Migraine Headaches after Major Surgery with General or Neuraxial Anesthesia: A Nationwide Propensity-Score Matched Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Data
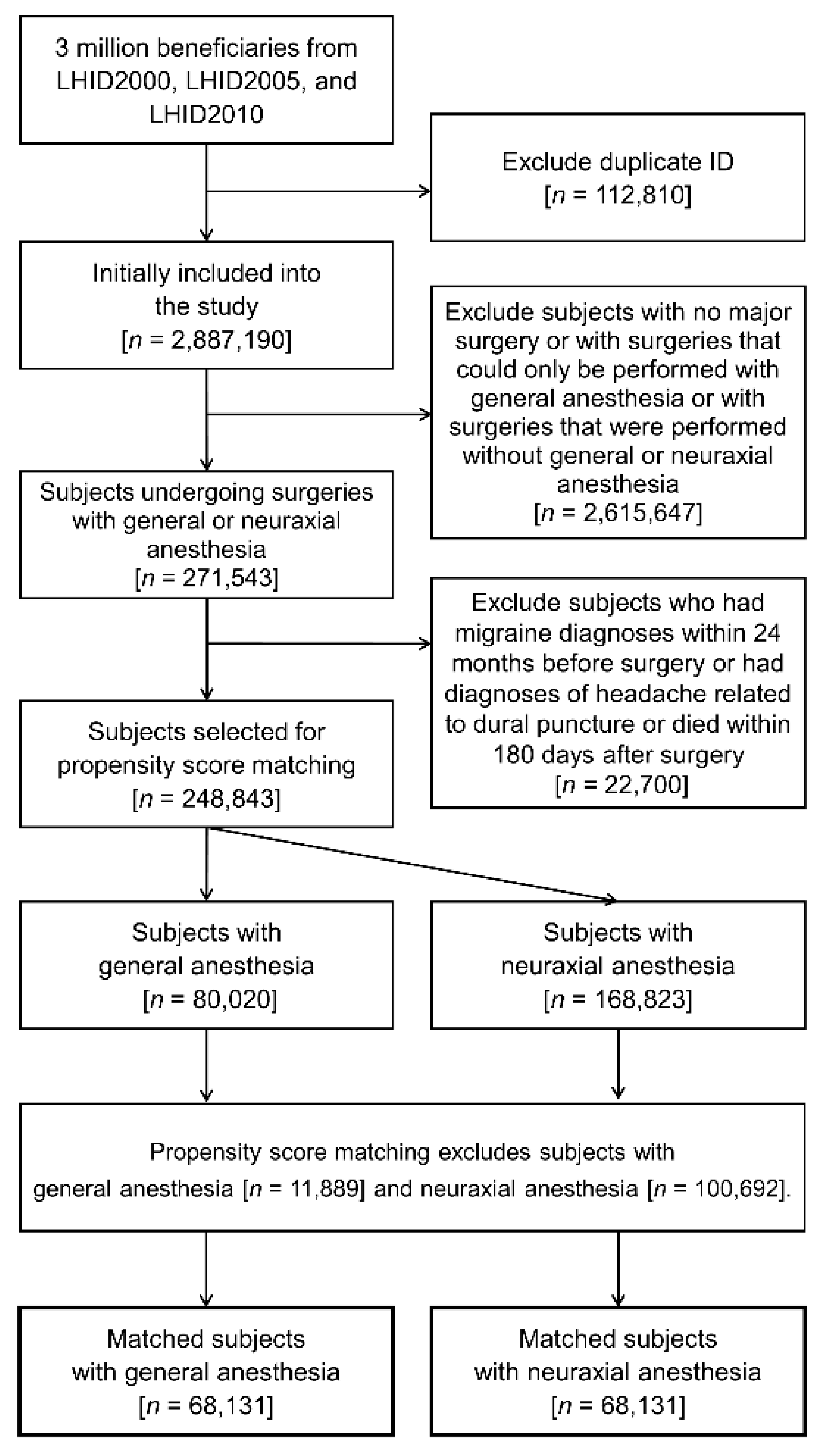
2.2. Study Population and Exposure Factors
2.3. Outcome of Interest
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient Characteristics
3.2. Risk of Postoperative Migraine Headaches
3.3. Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashina, M.; Katsarava, Z.; Do, T.P.; Buse, D.C.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Özge, A.; Krymchantowski, A.V.; Lebedeva, E.R.; Ravishankar, K.; Yu, S.; et al. Migraine: Epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet 2021, 397, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine: Epidemiology, Burden, and Comorbidity. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faithfull, N.S. Post-operative headache—A multifactorial analysis. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 1991, 8, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, V.; Olesen, J.; Gervil, M.; Russell, M.B. Possible Risk Factors and Precipitants for Migraine with Aura in Discordant Twin-Pairs: A Population-Based Study. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lim, M.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Lee, J.J.; Sohn, J.-H. Consideration of Migraines among Risk Factors for Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timm, F.P.; Houle, T.; Grabitz, S.D.; Lihn, A.-L.; Stokholm, J.B.; Eikermann-Haerter, K.; Nozari, A.; Kurth, T.; Eikermann, M. Migraine and risk of perioperative ischemic stroke and hospital readmission: Hospital based registry study. BMJ 2017, 356, i6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurth, T.; Winter, A.C.; Eliassen, A.H.; Dushkes, R.; Mukamal, K.J.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; E Manson, J.; Rexrode, K. Migraine and risk of cardiovascular disease in women: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2016, 353, i2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, D.; Ramírez, A.L.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Current understanding of meningeal and cerebral vascular function underlying migraine headache. Cephalalgia 2018, 39, 1606–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashina, M. Migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1866–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, H.; Ohata, H.; Iida, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Dohi, S. Isoflurane and Sevoflurane Induce Vasodilation of Cerebral Vessels via ATP-sensitive K+ Channel Activation. Anesthesiol. 1998, 89, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kurehara, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Kishi, K.; Einaga, T.; Kitaguchi, K.; Furuya, H. Mild hypothermia can enhance pial arteriolar vasodilation induced by isoflurane and sevoflurane in cats. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A. Propofol in the treatment of refractory migraine headaches. