The Effect of Cognitive Strategies and Facial Attractiveness on Empathic Neural Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stimuli
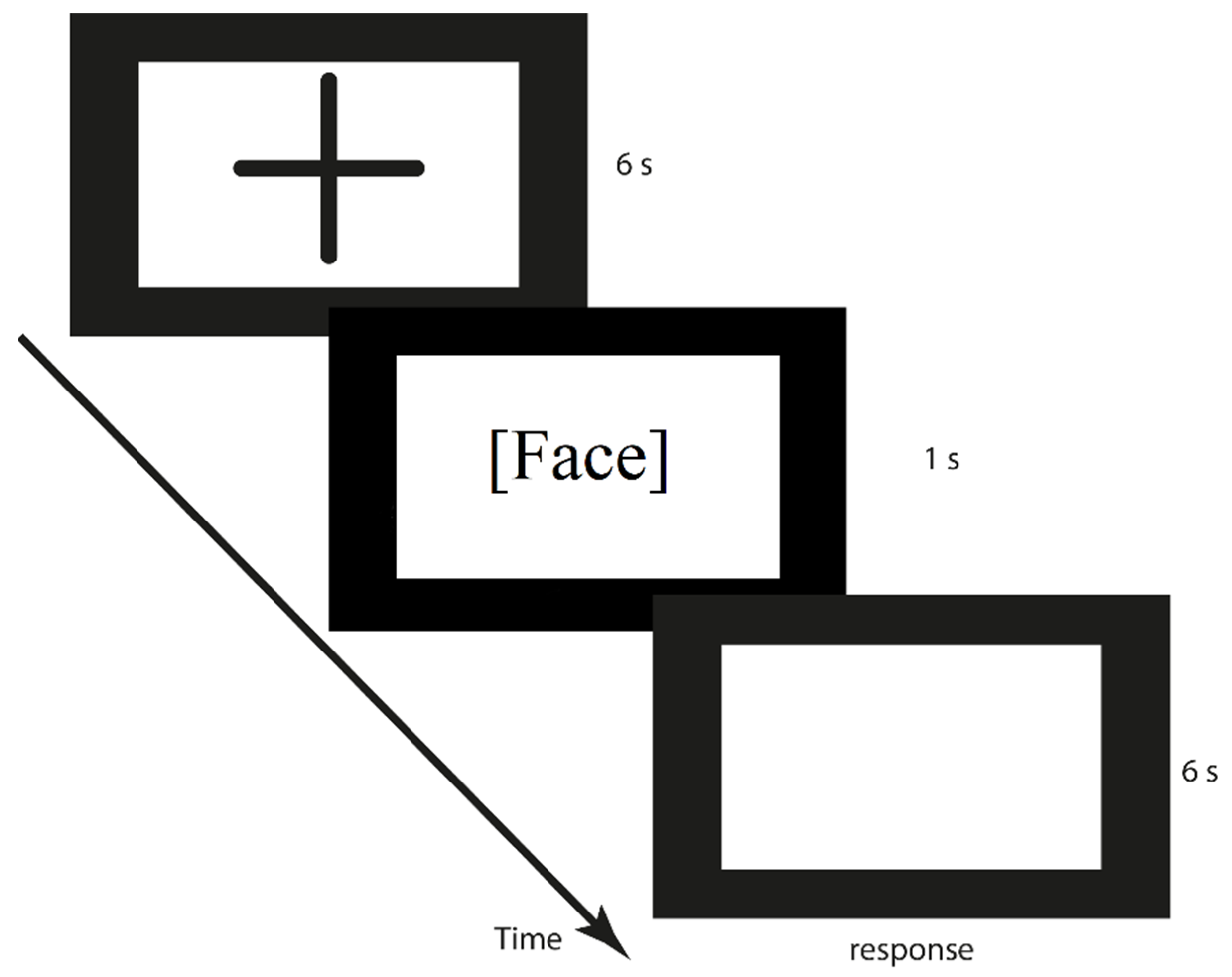
2.3. Procedure
2.4. EEG Acquisition and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
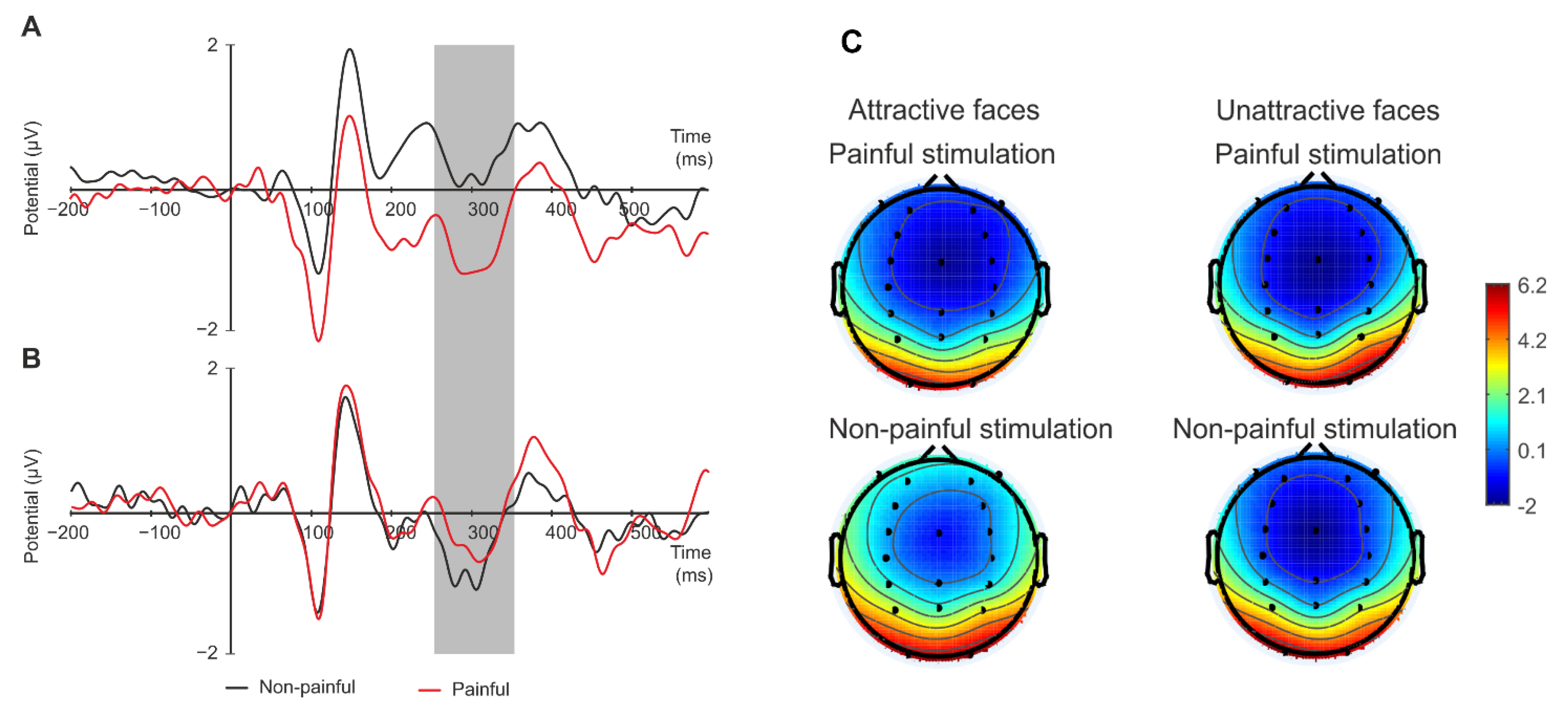
3.1. ERP: N2 (250–350 ms)
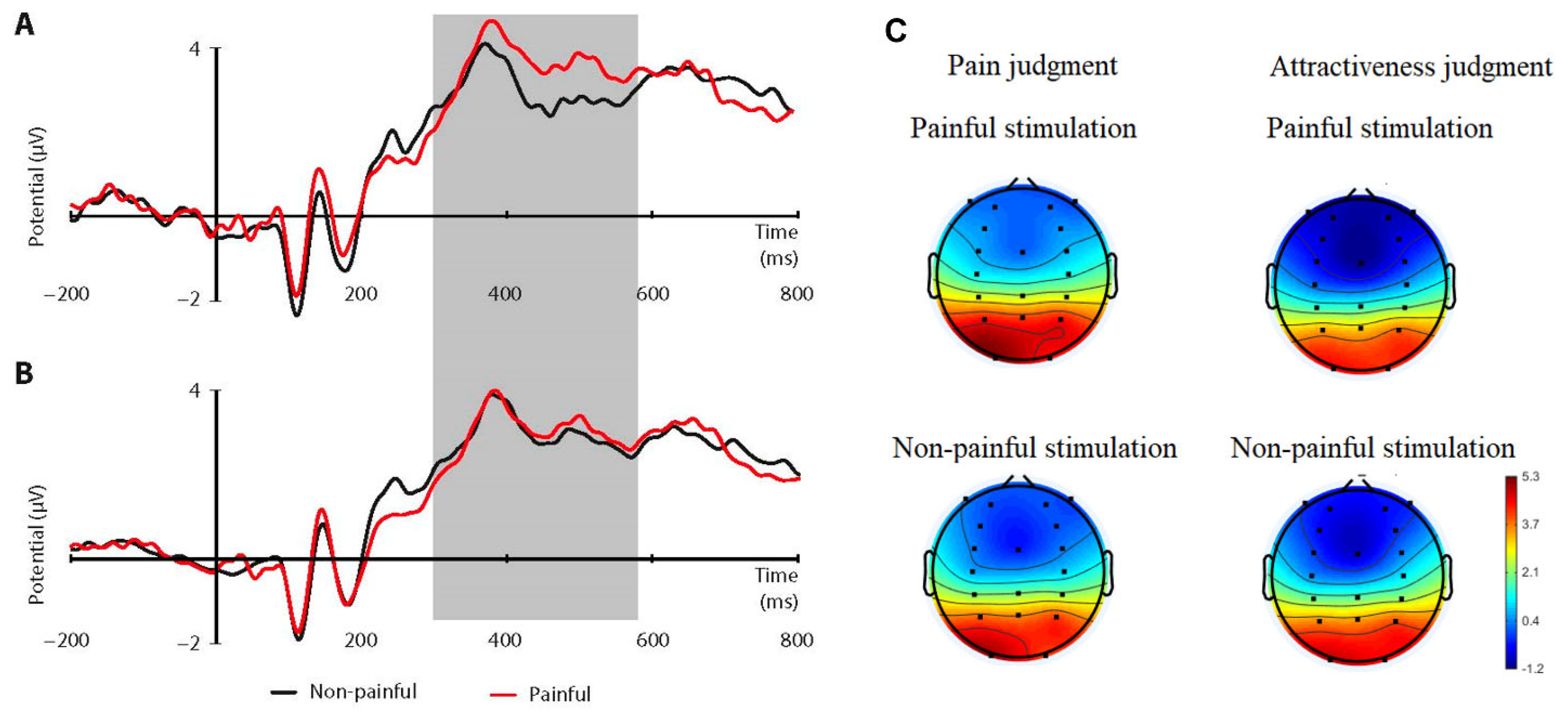
3.2. ERP: P3 (320–580 ms)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Decety, J.; Bartal, I.B.A.; Uzefovsky, F.; Knafo-Noam, A. Empathy as a driver of prosocial behaviour: Highly conserved neurobehavioural mechanisms across species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decety, J.; Jackson, P.L. A Social-Neuroscience Perspective on Empathy. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 15, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsee, C.K.; Hatfield, E.; Carlson, J.G.; Chemtob, C. The effect of power on susceptibility to emotional contagion. Cogn. Emot. 1990, 4, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decety, J.; Michalska, K.J.; Akitsuki, Y. Who caused the pain? An fMRI investigation of empathy and intentionality in children. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Duncan, N.W.; de Greck, M.; Northoff, G. Is there a core neural network in empathy? An fMRI based quantitative meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, C.; Decety, J.; Singer, T. Meta-analytic evidence for common and distinct neural networks associated with directly experienced pain and empathy for pain. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzdok, D.; Schilbach, L.; Vogeley, K.; Schneider, K.; Laird, A.R.; Langner, R.; Eickhoff, S.B. Parsing the neural correlates of moral cognition: ALE meta-analysis on morality, theory of mind, and empathy. Brain Struct. Funct. 2012, 217, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, J.; Ochsner, K.N. The neuroscience of empathy: Progress, pitfalls and promise. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, T.; Seymour, B.; O’Doherty, J.; Kaube, H.; Dolan, R.J.; Frith, C.D. Empathy for Pain Involves the Affective but not Sensory Components of Pain. Science 2004, 303, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaansen, J.A.; Thioux, M.; Keysers, C. Evidence for mirror systems in emotions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, P.; Meconi, F.; Castelli, L.; Dell’Acqua, R. Taking one’s time in feeling other-race pain: An event-related potential investigation on the time-course of cross-racial empathy. