Aquatic Exercise on Brain Activity in Type 2 Diabetic: Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
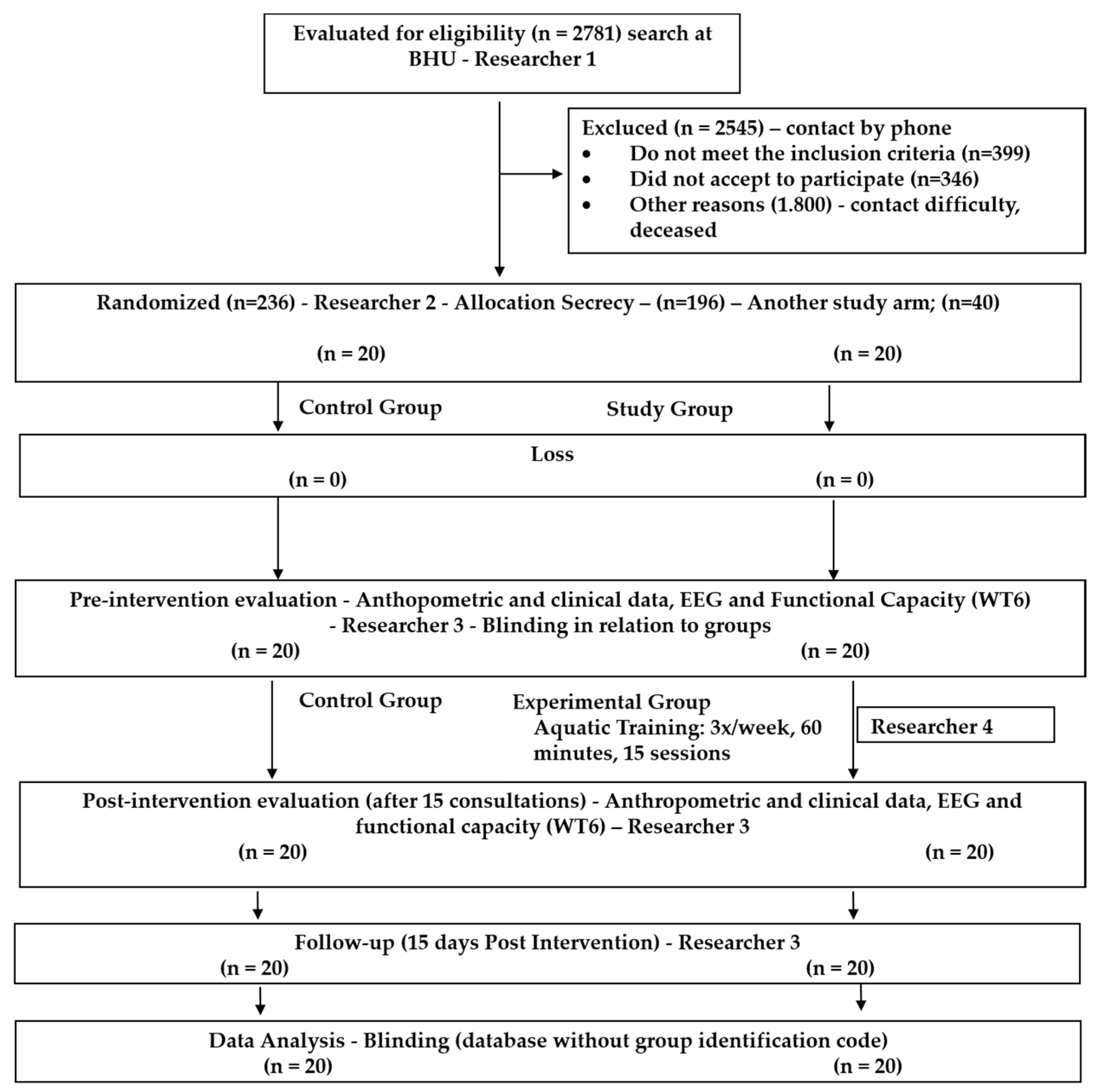
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Pilot Study and Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Assessment Measures
2.4. Anthropometric Data
2.5. International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)
2.6. Assessment of Functional Capacity
2.7. Assessment of Electroencephalographic (EEG) Activity
2.8. Processing and Analysis of EEG Data
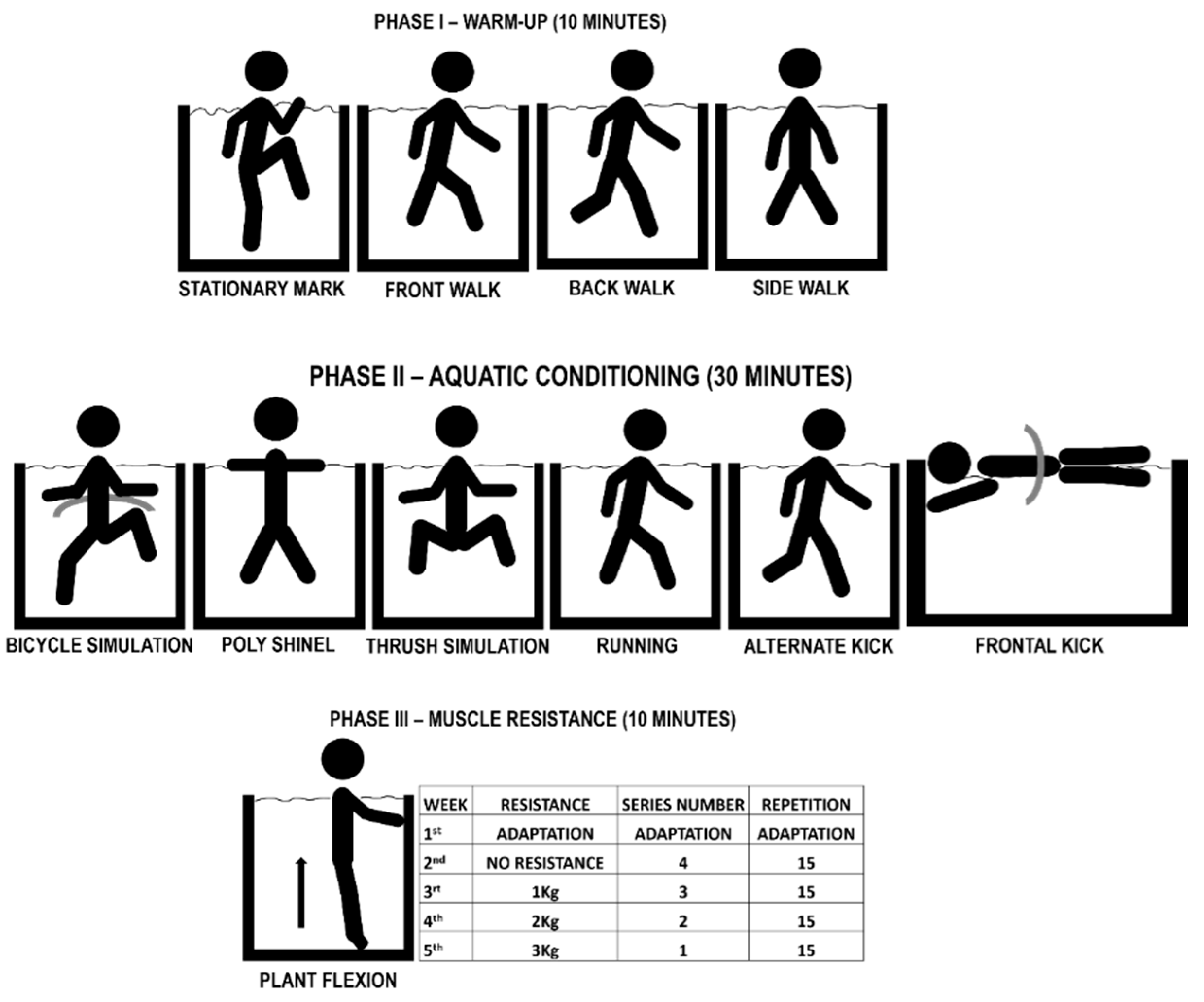
2.9. Training Protocol
2.9.1. Experimental Group (SG)
2.9.2. Control Group (CG)
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petersmann, A.A.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Müller, U.A.; Landgraf, R.; Nauck, M.; Freckmann, G.; Heinemann, L.; Schleicher, E. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2019 and Projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correr, C.J.; Coura-Vital, W.; Frade, J.C.Q.P.; Nascimento, R.C.R.M.; Nascimento, L.G.; Pinheiro, E.B.; Ferreira, W.M.; Reis, J.S.; Melo, K.F.S.; Pontarolo, R.; et al. Prevalence of People at Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Involvement of Community Pharmacies in a National Screening Campaign: A Pioneer Action in Brazil. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, D.C.; de Morais Neto, O.L.; Silva Junior, J.B. da Apresentação Do Plano de Ações Estratégicas Para o Enfrentamento Das Doenças Crônicas Não Transmissíveis No Brasil, 2011 a 2022. Epidemiol. Serviços Saúde 2011, 20, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.D.; Arena, R.; Riebe, D.; Pescatello, L.S. ACSM’s New Preparticipation Health Screening Recommendations from ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, Ninth Edition. Curr. Sport. Med. Rep. 2013, 12, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.L. Changes and Consistencies in Diabetes Education Over 5 Years. Diabetes Educ. 2012, 38, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melmer, A.; Kempf, P.; Laimer, M. The Role of Physical Exercise in Obesity and Diabetes. Praxis 2018, 107, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulé, N.G.; Kenny, G.P.; Haddad, E.; Wells, G.A.; Sigal, R.J. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Structured Exercise Training on Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delevatti, R.S.; Kanitz, A.C.; Alberton, C.L.; Marson, E.C.; Lisboa, S.C.; Pinho, C.D.F.; Lovatel, G.A.; Korb, A.; Bertoldi, K.; Macedo, R.C.O.; et al. Glucose Control Can Be Similarly Improved after Aquatic or Dry-Land Aerobic Training in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Johnson, S.T.; Loucaides, C.A.; Bauman, A.E.; Karunamuni, N.D.; Pickering, M.A. Population-Based Estimates of Physical Activity for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cautionary Tale of Potential Confounding by Weight Status. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 561432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convertino, V.A.; Tatro, D.L.; Rogan, R.B. Renal and Cardiovascular Responses to Water Immersion in Trained Runners and Swimmers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1993, 67, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, T.; Dowzer, C.N.; Cable, N. The Physiology of Deep-Water Running. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colcombe, S.; Kramer, A.F. Fitness Effects on the Cognitive Function of Older Adults. Psychol. Sci. 2003, 14, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.F.; Colcombe, S. Fitness Effects on the Cognitive Function of Older Adults: A Meta-Analytic Study—Revisited. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 13, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, D.L.; Johannsen, N.M.; Myers, V.H.; Earnest, C.P.; Smits, J.A.J.; Blair, S.N.; Church, T.S. The Effect of Exercise Training Modality on Serum Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Graubard, B.I.; Williamson, D.F. Methods of Calculating Deaths Attributable to Obesity. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecke, J.A.; Burema, J.; Frijters, J.E. A Short Questionnaire for the Measurement of Habitual Physical Activity in Epidemiological Studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 36, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, T.R.B.; de Cesaro Antunes, P.; Rodriguez-Añez, C.R.; Mazo, G.Z.; Petroski, É.L. Reprodutibilidade e Validade Do Questionário Internacional de Atividade Física (IPAQ) Em Homens Idosos. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2007, 13, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATS Statement. Guidelines for the Six-Minute Walk Test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, H.N.; Barker, K.L.; Cockburn, J.; Roach, N.; Scott, O.; Wade, D. Borg’s Rating of Perceived Exertion Scales: Do the Verbal Anchors Mean the Same for Different Clinical Groups? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, V.M.D.; Martins, B.D.C.D.S.; Jardim, C.; Fernandes, C.J.C.; Hovnanian, A.; Souza, R. Validação de Um Protocolo Para o Teste de Caminhada de Seis Minutos Em Esteira Para Avaliação de Pacientes Com Hipertensão Arterial Pulmonar. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2009, 35, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badcock, N.A.; Mousikou, P.; Mahajan, Y.; de Lissa, P.; Thie, J.; McArthur, G. Validation of the Emotiv EPOC ® EEG Gaming System for Measuring Research Quality Auditory ERPs. PeerJ 2013, 1, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, T.; Parberry, I.; Parsons, T.D. Modality Specific Assessment of Video Game Player’s Experience Using the Emotiv. Entertain. Comput. 2015, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Greenacre, L.; Kodagoda, S.; Louviere, J.; Burke, S.; Dissanayake, G. Choice Modeling and the Brain: A Study on the Electroencephalogram (EEG) of Preferences. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 12378–12388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koessler, L.; Maillard, L.; Benhadid, A.; Vignal, J.P.; Felblinger, J.; Vespignani, H.; Braun, M. Automated Cortical Projection of EEG Sensors: Anatomical Correlation via the International 10–10 System. Neuroimage 2009, 46, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyvärinen, A.; Oja, E. Independent Component Analysis: Algorithms and Applications. Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kirar, J.S. A Novel Approach for Extracting Feature from EEG Signal for Mental Task Classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computing and Network Communications (CoCoNet), Trivandrum, India, 16–19 December 2015; pp. 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, T.; Ueta, K.; Imai, R.; Morioka, S. EEG Frequency Analysis of Cortical Brain Activities Induced by Effect of Light Touch. Exp. Brain Res. 2016, 234, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, L.C.; Marshall, P.J.; Shipley, T.F.; Beilock, S.L.; Goldin-Meadow, S. Sensitivity of Alpha and Beta Oscillations to Sensorimotor Characteristics of Action: An EEG Study of Action Production and Gesture Observation. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 2745–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntraluck, S.; Tanaka, H.; Suksom, D. The Relative Efficacy of Land-Based and Water-Based Exercise Training on Macro- and Microvascular Functions in Older Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2017, 25, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugusi, L.; Cadeddu, C.; Nocco, S.; Orrù, F.; Bandino, S.; Deidda, M.; Caria, A.; Bassareo, P.P.; Piras, A.; Cabras, S.; et al. Effects of an Aquatic-Based Exercise Program to Improve Cardiometabolic Profile, Quality of Life, and Physical Activity Levels in Men