Listening to White Noise Improved Verbal Working Memory in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test-Revised Edition
2.3.2. Test of Nonverbal Intelligence, Third Edition
2.3.3. Chinese Version of the SNAP-IV Parent Rating Scale
2.3.4. Digit Span Test
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
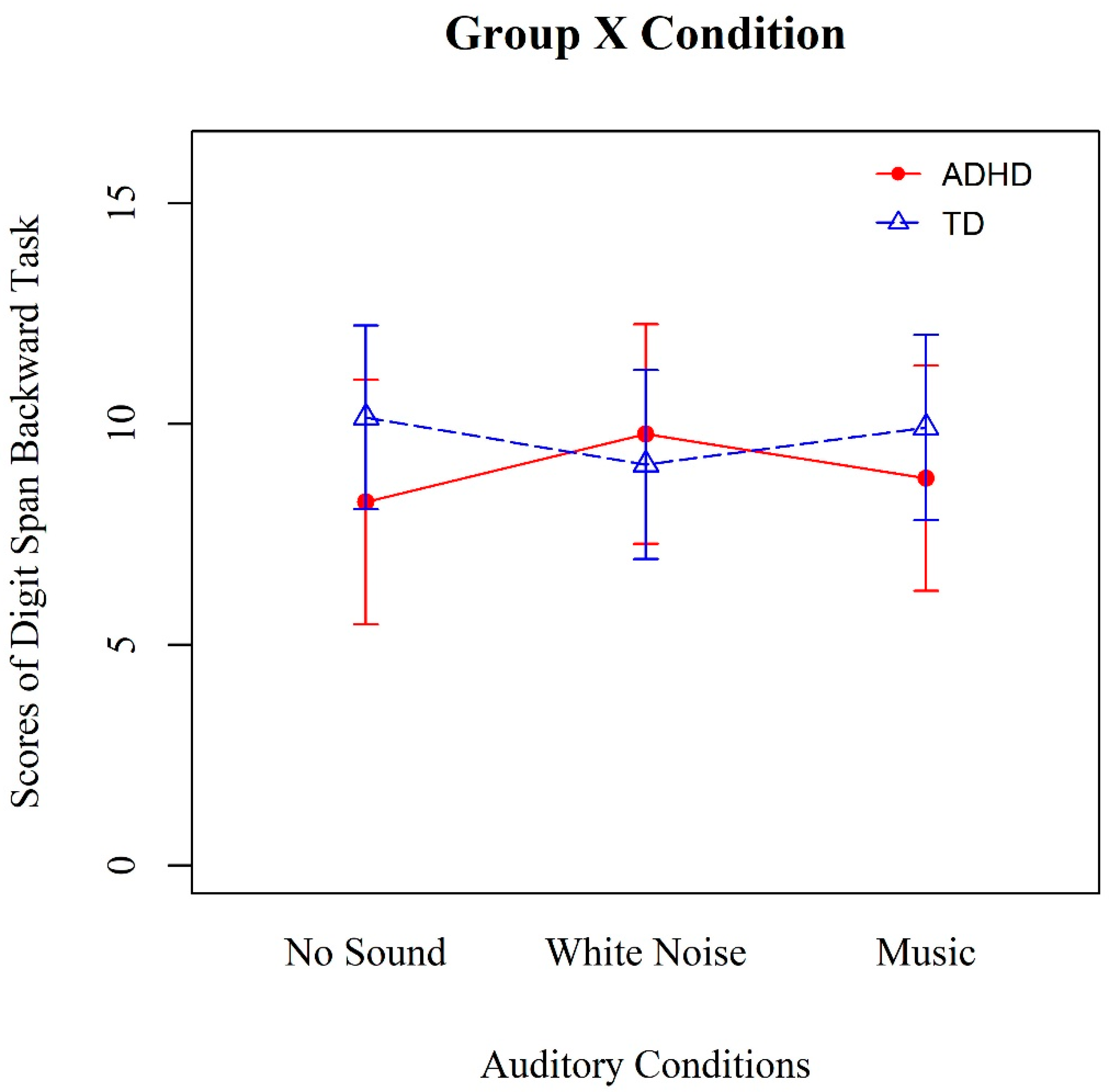
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Verbal Working Memory Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatry Association. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatry Association: Arlington, TX, USA, 2013; pp. 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Martinussen, R.; Hayden, J.; Hogg-Johnson, S.; Tannock, R. A Meta-Analysis of Working Memory Impairments in Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2005, 44, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pievsky, M.; McGrath, R. The Neurocognitive Profile of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Review of Meta-Analyses. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2017, 33, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubia, K. Cognitive Neuroscience of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Its Clinical Translation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayal, K.; Prasad, V.; Daley, D.; Ford, T.; Coghill, D. ADHD in Children and Young People: Prevalence, Care Pathways, and Service Provision. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyandt, L.; Gudmundsodottir, B. Developmental and Neuropsychological Deficits in Children with ADHD. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment, 4th ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 116–139. [Google Scholar]
- Baddeley, A. The Episodic Buffer: A New Component of Working Memory? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A. Working Memory: Looking Back and Looking Forward. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddeley, A. Working Memory. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R136–R140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaroslawska, A.J.; Gathercole, S.E.; Logie, M.R.; Holmes, J. Following Instructions in a Virtual School: Does Working Memory Play a Role? Mem. Cognit. 2016, 44, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kofler, M.; Sarver, D.; Spiegel, J.; Day, T.; Harmon, S.; Wells, E. Heterogeneity in ADHD: Neurocognitive Predictors of Peer, Family, and Academic Functioning. Child Neuropsychol. 2017, 23, 733–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, S.; Coghill, D. Twenty Years of Research on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Looking Back, Looking Forward. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2018, 21, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.; Östlund, P.; Wallgren, L.; Österberg, M.; Tranæus, S. Top Ten Research Priorities for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Treatment. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2016, 32, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisk, A.; Tam, S.; Brown, L.; Vyazovskiy, V.; Bannerman, D.; Peirson, S. Light and Cognition: Roles for Circadian Rhythms, Sleep, and Arousal. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badgaiyan, R.D.; Sinha, S.; Sajjad, M.; Wack, D. Attenuated Tonic and Enhanced Phasic Release of Dopamine in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barkley, R. Etiologies of ADHD. In Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment, 4th ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 356–390. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, R.; Johnstone, S.; Clarke, A. A Review of Electrophysiology in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: II. Event-Related Potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Couture, J. A Review of the Pathophysiology, Etiology, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikström, S.; Söderlund, G. Stimulus-Dependent Dopamine Release in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 114, 1047–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zentall, S.; Zentall, T. Optimal Stimulation: A Model of Disordered Activity and Performance in Normal and Deviant Children. Psychol. Bull. 1983, 94, 446–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, G.; Isen, A.; Turken, A. A Neuropsychological Theory of Positive Affect and Its Influence on Cognition. Psychol. Rev. 1999, 106, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, G.; Sikström, S.; Smart, A. Listen to the Noise: Noise Is Beneficial for Cognitive Performance in ADHD. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2007, 48, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abikoff, H.; Courtney, M.; Szeibel, P.; Koplewicz, H. The Effects of Auditory Stimulation on the Arithmetic Performance of Children with ADHD and Nondisabled Children. J. Learn. Disabil. 1996, 29, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.F.; Schellenberg, G.; Husain, G. Arousal, Mood, and The Mozart Effect. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 12, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baijot, S.; Slama, H.; Söderlund, G.; Dan, B.; Deltenre, P.; Colin, C.; Deconinck, N. Neuropsychological and Neurophysiological Benefits from White Noise in Children with and without ADHD. Behav. Brain Funct. BBF 2016, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Söderlund, G.; Jobs, E.N. Differences in Speech Recognition Between Children with Attention Deficits and Typically Developed Children Disappear When Exposed to 65 DB of Auditory Noise. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cook, A.; Bradley-Johnson, S.; Johnson, M. Effects of White Noise on Off-Task Behavior and Academic Responding for Children with ADHD: WHITE NOISE AND ADHD. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 2014, 47, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helps, S.; Bamford, S.; Sonuga-Barke, E.; Söderlund, G. Different Effects of Adding White Noise on Cognitive Performance of Sub-, Normal and Super-Attentive School Children. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Söderlund, G.; Sikström, S.; Loftesnes, J.; Sonuga-Barke, E. The Effects of Background White Noise on Memory Performance in Inattentive School Children. Behav. Brain Funct. 2010, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-K.; Shang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Tu, C.-L.; Gau, S.-F. Norm of the Chinese Version of the Swanson, Nolan and Pelham, Version IV Scale for ADHD. Taiwan. J. Psychiatry 2006, 20, 290–304. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Liu, H. Manual of Chinese Version of Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test, Revised ed.; Psychological Publishing: Taiwan, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Hu, H.; Tsai, C.; Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Kuo, C. Manual of Chinese Version of Test of Nonverbal Intelligence, 3rd ed.; Psychological Publishing: Taiwan, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Chen, H. Manual of Chinese Version of Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 4th ed.; Chinese Behavioral Science: Taiwan, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pickens, T.; Khan, S.; Berlau, D. White Noise as a Possible Therapeutic Option for Children with ADHD. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 42, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiero, M.; Nori, R.; Rogolino, C.; D’Amico, S.; Piccardi, L. Situated Mavigational Working Memory: The Role of Positive Mood. Cogn Process. 2015, 16 (Suppl. 1), S327–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, T.; Dromey, C.; Nelson, B.; Chapman, K. Effects of Background Noise on Speech and Language in Young Adults. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2021, 64, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | ADHD (n = 13) | TD (n = 13) | t/χ2 | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) [M(SD)] | 8.25 | (1.22) | 8.42 | (1.28) | 0.36 | 0.27 |
| VIQ [M(SD)] | 114.54 | (13.06) | 106.92 | (11.85) | 1.56 | 0.71 |
| NVIQ [M(SD)] | 98.15 | (15.06) | 94.77 | (9.23) | 0.69 | 0.28 |
| SNAP-IV scores | ||||||
| Inattention [M(SD)] | 16.46 | (4.24) | 7.46 | (5.17) | 4.85 *** | 1.92 |
| Impulsivity [M(SD)] | 12.69 | (5.76) | 5.69 | (4.63) | 3.42 ** | 1.62 |
| Enjoyment in music a [M(SD)] | 8.82 | (2.16) | 8.87 | (1.31) | 0.07 | 0.54 |
| Learn musical instrument b (n) | 10 | 11 | 0.25 | |||
| Listen to music c (n) | 2 | 6 | 2.89 | |||
| Source | df | Mean Square | F | Effect Size (ŋ2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | 2 | 1.74 | 0.54 | 0.02 |
| Group | 1 | 11.32 | 1.02 | 0.04 |
| Condition × Group | 2 | 13.39 | 4.19 * | 0.16 |
| Error | 44 | 3.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, I.-C.; Chan, H.-Y.; Lin, K.-C.; Huang, Y.-T.; Tsai, P.-L.; Huang, Y.-M. Listening to White Noise Improved Verbal Working Memory in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127283
Chen I-C, Chan H-Y, Lin K-C, Huang Y-T, Tsai P-L, Huang Y-M. Listening to White Noise Improved Verbal Working Memory in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(12):7283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127283
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, I-Chen, Hsun-Yu Chan, Keh-Chung Lin, Yu-Ting Huang, Pei-Luen Tsai, and Yen-Ming Huang. 2022. "Listening to White Noise Improved Verbal Working Memory in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 12: 7283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127283
APA StyleChen, I.-C., Chan, H.-Y., Lin, K.-C., Huang, Y.-T., Tsai, P.-L., & Huang, Y.-M. (2022). Listening to White Noise Improved Verbal Working Memory in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(12), 7283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127283






