Contamination Assessment and Temporal Evolution of Nitrates in the Shallow Aquifer of the Metauro River Plain (Adriatic Sea, Italy) after Remediation Actions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
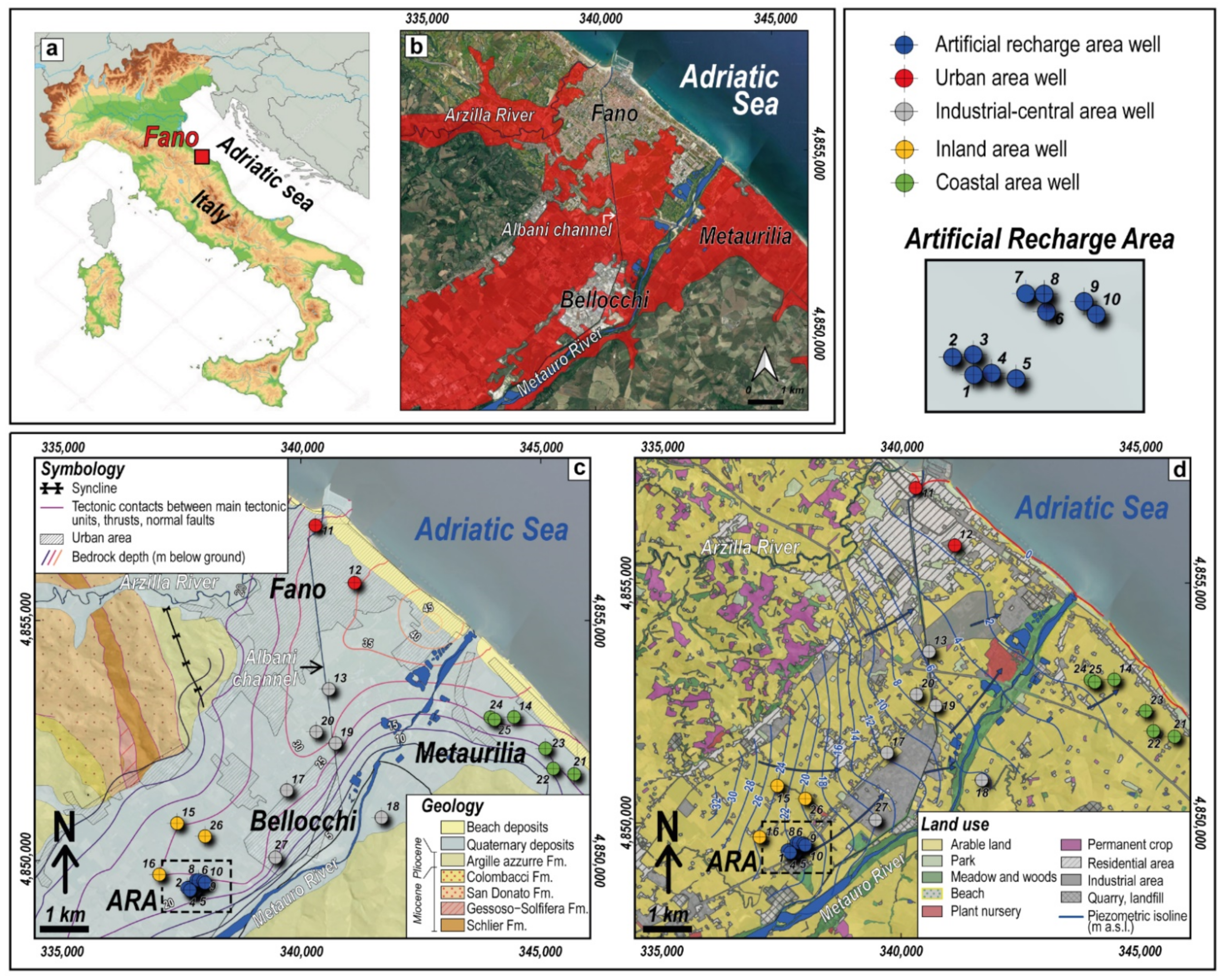
2. Geology, Hydrogeology and Land Use
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Geochemical Methods
3.2. Compositional Data Analysis
3.3. Temporal Trend Analysis
4. Results
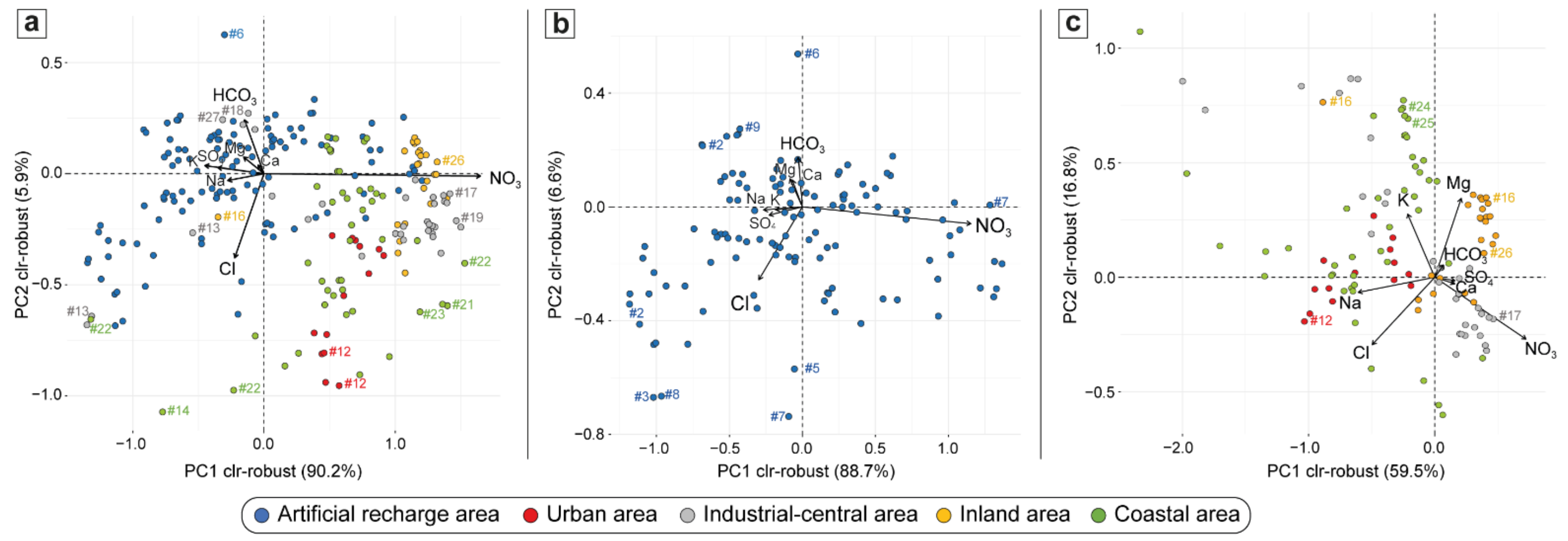
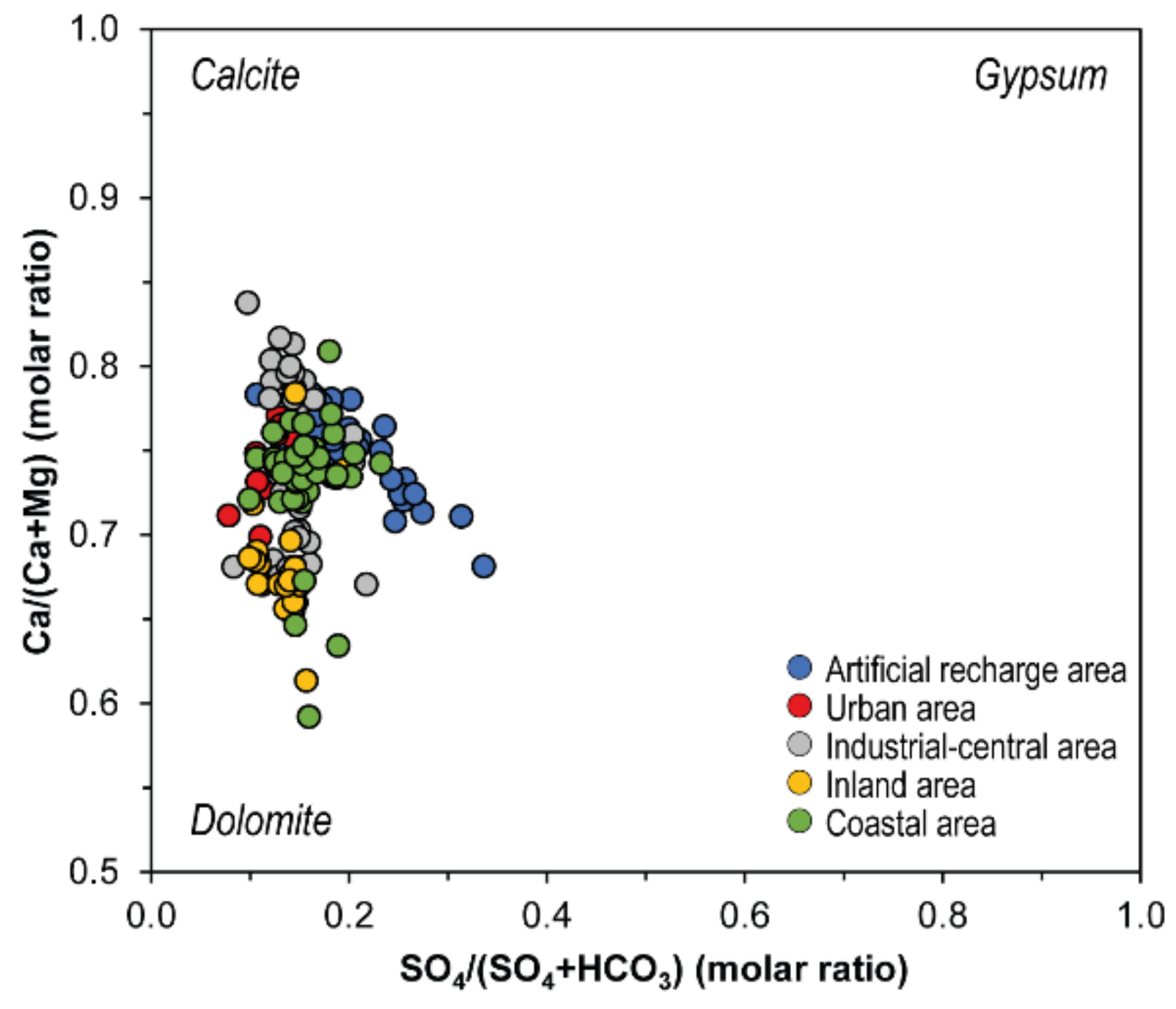
4.1. Hydrogeochemical Characterization
4.2. Nitrate Contents
4.3. Temporal Trend Evolution of Nitrates
5. Discussion
5.1. Nitrate Sources Interpreted by Geochemical Indicators
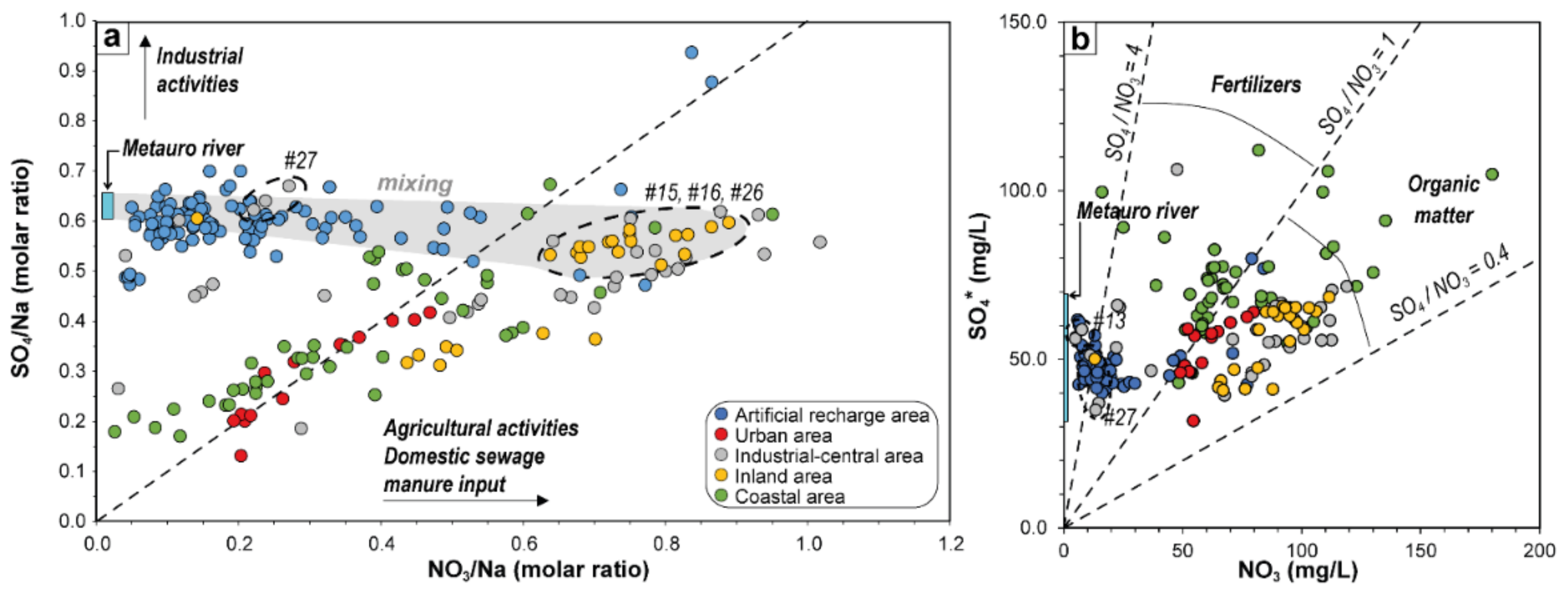
5.2. Nitrates Temporal Trend Analysis
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, G.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capri, E.; Civita, M.; Corniello, A.; Cusimano, G.; De Maio, M.; Ducci, D.; Fait, G.; Fiorucci, A.; Hauser, S.; Pisciotta, A.; et al. Assessment of nitrate contamination risk: The Italian experience. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisi, B.; Vaselli, O.; Delgado Huertas, A.; Tassi, F. Dissolved nitrates in the groundwater of the Cecina Plain (Tuscany, Central-Western Italy): Clues from the isotopic signature of NO3−. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 34, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, G.; Dadomo, A.; De Luca, D.A.; Mazzola, M.; Lasagna, M.; Pennisi, M.; Pilla, G.; Sacchi, E.; Saccon, P. Nitrate sources, accumulation and reduction in groundwater from Northern Italy: Insights provided by a nitrate and boron isotopic database. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 91, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Daesslé, L.W.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.A.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R. Estimation of nitrate pollution sources and transformations in groundwater of an intensive livestock-agricultural area (Comarca Lagunera), combining major ions, stable isotopes and MixSIAR model. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abascal, E.; Gómez-Coma, L.; Ortiz, I.; Ortiz, A. Global diagnosis of nitrate pollution in groundwater and review of removal technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; De Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; Van Breda, S.G. Drinking Water Nitrate and Human Health: An Updated Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Recent advances in the understanding and management of eutrophication. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doveri, M.; Menichini, M.; Scozzari, A. Protection of Groundwater Resources: Worldwide Regulations and Scientific Approaches. In Threats to the Quality of Groundwater Resources; Scozzari, A., Dotsika, E., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 40, pp. 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater use for irrigation—A global inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Navarrete, C.; Grima Olmedo, J.; Durán Valsero, J.J.; Gómez Gómez, J.D.; Luque Espinar, J.A.; de la Orden, G.J.A. Groundwater protection in Mediterranean countries after the European water framework directive. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccianti, A.; Nisi, B.; Martín-Fernández, J.A.; Palarea-Albaladejo, J. Methods to investigate the geochemistry of groundwaters with values for nitrogen compounds below the detection limit. