Abstract
The small size of microplastics and their wide distribution in water environments have attracted worldwide attention and heated discussion, because of their ingestion by aquatic organisms. At present, there are few studies on microplastics pollution in freshwater aquaculture ponds, especially shrimp ponds. In this study, the aquaculture ponds in the Pearl River Estuary were investigated. The abundance and composition of microplastics in different environmental media were studied to explore the potential sources and risk levels of microplastics, so as to provide basic data for the study of microplastics pollution in aquaculture ponds. Microplastics were observed in water and sediment samples at all sampling sites, with the abundance of 6.6 × 103–263.6 × 103 items/m3 (surface water) and 566.67–2500 items/kg (sediment), respectively. Thirty-seven individuals collected in six ponds belong to four species. Microplastics were observed in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of all fishes and shrimps, with the abundance ranging from 3–92 items/individual (fish) and 4–21 items/individual (shrimp). Among all samples, microplastics with the size range of <1 mm and fiber shape were the most common. The main microplastic components were cellulose, polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene (PE). The results of potential risk assessment showed that the pollution investigation of microplastics should not only consider the abundance. Low abundance does not mean low risk. Taking the toxicity score and abundance of microplastics as evaluation indexes to reflect the pollution status of microplastics may make the results more reliable.
1. Introduction
After weathering and wear, plastic waste is broken into small polymer particles with a length of less than 5 mm, which are called microplastics (MPs) [1,2,3,4]. According to their source, MPs can usually be divided into two categories: primary (they are intendedly produced in small size, mostly spherical and commonly used in personal care products) [5] and secondary MPs (formed by weathering of large plastic products, most of which are irregular in shape) [1]. Since the 1950s, the plastic industry in China has developed rapidly, and daily necessities made of plastics have been widely used [6]. MPs can be found in all types of environments, such as oceans [7], freshwater [8,9,10,11,12,13] and tap water [14]. About 300 million tons of microplastics enter the environment every year [15]. It is estimated that the plastic waste in 2015 exceeded 6 billion tons [16], of which only 1% was directly discharged into the marine environment, and most of them entered the soil and freshwater environment [17]. The different densities of microplastics lead to their different buoyancy, which makes them ubiquitous in water, and they can be ingested by aquatic organisms at different depths. A previous study showed that the aging of MPs will lead to cracks and fragmentation on the surface, thus increasing the surface area and carbonyl content and promoting the release of lead chromate pigment [18]. Many studies have shown that MPs are efficient adsorbents for hydrophobic/hydrophilic organic pollutants [19,20]. Furthermore, MPs can adsorb heavy metals (mainly through electrostatic adsorption and surface complexation) and transfer along the food chain, which is an important carrier of heavy metals migration in various environmental media, thus posing a huge challenge to ecosystem security [21,22]. Although studies have been conducted on MPs contamination in aquaculture [23,24], there are few studies on MPs contamination in freshwater aquaculture, especially in culture ponds. The rapid economic growth and urban development in recent decades have made the Nansha District seriously polluted by effluent (mainly from industry, agriculture, and daily life) and waste. In addition to having the largest mariculture area [25], China is the world’s largest freshwater aquaculture country. In 2015, China’s aquaculture production reached 67 million tons [26]. Pond farming is the most common farming mode in China, and its output accounts for 70% of total freshwater farming output [27]. Most aquaculture farms are traditionally operated on a small scale, lacking effective management measures [28]. Aquaculture sites, especially ponds, are good reservoirs for MPs. This closed farming environment is easily polluted by MPs, and MPs are not easy to be washed into the sea [24]. In highly urbanized and industrialized areas, microplastic pollution is serious, which may decrease the quality and quantity of aquaculture products [29,30,31]. In this study, fish ponds and shrimp ponds in the Nansha District of Guangzhou were selected as the research sites. Our research aims to reveal the contamination among different samples in aquaculture ponds, and to access the risk level of microplastics pollution in each aquaculture pond.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Sampling Sites
Nansha is located at the geographical geometric center of the Pearl River estuary (located in the south-central part of Guangdong Province, China, formed by the outflow of the Pearl River to the South China Sea) and the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, where the Xijiang River, Beijiang River and Dongjiang River meet. Its fishery resources are abundant, the existing contiguous aquaculture area exceeds 18 million m2, and the standardized aquaculture area is over 70%, making it one of the largest contiguous aquaculture bases in the province. Since the late 1970s, the Pearl River Delta region has become the most populous and economically active region in China [32]. Some studies have shown that the main stream of the Pearl River has a high abundance of MPs [33], so the culture pond near the Pearl River Estuary may be seriously polluted by MPs.
Four fish ponds in Shisiyong Aquatic Center (S1, S2: Oreochroms mossambcus; S3, S4: Micropterus salmoides) and two shrimp ponds (S5: Penaeus vannamei and S6: Macrobrachium rosenbergii) in Seagull Island were selected as sampling points (Figure 1).
