Association between Physical Activity and Fundamental Movement Skills in Preschool-Aged Children: Does Perceived Movement Skill Competence Mediate This Relationship?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Measures
2.4. Data Analysis
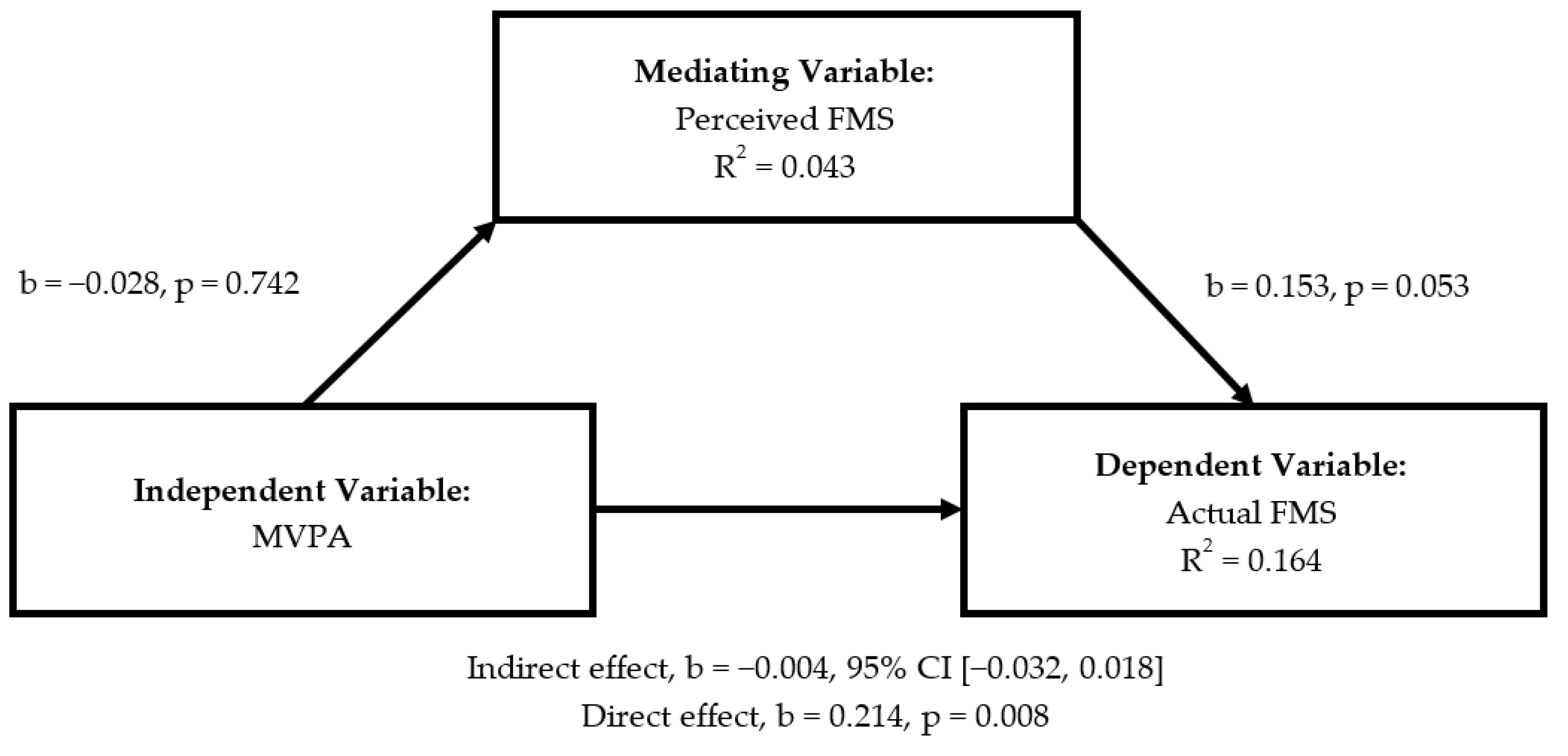
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, L.A.; Fletcher, E.A.; Timperio, A.; Vuillermin, P.; Hesketh, K. Preschool children’s physical activity and cardiovascular disease risk: A systematic review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 22, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, V.; Lee, E.Y.; Hewitt, L.; Jennings, C.; Hunter, S.; Kuzik, N.; Stearns, J.A.; Unrau, S.P.; Poitras, V.J.; Gray, S.; et al. Systematic review of the relationships between physical activity and health indicators in the early years (0-4 years). BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.; Hinkley, T.; Okely, A.D.; Salmon, J. Tracking physical activity and sedentary behaviour in childhood: A systematic review. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 44, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Community Sports Committee of the Sports Commission. The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Healthy Exercise for All Campaign-Physical Fitness Test for the Community. Available online: https://www.lcsd.gov.hk/en/healthy/physical_fitness_test/common/physical_fitness_test/download/SummaryReport_en.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2013).