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 141, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raco, B.; Vivaldo, G.; Doveri, M.; Menichini, M.; Masetti, G.; Battaglini, R.; Irace, A.; Fioraso, G.; Marcelli, I.; Brussolo, E. Geochemical, geostatistical and time series analysis techniques as a tool to achieve the Water Framework Directive goals: An example from Piedmont region (NW Italy). J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 229, 106832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review of emerging adsorbents for nitrate removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhoff, B. Deciphering natural and anthropogenic nitrate and recharge sources in arid region groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y. An overview of in-situ remediation for nitrate in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 149981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisi, B.; Vaselli, O.; Taussi, M.; Dover, M.; Menichini, M.; Cabassi, J.; Raco, R.; Botteghi, S.; Mussi, M.; Masetti, G. Hydrogeochemical surveys of shallow coastal aquifers: A conceptual model to set-up a monitoring network and increase the resilience of a strategic groundwater system to climate change and anthropogenic pressure. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 142, 105350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, J. The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data; Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability; Chapman & Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Regione Marche. Prima Individuazione Delle Zone Vulnerabili da Nitrati di Origine Agricola. 2003. Available online: https://www.regione.marche.it/Regione-Utile/Ambiente/Tutela-delle-acque/ZVN (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Conti, P.; Cornamusini, G.; Carmignani, L. An outline of the geology of the Northern Apennines (Italy), with geological map at 1:250,000 scale. Ital. J. Geosci. 2020, 139, 149–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taussi, M.; Borghi, W.; Gliaschera, M.; Renzulli, A. Defining the Shallow Geothermal Heat-Exchange Potential for a Lower Fluvial Plain of the Central Apennines: The Metauro Valley (Marche Region, Italy). Energies 2021, 14, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regione Marche. Carta Uso del Suolo Della Regione Marche “ADS40 2007”. 2007. Available online: https://www.regione.marche.it/Regione-Utile/Paesaggio-Territorio-Urbanistica/Cartografia/Repertorio/Cartausosuolo10000_2007#Caratteristiche-e-disponibilit%C3%A0 (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Nanni, T. Le falde di subalveo delle Marche: Inquadramento idrogeologico, qualità delle acque (ed) elementi di neotettonica. In Materiali per la Programmazione 2; Regione Marche: Ancona, Italy, 1985; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo, M. Analisi Delle Risorse Idriche e Valutazione Della Vulnerabilità, con L’ausilio di Metodologie GIS, Dell’acquifero Alluvionale del Fiume Metauro tra Montemaggiore e Fano (PU). Master’s Thesis, University of G. D’Annunzio Chieti and Pescara, Chieti, Italy, 2004; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
