Obesity Prevalence and Associated Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Health Behaviors in Russia and Norway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.1.1. Know Your Heart (KYH)
2.1.2. The Seventh Tromsø Study (Tromsø7)
2.2. Measurements of Obesity
2.3. Socio-Demographic Characteristics
2.4. Health Behaviours
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Health Behaviors
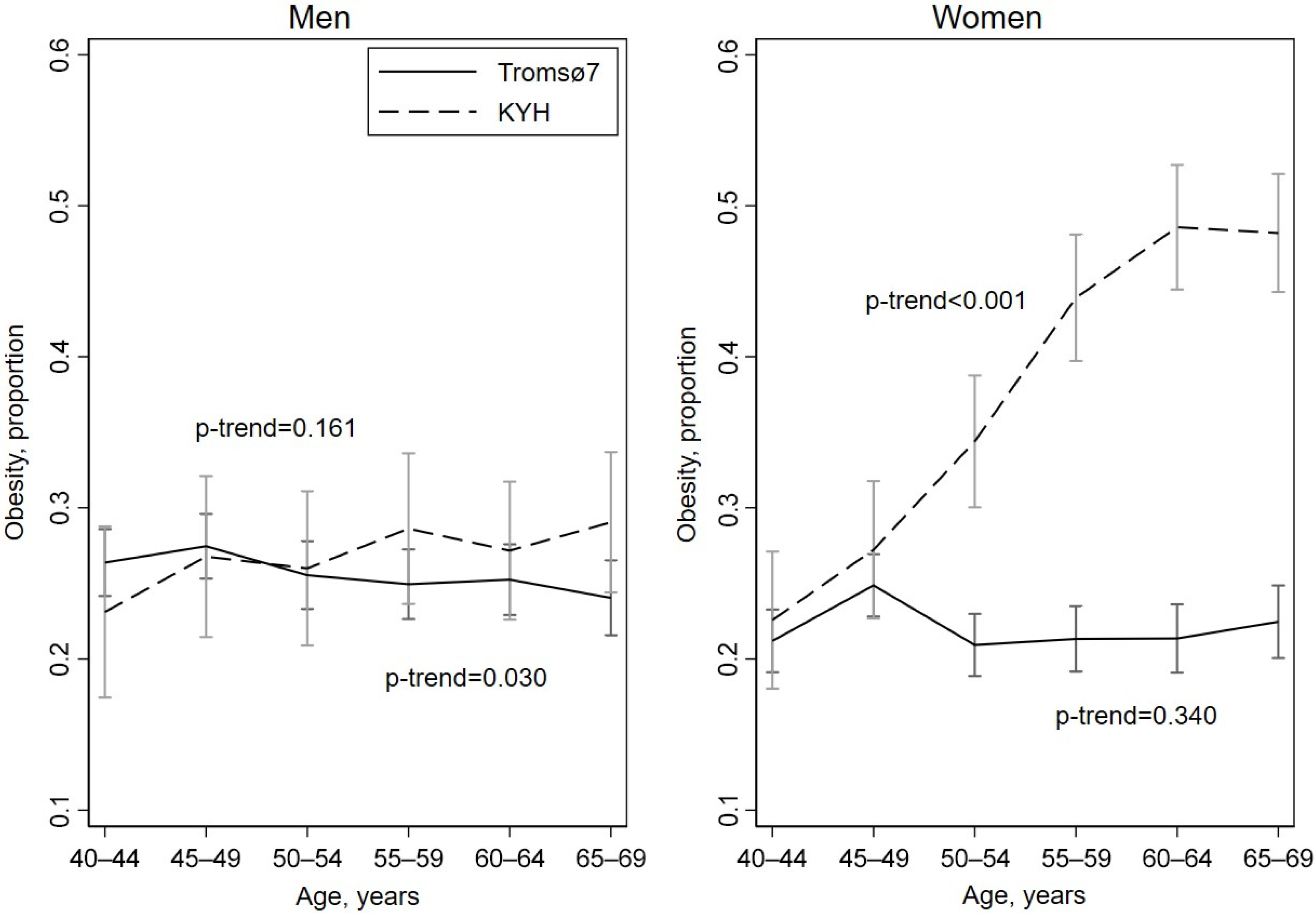
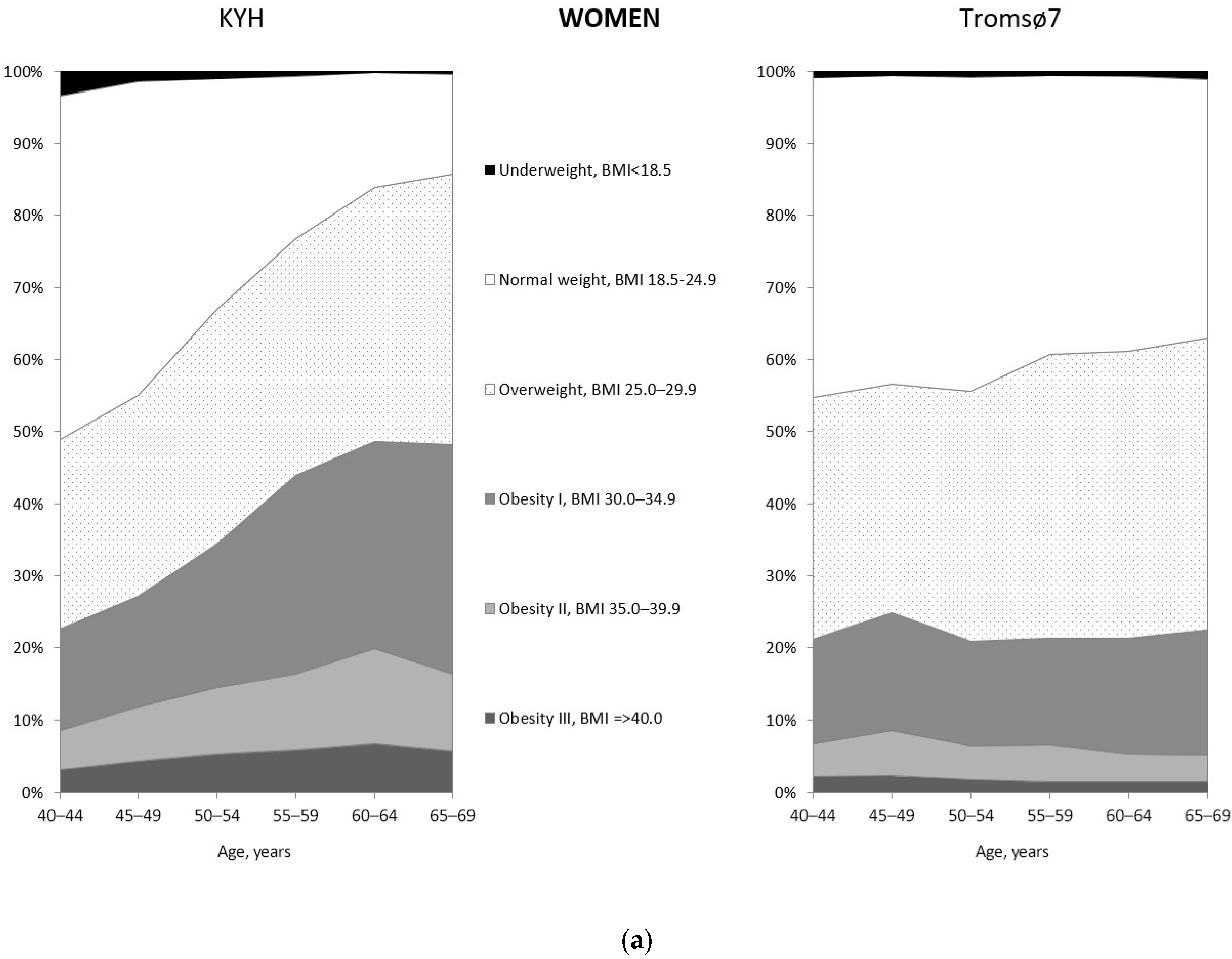
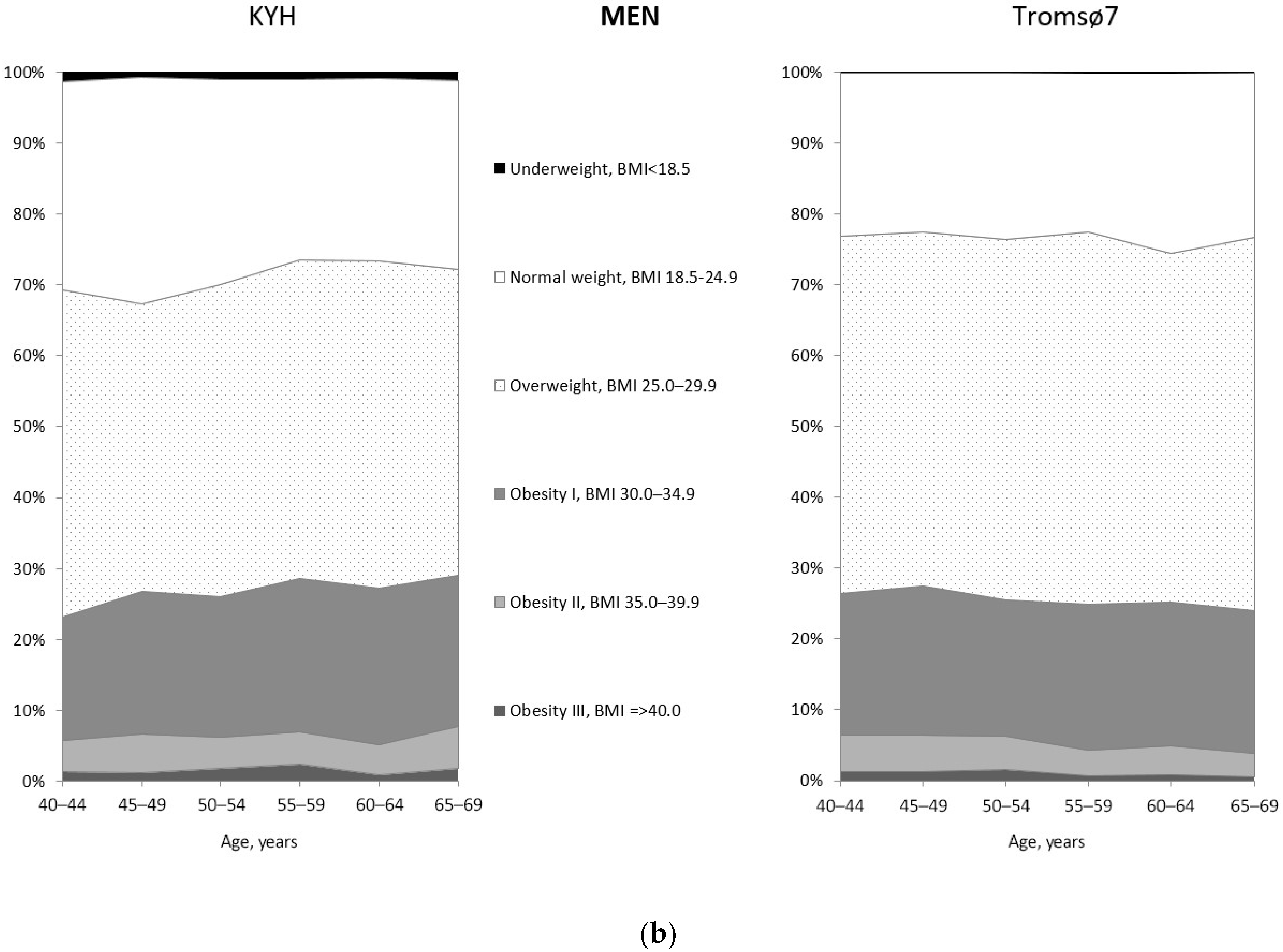
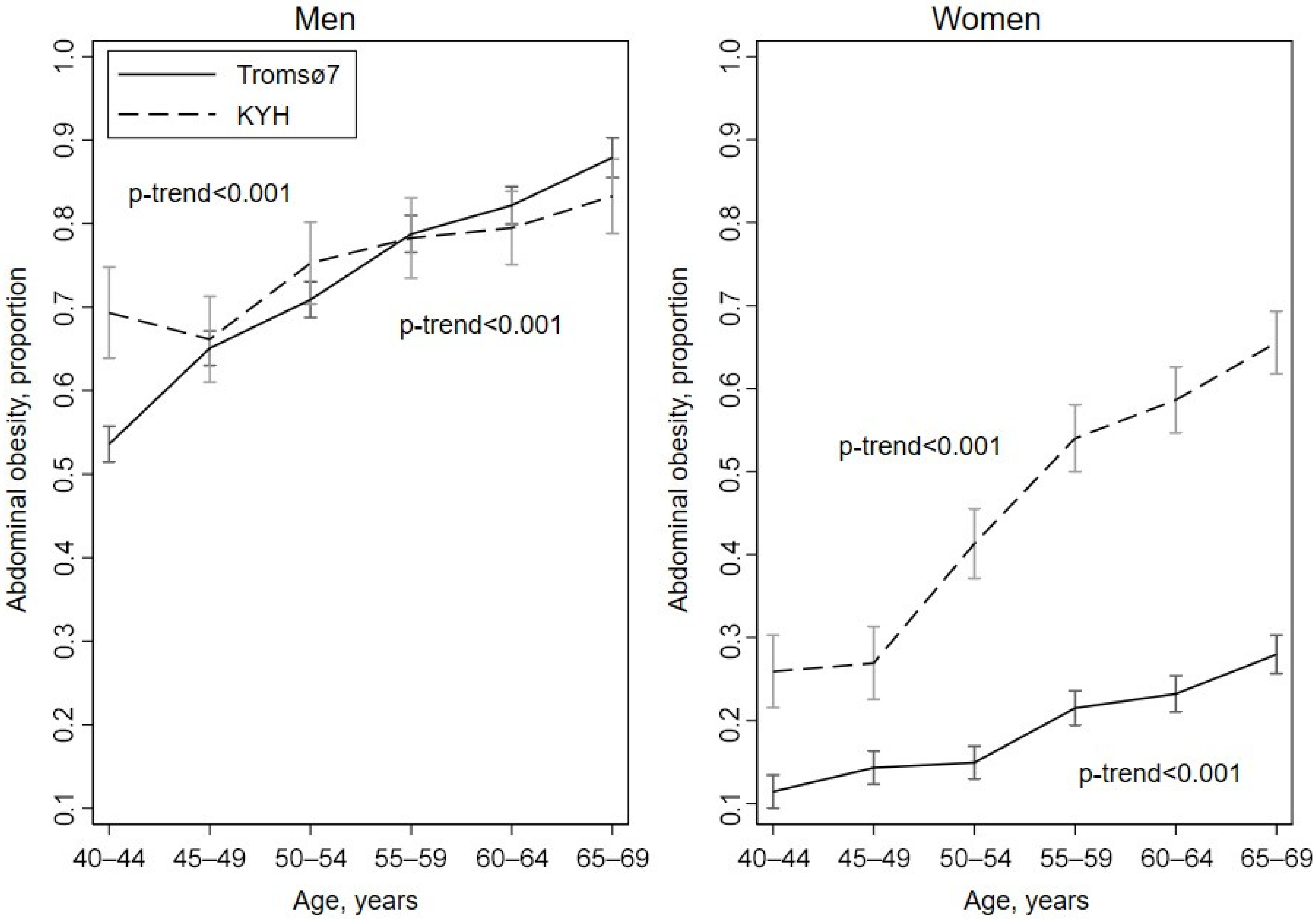
3.2. Prevalence of Obesity
3.3. Age of Participants
3.4. Education
3.5. Marital Status
3.6. Financial Situation
3.7. Smoking
3.8. Alcohol Consumption
3.9. Country Effect on Associations of Obesity with Socio-Demographic and Lifestyle Characteristics
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19·2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- World Health Organization Global Health Observatory Data Repository. Prevalence of Obesity among Adults, BMI ≥ 30, Age-Standardized. Estimates by Country. Available online: https://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.A900A?lang=en (accessed on 17 December 2021).
- Bastien, M.; Poirier, P.; Lemieux, I.; Despres, J.P. Overview of epidemiology and contribution of obesity to cardiovascular disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskaran, K.; Douglas, I.; Forbes, H.; dos-Santos-Silva, I.; Leon, D.A.; Smeeth, L. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: A population-based cohort study of 5.24 million UK adults. Lancet 2014, 384, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Manson, J.E.; Qi, L.; Malik, V.S.; Rimm, E.B.; Sun, Q.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Determinants and Consequences of Obesity. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Hussain, M.E. Obesity and diabetes: An update. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017, 11, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Jousilahti, P.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Soderberg, S.; Onat, A.; Laatikainen, T.; Yudkin, J.S.; Dankner, R.; Morris, R.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. Cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in relation to various anthropometric measures of obesity in Europeans. Nutr. Metab Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.S.; Manolis, A.A.; Manolis, T.A.; Apostolaki, N.E.; Melita, H. COVID-19 infection and body weight: A deleterious liaison in a J-curve relationship. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skolnik, N.S.; Ryan, D.H. Pathophysiology, epidemiology, and assessment of obesity in adults. J. Fam. Pract. 2014, 63 (Suppl. 7), S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carbone, S.; Del Buono, M.G.; Ozemek, C.; Lavie, C.J. Obesity, risk of diabetes and role of physical activity, exercise training and cardiorespiratory fitness. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 62, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, S.H.; Kahathuduwa, C.N.; Binks, M. Physical activity and obesity: What we know and what we need to know. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 1226–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morseth, B.; Jacobsen, B.K.; Emaus, N.; Wilsgaard, T.; Jorgensen, L. Secular trends and correlates of physical activity: The Tromso Study 1979–2008. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affenito, S.G.; Franko, D.L.; Striegel-Moore, R.H.; Thompson, D. Behavioral determinants of obesity: Research findings and policy implications. J. Obes. 2012, 2012, 150732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, S.; Braithwaite, D.; Akinyemiju, T.F. Socio-economic status over the life course and obesity: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaacks, L.M.; Vandevijvere, S.; Pan, A.; McGowan, C.J.; Wallace, C.; Imamura, F.; Mozaffarian, D.; Swinburn, B.; Ezzati, M. The obesity transition: Stages of the global epidemic. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltopoulou, T.; Hatzis, G.; Papageorgiou, N.; Androulakis, E.; Briasoulis, A.; Tousoulis, D. Socioeconomic status and risk factors for cardiovascular disease: Impact of dietary mediators. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2017, 58, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boytsov, S.A.; Deev, A.D.; Shalnova, S.A. Mortality and risk factors for non-communicable diseases in Russia: Specific features, trends, and prognosis. Ter. Arh. 2017, 89, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkolnikov, V.M.; Andreev, E.M.; Tursun-Zade, R.; Leon, D.A. Patterns in the relationship between life expectancy and gross domestic product in Russia in 2005-15: A cross-sectional analysis. Lancet Public Health 2019, 4, e181–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, J.G.; Hartley, K.G.; Steffen, L.M.; Nair, S.; Alman, A.C.; Wellons, M.F.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Tindle, H.A.; Carr, J.J. Association of smoking with abdominal adipose deposition and muscle composition in Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) participants at mid-life: A population-based cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtemanche, C.; Tchernis, R.; Ukert, B. The effect of smoking on obesity: Evidence from a randomized trial. J. Health Econ. 2018, 57, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dare, S.; Mackay, D.F.; Pell, J.P. Relationship between smoking and obesity: A cross-sectional study of 499,504 middle-aged adults in the UK general population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversy, G.; Chaput, J.P. Alcohol Consumption and Obesity: An Update. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotar, O.; Boyarinova, M.; Orlov, A.; Solntsev, V.; Zhernakova, Y.; Shalnova, S.; Deev, A.; Konradi, A.; Baranova, E.; Chazova, I.; et al. Metabolically healthy obese and metabolically unhealthy non-obese phenotypes in a Russian population. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrenya, N.; Brustad, M.; Dobrodeeva, L.; Bichkaeva, F.; Lutfalieva, G.; Cooper, M.; Odland, J.O. Obesity and obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk factors in indigenous Nenets women from the rural Nenets Autonomous Area and Russian women from Arkhangelsk city. Int. J. Circumpolar. Health 2014, 73, 23859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorenkov, O.; Nilssen, O.; Brenn, T.; Martiushov, S.; Arkhipovsky, V.L.; Grjibovski, A.M. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and its components in Northwest Russia: The Arkhangelsk study. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhernakova, Y.V.; Zheleznova, E.A.; Chazova, I.E.; Oshchepkova, E.V.; Dolgusheva, Y.A.; Yarovaya, E.B.; Blinova, N.V.; Orlovsky, A.A.; Konosova, I.D.; Shalnova, S.A.; et al. The prevalence of abdominal obesity and the association with socioeconomic status in Regions of the Russian Federation, the results of the epidemiological study—ESSE-RF. Ter. Arh. 2018, 90, 14–22. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontsevaya, A.; Shalnova, S.; Deev, A.; Breda, J.; Jewell, J.; Rakovac, I.; Conrady, A.; Rotar, O.; Zhernakova, Y.; Chazova, I.; et al. Overweight and Obesity in the Russian Population: Prevalence in Adults and Association with Socioeconomic Parameters and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Obes. Facts. 2019, 12, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunsina, K.; Dibaba, D.T.; Akinyemiju, T. Association between life-course socio-economic status and prevalence of cardio-metabolic risk ractors in five middle-income countries. J. Glob. Health 2018, 8, 020405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandkvist, M.; Bjorngaard, J.H.; Odegard, R.A.; Brumpton, B.; Smith, G.D.; Asvold, B.O.; Sund, E.R.; Kvaloy, K.; Willer, C.J.; Vie, G.A. Genetic associations with temporal shifts in obesity and severe obesity during the obesity epidemic in Norway: A longitudinal population-based cohort (the HUNT Study). PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapminder Dependance of Life Expactancy on Gross Domestic Product per Capita. Available online: https://www.gapminder.org (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Cook, S.; Malyutina, S.; Kudryavtsev, A.V.; Averina, M.; Bobrova, N.; Boytsov, S.; Brage, S.; Clark, T.G.; Diez Benavente, E.; Eggen, A.E.; et al. Know Your Heart: Rationale, design and conduct of a cross-sectional study of cardiovascular structure, function and risk factors in 4500 men and women aged 35–69 years from two Russian cities, 2015–2018. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, B.K.; Eggen, A.E.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Wilsgaard, T.; Njolstad, I. Cohort profile: The Tromso Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopstock, L.A.; Grimsgaard, S.; Johansen, H.; Kanstad, K.; Wilsgaard, T.; Eggen, A.E. The seventh survey of the Tromsø Study (Tromsø7) 2015–2016: Study design, data collection, attendance, and prevalence of risk factors and disease in a multipurpose population-based health survey. Scand. J. Public Health. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic of Obesity: Report of the WHO Consultation of Obesity; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997; pp. 7–9. ISBN 9241208945. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio; Report of a WHO Expert Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 8–9, 12–14, 27. ISBN 9789241501491. [Google Scholar]
- Imahori, Y.; Frost, C.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Ryabikov, A.; Kudryavtsev, A.V.; Malyutina, S.; Kornev, M.; Hughes, A.D.; Hopstock, L.A.; Leon, D.A. Effect of adiposity on differences in carotid plaque burden in studies conducted in Norway and Russia: A cross-sectional analysis of two populations at very different risk of cardiovascular mortality. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, C.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Variability in waist circumference measurements according to anatomic measurement site. Obesity 2009, 17, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, J.B.; Aasland, O.G.; Babor, T.F.; de la Fuente, J.R.; Grant, M. Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO Collaborative Project on Early Detection of Persons with Harmful Alcohol Consumption—II. Addiction 1993, 88, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalkowska, J.; Poinhos, R.; Franchini, B.; Afonso, C.; Correia, F.; Pinhao, S.; Vaz de Almeida, M.D.; Rodrigues, S. General and abdominal adiposity in a representative sample of Portuguese adults: Dependency of measures and socio-demographic factors’ influence—CORRIGENDUM. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederiksen, P.; Jensen, K.E.; Kjaer, S.K. Sociodemographic factors and risk-taking behaviour during adolescence and obesity among more than 40,000 Danes. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, A.; Cupellaro, E.; Vassallo, M. Which dimensions of food-related lifestyle are likely to be associated with obesity in Italy? Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaio, V.; Antunes, L.; Namorado, S.; Barreto, M.; Gil, A.; Kyslaya, I.; Rodrigues, A.P.; Santos, A.; Bohler, L.; Castilho, E.; et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in Portugal: Results from the First Portuguese Health Examination Survey (INSEF 2015). Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 12, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart-Knox, B.; E Duffy, M.; Bunting, B.; Parr, H.; Vas de Almeida, M.D.; Gibney, M. Associations between obesity (BMI and waist circumference) and socio-demographic factors, physical activity, dietary habits, life events, resilience, mood, perceived stress and hopelessness in healthy older Europeans. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balhareth, A.; Meertens, R.; Kremers, S.; Sleddens, E. Overweight and obesity among adults in the Gulf States: A systematic literature review of correlates of weight, weight-related behaviours, and interventions. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 763–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura, M.; Kozak, L.P. Obesity and related consequences to ageing. Age 2016, 38, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa Pimenta, W.; Santos Brant Rocha, J.; Prates Caldeira, A.; Araujo Veloso Popoff, D.; Maia Santos, V.; Murca de Souza, J.E.; Marques, M.S.; Piana Santos Lima de Oliveira, F.; Rodrigues Caldeira, D.M.; Souza Guerra Junior, G.E.; et al. Abdominal obesity and association with sociodemographic, behavioral and clinical data in climacteric women assisted in primary care. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, C.E.; Fatemifar, G.; Palmer, T.M.; White, J.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Zabaneh, D.; Engmann, J.E.L.; Shah, T.; Wong, A.; Warren, H.R.; et al. Causal Associations of Adiposity and Body Fat Distribution With Coronary Heart Disease, Stroke Subtypes, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Circulation 2017, 135, 2373–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. MONICA Monograph and Multimedia Sourcebook: World’s Largest Study of Heart Disease, Stroke, Risk Factors, and Population Trends 1979–2002 Hugh Tunstall-Pedoe; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 66–68, 117–118, 206–209. ISBN 9241562234. [Google Scholar]
- Jaehn, P.; Bobrova, N.; Saburova, L.; Kudryavtsev, A.V.; Malyutina, S.; Cook, S. The relation of gender role attitudes with depression and generalised anxiety disorder in two Russian cities. J. Affect Disord. 2020, 264, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanatova, D.K.; Yudina, T.N.; Korolev, I.V. The physical activity and sport in life of elder generation of Russian cities. Probl. Sotcialnoi Gig. Zdr. I Istor. Meditsini (Probl Sotsialnoi Gig Zdr. Istor Med.) 2021, 29, 107–112. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Institute of Public Health. Overweight and Obesity in Norway. Available online: https://www.fhi.no/en/op/hin/health-disease/overweight-and-obesity-in-norway---/ (accessed on 27 May 2022).
