Abstract
A systematic literature review was conducted to investigate which objective noise indicators related to various noise sources (i.e., aircraft, road-traffic, and ambient noise) are the best predictors of non-auditory health-effects in children. These relationships are discussed via a conceptual framework, taking into account main parameters such as the type of noise source, the exposure locations and their environments, the type of noise indicators, the children’s mediating factors, and the type of non-auditory health effects. In terms of the procedure, four literature databases were screened and data was extracted on study design, types of noise sources, assessment method, health-based outcomes and confounders, as well as their associations. The quality of the studies was also assessed. The inclusion criteria focused on both indoor and outdoor environments in educational buildings and dwellings, considering that children spend most of their time there. From the 3337 uniquely collected articles, 36 articles were included in this review based on the defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. From the included literature, it was seen that noise exposure, assessed by energetic indicators, has significant associations with non-auditory health effects: psychophysiological, cognitive development, mental health and sleep effects. Percentile and event-based indicators provided significant associations to cognitive performance tasks and well-being dimension aspects.
1. Introduction
Urban noise is one of the modern health threats for human beings [1]. Like the elderly, children can be considered a sensitive group of people [2]. Because of their continuous physical and mental development, noise exposure may cause detrimental and irreversible health-related effects later on in their lives [3]. Auditory health effects (e.g., hearing loss and tinnitus) are considered as direct consequences of noise exposure, corresponding to the injury of the auditory system [4]. Usually, environmental noise exposure does not reach harmful levels for traumatizing children’s hearing [3]. However, noise exposure has been characterized as a risk factor for the presence of tinnitus in youth [5]. Noise, as a nonspecific stressor, is also responsible for the presence of health effects as a result of chronic noise exposure [4]. The relation between non-auditory health effects and noise exposure in children has been investigated, including psychophysiological [6,7,8,9,10,11], cognitive [7,9,10,12,13], mental [14,15], sleep [16,17], as well as physical development aspects [18,19,20,21]. In contrast to adults, children are more sensitive to noise stimuli, indicating that coping repertoires may have not been entirely developed [22].
Various mechanisms have been proposed for the relationship between noise exposure and health effects in humans (e.g., [4,23,24,25,26]). Aspects, such as those related to noise exposure (e.g., type of noise source) and its characteristics (e.g., duration and temporal variations), as well as to human organism (e.g., stress reactions) are mainly considered. Furthermore, mediating factors, associated to personal appraisal and coping repertoires, are also included [24,25]. These correspond to the assessment of noise exposure as threat or no threat as well as to the presence of physiological reactions with respect to individuals acquired and genetic characteristics [24]. Noise-induced health effects have been divided into two main categories; the short-term and long-term effects. Short-term effects are associated to disturbance of intended activities (e.g., concentration, sleep, performance), annoyance, and stress responses [4,23,24,25], whereas psychophysiological reactions (e.g., cardiovascular, and neuroendocrine aspects), and disorders (e.g., cardiovascular, and mental disorders) are identified as long-term health effects [24].
In contrast to some other environmental factors (e.g., benzene exposure), which their components can be accumulated in organisms, noise exposure is not an exogenous factor [27]. Hence, its effects can only be estimated based on the characteristics of noise exposure through objective noise indicators [27,28]. For the quantification of the noise exposure, various types of noise indicators have been used. The most commonly used noise indicators are the energetic, statistical, and the event-based indicators, weighted by the A-filter. In general, the (energetic) A-weighted equivalent noise indicator, , is the most commonly used indicator in noise exposure studies. This indicator is defined as the equivalent sound level over a specific period of the time, T. The day-evening-night equivalent sound level () indicator is calculated using , adding a penalty factor of 5dB for the evening noise levels, from 19:00 to 23:00, and of 10 dB for the night noise level, from 23:00 to 07:00 [4]. The additional penalty factors express the increase in sensitivity with respect to the restoration and the sleep period [23]. Sub-divisions of into, day (), evening (), night (), day–evening (), evening–night (), and day–night () are also used in noise exposure studies.
Percentile (statistical) indicators are used for capturing both noise events and noise floors. The A-weighted percentile level indicators () are used for estimating the noise levels exceeded for of the measurement time. The most commonly used percentiles are the 1st, 5th, 10th, 50th, 90th, 95th, and 99th. The (median-based) indicator is correlated to the average perception, since it is not affected by extraneous temporary noise events [29,30]. The indicator is used for the identification of the most dominant noise levels. The and are used for the characterization of the intermittent/intrusive noise levels, while the and are used for the description of background noise levels, respectively. Furthermore, the indicator is used for the estimation of the underlying noise levels [31]. Combinations of indicators, such as – and –, are commonly used for describing noise variation with respect to noise levels [32]. The sound exposure level () indicator is similar to . However, instead of averaging the total sound energy over the measurement period, a reference duration of one second is used. This indicator is useful when multiple aircraft events need to be compared [33]. Both and are capable of identifying both the maximum level of noise events and the noise floor over the time-period T.
Other types of indicators have been developed for the discrimination of the sound environments, related to noise variation, spectrum and noise emergence. However, these indicators have not been used to investigate possible relationships between noise exposure and noise-induced health effects in children [32].
The aim of this systematic literature review is to assess the objective noise indicators associated to non-auditory health effects in children. Children’s appraisal and coping strategies are continuously and rapidly developed during the childhood period. Therefore, it is important to identify the objective noise indicators associated with non-auditory health effects in children with respect to the type of the noise source, the locations of noise assessment, the exposure locations and their environments, the age of children, as well as parameters that influence the identified relationships. To our knowledge, this is the first review focusing on the association between noise indicators and non-auditory health effects in children. Factors that influence noise exposure are also discussed.
This paper is structured as follows; Section 2 provides the procedure of the literature review. Section 3 presents the results extracted by the included literature. Section 4 discusses the results with respect to a conceptual framework. Section 5 and Section 6 pinpoint the limitations as well as a the main remarks of this work, respectively. Finally, in the Supplementary Materials, a detailed overview of the used literature is given.
2. Procedure
In this section, the search strategy and procedures for identifying and assessing the collected literature, with respect to the defined inclusion and exclusion criteria, are presented.
2.1. Search and Screening Strategy
A systematic literature review enables the improvement of decisions made from concluded literature [34], minimizing the risk of bias occurred by a subset of literature.
In this systematic literature review, three key terms were defined; (1) noise exposure, (2) health effects and (3) children. In this way, relevant publications were collected. Both key and search terms are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Defined key and search terms.
