On the Geochemistry of the Danube River Sediments (Serbian Sector)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hypothesis and Research Objectives
3. Materials and Methods
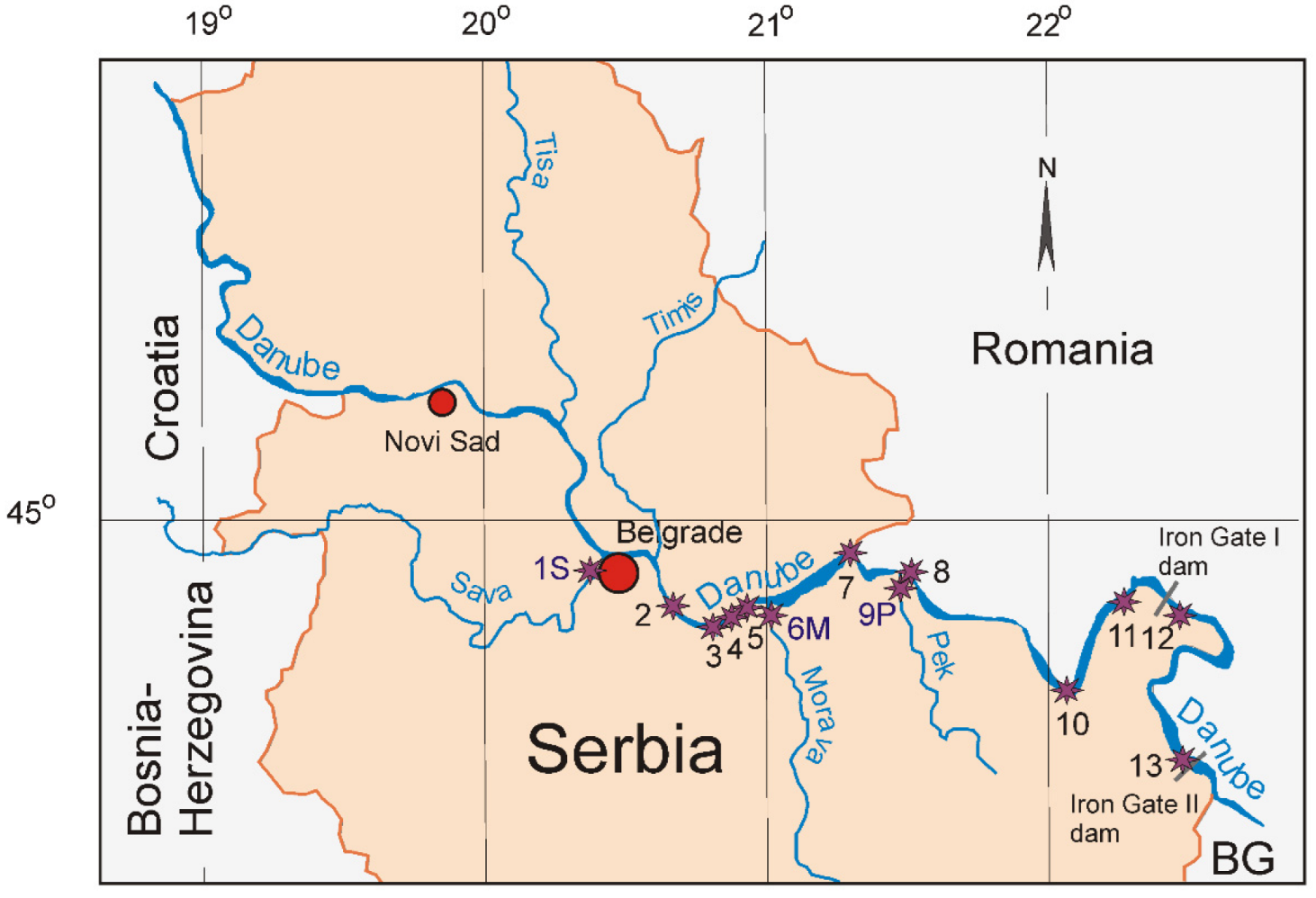
3.1. Sampling and Sample Preparation
3.2. INAA Measurements and Quality Control
3.3. Statistical Data Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Major Elements
4.2. Trace Elements
4.3. Environmental Contamination
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sampling Location | Enrichment Factor (EF) | PLI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Sb | ||
| 1S (Sava River) | 3.39 ± 0.15 | 3.29 ± 0.14 | 1.7 ± 0.08 | 4.86 ± 0.22 | 4.77 ± 0.27 | 13.52 ± 0.66 | 4.27 ± 0.52 |
| 2 (Ritopek—Upstream Iron Gate 1 dam) | 1.37 ± 0.07 | 1.16 ± 0.05 | 2.27 ± 0.12 | 3.9 ± 0.17 | 2.77 ± 0.14 | 5.79 ± 0.27 | 2.47 ± 0.27 |
| 3 (Smederovo) | 1.87 ± 0.09 | 2.12 ± 0.11 | 2.81 ± 0.15 | 1.16 ± 0.06 | 3.88 ± 0.21 | 4.05 ± 0.21 | 2.43 ± 0.25 |
| 4 (Smederovo) | 2.18 ± 0.13 | 2.42 ± 0.12 | 1.87 ± 0.1 | 1.21 ± 0.06 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 4.58 ± 0.21 | 2 ± 0.24 |
| 5 (Smederovo) | 2.59 ± 0.13 | 1.96 ± 0.09 | 1.64 ± 0.09 | 9.07 ± 0.52 | 5.13 ± 0.22 | 23.72 ± 1.28 | 4.59 ± 0.64 |
| 6M (Veliko Morava) | 3.5 ± 0.18 | 3.28 ± 0.16 | 1.61 ± 0.08 | 8.81 ± 0.44 | 4.5 ± 0.25 | 10.41 ± 0.53 | 4.45 ± 0.53 |
| 7 Ram—Upstream Iron Gate 1 dam) | 1.76 ± 0.1 | 2.02 ± 0.11 | 1.23 ± 0.07 | 4.64 ± 0.23 | 3.69 ± 0.18 | 7.13 ± 0.38 | 2.85 ± 0.33 |
| 8 (Veliko Gradiste) | 1.94 ± 0.09 | 2.14 ± 0.1 | 1.53 ± 0.08 | 3.64 ± 0.19 | 3.34 ± 0.15 | 6.53 ± 0.29 | 2.83 ± 0.34 |
| 9 (Pek) | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 1.98 ± 0.1 | 6.88 ± 0.31 | 2.49 ± 0.13 | 14.11 ± 0.61 | 2.48 ± 0.32 |
| 10 (Doni Milanovaci) | 1.6 ± 0.09 | 2.06 ± 0.1 | 2.14 ± 0.12 | 3.49 ± 0.17 | 3.57 ± 0.18 | 6.6 ± 0.37 | 2.89 ± 0.34 |
| 11 (Tekija—Upstream Iron Gate 1 dam | 1.63 ± 0.09 | 1.89 ± 0.1 | 2.28 ± 0.11 | 3.61 ± 0.2 | 3.2 ± 0.17 | 7.08 ± 0.4 | 2.89 ± 0.37 |
| 12 (Kladovo—Downstream Iron Gate 1 dam) | 1.56 ± 0.07 | 1.63 ± 0.07 | 2.01 ± 0.09 | 3.78 ± 0.19 | 3.81 ± 0.22 | 6.62 ± 0.31 | 2.81 ± 0.35 |
| 13 (Kus—Upstream Iron Gate 2 dam | 1.54 ± 0.08 | 1.84 ± 0.1 | 1.62 ± 0.08 | 3.97 ± 0.2 | 3.36 ± 0.16 | 8.9 ± 0.42 | 2.86 ± 0.34 |
References
- Babic-Mladenovici, M.; Olarov, V.; Damianovici, V. Sediment regime of the Danube River in Serbia. Int. J. Sedim. Res. 2013, 28, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Research Institute & Project Partners. The Sediment Balance of the Danube River; Water Research Institute (VÚVH): Bratislava, Slovakia, 2020; pp. 2–148. Available online: www.interreg-danube.eu/danubesediment (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Szilágyi, V.; Gméling, K.; Józsa, S.; Harsányi, I.; Szentmiklósi, L. Oligomictic alluvial aggregates: Petro-mineralogical and geochemical evaluation of sandy gravel formations on the middle course of the Danube (Hungary). Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 5957–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arato, R.; Obbagy, G.; Dunkl, I.; Józsa, S.; Lünsdorf, K.; Szepesi, J.; Molnár, K.; Benkó, Z.; von Eynatten, H. Multi-method comparison of modern river sediments in the Pannonian Basin System—A key step towards understanding the provenance of sedimentary basin-fil. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2021, 199, 103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.citypopulation.de/en/serbia/admin/ju%C5%BEna_ba%C4%8Dka/M02472__grad_novi_sad/ (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Available online: https://www.citypopulation.de/en/serbia/belgradecity/ (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Sakan, S.; Sakan, N.; Dordevici, D.S. Trace element study in Tisa River and Danube alluvial sediment in Serbia. Int. J. Sedim. Res. 2013, 28, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnković, D.M.; Crnković, N.S.; Filipović, A.J.; Rajaković, L.V.; Perić-Grujić, A.A., Jr.; Ristić, M.D. Danube and Sava River sediment monitoring in Belgrade and its surroundings. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2008, 43, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovic, N.; Damjanovic, M.; Ristic, M. Study of heavy metal pollution in sediments from the Iron Gate (Danube River), Serbia and Montenegro. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2005, 14, 781–787. Available online: https://www.pjoes.com/Study-of-Heavy-Metal-Pollution-in-Sediments-from-the-Iron-Gate-Danube-River-Serbia,87822,0,2.html (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Pavlović, P.; Marković, M.; Kostić, O.; Sakan, S.; Đorđević, D.; Perović, V.; Pavlović, D.; Pavlović, M.; Čakmak, D.; Jarić, S.; et al. Evaluation of potentially toxic element contamination in the riparian zone of the River Sava. Catena 2018, 174, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, S.; Dević, G.; Relić, D.; Anđelković, I.; Sakan, N.; Đorđević, D. Risk assessment of trace element contamination in river sediments in Serbia using pollution indices and statistical methods: A pilot study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6625–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, S.M.; Devici, G.J.; Relici, D.J.; Anđelković, I.B.; Sakan, N.M.; Đorđević, D.S. Environmental assessment of heavy metal pollution in freshwater sediment, Serbia. Clean Soil Air Water 2015, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, S.; Sakan, N.; Anđelković, I.; Trifunović, S.; Đorđević, D. Study of potential harmful elements (arsenic, mercury and selenium) in surface sediments from Serbian rivers and artificial lakes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 180, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Škrbić, B.; Čupić, S. Trace Metal Distribution in Surface Soils of Novi Sad and Bank Sediment of the Danube River. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2004, 39, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culicov, O.A.; Trtić-Petrović, T.; Balvanović, R.; Petković, A.; Ražić, S. Spatial distribution of multielements including lanthanides in sediments of Iron Gate I Reservoir in the Danube River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44877–44889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lučić, M.; Mikac, N.; Vdović, N.; Bačić, N.; Nava, V.; Vidmar, J.; Milačič, R. Spatial and temporal variability and sources of dissolved trace elements in the Sava River (Slovenia, Croatia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 31734–31748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Water Research Institute & project partners. Sediment Balance Assessment for the Danube, Interreg Danube Transnational Project. 2019. Available online: https://www.interreg-danube.eu/approved-projects/danubesediment (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Lučić, M.; Jurina, I.; Ščančar, J.; Mikac, N.; Vdović, N. Sedimentological and geochemical characterization of river suspended particulate matter (SPM) sampled by time-integrated mass flux sampler (TIMS) in the Sava River (Croatia). J. Soils Sediments 2018, 19, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duţu, L.; Secrieru, D.; Duţu, F.; Lupaşcu, N. Geochemical dataset of the Danube Delta sediments. Data Brief 2021, 39, 107529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontasyeva, M.V. Neutron activation analysis in the life sciences. Phys. Part. Nucl. 2011, 42, 332–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, W.; Ghanim, E.; Duliu, O.; El Samman, H.; Frontasyeva, M. Major and trace element distribution in soil and sediments from the Egyptian central Nile Valley. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 131, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier-Pergamon: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 13, pp. 1–64. ISBN 978-0-08-098300-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gromet, L.; Haskin, L.A.; Korotev, R.L.; Dymek, R.F. The “North American shale composite”: Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 2469–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenko, V.S. Chemical composition of sediment load carried by rivers. Geochem. Int. 2007, 45, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugulan, L.; Duliu, O.; Bojar, A.-V.; Dumitras, D.; Zinicovskaia, I.; Culicov, O.A.; Frontasyeva, M.V. On the geochemistry of the Late Quaternary loess deposits of Dobrogea (Romania). Quat. Int. 2015, 399, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, G.J. Loess stratigraphy of Central Europe. In After the Australopithecus, Stratigraphy, Ecology and Culture Change in the Middle Pleistocene; Butzer, K.W., Isaac, G.L., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1975; pp. 99–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdushukurov, D.A.; Abdusamadzoda, D.; Duliu, O.G.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Nekhoroshkov, P.S. On the Geochemistry of Major and Trace Elements Distribution in Sediments and Soils of Zarafshon River Valley, Western Tajikistan. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusamadzoda, D.; Abdushukurov, D.A.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Duliu, O.G.; Vergel, K.N. Assessment of the ecological and geochemical conditions in surface sediments of the Varzob river, Tajikistan. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, S.S.; Dmitriev, A.Y.; Frontasyeva, M.V. Automation system for neutron activation analysis at the reactor IBR-2, Frank Laboratory of Neutron Physics, Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. Artic. 2016, 309, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrance, I.; Frenkel, R. Uncertainty of Measurement: A Review of the Rules for Calculating Uncertainty Components through Functional Relationships. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2012, 33, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Duliu, O.G.; Culicov, O.A.; Frontasyeva, M.; Sturza, R. Major and trace elements distribution in Moldavian soils. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2018, 70, 701. Available online: https://www.rrp.infim.ro/IP/2018/AN70701.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. Available online: http://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.htm (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Bhatia, M.R.; Crook, K.A.W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins. Contrib. Miner. Pet. 1986, 92, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, S. Is chemical index of alteration (CIA) a reliable proxy for chemical weathering in global drainage basins? Am. J. Sci. 2010, 310, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, F.; Hu, R.; Chu, Y.; Yang, Y.-Z. Provenance and tectonic setting of Neoproterozoic sedimentary sequences in the South China Block: Evidence from detrital zircon ages and Hf-Nd isotopes. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2012, 101, 1723–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, P.A.; Leveridge, B.E. Tectonic environment of the Devonian Gramscatho basin, south Cornwall: Frame-work mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones. J. Geol. Soc. 1987, 144, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrels, R.M.; Mackenzie, F.T. Evolution of Sedimentary Rocks; Norton: New York, NY, USA, 1971; ISBN 978-0393099591. [Google Scholar]