- Nesci, O.; Savelli, D.; Troiani, F. Evoluzione tardo quaternaria dell’area di foce del Fiume Metauro (Marche settentrionali). In Collana dell’Autorità di Bacino della Basilicata, Proceedings of the Coste: Prevenire, Programmare, Pianificare Conference, Maratea, Italy, 15–17 May 2008; Autorità di Bacino della Basilicata: Potenza, Italy, 2008; Volume 9, pp. 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Calderoni, G.; Della Seta, M.; Fredi, P.; Lupia Palmieri, E.; Nesci, O.; Savelli, D.; Troiani, F. Late Quaternary geomorphological evolution of the Adriatic coast reach encompassing the Metauro, Cesano and Misa river mouths (Northern Marche, Italy). GeoActa Spec. Publ. 2010, 3, 109–124. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, D.; Cavitolo, P. Climate and land use changes as origin of the Water Cycle variations and sediment transport in Pesaro Urbino Province, Central and Eastern Italy. Acque Sotter.-Ital. J. Groundw. 2016, 5, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2005; p. 683. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Buccianti, A. Compositional Data Analysis: Theory and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; 400p. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J. Geometric approach to statistical analysis on the simplex. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2001, 15, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccianti, A.; Egozcue, J.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V. Variation diagrams to statistically model the behavior of geochemical variables: Theory and applications. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J.; Tolosana-Delgado, R. Modeling and Analysis of Compositional Data. Statistics in Practice; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; 272p. [Google Scholar]
- Egozcue, J.J.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Mateu-Figueras, G.; Barceló-Vidal, C. Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis. Math. Geol. 2003, 35, 270–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzi, C.; Sauro Graziano, R.; Buccianti, A. Part-Whole Relations: New Insights about the Dynamics of Complex Geochemical Riverine Systems. Minerals 2020, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J. Compositional Data in Geostatistics: A Log-Ratio Based Framework to Analyze Regionalize Compositions. Math. Geosci. 2020, 52, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, K. The biplot graphic display of matrices with application to principal component analysis. Biometrika 1971, 58, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, J.; Greenacre, M. Biplots of compositional data. Appl. Stat. 2002, 51, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filzmoser, P.; Hron, K.; Reimann, C. Principal component analysis for compositional data with outliers. Environmetrics 2009, 20, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templ, M.; Hron, K.; Filzmoser, P. RobCompositions: An R-Package for Robust Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 341–355. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses; R Package Version 1.0.6. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/factoextra/readme/README.html (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Gozzi, C.; Dakos, V.; Buccianti, A.; Vaselli, O. Are geochemical regime shifts identifiable in river waters? Exploring the compositional dynamics of the Tiber River (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsten, P. Trend: Non-Parametric Trend Tests and Change-Point Detection; R Package Version 1.1.4. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=trend (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipel, K.W.; McLeod, A.I. Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 1012. [Google Scholar]