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piatka, C.; Beckett, R.D. Propofol for Treatment of Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 27, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurlow, J.A. Hemiplegia following general anaesthesia: An unusual presentation of migraine. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 1998, 15, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Gouveia, R.; Wilkinson, P.A.; Kaube, H. Severe hemiplegic migraine attack precipitated by fentanyl sedation for esophagogastroscopy. Neurology 2004, 63, 2446–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Adey, C. Presentation of Hemiplegic Migraine—Hemiplegia and Hemi-Sensory Loss following General Anaesthesia. Anaesth. Intensiv. Care 2007, 35, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianezza, A.; Barthélémy, R.; Minville, V.; Martin, F.; Faggianelli, M. Migraine with Atypical Aura in the Recovery Room: A Sometimes Complicated Diagnosis! Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, J.; Kapur, S. Apnoeic spells following general anaesthesia in a patient with familial hemiplegic migraine. Anaesthesia 2007, 62, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levo, H.; Blomstedt, G.; Hirvonen, T.; Pyykko, I. Causes of persistent postoperative headache after surgery for vestibular schwannoma. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2001, 26, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkvold, B.K.R.; Sagberg, L.M.; Jakola, A.S.; Solheim, O. Preoperative and Postoperative Headache in Patients with Intracranial Tumors. World Neurosurg. 2018, 115, e322–e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraghavan, L.; Li, L.; Bailey, T.; Manninen, P.H.; Tymianski, M. Sumatriptan improves postoperative quality of recovery and reduces postcraniotomy headache after cranial nerve decompression. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.-X.; Tai, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, M.-H. Bidirectional Association between Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Dermatology 2021, 237, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Dai, Y.-X.; Tai, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, T.-J. Increased risk of alopecia areata among patients with endometriosis: A longitudinal study in Taiwan. Dermatol. Sin. 2021, 39, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wu, M.-Y.; Chang, W.-J.; Chen, J.-T.; Cherng, Y.-G.; Chen, T.-J.; Dai, Y.-X.; Wu, H.-L.; et al. Association between Dental Scaling and Reduced Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-M.; Kuo, H.-C.; Li, C.-C.; Wu, H.-L.; Chen, J.-T.; Cherng, Y.-G.; Chen, T.-J.; Dai, Y.-X.; Liu, H.-Y.; Tai, Y.