Contamination Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Karst Soil Using UNMIX Model and Pb-Cd Isotopes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
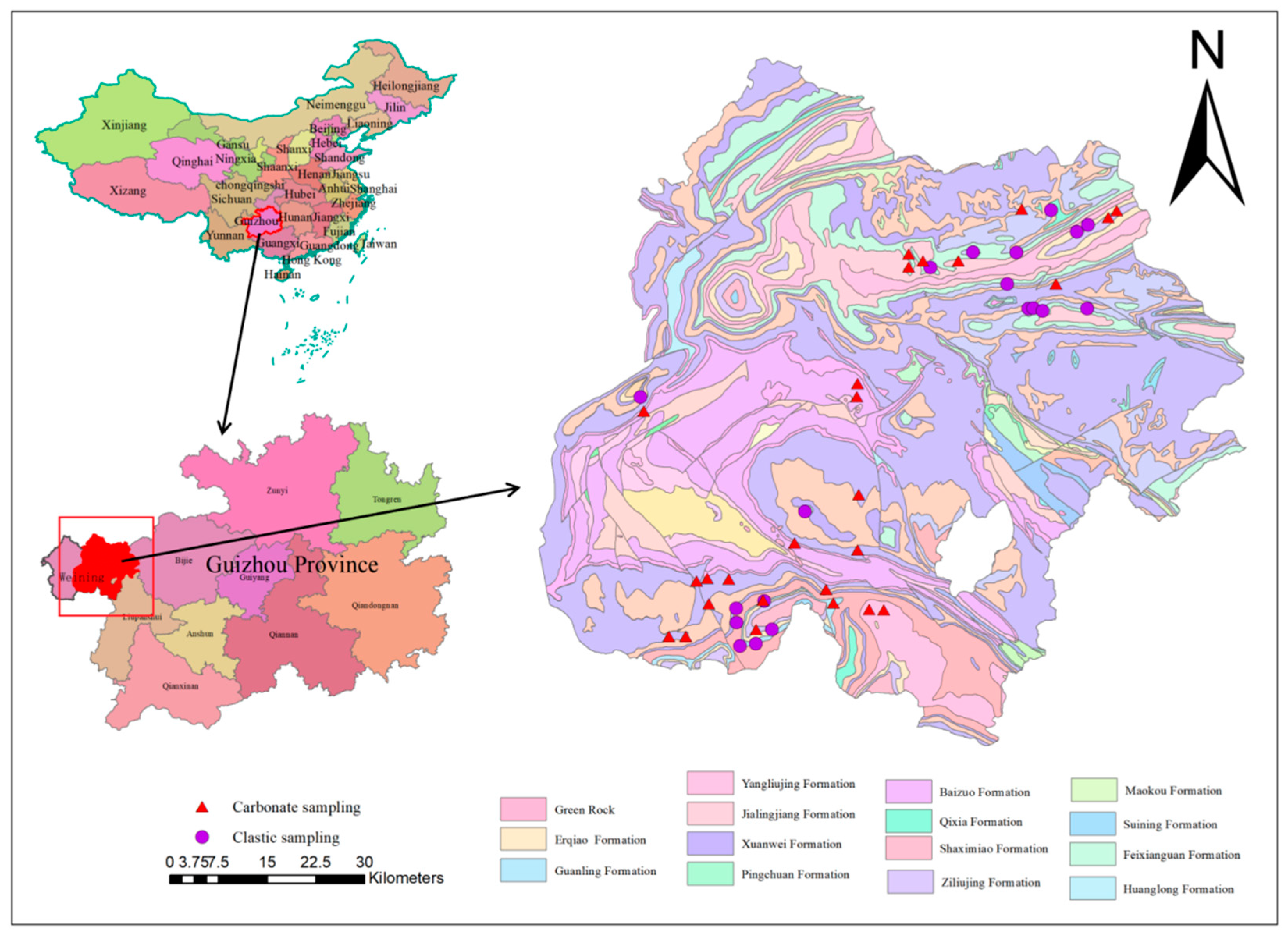
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.2.1. Rock Samples
2.2.2. Soil Samples
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.3.1. Soil Samples
2.3.2. Rock Samples
2.3.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
2.4. Assessment of Soil Contamination
2.4.1. Enrichment and Loss Assessment of Elements in Soils
2.4.2. Single-Factor Pollution Index
2.4.3. Geoaccumulation Index
2.4.4. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.4.5. Pb and Cd Isotopic Composition Analysis
Pb Isotope Analysis
Cd Isotope Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. UNMIX Model
2.5.2. Pb and Cd Isotopic “Binary Model”
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elemental Geochemical Characteristics in Rocks and Soils
3.1.1. Rocks
3.1.2. Soils
3.2. The Enrichment or Loss of Elements in Formation Process of the Soil-Forming Process
3.2.1. Relative to the Background Value
3.2.2. Relative to the Bedrocks
3.3. Contamination Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Soil
3.3.1. Single Factor Index and Geoaccumulation Index
3.3.2. Potential Ecological Risk Index
3.4. Source Analysis of Heavy Metals
3.4.1. Correlation Analysis
3.4.2. Source Apportionment by UNMIX Model
3.4.3. Identification of Heavy Metal Sources by Pb-Cd Isotopic Composition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, L.J.; Li, J.Y. Carcarbonate Weathering and Its Environmental Effect; Geological Press House: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ci, E.; Li, S.; Lian, M.; Zhong, S. The pedogenesis of soil derived from carbonate rocks along a climosequence in a subtropical mountain, China. Forests 2021, 12, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.B.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhuo, X.X.; Guan, D.X.; Song, Y.X.; Guo, C.; Ji, J.F. Evaluation of various approaches to predict cadmium bioavailability to rice grown in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.B.; Wang, S.J.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, C.X.; Liu, X.M.; Zhou, D.Q. Geochemistry of red residua underlying dolomites in karst terrains of YunnanGuizhou Plateau: I. The Formation of the Pingba profile. Chem. Geol. 2004, 203, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Ji, H.B.; Ou Yang, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.Q.; Zheng, L.P.; Li, T.Y. Preliminary study on weathering and pedogenesis of carbonate rock. Sci. China (Ser. D Earth Sci.) 1999, 42, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Yan, Y.; Wadood, S.A.; Sun, Q.Q.; Guo, B.L. Source apportionment of cadmium pollution in agricultural soil based on cadmium isotope ratio analysis. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 123, 104776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halami´c, J.; Peh, Z.; Miko, S.; Galović, L.; Šorša, A. Geochemical Atlas of Croatia: Environmental implications and geodynamical thread. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 115, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S.; Takeda, A.; Nunohara, K. Red soils derived from limestone contain higher amounts of trace elements than those derived from various other parent materials. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Wen, X.F.; Wu, P.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Pan, Q.Z.; Wei, X.; Wu, S.S. Excessive degrees and migration characteristics of heavy metals in typical weathering profiles in karst areas. Earth Environ. 2019, 47, 50–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.F.; Filippelli, G.M.; Ji, J.F.; Ji, W.B.