As shown in Table 1, only noise-based search terms were used, and no sound- or acoustics-related terms. The {Health Effects} key term focuses on the non-auditory health effects, including psychophysiological, cognitive, mental health, and sleep effects. Finally, the {Children} key term covers various developmental stages.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Literature from 2000 until 2020 is considered in this review. This is motivated by the high number of studies conducted after the year 2000. In terms of noise indicators, only objective noise indicators related to non-auditory health effects in children-based studies are considered. Studies based on subjective noise indicators (e.g., noise logs), corresponding to the individuals’ perception of noise, were excluded. Regarding the type of noise exposure, ambient, aircraft, and road traffic noise are selected. Ambient noise exposure corresponds to the inclusion of all noise sources in an environment in which road-traffic noise is the dominant one. Dwellings and educational buildings are considered as the main locations, since children spend most of their time in these settings. In addition to this, both indoor and outdoor environments are considered. Indoor environments may provide either a significant reduction of outdoor noise exposure or the presence of secondary indoor noise sources (e.g., irrelevant speech in classrooms). Finally, studies that do not include noise exposure in the statistical analyses as well as studies using reproduced sound levels played back by loudspeakers or headphones were also excluded. In Table 2, both the inclusion and exclusion criteria are summarized.

Table 2.
Defined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
2.3. Search Procedure
The search procedure was conducted in four different literature databases (ScienceDirect, Scopus, MDPI, and PubMed) in August 2020 and the collected literature was stored into the freeware software, Zotero (https://www.zotero.org/ (accessed on: 25 November 2020)), version 5.0.93. In the search procedure, the databases were searched based on the presence of the defined search terms (see Table 1) in the title and/or the abstract, and/or the full text of the articles. In the search query, the key terms were separated, using the AND operator, and the search terms were separated, using the OR operator. The full searching query is included in Supplementary Materials.
2.4. Screening Procedure
In this systematic literature review, the PRISMA (http://prisma-statement.org/ (accessed on: 17 November 2020)) approach was followed (see Figure 1). After collecting the literature from the four databases (n = 8766), the screening of the identified literature was conducted. This includes the identification of duplicate articles in the collected literature. During this phase, the articles were also screened in terms of the criteria (A), (B), and (C) via the automatic function and built-in search filters in Zotero software (n = 3337). Then, the three-stage screening procedure (i.e., title, abstract and full-text screening) was conducted based on the defined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
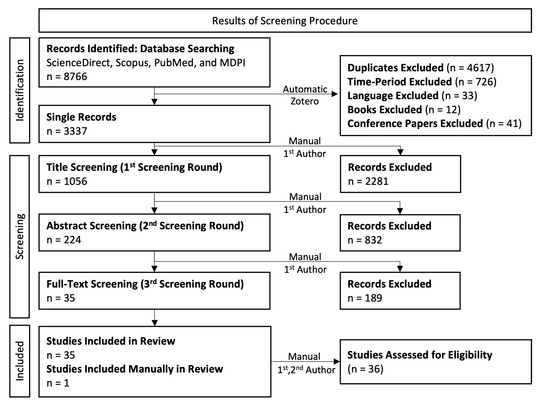
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the screening procedure.
In the first screening stage (title screening), the identification of key words, related to the inclusion and exclusion criteria (D)–(I), in the title of each article was conducted from the first author (M.E.T.). Papers with non-informative titles were passed to the next stage. From this stage, the literature was narrowed down to 1056 articles. In the second screening stage (abstract screening), the same procedure, as in the title screening, was followed, reducing the literature further to 224 articles. This stage was conducted by the first author (M.E.T.). When the abstracts did not provide sufficient information to judge, the conclusion sections were then evaluated. Again, when the abstracts and the conclusions of the papers were not informative, these papers were passed to the final stage. The third screening stage (full-text screening) corresponds to the reading of the remaining articles with respect to the defined criteria (D)–(I). This round was conducted in two steps. In the first step, the reading of the articles was performed by the first author (M.E.T.), narrowing down the literature to 35 articles. In the second step, these articles were read by the second author (M.D.), validating that these articles fulfill the defined criteria (i.e., eligibility assessment). During this procedure there was no deviation between both authors (M.E.T. and M.D.) in terms of the inclusion of 35 articles to the included literature. Furthermore, the second author (M.D.) validated that both the data and the outcomes per each article were extracted in a correct way.
Finally, although the searching procedure is conducted in four databases, important articles may be missing out. Hence, additional articles may be imported to the concluded literature, after the full-text screening procedure, through a manual insertion. In that way, the systematic approach was not violated. In this work, only a single article was added in the concluded literature, which was in first author’s (M.E.T.) knowledge, increasing the included literature to 36 (single) articles.
2.5. Criteria for Assessing the Risk of Bias
The quality (risk of bias) of each included article in this review was assessed with respect to the criteria in the Table 3. These criteria were developed by WHO [35] and lately further re-developed by van Kempen et al. [36]. These criteria have been adjusted to the needs of this systematic literature review. None of the original defined criteria was excluded. However, an additional criterion was added, assessing the short-term noise exposure. Overall, high quality of evidence is associated to a low risk of bias and vice versa. The grading of the risk of bias in each article per health effect is presented in the Supplementary Materials, Tables S8–S14.

Table 3.
Scoring protocol used to the assess the risk of bias in studies’ design.
3. Results
In this section, the results extracted by each article of the included literature are summarized. For a more detailed overview of the results extracted by each article, the reader is directed to the Supplementary Materials.
3.1. Results Overview per Health-Effect
From the included literature, information on health effects, health aspects, parameters, noise sources, and noise indicators was extracted (Table 4). This information is summarized with respect to the health effects: psychophysiological, cognitive, mental health, and sleep effects (Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11). It must be noted that some articles address multiple health effects, and therefore a doubling of articles occurs in Table 4. A detailed and extensive overview is included in Supplementary Materials, Tables S1–S7.

Table 4.
Overview of the collected information extracted from the included literature.

Table 5.
Cardiovascular-based studies. SBP and DBP refer to systolic and diastolic blood pressure, respectively. ”+” and ”−” refer to statistical and non-statistical significant associations between outcome and noise indicators, and OBR to the overall bias rating, where L and H correspond to low and high OBR. Finally, dwellings and educational buildings are assigned by  and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.
 and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.

Table 6.
Neuroendocrine-based studies. CL and CML refer to cortisol and its metabolite levels as well as GL and GML to glucocorticoid and its metabolite levels. For an explanation of symbols and notations, see the caption of Table 5.

Table 7.
Cognitive development-based studies. SA corresponds to sustained attention, RD to reading, WM to working memory, RGNM to recognition memory, RCLM to recall memory, and PM to prospective memory. For explanation of symbols and notations, see caption of Table 5.

Table 8.
Cognitive performance-based studies. AA corresponds to academic achievements, LNG to language, MTH to mathematics, SCN to science, and CF to cognitive functioning. For an explanation of symbols and notations, see the caption of Table 5.

Table 9.
Well-being dimensions-based studies. ANN corresponds to annoyance, MOT to motivation, and QOL to quality of life. For explanation of symbols and notations, see caption of Table 5.

Table 10.