-H. Preexisting Dementia Is Associated with Increased Risks of Mortality and Morbidity Following Major Surgery: A Nationwide Propensity Score Matching Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Research Database. Data Subsets. Available online: https://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/Data_Subsets.html (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Mayans, L.; Walling, A. Acute Migraine Headache: Treatment Strategies. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 97, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- May, A.; Schulte, A.M.L.H. Chronic migraine: Risk factors, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.-H.; Wu, H.-L.; Mandell, M.S.; Lin, S.-P.; Tsou, M.-Y.; Chang, K.-Y. The association of non–small cell lung cancer recurrence with allogenic blood transfusion after surgical resection: A propensity score analysis of 1,803 patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 140, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.H.; Wu, H.L.; Mandell, M.S.; Tsou, M.Y.; Chang, K.Y. The association of allogeneic blood transfusion and the recurrence of hepatic cancer after surgical resection. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-L.; Tai, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-P.; Chan, M.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Chang, K.-Y. The Impact of Blood Transfusion on Recurrence and Mortality Following Colorectal Cancer Resection: A Propensity Score Analysis of 4030 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhakal, L.P.; Harriott, A.; Capobianco, D.J.; Freeman, W.D. Headache and Its Approach in Today’s NeuroIntensive Care Unit. Neurocrit. Care 2016, 25, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.B.; Topcuoglu, M.A. Glucocorticoid-associated worsening in reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Neurology 2017, 88, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, K.U.; Mikkelsen, I.K.; Aanerud, J.; Espelund, U.S.; Tietze, A.; Oettingen, G.V.; Juul, N.; Nikolajsen, L.; Østergaard, L.; Rasmussen, M. Ephedrine versus Phenylephrine Effect on Cerebral Blood Flow and Oxygen Consumption in Anesthetized Brain Tumor Patients. Anesthesiology 2020, 133, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, P.M. Theophylline, aminophylline, caffeine and analogues for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, 2004, CD000211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. Balance diagnostics for comparing the distribution of baseline covariates between treatment groups in propensity-score matched samples. Stat. Med. 2009, 28, 3083–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyngberg, A.C.; Rasmussen, B.K.; Jørgensen, T.; Jensen, R. Incidence of Primary Headache: A Danish Epidemiologic Follow-up Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 161, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, A.B.W.; E Davis-Martin, R.; Houle, T.; Turner, D.P.; Smitherman, T. Perceived triggers of primary headache disorders: A meta-analysis. Cephalalgia 2017, 38, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jette, N.; Patten, S.; Williams, J.; Becker, W.; Wiebe, S. Comorbidity of Migraine