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2013, 9, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zuo, X.; Wang, X.; Han, S. Do you feel my pain? Racial group membership modulates empathic neural responses. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8525–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, F.; Han, S. Manipulations of cognitive strategies and intergroup relationships reduce the racial bias in empathic neural responses. NeuroImage 2012, 61, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartanian, O.; Goel, V.; Lam, E.; Fisher, M.; Granic, J. Middle temporal gyrus encodes individual differences in perceived facial attractiveness. Psychol. Aesthet. Creat. Arts 2013, 7, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion, K.K. Young children’s stereotyping of facial attractiveness. Dev. Psychol. 1973, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berscheid, E.; Walster, E. Physical attractiveness. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; Volume 7, pp. 157–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zelazniewicz, A.M.; Pawlowski, B. Female breast size attractiveness for men as a function of sociosexual orientation (restricted vs. unrestricted). Arch. Sex. Behav. 2011, 40, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, I.R.; Marshuetz, C. Facial attractiveness is appraised in a glance. Emotion 2005, 5, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.K.; Eckel, C.C. Judging a book by its cover: Beauty and expectations in the trust game. Polit. Res. Q. 2006, 59, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjistavropoulos, H.D.; Ross, M.A.; Von Baeyer, C.L. Are physicians’ ratings of pain affected by patients’ physical attractiveness? Soc. Sci. Med. 1990, 31, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.C.N.; Van Leeuwen, M.L.; Van Baaren, R.B.; Bekkering, H.; Dijksterhuis, A. Empathy is a beautiful thing: Empathy predicts imitation only for attractive others. Scand. J. Psychol. 2013, 54, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.J.; Ma, Y. The price of being beautiful: Negative effects of attractiveness on empathy for children in need. J. Consum. Res. 2014, 41, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowiak-Siuda, K.; Rymarczyk, K.; Żurawski, Ł.; Jednoróg, K.; Marchewka, A. Physical attractiveness and sex as modulatory factors of empathic brain responses to pain. