The Role of Polygenic Susceptibility on Air Pollution-Associated Asthma between German and Japanese Elderly Women
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
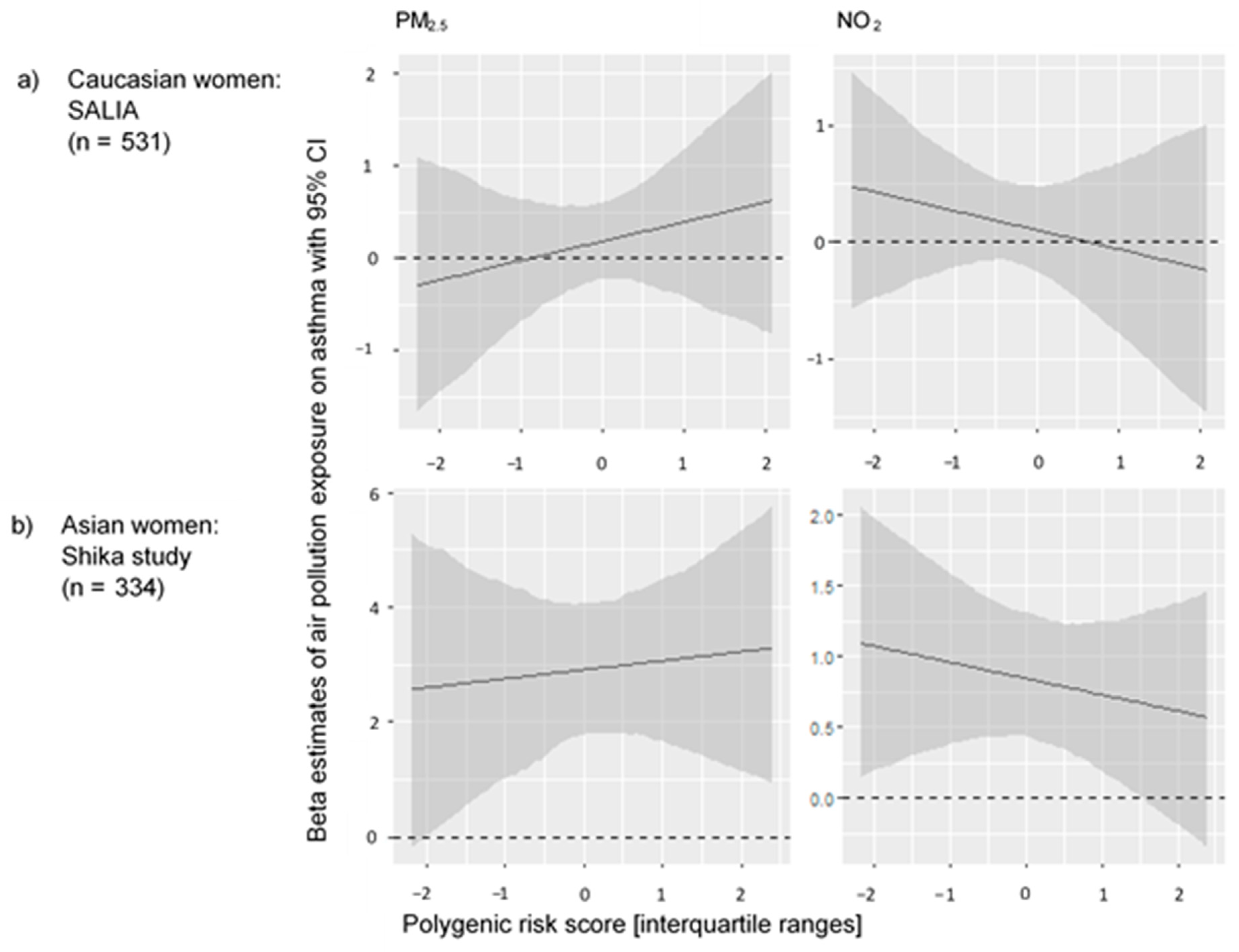
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bønnelykke, K.; Ober, C. Leveraging gene-environment interactions and endotypes for asthma gene discovery. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morales, E.; Duffy, D. Genetics and Gene-Environment Interactions in Childhood and Adult Onset Asthma. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Husseini, Z.W.; Gosens, R.; Dekker, F.; Koppelman, G.H. The genetics of asthma and the promise of genomics-guided drug target discovery. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.A.R.; Mathur, R.; Vonk, J.M.; Szwajda, A.; Brumpton, B.; Granell, R.; Brew, B.K.; Ullemar, V.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Genetic Architectures of Childhood- and Adult-Onset Asthma Are Partly Distinct. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2015 Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ober, C.; Loisel, D.A.; Gilad, Y. Sex-specific genetic architecture of human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demenais, F.; Margaritte-Jeannin, P.; Barnes, K.C.; Cookson, W.O.C.; Altmüller, J.; Ang, W.; Barr, R.G.; Beaty, T.H.; Becker, A.B.; Beilby, J.; et al. Multiancestry association study identifies new asthma risk loci that colocalize with immune-cell enhancer marks. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.; Shu, Y.; Cai, Y.-D. Genetic differences among ethnic groups. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, T.F.; Ko, F.W.S.; Sy, H.Y.; Tsui, S.K.W.; Wong, G.W.K. Differences in asthma genetics between Chinese and other populations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Tan, W. Association between ADAM33 polymorphisms and asthma risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, V.E.; Meyers, D.A. Pharmacogenetics: Implications of race and ethnicity on defining genetic profiles for personalized medicine. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peterson, R.E.; Kuchenbaecker, K.; Walters, R.K.; Chen, C.-Y.; Popejoy, A.B.; Periyasamy, S.; Lam, M.; Iyegbe, C.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Brick, L.; et al. Genome-wide Association Studies in Ancestrally Diverse Populations: Opportunities, Methods, Pitfalls, and Recommendations. Cell 2019, 179, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; Kanai, M.; Kamatani, Y.; Okada, Y.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J. Publisher Correction: Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gref, A.; Merid, S.K.; Gruzieva, O.; Ballereau, S.; Becker, A.; Bellander, T.; Bergström, A.; Bossé, Y.; Bottai, M.; Chan-Yeung, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Interaction Analysis of Air Pollution Exposure and Childhood Asthma with Functional Follow-up. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.M.; Jackson, D.J. Microbes, allergic sensitization, and the natural history of asthma. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 17, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacIntyre, E.A.; Brauer, M.; Melén, E.; Bauer, C.P.; Bauer, M.; Berdel, D.; Bergström, A.; Brunekreef, B.; Chan-Yeung, M.; Klümper, C.; et al. GSTP1 and TNF Gene variants and associations between air pollution and incident childhood asthma: The traffic, asthma and genetics (TAG) study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, R.L.; Peden, D.B. Environmental effects on immune responses in patients with atopy and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Palmo, E.; Cantarelli, E.; Catelli, A.; Ricci, G.; Gallucci, M.; Miniaci, A.; Pession, A. The Predictive Role of Biomarkers and Genetics in Childhood Asthma Exacerbations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, B.