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, T.; Wu, T.S.; Zhuo, X.X.; et al. Distribution and secondary enrichment of heavy metal elements in karstic soils with high geochemical background in Guangxi, China. Chem. Geol. 2021, 567, 120081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, S.; Sun, Q.; Wadood, S.A.; Guo, B. Source identification and spatial distribution of arsenic and heavy metals in agricultural soil around Hunan industrial estate by positive matrix factorization model, principle components analysis and geo statistical analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, W.; Gu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, P. Effects of Organic Fertilizers on Cd Activity in Soil and Cd Accumulation in Rice in Three Paddy Soils from Guizhou Province. B. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatoba, P.O.; Ogunkunle, C.O.; Folarin, O.O.; Oladele, F.A. Heavy metal pollution and ecological geochemistry of soil impacted by activities of oil industry in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.Q.; Yang, H.; Ippolito, J.A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Scheckel, K.G.; Li, L.P. Atmospheric deposition of arsenic, cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc near an operating and an abandoned lead smelter. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippelli, G.M.; Adamic, J.; Nichols, D.; Nichols, J.; Frix, E. Mapping the urban lead exposome: A detailed analysis of soil metal concentrations at the household scale using citizen science. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Meng, W.; Liu, N.T.; Wu, P. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on GIS, SOM and PMF: A case study in superposition areas of geochemical anomalies and zinc smelting, Southwest China. Pross Saf. Environ. 2022, 159, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.X.; Su, L.M. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekey, H.; Karakas, D.; Bakoglu, M. Source apportionment of trace metals in surface waters of a polluted stream using multivariate statistical analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovidesa, M.; G. Stephanoua, E.; Apostolaki, M.; Hadjicharalambousc, M.; Evansd, J.; Koutrakisd, P.; Achilleosd, S. Study of the occurrence of airborne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons associated with respirable particles in two coastal cities at Eastern Mediterranean: Levels, source apportionment, and potential risk for human health. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.T.; Seen, A.J. Historical lead isotope record of a sediment core from the Derwent River (Tasmania, Australia): A multiple source environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Cloquet, C.; Zhou, C.W.; Fan, H.F.; Luo, C.G. Tracing sources of pollution in soils from the Jinding Pb–Zn mining district in China using cadmium and lead isotopes. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 52, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Zhou, X.D.; Zhou, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Li, B.J.; Zhou, S.L. Identifification of the sources and inflfluencing factors of potentially toxic elements accumulation in the soil from a typical karst region in Guangxi, Southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloquet, C.; Rouxel, O.; Carignan, J.; Libourel, G. Natural cadmium isotopic variations in eight geological raeference materials (NIST SRM 2711, BCR 176, GSS-1, GXR-1, GXR-2, GSD-12, Nod-p-1, Nod-A-1) and anthropogenic samples, measured by MC-ICP-MS. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2005, 29, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.Y. Analysis of the source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Quanzhou Bay based on principal component analysis (PCA). J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait 2010, 29, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.B. Characteristics of the elemental abundance and content of near-shore neritic sediment in fujian province. Geol. Fujian 2008, 27, 392–401. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.H.; Yang, M.F.; Xi, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Cai, J.D.; Chen, C.G.; Zhong, S.L. Distribution of 5 heavy metals with relations to environmental factors in surface sediments of Dongshan Bay. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2014, 33, 251–257. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- MLR (Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China). DZ/T 0258-2014 Specification of Multi-Purpose Regional Geochemical Survey (1:250,000); Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 1–46. (In Chinese)