and Psychiatric Disorders—A National Population-Based Study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2008, 48, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breslau, N.; Lipton, R.B.; Stewart, W.F.; Schultz, L.R.; Welch, K.M. Comorbidity of migraine and depression: Investigating potential etiology and prognosis. Neurology 2003, 60, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, S.D.; Lee, L.; Gandhi, K.; Ma, T.F.; Bell, J.; Cohen, J.M. Health care Resource Utilization and Migraine Disability Along the Migraine Continuum Among Patients Treated for Migraine. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2018, 58, 1579–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumelahti, M.-L.; Sumanen, M.; Sumanen, M.S.; Tuominen, S.; Vikkula, J.; Honkala, S.M.; Rosqvist, S.; Korolainen, M.A. My Migraine Voice survey: Disease impact on healthcare resource utilization, personal and working life in Finland. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldeamanuel, Y.W.; Rapoport, A.M.; Cowan, R.P. What Is the Evidence for the Use of Corticosteroids in Migraine? Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2014, 18, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.; Friedman, B.W.; Christie, S.; Minen, M.T.; Bamford, C.; Kelley, N.E.; Tepper, D. Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2016, 56, 911–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelley, N.E.; Tepper, D.E. Rescue Therapy for Acute Migraine, Part 3: Opioids, NSAIDs, Steroids, and Post-Discharge Medications. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2012, 52, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger, T.; Viana, M.; Tassorelli, C. Current Prophylactic Medications for Migraine and Their Potential Mechanisms of Action. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sørensen, H.; Rasmussen, P.; Sato, K.; Persson, S.; Olesen, N.D.; Nielsen, H.B.; Olsen, N.V.; Ogoh, S.; Secher, N.H. External carotid artery flow maintains near infrared spectroscopy-determined frontal lobe oxygenation during ephedrine administration. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devereux, G.; Cotton, S.; Fielding, S.; McMeekin, N.; Barnes, P.J.; Briggs, A.; Burns, G.; Chaudhuri, R.; Chrystyn, H.; Davies, L.; et al. Effect of Theophylline as Adjunct to Inhaled Corticosteroids on Exacerbations in Patients With COPD: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 320, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, M. Life-Threatening Events after Theophylline Overdose. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayyah, M.; Saki-Malehi, A.; Javanmardi, F.; Forouzan, A.; Shirbandi, K.; Rahim, F. Which came first, the risk of migraine or the risk of asthma? A systematic review. Neurol. Neurochir. Polska 2018, 52, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.T.; Fanning, K.M.; Serrano, D.; Buse, D.C.; Reed, M.L.; Lipton, R.B. Asthma is a risk factor for new onset chronic migraine: Results from the American migraine prevalence and prevention study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2015, 56, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; Merlino, F.; Cocuzza, S.; Iannella, G.; Vicini, C.; Cammaroto, G.; Lechien, J.R.