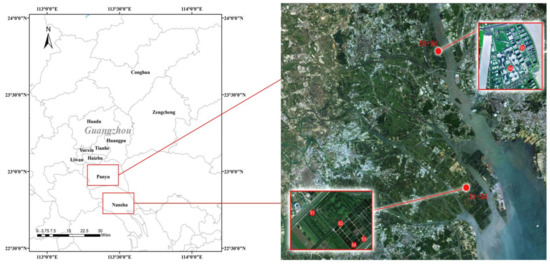
Figure 1.
Geographical location of six sampling sites.
2.2. Sample Collection
Samples were collected in October 2019 and the sampling sequence between different samples was defined before sampling. Commercial species need to be collected before collecting water samples and soil, because the collection process may startle the organisms, which can cause biological sample collection difficulties. Fish and shrimp samples (18 fish and 19 shrimps) from culture ponds were collected by casting a net and then the individual was wrapped in aluminum foil, placed in dry ice and transported back to the laboratory for subsequent treatments [23]. The containers used for sampling were rinsed with ultrapure water in advance. A 5 L stainless steel water collector was used to collect surface water samples, and three duplicate samples were collected from each culture pond [33]. The water sample was filtered with a 48 μm steel sieve, then rinsed the residue with ultrapure water and transferred it to a 100 mL glass container for subsequent treatment [34]. About 5 cm of pond sediment on the bottom surface of each culture pond, that was, the sediment sample of this study, was collected with a metal shovel (three duplicate samples were collected from each culture pond) [24]. Sediment samples were put into aluminum foil bags, the sampling point information and sampling time were also marked.
2.3. Sample Pretreatment
Fifteen mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide were added to the water sample to digest organic matter, and then the water sample was left to stand for 24 h in dark conditions [3,35]. After digestion, a 0.45 μm filter membrane was used to filter water samples to obtain all the suspected microplastic particles. A slight modification of the density flotation method described by Zhao et al. [31] was adopted to separate MPs from sediments in this study. Then, 50 g of dried sediment were placed in a beaker and mixed with 400 mL of zinc chloride solution (density = 1.60 g/mL), and three parallel samples were needed for each sampling site. The mixed solution was thoroughly stirred with a clean glass rod and then covered with tin foil for 2 h of precipitation. Then, the supernatant was transferred to another clean 500 mL beaker. This separation step was carried out three times to improve the recovery rate of MPs. Finally, 15 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide solution (H2O2) were added to the supernatant to digest the organic matter. After standing for 24 h, the solution was filtered by a vacuum device, and all particles were collected on the filter membrane. According to the research of Maes et al. [36], Zinc chloride was recommended for density flotation because its high density allowed flotation of most MPs [36]. Quinn et al. found that the recovery rate of MPs increased as the solution density increased [37]. Compared with saturated sodium chloride and saturated sodium iodide, the recovery rate of saturated zinc chloride was relatively high.
Body weight (g) and body length (cm) of fish and shrimps should be measured separately before dissecting biological samples (Table S1). The gastrointestinal tract of fish was separated with a scalpel, and the gastrointestinal tract of shrimp was taken out from the back of the shrimp. The gastrointestinal tract of the fish was separated with a scalpel, and the gastrointestinal tracts of shrimps were taken out from the back of the shrimps. Then, 10% potassium hydroxide was added to the glass bottle containing the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of fish and shrimp to submerge the tissues [38,39], and then the glass bottle was placed in an oven at 60 °C for at least four days. The glass bottle was shaken once a day to ensure complete digestion of organic matter [24]. After digestion, we filtered the solution through the filter membrane.
2.4. Microplastic Observation
The abundance, shape, size and color of MPs in samples were determined by observing the filter membrane with a stereo microscope. Based on the morphological characteristics of MPs, fibers, fragments, films, and pellets are considered to be the four main forms of MPs [40] (Figure 2). The sizes of MPs in this study are measured by software S-EYE and classified as follows: <0.5 mm, 0.5–1 mm, 1–2 mm, 2–3 mm, 3–4 mm, and 4–5 mm. Visual observation was mainly based on the physical characteristics of MPs described by Zhao et al., which mentioned that MPs are particles that were not easily damaged by tweezers, had uniform color and specific shape, and did not contain tissue or cellular structure [31].
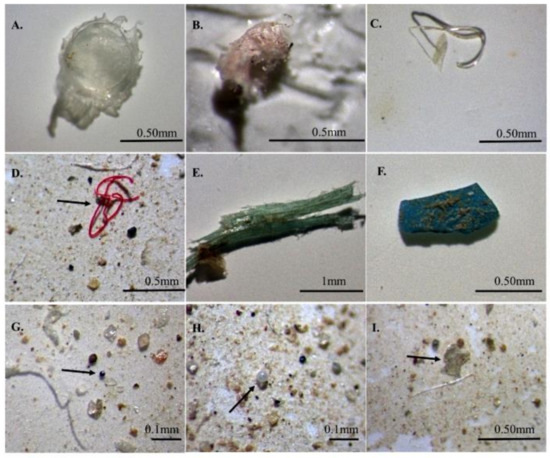
Figure 2.