With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. PM R 2015, 7, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, J.; Songsorn, P.; Haggett, M.; Edmonds, D.; Robinson, A.; Thompson, D.; Vollaard, N. A Comparison of the Health Benefits of Reduced-Exertion High-Intensity Interval Training (REHIT) and Moderate-Intensity Walking in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 42, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnick, J.J.; Sherman, W.M.; Habash, D.L.; Stout, M.B.; Failla, M.L.; Belury, M.A.; Schuster, D.P. Short-Term Aerobic Exercise Training in Obese Humans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Improves Whole-Body Insulin Sensitivity through Gains in Peripheral, Not Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallberg-Henriksson, H.; Rincon, J.; Zierath, J. Exercise in the Management of Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Sport. Med. 1998, 25, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colado, J.C.; Tella, V.; Triplett, N.T. A Method for Monitoring Intensity During Aquatic Resistance Exercises. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 2045–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, C.H.; Erickson, K.I.; Kramer, A.F. Be Smart, Exercise Your Heart: Exercise Effects on Brain and Cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardon, M.T.; Polich, J. EEG Changes from Long-Term Physical Exercise. Biol. Psychol. 1996, 44, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Påhlman, U.; Sävborg, M.; Tarkowski, E. Cognitive Dysfunction and Physical Activity After Stroke: The Gothenburg Cognitive Stroke Study in the Elderly. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 21, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radak, Z.; Hart, N.; Sarga, L.; Koltai, E.; Atalay, M.; Ohno, H.; Boldogh, I. Exercise Plays a Preventive Role Against Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 20, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor-Locke, C.E.; Bell, R.C.; Myers, A.M. Revisiting the Role of Physical Activity and Exercise in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 25, 466–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos, M.; Virally, M.-L.; Dejager, S. Exercise in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: What Are the Benefits and How Does It Work? Phys. Sportsmed. 2011, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberton, C.L.; Nunes, G.N.; Rau, D.G.D.S.; Bergamin, M.; Cavalli, A.S.; Pinto, S.S. Vertical Ground Reaction Force During a Water-Based Exercise Performed by Elderly Women: Equipment Use Effects. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2019, 90, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.S.Y.; Liu, G.; Liang, D.; Deng, K.; Wu, J.; Yan, J.H. Special Issue–Therapeutic Benefits of Physical Activity for Mood: A Systematic Review on the Effects of Exercise Intensity, Duration, and Modality. J. Psychol. 2019, 153, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, H.H.; Spence, A.L.; Pugh, C.J.A.; Ainslie, P.; Naylor, L.H.; Green, D.J. Cardiovascular Responses to Water Immersion in Humans: Impact on Cerebral Perfusion. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 306, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Henney, N.C.; Sathyapalan, T.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Neuromodulatory Effects of Anti-Diabetes Medications: A Mechanistic Review. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, S. Antihypertensive Drugs. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 124, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Control Group (n = 20) | Experimental Group (n = 20) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr.), mean (SD), CI 95% | 64.20 ± 12.08 58.54 to 69.85 | 62.22 ± 11.44 57.15 to 67.30 | 0.59 a |
| Height (m), mean (SD), CI 95% | 1.57 ± 0.09 1.53 to 1.62 | 1.58 ± 0.09 1.54 to 1.62 | 0.94 b |
| Body Mass (Kg), mean (SD), CI 95% | 79.77 ± 20.75 70.05 to 89.48 | 71.25 ± 9.84 66.88 to 75.62 | 0.10 a |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD), CI 95% | 25.10 ± 5.56 22.50 to 27.71 | 22.47 ± 2.76 21.24 to 23.69 | 0.05 a |
| Diagnostic time (yr), mean (SD), CI 95% | 11.75 ± 5.96 8.95 to 14.54 | 10.27 ± 5.24 7.94 to 12.59 | 0.44 b |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Feminine | 12 (60) | 13 (65) | 0.40 c |
| Male | 8 (40) | 7 (35) | |
| Physical activity, n (%) | |||
| No | 11 (55) | 10 (50) | 0.61 c |
| Yes | 9 (45) | 10 (50) | |
| Smoker, n (%) | |||
| No | 17 (85) | 16 (80) | 0.55 c |
| Yes | 3 (15) | 4 (20) | |
| Alcoholism, n (%) | |||
| No | 17 (85) | 16 (80) | 0.55 c |
| Yes | 3 (15) | 4 (20) | |
| Hypertension, n (%) | |||
| No | 6 (30) | 8 (40) | 0.45 c |
| Yes | 14 (70) | 12 (60) | |
| IPAQ questionnaire, n (%) | |||
| Sedentary | 4 (20) | 0 | 0.04 a* |
| Insufficient active A | 9 (45) | 8 (40) | |
| Insufficient active B | 5 (25) | 10 (50) | |
| Active | 2 (10) | 2 (10) | |
| Very Active |
| Outcome | Groups | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Intervention | Post-Intervention | Follow-Up | p Value | ||||||
| Con (n = 20) | Exp (n = 20) | Con (n = 20) | Exp (n = 20) | Con (n = 20) | Exp (n = 20) | Time | Groups versus Times | Groups | |