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; La Mantia, I. Endoscopic surgical treatment for rhinogenic contact point headache: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coeytaux, R.R.; Befus, D. Role of Acupuncture in the Treatment or Prevention of Migraine, Tension-Type Headache, or Chronic Headache Disorders. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2016, 56, 1238–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline Characteristic | General Anesthesia n = 68,131 | Neuraxial Anesthesia n = 68,131 | SDD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 51.4 | 19.8 | 51.1 | 19.5 | 0.0153 |
| Sex, male, n (%) | 36,890 | 54.2 | 37,003 | 54.3 | −0.0037 |
| Insurance premium (USD/month), n (%) | 0.0028 | ||||
| 0–500 | 29,888 | 43.9 | 30,182 | 44.3 | |
| 501–800 | 22,810 | 33.5 | 22,375 | 32.8 | |
| ≥801 | 15,433 | 22.7 | 15,574 | 22.9 | |
| Type of surgery, n (%) | |||||
| Orthopedic, lower limbs | 29,824 | 43.8 | 29,629 | 43.5 | 0.0064 |
| Genitourinary | 18,018 | 26.5 | 17,692 | 26.0 | 0.0136 |
| Anal | 7373 | 10.8 | 7613 | 11.2 | −0.0198 |
| Obstetric | 6972 | 10.2 | 6966 | 10.2 | 0.0005 |
| Hernia repair | 6168 | 9.1 | 6506 | 9.6 | −0.0324 |
| Lifestyle factors, n (%) | |||||
| Obesity | 371 | 0.5 | 381 | 0.6 | −0.0147 |
| Smoking disorder | 434 | 0.6 | 437 | 0.6 | −0.0038 |
| Alcohol use disorder | 945 | 1.4 | 925 | 1.4 | 0.0120 |
| Malnutrition | 477 | 0.7 | 486 | 0.7 | −0.0104 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | |||||
| Hypertension | 20,416 | 30.0 | 20,149 | 29.6 | 0.0103 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 9719 | 14.3 | 9542 | 14.0 | 0.0118 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 7363 | 10.8 | 7357 | 10.8 | 0.0005 |
| Atherosclerosis | 604 | 0.9 | 594 | 0.9 | 0.0093 |
| Heart failure | 2242 | 3.3 | 2212 | 3.3 | 0.0077 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 5453 | 8.0 | 5429 | 8.0 | 0.0026 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 3708 | 5.4 | 3692 | 5.4 | 0.0025 |
| COPD | 5663 | 8.3 | 5685 | 8.3 | −0.0023 |
| Malignancy | 4478 | 6.6 | 4446 | 6.5 | 0.0042 |
| Anxiety disorder | 7127 | 10.5 | 7131 | 10.5 | −0.0003 |
| Depressive disorder | 723 | 1.1 | 734 | 1.1 | −0.0084 |
| Schizophrenia | 383 | 0.6 | 374 | 0.6 | 0.0132 |
| Bipolar disorder | 268 | 0.4 | 281 | 0.4 | −0.0262 |
| Concurrent sympathomimetic drugs, n (%) | |||||
| Systemic corticosteroids | 11,439 | 16.8 | 11,291 | 16.6 | 0.0086 |
| Ephedrine | 11,961 | 17.6 | 12,099 | 17.8 | −0.0077 |
| Theophylline | 6623 | 9.7 | 6702 | 9.8 | −0.0072 |
| Number of hospitalizations, n (%) | 0.0238 | ||||
| 0 | 52,007 | 76.3 | 52,997 | 77.8 | |
| 1 | 10,502 | 15.4 | 9750 | 14.3 | |
| 2 | 3217 | 4.7 | 2934 | 4.3 | |