- Lovsletten, O.; Jacobsen, B.K.; Grimsgaard, S.; Njolstad, I.; Wilsgaard, T.; Lochen, M.L.; Eggen, A.E.; Hopstock, L.A. Prevalence of general and abdominal obesity in 2015–2016 and 8-year longitudinal weight and waist circumference changes in adults and elderly: The Tromso Study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, B.K.; Aars, N.A. Changes in waist circumference and the prevalence of abdominal obesity during 1994–2008—Cross-sectional and longitudinal results from two surveys: The Tromso Study. BMC Obes. 2016, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droyvold, W.B.; Nilsen, T.I.; Kruger, O.; Holmen, T.L.; Krokstad, S.; Midthjell, K.; Holmen, J. Change in height, weight and body mass index: Longitudinal data from the HUNT Study in Norway. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.E.; Tverdal, A. Development of body weight in the Norwegian population. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat. Acids 2005, 73, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Xiang, X. Age-period-cohort analyses of obesity prevalence in US adults. Public Health 2016, 141, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, T.; Liu, J.; Probst, J.; Merchant, A.; Jhones, S.; Martin, A.B. Obesity and obesity-related behaviors among rural and urban adults in the USA. Rural Remote Health 2015, 15, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czernichow, S.; Renuy, A.; Rives-Lange, C.; Carette, C.; Airagnes, G.; Wiernik, E.; Ozguler, A.; Kab, S.; Goldberg, M.; Zins, M.; et al. Evolution of the prevalence of obesity in the adult population in France, 2013–2016: The Constances study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienaber-Rousseau, C.; Sotunde, O.F.; Ukegbu, P.O.; Myburgh, P.H.; Wright, H.H.; Havemann-Nel, L.; Moss, S.J.; Kruger, I.M.; Kruger, H.S. Socio-Demographic and Lifestyle Factors Predict 5-Year Changes in Adiposity among a Group of Black South African Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Heterogeneous contributions of change in population distribution of body mass index to change in obesity and underweight. Elife 2021, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, Y.D.; Kolosnitsyna, M.G. Overweight Population in Russia: Statistical Analysis. Vopr. Stat. 2018, 25, 61–77. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, S.K.; Rizov, M. Determinants of obesity in transition economies: The case of Russia. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2007, 5, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukovsky, G.S.; Konstantinov, V.V.; Varlamova, T.A.; Kapustina, A.V. Arterial hypertension: The epidemiological situation in Russia and other countries. Rus. Med. Zhurnal (Russ. Med. J.) 1997, 5, 551–558. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Petursson, H.; Sigurdsson, J.A.; Bengtsson, C.; Nilsen, T.I.; Getz, L. Body configuration as a predictor of mortality: Comparison of five anthropometric measures in a 12 year follow-up of the Norwegian HUNT 2 study. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Natarajan, P.; Klarin, D.; Zekavat, S.M.; Hsiao, A.J.; Kathiresan, S. Genetic Association of Waist-to-Hip Ratio With Cardiometabolic Traits, Type 2 Diabetes, and Coronary Heart Disease. JAMA 2017, 317, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Examination Committee of Criteria for ‘Obesity Disease’ in Japan; Japan Society for the Study of Obesity, New criteria for ‘obesity disease’ in Japan. Circ. J. 2002, 66, 987–992. [CrossRef]
- Imahori, Y.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Morgan, K.E.; Frost, C.; Hughes, A.D.; Hopstock, L.A.; Johnsen, S.H.; Emaus, N.; Leon, D.A. The association between anthropometric measures of adiposity and the progression of carotid atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonova, G.I.; Mustafina, S.V.; Rymar, O.D.; Shcherbakova, I.V.; Nikitenko, T.M.; Bobak, M.; Malyutina, S.K. Metabolic syndrome and risk of cardiovascular and total mortality: Data from a 14-year prospective cohort study in Siberia. Ross. Kardiol. Zhurnal (Russ. J. Cardiol.) 2020, 25, 86–94. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, D.; Seenivasan, S.; Cameron, A.J.; Sacks, G. The association between national income and adult obesity prevalence: Empirical insights into temporal patterns and moderators of the association using 40 years of data across 147 countries. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikhart, H.; Bobak, M.; Malyutina, S.; Pajak, A.; Kubinova, R.; Marmot, M. Obesity and education in three countries of the Central and Eastern Europe: The HAPIEE study. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2007, 15, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Shin, A.; Cho, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Kang, D.; Lee, J.K. Marital status and the prevalence of obesity in a Korean population. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 14, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teachman, J. Body Weight, Marital Status, and Changes in Marital Status. J. Fam. Issues 2016, 37, 74–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopylova, O.U. Sexial parts of a couple in family relations. Vestn. Mosk. Gumanit.-Ekon. Inst. (Bull. Mosc. Humanit. Econ. Inst.) 2018, 2, 137–143. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Shim, K.W.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Oh, S.W. Cigarette smoking increases abdominal and visceral obesity but not overall fatness: An observational study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayon-Orea, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Bes-Rastrollo, M. Alcohol consumption and body weight: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Munter, J.S.; Tynelius, P.; Magnusson, C.; Rasmussen, F. Longitudinal analysis of lifestyle habits in relation to body mass index, onset of overweight and obesity: Results from a large population-based cohort in Sweden. Scand. J. Public Health 2015, 43, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downer, M.K.; Bertoia, M.L.; Mukamal, K.J.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J. Change in Alcohol Intake in Relation to Weight Change in a Cohort of US Men with 24 Years of Follow-Up. Obesity 2017, 25, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannisto, S.; Harald, K.; Kontto, J.; Lahti-Koski, M.; Kaartinen, N.E.; Saarni, S.E.; Kanerva, N.; Jousilahti, P. Dietary and lifestyle characteristics associated with normal-weight obesity: The National FINRISK 2007 Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, L.; Popkin, B.M.; Poti, J.M. Associations of Alcoholic Beverage Consumption with Dietary Intake, Waist Circumference, and Body Mass Index in US Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2012. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 409–420 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.Y.; Park, H.K.; Hwang, H.S. Relationship between abdominal obesity and alcohol drinking pattern in normal-weight, middle-aged adults: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2013. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, M.E.J.; Vlachou, P.; Govan, L.; Han, T.S. Different associations between body composition and alcohol when assessed by exposure frequency or by quantitative estimates of consumption. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Kawakami, K. Eating and drinking habits and its association with obesity in Japanese healthy adults: Retrospective longitudinal big data analysis using a health check-up database. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 126, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopstock, L.A.; Kudryavtsev, A.V.; Malyutina, S.; Cook, S. Hazardous alcohol consumption and problem drinking in Norwegian and Russian women and men: The Tromso Study 2015–2016 and the Know Your Heart study 2015–2018. Scand. J Public Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenrud, B.; Kabashi, S.; Nadezhdin, A.; Bryun, E.; Koshkina, E.; Tetenova, E.; Lerdal, A.; Norby, G.; Kolgashkin, A.; Petukhov, A.; et al. The Association between the Alcohol Biomarker Phosphatidylethanol (PEth) and Self-Reported Alcohol Consumption among Russian and Norwegian Medical Patients. Alcohol Alcohol. 2021, 56, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatikainen, T.; Alho, H.; Vartiainen, E.; Jousilahti, P.; Sillanaukee, P.; Puska, P. Self-reported alcohol consumption and association to carbohydrate-deficient transferrin and gamma-glutamyltransferase in a random sample of the general population in the Republic of Karelia, Russia and in North Karelia, Finland. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002, 37, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neermark, S.; Holst, C.; Bisgaard, T.; Bay-Nielsen, M.; Becker, U.; Tolstrup, J.S. Validation and calibration of self-reported height and weight in the Danish Health Examination Survey. Eur. J. Public Health 2019, 29, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Norway (SSB) Population 2022. Available online: https://www.ssb.no/en/befolkning/folketall/statistikk/befolkning (accessed on 16 June 2022).
