Hearing Problems in Indonesia: Attention to Hypertensive Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
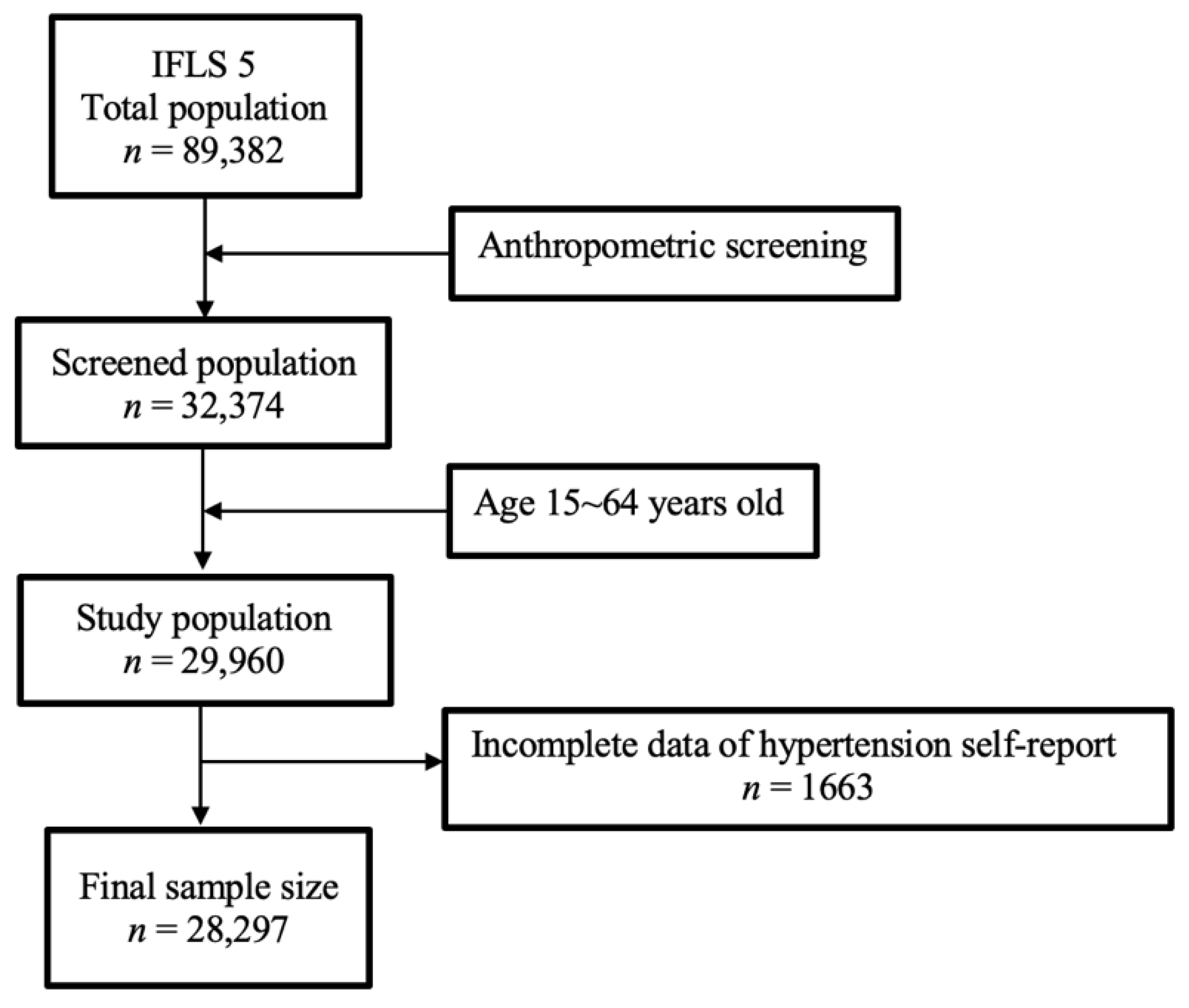
2.1. Study Population and Participants
2.2. Age Categories
2.3. Blood Pressure
2.4. Hearing Problems-Self Reported
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Population
3.2. Univariate Analysis of Hearing Problems with Demographic Data
3.3. Association of Self-Reported Hypertension and General Check-Ups with Hearing Problems in Adults
3.4. Protective Value of Self-Reported Hypertension and a General Check-Up to Hearing Problems in Early Adults
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Costs of Unaddressed Hearing Loss and Cost-Effectiveness of Interventions: A WHO Report, 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Addressing the Rising Prevalence of Hearing Loss; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Miyata, J.; Umesawa, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Iso, H. Association between high systolic blood pressure and objective hearing impairment among Japanese adults: A facility-based retrospective cohort study. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graydon, K.; Waterworth, C.; Miller, H.; Gunasekera, H. Global burden of hearing impairment and ear disease. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2019, 133, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, A.; Harper, M.; Pedersen, E.; Goman, A.; Suen, J.J.; Price, C.; Applebaum, J.; Hoyer, M.; Lin, F.R.; Reed, N.S. Hearing Loss, Loneliness, and Social Isolation: A Systematic Review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 162, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haile, L.M.; Kamenov, K.; Briant, P.S.; Orji, A.U.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Abdoli, A.; Rao, C.R. Hearing loss prevalence and years lived with disability, 1990-2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2021, 397, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboubi, H.; Lin, H.W.; Bhattacharyya, N. Prevalence, Characteristics, and Treatment Patterns of Hearing Difficulty in the United States. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, T.C.; Duffy, M.T.; Rogers, D.J. Hearing Loss in Adults: Differential Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 98–108. [Google Scholar]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Aparicio, H.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2021 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e254–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Danaei, G.; Riley, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Stevens, G.A.; Breckenkamp, J. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bu, X.; Wei, L.; Wang, X.; Lai, L.; Dong, C.; Ma, A.; Wang, T. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases attributable to hypertension in young adults from 1990 to 2019. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.Y.; Cheng, H.M.; Chuang, S.Y.; Chia, Y.C.; Soenarta, A.A.; Minh, H.V.; Siddique, S.; Turana, Y.; Tay, J.C.; Kario, K.; et al. Isolated systolic hypertension in Asia. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 23, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verulava, T.; Mikiashvili, G. Knowledge, awareness, attitude and medication compliance in patients with hypertension. Arterial. Hypertens. 2021, 25, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.E.; Lan, N.S.R.; Knuiman, M.W.; Divitini, M.L.; Swanepoel, D.W.; Hunter, M.; Brennan-Jones, C.G.; Hung, J.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Santa Maria, P.L. Associations between cardiovascular disease and its risk factors with hearing loss-A cross-sectional analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Okada, M.; Takagi, D.; Tanaka, K.; Senba, H.; Teraoka, M.; Yamada, H.; Matsuura, B.; Hato, N.; Miyake, Y. Association between hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes and prevalence of hearing impairment in Japan. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trune, D.R. Ion homeostasis in the ear: Mechanisms, maladies, and management. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 18, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Mishra, A.; Jagade, M.; Kasbekar, V.; Nagle, S.K. Effects of hypertension on hearing. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 65, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Evans, J.C.; Larson, M.G.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Levy, D. Differential impact of systolic and diastolic blood pressure level on JNC-VI staging. Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension 1999, 34, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Cheng, H.M.; Chou, P.; Chen, C.H. Prevalence of Isolated Systolic Hypertension and the Awareness, Treatment, and Control Rate of Hypertension in Kinmen. Acta. Cardiol. Sin. 2006, 22, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, J.; Witoelar, F.; Sikoki, B. The Fifth Wave of the Indonesia Family Life Survey (IFLS5): Overview and Field Report; Rand: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1953–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Report on Hearing; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Hoffman, H.J.; Dobie, R.A.; Losonczy, K.G.; Themann, C.L.; Flamme, G.A. Declining Prevalence of Hearing Loss in US Adults Aged 20 to 69 Years. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage-Morin, P.L.; Gilmour, H.; Banks, R.; Pineault, D.; Atrach, M. Hypertension associated with hearing health problems among Canadian adults aged 19 to 79 years. Health Rep. 2021, 32, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.U.; Vinayak, S.; Rivera, E.; Elahi, K.; Tahir, H.; Ahuja, V.; Jogezai, S.; Maher, W.; Naz, S. Association Between Hypertension and Hearing Loss. Cureus 2021, 13, e18025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yikawe, S.S.; Uguru, S.U.; Solomon, J.H.; Adamu, A.M.; Damtong, F.; Osisi, K.; Adeyeye, F.M. Hearing loss among hypertensive patients. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 35, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samelli, A.G.; Santos, I.S.; Padilha, F.; Gomes, R.F.; Moreira, R.R.; Rabelo, C.M.; Matas, C.G.; Bensenor, I.M.; Lotufo, P.A. Hearing loss, tinnitus, and hypertension: Analysis of the baseline data from the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Clinics 2021, 76, e2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Song, Y.; Cai, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, X. Blood Pressure Variability Is Associated with Hearing and Hearing Loss: A Population-Based Study in Males. Int. J. Hypertens. 2019, 2019, 9891025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umesawa, M.; Sairenchi, T.; Haruyama, Y.; Nagao, M.; Kobashi, G. Association between hypertension and hearing impairment in health check-ups among Japanese workers: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, B.M.; Curhan, S.G.; Wang, M.; Eavey, R.; Stankovic, K.M.; Curhan, G.C. Hypertension, Diuretic Use, and Risk of Hearing Loss. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peltzer, K.; Pengpid, S. The Prevalence and Social Determinants of Hypertension among Adults in Indonesia: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based National Survey. Int. J. Hypertens. 2018, 2018, 5610725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, H.; Barton, M.J.; Johnston, A.N.B. Isolated systolic hypertension in young males: A scoping review. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 27, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Gao, X.; Bao, L.; Shan, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, Y. The different risk factors for isolated diastolic hypertension and isolated systolic hypertension: A national survey. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N Total | Prevalence of Hearing Problems (%) | Hearing Problems | X2 | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | |||||
| Age group (years) | ||||||||
| 15~25 | 7452 | 0.48 | 7416 | 26.4 | 36 | 16.4 | 50.815 | 0.000 |
| 26~35 | 8179 | 0.48 | 8139 | 29 | 40 | 18.2 | ||
| 36~45 | 6193 | 0.85 | 6140 | 21.9 | 53 | 24.1 | ||
| 46~64 | 6473 | 1.4 | 6382 | 22.7 | 91 | 41.4 | ||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male | 13,147 | 0.85 | 13,034 | 46.4 | 113 | 51.4 | 2.14 | 0.143 |
| Female | 15,150 | 0.7 | 15,043 | 53.6 | 107 | 48.6 | ||
| Blood pressure | ||||||||
| AHA 2017 | ||||||||
| Normal | 11,153 | 0.63 | 11,082 | 39.5 | 71 | 32.3 | 4.741 | 0.093 |
| Elevated | 4301 | 0.86 | 4264 | 15.2 | 37 | 16.8 | ||