- Újvari, G.; Varga, A.; Raucsik, B.; Kovács, J. The Paks loess-palaeosol sequence: A record of chemical weathering and provenance for the last 800 ka in the mid-Carpathian Basin. Quat. Int. 2014, 319, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norman, J.C.; Haskin, L.A. The geochemistry of Sc: A comparison to the rare earths and Fe. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1968, 32, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.; McDaniel, D.K.; Hanson, G.N. Geochemical Approaches to Sedimentation, Provenance, and Tectonics. In GSA Special Paper; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1993; Volume 284, p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks; Blackwell Publisher: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; p. 312. ISBN 978-0632011483. [Google Scholar]
- Gallet, S.; Jahn, B.M.; Tori, M. Geochemical characterization of the Luochuan loess–paleosol sequence, China, and paleoclimatic implications. Chem. Geol. 1996, 133, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gasiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review, Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problem in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanes, P.S.; Buchhamer, E.E.; Giménez, M.C. Natural contamination with arsenic and other trace elements in groundwater of the Central-West region of Chaco, Argentina. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2011, 46, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, E.; Masuda, H.; Shibata, T.; Nojima, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Murasaki, Y.; Chiba, H. Geochemical distribution and fate of arsenic in water and sediments of rivers from the Hokusetsu area, Japan. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 9, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alonso, D.L.; Latorre, S.; Castillo, E.; Brandão, P.F.B. Environmental occurrence of arsenic in Colombia: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://oehha.ca.gov/media/downloads/water/chemicals/phg/antimonyphg092316.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Valentukeviciene, M.; Bagdžiunaite-Litvinaitiene, L.; Chadyšas, V.; Litvinatis, A. Evaluating the Impacts of Integrated Pollution on Water Quality of the Trans-Boundary Neris (Viliya) River. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Liu, G.; Balaram, V.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Lu, Z.; Stock, F.; Carmona, E.; Teixeira, M.R.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; et al. Worldwide cases of water pollution by emerging contaminants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2311–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, G. Transboundary water governance in the European Union: The (unresolved) allocation question. Water Policy 2019, 21, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Oxide | Average | St.Dev. | UCC | NASC | ABL | ADL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 66.79 | 3.84 | 66.62 | 64.8 | 79.52 | 62.83 |
| TiO2 | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.65 | 0.78 | 0.57 | 0.7 |
| Al2O3 | 13.45 | 2.54 | 15.4 | 16.9 | 8.62 | 14.53 |
| FeO | 5.38 | 0.88 | 5.04 | 5.7 | 3.41 | 5.34 |
| MnO | 0.0017 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.1 |
| MgO | 0.59 | 0.14 | 2.48 | 2.85 | 1.01 | 2.48 |
| CaO | 7.95 | 2.86 | 3.59 | 3.56 | 2.53 | 9.51 |
| Na2O | 1.16 | 0.46 | 3.27 | 1.15 | 1.13 | 2.51 |
| K2O | 2.2 | 0.39 | 2.8 | 3.99 | 1.41 | 1.99 |
| Element | Average | St.Dev. | UCC | NASC | ABL | ADL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sc | 14.9 | 2.5 | 14 | 14.9 | 10 | 10.1 |