- Statistics Norway (SSB) Educational Attainment of the Population 2022. Available online: https://www.ssb.no/en/utdanning/utdanningsniva/statistikk/befolkningens-utdanningsniva (accessed on 16 June 2022).
| Men | Women | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KYH † (N = 1732) | Tromsø7 ‡ (N = 8346) | KYH † (N = 2389) | Tromsø7 ‡ (N = 9300) | |
| Age, years (Mean, SD) | 55.7 (8.5) | 53.8 (8.5) | 55.4 (8.7) | 53.6 (8.4) |
| Abs (%) | Abs (%) | |||
| Age groups, years | ||||
| ˗ 40–44 | 226 (13.1) | 1473 (17.7) | 351 (14.7) | 1678 (18.0) |
| ˗ 45–49 | 254 (14.7) | 1581 (18.9) | 349 (14.6) | 1700 (18.3) |
| ˗ 50–54 | 279 (16.1) | 1434 (17.2) | 381 (16.0) | 1705 (18.3) |
| ˗ 55–59 | 290 (16.7) | 1356 (16.3) | 411 (17.2) | 1540 (16.6) |
| ˗ 60–64 | 347 (20.0) | 1320 (15.8) | 423 (17.7) | 1420 (15.3) |
| ˗ 65–69 | 336 (19.4) | 1182 (14.2) | 474 (19.8) | 1257 (13.5) |
| Education | ||||
| ˗ Primary/secondary | 519 (30.0) | 4090 (49.5) | 519 (21.7) | 4081 (44.3) |
| ˗ College/university | 1213 (70.0) | 4173 (50.5) | 1870 (78.3) | 5128 (55.7) |
| Living with spouse/partner (yes) | 1469 (84.8) | 6609 (81.8) | 1360 (56.9) | 6532 (75.4) |
| Financial situation, level | ||||
| ˗ Lower | 301 (17.8) | 537 (6.5) | 535 (22.7) | 968 (10.8) |
| ˗ Middle | 1284 (76.0) | 4991 (60.8) | 1709 (72.6) | 5769 (64.4) |
| ˗ Upper | 104 (6.2) | 2684 (32.7) | 110 (4.7) | 2226 (24.8) |
| Smoking status | ||||
| ˗ Never | 497 (28.7) | 3705 (45.3) | 1723 (72.1) | 3897 (42.7) |
| ˗ Ex-smoker | 617 (35.6) | 3349 (40.9) | 307 (12.9) | 3840 (42.0) |
| ˗ Current smoker | 618 (35.7) | 1133 (13.8) | 358 (15.0) | 1402 (15.3) |
| Drinking alcohol 2+ times per week (yes) | 357 (20.7) | 2845 (34.2) | 67 (2.81) | 2524 (27.3) |
| Drinking 5+ alcohol drinks per occasion (yes) | 615 (35.7) | 1225 (14.8) | 195 (8.19) | 387 (4.21) |
| (a) | ||||||||
| KYH, OR (95% CI) | Tromsø7, OR (95% CI) | p-Value for Interaction d | ||||||
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | |||
| Age, years | - 40–44 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - 45–49 | 1.15 (0.75–1.76) | 1.15 (0.75–1.77) | 1.21 (0.79–1.87) | 1.11 (0.94–1.31) | 1.08 (0.91–1.28) | 1.10 (0.93–1.30) | - | |
| - 50–54 | 1.14 (0.75–1.72) | 1.14 (0.75–1.73) | 1.22 (0.80–1.86) | 0.97 (0.82–1.15) | 0.92 (0.77–1.09) | 0.97 (0.82–1.16) | - | |
| - 55–59 | 1.31 (0.88–1.97) | 1.29 (0.86–1.95) | 1.39 (0.92–2.10) | 0.97 (0.81–1.15) | 0.90 (0.76–1.08) | 0.97 (0.81–1.16) | 0.423 | |
| - 60–64 | 1.19 (0.80–1.77) | 1.14 (0.76–1.70) | 1.19 (0.79–1.79) | 0.93 (0.78–1.11) | 0.87 (0.72–1.04) | 0.95 (0.79–1.14) | - | |
| - 65–69 | 1.34 (0.90–1.99) | 1.31 (0.88–1.96) | 1.33 (0.89–2.00) | 0.87 (0.73–1.05) | 0.79 (0.66–0.96) | 0.87 (0.71–1.05) | - | |
| p-value for trend | 0.161 | 0.244 | 0.256 | 0.030 | 0.001 | 0.049 | - | |
| Education | - College/university | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Primary/secondary | 1.05 (0.83–1.33) | 1.08 (0.85–1.37) | 1.18 (0.92–1.50) | 1.57 (1.42–1.75) | 1.51 (1.35–1.68) | 1.36 (1.21–1.52) | 0.296 | |
| Living with spouse/partner | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Yes | 1.63 (1.17–2.27) | 1.64 (1.17–2.29) | 1.58 (1.13–2.21) | 0.86 (0.75–0.98) | 0.90 (0.78–1.04) | 0.93 (0.81–1.08) | 0.005 | |
| Financial situation, level | - Upper | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Middle | 1.05 (0.67–1.66) | 1.02 (0.64–1.62) | 1.02 (0.64–1.63) | 1.37 (1.23–1.54) | 1.18 (1.05–1.34) | 1.12 (0.99–1.27) | - | |
| - Lower | 0.98 (0.59–1.64) | 0.99 (0.59–1.66) | 1.09 (0.65–1.85) | 1.39 (1.09–1.75) | 1.04 (0.80–1.36) | 1.00 (0.77–1.31) | 0.625 | |
| Smoking status | - Never | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Ex-smoker | 1.17 (0.90–1.52) | 1.09 (0.83–1.42) | 1.46 (1.30–1.63) | 1.32 (1.18–1.48) | - | |||
| - Current smoker | 0.61 (0.46–0.81) | 0.56 (0.42–0.74) | 1.04 (0.88–1.23) | 0.80 (0.68–0.96) | 0.100 | |||
| Drinking alcohol 2+ times per week | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.48 (1.14–1.91) | 1.48 (1.14–1.92) | 0.61 (0.54–0.68) | 0.66 (0.59–0.74) | <0.001 | |||
| Drinking 5+ alcohol drinks per occasion | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.25 (0.99–1.56) | 1.34 (1.06–1.69) | 1.84 (1.61–2.10) | 1.66 (1.44–1.91) | 0.118 | |||
| (b) | ||||||||
| KYH, OR (95% CI) | Tromsø7, OR (95% CI) | p-Value for Interaction d | ||||||
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | |||