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschi, L.; Rizzio, E.; Valcuvia, M.G.; Verza, G.; Profumo, A.; Gallorini, M. Determination of trace elements and evaluation of their enrichment factors in Himalayan lichens. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.J.; Ji, H.B. Application of chemometric methods to analyze the distribution and chemical fraction patterns of metals in sediment from a metropolitan river. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.X.; Yang, Y.; Su, C.T.; Meng, X.J. Contrasts of geochemical characteristics and environmental quality between soils of carbonate and clastic matrix. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2015, 43, 128–132. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, S.L.; Chen, Z. The zoning of surface tectonic geochemistry in Guizhou and its significance. Guizhou Geology. 2002, 3, 148–155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.T.; Chen, Y.L.; Yang, L.Y.; Xu, M.Q.; Jing, H.N.; Wu, P.; Wang, P. Spatial distribution, food chain translocation, human health risks, and environmental thresholds of heavy metals in a maize cultivation field in the heart of China’s karst region. J. Soil Sediment. 2022, 22, 2654–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouchami, W.; Galer, S.J.G.; Horner, T.J.; Rehkämper, M.; Wombacher, F.; Xue, Z.C.; Lambelet, M.; Gault-Ringold, M.; H. Stirling, C.; Schönbächler, M.; et al. A common reference material for cadmium isotope studies-NIST SRM 3108. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2013, 37, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.F.; Huang, F.; Yu, H.M. High-precision Cd isotope measurements of soil and rock reference materials by MC-ICP-MS with double spike correction. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2019, 44, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.S.; Jian, X.; Tian, Y.Z.; Shi, G.L.; Feng, Y.C. Potential source contributions and risk assessment of PAHs in sediments from Taihu Lake, China: Comparison of three receptor models. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.J.; He, Z.S.; Huo, S.L.; Zhang, J.T.; Xi, B.D.; Hu, S.B. Source apportionment of perfluoroalkyl substances in surface sediments from lakes in Jiangsu Province, China: Comparison of three receptor models. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.C.; Gu, T.X.; Chi, Q.H.; Wang, C.S. Abundance of chemical elements of soil in China and supergenesis geochemistry characteristics. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 1997, 21, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Temur, S.; Orhan, H.; Deli, A. Geochemistry of the limestone of Mortas Formation and related terra rossa, Seydisehir, Konya, Turkey. Geochem. Int. 2009, 47, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abimbola, A.F.; Kehinde-Phillips, O.O.; Olatunji, A.S. The Sagamu cement factory, SW Nigeria: Is the dust generated a potential health hazard? Environ. Geochem. Health 2007, 29, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.F.; Wu, Y.G.; Wang, H.; Xing, R.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, J.; Yang, L. Bacterial community structure and diversity responses to the direct revegetation of an artisanal zinc smelting slag after 5 years. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14773–14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ran, F.; Jiang, C. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils in Poyang Lake area. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Distribution and Formation conditions of gibbsite in the upland soils of humid Asia: Japan, Thailand and Indonesia. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World, Brisbane, Australia, 1–6 August 2010; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.F.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, Z.B.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, J. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments of Luoyuan Bay, Fujian. Environ. Res. 2020, 203, 111911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillardet, J.; Viers, J.; Dupr’e, B. Trace elements in river waters. Treatise Geochem. 2014, 5, 195–235. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Allen, H.E.; Toro, D.M.D.; Lee, S.Z.; Harsh, J.B. Predicting PbII adsorption on soils: The roles of soil organic matter, cation competition and iron (hydr) oxides. Environ. Chem. 2013, 10, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasooriya, R.; Dharmasena, B.; Aluthpatabendi, D. Copper–gibbsite interactions: An application of 1-pK surface complexation model. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 170, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.W.; Ma, Y.B.; Xu, M.G.; Luo, L.; Zhang, S.Z. Application of X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy to soil science. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2008, 45, 155–164. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, E.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Tu, Y.; Gu, X.F.; Ran, X.Z.; Yu, Z.; Wu, P. Superposition Effects of Zinc Smelting Atmospheric Deposition on Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Under Geochemical Anomaly. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 777894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jia, Z. Heavy metals in soils from a representative rapidly developing megacity (SW China): Levels, source identification, and apportionment. Catena 2018, 163, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; He, M.; Cheng, X.; Su, T.; Ni, S.J.; Zhang, C.J. Contamination, morphological status and sources of atmospheric dust in different land-using areas of a steel-industry city, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Hu, J.B.; Tian, S.L.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, W. Bulk deposition and source apportionment of atmospheric heavy metals and metalloids in agricultural areas of rural Beijing during 2016–2020. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, Q.D.; Tu, Y.; Yu, E.J.; Xing, D. Cadmium accumulation and migration of 3 peppers varieties in yellow and limestone soils under geochemical anomaly. Environ. Technol. 2020, 29, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.J.; Liu, H.Y. Effect of atmospheric deposition on cadmium accumulation in soils: A review. Environ. Anal. Ecol. Stud. 2021, 8, 432–846. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.T.; Wang, L.L.; Xiao, T.F.; Xiao, T.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Beiyuan, J.Z.; She, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.C.; Yin, M.L.; Liu, J.; et al. Legacy of multiple heavy metal(loid)s contamination and ecological risks in farmland soils from a historical artisanal zinc smelting area. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.C.; Wang, J.F.; Guo, J.Y.; Hu, X.P.; Bao, H.Y.; Chen, J.G. Record of heavy metals in Huguangyan Maar Lake sediments: Response to anthropogenic atmospheric pollution in Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.B. Enrichment Mechanism and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Soils with High Geochemical Background in the Karst Region of Guangxi Province, China. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Harlavan, Y.; Almogi-Labin, A.; Herut, B. Tracing natural and anthropogenic Pb in sediments along the Mediterranean coast of Israel using Pb isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6576–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, T.Q.; Wu, C.X.; He, Z.L.; Japenga, J.; Deng, M.; Yang, X. An integrated approach to assess heavy metal source apportionment in peri-urban agricultural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.C.; Li, Z.G.; Liu, J.L.; Bi, X.Y.; Ning, Y.Q.; Yang, S.C.; Yang, X.J. Apportionment of sources of heavy metals to agricultural soils using isotope fifingerprints and multivariate statistical analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.L.; Wu, S.H.; Wang, C.H.; Li, B.