Photographs of different types of typical microplastics (MPs) observed in six aquaculture ponds (A–I): (A,B,I) films; (C,D) fibers; (E,F) fragments; (G,H) pellets.
Chemical composition analysis must be carried out to verify the accuracy of visual observation. Raman spectroscopy (Thermo Fisher Scientific DXR2, 532 nm laser, Raman shift 50–3500 cm−1) was used to identify the chemical composition of suspicious particles. To ensure the reliability of the results, only those spectra that match the standard database by more than 60% are accepted (compared with OMIC polymer spectra library) [41] (Figure S1).
2.5. Risk Assessment of MPs in Ponds
The potential risk pollution index method was first proposed by Swedish scientist Hakanson (1980) according to the properties and environmental behavior characteristics of heavy metals, which was used to evaluate heavy metal pollution in soil or sediment [42]. The method considers the content, ecological effect, environmental effect and toxicology of pollutants in soil, and takes into account the regional differences of background values. In addition to the assessment of the risk of pollutants in a specific region, it can also reflect the comprehensive impact of various pollutants, which is one of the good means to evaluate the potential ecological risk of sediments [30]. Therefore, this study used this method to analyze and evaluate the microplastic pollution in the sediments of aquaculture ponds. The formulas used are as follows:
Cif = Ci/Cin;
Pn = Cn/Ci;
Eir = Tir × Cif
In the formula, Cif represents the pollution coefficient of a certain kind of MPs, Ci represents the measured value of MPs concentration in sediments, Cin is the reference value needed for calculation, represents the concentration of MPs in the uncontaminated sample; and Tir is the toxicity coefficient, which is used to reflect the toxicity level of MPs and the sensitivity of water to MPs in this study. Pn represents the percentage of MPs polymer types collected at each sampling site. Sn is the risk score of polymers containing MPs particles obtained by Lithner et al. [43]; Cn is the measured value of a certain microplastic at a sampling point; Eir is a risk index that can be used to evaluate the potential risk level of a pollutant.
2.6. Quality Assurance and Control
Blank experiments must be conducted to assess the potential contamination of the environment. All the solutions used in the experiment, including ultra-pure water, 30% H2O2, 10% KOH and ZnCl2 solution, were filtered according to the operation steps mentioned above, and three replicate samples were prepared for each solution. To reduce the MPs pollution from the laboratory, the experimenters should wear cotton lab clothes during the experiment [41]. All containers and anatomical tools must be cleaned with ultra-pure water prior to the experiment, and open containers needed to be covered with foil during microplastic extraction.
2.7. Data Analysis
Data analysis is carried out on the SPSS (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA). To compare the abundance of microplastics in water and sediments in different regions, one-way ANOVA was applied to the analysis. Pearson test was used to determine whether there is a correlation between the abundance of MPs in water and sediment. Descriptive data such as maximum, minimum, mean and standard deviation were also used in this study.
3. Results
3.1. MPs in Surface Water
MPs were observed in all culture ponds. The abundance of MPs in surface water varied greatly (ranging from 6.6 × 103–263.6 × 103 items/m3), in which the abundance of S1 and S2 MPs was relatively low (Figure 3A). By contrast, the abundance of S3–S6 MPs was much larger than S1 and S2. The abundance of MPs was lowest in S1 and highest in S3.
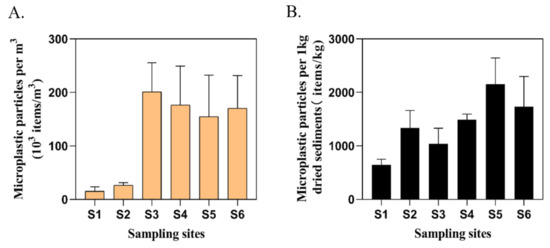
Figure 3.
The abundance of MPs in surface water (A) and sediment (B) of six aquaculture ponds in the Pearl River Estuary (mean ± S.D.).
Given the results of component analysis, different types of polymers were identified in the selected samples, mainly cellulose, polystyrene (PS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polyethylene (PE) (Figure 4). Consistent with other findings on seawater [44,45], fresh water [46,47], and mariculture [23,24], more small-sized MPs were found in surface water, especially <0.5 mm, accounting for 42.78% of all MPs in water samples (Figure 5C). The colors of MPs observed in surface water samples were mainly transparent (90.65%) and blue (7.62%) (Figure 5E). The dominant form of MPs was fibers, accounting for 98.04%, followed by fragments (1.14%) (Figure 5A). There was no significant difference in microplastic morphology among sampling sites.
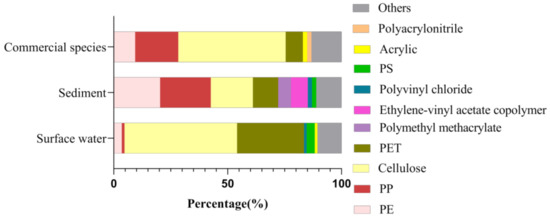
Figure 4.
MPs composition in different samples of aquaculture ponds in the Pearl River Estuary.
