Lifetime Carcinogenic Risk Proportions from Inhalation Exposures in Industrial and Non-Industrial Regions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Input Data
2.1.1. Study Population
2.1.2. Incidence Rates
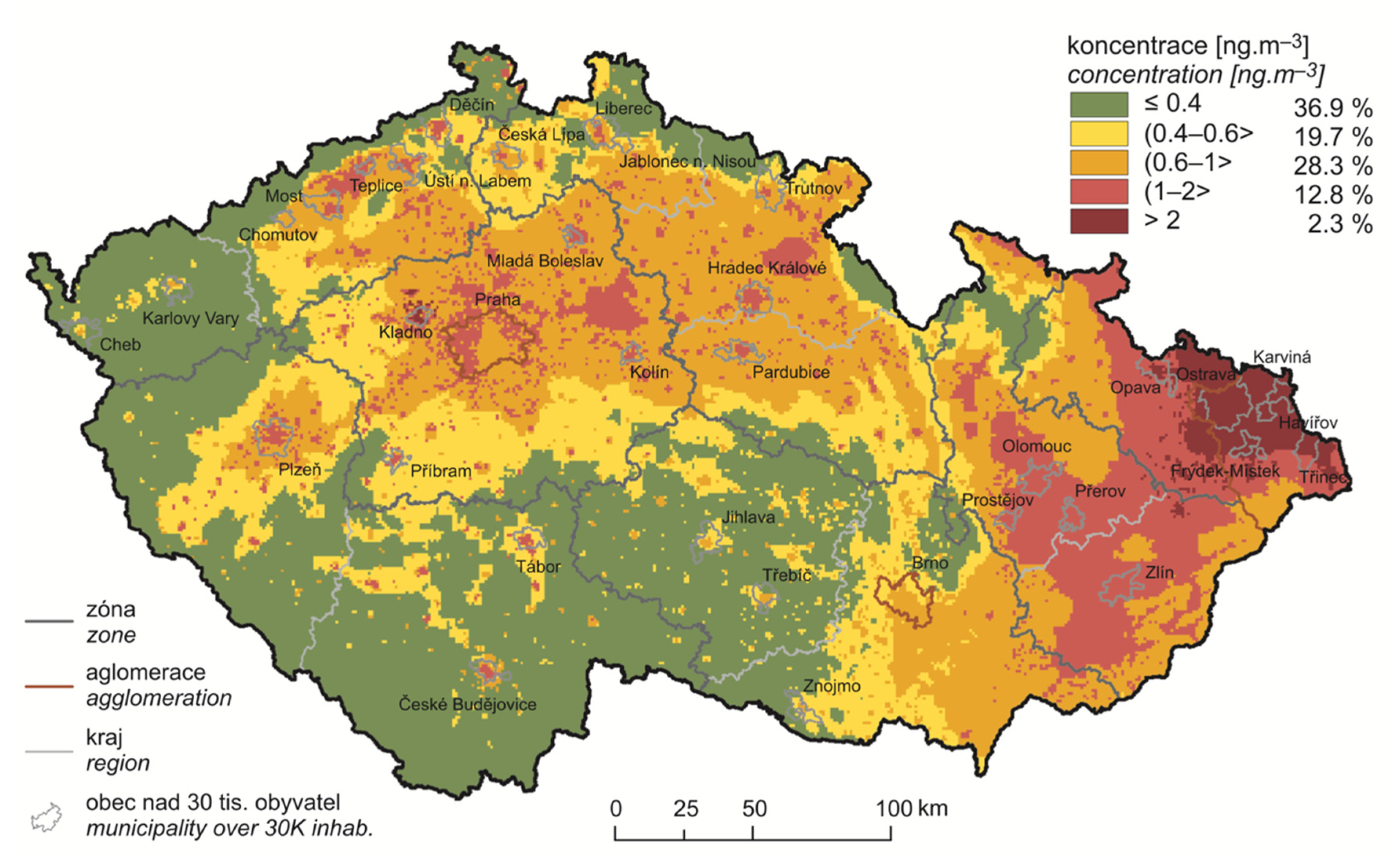
2.1.3. Risk Factors and Exposure Assessment
Radon
Benzo[a]pyrene
Fibrogenic Dust
Others Risk Factors
2.2. Data Processed
2.2.1. Lifetime Exposure
- LD—lifetime cumulative effective dose (mSv) per 1 inhabitant;
- VAR—constant volume activity of radon in the observe period (Bq/m3);
- ED—exposure duration (75 years);
- CF—conversion factor (365.25 × 24 h);
- OF—occupancy factor (0.7);
- RCF—radon dose conversion factor (6.70 × 10−6 mSv/Bq·hours·m−3).
