Accuracy of Computer-Aided Detection of Occupational Lung Disease: Silicosis and Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Ex-Miners from the South African Gold Mines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population and Sampling
2.2. Reading of CXRs
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Outcome Frequencies
3.2. Inter-Reader Agreement
3.3. Comparative Performance of the CAD Systems against External Readers
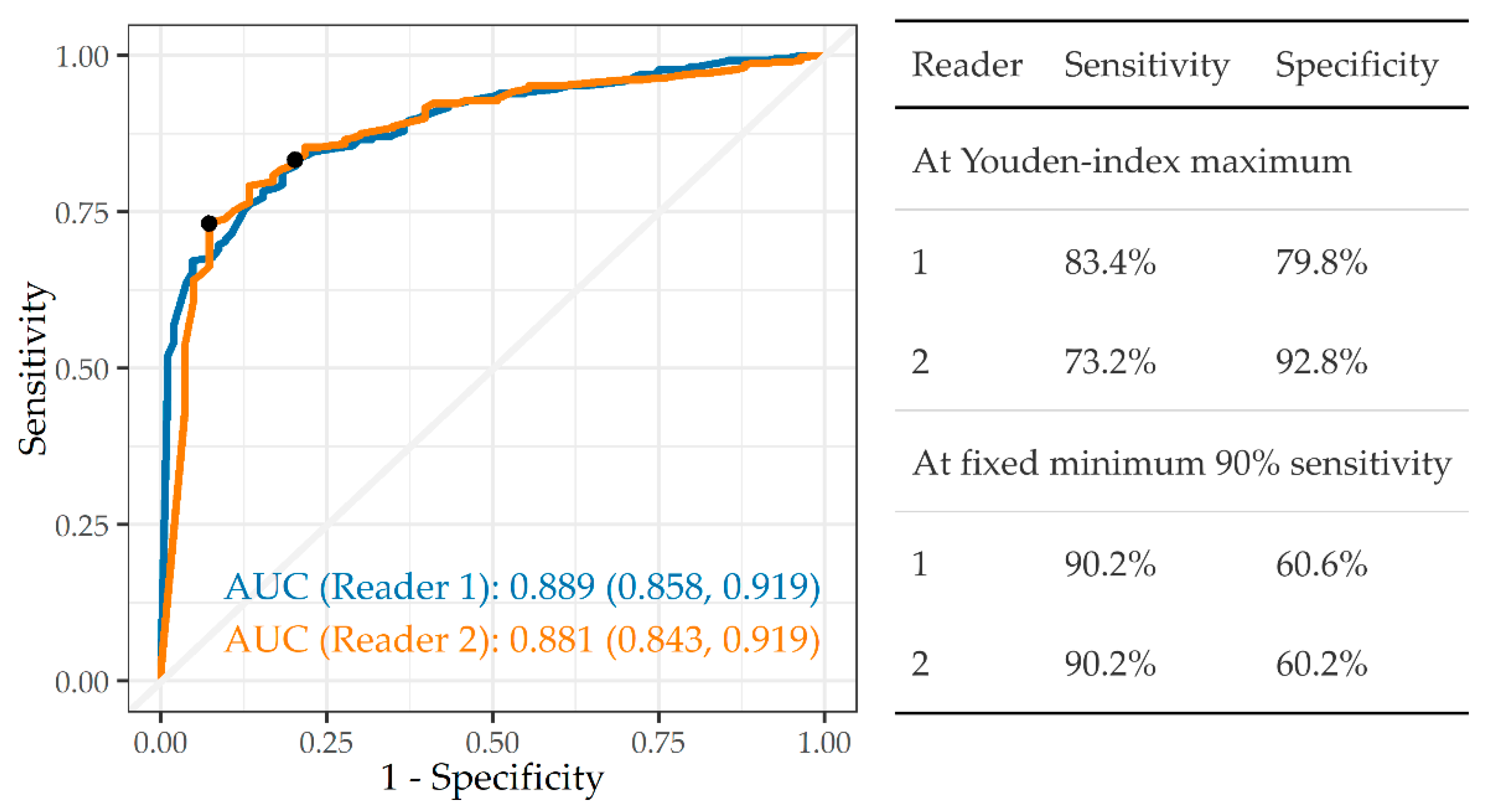
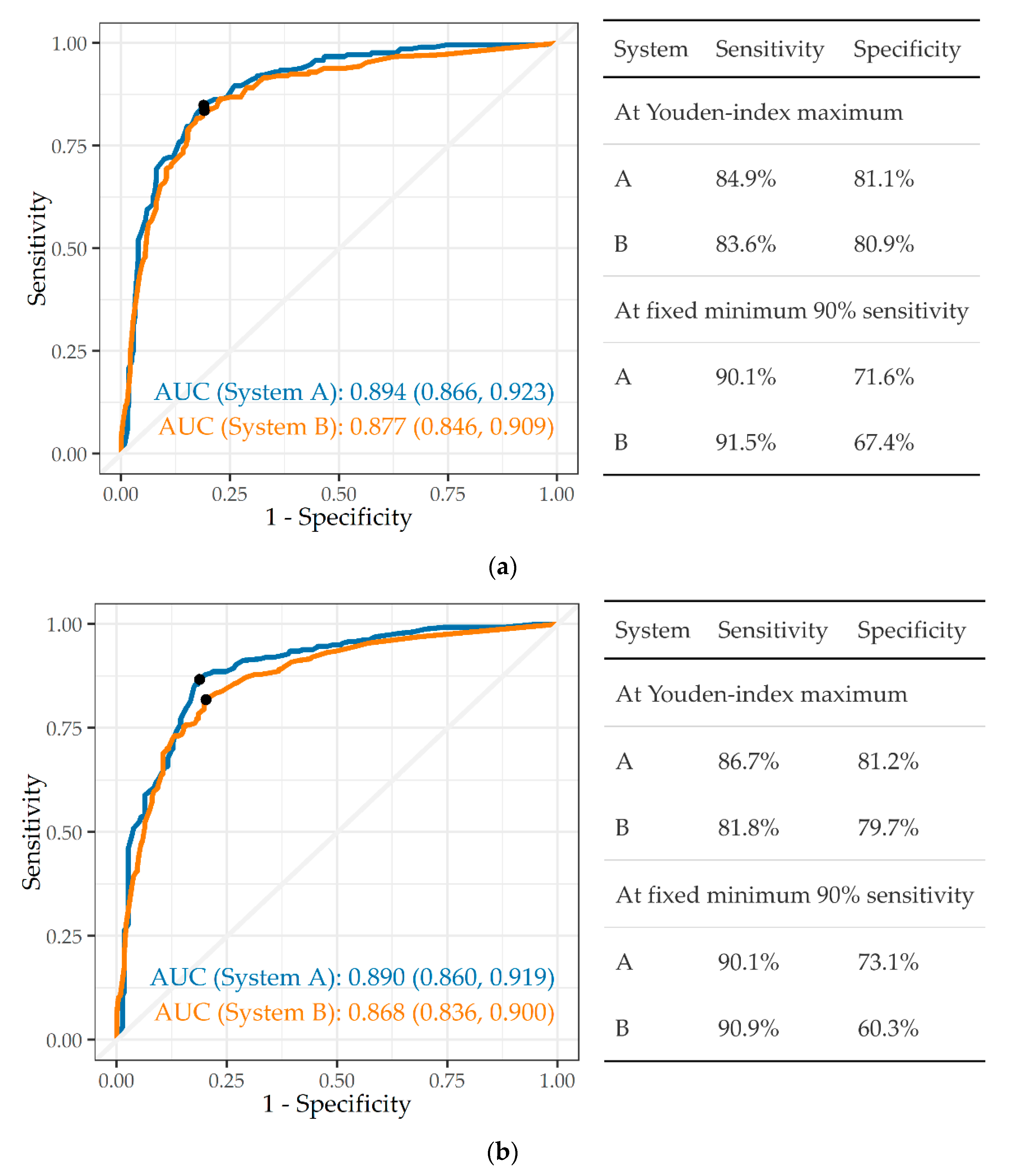
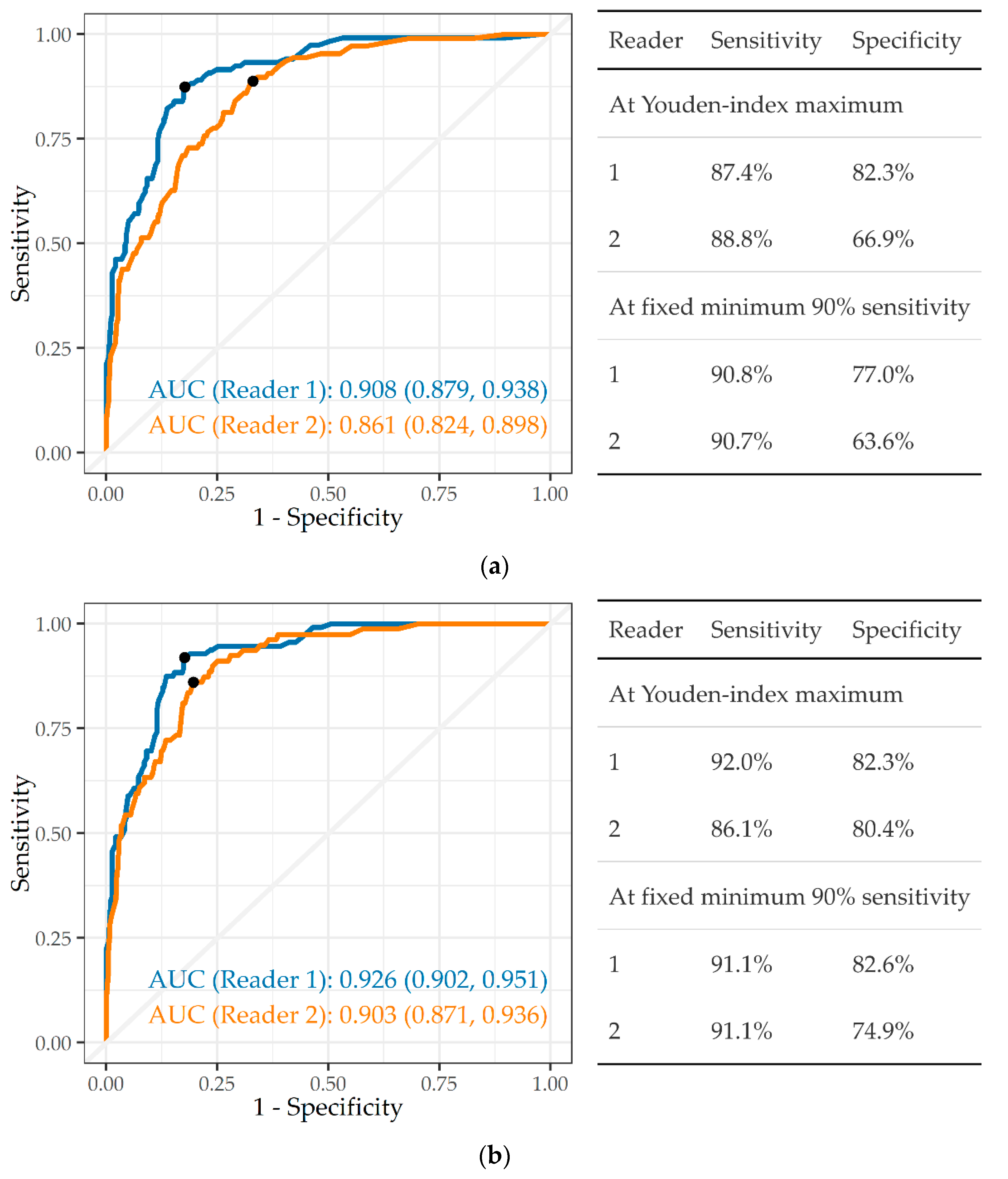
3.3.1. Any Abnormality
3.3.2. Tuberculosis
3.3.3. Silicosis and Silicotuberculosis
3.4. Variation in AUC by Covariates
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous CAD Study
4.2. Performance in Relation to WHO TB Screening Guideline
4.3. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehrlich, R. A century of miners’ compensation in South Africa. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2012, 55, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, R.; Barker, S.; Tsang, V.; Kistnasamy, B.; Yassi, A. Access of migrant gold miners to workers’ compensation for occupational lung disease: Quantifying a legacy of injustice. J. Migration Health 2021, 4, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Ehrlich RIsmail, N.; Quail, Z.; Jeebhay, M.F. Occupational health challenges facing the Department of Health. In South African Health Review 2012/2013; Padarath, A., English, R., Eds.; Health Systems Trust: Durban, South Africa, 2013; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Baleta, A. Southern African declaration targets TB in mining sector. Lancet 2012, 380, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Benefits and Costs of Reducing Tuberculosis among Southern Africa’s Mineworkers—Overview; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Available online: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/333441468114546136/benefits-and-costs-of-reducing-tuberculosis-among-southern-africas-mineworkers-overview (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Ehrlich, R.; Akugizibwe, P.; Siegfried, N.; Rees, D. Silica exposure, silicosis and tuberculosis—A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TB in the Mining Sector in Southern Africa (TIMS) (Website, Undated). Available online: https://www.timssa.co.za/Whoweare/AboutTIMS.aspx (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Kistnasamy, B.; Yassi, A.; Yu, J.; Spiegel, S.J.; Fourie, A.; Barker, S.; Spiegel, J.M. Tackling injustices of occupational lung disease acquired in South African mines: Recent developments and ongoing challenges. Glob. Health 2018, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, T. Landmark Silicosis Settlement Made Order of Court. Groundup. 