| Six-minute walk test (m) | 434.68 ± 81.02 397.79 to 471.56 | 440.49 ± 85.68 394.83 to 486.14 | 459.69 ± 77.54 424.39 to 494.98 | 460.55 ± 48.90 434.49 to 486.61 | 450.31 ± 87.08 410.67 to 489.95 | 468.14 ± 50.05 441.47 to 494.81 | 0.01 * PrexPos | 0.51 | 0.72 |
| Six-minute walk test provided (m) | 454.01 ± 54.29 429.30 to 478.73 | 491.58 ± 82.09 491.58 to 535.33 | 453.74 ± 53.73 429.28 to 478.20 | 491.34 ± 82.45 447.40 to 535.28 | 454.87 ± 53.97 430.32 to 479.42 | 491.46 ± 82.34 447.57 to 535.34 | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.10 |
| Capillary blood glucose (mg/dL) | 195.19 ± 79.59 158.95 to 231.42 | 196.68 ± 77.97 155.13 to 238.23 | 185.61 ± 70.07 153.72 to 217.51 | 209.37 ± 80.61 166.42 to 252.32 | 183.38 ± 58.83 156.60 to 210.16 | 182.00 ± 72.42 143.41 to 220.58 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.70 |
| Groups | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Intervention | Post-Intervention | Follow-Up | p Value | ||||||
| Channel | Con (n = 20) | Exp (n = 20) | Con (n = 20) | Exp (n = 20) | Con (n = 20) | Exp (n = 20) | Time | Groups versus Time | Groups |
| AF3 (µv) | 41.29 ± 20.38 32.01 to 50.57 | 41.50 ± 21.56 30.01 to 53.00 | 34.35 ± 22.80 23.97 to 44.73 | 45.64 ± 21.46 34.20 to 57.07 | 40.39 ± 23.11 29.87 to 50.91 | 24.21 ± 18.50 14.35 to 34.07 | 0.050 | 0.004 * Exp PrexFollow PosxFollow | 0.77 |
| AF4 (µv) | 43.78 ± 20.97 34.23 to 53.33 | 44.48 ± 21.85 32.83 to 56.12 | 35.96 ± 22.77 25.60 to 46.33 | 45.47 ± 21.05 34.24 to 56.69 | 39.53 ± 21.36 29.80 to 49.25 | 25.45 ± 18.84 15.40 to 35.49 | 0.010 * PrexFollow | 0.19 | 0.80 |
| F7 (µv) | 44.20 ± 22.20 34.09 to 54.31 | 43.50 ± 21.95 31.80 to 55.20 | 35.04 ± 22.45 24.82 to 45.26 | 42.52 ± 24.30 29.57 to 55.47 | 38.71 ± 21.93 28.72 to 48.69 | 21.02 ± 20.04 10.34 to 31.70 | 0.004 * PrexFollow | 0.010 * Exp PrexFollow PosxFollow | 0.52 |
| F8 (µv) | 44.78 ± 20.80 35.30 to 54.25 | 44.32 ± 20.96 33.14 to 55.49 | 36.51 ± 22.75 26.15 to 46.87 | 40.43 ± 23.16 28.09 to 52.78 | 40.41 ± 21.38 30.68 to 50.15 | 19.87 ± 17.94 10.30 to 29.43 | 0.004 * PrexFollow | 0.010 * Exp PrexFollow PosxFollow | 0.27 |
| F3 (µv) | 40.66 ± 19.35 31.85 to 49.47 | 40.33 ± 20.30 29.51 to 51.15 | 32.10 ± 20.67 22.69 to 41.51 | 42.46 ± 19.10 32.28 to 52.64 | 38.58 ± 22.58 28.30 to 48.86 | 21.76 ± 17.09 12.65 to 30.86 | 0.030 * PrexFollow | 0.004 * Exp PrexFollow PosxFollow | 0.64 |
| F4 (µv) | 42.75 ± 19.60 33.83 to 51.68 | 39.69 ± 23.55 27.14 to 52.24 | 35.09 ± 21.44 25.33 to 44.85 | 40.90 ± 21.58 29.39 to 52.40 | 39.51 ± 21.30 28.81 to 48.21 | 21.10 ± 19.28 10.82 to 31.37 | 0.020 * PrexFollow | 0.020 * Exp PrexFollow PosxFollow | 0.34 |
