Effects of Exercise on the Oral Microbiota and Saliva of Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
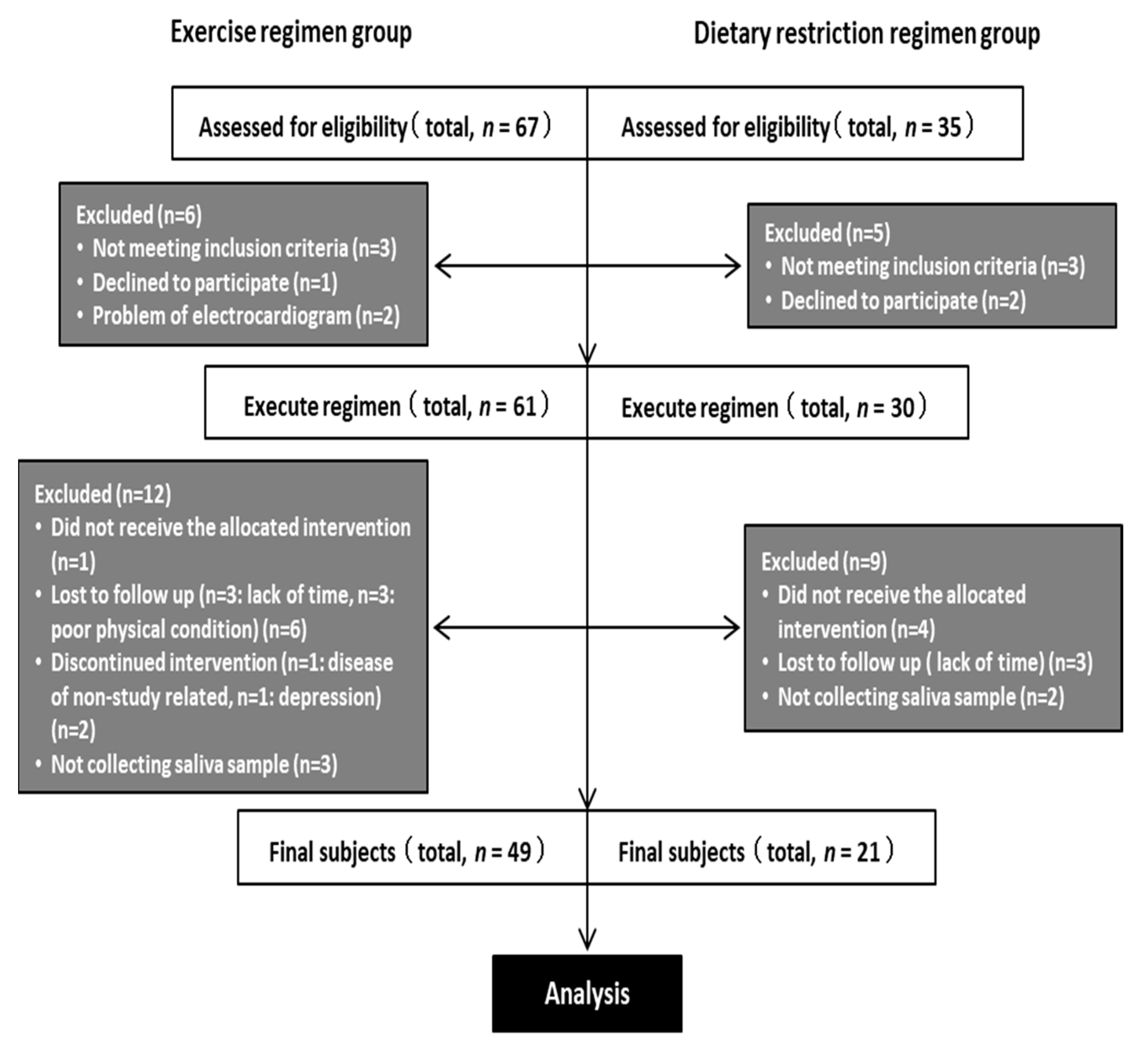
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Exercise Regimen
2.3. Dietary Restriction Regimen
2.4. Saliva Sampling
2.5. Saliva Analysis
2.6. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.7. Sequence Quality Control
2.8. Microbiome Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric Characteristics
3.2. Biochemical Characteristics
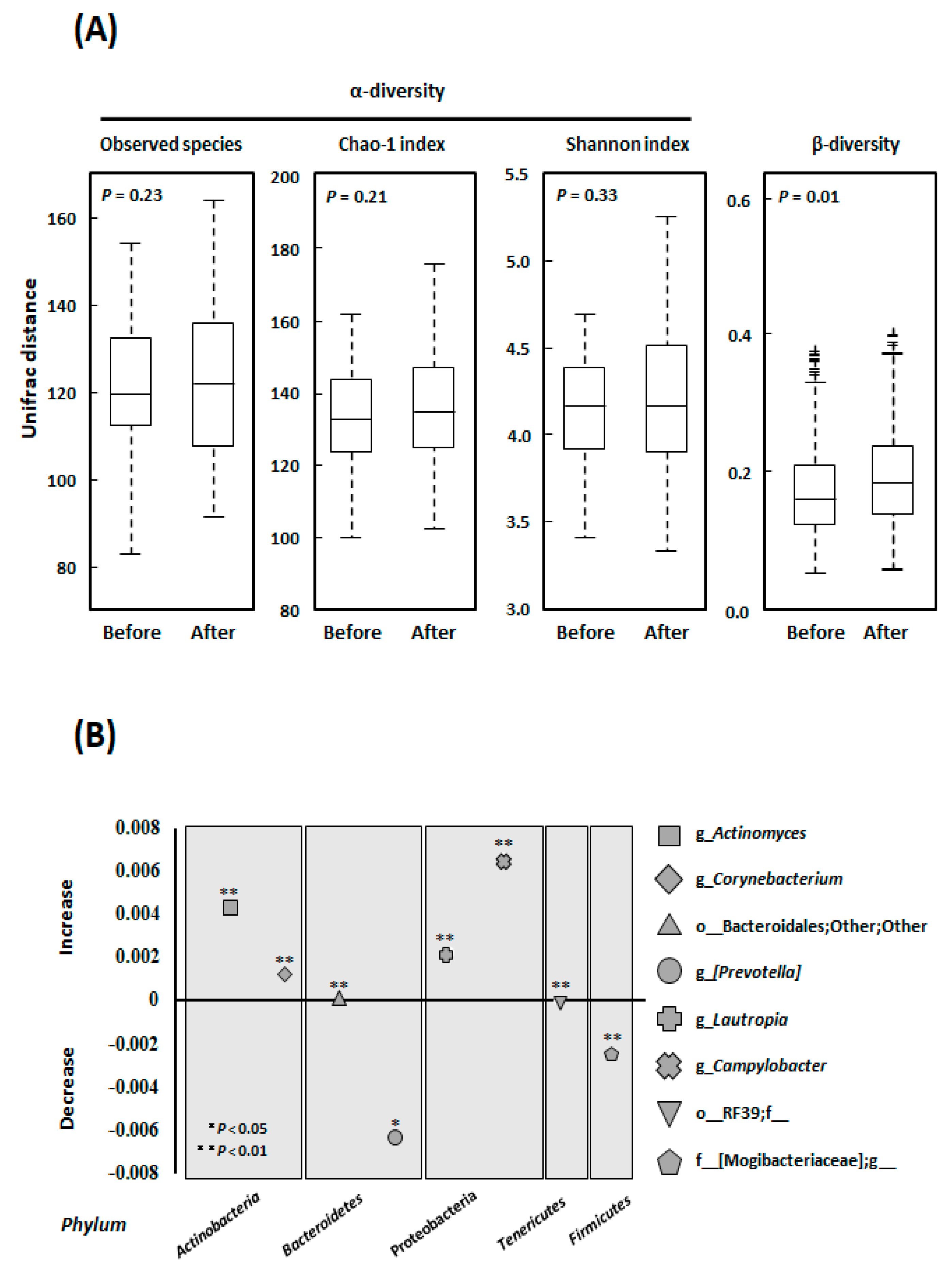
3.3. Alpha- and Beta-Diversity
3.4. Microbial Community Composition at the Genus Level
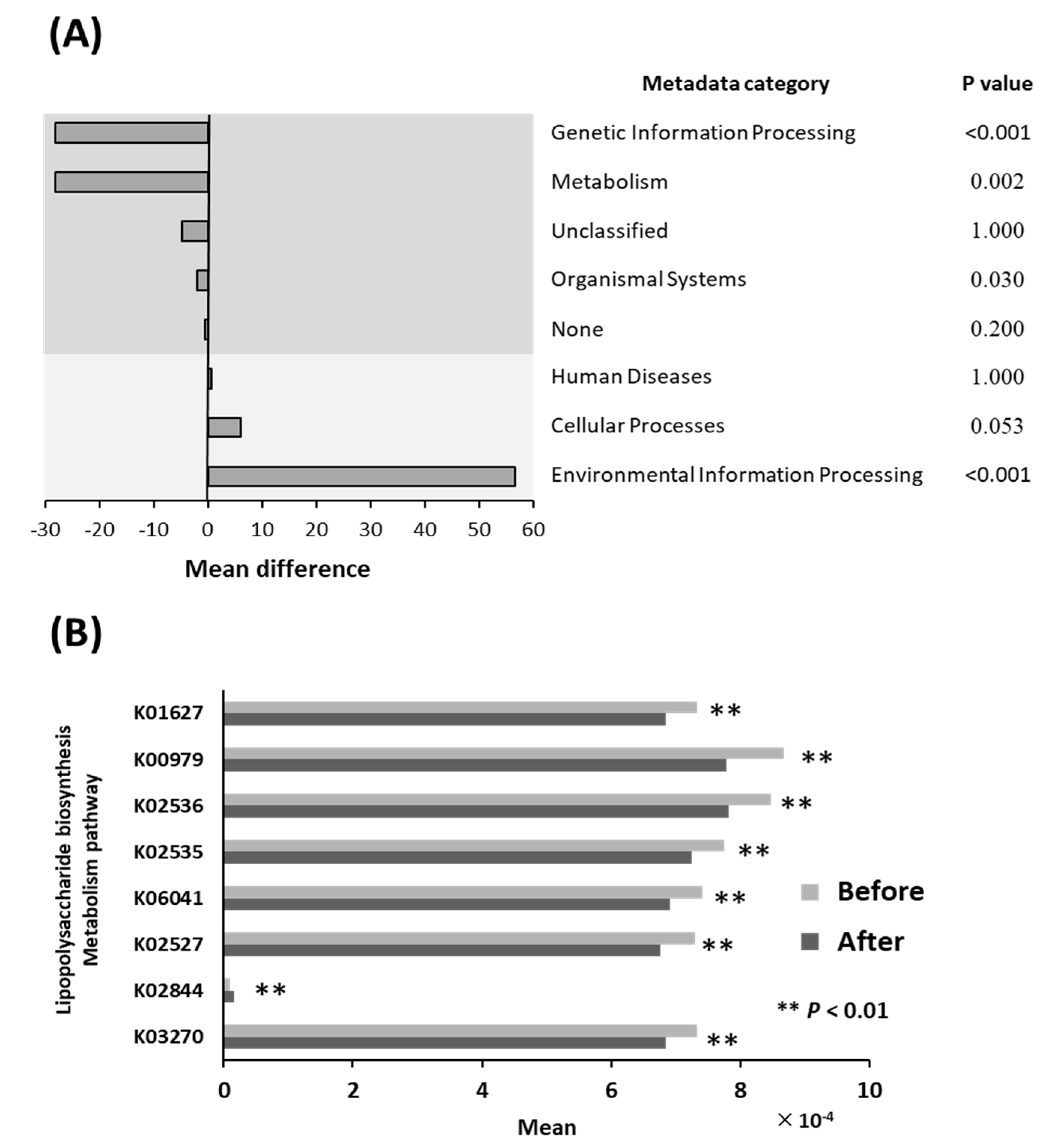
3.5. Differential Abundance of Bacterial Pathways
3.6. Lipopolysaccharide Biosynthesis Pathways
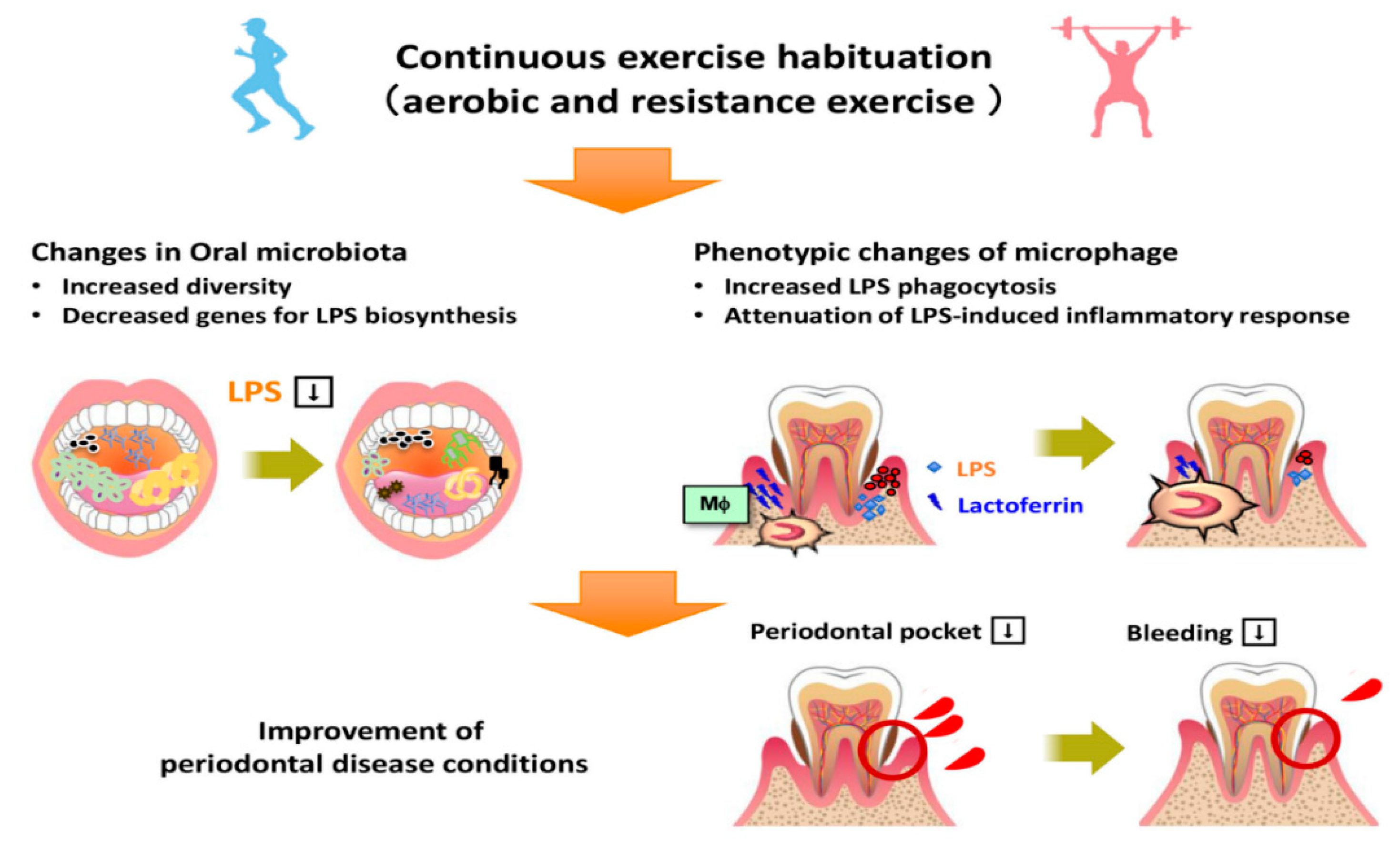
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamster, I.B.; Pagan, M. Periodontal disease and the metabolic syndrome. Int. Dent. J. 2017, 67, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timonen, P.; Niskanen, M.; Suominen-Taipale, L.; Jula, A.; Knuuttila, M.; Ylöstalo, P. Metabolic syndrome, periodontal infection, and dental caries. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Cho, Y.D. Periodontal disease and metabolic syndrome: A qualitative critical review of their association. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Hyogo, H.; Ono, M.; Mizuta, T.; Ono, N.; Fujimoto, K.; Chayama, K.; Saibara, T. Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the general population from 2009 to 2010 in Japan: A multicenter large retrospective study. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, M.; Naka, S.; Nakano, K.; Wada, K.; Endo, H.; Mawatari, H.; Imajo, K.; Nomura, R.; Hokamura, K.; Ono, M.; et al. Involvement of a periodontal pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis on the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusho, H.; Miyauchi, M.; Hyogo, H.; Inubushi, T.; Ao, M.; Ouhara, K.; Hisatune, J.; Kurihara, H.; Sugai, M.; Hayes, C.N.; et al. Dental infection of Porphyromonas gingivalis exacerbates high fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, A.; Sakamoto, S.; Chea, C.; Ishida, E.; Furusho, H.; Fujii, M.; Takata, T.; Miyauchi, M. Odontogenic infection by Porphyromonas gingivalis exacerbates fibrosis in NASH via hepatic stellate cell activation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Arimatsu, K.; Kato, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Minagawa, T.; Takahashi, N.; Ohno, H.; Yamazaki, K. Oral Administration of P. gingivalis Induces Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota and Impaired Barrier Function Leading to Dissemination of Enterobacteria to the Liver. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.; Sachinwalla, T.; Walton, D.W.; Smith, K.; Armstrong, A.; Thompson, M.W.; George, J. Aerobic exercise training reduces hepatic and visceral lipids in obese individuals without weight loss. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promrat, K.; Kleiner, D.E.; Niemeier, H.M.; Jackvony, E.; Kearns, M.; Wands, J.R.; Fava, J.L.; Wing, R.R. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, G.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Chu, Z.D.; Sauer, P.J.; Haymond, M.W.; Rodriguez, L.M.; Sunehag, A.L. A 12-week aerobic exercise program reduces hepatic fat accumulation and insulin resistance in obese, Hispanic adolescents. Obesity 2010, 18, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar Gomez, E.; Rodriguez De Miranda, A.; Gra Oramas, B.; Arus Soler, E.; Llanio Navarro, R.; Calzadilla Bertot, L.; Yasells Garcia, A.; Del Rosario Abreu Vazquez, M. Clinical trial: A nutritional supplement Viusid, in combination with diet and