Mental health effects-based studies. SDQ corresponds to the total score of the psychological morbidity SDQ test. ES corresponds to emotional symptoms, CP to conduct problems, HI to hyperactivity/inattention, PP to peer problems, PSB to pro-social behavior problems (SDQ sub-scales). AD to anxiety/depression, PH to perceived general and mental health, BP to behavioral problems, and EF to executive functioning skills. For explanation of symbols and notations, see caption of Table 5.

Table 11.
Sleep-based studies. DFS corresponds to difficulties fall sleeping, SP to sleep problems, SQ to sleep quality, WE to waking episodes, and FA to feeling alertness. For explanation of symbols and notations, see the caption of Table 5.
3.2. Noise-Induced Effects and Noise Indicators
In this sub-section, the main results are summarized, such as presented in Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11. Further details can be found in the Supplementary Materials, Tables S1–S7.
3.2.1. Cardiovascular Effects
Cardiovascular aspects related to systolic and diastolic blood pressure were significantly associated with both aircraft and road-traffic noise. The indicator presented significant associations with both types of blood pressure [38,40]. In the case of the van Kempen study [40], significant associations between the indicator and the diastolic blood pressure were presented when aircraft noise and annoyance were simultaneously considered. Focusing on road-traffic noise exposure, the indicator [37,39] provided significant associations mostly with systolic and less so with diastolic blood pressure. Finally, the indicator showed no significant relationship with any type of blood pressure [41].
3.2.2. Neuroendocrine Effects
Cortisol, gluccocorticoid, and their metabolites were the main neuroendocrine aspects explored with respect to road-traffic and aircraft noise exposure. Although the indicator provided significant relationships between road-traffic noise exposure and some cortisol [43] and gluccocorticoid [43] metabolites, these associations were not seen in terms of their total levels [42,43]. Focusing on the indicator, significant associations to cortisol and its 20a-dihydcortisol metabolite were found with respect to road-traffic noise exposure [41]. With regard to aircraft noise exposure, non-significant associations with cortisol levels relative to the indicator were extracted [44].
3.2.3. Cognitive Development Effects
Cognitive development tasks related to sustained attention, reading/comprehension, short-term memory (i.e., working memory) and long-term memory (i.e., recognition, recall, and prospective memory) were explored with respect to both aircraft and road-traffic noise exposure. Studies based on both types of noise exposure showed no significant associations with sustained attention with respect to the indicator [47,51]. However, a significant relationship between sustained attention and exposure to aircraft noise, expressed by the indicator, was identified [44].
Although no clear associations between reading/comprehension tasks and both types of noise exposures were extracted based on the indicator [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51], the more consistent ones were found in studies where the age of the children was between 7 and 11 years [44,46,47,50]. In terms of the indicator-based study [49], significant associations between aircraft noise exposure and reading tasks were identified.
Regarding memory tasks, long-term memory was found to be impaired by noise exposure, when it is expressed by the indicator, compared to short-term memory. More specifically, working memory tasks, associated to short-term memory, did not reveal any significant association with respect to aircraft [44,47] and road-traffic [47] noise exposure. However, recognition memory tasks, associated to long-term memory, were significantly impacted by both types of noise exposure [44,47,52]. Although both significant [51,52] and non-significant [47,48] associations were with respect to recall memory, prospective memory showed no significant effects with regard to exposure to noise from both aircraft and road-traffic [47,52].
3.2.4. Cognitive Performance Effects
Noise events, expressed by the and the indicator, as well as background level, expressed by the indicator, presented significant associations to cognitive performance tasks (i.e., language, mathematics, and science), considering exposure in educational buildings [56]. Ambient exposure in both dwellings, expressed by the indicator, and educational buildings, expressed by the or the or the indicator, revealed significant associations to performance tasks (i.e., mathematics and language) [54]. However, neither the levels at dwellings nor the levels at educational buildings provided significant associations with complex cognitive tasks (e.g., mathematics) [54]. Due to aircraft noise, both language and mathematics tasks were found to be significantly affected in educational buildings, expressed by the indicator [55]. Considering cognitive functioning tasks, significant associations were seen with respect to both aircraft and road-traffic noise exposure in educational buildings, expressed by the indicator [40,57]. Finally, academic achievements were not impacted by road-traffic noise exposure, expressed by energetic, statistical, and event-based noise indicators [53].
3.2.5. Well-Being Dimensions
Well-being dimensions related to annoyance, motivation and quality of life were investigated with respect to both aircraft and road-traffic noise exposure. Annoyance was the well-being dimension which presented strong associations with both aircraft and road traffic noise exposure, expressed by various indicators, such as the [44,45,46,47,58,59,60,61,63], the [62], the [63], the [63] and the [49] indicator.
The impact of aircraft noise exposure on motivation was only addressed by one study. In this study [44], a non-significant relationship was found between motivation and the indicator.
Finally, the well-being dimension that corresponds to the quality of life showed significant associations with both exposure to aircraft and road traffic noise with respect to the [46] and the [41] indicator, respectively.
3.2.6. Mental Health Effects
Mental health effects related to mental disorders, behavioral problems, executive functioning, and perceived general and mental health were investigated with respect to aircraft and road-traffic noise exposure. Mental disorders associated with anxiety and depression did not present a significant association with aircraft noise exposure, expressed by either the [44] or the [49] indicator. Focusing on the behavioral problems, significant associations were revealed with respect to the indicator, expressing road traffic noise exposure [68]. However, this significance was not present with respect to the externalizing or internalizing behavior problems [68]. Executive functioning skills, related to attention deficit disorders, only showed significant associations for boys in relation to road traffic noise expressed by the indicator [70].
Psychological morbidity is assessed via the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ), mainly including five items; hyperactivity/inattention, emotional symptoms, conduct problems, pro-social behavior and peer problems. The total SDQ scores did not provide significant associations with both aircraft [44,45,65,69] and road traffic noise [64,65,66,69] exposure, expressed by the energetic indicators [44,45,65,69] and [64,66]. Focusing on each item separately, both significant and non-significant relationships were extracted. More specifically, the hyperactivity/inattention item presented the strongest associations with respect to the indicator and road traffic noise exposure in dwellings [64,66] as well as the and aircraft noise exposure in educational buildings [65,69]. The inattention-based study [67] revealed significant associations to road traffic noise exposure and the indicator. In terms of the emotional symptoms item, this presented mostly non-significant associations with regard to both types of noise exposures, assessed by both energetic indicators, [44,45,65,69] and [66]. Only one study [64] presented significant associations between road-traffic noise exposure levels, expressed by the indicator, and the emotional symptoms item. The conduct problems item presented a non-significant association with noise exposure in most studies [44,45,64,66]. However, the -based studies on aircraft and road-traffic noise exposure identified significant associations with this item [65,69]. The pro-social behavior [44,64,65,66] and peer problem [44,64,65,66] items did not reveal any significant association with regard to any type of noise exposure and noise indicator.
