Contamination of Fresh Produce with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Associated Risks to Human Health: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
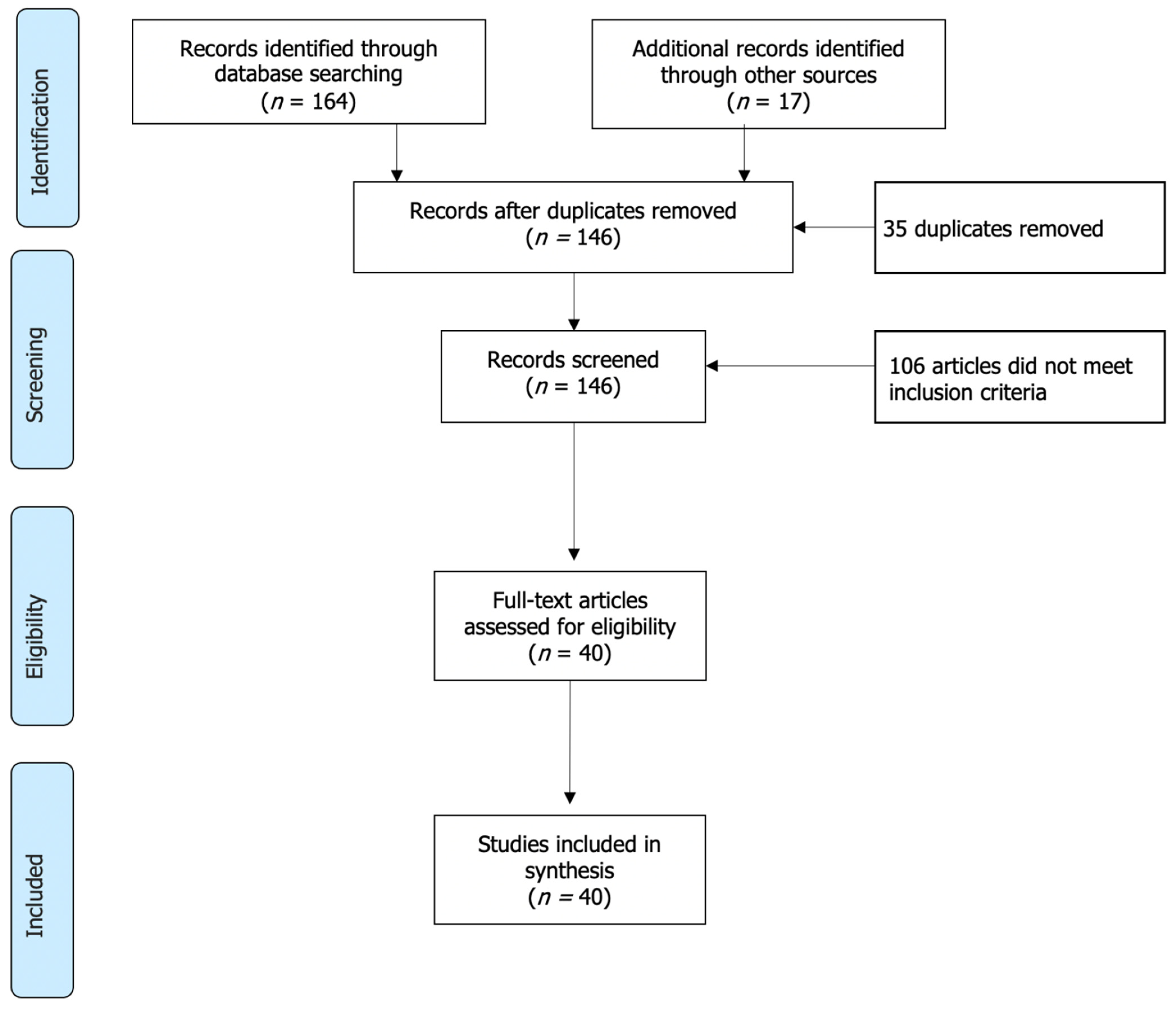
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Search Strategies
2.3. Screening, Data Extraction and Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria on Fresh Produce
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance Genes on Fresh Produce
3.3. Potential for Adverse Health Outcomes from the Consumption of Fresh Produce Contaminated with ARB/ARGs
3.4. Pathways of Contamination of Fresh Produce with ARB
3.5. Recommendations to Reduce Contamination of Fresh Produce with ARB
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Promoting Fruit and Vegetable Consumption around the World. 2003. Available online: https://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/fruit/en/ (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Darmon, N.; Darmon, M.; Maillot, M.; Drewnowski, A. A nutrient density standard for vegetables and fruits: Nutrients per calorie and nutrients per unit cost. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzel, C.S.; Tetens, J.L.; Schwaiger, K. Unraveling the Role of Vegetables in Spreading Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria: A Need for Quantitative Risk Assessment. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulger, T.G.; Songur, A.N.; Cirak, O.; Cakiroglu, F.P. Role of Vegetable in Human Nutrition and Disease Prevention. Veg. Importance Qual. Veg. Hum. Health 2018, 7–32. [Google Scholar]
- Founou, L.L.; Founou, R.C.; Essack, S.Y. Antimicrobial resistance in the farm-to-plate continuum: More than a food safety issue. Future Sci. OA 2021, 7, FSO692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, A.H.A.M.v.; Veenman, C.; van Overbeek, W.M.; Lynch, G.; Husman, A.M.d.R.; Blaak, H. Prevalence and characterization of ESBL- and AmpC-producing Enterobacteriaceae on retail vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, F.; Mercanoglu Taban, B. A State-of-Art Review on Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens in Foods of Animal Origin: Risk Factors and Mitigation Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, M.; Ozeki, K.; Komatsu, T.; Fukuda, A.; Tamura, Y. Prevalence of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase–Producing Bacteria on Fresh Vegetables in Japan. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1663–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abatcha, M.G.; Effarizah, M.E.; Rusul, G. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, resistance genes and class 1 integrons of Salmonella serovars in leafy vegetables, chicken carcasses and related processing environments in Malaysian fresh food markets. Food Control 2018, 91, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janalíková, M.; Pleva, P.; Pavlíčková, S.; Lecomte, M.; Godillon, T.; Holko, I. Characterization of Escherichia coli strains isolated from raw vegetables. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2018, 12, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, C.; Michael, G.B.; Li, J.; Kadlec, K.; Wang, Y.; Hassel, M.; Schwarz, S. Occurrence and characterisation of ESBL-encoding plasmids among Escherichia coli isolates from fresh vegetables. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A. Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria from U.S.-Grown and Imported Fresh Produce Retailed in Chain Supermarkets and Ethnic Stores of Davidson County, Tennessee. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanson, G.S.; MacInnis, R.; Potter, G.; Hughes, T. Presence and potential for horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance in oxidase-positive bacteria populating raw salad vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 127, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylis, C.; Uyttendaele, M.; Joosten, H.; Davies, A. The Enterobacteriaceae and their significance to the food industry. Enterobact. Signif. Food Ind. 2011, 52, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Österblad, M.; Pensala, O.; Peterzéns, M.; Heleniusc, H.; Huovinen, P. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from vegetables. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1999, 43, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Kharousi, Z.S.; Guizani, N.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Al-Bulushi, I.M.; Shaharoona, B. Hiding in Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: Opportunistic Pathogens May Cross Geographical Barriers. Int. J. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 4292417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspanadan, S.; Loo, Y.; Kuan, C.H.; Goh, S.G.; Son, R.; Nillian, E.; Leili, A.; Tang, J.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Nishibuchi, M.; et al. Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae in raw vegetables using Most Probable Number-Polymerase Chain Reaction (MPN-PCR). Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Chee-Sanford, J.; Mackie, R.; Koike, S.; Krapac, I.; Lin, Y.F.; Yannarell, A.; Maxwell, S.; Aminov, R. Fate and transport of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes following land application of manure waste. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1086–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Mathieu, J.; Stadler, L.; Senehi, N.; Sun, R.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Antibiotic resistance genes from livestock waste: Occurrence, dissemination, and treatment. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Jang, H.; Matthews, K.R. Effect of the food production chain from farm practices to vegetable processing on outbreak incidence. Microb. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.S.; Eppinger, M.; Ahmed, S.; Shah, A.A.; Hameed, A.; Hasan, F. Multidrug-resistant diarrheagenic E. coli pathotypes are associated with ready-to-eat salad and vegetables in Pakistan. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2015, 58, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Cerna-Cortes, J.F.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Torres-Vitela, M.R.; Villarruel-López, A.; Gutiérrez-Alcántara, E.J.; Castro-Rosas, J. Presence of Multidrug-Resistant Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli, Enteropathogenic E. coli and Enterotoxigenic E. coli, on Raw Nopalitos (Opuntia ficus-indica L.) and in Nopalitos Salads from Local Retail Markets in Mexico. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Yao, X.; Lv, L.; Doi, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.-H. Emergence of mcr-1 in Raoultella ornithinolytica and Escherichia coli from retail vegetables, China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01139-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesbah Zekar, F.; Granier, S.A.; Touati, A.; Millemann, Y. Occurrence of Third-Generation Cephalosporins-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Purchased at Markets in Algeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 26, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saksena, R.; Malik, M.; Gaind, R. Bacterial contamination and prevalence of antimicrobial resistance phenotypes in raw fruits and vegetables sold in Delhi, India. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseppi, R.; de Niederhäusern, S.; Bondi, M.; Messi, P.; Sabia, C. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase, AmpC, and MBL-Producing Gram-Negative Bacteria on Fresh Vegetables and Ready-to-Eat Salads Sold in Local Markets. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.P.; Wang, H.; Adams, J.K.; Feng, P.C.H. Prevalence and Characteristics of Salmonella Serotypes Isolated from Fresh Produce Marketed in the United States. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, C.H.; Radzi, W.; Kuan, C.S.; New, C.; Loo, Y.; Fadzil, M.; Kwan, S.; Son, R. Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enteritidis isolated from vegetable farms and retail markets in Malaysia. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Niyomdecha, N.; Mungkornkaew, N.; Samosornsuk, W. Serotypes and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica isolated from pork, chicken meat and lettuce, bangkok and central Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2016, 47, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Najwa, M.S.; Loo, Y.; Lye, Y.; Aimi, S.; Goh, S.G.; Kuan, C.H.; Yoshitsugu, N.; Nishibuchi, M.; Son, R. Quantification and antibiotic susceptibility of Salmonella spp., Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium in raw vegetables (ulam). Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, J.M.; Mondragón, A.C.; Martinez, B.; Guarddon, M.; Rodriguez, J.A. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Salmonella from Different Raw Foods in Mexico. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allydice-Francis, K.; Brown, P.D. Diversity of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Determinants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Associated with Fresh Vegetables. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 426241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesbah Zekar, F.; Granier, S.A.; Marault, M.; Yaici, L.; Gassilloud, B.; Manceau, C.; Touati, A.; Millemann, Y. From Farms to Markets: Gram-Negative Bacteria Resistant to Third-Generation Cephalosporins in Fruits and Vegetables in a Region of North Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton-Miller, J.M.T.; Shah, S. Identity and antibiotic susceptibility of enterobacterial flora of salad vegetables. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2001, 18, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, L.L.; Jackson, C.R.; Barrett, J.B.; Hiott, L.M.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of enterococci isolated from retail fruits, vegetables, and meats. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2976–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, G.; Schneider, C.; Igbinosa, E.O.; Kabisch, J.; Brinks, E.; Becker, B.; Stoll, D.A.; Cho, G.-S.; Huch, M.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Antibiotics resistance and toxin profiles of Bacillus cereus-group isolates from fresh vegetables from German retail markets. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, L.; Du Plessis, E.M.; Duvenage, S.; Korsten, L. Occurrence, Identification, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Extended-Spectrum and AmpC β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae from Fresh Vegetables Retailed in Gauteng Province, South Africa. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vasconcelos Byrne, V.; Hofer, E.; Vallim, D.C.; de Castro Almeida, R.C. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from vegetables. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.-S.; Chon, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, M.-s.; Seo, K.-H. Prevalence and characterization of extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in ready-to-eat vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 207, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abriouel, H.; Omar, N.B.; Molinos, A.C.; López, R.L.; Grande, M.J.; Martínez-Viedma, P.; Ortega, E.; Cañamero, M.M.; Galvez, A. Comparative analysis of genetic diversity and incidence of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance among enterococcal populations from raw fruit and vegetable foods, water and soil, and clinical samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 123, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skočková, A.; Karpíšková, R.; Koláčková, I.; Cupáková, Š. Characteristics of Escherichia coli from raw vegetables at a retail market in the Czech Republic. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 167, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Shen, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.E.; Zhao, Z.; Liao, K.; Shi, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhong, R.; et al. Plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene mcr-1 in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from market retail fruits in Guangzhou, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manageiro, V.; Jones-Dias, D.; Ferreira, E.; Caniça, M. Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance (mcr-1) in Escherichia coli from Non-Imported Fresh Vegetables for Human Consumption in Portugal. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.l.; Chen, J.C.; Friesen, E.; Delaquis, P.; Allen, K.J. Microbiological Survey of Locally Grown Lettuce Sold at Farmers’ Markets in Vancouver, British Columbia. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-T.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shan, H.; Zou, M.; Song, F.-J. Colistin-Resistant mcr-Positive Enterobacteriaceae in Fresh Vegetables, an Increasing Infectious Threat in China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Siddique, M.; Rahman, M.; Bari, L.; Ferdousi, S. A study on the prevalence of heavy metals, pesticides, and microbial contaminants and antibiotics resistance pathogens in raw salad vegetables sold in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Ji, H. Antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from retail foods in northern Xinjiang, China. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2035–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Bayas Morejon, I.F.; Ferrus, M.A. Isolation, molecular identification and quinolone-susceptibility testing of Arcobacter spp. isolated from fresh vegetables in Spain. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Das, A.; Kabir, M. Incidence of antibiotic resistant pathogenic bacteria in vegetable items sold by local and super shops in Dhaka city. Stamford J. Microbiol. 2015, 4, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Chon, J.W.; Kim, H.; Om, A.S.; Seo, K.H. Comparison of the isolation rates and characteristics of Salmonella isolated from antibiotic-free and conventional chicken meat samples. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falomir, M.P.; Rico, H.; Gozalbo, D. Enterobacter and Klebsiella Species Isolated from Fresh Vegetables Marketed in Valencia (Spain) and Their Clinically Relevant Resistances to Chemotherapeutic Agents. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, E.; Wong, L.K.; Riley, L.W. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Gene Sequences in Gram-Negative Saprophytes on Retail Organic and Nonorganic Spinach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nipa, M.; Mazumdar, R.; Mahmud, M.; Md, F.; Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, H.; Iqbal, A. Prevalence of Multi Drug Resistant Bacteria on Raw Salad Vegetables Sold in Major Markets of Chittagong City, Bangladesh. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2011, 10, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Schwaiger, K.; Helmke, K.; Hölzel, C.S.; Bauer, J. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria isolated from vegetables with regards to the marketing stage (farm vs. supermarket). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 148, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, C.H.; Goh, S.G.; Loo, Y.Y.; Chang, W.S.; Lye, Y.L.; Puspanadan, S.; Tang, J.Y.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Nishibuchi, M.; Mahyudin, N.A.; et al. Prevalence and quantification of Listeria monocytogenes in chicken offal at the retail level in Malaysia. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponniah, J.; Robin, T.; Paie, M.S.; Radu, S.; Ghazali, F.M.; Kqueen, C.Y.; Nishibuchi, M.; Nakaguchi, Y.; Malakar, P.K. Listeria monocytogenes in raw salad vegetables sold at retail level in Malaysia. Food Control 2010, 21, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang Salleh, N.; Rusul, G.; Hassan, Z.; Reezal, A.; Hajar Isa, S.; Nishibuchi, M.; Radu, S. Incidence of Salmonella spp. in raw vegetables in Selangor, Malaysia. Food Control 2003, 14, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Maia, C.; Carvalho, I.; Silva, N.; André, M.; Serafini, Á. Microbiological Quality of Organic Vegetables Produced in Soil Treated with Different Types of Manure and Mineral Fertilizer. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, F.A.; Brandelli, A.; Tondo, E.C. Antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enteritidis from foods involved in human salmonellosis outbreaks in southern Brazil. New Microbiol. 2006, 29, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Singleton, I.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Sources and contamination routes of microbial pathogens to fresh produce during field cultivation: A review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, W. Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 32, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasho, R.P.; Cho, J.Y. Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faour-Klingbeil, D.; Murtada, M.; Kuri, V.; Todd, E.C.D. Understanding the routes of contamination of ready-to-eat vegetables in the Middle East. Food Control 2016, 62, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HausdorfLena; FröhlingAntje; SchlüterOliver; KlockeMichael. Analysis of the bacterial community within carrot wash water. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabašinskienė, A.; Novoslavskij, A. In-store hygiene evaluation and its relationship with microbiological indices of some foods, sold in different retail market places in Lithuania. J. Food Microbiol. Saf. Hyg. 2018, 3, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, S.; Henriques, I.S.; Leandro, S.M.; Alves, A.; Pereira, A.; Correia, A. Gulls identified as major source of fecal pollution in coastal waters: A microbial source tracking study. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, E.; Solimini, A.G.; Pantanella, F.; De Giusti, M.; Cummins, E. Human exposure to antibiotic resistant-Escherichia coli through irrigated lettuce. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Title | Contamination of fresh produce with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and associated risks to human health: a scoping review | ||