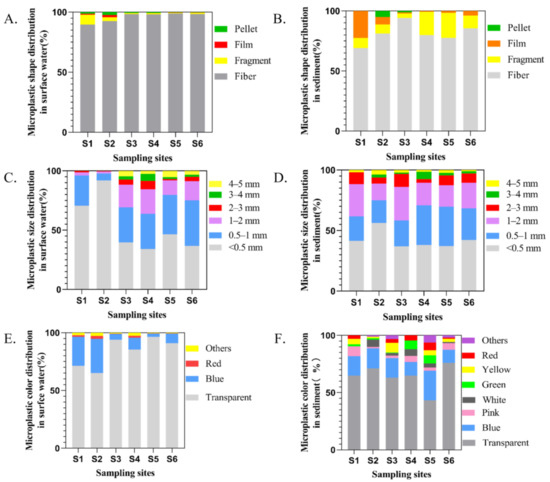
Figure 5.
Types of microplastics in water (A) and sediments (B); size distribution of microplastics in water (C) and sediment (D); the proportion of microplastic color in water (E) and sediment (F).
3.2. MPs in Sediment
The abundance of MPs among sampling sites in sediments was ranging from 566.67 items/kg to 2500 items/kg, with an average value of 1330 ± 554.33 items/kg (Figure 3B). All sediment samples in culture ponds contained MPs, with the lowest values at S1, while highest in S5. Several kinds of MPs were found in sediment samples. After Raman identification, the main polymer types were cellulose, high-density PP, polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and PE (Figure 4). Fibers (81.73%) were the most common MPs morphology in sediments, followed by fragments (13.08%) and films (4.36%) (Figure 5B), which was consistent with the findings of Wu et al. [24]. By classifying and counting the sizes of MPs, the results showed that the number of MPs with small size was the largest (Figure 5D). As with surface water samples, MPs of various colors were observed in sediments, but the main colors were transparent (62.73%), blue (16.92%), pink (4.11%), green (3.65%), white (3.44%), yellow (3.40%) and red (3.40%) (Figure 5F). Pearson analysis results showed that there was no correlation between MPs in water samples and sediment samples.
3.3. MPs in Commercial Species
In this study, 37 biological samples of two kinds of fish and two kinds of shrimp were collected from six ponds, and MPs were detected in all biological samples. Among them, the abundance of MPs in Oreochroms mossambcus ranged from 3 to 13 items/individual, with an average value of 6.14 ± 3.80 items/individual; the microplastic abundance ranged from 12 to 92 items/individual in Micropterus salmoides, with an average value of 39.64 ± 23.38 items/individual; the abundance of MPs in Penaeus vannamei ranged from 4 to 21 items/individual, with an average value of 10.87 ± 4.94 items/individual; and the abundance of MPs in Macrobrachium rosenbergii ranged from 5 to 12 items/individual, with an average value of 9 ± 3.16 items/individual (Figure 6A). Since the gastrointestinal tissues were not weighed separately in this study, the MP abundance per gram of GIT was not calculated here. The species, weight and body length information of fish and shrimp are shown in Table S1. Cellulose, PP and PE were the main polymer types in organisms (Figure 4). As for colors, transparent and blue dominated, while more yellow and white MPs were also observed (Figure 6C). The most abundant MPs were fibers, and a certain number of fragments were also found in the GITs of fish (Figure 6B).
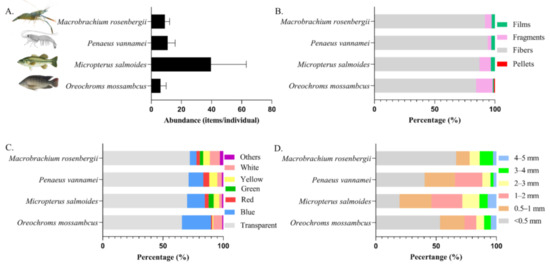
Figure 6.
Microplastic abundance in gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of different commercial species in the Pearl River Estuary (mean S.D., n = 4–15) (A); types (B), color distribution (C) and size distribution (D) of microplastics in gastrointestinal tract of different commercial species in the Pearl River Estuary.