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Carlquist, J.F.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Renlund, D.G.; Bair, T.L.; Pearson, R.R.; Camp, N.J. Generating genetic risk scores from intermediate phenotypes for use in association studies of clinically significant endpoints. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2005, 69, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-L.; Tsai, S.-J.; Kuo, P.-H. Polygenic approaches to detect gene–environment interactions when external information is unavailable. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 2236–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Brightling, C.; Pedersen, S.E.; Reddel, H.K. Asthma. Lancet 2018, 391, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schikowski, T.; Ranft, U.; Sugiri, D.; Vierkötter, A.; Brüning, T.; Harth, V.; Krämer, U. Decline in air pollution and change in prevalence in respiratory symptoms and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in elderly women. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichert, T.; Vossoughi, M.; Vierkötter, A.; Sugiri, D.; Schikowski, T.; Schulte, T.; Roden, M.; Luckhaus, C.; Herder, C.; Krämer, U. Association between traffic-related air pollution, subclinical inflammation and impaired glucose metabolism: Results from the SALIA study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narukawa, N.; Tsujiguchi, H.; Hara, A.; Miyagi, S.; Kannon, T.; Suzuki, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Pham, K.O.; Suzuki, F.; et al. Relationship between Vitamin Intake and Health-Related Quality of Life in a Japanese Population: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Shika Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Tsujiguchi, H.; Miyagi, S.; Thi Thu Nguyen, T.; Hara, A.; Nakamura, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Minh Nguyen, P.; et al. Association Between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations and Chronic Pain: Effects of Drinking Habits. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beelen, R.; Hoek, G.; Vienneau, D.; Eeftens, M.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Pedeli, X.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Künzli, N.; Schikowski, T.; Marcon, A.; et al. Development of NO2 and NOx land use regression models for estimating air pollution exposure in 36 study areas in Europe—The ESCAPE project. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 72, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeftens, M.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Bellander, T.; Cesaroni, G.; Cirach, M.; Declercq, C.; Dėdelė, A.; Dons, E.; de Nazelle, A.; et al. Development of Land Use Regression models for PM(2.5), PM(2.5) absorbance, PM(10) and PM(coarse) in 20 European study areas; results of the ESCAPE project. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11195–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, E.; Nunez, S.; Kulp, D.; Qian, J.; Reilly, M.P.; Foulkes, A.S. A guide to genome-wide association analysis and post-analytic interrogation. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 3769–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishigaki, K.; Akiyama, M.; Kanai, M.; Takahashi, A.; Kawakami, E.; Sugishita, H.; Sakaue, S.; Matoba, N.; Low, S.