- Komsta, L. MBLM: Median-Based Linear Models; R Package Version 0.12.1. 2019. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/mblm/ (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Theil, H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis. Indag. Math. 1950, 12, 173. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.F. Robust regression using repeated medians. Biometrika 1982, 69, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. LOWESS: A program for smoothing scatterplots by robust locally weighted regression. Am. Stat. 1981, 35, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astivia, O.L.O.; Zumbo, B.D. Heteroskedasticity in Multiple Regression Analysis: What it is, How to Detect it and How to Solve it with Applications in R and SPSS. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2019, 24, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Breusch, T.S.; Pagan, A.R. A Simple Test for Heteroscedasticity and Random Coefficient Variation. Econometrica 1979, 47, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeileis, A.; Hothorn, T. Diagnostic Checking in Regression Relationships. R News 2002, 2, 7–10. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/doc/Rnews/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Martín-Fernández, J.A.; Barceló-Vidal, C.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V. Dealing with zeros and missing values in compositional data sets using nonparametric imputation. Math. Geol. 2003, 35, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palarea-Albaladejo, J.; Martín-Fernández, J.A. Values below detection limit in compositional chemical data. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 764, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langelier, W.F.; Ludwig, H.F. Graphical method for indicating the mineral character of natural waters. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1942, 34, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daunis-I-Estadella, J.; Barceló-Vidal, C.; Buccianti, A. Exploratory compositional data analysis. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2006, 264, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupré, B.; Louvat, P.; Allègre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liu, C.Q. Water geochemistry controlled by carbonate dissolution: A study of the river waters draining karst-dominated terrain, Guizhou Province, China. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M. Geochemistry characterization of groundwater in an agricultural area of Razan, Hamadan, Iran. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busico, G.; Kazakis, N.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Voudouris, K.; Tedesco, D. A modified SINTACS method for groundwater vulnerability and pollution risk assessment in highly anthropized regions based on NO3− and SO42− concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Mahlknecht, J. Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Pei, Q. Hydrochemistry, quality and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater in the Nanchong area, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Gaillardet, J.; Allegre, C.J. Geochemistry of dissolved and suspended loads of the Seine river, France: Anthropogenic impact, carbonate and silicate weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetelat, B.; Liu, C.-Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.L. Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin rivers: Anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4254–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, R.J.; Brunett, J.O. Overview of the occurrence of nitrate in groundwater of the United States. In National Water Summary 1984—Hydrologic Events, Selected Water-Quality Trends, and Ground-Water Resources; Water-Supply Paper; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1985; Volume 2275, pp. 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Widory, D.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Negrel, P.; Ladouche, B. Tracking the sources of nitrate in groundwater using coupled nitrogen and boron isotopes: A synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrinc, N.; Tamse, S.; Zavadlav, S.; Vrzel, J.; Jin, L. Evaluation of geochemical processes and nitrate pollution sources at the Ljubljansko polje aquifer (Slovenia): A stable isotope perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1588–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespasiano, G.; Cianflone, G.; Cannata, C.B.; Apollaro, C.; Dominici, R.; De Rosa, R. Analysis of groundwater pollution in the Sant’Eufemia plain (Calabria—South Italy). Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2016, 2, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Frondini, F. Geochemistry of regional aquifer systems hosted by carbonate-evaporite formations in Umbria and southern Tuscany (central Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2091–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccioni, B.; Didero, M.; Paletta, C.; Salvadori, P. Hydrogeochemistry of groundwaters from carbonate formations with basal gypsiferous layers: An example from the Mt Catria-Mt Nerone ridge (Northern Apennines, Italy). J. Hydrol. 2001, 253, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menció, A.; Mas-Pla, J.; Otero, N.; Regàs, O.; Boy-Roura, M.; Puig, R.; Bach, J.; Domènech, C.; Zamorano, M.; Brusi, D.; et al. Nitrate pollution of groundwater; all right…, but nothing else? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, C.; Aiuppa, A.; Favara, R.; Gurrieri, S.; Valenza, M. Geochemical monitoring of groundwaters (1998–2001) at Vesuvius volcano (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 133, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuoco, E.; Darrah, T.H.; Buono, G.; Verrengia, G.; De Francesco, S.; Eymold, W.K.; Tedesco, D. Inorganic contaminants from diffuse pollution in shallow groundwater of the Campanian Plain (Southern Italy). Implications for geochemical survey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, F.; Busico, G.; Cuoco, E.; Darrah, T.H.; Tedesco, D. Evaluating the suitability of urban groundwater resources for drinking water and irrigation purposes: An integrated approach in the Agro-Aversano area of Southern Italy. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Q.; Li, S.L.; Lang, Y.C.; Xiao, H.Y. Using δ15N- and δ18O-Values to Identify Nitrate Sources in Karst Ground Water, Guiyang, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6928–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wu, J. Tracing the nitrate sources of the Yili River in the Taihu Lake watershed: A dual isotope approach. Water 2015, 7, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yan, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Yang, F. Quantitative identification of nitrate sources in a coastal peri-urban watershed using hydrogeochemical indicators and dual isotopes together with the statistical approaches. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awaleh, M.O.; Boschetti, T.; Adaneh, A.E.; Chirdon, M.A.; Ahmed, M.M.; Dabar, O.A.; Soubaneh, Y.D.; Egueh, N.M.; Kawalieh, A.D.; Kadieh, I.H.; et al. Origin of nitrate and sulfate sources in volcano-sedimentary aquifers of the East Africa Rift System: An example of the Ali-Sabieh groundwater (Republic of Djibouti). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Cheng, H.; Pu, X.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Q. Nitrate behaviors and source apportionment in an aquatic system from a watershed with intensive agricultural activities. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2015, 17, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Ding, H. Tracing nitrate sources with dual isotopes and long term monitoring of nitrogen species in the Yellow River, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibrilla, A.; Fianko, J.R.; Ganyaglo, S.; Adomako, D.; Anornu, G.; Zakaria, N. Nitrate contamination and source apportionment in surface and groundwater in Ghana using dual isotopes (15N and 18O-NO3) and a Bayesian isotope mixing model. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2020, 233, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzi, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Buccianti, A.; Vaselli, O.; Nisi, B. Statistical methods for the geochemical characterisation of surface waters: The case study of the Tiber River basin (Central Italy). Comput. Geosci. 2019, 131, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



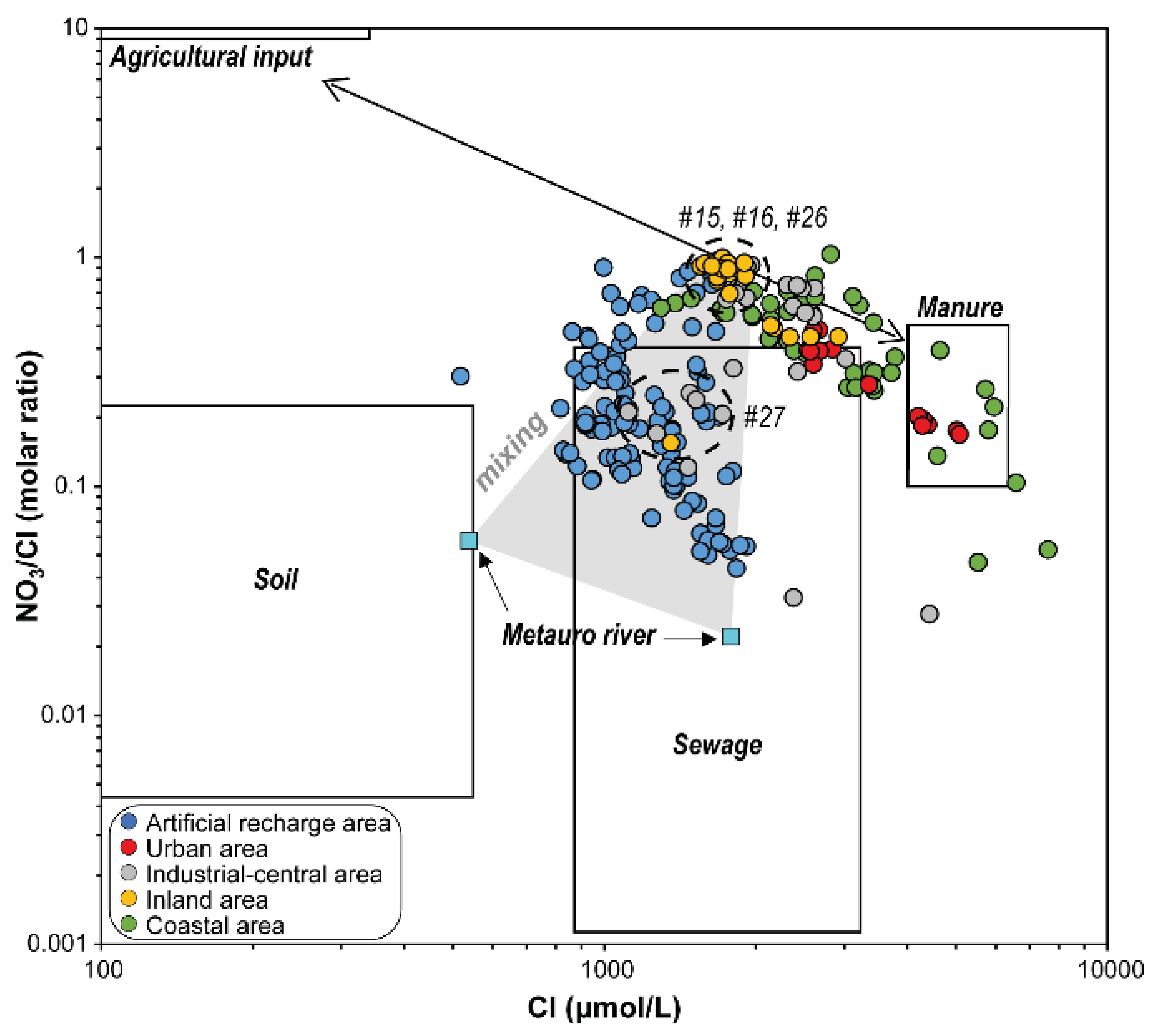
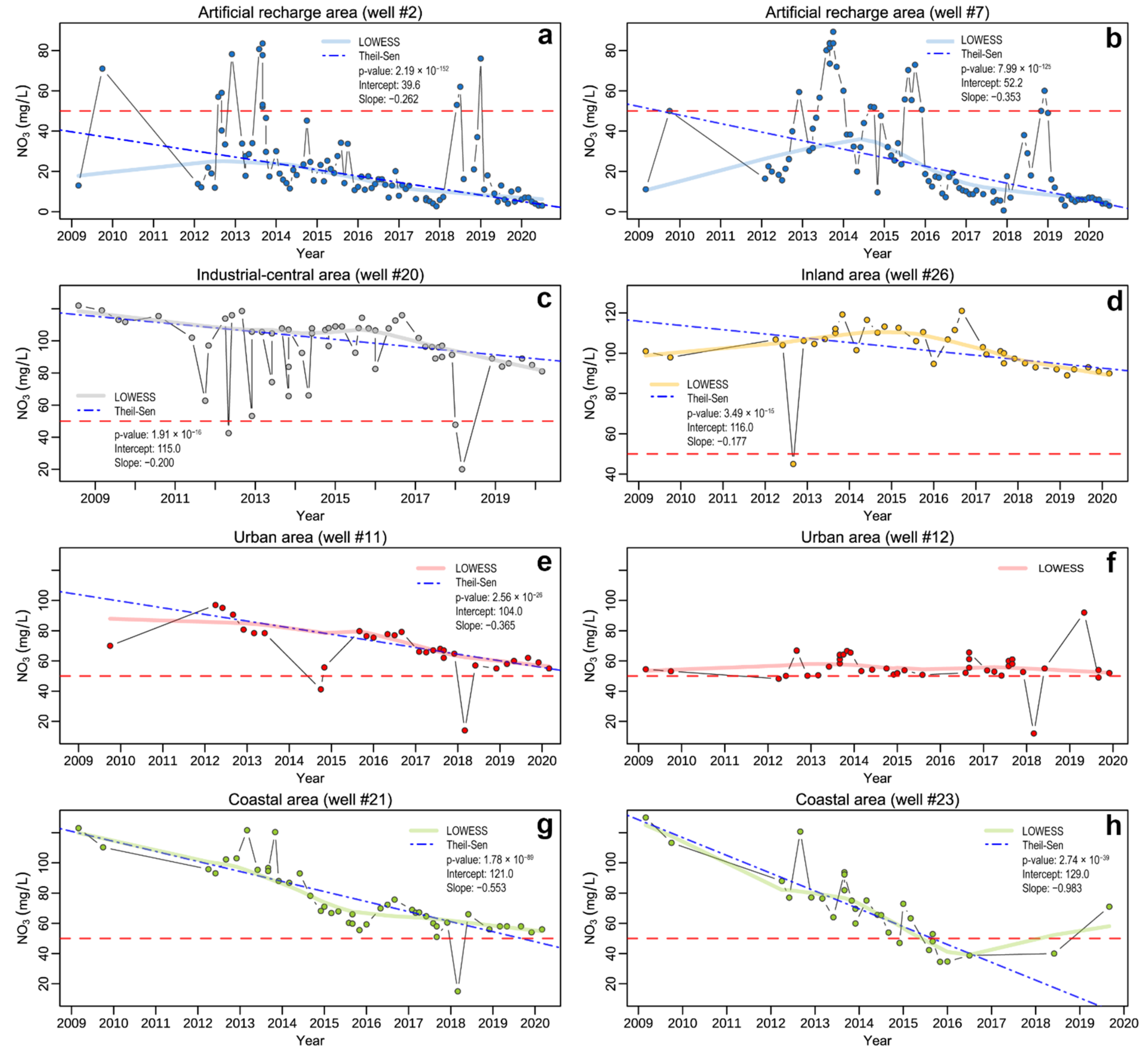
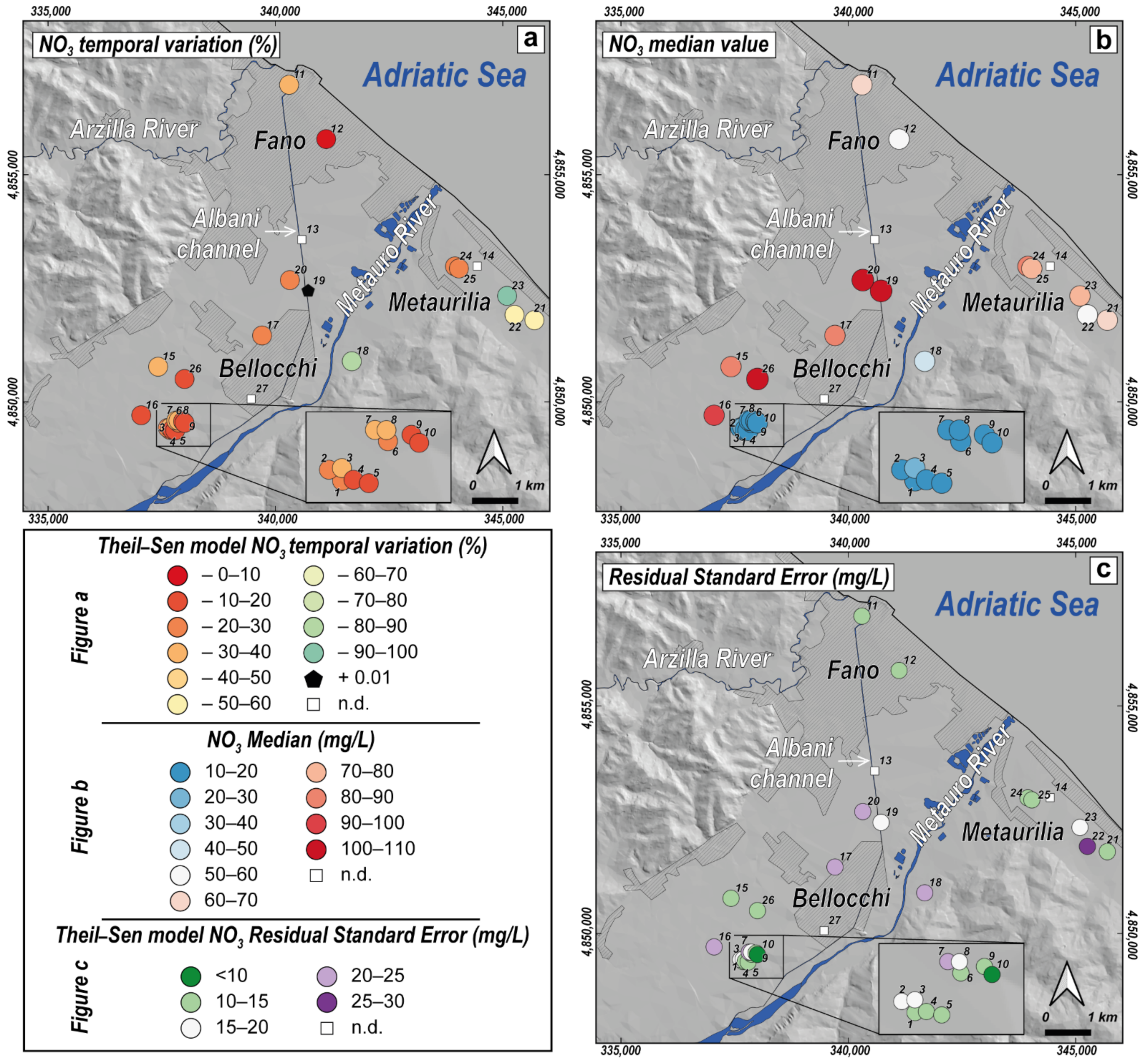
| Artificial Recharge Area (ARA) Wells | ||||||
| Parameter | N. obs. | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD |
| HCO3 | 118 | 123 | 388 | 272 | 273 | 39.9 |
| Cl | 158 | 18.4 | 68.0 | 43.1 | 40.3 | 10.5 |
| NO3 | 926 | 0.60 | 89.3 | 22.0 | 16.1 | 17.7 |
| NO2 | 12 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| SO4 | 158 | 65.6 | 137 | 82.9 | 81.0 | 11.0 |
| Na | 158 | 24.8 | 52.0 | 33.7 | 32.9 | 5.08 |
| NH4 | 2 | 0.40 | 19.0 | 9.70 | 9.70 | 13.2 |
| K | 148 | 1.90 | 4.00 | 2.82 | 2.80 | 0.37 |
| Mg | 158 | 14.2 | 24.0 | 18.0 | 17.8 | 1.84 |
| Ca | 158 | 60.0 | 143 | 94.0 | 91.4 | 11.9 |
| SiO2 | 18 | 5.00 | 15.0 | 10.4 | 11.0 | 2.55 |
| pH | 158 | 7.00 | 8.21 | 7.54 | 7.53 | 0.27 |
| TDS | 118 | 410 | 848 | 564 | 555 | 63.2 |
| EC | 158 | 517 | 907 | 657 | 649 | 62.1 |
| Alluvial Plain (AP) Wells | ||||||
| Parameter | N. obs. | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD |
| HCO3 | 121 | 162 | 573 | 410 | 416 | 55.8 |
| Cl | 222 | 39.5 | 366 | 98.0 | 84.4 | 49.8 |
| NO3 | 544 | 4.82 | 180 | 76.7 | 80.4 | 25.8 |
| NO2 | 26 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.08 |
| SO4 | 222 | 52.0 | 197 | 113 | 109 | 30.2 |
| Na | 205 | 24.5 | 313 | 70.7 | 61.0 | 40.8 |
| NH4 | 64 | 0.01 | 2.00 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.54 |
| K | 202 | 1.70 | 15.0 | 4.76 | 3.50 | 2.97 |
| Mg | 204 | 12.5 | 44.7 | 31.5 | 31.9 | 7.27 |
| Ca | 190 | 58.9 | 178 | 138 | 142 | 20.7 |
| SiO2 | 31 | 9.00 | 19.0 | 14.2 | 15.0 | 2.99 |
