex Differences in the Clustering of Metabolic Syndrome Factors. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2457–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, X.Q.; Ma, W.J.; Sobko, T.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, Y.J.; Xu, X.J.; Yu, D.M.; Nie, S.P.; Cai, Q.M.; Wei, X.L.; et al. Dramatic Escalation in Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Risk in a Chinese Population Experiencing Rapid Economic Development. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Qi, J.; Ma, W.; Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, M. SUMO4 Gene SNP Rs237025 and the Synergistic Effect With Weight Management: A Study of Risk Factors and Interventions for MetS. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 786393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.L.; Bauman, A.; Owen, N. Perceived Barriers to Physical Activity among Older Australians. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2002, 10, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.H.; Sadarangani, T.; Wyatt, L.C.; Zanowiak, J.M.; Kwon, S.C.; Trinh-Shevrin, C.; Lee, L.; Islam, N.S. Correlates of Physical Activity Among Middle-Aged and Older Korean Americans at Risk for Diabetes: Physical Activity Among Older Koreans. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2016, 48, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichler, C.S.; Niedermeier, M.; Gufler, A.; Gálffy, M.; Sperner-Unterweger, B.; Kopp, M. A Case-Control Study on Physical Activity Preferences, Motives, and Barriers in Patients with Psychiatric Conditions. Compr. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 152276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantu, A.G.; Fleuriet, J.K. The Sociocultural Context of Physical Activity in Older Mexican American Women. Hisp. Health Care Int. 2008, 6, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, P.; Luo, S.; Zhang, G.; Tang, X.; Liu, L. The Association of Quality of Life and Personality Characteristics with Adolescent Metabolic Syndrome: A Cohort Study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2021, 19, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommersteeg, P.M.C.; Pouwer, F. Personality as a Risk Factor for the Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2012, 73, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, K.; Broom, D.; Hassan Bekhet, A.; Xerri de Caro, J.; Laventure, B.; Grafton, K. Barriers and Motivators of Physical Activity Participation in Middle-Aged and Older Adults—A Systematic Review. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2019, 27, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassou, A.C.N.; Fermino, R.; Añez, C.R.R.; Santos, M.S.; Domingues, M.R.; Reis, R.S. Barriers to Physical Activity among Brazilian Elderly Women from Different Socioeconomic Status: A Focus-Group Study. J. Phys. Act. Health 2011, 8, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.; Brown, P.R. Motivators, Facilitators, and Barriers to Physical Activity in Older Adults: A Qualitative Study. Holist. Nurs. Pract. 2017, 31, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoveling, L.A.; Liefbroer, A.C.; Bültmann, U.; Smidt, N. Understanding Socioeconomic Differences in Metabolic Syndrome Remission among Adults: What Is the Mediating Role of Health Behaviors? Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassou, C.; Georgousopoulou, E.N.; Chrysohoou, C.; Yannakoulia, M.; Pitsavos, C.; Cropley, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Psychological Factors in Relation to the 10-Year Incidence of Metabolic Syndrome: The ATTICA Epidemiological Study (2002–2012). Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadzir, M.D.A.; Quek, K.F.; Ramadas, A. Group-Based Lifestyle Intervention Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: A Scoping Review and Strategic Framework for Future Research. Medicina 2021, 57, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, A.; Kitzman, H.; Dodgen, L. Reducing Metabolic Syndrome through a Community-Based Lifestyle Intervention in African American Women. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jou, H.-J.; Hsu, I.-P.; Huang, H.-T.; Liu, I.-L.; Chien, P.-L.; Li, I.-C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, S.-M. A Hospital-Based Therapeutic Lifestyle Program for Women with Metabolic Syndrome. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 49, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mattina, A.; Argano, C.; Brunori, G.; Lupo, U.; Raspanti, M.; Lo Monaco, M.; Bocchio, R.M.; Natoli, G.; Giusti, M.A.; Corrao, S. Clinical Complexity and Diabetes: A Multidimensional Approach for the Management of Cardiorenal Metabolic Syndrome. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.X.; Gurka, M.J.; Deboer, M.D. Metabolic Syndrome Severity and Lifestyle Factors among Adolescents. Minerva Pediatr. 2018, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saboya, P.P.; Bodanese, L.C.; Zimmermann, P.R.; Gustavo, A.d.S.; Macagnan, F.E.; Feoli, A.P.; da Silva Oliveira, M. Lifestyle Intervention on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Impact on Quality of Life: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2016, 108, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ND (n = 42) | D (n = 28) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | Range | |
| Age (years) | 70.1 ± 4.73 | 62–83 | 71.0 ± 5.66 | 63–84 |
| Weight (kg) | 75.1 ± 13.16 | 43.9–102.0 | 75.6 ± 19.96 | 44.4–135.9 |
| Height (m) | 1.59 ± 0.06 | 1.47–1.71 | 1.61 ± 0.07 | 1.47–1.74 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.65 ± 4.89 | 19.25–39.94 | 29.03 ± 5.39 | 18.0–47.58 |
| Waist ratio (cm) | 95.9 ± 9.13 | 78–130 | 94.1 ± 12.64 | 61.0–120.0 |
| Body weight classification | n | % | n | % |
| Normal weight | 7 | 17 | 5 | 18 |
| Overweight | 19 | 45 | 13 | 46.3 |
| Class I obesity | 9 | 21 | 8 | 28.5 |
| Class II obesity | 7 | 17 | 1 | 3.6 |
| Class III obesity | - | - | 1 | 3.6 |
| Education | ||||
| Basic/vocational | 5 | 12 | 4 | 14 |
| Secondary | 21 | 50 | 16 | 57 |
| Higher education | 16 | 38 | 8 | 29 |
| Marital status of the subject | ||||
| Married | 19 | 45 | 11 | 39 |
| Single | 6 | 14 | 5 | 18 |
| Divorced | 3 | 7 | 2 | 7 |
| Widow | 14 | 34 | 10 | 36 |
| ND (n = 42) | D (n = 28) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | Mean ± SD | Range | |
| Blood pressure [mmHg] | ||||
| Systolic | 134.17 ± 19.73 | 90–186 | 135.4 ± 21.38 | 110–198 |
| Diastolic | 76.98 ± 10.51 | 56–114 | 74.1 ± 8.62 | 59–88 |
| Cholesterol [mg/dL] | ||||
| Total | 221.16 ± 45.96 | 138–342 | 192.48 ± 35.88 | 132–265 |
| HDL | 71.86 ± 13.16 | 44.0–183.0 | 63.56 ± 22.40 | 42.0–154.0 |