26 July 2019. Available online: https://www.groundup.news/article/landmark-silicosis-settlement-made-order-court/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Tshiamiso Trust (Website, Undated). Medical Workshop on Sustainable Models of Medical Service Delivery for Mineworkers in Southern Africa. Available online: https://www.tshiamisotrust.com/resources/medical-workshop/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- World Health Organization. Chest Radiography in Tuberculosis Detection—Summary of Current WHO Recommendations and Guidance on Programmatic Approaches; WHO/HTM/TB/2016.20; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. High-Priority Target Product Profiles for New Tuberculosis Diagnostics: Report of a Consensus Meeting, 28–29 April 2014, Geneva, Switzerland; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 2: Screening—Systematic Screening for Tuberculosis Disease; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pande, T.; Cohen, C.; Pai, M.; Ahmad Khan, F. Computer-aided detection of pulmonary TB on digital chest radiographs: A systematic review. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2016, 20, 1226–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.; Qi, A.; Jeagal, L.; Torabi, N.; Menzies, D.; Korobitsyn, A.; Pai, M.; Nathavitharana, R.R.; Ahmad Khan, F. A systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of artificial intelligence-based computer programs to analyze chest X-rays for pulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuninger, M.; van Ginneken, B.; Philipsen, R.H.; Mhimbira, F.; Hella, J.J.; Lwilla, F.; van den Hombergh, J.; Ross, A.; Jugheli, L.; Wagner, D.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of computer-aided detection of pulmonary TB in chest radiographs: A validation study from sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Pande, T.; Tessema, B.; Song, R.; Benedetti, A.; Pai, M.; Lönnroth, K.; Denkinger, C.M. Computer-aided reading of tuberculosis chest radiography: Moving the research agenda forward to inform policy. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, B. Potential of deep learning in assessing pneumoconiosis depicted on digital chest radiography. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 77, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Rong, R.; Li, Q.; Yang, D.M.; Yao, B.; Luo, D. A deep learning-based mode for screening and staging pneumoconiosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girdler-Brown, B.V.; White, N.W.; Ehrlich, R.I.; Churchyard, G.J. The burden of silicosis, pulmonary tuberculosis and COPD among former Basotho goldminers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2008, 51, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboso, B.M.; Moyo, D.M.; Muteba, K.M.; Govender, V.G.; Barnes, D.F.; Maama-Maime, L.B.M.; Makiti, S.J.; Lerotholi, M.; Ehrlich, R.I. Burden of disease among Basotho ex-miners in a large out-reach medical assessment programme. Occup. Health South. Afr. 2020, 26, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, A.; Rees, D.; Felix, M.; Venter, M. A proposed radiographic classification of TB to accompany the ILO International Classification of Radiographs of Pneumoconiosis. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2000, 6, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, A. Part 2—A radiographic presentation of nodular TB and silicosis. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2001, 7, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, A.; Rees, D. Back to Basics-the chest radiograph in silica associated tuberculosis. Occup. Health South. Afr. 2010, 16, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Schepers, G.W.H. Silicosis and tuberculosis. Ind. Med. Surg. 1964, 33, 381–399. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Determining the Local Calibration of Computer-Assisted Detection (CAD) Thresholds and Other Parameters: A Toolkit to Support the Effective Use of CAD for TB Screening; Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGOWHO Handbook; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Young, C.; Barker, S.; Ehrlich, R.; Kistnasamy, B.; Yassi, A. Computer-aided Detection for TB and silicosis in chest radiographs of Southern African gold miners. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Area under the Curve (AUC): A Diagnostic Measure for Evaluating the Accuracy of Predictors of Education Outcomes; Teachers College Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.tc.columbia.edu/elda/blog/content/receiver-operating-characteristic-roc-area-under-the-curve-auc/ (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- International Labour Organization. ILO International Classification of Radiographs of Pneumoconioses (Digital Format). 