Occurrence and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water of Self-Supplied Wells in Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sampling Preparation and Analysis
2.3. Health-Risk Assessment
2.4. Data Treatment and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
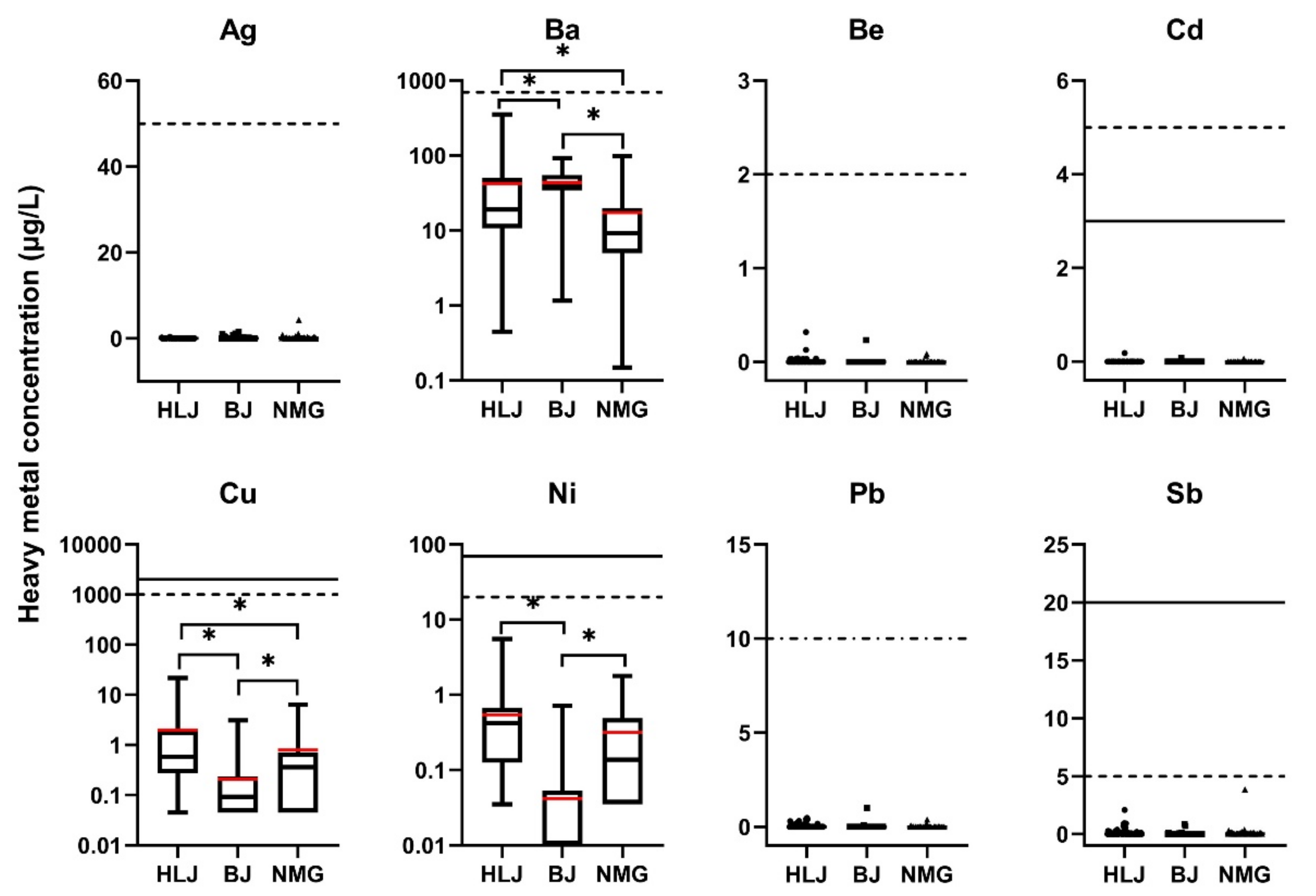
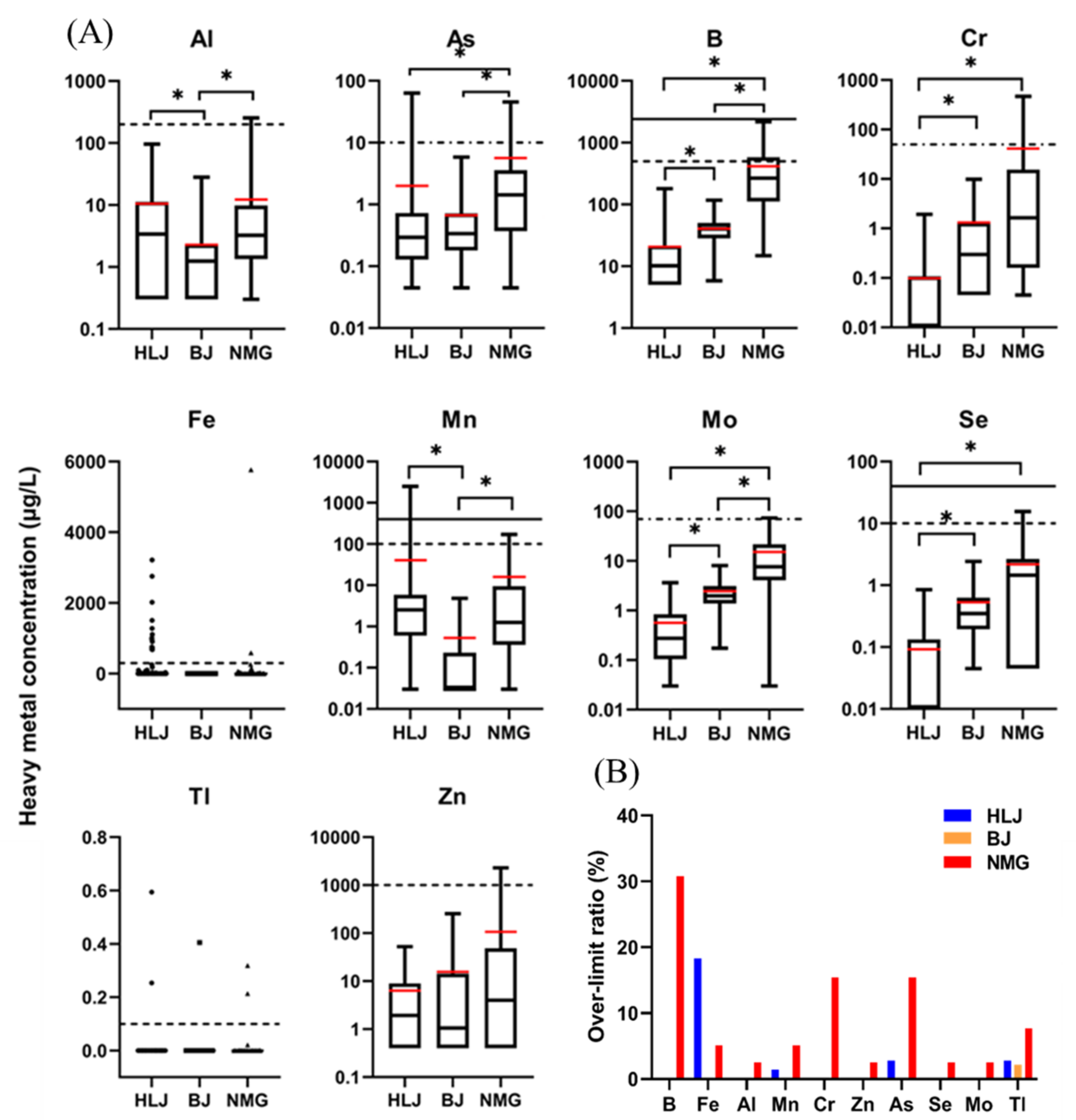
3.1. Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in Self-Supplied Wells
3.1.1. Elements Not Mentioned in SDW and WHO Standards
3.1.2. Elements Mentioned in SDW and WHO Standards
- (1)
- Element levels not exceeding the SDW and WHO standards
- (2)
- Elements’ levels exceeding SDW standards
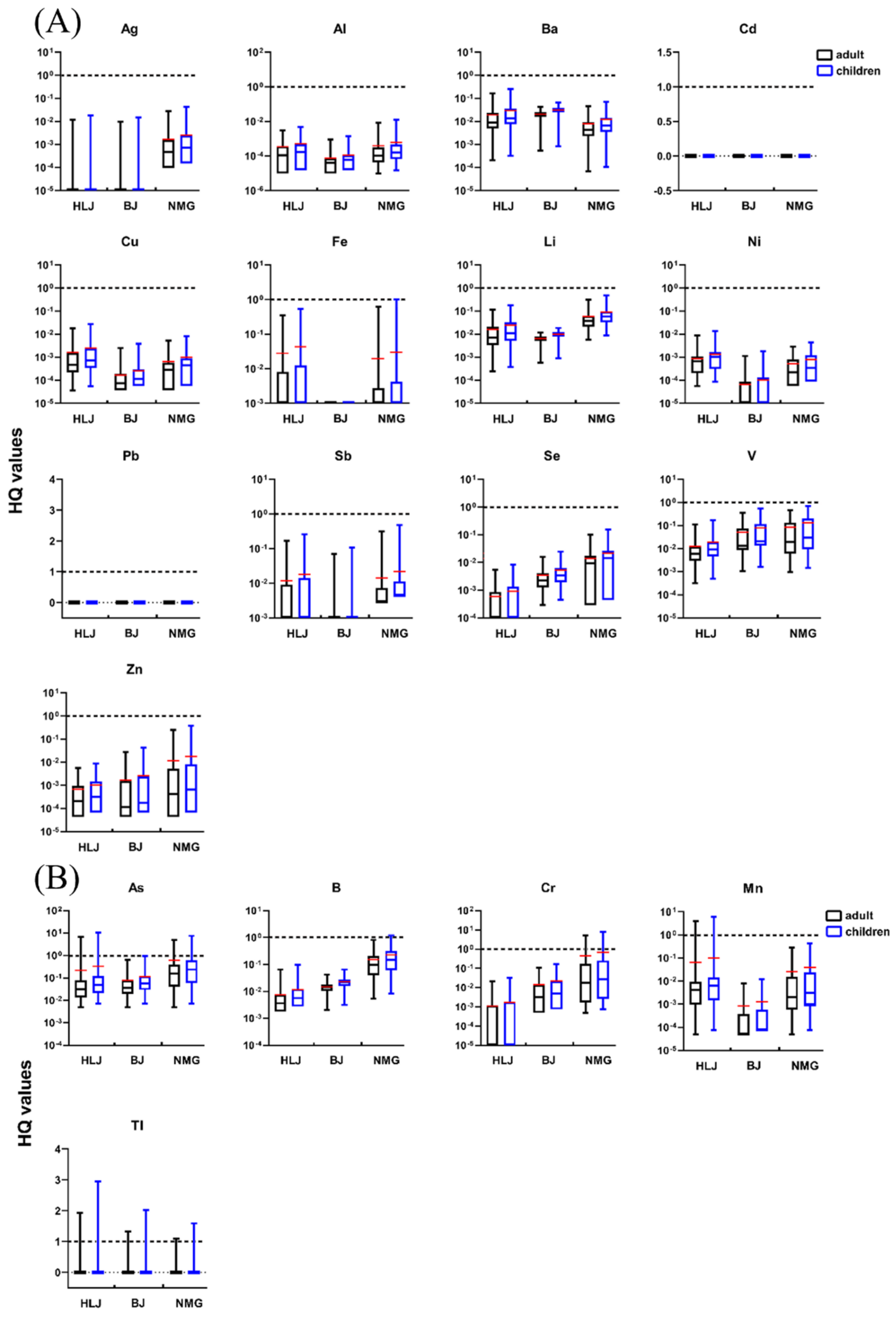
3.2. Human Health-Risk Assessment
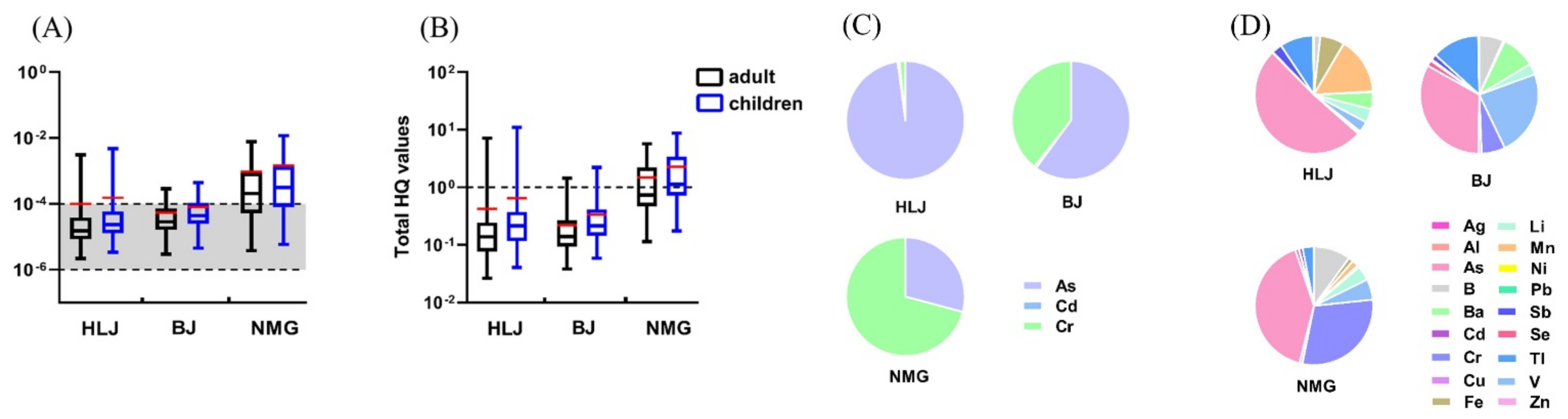
3.2.1. Carcinogenic Risk
3.2.2. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
3.2.3. Total Health Risk
- (1)
- Total Carcinogenic Risk
- (2)
- Total non-carcinogenic risk
3.3. Possible Sources of Heavy Metals in Wells Water
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, A.; Hall, A.; Weaver, J.; Kremer, F. Methods for estimating locations of housing units served by private domestic wells in the United States applied to 2010. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2021, 57, 828–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.G.; Fang, X.; Zhang, N.; Xu, X.Q.; Li, L.H.; Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Xia, Y. Characterization of drinking groundwater quality in rural areas of Inner Mongolia and assessment of human health risks. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.M.; Huang, G.X.; Han, D.Y.; Hou, Q.X.; Gan, L.; Zhang, M. A review of reactive media within permeable reactive barriers for the removal of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater: Current status and future prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Ministry of Environment Protection. China Environmental Status Bulletin 2016; Chinese Ministry of Environment Protection: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.Z.; Li, M.; Wu, H.M. Distributions and interactions of dissolved organic matter and heavy metals in shallow groundwater in Guanzhong basin of China. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Sheng, Y.Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, G.Q.; Li, C.Y. Attempt of basin-scale sediment quality standard establishment for heavy metals in coastal rivers. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.; Nezhad, N.T.; Dehghan, A.; Alidadi, H.; Paydarb, M.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Zarei, A. Heavy metals exposure, carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic human health risks assessment of groundwater around mines in Joghatai, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 1884–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.K.; Ramanathan, A.L.; Subramanian, V. Groundwater chemistry and human health risk assessment in the mining region of East Singhbhum, Jharkhand, India. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.; Guo, J. Aquatic Arsenic Toxicity and Treatment; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ukah, B.U.; Egbueri, J.C.; Unigwe, C.O.; Ubido, O.E. Extent of heavy metals pollution and health risk assessment of groundwater in a densely populated industrial area, Lagos, Nigeria. Int. J. Energ. Water Res. 2019, 3, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Su, Q.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.J.; Liu, J.T. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of dissolved heavy metals in groundwater of eastern China coastal zone. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.K.; Jena, R.K.; Ray, P.; Yadav, K.K.; Moharana, P.C.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Bordoloi, G. Evaluating the geochemistry of groundwater contamination with iron and manganese and probabilistic human health risk assessment in endemic areas of the world’s largest River Island, India. Environ. Toxicol. Pharm. 2021, 87, 103690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, H.; Esmaeili, A.; Razaeian, M.; Salari, M.; Hosseini, A.N.; Mobini, M.; Barani, A. Potentially toxic metal concentration, spatial distribution, and health risk assessment in drinking groundwater resources of southeast Iran. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josiah, N.J.; Isa, N.M.; Aris, A.Z.; Ramli, M.F.; Abubakar, M.B. Geochemometric approach to groundwater quality and health risk assessment of heavy metals of Yankari Game Reserve and its environs, Northeast Nigeria. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129916. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Ministry of Environment Protection. Water Quality-Determination of 65 Elements-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry, HJ 700-2014; Chinese Ministry of Environment Protection: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Chinese Ministry of Environment Protection. Water Quality-Determination of 32 Elements-Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry, HJ 776-2015; Chinese Ministry of Environment Protection: Beijing, China, 2015.