- LC—lifetime average exposure concentration (µg/m3);
- cavg—average air pollution concentration (µg/m3) replaced by an approximation for all years and the approximation using a linear trend based on the closest known and back extrapolation (1945–2019);
- ED—exposure duration (75 years);
- AT—average lifetime (80 years).
2.2.2. Lifetime Risk
- LRo—lifetime risk of LBC from all risk factors for a 75-year-old (i.e., the cumulative incidence rate);
- LR1—lifetime risk of LBC from exposure to radon;
- LR2—lifetime risk of LBC from exposures to benzo[a]pyrene;
- LR3—lifetime risk of LBC from occupational exposure;
- LR4—lifetime risk of LBC from others risk factors.
- ANP—the average annual number of pneumoconiosis (1996–2016) in monitored regions [11];
- PCP—the average proportion of all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis [18];
- ANC—the average annual number of all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis;
- PLC—the average proportion of LBC from all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis [18];
- ANL—the average annual number of LBC in employees with pneumoconiosis;
- POP—the average population in monitored regions in years 1996–2016;
- ARL—the average annual risk of LBC from occupational exposures (expressed for whole population in the region);
- LR3—lifetime risk of LBC from occupational exposure (expressed on whole population in the region) for 75 old persons.
2.2.3. Lifetime Risk Proportion
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANC | The average annual number of all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis |
| ANL | The average annual number of LBC in employees with pneumoconiosis |
| ANP | The average annual number of pneumoconiosis (1996–2016) in monitored regions |
| ARL | The average annual risk of LBC from occupational exposures (expressed for whole population in the region) |
| AT | Average lifetime |
| B[a]P | Benzo[a]pyrene |
| cavg | Average air pollution concentration |
| CF | Conversion factor |
| CIR | Crude incidence rate |
| CR | Czech Republic |
| ED | Exposure duration |
| IA | Industrial area |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| ICRP | International Commission on Radiological Protection |
| LBC | Cancer of respiratory tract (trachea, bronchus, and lung cancer) |
| LC | Lifetime average exposure concentration |
| LC | Lifetime average exposure concentration of benzo[a]pyrene |
| LCR | Lifetime cancer risk |
| LD | Lifetime cumulative effective dose of radon |
| LR1 | Lifetime risk of LBC from exposure to radon |
| LR2 | Lifetime risk of LBC from exposures to benzo[a]pyrene |
| LR3 | Lifetime risk of LBC from occupational exposure |
| LR4 | Lifetime risk of LBC from others risk factors |
| LRo | Lifetime risk of LBC from all risk factors for a 75-year-old (i.e., the cumulative incidence rate) |
| LRP1 | Lifetime risk proportion from exposure to radon |
| LRP2 | Lifetime risk proportion from exposure to benzo[a]pyrene |
| LRP3 | Lifetime risk proportion from occupational exposure |
| LRP4 | Lifetime risk proportion from exposure to other risk factors |
| NA | Non-industrial area |
| OF | Occupancy factor |
| PAF | Attributable fraction for the population |
| PCP | The average proportion of all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis |
| PLC | The average proportion of LBC from all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| POP | The average population in monitored regions in years 1996–2016 |
| RCF | Radon dose conversion factor |
| Rn | Radon |
| SIR | Age-standardized incidence rate |
| UCR | Unit cancer risk |