| Age, years | - 40–44 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - 45–49 | 1.24 (0.88–1.76) | 1.28 (0.90–1.82) | 1.30 (0.91–1.84) | 1.21 (1.02–1.43) | 1.17 (0.98–1.39) | 1.21 (1.02–1.44) | - | |
| - 50–54 | 1.70 (1.22–2.37) | 1.70 (1.22–2.38) | 1.75 (1.25–2.45) | 0.96 (0.80–1.14) | 0.88 (0.74–1.06) | 0.94 (0.79–1.13) | - | |
| - 55–59 | 2.66 (1.93–3.65) | 2.54 (1.84–3.50) | 2.60 (1.88–3.60) | 0.94 (0.78–1.13) | 0.83 (0.69–1.00) | 0.91 (0.75–1.10) | <0.001 | |
| - 60–64 | 3.17 (2.31–4.35) | 2.96 (2.15–4.08) | 3.08 (2.22–4.27) | 0.99 (0.82–1.19) | 0.84 (0.69–1.01) | 0.93 (0.77–1.13) | - | |
| - 65–69 | 3.18 (2.33–4.34) | 2.97 (2.17–4.06) | 3.08 (2.23–4.25) | 1.04 (0.86–1.26) | 0.82 (0.67–1.00) | 0.90 (0.74–1.11) | - | |
| p-value for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.340 | <0.001 | 0.026 | - | |
| Education | - College/university | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Primary/secondary | 1.57 (1.28–1.93) | 1.53 (1.25–1.88) | 1.54 (1.26–1.90) | 1.59 (1.43–1.78) | 1.44 (1.28–1.62) | 1.37 (1.21–1.54) | 0.317 | |
| Living with spouse/partner | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Yes | 0.94 (0.79–1.12) | 1.00 (0.84–1.20) | 1.00 (0.84–1.19) | 0.89 (0.79–1.01) | 0.99 (0.87–1.14) | 1.00 (0.87–1.14) | 0.996 | |
| Financial situation, level | - Upper | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Middle | 1.25 (0.81–1.93) | 1.24 (0.80–1.91) | 1.25 (0.81–1.94) | 1.67 (1.46–1.91) | 1.49 (1.29–1.72) | 1.40 (1.21–1.62) | - | |
| - Lower | 1.73 (1.10–2.74) | 1.66 (1.04–2.64) | 1.68 (1.06–2.68) | 1.84 (1.50–2.26) | 1.50 (1.18–1.91) | 1.37 (1.07–1.75) | 0.081 | |
| Smoking status | - Never | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Ex-smoker | 1.19 (0.91–1.54) | 1.14 (0.87–1.48) | 1.27 (1.13–1.43) | 1.21 (1.08–1.37) | - | |||
| - Current smoker | 1.02 (0.79–1.31) | 0.89 (0.68–1.15) | 0.95 (0.81–1.13) | 0.76 (0.64–0.91) | 0.500 | |||
| Drinking alcohol 2+ times per week | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.53 (0.92–2.54) | 1.58 (0.95–2.63) | 0.51 (0.45–0.58) | 0.55 (0.48–0.63) | 0.001 | |||
| Drinking 5+ alcohol drinks per occasion | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.32 (0.97–1.81) | 1.26 (0.91–1.75) | 1.84 (1.45–2.33) | 1.68 (1.31–2.14) | 0.173 | |||
| (a) | ||||||||
| KYH, OR (95% CI) | Tromsø7, OR (95% CI) | p-Value for Interaction d | ||||||
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | |||
| Age, years | - 40–44 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - 45–49 | 0.82 (0.55–1.21) | 0.82 (0.55–1.22) | 0.82 (0.55–1.23) | 1.60 (1.37–1.86) | 1.56 (1.34–1.82) | 1.58 (1.36–1.85) | - | |
| - 50–54 | 1.36 (0.91–2.04) | 1.37 (0.92–2.05) | 1.40 (0.93–2.10) | 2.06 (1.75–2.41) | 1.96 (1.67–2.30) | 2.04 (1.74–2.41) | - | |
| - 55–59 | 1.54 (1.03–2.31) | 1.54 (1.03–2.32) | 1.60 (1.06–2.41) | 3.22 (2.71–3.83) | 3.04 (2.56–3.62) | 3.22 (2.69–3.84) | <0.001 | |
| - 60–64 | 1.66 (1.12–2.46) | 1.64 (1.11–2.45) | 1.66 (1.11–2.49) | 3.97 (3.31–4.75) | 3.74 (3.12–4.49) | 3.90 (3.23–4.69) | - | |
| - 65–69 | 2.24 (1.48–3.39) | 2.26 (1.49–3.43) | 2.26 (1.48–3.46) | 6.28 (5.08–7.77) | 5.77 (4.65–7.16) | 6.13 (4.92–7.63) | - | |
| p-value for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | - | |
| Education | - College/university | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Primary/secondary | 0.99 (0.77–1.27) | 1.01 (0.78–1.30) | 1.05 (0.81–1.37) | 1.72 (1.55–1.91) | 1.63 (1.46–1.82) | 1.38 (1.23–1.55) | 0.062 | |
| Living with spouse/partner | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Yes | 1.22 (0.90–1.66) | 1.21 (0.89–1.65) | 1.16 (0.85–1.59) | 0.89 (0.78–1.03) | 0.95 (0.81–1.10) | 1.01 (0.87–1.18) | 0.427 | |
| Financial situation, level | - Upper | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Middle | 0.94 (0.58–1.52) | 0.93 (0.57–1.50) | 0.91 (0.56–1.48) | 1.48 (1.33–1.65) | 1.26 (1.12–1.42) | 1.18 (1.04–1.33) | - | |
| - Lower | 0.84 (0.49–1.44) | 0.85 (0.49–1.45) | 0.88 (0.51–1.53) | 1.26 (0.99–1.61) | 0.94 (0.72–1.24) | 0.84 (0.63–1.11) | 0.211 | |
| Smoking status | - Never | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Ex-smoker | 1.60 (1.19–2.16) | 1.54 (1.14–2.07) | 1.95 (1.74–2.18) | 1.75 (1.56–1.97) | - | |||
| - Current smoker | 0.94 (0.72–1.24) | 0.89 (0.67–1.18) | 1.87 (1.58–2.21) | 1.46 (1.22–1.74) | 0.012 | |||
| Drinking alcohol 2+ times per week | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.30 (0.97–1.74) | 1.25 (0.93–1.68) | 0.73 (0.66–0.82) | 0.81 (0.73–0.91) | 0.007 | |||