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.X. Combining emission inventory and isotope ratio analyses for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Gregg, J.W. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Wen, X.F.; W, X.; Liu, H.Y. Heavy metal migration and enrichment mechanism and the environmental risks during the weathering and soil Formation of carbonate rocks. Earth Environ. 2021, 4, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.H.; Li, B.J.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.H. Heavy metals in food crops, soil, and water in the Lihe River Watershed of the Taihu Region and their potential health risks when ingested. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 615, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloquet, C.; Carignan, J.; Libourel, G.; Sterckeman, T.; Perdrix, E. Tracing source pollution in soils using cadmium and lead isotopes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2525–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imseng, M.; Wiggenhauser, M.; Keller, A.; Müller, M.; Rehkämper, M.; Murphy, K.; Kreissig, K.; Frossard, E.; Wilcke, W.; Bigalke, M. Fate of Cd in agricultural soils: A stable isotope approach to anthropogenic impact, soil Formation and soilplant cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Stratum | Formation | Rock Types |
|---|---|---|
| Triassic | Erqiao Formation | Clastic rock |
| Feixianguan Formation | ||
| Permian | Xuanwei Formation | |
| Longtan Formation | ||
| Maokou Formation | Carbonate rocks | |
| Maping Formation | ||
| Carbonic | Huanglong Formation | |
| Triassic | Guanling Formation | |
| Jialingjiang Formation | ||
| Jurassic | Ziliujing Formation | |
| Suining Formation |
| Single-Factor Pollution Index | Geoaccumulation Index | Potential Ecological Risk Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi | Pollution Classification | Igeo | Grade | Pollution Classification | Ei | RI | Ecological Grade |
| Pi ≤ 1 | Unpolluted | Igeo ≤ 0 | 0 | Unpolluted | Ei ≤ 40 | RI ≤ 150 | Low risk |
| 1 < Pi ≤ 2 | Warning | 0 < Igeo ≤ 1 | 1 | Slightly polluted | 40 < Ei ≤ 80 | 150 < RI ≤ 300 | Moderate risk |
| 2 < Pi ≤ 3 | Slightly polluted | 1 < Igeo ≤ 2 | 2 | Moderately polluted | 80 < Ei ≤ 160 | 300 < RI ≤ 600 | High risk |
| 3 < Pi ≤ 5 | Moderately polluted | 2 < Igeo ≤ 3 | 3 | Moderately-heavily polluted | 160 < Ei ≤ 320 | 600 < RI < 1200 | Very high risk |
| Pi > 5 | Heavily polluted | 3 < Igeo ≤ 4 | 4 | Heavily polluted | Ei < 320 | RI > 1200 | Considerable risk |
| 4 < Igeo ≤ 5 | 5 | Heavily-extremely polluted | |||||
| Igeo > 5 | 6 | Extremely polluted | |||||
| Element | Units | Rocks in Carbonate Sub-Area (n = 39) | Rocks in Clastic Sub-Area (n = 30) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Abundances | ||
| Cd | mg/kg | 0.07 | 0.20 | 4.74 | 0.49 | 0.90 | 184.24 | 0.08 | 0.165 | 1.52 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 117.84 | 0.12 |
| As | - | 0.57 | 3.48 | 374.4 | 17.40 | 62.86 | 361.27 | 0.31 | 1.56 | 4.04 | 1.51 | 0.86 | 57.17 | 3.53 |
| Pb | - | 0.27 | 8.24 | 1144 | 42.68 | 184.42 | 432.06 | 0.69 | 8.79 | 24.9 | 9.70 | 6.84 | 70.58 | 9.02 |
| Cr | - | 25.10 | 65.25 | 823.60 | 97.71 | 127.20 | 130.18 | 84.40 | 227.8 | 698.3 | 297.30 | 194.26 | 65.34 | 9.49 |
| Cu | - | 1.37 | 15.60 | 1790.80 | 115.62 | 325.69 | 281.69 | 48.40 | 169.6 | 614.2 | 214.64 | 144.76 | 67.45 | 5.69 |
| Ni | - | 4.88 | 23.00 | 2298.30 | 91.53 | 368.76 | 402.88 | 21.90 | 90.65 | 130.00 | 84.27 | 31.78 | 37.72 | 6.09 |
| Zn | - | 1.58 | 31.35 | 1050.70 | 68.76 | 164.33 | 238.99 | 24.10 | 118.60 | 160.30 | 112.28 | 36.62 | 32.61 | 21.19 |