- Stodden, D.F.; Goodway, J.D.; Langendorfer, S.J.; Roberton, M.A.; Rudisill, M.E.; Garcia, C.; Garcia, L.E. A developmental perspective on the role of motor skill competence in physical activity: An emergent relationship. Quest 2008, 60, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, R.; An, R. Motor skill competence and physical activity in preschoolers: A review. Matern. Child Health J. 2017, 21, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.E.; Stodden, D.F.; Barnett, L.M.; Lopes, V.P.; Logan, S.W.; Rodrigues, L.P.; D’Hondt, E. Motor competence and its effect on positive developmental trajectories of health. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, S.W.; Ross, S.M.; Chee, K.; Stodden, D.F.; Robinson, L.E. Fundamental motor skills: A systematic review of terminology. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, L.L.; King, L.; Farrell, L.; Macniven, R.; Howlett, S. Fundamental movement skills among Australian preschool children. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.M.; Ridgers, N.D.; Salmon, J. Associations between young children’s perceived and actual ball skill competence and physical activity. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.M.; Morgan, P.J.; Van Beurden, E.; Beard, J.R. Perceived sports competence mediates the relationship between childhood motor skill proficiency and adolescent physical activity and fitness: A longitudinal assessment. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Ha, A.S.; Ng, J.Y.; Lubans, D.R. Associations between fundamental movement skill competence, physical activity and psycho-social determinants in Hong Kong Chinese children. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.R.; Naylor, P.J.; Cook, R.; Temple, V.A. Do perceptions of competence mediate the relationship between fundamental motor skill proficiency and physical activity levels of children in kindergarten? J. Phys. Act. Health 2015, 12, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, L.M.; Morgan, P.J.; Van Beurden, E.; Ball, K.; Lubans, D.R. A reverse pathway? Actual and perceived skill proficiency and physical activity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliff, D.P.; Reilly, J.J.; Okely, A.D. Methodological considerations in using accelerometers to assess habitual physical activity in children aged 0–5 years. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2009, 12, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pate, R.R.; Almeida, M.J.; McIver, K.L.; Pfeiffer, K.A.; Dowda, M. Validation and calibration of an accelerometer in preschool children. Obesity 2006, 14, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, R.M.; Sommer, E.C.; Tracy, D.; Banda, J.A.; Economos, C.D.; JaKa, M.M.; Evenson, K.R.; Buchowski, M.S.; Barkin, S.L. Novel patterns of physical activity in a large sample of preschool-aged children. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, D.A. The Test of Gross Motor Development, 2nd ed.; PRO-ED, Inc.: Austin, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Curriculum Development Council, The Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Kindergarten Education Curriculum Guide. Available online: https://www.edb.gov.hk/attachment/en/curriculum-development/major-level-of-edu/preprimary/ENG_KGECG_2017.pdf (accessed on 31 December 2017).