| US EPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| VAR | Constant volume activity of radon in the observe period |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Health Information and Statistics of the Czech Republic Cancer Incidence in the Czech Republic. 2016. Available online: https://www.uzis.cz/sites/default/files/knihovna/novotvary2016.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- De Groot, P.M.; Wu, C.C.; Carter, B.W.; Munden, R.F. The epidemiology of lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiřík, V.; Machaczka, O.; Miturová, H.; Tomášek, I.; Šlachtová, H.; Janoutová, J.; Velická, H.; Janout, V. Air pollution and potential health risk in Ostrava region–A review. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2016, 24, S4–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamra, G.B.; Guha, N.; Cohen, A.; Laden, F.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Samet, J.M.; Vineis, P.; Forastiere, F.; Saldiva, P.; Yorifuji, T.; et al. Outdoor particulate matter exposure and lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozákovác, J.; Leoni, C.; Klán, M.; Hovorka, J.; Racek, M.; Koštejn, M.; Ondráček, J.; Moravec, P.; Schwarz, J. Chemical Characterization of PM1-2.5 and its Associations with PM1, PM2.5-10 and Meteorology in Urban and Suburban Environments. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1684–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, K.H.; Yan, B.; Chillrud, S.N.; Perera, F.P.; Whyatt, R.; Camann, D.; Kinney, P.L.; Miller, R.L. Assessment of benzo(a)pyrene-equivalent carcinogenicity and mutagenicity of residential indoor versus outdoor polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposing young children in New York City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Enviromental Protection Agency. Toxicological Review of Benzo(a)pyrene. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/toxreviews/0136tr.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Radonový Program České Republiky. Available online: https://www.radonovyprogram.cz/uvodni-strana/ (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The National Institute of Public Health Nemoci z Povolání v České Republice. Available online: http://www.szu.cz/publikace/data/nemoci-z-povolani-a-ohrozeni-nemoci-z-povolani-v-ceske-republice?fbclid=IwAR18wyuzo-bcy-_eAo21PqFgA8lDfFRi7O4LCLclbwhCLOJQJMj61Lei0fU (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Santoro, A.; Tomino, C.; Prinzi, G.; Lamonaca, P.; Cardaci, V.; Fini, M.; Russo, P. Tobacco Smoking: Risk to Develop Addiction, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, and Lung Cancer. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech Hydrometeorological Institute. Five-Year Average of Annual Average Concentrations of Benzo[a]pyrene, 2014–2018. Available online: https://www.chmi.cz/files/portal/docs/uoco/isko/grafroc/18groc/gr18cz/IV.2.BaP_CHMU2018.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Czech Statistical Institute. Obyvatelstvo. Available online: https://www.czso.cz/csu/czso/obyvatelstvo_lide (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Dušek, L.; Mužk, J.; Malúsková, D.; Májek, O.; Pávhik, T.; Koptííková, J.; Gregor, J.; Brabec, P.; Abráhámova, J. Epidemiology of screening-targeted cancers according to new data of the czech national cancer registry. Klin. Onkol. 