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Li, X.; Peng, W.; Li, Z.; Shen, L. The interaction between pain and attractiveness perception in others. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopiś, N.; Francuz, P.; Zabielska-Mendyk, E.; Augustynowicz, P. Feeling Other People’s Pain: An Event-Related Potential Study on Facial Attractiveness and Emotional Empathy. Adv. Cogn. Psychol. 2020, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Meng, J.; Lou, Y.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Yan, D. Reduced empathic pain processing in patients with somatoform pain disorder: Evidence from behavioral and neurophysiological measures. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019, 139, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, M.P. Meta-analysis of ERP investigations of pain empathy underlines methodological issues in ERP research. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galang, C.M.; Jenkins, M.; Obhi, S.S. Exploring the effects of visual perspective on the ERP components of empathy for pain. Soc. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopiś-Posiej, N.; Cudo, A.; Tużnik, P.; Wojtasiński, M.; Augustynowicz, P.; Zabielska-Mendyk, E.; Bogucka, V. The impact of problematic Facebook use and Facebook context on empathy for pain processing: An event-related potential study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2021, 124, 106936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Huerta, L.S.; Hielscher, E.; Sherwell, C.S.; Rens, N.; Cunnington, R. Intergroup relationships do not reduce racial bias in empathic neural responses to pain. Neuropsychologia 2014, 64, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Han, X.; Du, N.; Han, S. Physical coldness enhances racial in-group bias in empathy: Electrophysiological evidence. Neuropsychologia 2018, 116, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Han, S. Temporal dynamic of neural mechanisms involved in empathy for pain: An event-related brain potential study. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, R.E.; Geurdes, F.I.; Bekker, M.H. Attachment styles are related to ERPs elicited to angry faces in an oddball paradigm. J. Behav. Brain Sci. 2012, 2, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polich, J. Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2128–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polich, J. Neuropsychology of P300. In The Oxford Handbook of Event-Related Potential Components; Luck, S.J., Kappenman, E.S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 159–188. [Google Scholar]