| SiO2 | wt% | 2.01 | 41.04 | 92.79 | 42.68 | 23.60 | 55.31 | 9.30 | 35.89 | 79.95 | 42.25 | 22.56 | 53.40 | 10.07 |
| Al2O3 | - | 1.40 | 13.66 | 41.06 | 14.86 | 10.17 | 68.40 | 0.32 | 17.40 | 30.85 | 14.57 | 9.12 | 62.61 | 1.77 |
| TFe2O3 | - | 1.12 | 3.65 | 41.80 | 5.94 | 7.53 | 126.75 | 5.44 | 11.80 | 24.85 | 12.34 | 5.74 | 46.52 | 0.50 |
| MgO | - | 0.3 | 1.82 | 8.28 | 2.61 | 2.23 | 85.47 | 0.50 | 3.13 | 4.25 | 2.41 | 1.49 | 61.75 | 6.36 |
| CaO | - | 0.21 | 7.67 | 67.58 | 24.27 | 27.12 | 111.77 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 5.12 | 0.74 | 1.34 | 181.81 | 39.7 |
| K2O | - | 0.20 | 1.00 | 5.13 | 1.58 | 1.43 | 90.19 | 0.49 | 1.03 | 2.96 | 1.24 | 0.84 | 68.28 | 0.54 |
| Region | Formation | Cd | As | Pb | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background value | 0.4668 | 20.1 | 33.4 | 139.6 | 66.58 | 56.89 | 111.4 | |
| Carbonate sub-area (n = 44) | Suining Formation | 1.74 (±0.70) | 17.98 (±1.61) | 54.20 (±25.25) | 78.40 (±12.54) | 41.03 (±11.97) | 39.43 (±5.84) | 188.83 (±86.50) |
| Ziliujing Formation | 0.49 (±0.40) | 9.34 (±1.03) | 29.08 (±3.98) | 83.11 (±21.49) | 34.30 (±3.76) | 35.59 (±6.40) | 87.05 (±16.57) | |
| Guanling Formation | 0.65 (±0.39) | 24.05 (±7.38) | 29.23 (±12.76) | 222.61 (±112.60) | 85.38 (±35.03) | 81.49 (±30.24) | 113.03 (±21.64) | |
| Jialingjiang Formation | 0.81 (±0.23) | 9.24 (±2.00) | 63.42 (±19.07) | 236.25 (±34.74) | 136.35 (±15.91) | 99.28 (±10.64) | 223.52 (±24.11) | |
| Maokou Formation | 1.15 (±0.47) | 25.27 (±13.34) | 35.59 (±6.86) | 134.74 (±17.74) | 115.18 (±81.27) | 79.21 (±49.30) | 139.86 (±20.90) | |
| Maping Formation | 1.95 (±1.82) | 27.35 (±2.60) | 65.43 (±14.04) | 131.67 (±4.62) | 35.88 (±2.89) | 51.40 (±6.41) | 148.03 (±39.99) | |
| Huanglong Formation | 5.21 (±0.71) | 46.30 (±0.62) | 68.12 (±11.18) | 216.00 (±4.56) | 43.77 (±6.61) | 96.93 (±5.71) | 244.33 (±31.30) | |
| Clastic Sub-area (n = 16) | Erqiao Formation | 1.59 (±0.25) | 66.75 (±16.44) | 28.58 (±4.94) | 147.48 (±61.10) | 205.65 (±48.49) | 257.80 (±38.40) | 391.98 (±50.33) |
| Feixianguan Formation | 2.42 (±0.75) | 67.59 (±9.37) | 210.20 (±19.50) | 351.35 (±18.73) | 199.65 (±17.94) | 491.84 (±21.91) | 567.21 (±39.93) | |
| Longtan Formation | 7.66 (±3.84) | 8.47 (±2.42) | 51.10 (±19.69) | 292.93 (±42.21) | 115.85 (±15.50) | 98.83 (±7.94) | 439.43 (±65.65) | |
| Xuanwei Formation | 2.54 (±0.92) | 7.28 (±1.19) | 34.48 (±9.01) | 199.38 (±61.17) | 278.75 (±56.67) | 123.58 (±18.54) | 222.25 (±55.79) |
| Units | Surface Soil in Carbonate Sub-Area (n = 39) | Surface Soil in Clastic Sub-Area (n = 30) | Background Value | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD | CV (%) | |||
| Cd | mg/kg | 0.31 | 1.11 | 8.37 | 1.90 | 2.10 | 125.74 | 0.11 | 1.17 | 6.65 | 1.61 | 1.52 | 77.54 | 0.4668 |
| As | - | 6.30 | 12.85 | 45.90 | 19.93 | 14.58 | 73.41 | 5.64 | 8.79 | 13.90 | 9.25 | 2.24 | 187.84 | 20.10 |
| Pb | - | 16.00 | 32.10 | 95.20 | 43.62 | 23.44 | 51.62 | 18.00 | 31.80 | 216.10 | 48.91 | 52.84 | 98.49 | 33.40 |
| Cr | - | 60.40 | 133.80 | 379.00 | 155.80 | 86.12 | 58.44 | 74.10 | 139.50 | 306.20 | 166.20 | 81.86 | 60.21 | 139.60 |
| Cu | - | 23.00 | 46.05 | 270.90 | 72.62 | 56.15 | 78.11 | 35.50 | 120.40 | 419.90 | 154.81 | 116.65 | 69.39 | 66.58 |
| Ni | - | 28.90 | 55.35 | 196.50 | 69.88 | 36.88 | 54.03 | 28.70 | 77.85 | 152.90 | 84.18 | 40.72 | 262.53 | 56.89 |
| Zn | - | 75.40 | 135.30 | 323.30 | 155.96 | 67.50 | 44.45 | 75.60 | 122.55 | 378.40 | 161.31 | 86.46 | 124.20 | 111.40 |
| pH | - | 4.69 | 6.53 | 8.03 | 6.43 | 0.91 | 14.00 | 5.45 | 6.25 | 7.74 | 6.43 | 0.70 | 10.90 | |
| SiO2 | wt% | 4.91 | 39.05 | 121.35 | 44.46 | 21.91 | 44.52 | 0.43 | 41.94 | 130.52 | 46.95 | 23.29 | 31.44 | 58.00 |
| Al2O3 | - | 3.12 | 22.47 | 39.23 | 21.86 | 6.92 | 32.15 | 0.08 | 1.30 | 10.20 | 1.79 | 1.86 | 101.73 | 14.11 |
| TFe2O3 | - | 5.70 | 9.74 | 16.58 | 10.27 | 3.40 | 35.33 | 5.86 | 13.66 | 111.67 | 17.22 | 19.33 | 109.75 | 9.82 |
| MgO | - | 0.22 | 2.11 | 6.02 | 2.32 | 1.43 | 74.54 | 0.30 | 18.23 | 31.15 | 18.91 | 7.59 | 37.18 | 1.47 |
