Bio-Control of Anopheles Mosquito Larvae Using Invertebrate Predators to Support Human Health Programs in Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Predators Sampling and Identification
2.2. Anopheles Mosquito Larvae Collection
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
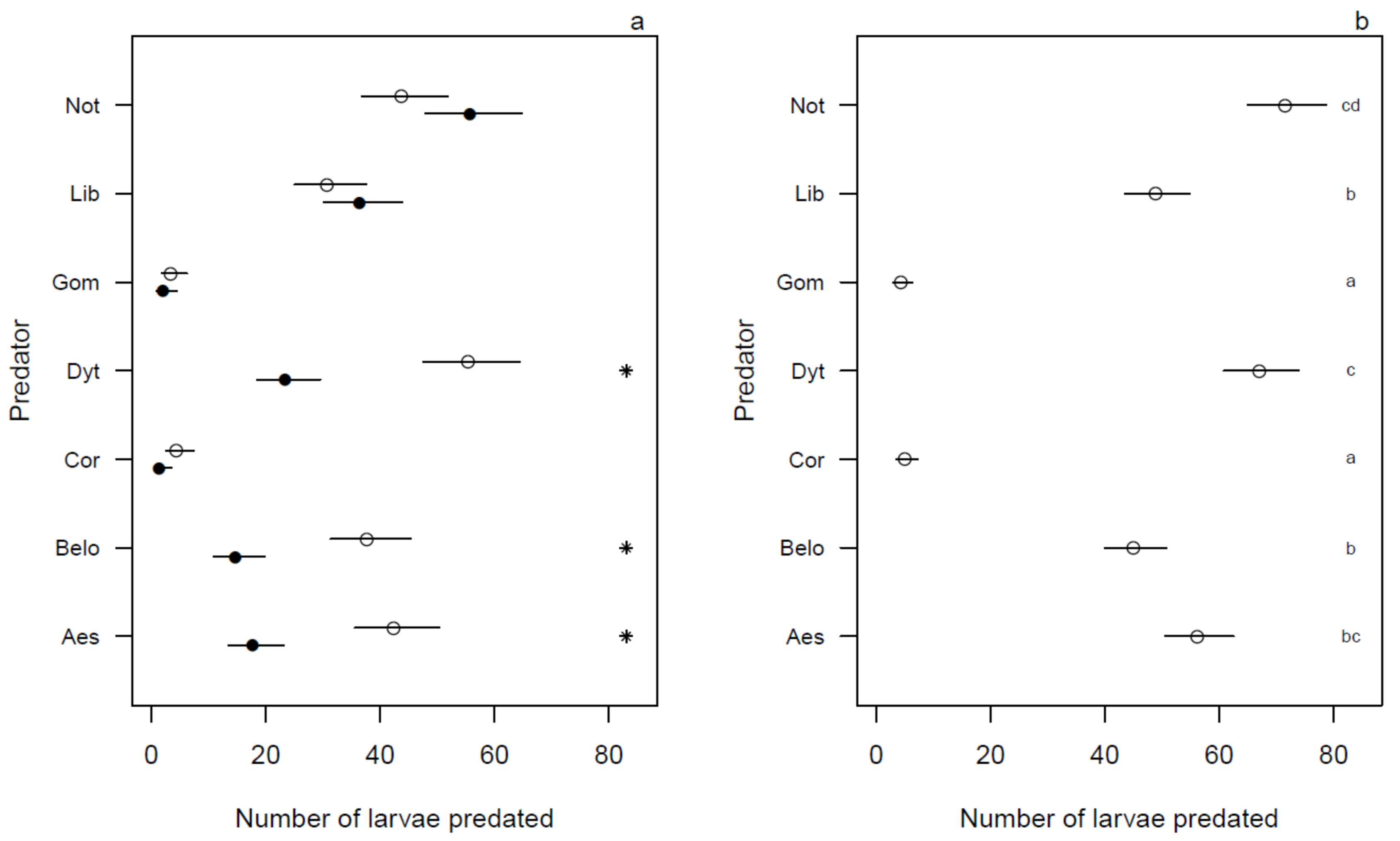
3.1. Optimum Predation Conditions
3.2. Predation Efficiency under Illuminated and Dark Conditions
3.3. Predation Efficiency during 24 h
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandler, J.A.; Highton, R. The breeding of Anopheles gambiae Giles (Diptera: Culicidae) in rice fields in the Kisumu area of Kenya. J. Med. Entomol. 1976, 13, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia. PATH Malaria Control and Elimination Partnership in Africa (MACEPA). Ethiopia Malaria Policy Landscape; FMOH: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2017.