Finally, perceived mental and general health aspects did not reach any significant association with either aircraft or road traffic noise exposure, expressed by the indicator [40]. However, a significant relationship was revealed between aircraft noise exposure, expressed by the indicator, and stress symptoms [49].
3.2.7. Sleep Effects
Sleep aspects such as sleep quality, waking-up episodes, sleepiness, and difficulties falling asleep were investigated with respect to road-traffic noise exposure. Sleeping problems and problems to fall asleep were significantly related to the indicator, only at the least exposed façade in dwellings, rather than at their most exposed façade [64]. Significant associations between noise exposure, expressed by the indicator, and sleep parameters, related to sleep quality, wrist activity, and feeling alertness in daytime [71] were also indicated. Non-significant associations were revealed with respect to noise exposure, expressed by the indicator, and sleep quality [72].
4. Discussion
Based on the included literature, it is seen that noise-induced health effects have shown significant relations to various noise indicators (see Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11). Aspects such as the type of noise source, the sound propagation path, and the acoustic characteristics of the environments influence both noise exposure and its quantification. In combination with the developmental characteristics of children, which act as mediators, non-auditory noise-induced health effects may be of short-term or long-term nature. Hence, a conceptual framework is introduced, representing and discussing all the components associated to the possible noise-induced health effects in children with respect to the findings from the included literature.
4.1. Conceptual Framework
The conceptual framework in Figure 2 describes the relationship between noise exposure and non-auditory health effects. The main components of this framework are: (1) the type of noise source, (2) the exposure locations, (3) the exposure environments (i.e., outdoor and indoor environments), including the acoustic factors of both environments as well as of the outdoor-to-indoor infrastructure (i.e., building’s façade), (4) the assessment of noise exposure through objective noise indicators, (5) the children’s mediating factors, and (6) the types of non-auditory health effects (i.e., degree of severity).
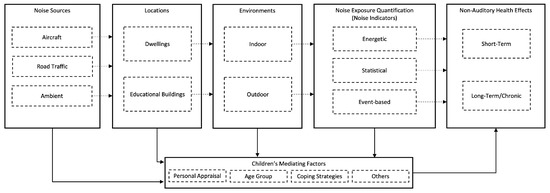
Figure 2.
Conceptual framework of the relationship between noise exposure and non-auditory health effects in children.
Overall, the conceptual framework can be interpreted in the following way. Although noise sources are defined based on their own characteristics (i.e., temporal and spectra), noise exposure is associated with the type of the noise source, the location’s and its environments’ characteristics. In outdoor environments, mostly no free-field conditions are encountered. Therefore, outdoor environment characteristics, such as, the street width and height as well as the distance between building blocks, modify both the temporal and spectra acoustic characteristics of the noise sources, defining the outdoor noise exposure. Furthermore, parameters related to building acoustics (i.e., façade sound insulation) and room acoustics are responsible for the further modification of the outdoor exposure transmitted into the indoor environment. In that way, noise indicators (energetic, statistical or event-based) are the quantities for correlating noise exposure and/or its characteristics with non-auditory health effects. Finally, mediating factors are responsible for the possible strengthening of the associations between noise exposure quantification and possible health effects in children.
4.1.1. Noise Source
The noise source defines the type of noise exposure based on characteristics related to its spectral and temporal components. These parameters are perceived differently by each child (i.e., suggesting that factors such as personal assessment and coping strategies are responsible for the perception of noise exposure as harmful or not harmful), influencing non-auditory health effects (e.g., degree of discomfort).
From the included literature, it was seen that 47% of the studies focused on the road-traffic noise exposure, 20% focused on the aircraft noise exposure, 22% focused on both the road-traffic and aircraft noise exposure, and the remaining 11% focused on ambient noise exposure, in which its dominant noise source is usually road-traffic noise.
Both spectral and temporal characteristics of environmental noise sources, such as cars, motorcycles, and aircraft, have changed over the years. As a typical example, the improvement in aircraft jet engines over the decades can be considered, in which the generated sound power was significantly reduced since their introduction [73]. Consequently, this indicates that spectral characteristics of noise sources have been modified. Although this is known, spectral information was not presented by any of the studies in the included literature. This indicates the importance of interpreting the associations between noise exposure and health effects in various studies with caution, especially in the case of studies with a large time gap between them.
4.1.2. Locations and Environments
Considering that children spend most of their time in residential and educational buildings, noise exposure in indoor environments is of greater importance in comparison to the noise exposure in outdoor environments.
As regards the outdoor noise exposure, this depends on parameters such as the type of street (e.g., a street canyon or an open street), the width of the street, the distance to the noise sources as well as the acoustic characteristics of the outdoor environment. For the indoor environment, the characteristics of the building skin and indoor room acoustic characteristics influence the transmitted environmental noise exposure. Note that secondary noise sources from surrounding indoor environments (e.g., irrelevant speech in school environments and neighbor noise in dwellings) may either influence or even dominate the noise transmitted from outdoors. When considering the effect of outdoor noise exposure on the indoor environment, it is therefore important to ensure that secondary noise sources do not dominate the indoor noise exposure. Considering the façade characteristics, factors such as the façade material, the presence of balconies or obstacles, the type of the windows (i.e., single or double glazing), as well as the glazing area over façade area (of the room under consideration) influence the temporal and spectral characteristics of indoor noise exposure.
Looking at the locations and the environments where noise exposure was assessed (Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11), approximately 33% of the items were for homes, 47% for educational buildings, and 20% for both locations. In terms of the environments, in dwellings-based studies, all the studies considered outdoor environments. In educational buildings-based studies, approximately 31% focused on outdoor environments, 8% on indoor environments, and 8% on both indoor and outdoor environments. Studies based on both dwellings and educational buildings considered only outdoor environments.
The absence of the assessment of indoor noise exposure (i.e., not taking into account the acoustic characteristics of the building façade and indoor environment) may lead to weak relationships between indoor noise exposure, based on outdoor noise exposure, and non-auditory health effects, even though these are statistically significant.
Focusing on façade characteristics, these modify the transmitted outdoor exposure into the indoor environment. In particular, the glazing area of the windows and its ratio over the façade area can be considered as important parameters. It was found that indoor noise levels are affected by the positions of the windows (i.e., open, tilted, and closed) [74]. This is important in both sleep and cognitive studies, taking into account the effects of sleep quality on cognitive tasks [75]. According to Locher et al. [74], the equivalent noise level difference of between outdoor and indoor environments in dwellings ranges from to dBA, when measurements with open windows were conducted.