| CaO | - | 0.18 | 1.06 | 2.55 | 1.03 | 0.60 | 60.94 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 3.37 | 0.75 | 0.59 | 56.16 | 0.93 |
| K2O | - | 0.47 | 2.18 | 5.46 | 2.45 | 1.30 | 58.30 | 0.06 | 0.99 | 5.54 | 1.52 | 1.40 | 87.76 | 1.27 |
| Index | Cd | As | Pb | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonate rock | Mean | 0.49 | 17.40 | 42.68 | 97.71 | 115.62 | 91.53 | 68.76 | 42.68 | 14.86 | 5.94 | 2.61 | 24.27 | 1.58 |
| Abundances | 0.12 | 3.53 | 9.02 | 9.49 | 5.69 | 6.09 | 21.19 | 10.07 | 0.5 | 6.36 | 1.77 | 39.7 | 0.54 | |
| enrichment coefficient | 4.08 | 4.93 | 4.73 | 10.30 | 20.32 | 15.03 | 3.24 | 4.24 | 29.72 | 0.93 | 1.47 | 0.61 | 2.93 | |
| Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Loss | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Strong Enrichment | |
| Carbonate soil | Mean | 1.51 | 18.39 | 41.59 | 147.91 | 67.22 | 64.55 | 143.88 | 45.45 | 21.63 | 9.82 | 2.35 | 0.94 | 2.73 |
| Abundances | 0.467 | 20.10 | 33.40 | 139.6 | 66.58 | 56.89 | 111.4 | 58.00 | 14.11 | 9.82 | 1.47 | 0.93 | 1.27 | |
| enrichment coefficient | 3.23 | 0.91 | 1.25 | 1.06 | 1.01 | 1.13 | 1.29 | 0.78 | 1.53 | 1.00 | 1.60 | 1.01 | 2.15 | |
| Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Loss | Strong Enrichment | Moderate Enrichment | Moderate | Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Strong Enrichment | Moderate | Strong Enrichment | Moderate | Strong Enrichment | |
| Q value | 3.08 | 1.06 | 0.97 | 1.51 | 0.58 | 0.71 | 2.09 | 1.06 | 1.46 | 1.65 | 0.90 | 0.04 | 1.73 | |
| Rock | Mean | 0.37 | 1.51 | 9.70 | 297.30 | 214.64 | 84.27 | 112.28 | 42.25 | 14.57 | 12.34 | 2.41 | 0.74 | 1.24 |
| Abundances | 0.09 | 5.10 | 17.54 | 39.16 | 15.91 | 17.59 | 50.48 | 73.8 | 2.39 | 1.21 | 10.59 | 2.22 | 2.34 | |
| enrichment coefficient | 4.11 | 0.30 | 0.55 | 7.58 | 13.45 | 4.79 | 2.22 | 0.57 | 6.11 | 10.17 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.53 | |
| Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Strong Loss | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Strong Loss | Strong Loss | |
| Soil | Mean | 1.66 | 17.18 | 79.64 | 257.07 | 170.97 | 333.49 | 287.63 | 42.90 | 19.50 | 22.59 | 2.43 | 0.86 | 1.27 |
| Abundances | 0.47 | 20.10 | 33.40 | 139.60 | 66.58 | 56.89 | 111.40 | 58.00 | 14.11 | 9.82 | 1.47 | 0.93 | 1.27 | |
| enrichment coefficient | 3.53 | 0.85 | 2.83 | 1.84 | 2.57 | 5.86 | 2.58 | 0.74 | 1.38 | 2.30 | 1.65 | 0.92 | 1.00 | |
| Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Enrichment | Strong Loss | Moderate | |
| Q value | 4.49 | 11.38 | 8.21 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 3.96 | 2.56 | 1.02 | 1.34 | 1.83 | 1.01 | 1.16 | 1.02 |
| Region | Elements | Pollution Index | Sampling (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unpolluted | Warning | Slightly Polluted | Moderately Polluted | Heavily Polluted | |||
| Carbonate sub-area (n = 39) | Cd | Pi | 18.75 | 15.63 | 31.25 | 9.38 | 25.00 |
| As | Pi | 68.75 | 12.50 | 18.75 | - | - | |
| Pb | Pi | 53.13 | 25.00 | 21.88 | - | - | |
| Cr | Pi | 65.63 | 21.88 | 12.50 | - | - | |
| Cu | Pi | 68.75 | 18.75 | 9.38 | 3.13 | - | |
| Ni | Pi | 53.13 | 40.63 | 3.13 | 3.13 | - | |
| Zn | Pi | 28.13 | 59.38 | 12.50 | - | - | |
| Clastic sub-area (n = 30) | Cd | Pi | 17.86 | 25.00 | 28.57 | 3.57 | 25.00 |
| As | Pi | 100.00 | - | - | - | - | |
| Pb | Pi | 67.86 | 21.43 | - | - | 10.71 | |
| Cr | Pi | 50.00 | 35.71 | 14.29 | - | - | |
| Cu | Pi | 32.14 | 25.00 | 14.29 | 25.00 | 3.57 | |
| Ni | Pi | 46.43 | 21.43 | 32.14 | - | - | |
| Zn | Pi | 50.00 | 14.29 | 32.14 | 3.57 | - | |
| Carbonate sub-area (n = 39) | Cd | Igeo | 90.63 | 9.38 | - | - | |
| As | Igeo | 68.75 | 31.25 | - | - | ||
| Pb | Igeo | 78.13 | 21.88 | - | - | ||
| Cr | Igeo | 78.13 | 21.88 | - | - | ||
| Cu | Igeo | 71.88 | 28.13 | - | - | ||
| Ni | Igeo | 65.63 | 31.25 | 3.13 | - | ||
| Zn | Igeo | 62.50 | 37.50 | - | - | ||
| Clastic sub-area (n = 30) | Cd | Igeo | 100.00 | - | - | - | |
| As | Igeo | 100.00 | - | - | - | ||