| Hypertensive | 12,843 | 0.87 | 12,731 | 45.3 | 112 | 50.9 | ||
| INAHS 2019 | ||||||||
| Non-isolated systolic hypertensive | 26,510 | 0.75 | 26,311 | 93.7 | 199 | 90.5 | 3.911 | 0.048 |
| Isolated systolic hypertensive | 1787 | 1.17 | 1766 | 6.3 | 21 | 9.5 | ||
| Hypertension medication | ||||||||
| Yes | 581 | 2.92 | 465 | 2 | 17 | 7.7 | 35.49 | 0.000 |
| No | 27,716 | 0.73 | 27,513 | 98 | 203 | 92.3 | ||
| Self-reported hypertension | ||||||||
| Yes | 3004 | 1.96 | 2945 | 10.5 | 59 | 26.8 | 61.34 | 0.000 |
| No | 25,293 | 0.63 | 25,132 | 89.5 | 161 | 73.2 | ||
| Body mass index group | ||||||||
| Underweight | 3366 | 0.38 | 3353 | 11.9 | 13 | 5.9 | 7.76 | 0.053 |
| Normal | 15,856 | 0.83 | 15,723 | 56 | 133 | 60.5 | ||
| Overweight–mild | 3543 | 0.79 | 3515 | 12.5 | 28 | 12.7 | ||
| Overweight–severe | 5532 | 0.83 | 5486 | 19.5 | 46 | 20.9 | ||
| Education | ||||||||
| No schooling | 7920 | 0.77 | 7859 | 28 | 61 | 27.7 | 1.88 | 0.39 |
| Senior high school or lower | 17,664 | 0.75 | 17,532 | 62.4 | 132 | 60 | ||
| Above senior high school | 2713 | 0.99 | 2686 | 9.6 | 27 | 12.3 | ||
| Occupation | ||||||||
| Working | 19,474 | 0.87 | 19,304 | 68.8 | 170 | 77.3 | 7.38 | 0.007 |
| Not working | 8823 | 0.57 | 8773 | 31.2 | 50 | 22.7 | ||
| General check-up | ||||||||
| Yes | 2514 | 1.63 | 2473 | 8.8 | 41 | 18.6 | 26.05 | 0.000 |
| No | 25,783 | 0.69 | 25,604 | 91.2 | 179 | 81.4 | ||
| Outpatient care | ||||||||
| Yes | 5015 | 1.12 | 4959 | 17.7 | 56 | 25.5 | 9.09 | 0.003 |
| No | 23,282 | 0.7 | 23,118 | 82.3 | 164 | 74.5 | ||
| Insurance ownership | ||||||||
| Yes | 14,183 | 0.8 | 14,069 | 50.1 | 114 | 51.8 | 0.25 | 0.613 |
| No | 14,114 | 0.75 | 14,008 | 49.9 | 106 | 48.2 | ||
| Hearing aid usage | ||||||||
| Yes | 19 | 0 | 19 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.7 |
| No | 28,278 | 0.78 | 28,058 | 99.9 | 220 | 100 | ||
| Predictor | Coef. | SE Coef. | Wald | p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age group (years) | |||||||
| 15~25 | −0.576 | 0.217 | 7.057 | 0.008 | 0.562 | 0.368 | 0.86 |
| 26~35 | −0.563 | 0.21 | 7.185 | 0.007 | 0.569 | 0.377 | 0.859 |
| 36~45 | 1.0 | ||||||
| 46~64 | 0.502 | 0.174 | 8.348 | 0.004 | 1.652 | 1.175 | 2.322 |
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 0.198 | 0.135 | 2.136 | 0.144 | 1.219 | 0.935 | 1.589 |
| Female | 1.0 | ||||||
| Blood pressure | |||||||
| AHA 2017 | |||||||
| Normal | 1.0 | ||||||
| Elevated | 0.303 | 0.204 | 2.221 | 0.136 | 1.354 | 0.909 | 2.018 |
| Hypertensive | 0.317 | 0.152 | 4.338 | 0.037 | 1.373 | 1.019 | 1.851 |
| INAHS 2019 | |||||||
| Non-isolated systolic hypertensive | 1.0 | ||||||
| Isolated systolic hypertensive | 0.452 | 0.231 | 3.845 | 0.05 | 1.572 | 1.0 | 2.471 |
| Hypertension medication | |||||||
| Yes | 1.407 | 0.256 | 30.212 | 0.000 | 4.085 | 2.473 | 6.748 |
| No | 1.0 | ||||||
| Self-reported hypertension | |||||||
| Yes | 1.140 | 0.153 | 55.225 | 0.000 | 3.127 | 2.315 | 4.224 |