| Drinking 5+ alcohol drinks per occasion | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.34 (1.05–1.71) | 1.35 (1.06–1.73) | 2.35 (2.00–2.78) | 1.96 (1.66–2.33) | 0.015 | |||
| (b) | ||||||||
| KYH, OR (95% CI) | Tromsø7, OR (95% CI) | p-Value for Interaction d | ||||||
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | |||
| Age, years | - 40–44 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - 45–49 | 1.02 (0.73–1.43) | 1.05 (0.75–1.48) | 1.06 (0.75–1.49) | 1.30 (1.04–1.61) | 1.25 (1.00–1.55) | 1.26 (1.01–1.56) | - | |
| - 50–54 | 1.90 (1.39–2.61) | 1.91 (1.39–2.62) | 1.98 (1.43–2.73) | 1.36 (1.10–1.69) | 1.25 (1.01–1.56) | 1.26 (1.02–1.57) | - | |
| - 55–59 | 3.31 (2.43–4.51) | 3.19 (2.33–4.35) | 3.56 (2.59–4.90) | 2.11 (1.71–2.59) | 1.85 (1.50–2.29) | 1.89 (1.53–2.34) | <0.001 | |
| - 60–64 | 3.94 (2.89–5.36) | 3.69 (2.71–5.04) | 4.38 (3.17–6.04) | 2.29 (1.86–2.83) | 1.94 (1.56–2.40) | 2.01 (1.61–2.49) | - | |
| - 65–69 | 5.38 (3.96–7.31) | 5.08 (3.73–6.93) | 6.10 (4.42–8.43) | 3.09 (2.50–3.81) | 2.36 (1.90–2.92) | 2.49 (1.99–3.10) | - | |
| p-value for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | - | |
| Education | - College/university | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Primary/secondary | 1.48 (1.20–1.82) | 1.43 (1.16–1.76) | 1.34 (1.08–1.65) | 1.66 (1.47–1.86) | 1.45 (1.28–1.65) | 1.33 (1.17–1.52) | 0.981 | |
| Living with spouse/partner | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Yes | 0.95 (0.80–1.13) | 1.02 (0.85–1.21) | 1.06 (0.88–1.26) | 0.87 (0.76–0.99) | 1.01 (0.87–1.16) | 1.03 (0.89–1.19) | 0.804 | |
| Financial situation, level | - Upper | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| - Middle | 1.37 (0.89–2.10) | 1.36 (0.89–2.09) | 1.30 (0.85–2.01) | 1.73 (1.48–2.01) | 1.53 (1.30–1.81) | 1.44 (1.22–1.70) | - | |
| - Lower | 1.98 (1.26–3.11) | 1.92 (1.21–3.03) | 1.80 (1.13–2.86) | 2.32 (1.87–2.88) | 1.89 (1.46–2.43) | 1.70 (1.32–2.20) | 0.534 | |
| Smoking status | - Never | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Ex-smoker | 1.17 (0.90–1.53) | 1.11 (0.85–1.46) | 1.34 (1.18–1.53) | 1.28 (1.12–1.46) | - | |||
| - Current smoker | 2.04 (1.59–2.63) | 1.79 (1.38–2.33) | 1.64 (1.39–1.94) | 1.35 (1.13–1.61) | 0.077 | |||
| Drinking alcohol 2+ times per week | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.16 (0.69–1.94) | 1.15 (0.68–1.94) | 0.65 (0.56–0.74) | 0.72 (0.63–0.83) | 0.090 | |||
| Drinking 5+ alcohol drinks per occasion | - No | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | ||
| - Yes | 1.80 (1.31–2.47) | 1.48 (1.06–2.05) | 1.62 (1.23–2.12) | 1.28 (0.97–1.70) | 0.521 | |||
| Model 1 a | Model 2 b | Model 3 c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| General obesity | |||
| Men | 1.09 (0.97–1.23) | 1.13 (1.00–1.29) | 1.06 (0.92–1.21) |
| Women | 2.20 (2.00–2.43) | 2.23 (2.01–2.49) | 2.02 (1.80–2.26) |
| Abdominal obesity | |||
| Men | 1.11 (0.98–1.26) | 1.15 (1.00–1.32) | 0.96 (0.83–1.11) |
| Women | 3.86 (3.49–4.27) | 3.88 (3.47–4.34) | 3.76 (3.33–4.24) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kholmatova, K.; Krettek, A.; Leon, D.A.; Malyutina, S.; Cook, S.; Hopstock, L.A.; Løvsletten, O.; Kudryavtsev, A.V. Obesity Prevalence and Associated Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Health Behaviors in Russia and Norway. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159428
Kholmatova K, Krettek A, Leon DA, Malyutina S, Cook S, Hopstock LA, Løvsletten O, Kudryavtsev AV. Obesity Prevalence and Associated Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Health Behaviors in Russia and Norway. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(15):9428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159428
Chicago/Turabian StyleKholmatova, Kamila, Alexandra Krettek, David A. Leon, Sofia Malyutina, Sarah Cook, Laila A. Hopstock, Ola Løvsletten, and Alexander V. Kudryavtsev. 2022. "Obesity Prevalence and Associated Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Health Behaviors in Russia and Norway" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 15: 9428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159428
APA StyleKholmatova, K., Krettek, A., Leon, D. A., Malyutina, S., Cook, S., Hopstock, L. A., Løvsletten, O., & Kudryavtsev, A. V. (2022). Obesity Prevalence and Associated Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Health Behaviors in Russia and Norway. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(15), 9428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159428