3.4. Potential Risk Assessment of MPs in Sediments
The types of polymers observed in sediments at each sampling point in this study are shown in Table 1. Through the potential risk assessment of MPs in sediments, it was found that the abundance in sediment was lower than that of surface water, but the chemical toxicity of some detected polymers, such as PMMA and Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), cannot be ignored. Vinyl chloride, the main monomer of PVC, has been proved to cause hepatic angiosarcoma [48] and increase cardiovascular risk [49]. In addition, animals that inhaled vinyl chloride showed renal parenchymal lesions and swelling [50]. MPs in sediments can not only reflect the long-term interaction between land and water but also master the source and migration information of MPs [51,52,53]. Several studies have shown that, apart from density, the distribution of MPs is affected by other factors [54,55], especially in closed environments such as ponds, where the hydrodynamic is weak, the fluidity of MPs is poor and MPs may eventually tend to deposit in sediments. During the plastic manufacturing process, the polymerization reaction is incomplete, which leads to the release of unreacted residual monomers into the environment [56], posing a threat to the health of organisms and human beings. Raman results showed that some of the particles to be tested could not be identified as specific polymers, instead, they were identified as plastic additives, such as octadecanoic acid (commonly used as plasticizer and stabilizer) and copper (II) Phthalocyanine (commonly used in plastic spraying or dye). Combined with visual observation results, MPs have uneven structure, pits with different sizes on the surface and curled edges, indicating that MPs are obviously aged and degraded after weathering, thus residual monomers and additives added in the production process will be released into the environment [57]. In this study, the abundance of MPs and the chemical toxicity (toxicity of all monomers of polymer) of MPs were taken as indicators of risk assessment, and the chemical toxicity is represented by the risk score obtained by Litnner et al. [43]. Despite the high abundance of MPs, it was undeniable that more than half of the particles were identified as cellulose (mainly came from clothing), which was assumed to be non-toxic. Combined with the method of Peng et al. [30], Eir × Cin is used to compare the risks of each sampling site for the convenience of calculation because the value of Cin is unknown (Table 2). The results of risk assessment showed that the aquaculture ponds in this study generally showed high risk, two high-hazard compounds and five relatively friendly compounds were found. Compared with S3–S4, the surface water of S1 and S2 showed lower MPs abundance, but there was no obvious difference in MPs abundance among the four sampling sites in sediment samples, and high-risk MPs were detected in S1 and S2. There are some limitations in using this method to carry out the pollution risk of MPs, because the background value of MPs is unknown, and the exact risk index value cannot be obtained. In addition, there is no clear basis for dividing the pollution risk level of MPs. In this study, the differences of risk levels in different ponds were generally reflected by this method, which indicated that the risk assessment of MPs could not only consider abundance data or observe MPs in water samples.

Table 1.
Identification results of microplastics in sediments at each sampling site.

Table 2.
Potential risk assessment of microplastics in sediments of aquaculture ponds.
4. Discussion
4.1. Pollution of MPs in Surface Water
This study has opened up a new field for investigating the pollution of MPs in different media of pond water environment and evaluating the pollution risk of MPs in aquaculture ponds. Compared with other estuaries [34,58,59], freshwater fish ponds in the Carpathian Basin of Europe [60] and marine aquaculture areas in Xiangshan Bay [61], the abundance of MPs in surface water in this study is significantly higher (Table S2). A study had been conducted to investigate the abundance of MPs in fish ponds at the Pearl River Estuary [62], whose abundance of MPs at the inlet of the fish pond was 32.1 items/L. Similarly, the Pearl River Basin in Guangzhou showed high MPs abundance (19.8 items/L) [63], from which we can draw a conclusion that the abundance of MPs in aquaculture water is obviously higher than that in pond influent. S1 and S2 had transferred fish before sampling, and then the two aquaculture ponds were idle, with only a small number of small fish in the pond. Therefore, compared with S3–S6, the lower abundance of MPs in S1 and S2 indicates that aquaculture activities are the main cause of high MPs abundance in fish ponds, such as feeding, fishing and degradation of feed woven bags. The woven bags filled with feed can also cause microplastics pollution to a certain extent, so further improvement should be made on feed packaging. Moreover, the fish pond is a closed environment with poor water exchange capacity and weaker hydrodynamic, which is a good reservoir for MPs [64]. In view of the morphology of MPs, except for the films (ANOVA, P > 0.05), there were significant differences in the number of fibers, fragments and pellets at each sampling site (ANOVA, P < 0.05). There was a great difference in microplastic abundance among repeated samples, which may be because the wind, water waves and fish swimming can have great disturbance on microplastic distribution in surface water in an enclosed environment. Therefore, the sampling sites in this study were separated by three meters to avoid the influence of exogenous factors on microplastic abundance.
4.2. Pollution of MPs in Sediment
Compared with previous studies [65,66], the abundance of MPs in sediments in this study is significantly higher (Table S2). The results showed that fiber was the most dominant MP, followed by fragment and film; however, compared with surface water, the sediment contained more fragments, their smaller specific surface area made them easier to sink and accumulate at the bottom [67]. The low detection rate of pellets indicated that most MPs were derived from secondary MPs. As with surface water, sediments contained more small-sized MPs, which was consistent with the results of Di [47]. The high content of small-sized MPs may be due to mechanical or weathering degradation of large particles or direct crushing of plastic products [68,69]. The main color of MPs in sediments was transparent, and most MPs of this color came from fishing tools, such as fishing ropes and fishing nets [67,70]. However, the sediment contained a certain proportion of yellow MPs, which were highly degraded, indicating that the plastic degradation activity in the sediment of the culture pond was obvious, a large part of MPs come from far away and accumulate in ponds. There is no correlation between MPs in water samples and sediment samples, which could be explained by several factors, such as organism swimming, hydraulic action, MPs characteristics and so on [71].