2014, 27, 2S19–2S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech Hydrometeorological Institute. Znečištění Ovzduší a Atmosférická Depozice v Datech, Česká Republika. Available online: https://www.chmi.cz/files/portal/docs/uoco/isko/tab_roc/tab_roc_CZ.html (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Pozzolini, M.; Scarfì, S.; Gallus, L.; Ferrando, S.; Cerrano, C.; Giovine, M. Silica-induced fibrosis: An ancient response from the early metazoans. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 4007–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomášková, H. Karcinogenní Riziko u Horníků Černouhelných Hlubinných dolů v České Republice, Univerzita Karlova. 2017. Available online: https://dspace.cuni.cz/bitstream/handle/20.500.11956/111559/Habilitace_TomáškováH_Text.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Papaefthymiou, H.; Mavroudis, A.; Kritidis, P. Indoor radon levels and influencing factors in houses of Patras, Greece. J. Environ. Radioact. 2003, 66, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. International Commission on Radiological Protection Statement on Radon. Available online: https://www.icrp.org/docs/ICRP_Statement_on_Radon(November_2009).pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- US-EPA. EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes. Off. Radiat. Indoor Air 2003, 88. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-05/documents/402-r-03-003.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Sowby, F.D. Annals of the ICRP. Ann. ICRP 1981, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Annals of the ICRP; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2015; Volume 44, ISBN 9781473939509. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Air quality guidelines for particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Air Qual. Guidel. 2006, 1–496. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/69477/WHO_SDE_PHE_OEH_06.02_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- US EPA. Regional Screening Levels (RSLs)-Generic Tables Tables as of: November 2019; United States Environtal Protection Agency 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-generic-tables (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Brown, C.C.; Fears, T.R.; Gail, M.H.; Schneiderman, M.A.; Tarone, R.E.; Mantel, N. Models for carcinogenic risk assessment. Science 1978, 202, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, J.-F.; Solomon, S.; Takala, J.; Jung, T.; Strand, P.; Murith, C.; Kiselev, S.; Zhuo, W.; Shannoun, F.; Janssens, A. ICRP Publication 126: Radiological Protection against Radon Exposure. Ann. ICRP 2014, 43, 5–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Air Quality Guidelines for Europe, 2nd ed.; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000; Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/74732/E71922.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Appleton, J.D. Radon: Sources, Health Risks, and Hazard Mapping. Ambio 2007, 36, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Environment Agency. Population-Weighted Concentration Field of Annual Mean BaP. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/figures/population-weighted-concentration-field-of (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- WHO Regional Office for Europe. Review of Evidence on Health Aspects of Air Pollution–REVIHAAP Project. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/environment-and-health/air-quality/publications/2013/review-of-evidence-on-health-aspects-of-air-pollution-revihaap-project-final-technical-report (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Malhotra, J.; Malvezzi, M.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Boffetta, P. Risk factors for lung cancer worldwide. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csémy, L.; Dvořáková, Z.; Fialová, A.; Kodl, M.; Malý, M.; Skývová, M. Užívání Tabáku a Alkoholu v České Republice 2019. Available online: http://www.szu.cz/uploads/documents/szu/aktual/Zprava_o_uzivani_tabaku_a_alkoholu_v_Ceske_republice.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).