- Barnett, L.M.; Ridgers, N.D.; Zask, A.; Salmon, J. Face validity and reliability of a pictorial instrument for assessing fundamental movement skill perceived competence in young children. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, S.; Pike, R. The pictorial scale of perceived competence and social acceptance for young children. Child Dev. 1984, 55, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Dong, C.; Barnett, L.M.; Estevan, I.; Li, J.; Ji, L. Validity and reliability of a pictorial instrument for assessing fundamental movement skill perceived competence in Chinese children. J. Mot. Learn Dev. 2018, 6, S223–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preacher, K.J.; Hayes, A.F. SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 2004, 36, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, S. The Construction of the Self: Developmental and Sociocultural Foundations; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, F.; Chen, S.T.; Clark, C.; Hong, J.T.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Y.J. Relationship between fundamental movement skills and physical activity in preschool-aged children: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slykerman, S.; Ridgers, N.D.; Stevenson, C.; Barnett, L.M. How important is young children’s actual and perceived movement skill competence to their physical activity? J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeGear, M.; Greyling, L.; Sloan, E.; Bell, R.I.; Williams, B.L.; Naylor, P.J.; Temple, V.A. A window of opportunity? Motor skills and perceptions of competence of children in Kindergarten. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L.E. The relationship between perceived physical competence and fundamental motor skills in preschool children. Child Care Health Dev. 2011, 37, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, G.H.; Ridgers, N.D.; Barnett, L.M. Associations between skill perceptions and young children’s actual fundamental movement skills. Percept. Mot. Skills 2015, 120, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.S.; Macdonald, D.; Pang, B.O. Physical activity in the lives of Hong Kong Chinese children. Sport Educ. Soc. 2010, 15, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, Y.N.; Cerin, E.; Wu, S.L. Parental practices encouraging and discouraging physical activity in Hong Kong Chinese preschoolers. J. Phys. Act. Health 2015, 12, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.S.; Chan, W.; Ng, J.Y. Relation between perceived barrier profiles, physical literacy, motivation and physical activity behaviors among parents with a young child. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Total (n = 148) | Boys (n = 85) | Girls (n = 63) | P a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Age (years) | 4.52 (0.67) | 4.58 (0.71) | 4.43 (0.61) | 0.178 |
| Actual FMS (0−32) | 16.81 (4.82) | 17.56 (4.88) | 15.80 (4.57) | 0.026 |
| ALM (0−16) | 10.21 (2.95) | 9.99 (2.77) | 10.49 (3.17) | 0.321 |
| AOC (0−16) | 6.86 (2.93) | 7.74 (3.01) | 5.68 (2.37) | <0.001 |
| Perceived FMS (4−16) | 12.61 (2.64) | 12.86 (2.79) | 12.29 (2.42) | 0.184 |
| PLM (2−8) | 6.43 (1.46) | 6.62 (1.41) | 6.17 (1.49) | 0.066 |
| POC (2−8) | 6.18 (1.65) | 6.24 (1.80) | 6.11 (1.42) | 0.651 |
| LMVPA (mins) | 144.33 (32.79) | 151.20 (32.91) | 135.07 (30.51) | 0.003 |
| MVPA (mins) | 67.77 (20.41) | 72.19 (21.44) | 61.81 (17.37) | 0.001 |
| Variable | ALM | AOC | Perceived FMS | PLM | POC | MVPA | LMVPA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual FMS | 0.774 ** | 0.823 ** | 0.206 * | 0.171 * | 0.179 * | 0.246 ** | 0.252 ** |
| ALM | 0.420 ** | 0.223 ** | 0.165 * | 0.213 ** | 0.139 | 0.114 | |
| AOC | 0.172 * | 0.168 * | 0.127 | 0.192 * | 0.210 * | ||
| Perceived FMS | 0.831 ** | 0.870 ** | 0.019 | 0.008 | |||
| PLM | 0.449 ** | 0.028 | 0.027 | ||||
| POC | 0.006 | −0.012 | |||||
| MVPA | 0.924 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Ng, J.Y.Y.; Cairney, J.; Bedard, C.; Ha, A.S.C. Association between Physical Activity and Fundamental Movement Skills in Preschool-Aged Children: Does Perceived Movement Skill Competence Mediate This Relationship? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031289
He Q, Ng JYY, Cairney J, Bedard C, Ha ASC. Association between Physical Activity and Fundamental Movement Skills in Preschool-Aged Children: Does Perceived Movement Skill Competence Mediate This Relationship? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031289
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Qing, Johan Y. Y. Ng, John Cairney, Chloe Bedard, and Amy S. C. Ha. 2021. "Association between Physical Activity and Fundamental Movement Skills in Preschool-Aged Children: Does Perceived Movement Skill Competence Mediate This Relationship?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031289
APA StyleHe, Q., Ng, J. Y. Y., Cairney, J., Bedard, C., & Ha, A. S. C. (2021). Association between Physical Activity and Fundamental Movement Skills in Preschool-Aged Children: Does Perceived Movement Skill Competence Mediate This Relationship? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031289