4.3. Pollution of MPs in Commercial Species
In this study, the abundance of MPs in biological samples of different sizes and varieties was detected. The abundance of MPs observed in fish was higher than that in many previous studies [24,72,73,74,75,76] (Table S3), and the GITs of shrimps in this study showed higher MP abundance than in the findings of Wu et al. [24], which may be related to the living environment and the individual size of shrimps. In general, shrimp is selective feeding [77], which enables it to refuse to eat non-edible substances, so the accumulation potential for MPs is relatively low. Compared with small Oreochroms mossambcus, Micropterus salmoides had a considerable proportion of large-size MPs and fragments in their GITs (Figure 6D), which may be related to the physiological characteristics of Micropterus salmoides. First, the Micropterus salmoides in this study were about one-year-old and larger; second, their big mouth enabled them easily intake, moreover, they were demersal organisms, and the high concentration of fragments at the bottom of the pond leads to high levels of fragments in their bodies, which was different from the results of Neves et al., indicating that habitat can affect MPs intake.
Furthermore, many yellow and white MPs were found in biological samples, and the yellow color was caused by the yellowing effect of MPs after long-term weathering in the environment. As some organisms are visual predators, it may affect the absorption of MPs by organisms [78,79]; most of the white MPs were identified as PP, and there were two main sources: 1, Fishing tools such as fishing nets; 2, The feed woven bag can be broken directly and enter the pond with the feed. By observing the abundance of MPs in the gastrointestinal tract of each species, it was found that the abundance of MPs in larger individuals (higher body weight) was higher. Therefore, the uptake of MPs by organisms is dependent on multiple factors, such as physiological characteristics, age, habitats and MPs pollution in the living environment.
4.4. Potential Effects of MPs on Freshwater Culture, Especially Pond Culture
Although the risk value of S5 and S6 was the lowest, the concentration of MPs was the highest among all sampling sites, and a certain amount of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) was detected in S5. Peng et al. thought that PET can often be considered as polyester when it appears as fiber [30], and polyester was considered to have a high risk score. Therefore, it is equally important to count the abundance of MPs and evaluate the chemical toxicity of different polymers. The lower detection rate of high-risk MPs in S5 and S6 indicated that shrimps have higher requirements on water quality, thus, the water purification equipment and measures in aquaculture ponds may play an important role in reducing the entry of exotic MPs into ponds. It is far from enough to detect the abundance of MPs in surface water only. The composition identification and risk assessment of MPs in sediments can provide a basis for the formulation of environmental policies and the management of aquaculture ponds.
5. Conclusions
MPs are an emerging pollutant with a small size and widely distributed in the water environment, which can easily be eaten by aquatic organisms and affects the quality and quantity of aquatic organisms. Aquaculture has played an important role in providing high-quality aquatic products for human beings. However, there are few studies on microplastics pollution in freshwater ponds. By studying the aquaculture ponds in the Pearl River Estuary, it was found that the aquaculture activities would cause microplastic pollution in the culture ponds. In addition, the abundance of MPs in the culture ponds was significantly higher than that in the main stream of the Pearl River and the pond inlet, indicating that the low flow rate and poor water exchange capacity in the ponds would cause the accumulation of MPs. Yellow MPs are highly degradable, so the exposure risk of harmful monomers is greatly increased. However, aquatic organisms easily ingest such MPs, and the negative effects on organisms need to be studied. The potential risk assessment of MPs in sediments showed that the hazard score and abundance of MPs were two important indicators for evaluating MPs pollution. Low abundance was not equal to low risk. High MPs abundance existed in shrimp ponds, but high-risk MPs were not observed. The water purification equipment in shrimp ponds may play an important role in reducing the pollution of exotic MPs. In the future, the risk levels of MPs in sediments should be classified to clarify the pollution status of MPs in the region.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/4/1869/s1, Figure S1: Composition of typical MPs identified by Raman spectroscopy, Table S1: Body weight and body length information of commercial species collected from aquaculture farms in the Pearl River Estuary, Table S2: The microplastic abundance of water and sediment in other studies compared with this study, Table S3: The microplastic abundance of aquatic organisms in other studies compared with this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and G.C.; methodology, K.X.; software, Y.L.; validation, Y.L. and G.C.; formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, J.W.; data curation, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing—review and editing, J.W.; visualization, K.H.; supervision, G.C.; project administration, J.W.; funding acquisition, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. The study did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
This research were funded by the Guangdong Province Universities and Colleges Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (2018), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42077364), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0900604), Key Research Projects of Universities in Guangdong Province (2019KZDXM003 and 2020KZDZX1040). We appreciate the provision of SCAU Wushan Campus Teaching & Research Base.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- GESAMP. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Global Assessment; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2016.