- Federal Ministry of Health of Ethiopia, PATH Malaria Control, and Elimination Partnership in Africa (MACEPA). Ethiopia: Accelerating toward Malaria Elimination; Stakeholder Perspectives: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Amer, A.; Mehlhorn, H. Larvicidal effects of various essential oils against Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex larvae (Diptera, Culicidae). Parasitol. Res. 2006, 99, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Caselli, A.; Canale, A. Nanoparticles for mosquito control: Challenges and constraints. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2017, 29, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.E.; Blackwell, A. The biology of Toxorhynchites mosquitoes and their potential as biocontrol’agents. Biocontrol News Inf. 2000, 21, 105N–116N. [Google Scholar]
- Strode, C.; Donegan, S.; Garner, P.; Enayati, A.A.; Hemingway, J. The impact of pyrethroid resistance on the efficacy of insecticide-treated bed nets against African anopheline mosquitoes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N. Insecticide resistance in mosquitoes: Impact, mechanisms, and research directions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, S.; Thomas, A.; Manju, E. Bio-control efficiency of Odonata nymphs on Aedes aegypti larvae. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2017, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries, C.L.; Walker, T. The potential use of Wolbachia-based mosquito bio-control strategies for Japanese encephalitis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cheng, F.; Wei, Y.; Lydy, M.J.; You, J. Global occurrence of pyrethroid insecticides in sediment and the associated toxicological effects on benthic invertebrates: An overview. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, J.; Yi, X.; You, J. Legacy and current-use insecticides in agricultural sediments from south China: Impact of application pattern on occurrence and risk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschet, C.; Vermeirssen, E.L.; Seiz, R.; Pfefferli, H.; Hollender, J. Picogram per liter detections of pyrethroids and organophosphates in surface waters using passive sampling. Water Res. 2014, 66, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi, F.B.; Reddy, G.V. Toxicological effects of pyrethroids on non-target aquatic insects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 3, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Service, M.W. Mortalities of the immature stages of species B of the Anopheles gambiae complex in Kenya: Comparison between rice fields and temporary pools, identification of predators, and effects of insecticidal spraying. J. Med. Entomol. 1977, 13, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yewhalaw, D.; Wassie, F.; Steurbaut, W.; Spanoghe, P.; Van Bortel, W.; Denis, L.; Tessema, D.; Getachew, L.; Coosemans, M.; Duchateau, L. Multiple insecticide resistance: An impediment to insecticide-based malaria vector control program. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamareddine, L. The biological control of the malaria vector. Toxins 2012, 4, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moirangthem, B.D.; Singh, S.N.; Singh, D.C. Comparative studies of three potent bioagent against mosquito larvae. Int. J Mosq. Res. 2018, 5, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi, A.; Hoopes, M.F.; Marchetti, M.P.; Lockwood, J.L. Progress toward understanding the ecological impacts of nonnative species. Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, B.R. Biological Control of Culex quinquefasciatus Say, 1823 (Diptera: Culicidae), the Ubiquitous Vector for Lymphatic Filariasis: A Review. In Lymphatic Filariasis; Tyagi, B.K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, O.; Robert, V. Larval predation in malaria vectors and its potential implication in malaria transmission: An overlooked ecosystem service? Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aditya, G.; Saha, G.K. Predation of the beetle Rhantus sikkimensis (Coleoptera: Dytiscidae) on the larvae of Chironomus Meigen (Diptera: Chironomidae) of the Darjeeling Himalayas of India. Limnologica 2006, 36, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Ghosh, A.; Bhattacharjee, I.; Chandra, G. Bio-control efficiency of odonate nymphs against larvae of the mosquito, Culex quinquefasciatus Say, 1823. Acta Trop. 2008, 106, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, K.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Dick, J.T.; Kregting, L.; MacIsaac, H.J.; Coughlan, N.E. Full steam ahead: Direct steam exposure to inhibit spread of invasive aquatic macrophytes. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereta, S.T.; Yewhalaw, D.; Boets, P.; Ahmed, A.; Duchateau, L.; Speybroeck, N.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Legesse, W.; De Meester, L.; Goethals, P.L. Physico-chemical and biological characterization of anopheline mosquito larval habitats (Diptera: Culicidae): Implications for malaria control. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, S.A. Population dynamics. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2007, 23, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, R. Guide to Aquatic Macroinvertebrates of the Upper Midwest; Water Resources Center, University of Minnesota: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2004; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Kweka, E.J.; Zhou, G.; Gilbreath, T.M.; Afrane, Y.; Nyindo, M.; Githeko, A.K.; Yan, G. Predation efficiency of Anopheles gambiae larvae by aquatic predators in western Kenya highlands. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkarenko, L.; Hulsman, K.; Mottram, P.; Dale, P.; Kay, B. Reliability of using head capsule width and body length to identify larval instars of Aedes vigilax (Diptera: Culicidae). Aust. J. Entomol. 1986, 25, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerberg, E.J.; Barnard, D.R.; Ward, R.A. Manual for Mosquito Rearing and Experimental Techniques; Bulettin No. 5; American Mosquito Control Association Inc.: Lake Charles, LO, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Shaalan, E.A.; Canyon, D.V. Aquatic insect predators and mosquito control. Trop. Biomed. 2009, 26, 223–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quiroz-Martínez, H.; Rodríguez-Castro, A. Aquatic insects as predators of mosquito larvae. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2007, 23, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muiruri, S.K.; Mwangangi, J.M.; Carlson, J.; Kabiru, E.W.; Kokwaro, E.; Githure, J.; Mbogo, C.M.; Beier, J.C. Effect of predation on Anopheles larvae by five sympatric insect families in coastal Kenya. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2013, 50, 45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sivagnaname, N. A Novel Method of Controlling a Dengue Mosquito Vector, Aedes Aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Using an Aquatic Mosquito Predator, Diplonychus Indicus (Hemiptera: Belostomatidae) in Tyres; WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia. 2009. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/170732 (accessed on 11 February 2021).
- Saha, N.; Aditya, G.; Banerjee, S.; Saha, G.K. Predation potential of odonates on mosquito larvae: Implications for biological control. Biol. Control 2012, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, S.Y.; Kawada, H.; Dida, G.O.; Juma, D.; Sonye, G.; Minakawa, N.; Takagi, M. Predators of Anopheles gambiae sensu lato (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae in wetlands, western Kenya: Confirmation by polymerase chain reaction method. J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dida, G.O.; Gelder, F.B.; Anyona, D.N.; Abuom, P.O.; Onyuka, J.O.; Matano, A.S.; Adoka, S.O.; Kanangire, C.K.; Owuor, P.O.; Ouma, C. Presence and distribution of mosquito larvae predators and factors influencing their abundance along the Mara River, Kenya and Tanzania. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, A.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Dick, J.T.; Gupta, S. Water depth-dependent notonectid predatory impacts across larval mosquito ontogeny. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, W.W.; Scott, M.A.; Ebsworth, P. Effects of the general predator, Notonecta (Hemiptera) upon a freshwater community. J Anim Ecol. 1984, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, E.C. Predator-prey relationships among aquatic insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1974, 19, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.E.; Wesson, D.M.; Sutherland, I.W.; Impoinvil, D.E.; Mbogo, C.M.; Githure, J.I.; Beier, J.C. Determination of Anopheles gambiae larval DNA in the gut of insectivorous dragonfly (Libellulidae) nymphs by polymerase chain reaction. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2003, 19, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalal, A.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Dick, J.T.; Gupta, S. Prey preferences of notonectids towards larval mosquitoes across prey ontogeny and search area. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 76, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundkvist, E.; Landin, J.; Jackson, M.; Svensson, C. Diving beetles (Dytiscidae) as predators of mosquito larvae (Culicidae) in field experiments and in laboratory tests of prey preference. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2003, 93, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Gao, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z.; Ji, H.; Plath, M. Characterizing a novel predator–prey relationship between native Diplonychus esakii (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae) and invasive Gambusia affinis (Teleostei: Poeciliidae) in central China. Int. Aquat. Res. 2017, 9, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, R. Ecology and Predatory Efficiency of Aquatic (Odonate) Insect over the Developmental Stages of Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Acad. Ind. Res. 2013, 2, 429. [Google Scholar]
- Norma-Rashid, Y.; Saleeza, S. Eco-friendly Control of Three Common Mosquito Larvae Species by Odonata Nymphs. In Basic and Applied Aspects of Biopesticides, 2nd ed.; Sahayaraj, K., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2014; pp. 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Pereyra, D.; Fernández, L. Predation ability and non-consumptive effects of Notonecta sellata (Heteroptera: Notonectidae) on immature stages of Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Vector Ecol. 2012, 37, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahmed, A.; Alamr, S.; Kheir, S. Seasonal activity and predatory efficacy of the water bug Sigara hoggarica Poisson (Hemiptera: Corixidae) against the mosquito larvae Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia. J. Entomol. 2009, 6, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.P.; Chandra, G.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, A. Effect of temperature and search area on the functional response of Anisops sardea (Hemiptera: Notonectidae) against Anopheles stephensi in laboratory bioassay. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, W.; Ali-Khan, H.A. Odonate nymphs: Generalist predators and their potential in the management of dengue mosquito, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Arthropod. Borne Dis. 2016, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vershini, R.; Kanagapan, M. Effect of quantity of water on the feeding efficiency of dragonfly nymph-Bradynopyga geminate (Rambur). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2014, 2, 249–252. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, I.; Aditya, G.; Chandra, G. Laboratory and field assessment of the potential of larvivorous, air-breathing fishes as predators of culicine mosquitoes. Biol. Control 2009, 49, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Predator Family | Mosquito Instar | Water Volume | # of Predators | # of Larvae Consumed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aeshinidae | 4 | 2 | 15 | 109 (98;121) |
| Belostomatidae | 2 | 2 | 15 | 90 (80;101) |
| Corixidae | 2 | 2 | 15 | 20 (16;26) |
| Dytiscidae | 4 | 3 | 15 | 168 (154;184) |
| Gomphidae | 3 | 3 | 15 | 33 (27;40) |
| Libellulidae | 4 | 2 | 15 | 29 (24;36) |
| Notonectidae | 1 | 1 | 15 | 140 (127;154) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eba, K.; Duchateau, L.; Olkeba, B.K.; Boets, P.; Bedada, D.; Goethals, P.L.M.; Mereta, S.T.; Yewhalaw, D. Bio-Control of Anopheles Mosquito Larvae Using Invertebrate Predators to Support Human Health Programs in Ethiopia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041810
Eba K, Duchateau L, Olkeba BK, Boets P, Bedada D, Goethals PLM, Mereta ST, Yewhalaw D. Bio-Control of Anopheles Mosquito Larvae Using Invertebrate Predators to Support Human Health Programs in Ethiopia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041810
Chicago/Turabian StyleEba, Kasahun, Luc Duchateau, Beekam Kebede Olkeba, Pieter Boets, Dechasa Bedada, Peter L. M. Goethals, Seid Tiku Mereta, and Delenasaw Yewhalaw. 2021. "Bio-Control of Anopheles Mosquito Larvae Using Invertebrate Predators to Support Human Health Programs in Ethiopia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 4: 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041810
APA StyleEba, K., Duchateau, L., Olkeba, B. K., Boets, P., Bedada, D., Goethals, P. L. M., Mereta, S. T., & Yewhalaw, D. (2021). Bio-Control of Anopheles Mosquito Larvae Using Invertebrate Predators to Support Human Health Programs in Ethiopia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(4), 1810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041810