| Region and Districts | CIR a | SIR b | LRo c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | |
| Moravian-Silesian (IA) | 61.1 | 94.6 | 31.4 | 75.4 | 136.9 | 33.1 | 4671.62 | 8189.49 | 2021.74 |
| Karviná | 64.9 | 103.0 | 34.1 | 80.4 | 151.3 | 34.6 | 5035.17 | 9058.79 | 2191.98 |
| Nový Jičín | 51.3 | 79.5 | 22.3 | 67.0 | 118.0 | 24.4 | 4045.14 | 6973.28 | 1528.64 |
| Opava | 56.3 | 89.2 | 22.7 | 70.2 | 129.2 | 24.4 | 4356.91 | 7750.49 | 1524.20 |
| Ostrava | 64.9 | 97.7 | 38.5 | 77.8 | 137.7 | 40.3 | 4814.85 | 8255.79 | 2358.01 |
| South Bohemian (NA) | 63.0 | 93.3 | 28.1 | 75.5 | 126.8 | 29.6 | 4626.42 | 7595.26 | 1746.47 |
| České Budějovice | 60.9 | 79.3 | 28.5 | 74.8 | 112.5 | 30.1 | 4570.86 | 6489.86 | 1803.11 |
| Český Krumlov | 61.3 | 88.7 | 33.6 | 84.0 | 139.2 | 38.9 | 5261.90 | 8563.57 | 2445.38 |
| Jindřichův Hradec | 65.4 | 104.2 | 21.9 | 77.7 | 145.2 | 23.7 | 4723.50 | 8229.25 | 1485.94 |
| Písek | 71.1 | 111.2 | 35.2 | 78.6 | 137.8 | 34.4 | 4719.71 | 8642.65 | 1875.69 |
| Prachatice | 58.4 | 92.6 | 23.3 | 73.9 | 129.4 | 26.8 | 4687.91 | 8498.61 | 1654.19 |
| Strakonice | 56.3 | 87.0 | 25.6 | 64.9 | 110.5 | 26.3 | 4140.63 | 6901.24 | 1491.72 |
| Tábor | 66.9 | 103.4 | 28.9 | 75.8 | 131.0 | 29.4 | 4562.21 | 7876.52 | 1618.21 |
| Difference d | −1.9 | 1.3 | 3.3 | −0.1 | 10.1 | 3.5 | 45.21 | 594.22 | 275.26 |
| p-value e | 0.927 | 0.927 | 0.925 | ||||||
| Region and Districts | Radon | Benzo[a]pyrene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radon Activity (Bq/m3) a | LD (mSv) b | Cavg (ng/m3) c | LC (ng/m3) d | |
| Moravian-Silesian (IA) | 77 | 238 | 3.378 | 3.167 |
| Karviná | 72 | 222 | 2.989 | 2.802 |
| Nový Jičín | 92 | 284 | 1.142 | 1.070 |
| Opava | 88 | 271 | 1.163 | 1.090 |
| Ostrava | 69 | 213 | 8.217 | 7.704 |
| South Bohemian (NA) | 120 | 369 | 0.406 | 0.381 |
| České Budějovice | 93 | 287 | 0.440 | 0.412 |
| Český Krumlov | 94 | 290 | 0.357 | 0.335 |
| Jindřichův Hradec | 125 | 385 | 0.440 | 0.412 |
| Písek | 160 | 493 | 0.440 | 0.412 |
| Prachatice | 128 | 395 | 0.395 | 0.370 |
| Strakonice | 204 | 629 | 0.334 | 0.313 |
| Tábor | 89 | 274 | 0.437 | 0.410 |
| Difference e | −43 | −131 | 2.972 | 2.786 |
| p-value f | 0.012 | 0.010 | ||
| Region and Districts | Lifetime Risk (per 100,000) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radon | Benzo[a]pyrene | Radon + B[a]P | ||||
| LR1 a | LR2 b | LR1 + LR2 c | ||||
| EPA | ICRP | EPA | WHO | EPA | WHO | |
| Moravian-Silesian (IA) | 1216 | 1130 | 0.190 | 27.55 | 1216 | 1158 |
| Karviná | 1134 | 1055 | 0.168 | 24.38 | 1135 | 1079 |
| Nový Jičín | 1450 | 1347 | 0.064 | 9.312 | 1450 | 1357 |
| Opava | 1387 | 1289 | 0.065 | 9.484 | 1387 | 1298 |
| Ostrava | 1087 | 1011 | 0.462 | 67.02 | 1088 | 1078 |
| South Bohemian (NA) | 1887 | 1754 | 0.023 | 3.313 | 1887 | 1758 |
| České Budějovice | 1465 | 1362 | 0.025 | 3.588 | 1465 | 1366 |
| Český Krumlov | 1481 | 1377 | 0.020 | 2.916 | 1481 | 1380 |
| Jindřichův Hradec | 1970 | 1831 | 0.025 | 3.588 | 1970 | 1834 |
| Písek | 2521 | 2343 | 0.025 | 3.588 | 2521 | 2347 |
| Prachatice | 2017 | 1875 | 0.022 | 3.220 | 2017 | 1878 |
| Strakonice | 3214 | 2988 | 0.019 | 2.724 | 3214 | 2991 |
| Tábor | 1402 | 1304 | 0.025 | 3.568 | 1402 | 1307 |
| Difference d | −671.3 | −624.0 | 0.167 | 24.24 | −671.1 | −599.8 |