- Miller, R.Z.; Watts, A.J.R.; Winslow, B.O.; Galloway, T.S.; Barrows, A.P.W. Mountains to the sea: River study of plastic and non-plastic microfiber pollution in the Northeast USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Tassin, B. Synthetic and non-synthetic anthropogenic fibers in a river under the impact of Paris megacity: Sampling methodological aspects and flux estimations. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 618, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivleva, N.P.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Niessner, R. Microplastic in Aquatic Ecosystems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 1720–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; Saal, F.S.V.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozar, A.; Echevarria, F.; Gonzalez-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Ubeda, B.; Hernandez-Leon, S.; Palma, A.T.; Navarro, S.; Garcia-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Mason, S.; Wilson, S.; Box, C.; Zellers, A.; Edwards, W.; Farley, H.; Amato, S. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. 2013, 77, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, C.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Nicholas, M.E.; Williamson, J.; Boldgiv, B. Highlevels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, R.A.; Avlijas, S.; Simard, M.A.; Ricciardi, A. Microplastic pollution in St. Lawrence river sediments. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 71, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedger, A.G.J.; Durr, H.H.; Mitchell, K.; Van Cappellen, P. Plastic debris in the Laurentian Great Lakes: A review. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, T.; Hauk, A.; Walter, U.; Burkardt-Holm, P. Microplastics profile along the Rhine River. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, L.; Heard, M.J. Variation in the presence and abundance of anthropogenic microfibers in the Cumberland River in Nashville, TN, USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10135–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 19, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sebille, E.; Wilcox, C.; Lebreton, L.; Maximenko, N.; Hardesty, B.D.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Eriksen, M.; Siegel, D.; Galgani, F.; Law, K.L. A global inventory of small floating plastic debris. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124006. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; He, D.; Pan, X. Effects of accelerated aging on characteristics, leaching, and toxicity of commercial lead chromate pigmented microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, R. Sorption behaviors of phenanthrene on the microplastics identified in a mariculture farm in Xiangshan Bay, southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Cui, B.; Bai, J.; Zhang, W. Size effect of polystyrene microplastics on sorption of phenanthrene and nitrobenzene. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Lang, M.; Yu, X.; Wu, R.; Yang, X.; Guo, X. Aging mechanism of microplastics with UV irradiation and its effects on the adsorption of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, V.; Blázquez, G.; Calero, M.; Quesada, L.; Martín-Lara, M.A. The potential of microplastics as carriers of metals. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Tan, S.; Kang, Z.; Yu, X.; Lan, W.; Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Shi, H. Microplastic pollution in the Maowei Sea, a typical mariculture bay of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Leung, J.Y.S.; Huang, W.; Zeng, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, A.; Yu, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Accumulation of microplastics in typical commercial aquatic species: A case study at a productive aquaculture site in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Su, J. Vulnerability of China’s nearshore ecosystems under intensive mariculture development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 8957–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MAPRC. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. 2016. Available online: http://www.cnfm.gov.cn/yyywyzj/201605/t20160531_5156281.htm/ (accessed on 31 May 2016). (In Chinese)
- Yu, H.B. Current situation and problems in freshwater fish production. S. China Agr. 2015, 9, 167–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Qi, Z.; Chen, H.; Hao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ying, G. Steroid bioaccumulation profiles in typical freshwater aquaculture environments of South China and their human health risks via fish consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, L.; Cheung, P.K.; Tang, G.; Li, W.C. Size distribution of stranded small plastic debris on the coast of Guangdong, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Zhu, B.; Yang, D.; Su, L.; Shi, H.; Li, D. Microplastics in sediments of the Changjiang estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.M.; Ran, W.; Teng, J.; Liu, Y.L.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.N.; Cao, R.W.; Wang, Q. Microplastic pollution in sediments from the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, N. Study on the decomposition of factors affecting energy-related carbon emissions in Guangdong province, China. Energies 2011, 4, 2249–2272. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Su, L.; Li, H.; Liang, M.; Shi, H. Assessing the relationship between the abundance and properties of microplastics in water and in mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Microplastic in three urban estuaries, China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuelle, M.T.; Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Fries, E. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, T.; Jessop, R.; Wellner, N.; Haupt, K.; Mayes, A.G. A rapid-screening approach to detect and quantify microplastics based on fluorescent tagging with Nile red. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.; Murphy, F.; Ewins, C. Validation of density separation for the rapid recovery of microplastics from sediment. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Shi, H.; Luo, Z.; Wu, C. Sources and distribution of microplastics in China’s largest inland Lake—Qinghai Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 899–906. [Google Scholar]