- US EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment) Final; Office of Superfund Remediation and Technology Innovation U.S., Environmental Protection Agency, Eds.; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Chen, L.Z.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y.X.; Zheng, J.J. Health risks associated with multiple metal(loid)s in groundwater: A case study at Hetao Plain, northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Gao, L.; Gao, J.J.; Xu, D.Y.; Wang, Q.W.; Sun, K. Simultaneous evaluations of occurrence and probabilistic human health risk associated with trace elements in typical drinking water sources from major river basins in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Jari, H. Evaluation of drinking water quality and non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals in rural areas of Kurdistan, Iran. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, D.; Jin, Z.D. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüml, V.; Regier, M.D.; Hlavin, G.; Rockett, I.R.H.; König, F.; Vyssoki, B.; Bschor, T.; Kapusta, N.D. Lithium in the public water supply and suicide mortality in Texas. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, K.; Concha, G.; Engstrm, K.; Lindvall, M.; Grandér, M.; Vahter, M. Lithium in drinking water and thyroid function. Environ. Health Perspec. 2011, 119, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, F.; Langeen, M.; Casimiro, E.; Bottai, M.; Palm, B.; Nordqvist, H.; Vahter, M. Environmental exposure to lithium during pregnancy and fetal size: A longitudinal study in the Argentinean Andes. Environ. Int. 2015, 77, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewuzie, U.; Nnorom, I.C.; Eze, S.O. Lithium in drinking water sources in rural and urban communities in Southeastern Nigeria. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, B.D.; Belitz, K.; Cravotta, C.A.; Toccalino, P.L.; Dubrovsky, N.M. Lithium in groundwater used for drinking-water supply in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; An, H.; Pang, Y.M.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Yan, L.L.; Wang, B.; Ye, R.W.; et al. Environmental titanium exposure and reproductive health: Risk of low birth weight associated with maternal titanium exposure from a nested case-control study in northern China. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, M.; Schullehner, J.; Hansen, B.; Sigsgaard, T.; Voutchkova, D.D.; Kristiansen, S.M.; Pedersen, C.B.; Dalsgaard, S. Trace elements in drinking water and the incidence of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2021, 68, 126828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.H.; Qi, H.J.; Liu, X.L.; Gao, B.; Yang, Z.; Lu, W.; Sun, R.B. Occurrence and health risk assessment of selected metals in drinking water from two typical remote areas in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2016, 23, 8462–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondu, R.; Cloutier, V.; Rosa, E.; Roy, M. An exploratory data analysis approach for assessing the sources and distribution of naturally occurring contaminants (F, Ba, Mn, As) in groundwater from southern Quebec (Canada). Appl. Geochem. 2020, 114, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanachaiwong, S.; Singer, P. Diets and Diet Therapy: Trace Elements. Encycl. Food Secur. Sustain. 2019, 2, 143–160. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, S.S.; Martins, H.; Gutiérrez-Merino, C.; Aureliano, M. Vanadium and cadmium in vivo effects in teleost cardiac muscle: Metal accumulation and oxidative stress markers. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2008, 147, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, C.E.; Paoloni, J.D.; Sequeira, M.E.; Arosteguy, P. The presence of vanadium in groundwater of southeastern extreme the pampean region Argentina: Relationship with other chemical elements. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2007, 93, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdey, M. Chronic barium intoxication disrupts sulphated proteoglycan synthesis: A hypothesis for the origins of multiple sclerosis. Med. Hypotheses 2004, 62, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, H.N.; Panahande, M.; Yousefi, M.; Asghari, F.B.; Conti, G.O.; Talaee, E.; Mohammadi, A.A. Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater wells in Neyshabur Plain, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Shabnam, A.A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Malyan, S.K.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Gupta, D.K.; et al. Nickel in terrestrial biota: Comprehensive review on contamination, toxicity, tolerance and its remediation approaches. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, L. Distribution of arsenic and other minor trace elements in the groundwater of Ischia Island (southern Italy). Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, H.J.