- Hajcak, G.; Weinberg, A.; MacNamara, A.; Foti, D. ERPs and the study of emotion. In The Oxford handbook of event-related potential components; Luck, S.J., Kappenman, E.S., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 441–472. [Google Scholar]
- Fabi, S.; Leuthold, H. Racial bias in empathy: Do we process dark-and fair-colored hands in pain differently? An EEG study. Neuropsychologia 2018, 114, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donchin, E. Event-related brain potentials: A tool in the study of human information processing. In Evoked Brain Potentials and Behavior; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1979; pp. 13–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Z. Gender, facial attractiveness, and early and late event-related potential components. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2012, 11, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.S.; Correll, J.; Wittenbrink, B. The Chicago face database: A free stimulus set of faces and norming data. Behav. Res. Methods 2015, 47, 1122–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balconi, M.; Kopis, N.; Angioletti, L. Does aesthetic judgment on face attractiveness affect neural correlates of empathy for pain? A fNIRS study. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, T.R.; Kothe, C.A.E.; Chi, Y.M.; Ojeda, A.; Kerth, T.; Makeig, S.; Jung, T.-P.; Cauwenberghs, G. Real-time neuroimaging and cognitive monitoring using wearable dry EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Xiang, B.; Meng, J. Empathy for pain in Individuals with autistic traits influenced by attention cues: Evidence from an ERP study. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2020, 52, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjistavropoulos, T.; Craig, K.D.; Duck, S.; Cano, A.; Goubert, L.; Jackson, P.L.; Mogil, J.S.; Rainville, P.; Sullivan, M.J.L.; Williams, A.C.d.C.; et al. A biopsychosocial formulation of pain communication. Psychol. Bull. 2011, 137, 910–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Fan, Y.; Mao, L. Gender difference in empathy for pain: An electrophysiological investigation. Brain Res. 2008, 1196, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.M.; Hamby, S.; Löw, A.; Lang, P.J. Brain potentials in perception: Picture complexity and emotional arousal. Psychophysiology 2007, 44, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.J.; Bradley, M.M.; Cuthbert, B.N. International affective picture system (IAPS): Technical manual and affective ratings. NIMH Cent. Study Emot. Atten. 