| pH | 205 | 6.70 | 8.14 | 7.24 | 7.19 | 0.22 |
| TDS | 120 | 511 | 1374 | 926 | 936 | 135 |
| EC | 211 | 603 | 2020 | 1095 | 1067 | 197 |
| Artificial Recharge Area (ARA) Wells | |||||||||||
| Parameter | N. obs. | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | MAD | Skew | Kurtosis | 25% (Q1) | 75% (Q3) |
| HCO3 | 118 | 123 | 388 | 272 | 273 | 39.9 | 16.5 | −0.94 | 2.83 | 265 | 290 |
| Cl | 118 | 18.4 | 68.0 | 44.7 | 41.8 | 10.7 | 10.6 | 0.34 | −0.82 | 36.5 | 53.8 |
| NO3 | 116 | 5.00 | 84.0 | 18.8 | 13.0 | 16.4 | 8.08 | 2.14 | 4.45 | 8.68 | 21.0 |
| SO4 | 118 | 66.7 | 137 | 82.9 | 80.7 | 10.9 | 7.93 | 1.99 | 6.59 | 76.0 | 87.0 |
| Na | 118 | 24.8 | 52.0 | 33.6 | 32.5 | 5.53 | 3.78 | 1.50 | 2.42 | 30.0 | 35.3 |
| K | 118 | 1.90 | 4.00 | 2.86 | 2.90 | 0.39 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.48 | 2.60 | 3.08 |
| Mg | 118 | 14.2 | 24.0 | 17.7 | 17.3 | 1.85 | 1.11 | 1.01 | 1.56 | 16.7 | 18.4 |
| Ca | 118 | 60.0 | 143 | 92.7 | 90.0 | 12.4 | 7.41 | 1.35 | 3.4 | 86.3 | 96.5 |
| pH | 118 | 7.00 | 8.21 | 7.62 | 7.60 | 0.26 | 0.24 | −0.15 | −0.06 | 7.47 | 7.82 |
| TDS | 118 | 410 | 848 | 565 | 555 | 63.5 | 36.8 | 1.70 | 5.26 | 533 | 580 |
| EC | 118 | 517 | 907 | 654 | 647 | 64.5 | 40.0 | 1.37 | 3.28 | 620 | 670 |
| Alluvial Plain (AP) Wells | |||||||||||
| Parameter | N. obs. | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | MAD | Skew | Kurtosis | 25% (Q1) | 75% (Q3) |
| HCO3 | 117 | 217 | 573 | 411 | 416 | 49.7 | 28.4 | −0.76 | 3.96 | 386 | 432 |
| Cl | 117 | 39.5 | 270 | 91.9 | 82.0 | 43.0 | 31.1 | 1.70 | 2.92 | 62.0 | 107 |
| NO3 | 117 | 4.82 | 180 | 74.5 | 76.2 | 29.6 | 27.0 | −0.03 | 0.68 | 58.0 | 94.0 |
| SO4 | 117 | 54.5 | 192 | 108 | 107 | 25.8 | 17.6 | 0.84 | 1.31 | 95.0 | 118 |
| Na | 117 | 24.5 | 228 | 69.0 | 60.3 | 34.8 | 21.3 | 2.26 | 6.07 | 46.8 | 76.2 |
| K | 117 | 1.80 | 15.0 | 4.79 | 3.60 | 2.90 | 1.04 | 1.41 | 0.79 | 3.05 | 4.39 |
| Mg | 117 | 14.0 | 44.7 | 31.8 | 31.8 | 7.05 | 6.52 | −0.30 | −0.34 | 27.9 | 36.3 |
| Ca | 117 | 84.0 | 178 | 141 | 144 | 20.0 | 21.5 | −0.66 | 0.15 | 127 | 155 |
| pH | 117 | 7.00 | 8.03 | 7.33 | 7.30 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 1.04 | 1.38 | 7.18 | 7.42 |
| TDS | 117 | 511 | 1374 | 932 | 937 | 136 | 85.6 | 0.21 | 2.54 | 859 | 990 |
| EC | 117 | 603 | 1704 | 1086 | 1062 | 181 | 132 | 0.72 | 2.08 | 979 | 1158 |
| ID | N. Obs. | SlopeSieg | InterceptSieg | p-ValueSieg | RSESieg | SlopeTheil−Sen | InterceptTheil−Sen | p-ValueTheil−Sen | RSETheil−Sen | p-ValueMK | p-ValueBP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARA wells | |||||||||||
| 1 | 92 | −0.29 | 43.7 | 9.3 × 10−12 | 14.7 | −0.27 | 42.3 | 1.7 × 10−121 | 14.5 | 2.2 × 10−10 | 0.541 |
| 2 | 93 | −027 | 38.2 | 7.4 × 10−13 | 19.2 | −0.26 | 39.6 | 2.2 × 10−152 | 18.6 | 6.9 × 10−12 | 0.103 |
| 3 | 94 | −0.34 | 47.3 | 8.9 × 10−13 | 19.1 | −0.32 | 47.9 | 3.5 × 10−129 | 18.3 | 1.3 × 10−10 | 0.479 |
| 4 | 93 | −0.13 | 24.9 | 1.1 × 10−9 | 13.4 | −0.12 | 24.3 | 5.7 × 10−65 | 13.3 | 5.5 × 10−6 | 0.151 |
| 5 | 93 | −0.10 | 24.0 | 7.6 × 10−10 | 13.2 | −0.12 | 24.9 | 4.7 × 10−83 | 13.2 | 6.3 × 10−7 | 0.580 |
| 6 | 92 | −0.24 | 34.1 | 6.9 × 10−15 | 14.6 | −0.22 | 34 | 5.2 × 10−133 | 14.1 | 1.9 × 10−11 | 1.5 × 10−4 |
| 7 | 93 | −0.41 | 55.3 | 3.0 × 10−15 | 22.6 | −0.35 | 52.2 | 8.0 × 10−125 | 21.8 | 3.4 × 10−11 | 3.2 × 10−4 |
| 8 | 93 | −0.44 | 56.9 | 3.1 × 10−15 | 20.9 | −0.35 | 52.9 | 5.7 × 10−118 | 19.4 | 1.7 × 10−10 | 2.5 × 10−6 |