2011. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/global/publications/books/WCMS_168337/lang--en/index.htm (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; De Vet, H.C.; et al. STARD 2015: An updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Z.; Ahmed, S.; Sarker, M.S.; Paul, K.; Adel, A.S.S.; Naheyan, T.; Barrett, R.; Banu, S.; Creswell, J. Tuberculosis detection from chest X-rays for triaging in a high tuberculosis-burden setting: An evaluation of five artificial intelligence algorithms. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e543–e554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnizdo, E.; Murray, J.; Sluis-Cremer, G.K.; Glyn Thomas, R. Correlation between radiological and pathological diagnosis of silicosis: An autopsy population based study. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1993, 24, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzblau, A.; te Water Naude, J.; Sen, A.; d’Arcy, H.; Smilg, J.S.; Mashao, K.S.; Meyer, C.A.; Lockey, J.E.; Ehrlich, R.I. Comparison of digital and film chest radiography for detection and medical surveillance of silicosis and pulmonary tuberculosis. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2018, 61, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.J.; Charalambous, S.; Day, J.H. HIV Infection does not affect active case finding of TB in South African gold miners. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.H.; Charalambous, S.; Fielding, K.L.; Hayes, R.J.; Churchyard, G.J.; Grant, A.D. Screening for TB prior to isoniazid preventive therapy among HIV-infected gold miners in South Africa. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2006, 10, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, S.; Ehrlich, R.; Spiegel, J.M.; Kistnasamy, B.; Riera, F.; Fourie, A.; Mtshali, N.; Rabada, M.; Lockhart, K.; Yassi, A. Reforming the workers’ compensation process for occupational lung disease among miners in South Africa—An efficiency study of claims assessment. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2022, 95, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J.M.; Ehrlich, R.; Yassi, A.; Riera, F.; Wilkinson, J.; Lockhart, K.; Barker, S.; Kistnasamy, B. Using artificial intelligence for high-volume identification of silicosis and tuberculosis: A bio-ethics approach. Ann. Glob. Health 2021, 87, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| System | A | B |
|---|---|---|