1997, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Drigas, A.; Mitsea, E. 8 Pillars X 8 Layers Model of Metacognition: Educational Strategies, Exercises &Trainings. International J. Online Biomed. Eng. 2021, 17, 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Decety, J.; Lamm, C. Human Empathy Through the Lens of Social Neuroscience. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 1146–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.J.; Carbine, K.A. Sample size calculations in human electrophysiology (EEG and ERP) studies: A systematic review and recommendations for increased rigor. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2017, 111, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| M/SD | Pain Judgment | Attractiveness Judgment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Painful | Non-Painful | Painful | Non-Painful | |||||
| Atr. | N.Atr | Atr. | N.Atr | Atr. | N.Atr | Atr. | N.Atr | |
| M | 29.68 | 29.05 | 29.16 | 28.89 | 29.26 | 29.37 | 29.36 | 28.68 |
| SD | 0.82 | 1.87 | 1.26 | 2.51 | 1.45 | 1.59 | 1.12 | 2.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balconi, M.; Kopiś-Posiej, N.; Venturella, I.; Zabielska-Mendyk, E.; Augustynowicz, P.; Angioletti, L. The Effect of Cognitive Strategies and Facial Attractiveness on Empathic Neural Responses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114617
Balconi M, Kopiś-Posiej N, Venturella I, Zabielska-Mendyk E, Augustynowicz P, Angioletti L. The Effect of Cognitive Strategies and Facial Attractiveness on Empathic Neural Responses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(21):14617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114617
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalconi, Michela, Natalia Kopiś-Posiej, Irene Venturella, Emilia Zabielska-Mendyk, Paweł Augustynowicz, and Laura Angioletti. 2022. "The Effect of Cognitive Strategies and Facial Attractiveness on Empathic Neural Responses" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 21: 14617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114617
APA StyleBalconi, M., Kopiś-Posiej, N., Venturella, I., Zabielska-Mendyk, E., Augustynowicz, P., & Angioletti, L. (2022). The Effect of Cognitive Strategies and Facial Attractiveness on Empathic Neural Responses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21), 14617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114617