The aforementioned aspects can be cast into acoustic parameters. Room acoustics parameters such as the reverberation time and speech intelligibility have shown significant relations to acoustic comfort [76]. The term acoustic comfort refers to the perceptual pleasant evaluation of an environment with respect to its acoustics characteristics [77]. Outdoor acoustics characteristics, such as these related to reverberation time, modify the noise exposure, which may lead to a significant impact on acoustic comfort. Finally, building acoustics characteristics related to parameters such as façade acoustics insulation have presented strong associations to acoustic comfort in the indoor environment [78].
Although these parameters are known, only 11% of the included literature took into consideration room and building acoustics parameters for investigating their impact to well-being dimensions aspects. For example, Minichilli et al. [61] included the reverberation time (), the speech transmission index (), the airborne façade insulation () as well as the wall sound reduction index () in classrooms. In this study, although annoyance presented only a good correlation with and not with any of the other aforementioned acoustics indicators, none of these acoustic factors was included in statistical analysis as adjusted factors. Reverberation time was also included by Klatte et al. [46], showing that was unrelated to aircraft noise exposure and children’s reading scores, excluding it from the analysis. The lack of measuring the reverberation time in a school that was relocated was another reason for excluding from the analyses. In terms of sound insulation, this was included in the analyses with respect to the type of window glazing as adjusting factors by Stansfeld et al. [47] and van Kempen et al. [60]. In the case of Klatte et al. [46], the acoustics insulation was estimated using a combination of variables, including fenestration, glazing and wall thickness. The need of including acoustics factors related to the indoor environments is pinpointed by both Silva et al. [59] and Stansfeld et al. [65]. It needs to be mentioned that in the acoustics factors, the frequency dependency was not considered. Finally, regarding the outdoor environment, it needs to be noted that the acoustics characteristics of the outdoor environments (e.g., reverberation time) have not been considered by any of articles in the included literature.
4.1.3. Noise Indicators
Looking at Table 4, mostly energy-based noise indicators have been used in children-based studies. More specifically, 83% of the included articles assessed noise exposures via energetic noise indicators, from which 50% corresponds to the indicator, 25% to the indicator, and the remaining 8% to relative subdivisions of the indicator, referring to the , the , the , the and the indicator. Short-term energetic noise indicators were also used, quantifying typical noise levels in focused spaces and time periods (e.g., during task periods). Although that energetic noise indicators are associated to long-term health effects, these hide information related to noise levels’ dynamics and temporal characteristics [32]. Hence, these factors may provide weak association even when the relationships between noise exposure and non-auditory health effects are statistically significant.
A lower percentage of the collected literature included statistic percentile-based indicators (e.g., and ) and event-based indicators (e.g., and ). These indicators cover 17% of the included literature for investigating mostly the relationship between noise exposure and cognitive performance tasks. By considering that the and the indicator describe the intermittent/intrusive levels and the background noise level, respectively, these indicators could provide important information in terms of the influence of the dominant noise events and background noise on health effects. Moreover, the indicator can provide similar information to the percentile-based indicator . According to Secchi et al. [79], the is characterized by a high dispersion of data in exposure levels in comparison to the under a defined time interval length [79]. Therefore, it is recommended to use the index instead of the index to investigate the effects of noise exposure on cognitive performance. In terms of noise events, the indicator is used when aircraft noise exposure is under consideration, indicating the transient nature of aircraft noise exposure.
It is important to note that all articles in the included literature looked at noise exposure in relation to the A-weighting filter, including those where the equivalent noise exposure levels were higher than 50–55 dBA [80]. Although the A-weighting filter mimics the human hearing response (i.e., approximate Fletcher–Manson curves [81]), low frequencies are underestimated [80,82], leading to a possible weak association with human perception [83]. In addition, this filter was only designed for levels around 40 dB. In high levels, its performance can be characterized as poor [82], considering the flattening of the Fletcher–Manson curves at these levels. In the included literature, no frequency-based indicators have been used. Although that spectrum-based indicators are known (see ref. [32]), these have never been explored in noise-based studies. The characterization of noise exposures (i.e., indoor and/or outdoor) with respect to noise indicators, based on their spectral characteristics, may lead to different exposure–response curves, especially when considering the transmission of outdoor noise exposure into an indoor environment through a building façade.
4.1.4. Children and Mediating Factors
Except for the direct associations between noise exposure and non-auditory health effects in children, there are parameters mediating these relationships. Such parameters correspond to personal appraisal, coping strategies, age group, and others. Regarding the perception of noise exposure, noise sensitivity is an important mediating personal appraisal factor. This factor is associated with the perception towards various types of noise sources and their characteristics, indicating the degree of reactivity to noise characteristics [84]. In addition, it has been characterized as an independent predictor of annoyance for urban noise [2]. Coping strategies are strongly associated to the degree of exposure, leading to actions of tuning out unwanted noise events [85]. Age group is also an important factor, considering the developmental period of children as well as the development of coping strategies for stress events, such as noise. Gender, genetic characteristics, lifestyle, socioeconomic status, beliefs, and social environment may provide a higher degree of consistency in the analyses of associating with noise exposure and health effects [24]. Approximately 83% of the included literature used mediating factors related to adjusted confounders in the statistical analyses (see Tables S8–S14). In addition, most of the studies included participants criteria, related to type of noise exposure, demographic characteristics, health aspects, and others (see Tables S8–S14).
4.1.5. Matching between Noise Indicators and Noise-Induced Health Effects
Exposure-based studies (i.e., road-traffic and aircraft noise) on psychophysiological [6,7,8,9,10,11], cognitive development [7,9,10,12,13], mental health [14,15], and sleep [16,17] effects have shown consistency with the studies quantifying noise exposure by the and the indicators. Regarding sleep effects, it is interesting to note that event-based indicators were not identified in children-based studies, even though it is known that noise events are responsible for distorting sleeping activity [86].
Both acute and temporal characteristics of noise exposure, corresponding to the transient nature of noise sources, have shown a significant impact on cognitive performance tasks [63]. More specifically, significant associations between noise exposure and cognitive performance tasks have been revealed with respect to the statistic percentile indicator and the noise event indicator , describing noise events, as well as to the percentile indicator and the equivalent noise indicator , describing the constant character of the noise exposure. Both the and the indicator presented significant correlations with cognitive performance tasks in older children. This may indicate that long-term exposure is responsible for the development of coping strategies, filtering out the time-independent patterns of noise exposure. In that way, noise exposure based on events has a dominant effect in the association between noise exposure and cognitive performance task [56]. In contrast to older children, younger children, who have had a shorter exposure, may have less developed coping strategies than chronically exposed children. Therefore, the effects on their performance tasks are possibly associated with the background noise indicator and the equivalent noise indicator [56].
Considering the pathways of exposure, the inclusion of both direct (e.g., noise exposure during learning activities) and indirect (e.g., noise exposure in dwellings) exposures affects the performance of children in cognitive tasks. Energy-based indicators, expressing noise exposure in homes, with reference to the indicator , and in schools, with reference to the indicator or the indicator or the indicator , showed a significant effect. The latter evidence is in agreement with previous exposure-based studies [7,13,85]. Finally, the association between the indicator in terms of road traffic noise exposure and cognitive functioning-based test results indicated the influence of noise exposure on complex tasks [57], which is in accordance with the study [87].