| Research question | What is the presence and abundance of ARB, ARGs and antimicrobial residues on fresh produce sold in the retail markets, and how do they affect human health? | ||
| Search Strategy | Inclusion Criteria | Studies that detect and/or quantify ARB, ARGs and antimicrobial residues on fresh produce (vegetables/leafy green/fruits) sold in retail markets (e.g., vendors, supermarkets, farmer markets) | |
| Types and abundance of antimicrobial residues present on fresh produce | |||
| Pathways for ARB, ARGs and antimicrobial residues entering fresh produce | |||
| Health risks associated with consumption of fresh vegetables, leafy greens or fruits contaminated with ARB, ARGs and antimicrobial residues | |||
| Full-text peer-reviewed journal articles and grey literature | |||
| Species: Human | |||
| Language: English | |||
| Exclusion Criteria | Articles that did not include fresh agricultural product consumption and its relationship with AMR | ||
| Articles that analysed AMR with relation to mixed or ready-to-eat salads with various dressings | |||
| AMR-related human health risks from exposures other than fresh produce | |||
| Animal-based foods (e.g., chicken, beef, pork, eggs, milk) | |||
| Animal agriculture (e.g., poultry, meat, dairy, fishery) | |||
| All types of review articles | |||
| Time Frame | 1 January 2001–18 October 2020 | ||
| Data Sources | Peer-reviewed articles | Ovid Medline, Web of Science, Hinari | |
| Grey literature | Google, Google Scholar, Proquest | ||
| Key search terms | Antimicrobial Resistance-related terms (combined by ‘OR’) (a) | Agriculture and fresh agricultural products-related terms (combined by ‘OR’) (b) | Place of items/sample collected (c) |
| Antimicrobial resistance, antimicrobial residues, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, antibiotic resistance genes, antimicrobial-resistant organisms, antibiotic-resistant pathogens, health risks | Agriculture, farming, fresh agricultural produce, fresh agriculture products, fresh vegetables, raw vegetables, salad vegetables, leafy greens, fruits | Retail markets | |
| Theme | Sub-Theme |
|---|---|
| Presence and abundance of ARB, ARGs and antimicrobial residues on fresh produce (raw consumed vegetables, fruits) sold in retail markets | Prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens on the fresh produce |
| Strains/serotypes of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria on fresh produce | |
| Antimicrobial resistance genes on fresh produce | |
| Public health risks from consuming raw agricultural products or fresh produce in relation to AMR | |
| Pathways of contamination of fresh produce with ARB/ARGs/antimicrobial residues | |
| Actions recommended to reduce the contamination of fresh produce with ARB, ARGs and antimicrobial residues |
| Pathogens | Pre-Harvesting (Number of Articles) | Post-Harvesting (Number of Articles) |
|---|---|---|
| Salmonella spp. E. coli Arcobacter spp. |
|
|
| Quinolone-resistant Salmonella spp. |
| |
| Staphlococcus aureus |
| |
| Listeria monocytogenes |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.; Alam, M.-U.; Luies, S.K.; Kamal, A.; Ferdous, S.; Lin, A.; Sharior, F.; Khan, R.; Rahman, Z.; Parvez, S.M.; et al. Contamination of Fresh Produce with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Associated Risks to Human Health: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010360
Rahman M, Alam M-U, Luies SK, Kamal A, Ferdous S, Lin A, Sharior F, Khan R, Rahman Z, Parvez SM, et al. Contamination of Fresh Produce with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Associated Risks to Human Health: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010360
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Mahbubur, Mahbub-Ul Alam, Sharmin Khan Luies, Abul Kamal, Sharika Ferdous, Audrie Lin, Fazle Sharior, Rizwana Khan, Ziaur Rahman, Sarker Masud Parvez, and et al. 2022. "Contamination of Fresh Produce with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Associated Risks to Human Health: A Scoping Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010360
APA StyleRahman, M., Alam, M.-U., Luies, S. K., Kamal, A., Ferdous, S., Lin, A., Sharior, F., Khan, R., Rahman, Z., Parvez, S. M., Amin, N., Hasan, R., Tadesse, B. T., Taneja, N., Islam, M. A., & Ercumen, A. (2022). Contamination of Fresh Produce with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Associated Risks to Human Health: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010360