| Pb | Igeo | 96.43 | 3.57 | - | - | ||
| Cr | Igeo | 78.57 | 21.43 | - | - | ||
| Cu | Igeo | 39.29 | 32.14 | 25.00 | 3.57 | ||
| Ni | Igeo | 50.00 | 50.00 | - | - | ||
| Zn | Igeo | 64.29 | 32.14 | 3.57 | - | ||
| pH | Cd | As | Pb | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Cd | −0.20 | 1 | |||||||||||
| As | −0.39 ** | 0.60 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| Pb | 0.07 | 0.30 * | 0.16 | 1 | |||||||||
| Cr | −0.08 | 0.26 | −0.10 | 0.42 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| Cu | −0.28 | 0.01 | −0.36 * | −0.01 | 0.48 ** | 1 | |||||||
| Ni | −0.16 | 0.34 * | −0.11 | 0.33 * | 0.86 ** | 0.78 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Zn | −0.10 | 0.75 ** | 0.20 | 0.61 ** | 0.58 ** | 0.33 * | 0.65 ** | 1 | |||||
| SiO2 | 0.28 | −0.29 | −0.20 | −0.16 | −0.20 | −0.20 | −0.29 | −0.22 | 1 | ||||
| Al2O3 | −0.25 | −0.02 | 0.23 | −0.05 | −0.08 | 0.03 | −0.05 | −0.07 | −0.07 | 1 | |||
| Fe2O3 | −0.34 * | 0.08 | −0.26 | 0.07 | 0.57 ** | 0.92 ** | 0.84 ** | 0.37 * | −0.34 * | 0.05 | 1 | ||
| MgO | 0.11 | 0.04 | −0.15 | 0.42 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.34 * | −0.28 | −0.12 | 0.07 | 1 | |
| CaO | 0.46 ** | 0.17 | −0.30 * | 0.10 | 0.44 ** | 0.09 | 0.34 * | 0.50 ** | 0.04 | −0.28 | 0.10 | 0.44 ** | 1 |
| Region | Famation | Cd (mg/kg) | δ114/110Cd |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rock in study area | Suining Formation | 0.40 ± 0.23 | −0.07 ± 0.06 |
| Guanling Formation | 0.14 ± 0.38 | 0.60 ± 0.08 | |
| Feixianguan Formation | 0.54 ± 0.14 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | |
| Jialingjiang Formation | 0.24 ± 0.18 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | |
| Maokou Formation | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.10 | |
| Huanglong Formation | 0.39 ± 0.18 | 0.61 ± 0.08 | |
| Soil in carbonate sub-area | Suining Formation | 1.74 ± 0.70 | 0.16 ± 0.09 |
| Ziliujing Formation | 0.49 ± 0.40 | −0.29 ± 0.08 | |
| Guanling Formation | 0.65 ± 0.39 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | |
| Jialingjiang Formation | 0.81 ± 0.23 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | |
| Maokou Formation | 1.15 ± 0.47 | 0.46 ± 0.05 | |
| Huanglong Formation | 5.21 ± 0.71 | 0.06 ± 0.07 | |
| Soil in clastic sub-area | Longtan Formation | 7.66 ± 3.84 | −0.12 ± 0.06 |
| Xuanwei Formation | 2.54 ± 0.92 | 0.20 ± 0.09 | |
| Erqiao Formation | 1.59 ± 2.25 | −0.03 ± 0.05 | |
| Atmospheric deposition | 0.69 ± 0.21 | −0.314 ± 0.03 |
| Region | Analytic Method | Geological Source | Atmospheric Deposition |
|---|---|---|---|
| All samples | Unmix model | 75.60 | 24.40 |
| Carbonate sub-area | 206Pb/207Pb | 78.02 | 21.98 |
| Carbonate sub-area | 208Pb/206Pb | 79.81 | 20.19 |
| Clastic sub-area | 206Pb/207Pb | 55.00 | 45.00 |
| Clastic sub-area | 208Pb/206Pb | 61.54 | 38.46 |
| Carbonate sub-area | 114Cd/110Cd | 80.15 | 19.85 |
| Clastic sub-area | 114Cd/110Cd | 87.13 | 12.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, E.; Liu, H.; Dinis, F.; Zhang, Q.; Jing, P.; Liu, F.; Ju, X. Contamination Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Karst Soil Using UNMIX Model and Pb-Cd Isotopes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912478
Yu E, Liu H, Dinis F, Zhang Q, Jing P, Liu F, Ju X. Contamination Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Karst Soil Using UNMIX Model and Pb-Cd Isotopes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912478
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Enjiang, Hongyan Liu, Faustino Dinis, Qiuye Zhang, Peng Jing, Fang Liu, and Xianhang Ju. 2022. "Contamination Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Karst Soil Using UNMIX Model and Pb-Cd Isotopes" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912478
APA StyleYu, E., Liu, H., Dinis, F., Zhang, Q., Jing, P., Liu, F., & Ju, X. (2022). Contamination Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Karst Soil Using UNMIX Model and Pb-Cd Isotopes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912478