| FC5 (µv) | 39.93 ± 20.61 30.55 to 49.31 | 42.58 ± 24.01 19.79 to 55.37 | 31.514 ± 20.81 22.04 to 40.98 | 40.36 ± 22.96 28.12 to 52.60 | 38.80 ± 22.96 28.35 to 49.26 | 18.10 ± 20.20 7.34 to 28.87 | 0.010 * PrexFollow | 0.002 * Exp PrexFollow PosxFollow | 0.57 |
| FC6 (µv) | 43.15 ± 21.98 33.14 to 53.16 | 42.80 ± 22.71 30.70 to 54.90 | 34.22 ± 21.53 24.42 to 44.02 | 42.44 ± 24.49 29.38 to 55.49 | 36.29 ± 21.37 26.56 to 50.86 | 18.30 ± 18.95 8.20 to 28.40 | 0.001 * PrexFollow | 0.009 * Exp PrexFollow PosxFollow | 0.53 |
| Outcome | Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con | Exp | Con | Exp | ||
| Post | Follow-Up | Post | Follow-Up | ||
| Channel EEG x Functional Capacity | |||||
| FC5 x 6MWT | r p | −0.05 0.83 | 0.2 0.41 | −0.20 0.38 | 0.27 0.25 |
| FC6 x 6MWT | r p | 0.19 0.40 | 0.2 0.41 | −0.01 0.96 | 0.13 0.57 |
| Channel EEG x Glycemia Capillary | |||||
| FC5 x Glycemia Capillary | r p | 0.25 0.28 | 0.28 0.24 | 0.04 0.84 | 0.18 0.44 |
| FC6 x Glycemia Capillary | r p | 0.33 0.14 | 0.21 0.37 | −0.09 0.68 | −0.04 0.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, G.C.V.; Santos, A.T.S.; Calixto Júnior, R.; Dias, M.P.F.; Iunes, D.H.; Chaves, E.d.C.L.; Marino, L.d.S.; Borges, J.B.C.; Silva Vilela Terra, A.M. Aquatic Exercise on Brain Activity in Type 2 Diabetic: Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214759
Gonçalves GCV, Santos ATS, Calixto Júnior R, Dias MPF, Iunes DH, Chaves EdCL, Marino LdS, Borges JBC, Silva Vilela Terra AM. Aquatic Exercise on Brain Activity in Type 2 Diabetic: Randomized Clinical Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):14759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214759
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Guilherme Cândido Viana, Adriana Teresa Silva Santos, Ruanito Calixto Júnior, Miqueline Pivoto Faria Dias, Denise Hollanda Iunes, Erika de Cássia Lopes Chaves, Ligia de Sousa Marino, Juliana Bassalobre Carvalho Borges, and Andréia Maria Silva Vilela Terra. 2022. "Aquatic Exercise on Brain Activity in Type 2 Diabetic: Randomized Clinical Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 14759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214759
APA StyleGonçalves, G. C. V., Santos, A. T. S., Calixto Júnior, R., Dias, M. P. F., Iunes, D. H., Chaves, E. d. C. L., Marino, L. d. S., Borges, J. B. C., & Silva Vilela Terra, A. M. (2022). Aquatic Exercise on Brain Activity in Type 2 Diabetic: Randomized Clinical Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 14759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214759