| ≥3 | 2405 | 3.5 | 2450 | 3.6 | |
| Number of ER visits, n (%) | −0.0004 | ||||
| 0 | 39,554 | 58.1 | 39,772 | 58.4 | |
| 1 | 16,202 | 23.8 | 15,864 | 23.3 | |
| 2 | 6423 | 9.4 | 6421 | 9.4 | |
| ≥3 | 5952 | 8.7 | 6074 | 8.9 | |
| Postoperative complications, n (%) | 8533 | 12.5 | 9105 | 13.4 | −0.0411 |
| Blood transfusion, n (%) | 986 | 1.5 | 815 | 1.2 | 0.1064 |
| ICU admission, n (%) | 430 | 0.6 | 374 | 0.6 | 0.0774 |
| Univariate | Multivariable | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cOR | 95% CI | p | aOR | 95% CI | p | |
| General vs. neuraxial anesthesia | 0.94 | 0.80–1.09 | 0.3900 | 0.93 | 0.80–1.09 | 0.3578 |
| Age (years) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.8573 | 0.99 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.0211 |
| Sex, male | 0.51 | 0.44–0.60 | <0.0001 | 0.50 | 0.42–0.60 | <0.0001 |
| Insurance premium (USD/month) | 0.5394 | 0.7854 | ||||
| 501–800 vs. 0–500 | 0.98 | 0.83–1.17 | 0.6495 | 0.97 | 0.81–1.16 | 0.9443 |
| ≥801 vs. 0–500 | 0.89 | 0.73–1.09 | 0.2815 | 0.93 | 0.75–1.15 | 0.5540 |
| Type of surgery | ||||||
| Orthopedic, lower limbs | 0.88 | 0.75–1.03 | 0.1136 | 0.43 | 0.06–3.14 | 0.4079 |
| Genitourinary | 0.95 | 0.80–1.13 | 0.5671 | 0.52 | 0.07–3.70 | 0.5096 |
| Anal | 1.32 | 1.06–1.64 | 0.0143 | 0.62 | 0.09–4.49 | 0.6356 |
| Obstetric | 1.20 | 0.95–1.52 | 0.1318 | 0.39 | 0.05–2.88 | 0.3592 |
| Hernia repair | 0.89 | 0.67–1.17 | 0.4044 | 0.59 | 0.08–4.23 | 0.6000 |
| Lifestyle factors | ||||||
| Obesity | 1.66 | 0.74–3.73 | 0.2164 | 1.30 | 0.58–2.93 | 0.5261 |
| Smoking disorder | 1.44 | 0.64–3.22 | 0.3778 | 1.50 | 0.66–3.37 | 0.3327 |
| Alcohol use disorder | 0.55 | 0.23–1.33 | 0.1823 | 0.51 | 0.21–1.24 | 0.1359 |
| Malnutrition | 1.08 | 0.45–2.60 | 0.8655 | 0.84 | 0.35–2.05 | 0.7078 |
| Comorbidity | ||||||
| Hypertension | 1.11 | 0.95–1.31 | 0.1966 | 0.92 | 0.75–1.14 | 0.4612 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.12 | 0.90–1.38 | 0.3135 | 1.03 | 0.82–1.30 | 0.8100 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 1.38 | 1.11–1.72 | 0.0041 | 1.12 | 0.87–1.45 | 0.3697 |
| Atherosclerosis | 1.57 | 0.81–3.03 | 0.1820 | 1.26 | 0.65–2.47 | 0.4948 |
| Heart failure | 1.32 | 0.90–1.93 | 0.1538 | 1.02 | 0.67–1.53 | 0.9442 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.31 | 1.02–1.69 | 0.0374 | 1.20 | 0.90–1.60 | 0.2110 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 1.37 | 1.02–1.84 | 0.0352 | 1.04 | 0.76–1.43 | 0.8015 |
| COPD | 1.38 | 1.08–1.76 | 0.0104 | 1.16 | 0.89–1.51 | 0.2772 |
| Malignancy | 0.92 | 0.67–1.27 | 0.6252 | 0.93 | 0.67–1.30 | 0.6651 |
| Anxiety disorder | 3.05 | 2.56–3.64 | <0.0001 | 2.43 | 2.01–2.95 | <0.0001 |
| Depressive disorder | 4.18 | 2.85–6.12 | <0.0001 | 2.29 | 1.53–3.44 | <0.0001 |
| Schizophrenia | 1.10 | 0.41–2.94 | 0.8563 | 0.86 | 0.31–2.33 | 0.7588 |
| Bipolar disorder | 1.13 | 0.36–3.53 | 0.8296 | 0.51 | 0.16–1.63 | 0.2555 |
| Concurrent sympathomimetic drugs | ||||||
| Systemic corticosteroids | 1.69 | 1.42–2.02 | <0.0001 | 1.45 | 1.21–1.74 | <0.0001 |