exercise, in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zahrani, M.S.; Borawski, E.A.; Bissada, N.F. Increased physical activity reduces prevalence of periodontitis. J. Dent. 2005, 33, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, M.S.; Borawski, E.A.; Bissada, N.F. Periodontitis and three health-enhancing behaviors: Maintaining normal weight, engaging in recommended level of exercise, and consuming a high-quality diet. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1362–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawadi, H.A.; Khader, Y.S.; Haroun, T.F.; Al-Omari, M.; Tayyem, R.F. The association between periodontal disease, physical activity and healthy diet among adults in Jordan. J. Periodontal. Res. 2011, 46, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, A.T.; Pitiphat, W.; Rimm, E.B.; Joshipura, K. Increased physical activity decreases periodontitis risk in men. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 18, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Shida, T.; Yamagishi, K.; Tanaka, K.; So, R.; Tsujimoto, T.; Shoda, J. Moderate to vigorous physical activity volume is an important factor for managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A retrospective study. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; So, R.; Shida, T.; Matsuo, T.; Kim, B.; Akiyama, K.; Isobe, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Shoda, J. High-Intensity Aerobic Exercise Improves Both Hepatic Fat Content and Stiffness in Sedentary Obese Men with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Tanaka, K.; Warabi, E.; Shoda, J. Exercise reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in obesity-related liver diseases. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, S.; Uchida, F.; Oh, S.; So, R.; Tsujimoto, T.; Yanagawa, T.; Sakai, S.; Shoda, J.; Tanaka, K.; Bukawa, H. Exercise habituation is effective for improvement of periodontal disease status: A prospective intervention study. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komine, S.; Akiyama, K.; Warabi, E.; Oh, S.; Kuga, K.; Ishige, K.; Togashi, S.; Yanagawa, T.; Shoda, J. Exercise training enhances in vivo clearance of endotoxin and attenuates inflammatory responses by potentiating Kupffer cell phagocytosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitturi, S.; Farrell, G.C.; Hashimoto, E.; Saibara, T.; Lau, G.K.; Sollano, J.D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region: Definitions and overview of proposed guidelines. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, G.C.; Chitturi, S.; Lau, G.K.; Sollano, J.D. Guidelines for the assessment and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region: Executive summary. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Tanaka, K.; Tsujimoto, T.; So, R.; Shida, T.; Shoda, J. Regular exercise coupled to diet regimen accelerates reduction of hepatic steatosis and associated pathological conditions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2014, 12, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. Data, information, knowledge and principle: Back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D199–D205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, T.; Akiyama, K.; Oh, S.; Sawai, A.; Isobe, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ishige, K.; Mizokami, Y.; Yamagata, K.; Onizawa, K.; et al. Skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio is an important determinant affecting hepatic conditions of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajo, K.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Nozaki, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Shinohara, Y.; Kato, S.; Mawatari, H.; Shibata, W.; Kitani, H.; et al. Hyperresponsivity to low-dose endotoxin during progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is regulated by leptin-mediated signaling. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K.; Warabi, E.; Okada, K.; Yanagawa, T.; Ishii, T.; Kose, K.; Tokushige, K.; Ishige, K.; Mizokami, Y.; Yamagata, K.; et al. Deletion of both p62 and Nrf2 spontaneously results in the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Exp. Anim. 2018, 67, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.J. Lactoferrin, a bird’s eye view. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugi, K.; Saitoh, O.; Hirata, I.; Katsu, K. Fecal lactoferrin as a marker for disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease: Comparison with other neutrophil-derived proteins. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 91, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glimvall, P.; Wickström, C.; Jansson, H. Elevated levels of salivary lactoferrin, a marker for chronic periodontitis? J. Periodontal Res. 2012, 47, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagalingam, N.A.; Lynch, S.V. Role of the microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | E | D | E vs. D |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 49 | n = 21 | p | |
| Age | 49.2 (8.3) | 53.0 (9.9) | 0.068 |
| Body mass, kg | 83.1 (13.5) | 82.1 (10.5) | 0.734 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28.2 (3.9) | 29.1 (2.4) | 0.055 |
| Fat mass, kg | 21.4 (6.6) | 20.9 (4.9) | 0.989 |
| Lean mass, kg | 62.3 (8.4) | 61.1 (7.9) | 0.660 |
| Parameters | E (n = 49) | D (n = 21) | E vs. D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | p | Before | After | p | p | |
| Anthropometric characteristics | |||||||
| Age, year | 49.2 ± 8.3 | 53 ± 9.9 | 0.068 | ||||