-K.; Okada, Y.; et al. Large-scale genome-wide association study in a Japanese population identifies novel susceptibility loci across different diseases. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jiang, W.; Hou, L.; Zhao, H. Leveraging effect size distributions to improve polygenic risk scores derived from summary statistics of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Hüls, A.; Krämer, U.; Carlsten, C.; Schikowski, T.; Ickstadt, K.; Schwender, H. Comparison of weighting approaches for genetic risk scores in gene-environment interaction studies. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and the Council on ambient air quality and cleaner air for Europe: RL 2008/50/EG. Off. J. Eur. 2008, 152. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/50/oj (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- WHO. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK574594/ (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Kim, K.W.; Ober, C. Lessons Learned From GWAS of Asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2019, 11, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, L.; Shen, H.; Gelaye, B.; Meijsen, J.; Ressler, K.; Feldman, M.; Peterson, R.; Domingue, B. Analysis of polygenic risk score usage and performance in diverse human populations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, Y.; Mimori, T.; Kojima, K.; Nariai, N.; Danjoh, I.; Saito, R.; Yasuda, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagasaki, M. Japonica array: Improved genotype imputation by designing a population-specific SNP array with 1070 Japanese individuals. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabieses, B.; Uphoff, E.; Pinart, M.; Antó, J.M.; Wright, J. A Systematic Review on the Development of Asthma and Allergic Diseases in Relation to International Immigration: The Leading Role of the Environment Confirmed. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beelen, R.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Wolf, K.; Samoli, E.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; et al. Effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on natural-cause mortality: An analysis of 22 European cohorts within the multicentre ESCAPE project. Lancet 2014, 383, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowatte, G.; Erbas, B.; Lodge, C.J.; Knibbs, L.D.; Gurrin, L.C.; Marks, G.B.; Thomas, P.S.; Johns, D.P.; Giles, G.G.; Hui, J.; et al. Traffic-related air pollution exposure over a 5-year period is associated with increased risk of asthma and poor lung function in middle age. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1602357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacquemin, B.; Siroux, V.; Sanchez, M.; Carsin, A.-E.; Schikowski, T.; Adam, M.; Bellisario, V.; Buschka, A.; Bono, R.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution and Adult Asthma Incidence in Six European Cohorts (ESCAPE). Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Alashkar Alhamwe, B.; Caraballo, L.; Ding, M.; Ferrante, A.; Garn, H.; Garssen, J.; Hii, C.S.; Irvine, J.; Llinás-Caballero, K.; et al. Perinatal and Early-Life Nutrition, Epigenetics, and Allergy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murcray, C.E.; Lewinger, J.P.; Gauderman, W.J. Gene-environment interaction in genome-wide association studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 169, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wyss, A.B.; Sofer, T.; Lee, M.K.; Terzikhan, N.; Nguyen, J.N.; Lahousse, L.; Latourelle, J.C.; Smith, A.V.; Bartz, T.M.; Feitosa, M.F.; et al. Multiethnic meta-analysis identifies ancestry-specific and cross-ancestry loci for pulmonary function. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potaczek, D.P.; Harb, H.; Michel, S.; Alhamwe, B.A.; Renz, H.; Tost, J. Epigenetics and allergy: From basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 539–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cohort Study | Cohort Inclusion Criteria, N | Included Examination in This Study (Year; N) | N, Study Sample Inclusion Criteria (Mean Age) | Ethics Committees and Written Informed Consent from All Participants | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| German elderly women | Study on the influence of Air pollution on Lung function, Inflammation and Aging (SALIA) [22,23] | 4874 women aged 55 years living between years 1985 and 1994 in the Ruhr area and the adjacent Münsterland in Germany | 1. follow-up (2006; 4027), 2. follow-up (2007–2010; 834) | 771 women with information on asthma status at the 2. follow-up (73 years) | Ruhr University, Bochum and the Heinrich Heine University, Düsseldorf |
| Japanese elderly women | Shika study [24,25] | 4544 adults aged 40 years or older living between years 2011 and 2016 in the four model areas of the Shika town in Japan | Baseline (2011–2016; 1506), 1. follow-up (2018; 802), 2. follow-up (2019; 245) | 847 women with information on asthma status at the 1. and 2. follow-up (67 years) | Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Ishikawa, Japan |
| German Women: SALIA | Japanese Women: Shika Study | |
|---|---|---|
| N | 771 | 847 |
| Diagnosed asthma (%) | 67 (8.7) | 50 (5.9) |
| Study characteristics | ||
| Mean age [years] ± sd | 73.5 ± 3.1 | 67.0 ± 12.9 |
| Mean height [cm] ± sd | 163.2 ± 5.8 | 151.6 ± 6.8 |
| Mean weight [kg] ± sd | 72.5 ± 12.4 | 51.9 ± 8.4 |
| <10 years education (%) | 137 (17.8) | 393 (46.4) |
| Ever-smoker (%) | 150 (19.5) | 97 (11.5) |
| Air pollution exposures five years prior to the asthma assessments | ||
| Median PM2.5 exposure [µg/m3] (IQR) | 17.4 (1.8) | 12.7 (3.3) |
| Median NO2 exposure [µg/m3] (IQR) | 25.9 (9.6) | 8.5 (3.6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kress, S.; Hara, A.; Wigmann, C.; Sato, T.; Suzuki, K.; Pham, K.-O.; Zhao, Q.; Areal, A.; Tajima, A.; Schwender, H.; et al. The Role of Polygenic Susceptibility on Air Pollution-Associated Asthma between German and Japanese Elderly Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169869
Kress S, Hara A, Wigmann C, Sato T, Suzuki K, Pham K-O, Zhao Q, Areal A, Tajima A, Schwender H, et al. The Role of Polygenic Susceptibility on Air Pollution-Associated Asthma between German and Japanese Elderly Women. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(16):9869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169869
Chicago/Turabian StyleKress, Sara, Akinori Hara, Claudia Wigmann, Takehiro Sato, Keita Suzuki, Kim-Oanh Pham, Qi Zhao, Ashtyn Areal, Atsushi Tajima, Holger Schwender, and et al. 2022. "The Role of Polygenic Susceptibility on Air Pollution-Associated Asthma between German and Japanese Elderly Women" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 16: 9869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169869
APA StyleKress, S., Hara, A., Wigmann, C., Sato, T., Suzuki, K., Pham, K.-O., Zhao, Q., Areal, A., Tajima, A., Schwender, H., Nakamura, H., & Schikowski, T. (2022). The Role of Polygenic Susceptibility on Air Pollution-Associated Asthma between German and Japanese Elderly Women. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), 9869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169869