- Jabeen, K.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Tong, C.; Mu, J.; Shi, H. Microplastics and mesoplastics in fifish from coastal and fresh waters of China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Shi, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Jabeen, K.; Kolandhasamy, P. Microplastic pollution in table salts from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13622–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasta, M.; Sattari, M.; Taleshi, M.S.; Namin, J.I. Identification and distribution of microplastics in the sediments and surface waters of Anzali Wetland in the Southwest Caspian Sea, Northern Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Zhang, S.; Qu Ling, J.; Fang, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. Microplastics abundance and characteristics in surface waters from the Northwest Pacific, the Bering Sea, and the Chukchi Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 143, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, T.; Khalid, S.; Taneez, M.; Muhammad, Z.H. Plastic driven pollution in Pakistan: The first evidence of environmental exposure to microplastic in sediments and water of Rawal Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15083–15092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, M.X.; Wang, J. Microplastics in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.C.; Wann, S.R.; Chang, H.T.; Lin, S.L.; Wang, J.S.; Guo, H.R. Arsenic, vinyl chloride, viral hepatitis, and hepatic angiosarcoma: A hospital-based study and review of literature in Taiwan. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Sirit, Y.; Acero, C.; Bellorin, M.; Portillo, R. Metabolic syndrome and other factors cardiovascular risk in workers of a plant of vinyl polychloride. Rev. Salud Publica 2008, 10, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.L.; Bigotti, A.; Caputo, A. Oncogenic response of rat skin, lungs, and bones to vinyl chloride. Cancer Res. 1971, 31, 516–522. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Munoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Kan, W.; Bao, S. Occurrence of microplastics in the beach sand of the Chinese inner sea: The Bohai Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ndungu, A.W.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Microplastics pollution in inland freshwaters of China: A case study in urban surface waters of Wuhan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.R.A.; Costa, M.F.; Barletta, M. Distribution patterns of microplastics within the plankton of a tropical estuary. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Moriceau, B.; Gallinari, M.; Lambert, C.; Huvet, A.; Raffray, J.; Soudant, P. Interactions between microplastics and phytoplankton aggregates: Impact on their respective fates. Mar. Chem. 2015, 175, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, P.H.H.; Sayer, C.; Poco, J.G.R.; Giudici, R. Techniques for reducing residual monomer content in polymers: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 1442–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Halle, A.; Ladirat, L.; Martignac, M.; Mingotaud, A.F.; Boyron, O.; Perez, E. To what extent are microplastics from the open ocean weathered? Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Li, D. Analysis of suspended microplastics in the Changjiang Estuary: Implications for riverine plastic load to the ocean. Water Res. 2019, 161, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, E.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y. Microplastics in the surface water of small-scale estuaries in Shanghai. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2019, 149, 110569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordos, G.; Urbanyi, B.; Micsinai, A.; Kriszt, B.; Palotai, Z.; Szabo, I.; Hantosi, Z.; Szoboszlay, S. Identification of microplastics in fish ponds and natural freshwater environments of the Carpathian basin, Europe. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jin, M.; Tao, P.; Wang, Z.; Xie, W.; Yu, X.; Wang, K. Assessment of microplastics derived from mariculture in Xiangshan Bay, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lu, L.; Ye, X.; Deng, W.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z. High levels of microplastic pollution in aquaculture water of fish ponds in the Pearl River Estuary of Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Nie, H.; Xu, K.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in the Pearl River along Guangzhou city and Pearl River estuary, China. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianello, A.; Boldrin, A.; Guerriero, P.; Moschino, V.; Rella, R.; Sturaro, A.; Da Ros, L. Microplastic particles in sediments of lagoon of Venice, Italy: First observations on occurrence spatial patterns and identification. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Williams, R.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E. Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK—Abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tata, T.; Belabed, B.E.; Bououdina, M.; Bellucci, S. Occurrence and characterization of surface sediment microplastics and litter from North African coasts of Mediterranean Sea: Preliminary research and first evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Cai, L. Microplastics in the surface sediments from the Beijiang River littoral zone: Composition, abundance, surface textures and interaction with heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Sang, H.H.; Mi, J.; Han, G.M.; Jung, S.W.; Shim, W.J. Combined effects of UV exposure duration and mechanical abrasion on microplastic fragmentation by polymer type. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3831–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julienne, F.; Delorme, N.; Lagarde, F. From macroplastics to microplastics: Role of water in the fragmentation of polyethylene. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Gong, W.; Lv, J.; Xiong, X.; Wu, C. Accumulation of floating microplastics behind the Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Di, M.; Wang, J. Microplastic abundance, distribution and composition in water, sediments and wild fish from Poyang Lake, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.A.; Thomas, P.A.; Rieper, K.B.; Bratton, S.P. Foraging preferences influence microplastic ingestion by six marine fish species from the Texas Gulf Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Russell, M.; Ewins, C.; Quinn, B. The uptake of macroplastic & microplastic by demersal & pelagic fish in the Northeast Atlantic around Scotland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Rummel, C.D.; Loder, M.G.; Fricke, N.F.; Lang, T.; Griebeler, E.M.; Janke, M.; Gerdts, G. Plastic ingestion by pelagic and demersal fifish from the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; d’Errico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellas, J.; Martínez-Armental, J.; Martínez-Cámara, A.; Besada, V.; Martínez-Gómez, C. Ingestion of microplastics by demersal fish from the Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focken, U.; Groth, A.; Coloso, R.M.; Becker, K. Contribution of natural food and supplemental feed to the gut content of Penaeus monodon fabricius in a semi-intensive pond system in the Philippines. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhan, X.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, S. Effect of weathering on environmental behavior of microplastics: Properties, sorption and potential risks. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sá, L.C.; Luís, L.G.; Guilhermino, L. Effects of microplastics on juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps): Confusion with prey, reduction of the predatory performance and efficiency, and possible influence of developmental conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 359–362. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).