| Ephedrine | 1.80 | 1.52–2.14 | <0.0001 | 1.45 | 1.21–1.75 | <0.0001 |
| Theophylline | 1.84 | 1.50–2.26 | <0.0001 | 1.40 | 1.12–1.74 | 0.0036 |
| Number of hospitalizations | 0.1994 | 0.2011 | ||||
| 1 vs. 0 | 1.24 | 1.01–1.52 | 0.2302 | 1.05 | 0.85–1.30 | 0.0668 |
| 2 vs. 0 | 1.16 | 0.82–1.65 | 0.7173 | 0.87 | 0.60–1.27 | 0.9935 |
| ≥3 vs. 0 | 1.02 | 0.67–1.56 | 0.6570 | 0.64 | 0.40–1.01 | 0.0676 |
| Number of ER visits | <0.0001 | 0.0012 | ||||
| 1 vs. 0 | 1.13 | 0.93–1.37 | 0.1220 | 1.12 | 0.92–1.36 | 0.3045 |
| 2 vs. 0 | 1.20 | 0.92–1.56 | 0.5957 | 1.14 | 0.87–1.50 | 0.5517 |
| ≥3 vs. 0 | 1.89 | 1.51–2.37 | <0.0001 | 1.68 | 1.30–2.16 | 0.0004 |
| Postoperative complications | 1.03 | 0.82–1.29 | 0.8300 | 0.92 | 0.73–1.17 | 0.5028 |
| Blood transfusion | 0.69 | 0.31–1.54 | 0.3608 | 0.58 | 0.24–1.39 | 0.2217 |
| ICU admission | 1.29 | 0.54–3.12 | 0.5686 | 1.55 | 0.59–4.06 | 0.3725 |
| General Anesthesia | Neuraxial Anesthesia | Migraine Risk | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event | Rate (%) | Crude Incidence Rate/1000 PY | Event | Rate (%) | Crude Incidence Rate/1000 PY | Incidence Rate Ratio | aOR (95% CI) † | p | |
| All migraine | 318 | 0.47 | 9.49 | 340 | 0.50 | 10.15 | 0.94 | 0.93 (0.80–1.09) | 0.3578 |
| Migraine with aura | 32 | 0.05 | 0.96 | 31 | 0.05 | 0.93 | 1.03 | 1.02 (0.62–1.68) | 0.9295 |
| Migraine without aura | 58 | 0.09 | 1.73 | 78 | 0.11 | 2.33 | 0.74 | 0.73 (0.52–1.03) | 0.0697 |
| Migraine, unspecified | 228 | 0.33 | 6.81 | 231 | 0.34 | 6.90 | 0.99 | 0.99 (0.82–1.19) | 0.8857 |
| Migraine with medications | 102 | 0.15 | 3.05 | 83 | 0.12 | 2.48 | 1.23 | 1.23 (0.92–1.64) | 0.1717 |
| 30-day migraine | 60 | 0.09 | 10.73 | 58 | 0.09 | 10.37 | 1.03 | 1.03 (0.72–1.48) | 0.8706 |
| 60-day migraine | 115 | 0.17 | 10.28 | 112 | 0.16 | 10.02 | 1.03 | 1.02 (0.79–1.33) | 0.8793 |
| 90-day migraine | 174 | 0.26 | 10.38 | 161 | 0.24 | 9.60 | 1.08 | 1.08 (0.87–1.34) | 0.4981 |
| 120-day migraine | 218 | 0.32 | 9.76 | 220 | 0.32 | 9.84 | 0.99 | 0.99 (0.82–1.19) | 0.8893 |
| 150-day migraine | 276 | 0.41 | 9.88 | 282 | 0.41 | 10.10 | 0.98 | 0.97 (0.82–1.15) | 0.7570 |
| Subgroup | n | Event | Rate (%) | aOR (95% CI) † | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 65 years | GA | 19,894 | 77 | 0.39 | 0.94 (0.69–1.29) | 0.6985 |
| NA | 20,074 | 83 | 0.41 | reference | ||
| Age < 65 years | GA | 48,237 | 241 | 0.50 | 0.93 (0.78–1.11) | 0.3972 |
| NA | 48,057 | 257 | 0.53 | reference | ||
| Male | GA | 36,890 | 112 | 0.30 | 0.84 (0.65–1.08) | 0.1672 |
| NA | 37,003 | 136 | 0.37 | reference | ||
| Female | GA | 31,241 | 206 | 0.66 | 0.98 (0.81–1.20) | 0.8629 |
| NA | 31,128 | 204 | 0.66 | reference | ||
| Anxiety disorder | GA | 7127 | 77 | 1.08 | 0.80 (0.59–1.08) | 0.1410 |
| NA | 7131 | 95 | 1.33 | reference | ||
| No anxiety disorder | GA | 61,004 | 241 | 0.40 | 0.98 (0.82–1.18) | 0.8551 |
| NA | 61,000 | 245 | 0.40 | reference | ||