| V | 122 | 29 | 97 | --- | 50 | 92 |
| Cr | 183 | 73 | 92 | 124.5 | 50 | 122 |
| Co | 21 | 5 | 17.3 | --- | 15 | 15 |
| Ni | 97 | 38 | 47 | 58 | 25 | 58 |
| Cu | 56 | 17 | 28 | 0 | 20 | --- |
| Zn | 328 | 192 | 67 | --- | 60 | 80 |
| As | 17.8 | 6.5 | 4.8 | 28.4 | 6 | 1 |
| Rb | 108 | 25 | 84 | 126 | 50 | 88 |
| Sr | 175 | 25 | 320 | 142 | 150 | 256 |
| Zr | 195 | 29 | 193 | 200 | 250 | 461 |
| Sb | 3.8 | 2.4 | 0.4 | --- | 2 | --- |
| Cs | 8.3 | 2.9 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 4 | 4.8 |
| Ba | 497 | 58 | 624 | 636 | 500 | 525 |
| La | 32.9 | 5.2 | 31 | 31 | 32 | 32 |
| Hf | 5.2 | 0.8 | 5.3 | 0 | 6 | 14.3 |
| Ta | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0 | 2 | 1.4 |
| W | 2.1 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 0.05 | 5 | 2.8 |
| Th | 12.2 | 2.7 | 10.5 | 12.3 | 10 | 11.6 |
| U | 2.3 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 3 | 3.1 |
| Sampling Point | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1S | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6R | 7 | 8 | 9P | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |
| 1S | --- | 0.98 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.76 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.94 |
| 2 | 0.93 | --- | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.74 | 0.95 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.97 | 0.96 |
| 3 | 0.79 | 1.00 | --- | 0.99 | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 0.94 |
| 4 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.89 | --- | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.64 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.86 | 0.92 |
| 5 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 1.00 | --- | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.78 | 0.99 | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.92 |
| 6R | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 1.00 | --- | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.97 | 0.91 |
| 7 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.86 | --- | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.84 |
| 8 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.86 | --- | 0.79 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.77 | 0.71 |
| 9P | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.86 | --- | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 0.91 |
| 10 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.93 | --- | 0.98 | 0.85 | 0.79 |
| 11 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.93 | --- | 0.83 | 0.77 |
| 12 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.76 | --- | 0.94 |
| 13 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.96 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.93 | --- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Culicov, O.A.; Trtić-Petrović, T.; Nekhoroshkov, P.S.; Zinicovscaia, I.; Duliu, O.G. On the Geochemistry of the Danube River Sediments (Serbian Sector). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912879
Culicov OA, Trtić-Petrović T, Nekhoroshkov PS, Zinicovscaia I, Duliu OG. On the Geochemistry of the Danube River Sediments (Serbian Sector). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912879
Chicago/Turabian StyleCulicov, Otilia A., Tatjana Trtić-Petrović, Pavel S. Nekhoroshkov, Inga Zinicovscaia, and Octavian G. Duliu. 2022. "On the Geochemistry of the Danube River Sediments (Serbian Sector)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912879
APA StyleCulicov, O. A., Trtić-Petrović, T., Nekhoroshkov, P. S., Zinicovscaia, I., & Duliu, O. G. (2022). On the Geochemistry of the Danube River Sediments (Serbian Sector). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912879