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.W. Removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero valent iron-reduced graphite oxide modified composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Espinosa, P.F.; Sabarathinam, C.; Ochoa-Guerrero, K.M.; Martínez-Tavera, E.; Panda, B. Geochemical evolution and Boron sources of the groundwater affected by urban and volcanic activities of Puebla Valley, south central Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zango, M.S.; Sunkari, E.D.; Abu, M.; Lermi, A. Hydrogeochemical controls and human health risk assessment of groundwater fluoride and boron in the semi-arid North East region of Ghana. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 207, 106363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Banerjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Bhattacharjee, C.R.; Raul, P.; Borah, K. High iron accumulation in hair and nail of people living in iron affected areas of Assam, India. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2014, 110, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostern, N.T. The effects of some metals in acidified waters on aquatic organisms. Oceanogr. Fish. 2017, 4, 555645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Pham, Q.B.; Gupta, N.; Rezania, S.; Kamyab, H.; Yadav, S.; Vymazal, J.; Kumar, V.; Tri, D.Q.; et al. Fluoride contamination, health problems and remediation methods in Asian groundwater: A comprehensive review. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guo, H.M.; Xiu, W.; Wei, C.; Li, X.M.; Di, Z.; Song, W. Biomarkers of arsenic exposure in arsenic-affected areas of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.F.; Cheng, H.G.; Sun, H.X.; Huang, J.H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Q. Human health and environment: Spatiotemporal variation of chinese cancer villages and its contributing factors. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and pesticides: A case study in the main drinking water source in Dalian, China. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.A.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Muhib, M.I.; Zahid, A.; Shammi, M.; Tareq, S.M.; Kurasaki, M. Spatio-temporal assessment of groundwater quality and human health risk: A case study in Gopalganj, Bangladesh. Expos. Health 2017, 10, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmel, N.K.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Lakkaboyana, S.K.; Majid, Z.A.; Salmiati, S. High concentration arsenic removal from aqueous solution using nano-iron ion enrich material (NIIEM) super adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Flores, H.; Pariona, N.; Herrera-Trejo, M.; Hdz-García, H.M.; Mtz-Enriquez, A.I. Concrete/maghemite nanocomposites as novel adsorbents for arsenic removal. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1171, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmara, S.; Suyanti; Adi, W.A.; Manaf, A. Mineral analysis and its extraction process of ilmenite rocks in titanium-rich cumulates from Pandeglang Banten Indonesia. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 3384–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etteieb, S.; Magdouli, S.; Zolfaghari, M.; Brar, S.K. Monitoring and analysis of selenium as an emerging contaminant in mining industry: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perks, C.; Mudd, G. Titanium, zirconium resources and production: A state of the art literature review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 107, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Study Area | TCR | THQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Children | Heavy Metals | Adult | Children | Heavy Metals | |
| HLJ | 2.19 × 10−6~3.09 × 10−3 (9.93 × 10−5) | 3.37 × 10−6~4.75 × 10−3 (1.53 × 10−4) | As (97.87%) | 2.65 × 10−2~7.17 (4.23 × 10−1) | 4.07 × 10−2~11 (6.49 × 10−1) | As (51.11%) |
| BJ | 2.92 × 10−6~2.85 × 10−4 (5.41×10−5) | 4.49 × 10−6~4.38×10−4 (8.31 × 10−5) | As (60.06%) | 3.83 × 10−2~1.44 (2.19 × 10−1) | 5.88 × 10−2~2.21 (3.36 × 10−1) | As (32.96%) |
| NMG | 3.79 × 10−6~7.66 × 10−3 (9.41 × 10−4) | 5.83 × 10−6~1.18 × 10−2 (1.45 × 10−3) | Cr (70.83%) | 1.14 × 10−1~5.70 (1.49) | 1.75 × 10−1~8.76 (2.29) | As (40.88%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, M.; Zhang, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, T.; Qu, S.; Qi, H.; Zhang, M.; Tan, C.; Zhang, C. Occurrence and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water of Self-Supplied Wells in Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912517
Bai M, Zhang C, Bai Y, Wang T, Qu S, Qi H, Zhang M, Tan C, Zhang C. Occurrence and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water of Self-Supplied Wells in Northern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912517
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Miao, Can Zhang, Yuchao Bai, Tianyi Wang, Shaojuan Qu, Hongjuan Qi, Minglu Zhang, Chaohong Tan, and Chuanfu Zhang. 2022. "Occurrence and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water of Self-Supplied Wells in Northern China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912517
APA StyleBai, M., Zhang, C., Bai, Y., Wang, T., Qu, S., Qi, H., Zhang, M., Tan, C., & Zhang, C. (2022). Occurrence and Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water of Self-Supplied Wells in Northern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12517. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912517