| Body mass, kg | 83.1 (13.5) | 83.6 (13.4) | 0.026 | 82.1 (10.5) | 72.8 (9.5) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28.2 (3.9) | 28.4 (3.9) | 0.024 | 29.1 (2.4) | 25.9 (2.3) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Fat mass, kg | 21.4 (6.6) | 20.6 (6.6) | <0.001 | 20.9 (4.9) | 15.9 (4.8) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Lean mass, kg | 62.3 (8.4) | 63.5 (8.1) | <0.001 | 61.1 (7.9) | 56.6 (7.5) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Biochemical characteristics | |||||||
| Lactoferrin, pg/mL | 4743.7 (3200.2) | 3826.3 (3375.7) | 0.024 | 5350.7 (3226.4) | 4133.1 (3466.8) | 0.279 | 0.88 |
| LPS, EU/mL | 13,252.2 (11,941) | 9959.5 (7417.1) | 0.039 | 6919.8 (7799.5) | 8423.5 (8524.4) | 0.339 | 0.05 |
| IgA, ug/mL | 207.8 (182.9) | 166.4 (142.2) | 0.022 | 251.1 (99.4) | 233.6 (142.0) | 0.394 | 0.715 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uchida, F.; Oh, S.; Shida, T.; Suzuki, H.; Yamagata, K.; Mizokami, Y.; Bukawa, H.; Tanaka, K.; Shoda, J. Effects of Exercise on the Oral Microbiota and Saliva of Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073470
Uchida F, Oh S, Shida T, Suzuki H, Yamagata K, Mizokami Y, Bukawa H, Tanaka K, Shoda J. Effects of Exercise on the Oral Microbiota and Saliva of Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(7):3470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073470
Chicago/Turabian StyleUchida, Fumihiko, Sechang Oh, Takashi Shida, Hideo Suzuki, Kenji Yamagata, Yuji Mizokami, Hiroki Bukawa, Kiyoji Tanaka, and Junichi Shoda. 2021. "Effects of Exercise on the Oral Microbiota and Saliva of Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 7: 3470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073470
APA StyleUchida, F., Oh, S., Shida, T., Suzuki, H., Yamagata, K., Mizokami, Y., Bukawa, H., Tanaka, K., & Shoda, J. (2021). Effects of Exercise on the Oral Microbiota and Saliva of Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073470