| No | 1.0 | ||||||
| Body mass index group | |||||||
| Underweight | −0.771 | 0.315 | 6.001 | 0.014 | 0.462 | 0.249 | 0.857 |
| Normal | 0.009 | 0.172 | 0.003 | 0.959 | 1.009 | 0.72 | 1.413 |
| Overweight–mild | −0.051 | 0.241 | 0.43 | 0.831 | 0.95 | 0.593 | 1.523 |
| Overweight–severe | 1.0 | ||||||
| Educational level | |||||||
| No schooling | −0.259 | 0.232 | 1.24 | 0.266 | 0.772 | 0.49 | 1.217 |
| Senior high school or lower | −0.289 | 0.212 | 1.854 | 0.173 | 0.749 | 0.494 | 1.135 |
| Above senior high school | 1.0 | ||||||
| Occupation | |||||||
| Working | 0.435 | 0.161 | 7.269 | 0.007 | 1.545 | 1.126 | 2.12 |
| Not working | 1.0 | ||||||
| General check-up | |||||||
| Yes | 0.864 | 0.174 | 24.511 | 0.000 | 2.371 | 1.685 | 3.338 |
| No | 1.0 | ||||||
| Outpatient care | |||||||
| Yes | 0.465 | 0.156 | 8.931 | 0.003 | 1.592 | 1.174 | 2.159 |
| No | 1.0 | ||||||
| Insurance ownership | |||||||
| Yes | 0.068 | 0.135 | 0.255 | 0.614 | 1.071 | 0.821 | 1.396 |
| No | 1.0 |
| Predictor | Model 1 | Model 2 | Full Model | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | ||
| (Constant) | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.005 | |||||||
| Age (years) * AHA category | |||||||||||||
| 1 | (15~25) * Normal BP | 0.45 | 0.783 | 0.414 | 1.478 | 0.339 | 0.733 | 0.388 | 1.386 | 0.461 | 0.787 | 0.417 | 1.488 |
| 2 | (15~25) * Elevated BP | 0.335 | 0.648 | 0.268 | 1.567 | 0.288 | 0.619 | 0.256 | 1.499 | 0.325 | 0.642 | 0.265 | 1.552 |
| 3 | (15~25) * Hypertension | 0.036 | 0.391 | 0.162 | 0.941 | 0.041 | 0.399 | 0.166 | 0.961 | 0.04 | 0.398 | 0.165 | 0.959 |
| 4 | (26~35) * Normal BP | 0.1 | 0.584 | 0.308 | 1.108 | 0.084 | 0.568 | 0.3 | 1.078 | 0.103 | 0.587 | 0.309 | 1.114 |
| 5 | (26~35) * Elevated BP | 0.037 | 0.315 | 0.107 | 0.931 | 0.044 | 0.329 | 0.111 | 0.972 | 0.042 | 0.325 | 0.11 | 0.961 |
| 6 | (26~35) * Hypertension | 0.078 | 0.551 | 0.284 | 1.068 | 0.136 | 0.604 | 0.312 | 1.171 | 0.091 | 0.564 | 0.291 | 1.095 |
| 7 | (36~45) * Normal BP | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||||
| 8 | (36~45) * Elevated BP | 0.984 | 1.027 | 0.461 | 2.288 | 0.781 | 1.12 | 0.503 | 2.496 | 0.855 | 1.077 | 0.483 | 2.402 |
| 9 | (36~45) * Hypertension | 0.305 | 0.727 | 0.395 | 1.337 | 0.593 | 0.848 | 0.462 | 1.554 | 0.344 | 0.745 | 0.405 | 1.371 |
| 10 | (46~64) * Normal BP | 0.799 | 1.102 | 0.52 | 2.335 | 0.808 | 1.097 | 0.518 | 2.324 | 0.836 | 1.083 | 0.511 | 2.294 |
| 11 | (46~64) * Elevated BP | 0.019 | 2.23 | 1.144 | 4.346 | 0.012 | 2.36 | 1.212 | 4.593 | 0.023 | 2.165 | 1.11 | 4.224 |
| 12 | (46~64) * Hypertension | 0.562 | 1.174 | 0.683 | 2.016 | 0.094 | 1.568 | 0.926 | 2.654 | 0.562 | 1.174 | 0.683 | 2.018 |
| Gender | 0.108 | 1.273 | 0.949 | 1.709 | 0.365 | 1.146 | 0.854 | 1.537 | 0.128 | 1.259 | 0.936 | 1.692 | |
| Body mass index group | |||||||||||||