| Any abnormality | - | Numerical: 0–100; Categorical: TB or other abnormalities (including silicosis) present vs. absent (CXR normal). |
| TB | Numerical: 0–100; Categorical: TB present vs. absent. | Numerical: 0–100; Categorical: TB present vs. absent. |
| Silicosis | Numerical: 0–100; Categorical: silicosis present vs. absent | - |
| Silicotuberculosis (calculated) | Numerical: 0–100 (Sum TB, silicosis scores)/2; Categorical: silicotuberculosis present vs. absent | - |
| N1 2 | N2 3 | Kappa | 95% CI | Agreement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any abnormality | 397 | 418 | 0.561 | 0.474, 0.648 | Moderate |
| TB (possible or probable/definite) 4 | 213 | 264 | 0.655 | 0.570, 0.741 | Substantial |
| TB probable/definite 4 | 128 | 216 | 0.572 | 0.491, 0.653 | Moderate |
| Silicosis ≥ ILO 1/0 (irrespective of TB) | 119 | 109 | 0.501 | 0.413, 0.588 | Moderate |
| Silicosis ≥ 1/1 (irrespective of TB) | 112 | 80 | 0.565 | 0.479, 0.650 | Moderate |
| Silicotuberculosis ≥ 1/0 | 74 | 66 | 0.320 | 0.232, 0.407 | Fair |
| Silicotuberculosis ≥ 1/1 | 72 | 47 | 0.384 | 0.299, 0.469 | Fair |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ehrlich, R.; Barker, S.; te Water Naude, J.; Rees, D.; Kistnasamy, B.; Naidoo, J.; Yassi, A. Accuracy of Computer-Aided Detection of Occupational Lung Disease: Silicosis and Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Ex-Miners from the South African Gold Mines. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912402
Ehrlich R, Barker S, te Water Naude J, Rees D, Kistnasamy B, Naidoo J, Yassi A. Accuracy of Computer-Aided Detection of Occupational Lung Disease: Silicosis and Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Ex-Miners from the South African Gold Mines. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912402
Chicago/Turabian StyleEhrlich, Rodney, Stephen Barker, Jim te Water Naude, David Rees, Barry Kistnasamy, Julian Naidoo, and Annalee Yassi. 2022. "Accuracy of Computer-Aided Detection of Occupational Lung Disease: Silicosis and Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Ex-Miners from the South African Gold Mines" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912402
APA StyleEhrlich, R., Barker, S., te Water Naude, J., Rees, D., Kistnasamy, B., Naidoo, J., & Yassi, A. (2022). Accuracy of Computer-Aided Detection of Occupational Lung Disease: Silicosis and Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Ex-Miners from the South African Gold Mines. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912402