| Depressive disorder | GA | 723 | 13 | 1.80 | 0.79 (0.34–1.83) | 0.5818 |
| NA | 734 | 15 | 2.04 | reference | ||
| No depressive disorder | GA | 67,408 | 305 | 0.45 | 0.94 (0.80–1.10) | 0.4096 |
| NA | 67,397 | 325 | 0.48 | reference | ||
| Use of systemic corticosteroids | GA | 11,439 | 82 | 0.72 | 0.98 (0.72–1.33) | 0.8769 |
| NA | 11,291 | 84 | 0.74 | reference | ||
| No use of systemic corticosteroids | GA | 56,692 | 236 | 0.42 | 0.92 (0.77–1.09) | 0.3280 |
| NA | 56,840 | 256 | 0.45 | reference | ||
| Use of ephedrine | GA | 11,961 | 84 | 0.70 | 0.86 (0.64–1.15) | 0.3119 |
| NA | 12,099 | 99 | 0.82 | reference | ||
| No use of ephedrine | GA | 56,170 | 234 | 0.42 | 0.96 (0.80–1.15) | 0.6469 |
| NA | 56,032 | 241 | 0.43 | reference | ||
| Use of theophylline | GA | 6623 | 48 | 0.72 | 0.78 (0.53–1.14) | 0.1996 |
| NA | 6702 | 61 | 0.91 | reference | ||
| No use of theophylline | GA | 61,508 | 270 | 0.44 | 0.96 (0.81–1.14) | 0.6500 |
| NA | 61,429 | 279 | 0.45 | reference | ||
| Postoperative complications complications | GA | 8533 | 41 | 0.48 | 0.94 (0.61–1.43) | 0.7581 |
| NA | 9105 | 46 | 0.51 | reference | ||
| No postoperative complications | GA | 59,598 | 277 | 0.46 | 0.93 (0.79–1.10) | 0.3777 |
| NA | 59,026 | 294 | 0.50 | reference | ||
| Admission to ICU | GA | 430 | 3 | 0.70 | 0.97 (0.08–12.33) | 0.9825 |
| NA | 374 | 2 | 0.53 | reference | ||
| No admission to ICU | GA | 67,701 | 315 | 0.47 | 0.93 (0.79–1.08) | 0.3357 |
| NA | 67,757 | 338 | 0.50 | reference |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, C.-Y.; Li, C.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Chen, J.-T.; Cherng, Y.-G.; Chen, T.-J.; Dai, Y.-X.; Wu, H.-L.; Liu, W.-C.; Tai, Y.-H. Migraine Headaches after Major Surgery with General or Neuraxial Anesthesia: A Nationwide Propensity-Score Matched Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010362
Liao C-Y, Li C-C, Liu H-Y, Chen J-T, Cherng Y-G, Chen T-J, Dai Y-X, Wu H-L, Liu W-C, Tai Y-H. Migraine Headaches after Major Surgery with General or Neuraxial Anesthesia: A Nationwide Propensity-Score Matched Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(1):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010362
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Chung-Yi, Chun-Cheng Li, Hsin-Yi Liu, Jui-Tai Chen, Yih-Giun Cherng, Tzeng-Ji Chen, Ying-Xiu Dai, Hsiang-Ling Wu, Wan-Chi Liu, and Ying-Hsuan Tai. 2022. "Migraine Headaches after Major Surgery with General or Neuraxial Anesthesia: A Nationwide Propensity-Score Matched Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 1: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010362
APA StyleLiao, C.-Y., Li, C.-C., Liu, H.-Y., Chen, J.-T., Cherng, Y.-G., Chen, T.-J., Dai, Y.-X., Wu, H.-L., Liu, W.-C., & Tai, Y.-H. (2022). Migraine Headaches after Major Surgery with General or Neuraxial Anesthesia: A Nationwide Propensity-Score Matched Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(1), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19010362