| Underweight | 0.115 | 0.592 | 0.309 | 1.136 | 0.101 | 0.58 | 0.303 | 1.112 | 0.164 | 0.63 | 0.328 | 1.208 | |
| Normal | 0.401 | 1.165 | 0.815 | 1.666 | 0.481 | 1.137 | 0.796 | 1.623 | 0.265 | 1.226 | 0.857 | 1.755 | |
| Overweight–mild | 0.936 | 0.981 | 0.61 | 1.577 | 0.848 | 0.954 | 0.594 | 1.535 | 0.974 | 0.992 | 0.617 | 1.596 | |
| Overweight–severe | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||||||||
| Self-reported hypertension | 0.000 | 2.715 | 1.948 | 3.785 | 0.000 | 2.48 | 1.77 | 3.474 | |||||
| General check-up | 0.000 | 2.192 | 1.54 | 3.121 | 0.000 | 1.976 | 1.384 | 2.821 | |||||
| Outpatient care | 0.066 | 1.343 | 0.981 | 1.839 | |||||||||
| Education | |||||||||||||
| No schooling | 0.157 | 0.712 | 0.444 | 1.14 | 0.49 | 0.844 | 0.521 | 1.366 | 0.487 | 0.843 | 0.521 | 1.364 | |
| Senior high school or lower | 0.266 | 0.788 | 0.517 | 1.199 | 0.586 | 0.888 | 0.58 | 1.361 | 0.604 | 0.893 | 0.583 | 1.369 | |
| Above senior high school | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||||||||
| Occupation | 0.257 | 1.225 | 0.862 | 1.742 | 0.362 | 1.179 | 0.828 | 1.678 | 0.242 | 1.233 | 0.868 | 1.753 | |
| Insurance ownership | 0.631 | 1.067 | 0.818 | 1.393 | 0.651 | 1.063 | 0.815 | 1.388 | 0.685 | 1.057 | 0.809 | 1.379 | |
| Predictors | Coef. | SE Coef. | Wald | p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * INASH-isosysht | ||||||||
| 1 | (15~25) * Non-isosysht | −0.315 | 0.232 | 1.849 | 0.174 | 0.73 | 0.463 | 1.149 |
| 2 | (15~25) * Isosysht | −16.398 | 2764.809 | 0.000 | 0.995 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - |
| 3 | (26~35) * Non-isosysht | −0.511 | 0.215 | 5.641 | 0.018 | 0.6 | 0.394 | 0.915 |
| 4 | (26~35) * Isosysht | −0.667 | 1.014 | 0.433 | 0.511 | 0.513 | 0.07 | 3.745 |
| 5 | (36~45) * Non-isosysht | 1.0 | ||||||
| 6 | (36~45) * Isosysht | −0.36 | 0.724 | 0.246 | 0.62 | 0.698 | 0.169 | 2.887 |
| 7 | (46~64) * Non-isosysht | 0.337 | 0.19 | 3.156 | 0.076 | 1.401 | 0.966 | 2.032 |
| 8 | (46~64) * Isosysht | 0.526 | 0.284 | 3.419 | 0.064 | 1.692 | 0.969 | 2.954 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fitriana, M.; Bai, C.-H. Hearing Problems in Indonesia: Attention to Hypertensive Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159222
Fitriana M, Bai C-H. Hearing Problems in Indonesia: Attention to Hypertensive Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(15):9222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159222
Chicago/Turabian StyleFitriana, Melysa, and Chyi-Huey Bai. 2022. "Hearing Problems in Indonesia: Attention to Hypertensive Adults" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 15: 9222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159222
APA StyleFitriana, M., & Bai, C.-H. (2022). Hearing Problems in Indonesia: Attention to Hypertensive Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(15), 9222. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19159222






