Water Quality Assessment Bias Associated with Long-Screened Wells Screened across Aquifers with High Nitrate and Arsenic Concentrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
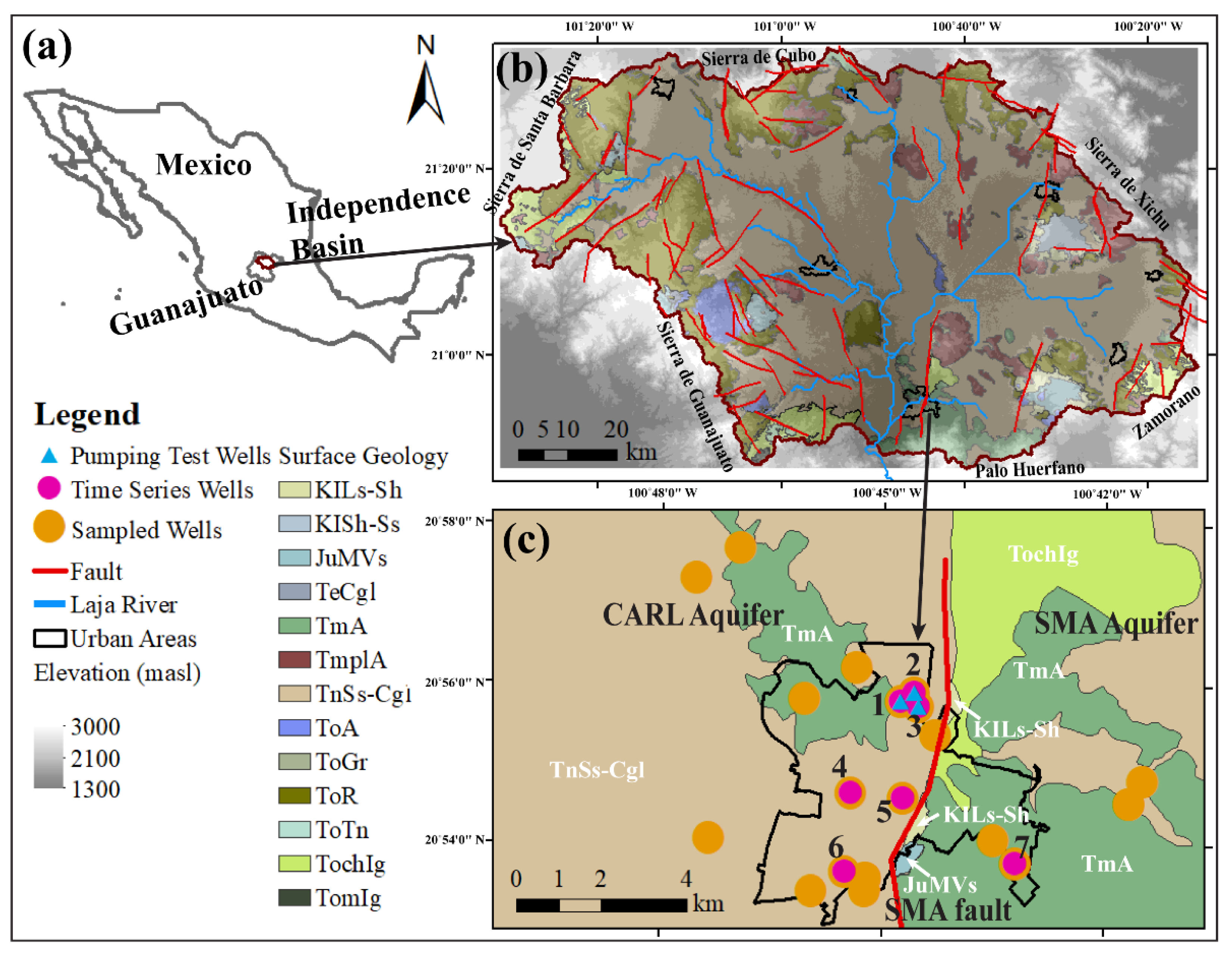
2.1. Study Area
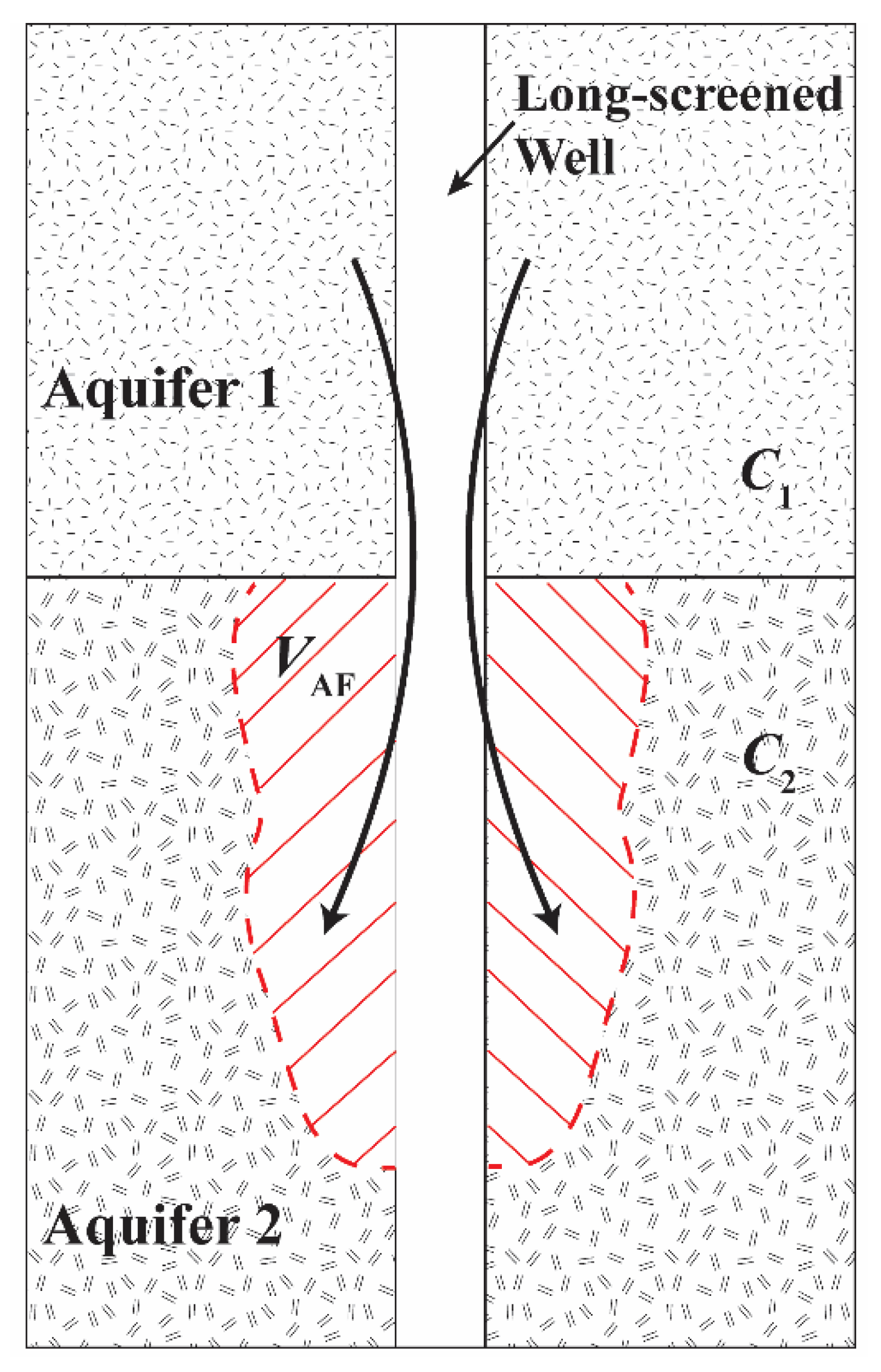
2.2. Conceptual Model
2.3. Sampling of Production Wells
2.4. Pumping Test
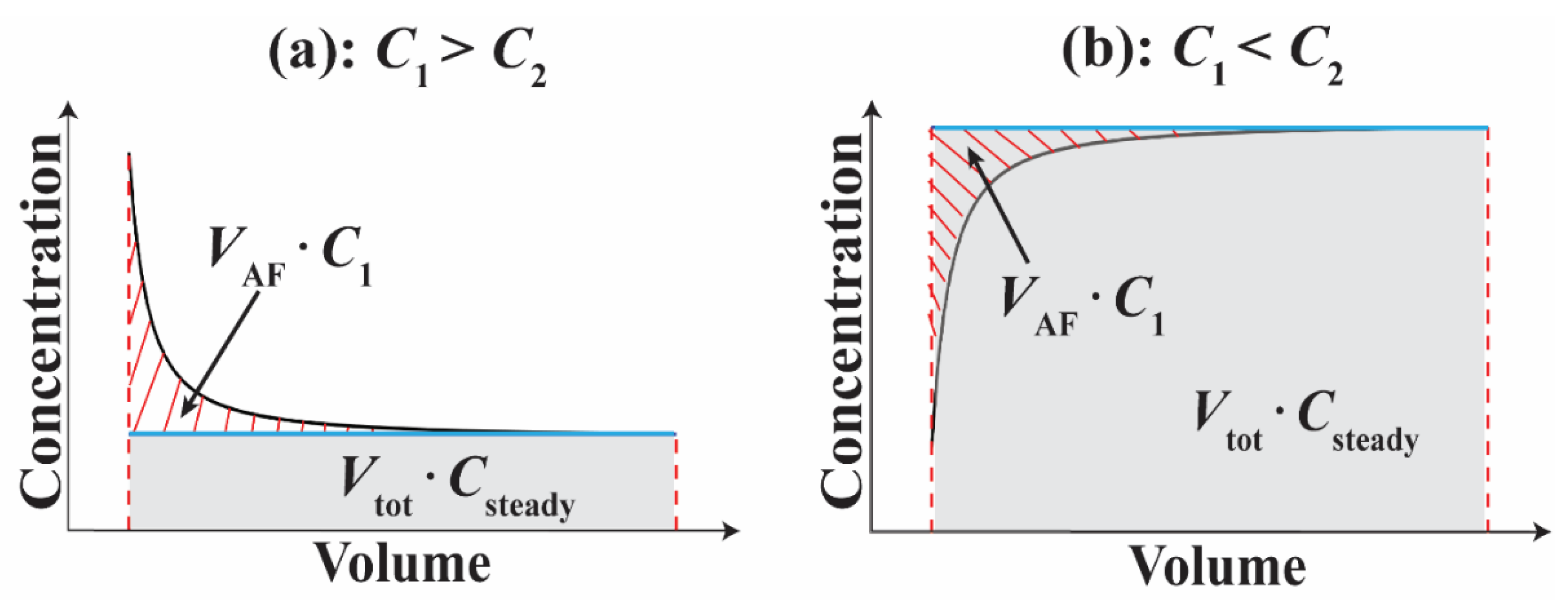
2.5. End-Member Mixing Model
2.6. Calculating Ambient Flow
3. Results
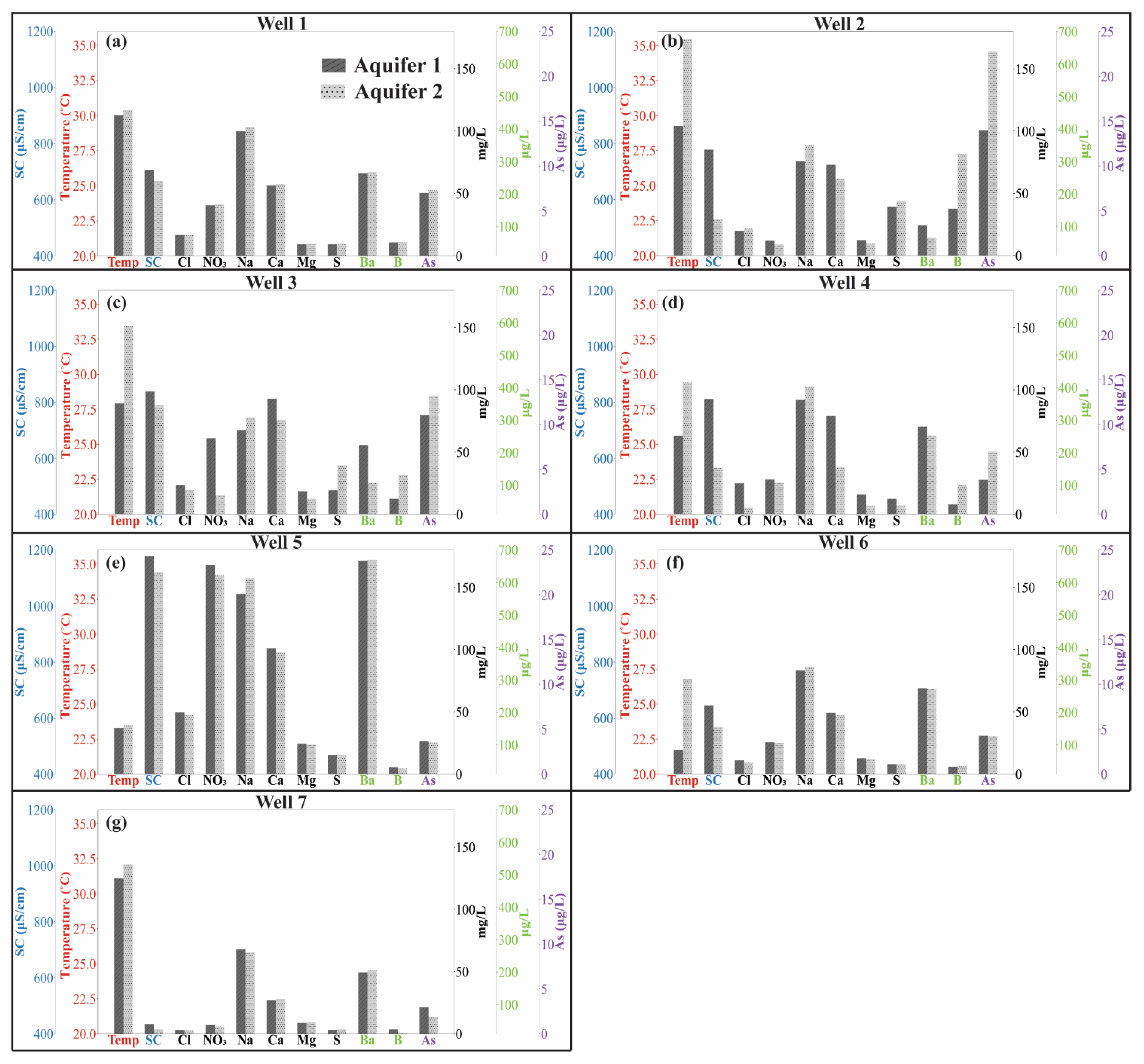
3.1. Temporal Variation in Produced Water Chemistry
3.2. Calculating End-Member Chemistries of Aquifers 1 and 2
3.3. Calculating Ambient Flow Rate
4. Discussion
4.1. Estimating Ambient Flow Rate
4.2. Implications for Best Practices for Sampling Long-Screened Wells
4.3. Health Concerns with Falling Water Tables in Aquifers with Anthropogenic and Geogenic Contaminants
4.4. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharp, J.M. The impacts of urbanization on groundwater systems and recharge. Aqua Mundi 2010, 1, S51–S56. [Google Scholar]
- Del Campo, M.M.; Esteller, M.; Expósito, J.; Hirata, R. Impacts of urbanization on groundwater hydrodynamics and hydrochemistry of the toluca valley aquifer (Mexico). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2979–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Castillo, E.; Marín-Celestino, A.E.; Otazo-Sánchez, E.M.; Gordillo-Martínez, A.J.; González-Ramírez, C.A.; Cabrera-Cruz, R.B. Modeling the groundwater response to megacity expansion demand and climate change. Case study: The Cuautitlán–Pachuca aquifer, in the Northeast of Mexico City. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.J.; Onodera, S.-I.; Shimizu, Y. An overview of the effects of urbanization on the quantity and quality of groundwater in south asian megacities. Limnology 2013, 14, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Koneshloo, M.; Knappett, P.S.; Ahmed, K.M.; Bostick, B.C.; Mailloux, B.J.; Mozumder, R.H.; Zahid, A.; Harvey, C.F.; Van Geen, A.; et al. Megacity pumping and preferential flow threaten groundwater quality. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, T.; Mohammad, A.H.; Hussein, H.; Ismail, M.; Almomani, T. Over-pumping of groundwater in irbid governorate, Northern Jordan: A conceptual model to analyze the effects of urbanization and agricultural activities on groundwater levels and salinity. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjderem, B.; Torres-Martínez, J.; Mahlknecht, J. Intensive long-term pumping in the Principal-Lagunera Region aquifer (Mexico) causing heavy impact on groundwater quality. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendarto, H.; Standing, J. Influence of Groundwater Extraction on Land Subsidence in Jakarta. In Proceedings of the XVII European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, ECSMGE 2019, Reykjavik, Iceland, 1–7 September 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, H.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Brinkman, J. Study on the risk and impacts of land subsidence in Jakarta. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 372, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Pohan, Y.E.; Deguchi, T. Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1753–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knappett, P.S.; Li, Y.; Loza, I.; Hernandez, H.; Avilés, M.; Haaf, D.; Majumder, S.; Huang, Y.; Lynch, B.; Piña, V. Rising arsenic concentrations from dewatering a geothermally influenced aquifer in central Mexico. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knappett, P.S.; Farias, P.; Gretchen, M.R.; Hoogesteger, J.; Li, Y.; Mendoza, I.; Woodward, R.T.; Hernandez, H.; Loza, I.; Datta, S.; et al. A systems approach to remediating human exposure to arsenic and fluoride from over-exploited aquifers. GeoHealth 2022, 6, e2022GH000592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.T.; Khosravi, K.; Karimi, M.; Busico, G.; Khozani, Z.S.; Nguyen, H.; Mastrocicco, M.; Tedesco, D.; Cuoco, E.; Kazakis, N. Enhancing nitrate and strontium concentration prediction in groundwater by using new data mining algorithm. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busico, G.; Cuoco, E.; Kazakis, N.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Tedesco, D.; Voudouris, K. Multivariate statistical analysis to characterize/discriminate between anthropogenic and geogenic trace elements occurrence in the Campania Plain, Southern Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafayette, G.N.; Knappett, P.S.; Li, Y.; Loza-Aguirre, I.; Polizzotto, M.L. Geogenic sources and chemical controls on fluoride release to groundwater in the Independence Basin, Mexico. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 123, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlknecht, J.; Medina-Mejía, M.G.; Gárfias-Solis, J.; Cano-Aguilera, I. Intrinsic aquifer vulnerability assessment: Validation by environmental tracers in San Miguel de Allende, Mexico. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, F.T. Arsenic and Fluoride Contamination in the Independence Basin Aquifer System of Guanajuato, Mexico. Master’s Thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; De Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; Van Breda, S.G. Drinking water nitrate and human health: An updated review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argos, M.; Kalra, T.; Rathouz, P.J.; Chen, Y.; Pierce, B.; Parvez, F.; Islam, T.; Ahmed, A.; Rakibuz-Zaman, M.; Hasan, R.; et al. Arsenic exposure from drinking water, and all-cause and chronic-disease mortalities in bangladesh (heals): A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2010, 376, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, A.P.; Minatel, B.C.; Ng, K.W.; Stewart, G.L.; Dummer, T.J.; Lam, W.L.; Martinez, V.D. Oncogenomic disruptions in arsenic-induced carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadani, J.D.; Tofail, F.; Nermell, B.; Gardner, R.; Shiraji, S.; Bottai, M.; Arifeen, S.; Huda, S.N.; Vahter, M. Critical windows of exposure for arsenic-associated impairment of cognitive function in pre-school girls and boys: A population-based cohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahar, M.; Inaoka, T.; Fujimura, M. A consecutive study on arsenic exposure and intelligence quotient (iq) of children in bangladesh. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahter, M.; Skröder, H.; Rahman, S.M.; Levi, M.; Hamadani, J.D.; Kippler, M. Prenatal and childhood arsenic exposure through drinking water and food and cognitive abilities at 10 years of age: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; Loiacono, N.J.; Cheng, Z.; Hussain, I.; et al. Water arsenic exposure and children’s intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Kline, J.; Siddique, A.B.; Shahriar, H.; Uddin, M.N.; Van Geen, A.; Mey, J.L. Child intelligence and reductions in water arsenic and manganese: A two-year follow-up study in Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Grosse, S.D.; Matte, T.D.; Schwartz, J.; Jackson, R.J. Economic gains resulting from the reduction in children’s exposure to lead in the United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elci, A.; Molz Iii, F.J.; Waldrop, W.R. Implications of observed and simulated ambient flow in monitoring wells. Groundwater 2001, 39, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, D.L.; Cook, P.G.; Simmons, C.T.; Solomon, D.K.; Dogramaci, S. Depth-resolved groundwater chemistry by longitudinal sampling of ambient and pumped flows within long-screened and open borehole wells. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9417–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeul, V.R.; Mckinley, J.P.; Newcomer, D.R.; Mackley, R.D.; Zachara, J.M. River-induced flow dynamics in long-screen wells and impact on aqueous samples. Groundwater 2011, 49, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, P.M.; Mccray, J.E.; Martens, J.L. Investigating cross-contamination of aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elçi, A.; Flach, G.P.; Molz, F.J. Detrimental effects of natural vertical head gradients on chemical and water level measurements in observation wells: Identification and control. J. Hydrol. 