4.2. Quality of Evidence
The defined assessment criteria (see Table 3) have been implemented in terms of the design and outcome in each individual study (see Tables S12–S14). In total, 56% of articles presented a low overall risk of bias, which corresponds to the high quality of evidence. The other 44% corresponds to a high overall risk of bias, indicating the low quality of evidence. From the latter percentage, 6% of the studies presented a high rate of bias with respect to noise exposure assessment, corresponding to non-continuous short-time noise measurements. The remaining 38% corresponds to the other three risk of bias assessment criteria.
5. Limitations
In terms of the weaknesses of this study, the search procedure was conducted to a limited number of literature databases, indicating that valuable articles may have not been included to this study due to their inclusion to other literature databases. The screening procedure was conducted by the first author (M.E.T.), meaning that possible biases related to inclusion/exclusion criteria may have been included. Although each screening round was validated in a continuous basis and the included literature was validated by the second author (M.D.), this type of bias can not be neglected.
6. Conclusions
Noise exposure in urban environments has been characterized as a health threat for humans. Children, due to their continuous mental and physical development, have been considered as a sensitive group, indicating that noise-induced health effects could be detrimental and possibly irreversible during their adulthood period. Hence, the objective of conducting this systematic literature review was the identification of objective noise indicators associated with non-auditory health effects in children. For the purposes of this review, psychophysiological, cognitive, mental and sleep effects have been considered. From the included literature, it is seen that mostly energetic noise indicators have been used for the association of noise exposure with all the considered non-auditory health effects in children-based studies. Only a small amount of studies (i.e., cognitive performance and mental health effects) used statistical and event-based indicators in combination with energy-based ones. The latter suggests that it is important to further examine what type of noise indicators affect children and to identify possible developed and undeveloped coping repertoires (mechanisms) with respect to noise indicators, indicating an open research topic.
Apart from the currently used indicators, spectral-based noise indicators could have a correlation with non-auditory health effects in children too, and should be subject of future research.
Considering that children spend most of their time at home and at school indoors, indoor noise levels are of greater concern than outdoor noise levels. This underscores the importance of developing and applying outdoor-to-indoor transition correction factors when studying the effects of outdoor noise exposure (e.g., noise maps) on children’s health. Correction factors could be derived either by measurements (e.g., outdoor and indoor measurements) or by modeled data (e.g., propagation-based models) and the application of statistical (learning) methods, including additional parameters related to the outdoor and indoor environment and the building façade characteristics.
Finally, the perceptual part of noise indicators needs to be considered, as noise exposure levels may deviate from the levels that justify A-weighting. Therefore, more appropriate weighting following the equal-loudness contours is recommended.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijerph192315633/s1, Table S1: Cardiovascular-based studies, Table S2: Neuroendocrine-based studies, Table S3: Cognitive development-based studies, Table S4: Cognitive performance-based studies, Table S5: Well-being dimensions-based studies, Table S6: Mental health effects-based studies, Table S7: Sleep-based studies, Table S8: Assessment of the risk of bias in cardiovascular-based studies, Table S9: Assessment of the risk of bias in neuroendocrine-based studies, Table S10: Assessment of the risk of bias in cognitive development-based studies, Table S11: Assessment of the risk of bias in cognitive performance-based studies, Table S12: Assessment of the risk of bias in well-being dimension-based studies, Table S13: Assessment of the risk of bias in mental health effects-based studies, Table S14: Assessment of the risk of bias in sleep effect-based studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H. and M.E.T.; literature search, M.E.T.; screening procedure, M.E.T.; eligibility, M.E.T. and M.D.; methodology: M.E.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E.T.; writing—editing: M.E.T.; supervision, M.H. and I.v.K.; review manuscript, M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 874724, Equal-Life Project, which is part of the European Human Exposome network.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the reviewers for their comments and contribution as well as the assigned proofreading editor for the revised suggestions. Additionally, the first author would like to thank Dimitra Chaniotaki for reviewing the English language. Finally, the first author would like to thank Ella Braat-Eggen for reviewing and providing feedback during the very first draft manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stansfeld, S.; Haines, M.; Brown, B. Noise and health in the urban environment. Rev. Environ. Health 2000, 15, 43–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kamp, I.; Davies, H. Noise and health in vulnerable groups: A review. Noise Health 2013, 15, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansfeld, S.; Clark, C. Health Effects of Noise Exposure in Children. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Burden of Disease from Environmental Noise Burden of Disease from Environmental Noise. Quantification of Healthy Life Years Lost in Europe; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Park, B.; Choi, H.G.; Lee, H.J.; An, S.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, H.J. Analysis of the Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Tinnitus in a Young Population. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W.; Monika, B.; Staffan, H. Chronic Noise Exposure and Physiological Response: A Prospective Study of Children Living under Environmental Stress. Psychol. Sci. 1998, 9, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Evans, G.W.; Krantz, D.S.; Stokols, D. Physiological, Motivational, and Cognitive Effects of Aircraft Noise on Children Moving from the Laboratory to the Field. Am. Psychol. 1980, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinmann, T.; Ehrenstein, V.; Kries, R.V.; Nowak, D.; Radon, K. Subjective and objective personal noise exposure and hypertension: An epidemiologic approach. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2012, 85, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, G.W.; Staffan, H.; Monika, B. Chronic Noise and Psychological Stress. Psychol. Stress 1995, 6, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W.; Lercher, P.; Meis, M.; Ising, H.; Kofler, W.W. Community noise exposure and stress in children. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 109, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, H.; Rebentisch, E.; Babisch, W.; Sharp, D.; Baumgsrtner, H. Medically Relevant Effects of Noise from Military Low-Altitude Flights-Results of an Interdisciplinary Pilot Study. Environ. Int. 1990, 16, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Glass, D.C.; Singer, J.E. Apartment Noise, Auditory Discrimination, and Reading Ability in Children. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1973, 9, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hygge, S.; Evans, G.W.; Bullinger, M. A Prospective Study of Some Effects of Aircraft Noise on Cognitive Performance in Schoolchildren. Psychol. Sci. 2002, 13, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Nakane, Y.; J, J.E. Effects of Aircraft Noise on the Mental Work of Pupils. J. Sound Vib. 1975, 43, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullinger, M.; Hygge, S.; Evans, G.; Meis, M.; Mackensen, S. The Psychological Cost of Aircraft Noise for Children* Psychologische Beeintrachtigung von Kindern durch Fluglarm. Zentralblatt Hyg. Umweltmed. 1998, 202, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt, J.L. The Influence of Road Traffic Noise on Sleep. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 127, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, H.; Ising, M. Chronic Cortisol Increases in the First Half of the Night Caused by Road Traffic Noise. Noise Health 2002, 4, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.S.; Hjortebjerg, D.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Ketzel, M.; Sørensen, T.I.; Sørensen, M. Pregnancy and childhood exposure to residential traffic noise and overweight at 7 years of age. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzhambov, A.M.; Markevych, I.; Lercher, P. Associations of residential greenness, traffic noise, and air pollution with birth outcomes across Alpine areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, L.M. Environmental Noise and Human Prenatal Growth. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1981, 56, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schell, L.M.; Ando, Y. Postnatal Growth of Children in Relation to Noise From Osaka International Airport. J. Sound Vib. 1991, 151, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bistrup, M. Prevention of Adverse Effects of Noise on Children. Noise Health 2003, 5, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Münzel, T.; Gori, T.; Babisch, W.; Basner, M. Cardiovascular effects of environmental noise exposure. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staatsen, B.A.M.; Nijland, H.A.; van Kempem, E.M.M.; de Hollander, A.E.M.; Franssen, A.E.M.; van Kamp, I. Assessment of Health Impacts and Policy Options in Relation to Transport-Related Noise Exposures; RIVM: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2004.