| p-value e | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.012 | |||
| Region and Districts | LRP1 and LRP2 (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA | WHO | |||||
| Rn | B(a)P | Rn + B[a]P | Rn | B[a]P | Rn + B[a]P | |
| LRP1 a | LRP2 b | LRP1 + LRP2 c | LRP1 a | LRP2 b | LRP1 + LRP2 c | |
| Moravian-Silesian | 26.03 | 0.004 | 26.03 | 24.20 | 0.590 | 24.79 |
| Karviná | 22.53 | 0.003 | 22.53 | 20.94 | 0.484 | 21.43 |
| Nový Jičín | 35.84 | 0.002 | 35.84 | 33.31 | 0.230 | 33.54 |
| Opava | 31.82 | 0.002 | 31.83 | 29.58 | 0.218 | 29.80 |
| Ostrava | 22.58 | 0.010 | 22.59 | 20.99 | 1.392 | 22.38 |
| South Bohemian | 40.79 | 0.000 | 40.79 | 37.92 | 0.072 | 37.99 |
| České Budějovice | 32.06 | 0.001 | 32.06 | 29.80 | 0.079 | 29.88 |
| Český Krumlov | 28.15 | 0.000 | 28.15 | 26.16 | 0.055 | 26.22 |
| Jindřichův Hradec | 41.70 | 0.001 | 41.70 | 38.76 | 0.076 | 38.84 |
| Písek | 53.41 | 0.001 | 53.42 | 49.65 | 0.076 | 49.73 |
| Prachatice | 43.02 | 0.000 | 43.02 | 39.99 | 0.069 | 40.06 |
| Strakonice | 77.63 | 0.000 | 77.63 | 72.16 | 0.066 | 72.23 |
| Tábor | 30.74 | 0.001 | 30.74 | 28.57 | 0.078 | 28.65 |
| Difference d | −14.76 | 0.004 | −14.76 | −13.72 | 0.518 | −13.21 |
| p-value e | 0.109 | 0.006 | 0.109 | 0.109 | 0.006 | 0.109 |
| Occupational Exposure | ||
|---|---|---|
| Male | ||
| Moravian Silesian (IA) | South Bohemian (NA) | |
| POP—Annual arithmetic mean of the population (1996–2016) in monitored regions | 942,873 | 626,419 |
| ANP—The average annual number of pneumoconiosis (1996–2016) in monitored regions | 85.4 | 0.05 |
| PCP—The average proportion of all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis | 14% | 14% |
| ANC—The average annual number of all cancers in employees with pneumoconiosis | 11.96 | 0.01 |
| PLC—The average proportion of LBC cancer of all cancer in pneumoconiosis | 30% | 30% |
| ANL—The average annual number of LBC in employees with pneumoconiosis | 3.59 | 0.0021 |
| ARL—The average risk of LBC from occupational exposures (per 100.000) | 0.34 | 0.00034 |
| LR3—Lifetime risk of LBC from occupational exposure (per 100.000) | 28.53 | 0.025 |
| LRP3—Lifetime risk proportion from occupational exposure | 0.35% | 0.00033% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiřík, V.; Tomášek, L.; Fojtíková, I.; Janoš, T.; Stanovská, M.; Guňková, P.; Dalecká, A.; Vrtková, A.; Šrám, R.J. Lifetime Carcinogenic Risk Proportions from Inhalation Exposures in Industrial and Non-Industrial Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413295
Jiřík V, Tomášek L, Fojtíková I, Janoš T, Stanovská M, Guňková P, Dalecká A, Vrtková A, Šrám RJ. Lifetime Carcinogenic Risk Proportions from Inhalation Exposures in Industrial and Non-Industrial Regions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413295
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiřík, Vítězslav, Ladislav Tomášek, Ivana Fojtíková, Tomáš Janoš, Markéta Stanovská, Pavlína Guňková, Andrea Dalecká, Adéla Vrtková, and Radim J. Šrám. 2021. "Lifetime Carcinogenic Risk Proportions from Inhalation Exposures in Industrial and Non-Industrial Regions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 13295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413295
APA StyleJiřík, V., Tomášek, L., Fojtíková, I., Janoš, T., Stanovská, M., Guňková, P., Dalecká, A., Vrtková, A., & Šrám, R. J. (2021). Lifetime Carcinogenic Risk Proportions from Inhalation Exposures in Industrial and Non-Industrial Regions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 13295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413295