2003, 281, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmillan, L.A.; Rivett, M.O.; Tellam, J.H.; Dumble, P.; Sharp, H. Influence of vertical flows in wells on groundwater sampling. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 169, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, A.; Cassiraga, E.; Sahuquillo, A. Influence of hydraulic conductivity and wellbore design in the fate and transport of nitrate in multi-aquifer systems. Math. Geosci. 2012, 44, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, A.L. Ambient well-bore mixing, aquifer cross-contamination, pumping stress, and water quality from long-screened wells: What is sampled and what is not? Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, J.A.; Teague, N.F.; Hatzinger, P.B.; Böhlke, J.K.; Sturchio, N.C. Groundwater movement, recharge, and perchlorate occurrence in a faulted alluvial aquifer in California (USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, D.L.; Cook, P.G.; Simmons, C.T.; Mccallum, J.L.; Dogramaci, S. Effects of intraborehole flow on purging and sampling long-screened or open wells. Groundwater 2019, 57, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldrath, D.; Izbicki, J.; Thorbjarnarson, K. Simulating arsenic mitigation strategies in a production well. J. Geol. Geophys. 2015, 4, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, T.E.; Leblanc, D.R. Experimental evaluation of factors affecting temporal variability of water samples obtained from long-screened wells. Groundwater 1998, 36, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devic, G.; Djordjevic, D.; Sakan, S. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in Serbia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; An, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, C. Spatial and temporal patterns of groundwater arsenic in shallow and deep groundwater of Yinchuan Plain, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-L.; Peng, W.-H.; Gui, H.-R. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of deep groundwater from the coal-bearing aquifer of the Linhuan coal-mining district, Northern Anhui province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Wei, A.; Deng, Q.; Zhao, H. Hydrochemical characteristics and the suitability of groundwater in the coastal region of Tangshan, China. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 25, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narany, T.S.; Aris, A.Z.; Sefie, A.; Keesstra, S. Detecting and predicting the impact of land use changes on groundwater quality, a case study in northern Kelantan, Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, T.; Abbasi Maedeh, P. Groundwater quality assessment in southern parts of Tehran Plain, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Niu, X.; Liu, J. Distributions of arsenic and other heavy metals, and health risk assessments for groundwater in the Guanzhong Plain region of China. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutharsiny, A.; Pathmarajah, S.; Thushyanthy, M.; Meththika, M. Characterization of irrigation water quality of Chunnakam aquifer in Jaffna Peninsula. Trop. Agric. Res. 2012, 23, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.K.; Gosk, E.; Burston, M.W.; Lerner, D.N. Level-determined groundwater sampling from open boreholes. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1992, 25, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte, P.T. Hydraulically controlled discrete sampling from open boreholes. Groundwater 2013, 51, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.; Williams, A.; BGS. A pumped double-packer system for use in aquifer evaluation and groundwater sampling. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Water Marit. Energy 1993, 101, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, G.J.; Koeniger, P.; Schloemer, S.; Gröger-Trampe, J.; Sültenfuß, J. Comparison of depth-specific groundwater sampling methods and their influence on hydrochemistry, isotopy and dissolved gases—Experiences from the Fuhrberger Feld, Germany. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, S.R.; Acree, S.D. Ground water sampling bias observed in shallow, conventional wells. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2000, 20, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Guerrero, M.A. Occurrence, distribution, hydrochemistry and origin of arsenic, fluoride and other trace elements dissolved in groundwater at basin scale in Central Mexico. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2009, 26, 143–161. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hernandez, J.H.; Aviles, M.; Knappett, P.S.; Giardino, J.R.; Miranda, R.; Puy, M.J.; Padilla, F.; Morales, J. Empirical Bayesian Kriging method to evaluate inter-annual water-table evolution in the Cuenca Alta del Río Laja aquifer, Guanajuato, México. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, R.P. Diagnostic tools for mixing models of stream water chemistry. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaniz-Álvarez, S.A.; Nieto-Samaniego, Á.F. The Taxco–San Miguel de Allende Fault System and the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt: Two Tectonic Boundaries in Central México Active during the Cenozoic; Geological Society of America Special Paper 422; Geological Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, C.A. The water-energy-climate nexus: Resources and policy outlook for aquifers in Mexico. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W00L04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI 2020. National Institute of Statistics. Available online: https://en.www.inegi.org.mx/ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Knappett, P.S.; Li, Y.; Hernandez, H.; Rodriguez, R.; Aviles, M.; Deng, C.; Piña, V.; Giardino, J.R.; Mahlknecht, J.; Datta, S. Changing recharge pathways within an intensively pumped aquifer with high fluoride concentrations in Central Mexico. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlknecht, J.; Gárfias-Solis, J.; Aravena, R.; Tesch, R. Geochemical and isotopic investigations on groundwater residence time and flow in the Independence Basin, Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA. Actualización de la Disponibilidad Media Anual de Agua en El Acuífero San Miguel de Allende (1107) Estado de Guanajuato; Comision Nacional del Agua: Mexico City, Mexico, 2020.
- Alaniz-Álvarez, S.A.; Nieto-Samaniego, A.F.; Orozco-Esquivel, M.T.; Vassallo, L.F.; Xu, S. El sistema de fallas Taxco-San Miguel de Allende: Implicaciones en la deformación post-eocénica del centro de México. Bol. Soc. Geol. Mex. 2002, 55, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaniz-Álvarez, S.A.; Nieto-Samaniego, Á.F.; Reyes-Zaragoza, M.A.; Ojeda-Gracia, A.C.; Orozco-Esquivel, M.T.; Vassallo, Y.L.F. Estratigrafía y deformación extensional en la región San Miguel de Allende-Querétaro, México. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2001, 18, 129–148. [Google Scholar]
- Pilar-Martínez, A.D.; Nieto-Samaniego, Á.F.; Angeles-Moreno, E.; Suárez-Arias, A.M.; de Jesús Paulina Olmos-Moya, M.; Alaniz-Álvarez, S.A.; Levresse, G. Digital geological map and geochronological database of the Cenozoic cover of the southern Mesa Central province, Mexico. Terra Digit. 2021, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Río Varela, P.D.; Nieto-Samaniego, Á.F.; Alaniz-Álvarez, S.A.; Ángeles-Moreno, E.; Escalona-Alcázar, F.D.J.; Pilar-Martínez, A.D. Geology and structure of Guanajuato and Codornices ranges, Mesa Central, Mexico. Bol. Soc. Geol. Mex. 2020, 72, e071019. [Google Scholar]
- Consultores en Geologia, S.A.; De, C.V. Modelo Matematico de la Cuenca Alta del Rio de la Laja: Prepared for Comision Nacional del Agua; CONAGUA: Mexico City, Mexico, 1992.