- Porter, N.; Kershaw, A.; Ollerhead, J. Adverse Effects of Night-Time Aircraft Noise: Review of 1992 UK Findings and Introduction to New UK Work. In Proceedings of the 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering, Nice, France, 27–30 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Spreng, M. Noise induced nocturnal cortisol secretion and tolerable overhead flights. Noise Health 2004, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babisch, W.; Ising, H.; Gallacher, J. Health status as a potential effect modifier of the relation between noise annoyance and incidence of ischaemic heart disease. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 60, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, M. A review of potential mechanisms in the genesis of long-term health effects due to noise-induced sleep disturbances. In Proceedings of the Internoise 2012—41st International Congress on Noise Control Engineering, New York, NY, USA, 19–22 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lavandier, C.; Delaitre, P.; Ribeiro, C. Global and local sound quality indicators for urban context based on perceptive and acoustic variables. In Proceedings of the Euronoise 2015, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 31 May–3 June 2015; pp. 1471–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Bartalucci, C.; Borchi, F.; Carfagni, M.; Governi, L.; Luzzi, S.; Aspuru, I.; Gaudibert, P.; Wolfert, H. LIFE+2010 QUADMAP Project: Results obtained from the analysis of data collected during the application of the new methodology to the pilot quiet areas. Noise Mapp. 2019, 6, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shield, B.M.; Dockrell, J.E. The Effects of Noise on Children at School: A Review. Build. Acoust. 2003, 10, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Aumond, P.; Michel, S.; de Coensel, B.; Ribeiro, C.; Botteldooren, D.; Lavandier, C. Comparison of noise indicators in an urban context. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2016, 45th International Congress and Exposition of Noise Control Engineering, Hamburg, Germany, 21–24 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Makarewicz, R.; Galuszka, M.; Kokowski, P. Evaluation of aircraft noise measurements. Noise Control Eng. J. 2014, 62, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofaer, N.; Stratch, D. The need for systematic reviews of reasons. Bioethics 2012, 26, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Handbook for Guideline Development; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kempen, E.; Casas, M.; Pershagen, G.; Foraster, M. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Effects of Environmental Noise Systematic Evidence Review in the Framework of the Development of the WHO Environmental Noise Guidelines for the European Region; RIVM: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2017.
- Wallas, A.E.; Eriksson, C.; Bonamy, A.K.E.; Gruzieva, O.; Kull, I.; Ögren, M.; Pyko, A.; Sjöström, M.; Pershagen, G. Traffic noise and other determinants of blood pressure in adolescence. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babisch, W.; Neuhauser, H.; Thamm, M.; Seiwert, M. Blood pressure of 8–14 year old children in relation to traffic noise at home—Results of the German Environmental Survey for Children (GerES IV). Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5839–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belojevic, G.; Jakovljevic, B.; Stojanov, V.; Paunovic, K.; Ilic, J. Urban road-traffic noise and blood pressure and heart rate in preschool children. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kempen, E.; van Kamp, I.; Nilsson, M.; Lammers, J.; Emmen, H.; Clark, C.; Stansfeld, S. The role of annoyance in the relation between transportation noise and children’s health and cognition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2817–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lercher, P.; Evans, G.W.; Widmann, U. The ecological context of soundscapes for children’s blood pressure. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallas, A.; Eriksson, C.; Gruzieva, O.; Lind, T.; Pyko, A.; Sjöström, M.; Ögren, M.; Pershagen, G. Road traffic noise and determinants of saliva cortisol levels among adolescents. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantuaria, M.L.; Usemann, J.; Proietti, E.; Blanes-Vidal, V.; Dick, B.; Flück, C.E.; Rüedi, S.; Héritier, H.; Wunderli, J.M.; Latzin, P.; et al. Glucocorticoid metabolites in newborns: A marker for traffic noise related stress? Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, N.; Stansfeld, S.; Job, R.; Berglund, B.; Head, J. Chronic aircraft noise exposure, stress responses, mental health and cognitive performance in school children. Psychol. Med. 2001, 31, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.; Head, J.; Stansfeld, S.A. Longitudinal effects of aircraft noise exposure on children’s health and cognition: A six-year follow-up of the UK RANCH cohort. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, M.; Spilski, J.; Mayerl, J.; Möhler, U.; Lachmann, T.; Bergström, K. Effects of Aircraft Noise on Reading and Quality of Life in Primary School Children in Germany: Results From the NORAH Study. Environ. Behav. 2017, 49, 390–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansfeld, S.; Berglund, B.; Clark, C.; Lopez-Barrio, I.; Fischer, P.; Öhrström, E.; Haines, M.; Head, J.; Hygge, S.; van Kamp, I.; et al. Aircraft and road traffic noise and children’s cognition and health: A cross-national study. Lancet 2005, 365, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabi, J.; Cockcroft, K.; Goldschagg, P.; Greyling, M. A prospective follow-up study of the effects of chronic aircraft noise exposure on learners’ reading comprehension in South Africa. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, M.; Stansfeld, S.; Soames Job, R.; Berglund, B.; Head, J. A follow-up study of effects of chronic aircraft noise exposure on child stress responses and cognition. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 30, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.; Martin, R.; Kempen, E.V.; Alfred, T.; Head, J.; Davies, H.W.; Haines, M.M.; Barrio, I.L.; Matheson, M.; Stansfeld, S.A. Exposure-effect relations between aircraft and road traffic noise exposure at school and reading comprehension: The RANCH project. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Stansfeld, S.; Haines, M.; Head, J. Children’s Cognition and Aircraft Noise Exposure at Home—The West London Schools Study. Noise Health 2004, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matheson, M.; Clark, C.; Martin, R.; van Kempen, I.; Haines, M.; Lopez-Bario, I.; Hygge, S.; Stansfeld, S. The Effects of Road Traffic Noise Exposure on children’s Episodic Memory: The RANCH Project. Noise Health 2010, 12, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Kang, J.; Tompsett, R. The impacts of environmental noise on the academic achievements of secondary school students in Greater London. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, S.; Levain, J.P.; Houot, H.; Petit, R.; Berthillier, M.; Defrance, J.; Lardies, J.; Masselot, C.; Mauny, F. Association between ambient noise exposure and school performance of children living in an urban area: A cross-sectional population-based study. J. Urban Health 2014, 91, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, M.M.; Stansfeld, S.A.; Head, J.; Job, R.F. Multilevel modelling of aircraft noise on performance tests in schools around Heathrow Airport London. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2002, 56, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shield, B.M.; Dockrell, J.E. The effects of environmental and classroom noise on the academic attainments of primary school children. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kempen, E.; van Kamp, I.; Lebret, E.; Lammers, J.; Emmen, H.; Stansfeld, S. Neurobehavioral effects of transportation noise in primary schoolchildren: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Health 2010, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.A.A. Study effects of school noise on learning achievement and annoyance in Assiut city, Egypt. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.T.; Oliveira, I.S.; Silva, J.F. The impact of urban noise on primary schools. Perceptive evaluation and objective assessment. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 106, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, E.E.; van Kamp, I.; Stellato, R.K.; Lopez-Barrio, I.; Haines, M.M.; Nilsson, M.E.; Clark, C.; Houthuijs, D.; Brunekreef, B.; Berglund, B.; et al. Children’s annoyance reactions to aircraft and road traffic noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minichilli, F.; Gorini, F.; Ascari, E.; Bianchi, F.; Coi, A.; Fredianelli, L.; Licitra, G.; Manzoli, F.; Mezzasalma, L.; Cori, L. Annoyance judgment and measurements of environmental noise: A focus on italian secondary schools. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birk, M.; Ivina, O.; Klot, S.V.; Babisch, W.; Heinrich, J. Road traffic noise: Self-reported noise annoyance versus GIS modelled road traffic noise exposure. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 3237–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockrell, J.E.; Shield, B. Children’s perceptions of their acoustic environment at school and at home. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 115, 2964–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiesler, C.M.; Birk, M.; Thiering, E.; Kohlböck, G.; Koletzko, S.; Bauer, C.P.; Berdel, D.; Berg, A.V.; Babisch, W.; Heinrich, J.; et al. Exposure to road traffic noise and children’s behavioural problems and sleep disturbance: Results from the GINIplus and LISAplus studies. Environ. Res. 2013, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansfeld, S.A.; Clark, C.; Cameron, R.M.; Alfred, T.; Head, J.; Haines, M.M.; van Kamp, I.; van Kempen, E.; Lopez-Barrio, I. Aircraft and road traffic noise exposure and children’s mental health. J. Environ. Psychol. 2009, 29, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortebjerg, D.; Andersen, A.M.N.; Christensen, J.S.; Ketzel, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Sunyer, J.; Julvez, J.; Forns, J.; Sørensen, M. Exposure to road traffic noise and behavioral problems in 7-year-old children: A cohort study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyde, K.V.; Krog, N.H.; Oftedal, B.; Evandt, J.; Magnus, P.; Øverland, S.; Clark, C.; Stansfeld, S.; Aasvang, G.M. Nocturnal road traffic noise exposure and children’s sleep duration and sleep problems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Kweon, K.; Kim, H.W.; Cho, S.W.; Park, J.; Sim, C.S. Negative impact of noise and noise sensitivity on mental health in childhood. Noise Health 2018, 20, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crombie, R.; Clark, C.; Stansfeld, S.A. Environmental noise exposure, early biological risk and mental health in nine to ten year old children: A cross-sectional field study. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belojevic, G.; Evans, G.W.; Paunovic, K.; Jakovljevic, B. Traffic noise and executive functioning in urban primary school children: The moderating role of gender. J. Environ. Psychol. 2012, 32, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhrström, E.; Hadzibajramovic, E.; Holmes, M.; Svensson, H. Effects of road traffic noise on sleep: Studies on children and adults. J. Environ. Psychol. 2006, 26, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyde, K.V.; Krog, N.H.; Oftedal, B.; Magnus, P.; Øverland, S.; Stansfeld, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Vrijheid, M.; Pascual, M.D.C.; Aasvang, G.M. Road traffic noise and children’s inattention. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airports Commission. Airports Commission: Final Report; Technical Report; Airports Commission: London, UK, 2015.
- Locher, B.; Piquerez, A.; Habermacher, M.; Ragettli, M.; Röösli, M.; Brink, M.; Cajochen, C.; Vienneau, D.; Foraster, M.; Müller, U.; et al. Differences between Outdoor and Indoor Sound Levels for Open, Tilted, and Closed Windows. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, Y.; Kelly, J.; Sacker, A. Time for bed: Associations with cognitive performance in 7-year-old children: A longitudinal population-based study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2013, 67, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannin, P.H.T.; Marcon, C.R. Objective and subjective evaluation of the acoustic comfort in classrooms. Appl. Ergon. 2007, 38, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangeer, F. Acoustic comfort in the living environment and its association with noise representation: A systematic review. SHS Web Conf. 2019, 64, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rasmussen, B. Sound insulation between dwellings—Comparison of national requirements in Europe and interaction with acoustic classification schemes. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress on Acoustics, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Secchi, S.; Brambilla, G.; Casini, D.; Cellai, G. A Method to Estimate Students’ Exposure to Road Traffic Noise Events. Environments 2018, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, B.; Lindvall, T.; Schwela, D.H. Guidelines for Community Noise; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Fletcher, H.; Manson, W. Loudness, Its Definition, Measurement and Calculation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1933, 5, 82–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, J.; Novak, C.; Gaspar, R.; Ule, H. A-weighting the equal loudness contours. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 3502–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozalo, G.R.; Carmona, J.T.; Morillas, J.B.; Vílchez-Gómez, R.; Escobar, V.G. Relationship between objective acoustic indices and subjective assessments for the quality of soundscapes. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 97, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, D.; Heinonen-Guzejev, M.; Hautus, M.J.; Heikkilä1, K. Elucidating the relationship between noise sensitivity and personality. Noise Health 2015, 17, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Krantz, D.S.; Evans, G.; Stokols, D.; Kelly, S. Aircraft noise and children: Longitudinal and cross-sectional evidence on adaptation to noise and the effectiveness of noise abatement. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1981, 40, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, S.A.; Centen, M.R.; Vos, H.; van Kamp, I. The effect of the number of aircraft noise events on sleep quality. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 84, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Payne, C. Effects of noise level and difficulty of task in performing division. J. Appl. Psychol. 1963, 47, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).