| LDL | 123.5 ± 40.50 | 70.0–238.0 | 111.3 ± 36.86 | 42.0–203.0 |
| Triglycerides [mg/dL] | 128.3 ± 48.56 | 52.0–293.0 | 124.2 ± 52.18 | 48.0–253.0 |
| Blood sugar level [mg%] | 102.5 ± 18.96 | 60.0–167.0 | 101.0 ± 14.70 | 78.0–140.0 |
| Feature | ND Group, n = 42 (%) | D Group, n = 28 (%) | U | Z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 70.1 ± 4.73 | 71.0 ± 5.66 | 518.00 | −0.99 | 0.32 | |
| Education | Basic/vocational | 14.29% | 11.63% | 558.00 | 0.57 | 0.60 |
| Secondary | 57.14% | 53.49% | ||||
| Higher education | 28.57% | 34.88% | ||||
| Marital status | Married | 42.86% | 46.51% | 574.00 | −0.32 | 0.74 |
| Single | 14.29% | 16.28% | ||||
| Divorced | 35.71% | 32.56% | ||||
| Widowed | 35.71% | 32.56% | ||||
| Stress Components | Rank Sum ND Group | Rank Sum D Group | U | Z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional tension | 1142.0 | 1414.0 | 196.0 | −4.77 | >0.0001 * |
| External stress | 1259.5 | 1296.5 | 313.5 | −3.38 | 0.0007 * |
| Intrapsychic stress | 1252.0 | 1304.0 | 306.0 | −3.48 | 0.0005 * |
| General PSQ score | 1165.5 | 1390.5 | 219.5 | −4.49 | >0.0001 * |
| Type | ND Group | D Group | Pearson’s χ2 | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improving/maintaining physical condition | 73.8% | 85.7% | 1.414 | 1 | 0.234 |
| Improving health | 52.3% | 60.7% | 0.473 | 1 | 0.491 |
| Improving well-being | 50% | 60.7% | 0.777 | 1 | 0.378 |
| Improving appearance/preventing obesity | 45% | 50% | 0.153 | 1 | 0.696 |
| Willingness to spend time with other people | 45% | 21% | 4.148 | 1 | 0.042 * |
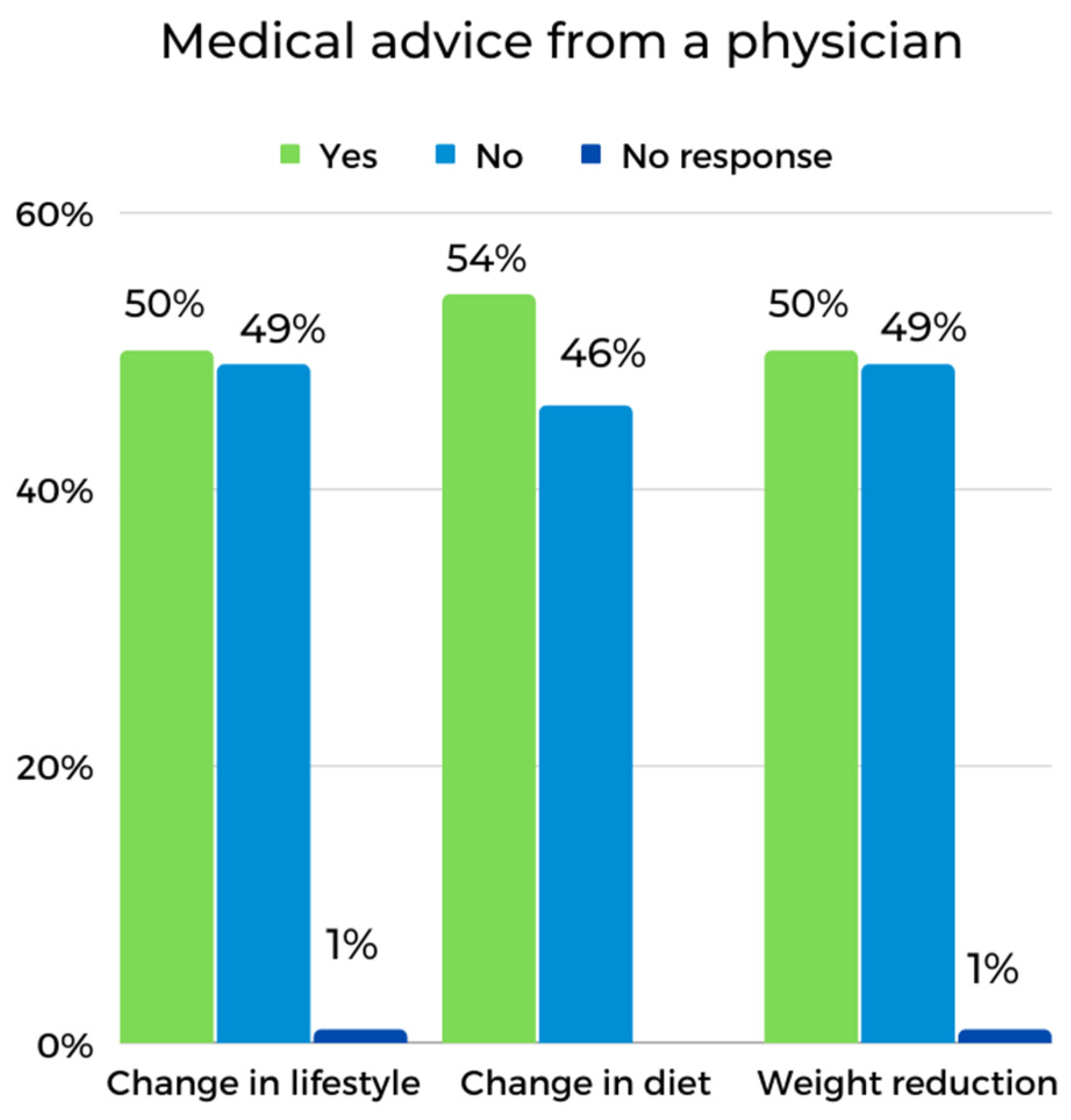
| Receiving medical advice (primary care physician) | 11.9% | 7.1% | Two-sided Fisher’s test | 0.694 | |
| Lack of motivation | 38.1% | 46.4% | 0.481 | 1 | 0.488 |
| Lack of time | 14.3% | 46.4% | 8.777 | 1 | 0.003 * |
| Lack of opportunity to participate | 21.4% | 21.4% | 0.000 | 1 | 0.100 |
| Lack of money | 11.9% | 25% | 2.028 | 1 | 0.154 |
| Poor health | 16.7% | 7.1% | Two-sided Fisher’s test | 0.299 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusowicz, J.; Serweta, A.; Juszko, K.; Idzikowski, W.; Gajda, R.; Szczepańska-Gieracha, J. Factors Associated with Undertaking Health-Promoting Activities by Older Women at High Risk of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315957
Rusowicz J, Serweta A, Juszko K, Idzikowski W, Gajda R, Szczepańska-Gieracha J. Factors Associated with Undertaking Health-Promoting Activities by Older Women at High Risk of Metabolic Syndrome. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(23):15957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315957
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusowicz, Jagoda, Anna Serweta, Karolina Juszko, Wojciech Idzikowski, Robert Gajda, and Joanna Szczepańska-Gieracha. 2022. "Factors Associated with Undertaking Health-Promoting Activities by Older Women at High Risk of Metabolic Syndrome" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 23: 15957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315957
APA StyleRusowicz, J., Serweta, A., Juszko, K., Idzikowski, W., Gajda, R., & Szczepańska-Gieracha, J. (2022). Factors Associated with Undertaking Health-Promoting Activities by Older Women at High Risk of Metabolic Syndrome. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(23), 15957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315957