- Ingenieros Civiles y Geologos Asociados. Estudio Geohydrologico en El Valle de San Jose Iturbide, Guanajuato; Ingenieros Civiles y Geologos Asociados: Mendoza, Argentina, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Burté, L.; Cravotta Iii, C.A.; Bethencourt, L.; Farasin, J.; Pédrot, M.; Dufresne, A.; Gerard, M.-F.; Baranger, C.; Le Borgne, T.; Aquilina, L. Kinetic study on clogging of a geothermal pumping well triggered by mixing-induced biogeochemical reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5848–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos Medina, D.A.; Van Den Berg, G.A.; Van Breukelen, B.M.; Juhasz-Holterman, M.; Stuyfzand, P.J. Iron-hydroxide clogging of public supply wells receiving artificial recharge: Near-well and in-well hydrological and hydrochemical observations. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 1393–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, C.; Hubeek, A.; De La Loma Gonzalez, B.; Stuyfzand, P. Chemical and mechanical clogging of groundwater abstraction wells at well field heel, the netherlands. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beek, K.; Breedveld, R.; Stuyfzand, P. Preventing two types of well clogging. J.-Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2009, 101, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.H.; Hess, A.E.; Paillet, F.L. Determining the distribution of hydraulic conductivity in a fractured limestone aquifer by simultaneous injection and geophysical logging. Groundwater 1988, 26, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zheng, C.; Tonkin, M.; Zachara, J.M. Importance of considering intraborehole flow in solute transport modeling under highly dynamic flow conditions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 123, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassington, F. Measurements of head variations within observation boreholes and their implications for groundwater monitoring. Water Environ. J. 1992, 6, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumble, P.; Fuller, M.; Beck, P.; Sojka, P. Assessing contaminant migration pathways and vertical gradients in a low-permeability aquifer using multilevel borehole systems. Land Contam. Reclam. 2006, 14, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, P.E.; Granato, G.E. Bias in ground-water data caused by well-bore flow in long-screen wells. Groundwater 1996, 34, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophersen, N.; Neal, C.; Hooper, R.P.; Vogt, R.D.; Andersen, S. Modelling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members—A step towards second-generation acidification models. J. Hydrol. 1990, 116, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, R.P.; Christophersen, N.; Peters, N.E. Modelling streamwater chemistry as a mixture of soilwater end-members—An application to the Panola mountain catchment, Georgia, USA. J. Hydrol. 1990, 116, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, J.A.; Christensen, A.H.; Newhouse, M.W.; Smith, G.A.; Hanson, R.T. Temporal changes in the vertical distribution of flow and chloride in deep wells. Groundwater 2005, 43, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, V.P.; Avilés, R.M.; Anguiano, J.H.H.; Knappett, P.S.; Martinez, J.L.M.; Alquiza, M.D.J.P.; Naves, A.; Bian, J.; Liu, J.; González, L.M.R.; et al. Influence of geological faults on dissolved arsenic concentrations in an overexploited aquifer with shallow geothermal heat. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.T.; López-Carrillo, L.; Gamboa-Loira, B.; Cebrián, M.E. Standards for arsenic in drinking water: Implications for policy in Mexico. J. Public Health Policy 2017, 38, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rango, T.; Vengosh, A.; Dwyer, G.; Bianchini, G. Mobilization of arsenic and other naturally occurring contaminants in groundwater of the main ethiopian rift aquifers. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5801–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Graziano, J.H.; Parvez, F.; Liu, M.; Slavkovich, V.; Kalra, T.; Argos, M.; Islam, T.; Ahmed, A.; Rakibuz-Zaman, M. Arsenic exposure from drinking water and mortality from cardiovascular disease in Bangladesh: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2011, 342, d2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Acien, A.; Sharrett, A.R.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Schwartz, B.S.; Nachman, K.E.; Burke, T.A.; Guallar, E. Arsenic exposure and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review of the epidemiologic evidence. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quansah, R.; Armah, F.A.; Essumang, D.K.; Luginaah, I.; Clarke, E.; Marfoh, K.; Cobbina, S.J.; Nketiah-Amponsah, E.; Namujju, P.B.; Obiri, S. Association of arsenic with adverse pregnancy outcomes/infant mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.H.; Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Bates, M.N.; Goeden, H.M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Duggan, H.M.; Wood, R.; Kosnett, M.J.; Smith, M.T. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO Chronicle; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zoughool, M.; Krewski, D. Health effects of radon: A review of the literature. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Ha, W.-H.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, D.; Park, S.; Kwon, T.-E.; Jin, Y.W. Health effects of exposure to radon: Implications of the radon bed mattress incident in Korea. Epidemiol. Health 2019, 41, e2019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayotte, J.D.; Szabo, Z.; Focazio, M.J.; Eberts, S.M. Effects of human-induced alteration of groundwater flow on concentrations of naturally-occurring trace elements at water-supply wells. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudron, P.; Alonso-Sarría, F.; García-Aróstegui, J.L.; Cánovas-García, F.; Martínez-Vicente, D.; Moreno-Brotóns, J. Identifying the origin of groundwater samples in a multi-layer aquifer system with random forest classification. J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collar, R.J.; Mock, P.A. Using water-supply wells to investigate vertical ground-water quality. Groundwater 1997, 35, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theis, C.V. The relation between the lowering of the piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using ground-water storage. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera-Hernández, J.; Carreón-Freyre, D.; Cerca-Martínez, M.; Levresse, G. Groundwater flow in a transboundary fault-dominated aquifer and the importance of regional modeling: The case of the city of querétaro, mexico. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, S.-Y.; Kim, M.; Cheong, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Son, M.; Kim, T.-W. Relationship between hydraulic conductivity and fracture properties estimated from packer tests and borehole data in a fractured granite. Eng. Geol. 2007, 92, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Rong, G.; Zhan, H.; He, R.; Sha, S.; Li, B. An innovative method to evaluate hydraulic conductivity of a single rock fracture based on geometric characteristics. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 4767–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, R.W.; Bodvarsson, G.S. Hydraulic conductivity of rock fractures. Transp. Porous Media 1996, 23, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, P.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Hossain, S.; Hosain, A.; Rhodes, K.; Ahmed, K.M.; Cardenas, M.B. The impact of the degree of aquifer confinement and anisotropy on tidal pulse propagation. Groundwater 2017, 55, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, S.P. Theory of flow in unconfined aquifers considering delayed response of the water table. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Well ID | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well Top Elevation (masl 1) | 1892 | 1904 | 1919 | 1879 | 1903 | 1939 | 2081 | ||
| Diameter of Well (cm) | 30 | 24 | 29 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 29 | ||
| Pumping Rate (L/s) | 35.0 | 22.5 | 27.0 | 29.3 | 23.0 | 20.0 | 16.1 | ||
| Perforated Interval (masl) | Top | 1820 | 1812 | na 2 | 1822 | 1808 | 1843 | 2007 | |
| Bottom | 1622 | 1607 | na | 1656 | 1653 | 1713 | 1836 | ||
| Observed Groundwater Level (masl) | Year | 2010 | 2014 | 2006 | 2011 | 2016 | 2014 | ||
| From downhole camera | 1815 | 1802 | na | 1803 | 1834 | 1846 | 1892 | ||
| Year | 2018 | ||||||||
| From SAPASMA | 1793 | 1789 | 1801 | 1774 | 1829 | 1845 | 1883 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Montiel, D.; Wang, J.; Aviles, M.; Hernandez, H.; Mendoza-Sanchez, I.; Loza-Aguirre, I. Water Quality Assessment Bias Associated with Long-Screened Wells Screened across Aquifers with High Nitrate and Arsenic Concentrations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169907
Huang Y, Li Y, Knappett PSK, Montiel D, Wang J, Aviles M, Hernandez H, Mendoza-Sanchez I, Loza-Aguirre I. Water Quality Assessment Bias Associated with Long-Screened Wells Screened across Aquifers with High Nitrate and Arsenic Concentrations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):9907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169907
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yibin, Yanmei Li, Peter S. K. Knappett, Daniel Montiel, Jianjun Wang, Manuel Aviles, Horacio Hernandez, Itza Mendoza-Sanchez, and Isidro Loza-Aguirre. 2022. "Water Quality Assessment Bias Associated with Long-Screened Wells Screened across Aquifers with High Nitrate and Arsenic Concentrations" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 9907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169907
APA StyleHuang, Y., Li, Y., Knappett, P. S. K., Montiel, D., Wang, J., Aviles, M., Hernandez, H., Mendoza-Sanchez, I., & Loza-Aguirre, I. (2022). Water Quality Assessment Bias Associated with Long-Screened Wells Screened across Aquifers with High Nitrate and Arsenic Concentrations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 9907. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169907