| 9 | 92 | −0.19 | 28.9 | 2.5 × 10−14 | 13.6 | −0.15 | 26.2 | 5.0 × 10−98 | 13.5 | 3.7 × 10−9 | 2.0 × 10−5 |
| 10 | 93 | −0.16 | 27.5 | 5.3 × 10−14 | 9.19 | −0.13 | 24.3 | 2.9 × 10−122 | 9.21 | 5.9 × 10−9 | 0.298 |
| AP wells—urban area | |||||||||||
| 11 | 30 | −0.39 | 109 | 2.1 × 10−7 | 15.5 | −0.37 | 104 | 2.6 × 10−26 | 14.5 | 8.1 × 10−6 | 0.699 |
| 12 | 41 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6.5 × 10−1 | 0.107 |
| AP wells—industrial-central area | |||||||||||
| 13 | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 17 | 17 | −0.39 | 129 | 4.6 × 10−5 | 30.6 | −0.23 | 106 | 3.8 × 10−7 | 21.9 | 9.5 × 10−3 | 0.483 |
| 18 | 26 | −0.97 | 99.6 | 8.8 × 10−6 | 22.3 | −0.83 | 93.6 | 2.2 × 10−20 | 20.4 | 5.9 × 10−4 | 2.4 × 10−2 |
| 19 | 38 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.3 × 10−1 | 0.284 |
| 20 | 55 | −0.18 | 116 | 6.6 × 10−4 | 21.5 | −0.20 | 115 | 1.9 × 10−16 | 21.0 | 1.2 × 10−3 | 0.888 |
| 27 | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| AP wells—inland area | |||||||||||
| 15 | 36 | −0.41 | 115 | 4.1 × 10−7 | 12.2 | −0.36 | 111 | 2.0 × 10−16 | 11.4 | 5.7 × 10−6 | 1.9 × 10−2 |
| 16 | 34 | −0.18 | 110 | 7.5 × 10−6 | 21.5 | −0.19 | 111 | 2.0 × 10−22 | 21.5 | 1.1 × 10−5 | 0.763 |
| 26 | 35 | −0.25 | 126 | 2.1 × 10−5 | 14.7 | −0.18 | 116 | 3.5 × 10−15 | 13.3 | 1.3 × 10−3 | 0.244 |
| AP wells—coastal area | |||||||||||
| 14 | 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 21 | 44 | −0.62 | 120 | 7.9 × 10−9 | 13.4 | −0.55 | 121 | 1.8 × 10−89 | 12.5 | 4.4 × 10−12 | 0.712 |
| 22 | 46 | −0.36 | 85.8 | 2.4 × 10−5 | 27.9 | −0.52 | 106 | 2.3 × 10−27 | 27.3 | 7.7 × 10−4 | 4.5 × 10−4 |
| 23 | 30 | −1.02 | 132 | 3.7 × 10−9 | 18.1 | −0.98 | 129 | 2.7 × 10−39 | 18.0 | 1.6 × 10−7 | 3.1 × 10−2 |
| 24 | 44 | −0.36 | 106 | 7.2 × 10−8 | 14.0 | −0.27 | 101 | 2.5 × 10−27 | 14.5 | 5.8 × 10−4 | 0.219 |
| 25 | 43 | −0.33 | 106 | 5.4 × 10−10 | 14.5 | −0.27 | 101 | 5.4 × 10−27 | 14.4 | 5.9 × 10−4 | 0.086 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taussi, M.; Gozzi, C.; Vaselli, O.; Cabassi, J.; Menichini, M.; Doveri, M.; Romei, M.; Ferretti, A.; Gambioli, A.; Nisi, B. Contamination Assessment and Temporal Evolution of Nitrates in the Shallow Aquifer of the Metauro River Plain (Adriatic Sea, Italy) after Remediation Actions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912231
Taussi M, Gozzi C, Vaselli O, Cabassi J, Menichini M, Doveri M, Romei M, Ferretti A, Gambioli A, Nisi B. Contamination Assessment and Temporal Evolution of Nitrates in the Shallow Aquifer of the Metauro River Plain (Adriatic Sea, Italy) after Remediation Actions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912231
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaussi, Marco, Caterina Gozzi, Orlando Vaselli, Jacopo Cabassi, Matia Menichini, Marco Doveri, Marco Romei, Alfredo Ferretti, Alma Gambioli, and Barbara Nisi. 2022. "Contamination Assessment and Temporal Evolution of Nitrates in the Shallow Aquifer of the Metauro River Plain (Adriatic Sea, Italy) after Remediation Actions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912231
APA StyleTaussi, M., Gozzi, C., Vaselli, O., Cabassi, J., Menichini, M., Doveri, M., Romei, M., Ferretti, A., Gambioli, A., & Nisi, B. (2022). Contamination Assessment and Temporal Evolution of Nitrates in the Shallow Aquifer of the Metauro River Plain (Adriatic Sea, Italy) after Remediation Actions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912231










