Perfectionism, Mood States, and Choking in Asian University Baseball Players under Pressure during a Game
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Processing
2.3. Extremely Stressful Situations
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Mood States
3.3. Perfectionism
3.4. Choking
3.5. Pearson’s Correlation Analysis
3.6. Hypothesis Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, S.J.; Lim, S.M. Short but sensational life, Jang Myeong-Boo who was stranger on the ground. J. Sport Leis. Stud. 2018, 74, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A. Resilience in Professional Baseball Players: Bouncing Back from Adversity and Growth. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Won, Y.S.; Kim, E.J.; Heo, J.H. The effects of baseball players’ mindset on resilience. Korean Assoc. Learn. Cent. Curric. Instr. 2019, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Won, Y.S.; Cho, E.Y. The analysis on the career transition of early retired baseball student-athletes by grounded theory. J. Korean Alliance Health Phys. Educ. Recreat. Danc. 2016, 55, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H. Effects of Hypnotherapy on the Improvement of the Choking under Pressure of Athletes. Ph.D. Thesis, The Catholic University, Seoul, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, A.J.; Watson, D.C.; Powell, R.A.; Buro, K. Academic procrastination: The pattern and correlates of behavioural postponement. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2006, 40, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, P.L.; Caelian, C.F.; Flett, G.L.; Sherry, S.B.; Collins, L.; Flynn, C.A. Perfectionism in children: Associations with depression, anxiety, and anger. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2002, 32, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.E.; Shin, J.T.; Kim, J.S. The effects of a psychological skills training on competitive anxiety, intrinsic motivation, sports self-confidence, performance strategy and perceived performance of high school taekwondo players. J. Korean Soc. Wellness 2015, 10, 147–160. [Google Scholar]
- So, Y.H. Relationship among self-management, Sports Performance Strategies, and perceived performance of college athletes. J. Sport Leis. Stud. 2016, 65, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.M.; Lee, D.H. The effects of university athletes’ tenacity and positive psychological capital on perceived performance. J. Sport Leis. Stud. 2019, 76, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotwals, J.K.; Dunn, J.G.H.; Wayment, H.A. An examination of perfectionism and self-esteem in intercollegiate athletes. J. Sport Behav. 2003, 26, 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.I. The Effect of Perfectionist Tendencies of College Rugby Players on Exercise Stress and Perceived Performance. Unpublished Master’s Thesis, Kyunghee University, Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- So, Y.H.; Jung, J.H. Relationship between perfectionism, exercise stress, and goal orientation of college athletes. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2010, 49, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister, R.F. Choking under pressure: Self-consciousness and paradoxical effects of incentives on skillful performance. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1984, 46, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, R.F.; Showers, C.J. A review of paradoxical performance effects: Choking under pressure in sports and mental tests. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 16, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucciardi, D.F.; Dimmock, J.A. Choking under pressure in sensorimotor skills: Conscious processing or depleted attentional resources? Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2008, 9, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.M.; Hanton, S.; Matthews, N.; Fleming, S. A qualitative exploration of choking in Elite Golf. J. Clinic. Sport Psychol. 2010, 4, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesagno, C.; Mullane-Grant, T. A comparison of different pre-performance routines as possible choking interventions. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2010, 22, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesagno, C.; Hill, D.M. Definition of choking in sport: Re-conceptualization and debate. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2013, 44, 267–277. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.R.; Moon, C.I. Performance Disruption in Sport: A Case Report and Review of Choking Under Pressure. Korean Soc. Sport Sci. 2009, 18, 567–587. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E. Defining Choking: A Qualitative Examination. Unpublished Master’s Thesis, Victoria University, Victoria, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.P.; Tofler, I.R.; Lardon, M.T. The sport psychiatrist and golf. Clin. Sports Med. 2005, 24, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.; Chattington, M.; Marple-Horvat, D.E.; Smith, N.C. A comparison of self-focus versus attentional explanations of choking. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2007, 29, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Masters, R.S. Knowledge, knerves and know-how: The role of explicit versus implicit knowledge in the breakdown of a complex motor skill under pressure. Brit. J. Psychol. 1992, 83, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, K.S. The Proper Methods of Statistical Analysis for Dissertation: SPSS & AMOS; Hanbit Academy: Seoul, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, B.R. Structural Equation Modeling with Amos 24: Principles and Practice; Chung-Ram Press: Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.K.; Hong, S.H. A Siting the Structural Equation Model Analysis; Communication Books: Seoul. Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, D.; Coughlan, J.; Mullen, M.R. Structural Equation modelling: Guidelines for determining model fit. Electron. J. Bus. Res. Methods 2008, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.U. Effects of Sports Counseling on the Emotion and the Self-Confidence of Sports Players under Rehabilitation Training after Sports Injury. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Sungshin Women’s University, Seoul, Korea, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McNair, D.M.; Lorr, M.; Droppleman, L.F. Manual for the Profile of Mood States; Educational and Industrial Testing Service: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, P.L.; Flett, G.L. Perfectionism in the self and social contexts: Conceptualization, assessment, and association with psychopathology. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1991, 60, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, T.; Sekiya, H. Factors related to choking under pressure in sports and the relationships among them. Int. J. Sport Health Sci. 2015, 13, 201416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.W.; Lee, H.S.; Ahn, J.D. The study on influence of psychological skills training for gymnastics man player vault in a single subject design. Korean Soc. Sport Psychol. 2010, 27, 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- So, Y.H. Relationship among emotional intelligence, exercise passion, and sport commitment of high school athletes. Korean J. Phys. Educ. 2019, 58, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Lyu, H.S. The effects of psychological skills training on mood states, sports performance strategy and perceived performance of high school swimmers in slump. Korean J. Sport Psychol. 2020, 31, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kang, M.H.; Ju, J.M. The Effect of Elite Athlete’ Perfectionism on Their Stress and Jinx. J. World Soc. Taekwondo Cult. 2016, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Cho, S.L. The relationship among perfectionism, exercise stress and athlete burnout of badminton athletes. Korea J. Sport 2017, 15, 622–634. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Shin, J.T. The effect of multidimensional perfectionism on their burnout and mental toughness of university taekwondo players. J. World Soc. Taekwondo Cult. 2018, 9, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I. The effect of university taekwondo players’ multidimensional perfectionism on self-management and exercise flow. Korea J. Sport. 2017, 75, 669–679. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, Y.K.; Kim, J.T.; Lee, S.J. Causal relationship among perfectionism, exercise commitment and sport confidence of high school taekwondo players. J. Korea Soc. Wellness 2017, 12, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.S. The Effects of the perfectionism inclination on the exercise stress and exercise dropout intention of collegiate golf player. J. Golf Stud. 2017, 11, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Yook, D.W.; Chung, J.E.; Shin, J.T. Perfectionism, goal orientation, and athlete burnout in collegiate rugby. Korean Soc. Sports Sci. 2014, 23, 595–607. [Google Scholar]
- Katie, L.P. Understanding Performance under Pressure: Anxiety, Attention, Cognitive Biases and the Perception of Failure. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuys, A.; Oudejans, R. Anxiety and perceptual-motor performance: Toward an integrated model of concepts, mechanisms, and processes. Psychol. Res. 2012, 76, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, M.; Wilson, M. Sporting performance, pressure and cognition. In An Introduction to Applied Cognitive Psychology; Groome, D., Eysenck, M., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2016; pp. 329–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, D.M.; Cheesbrough, M.; Gorczynski, P.; Matthews, N. The consequences of choking in sport: A constructive or destructive experience? Sport Psychol. 2019, 33, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.L. A sport and exercise psychology perspective on stress. Quest 1994, 46, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, D.; Udry, E. Psychological skills for enhancing performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994, 26, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanin, Y.L. Optimal performance emotions in top athletes. In Sport Psychology: An Integrated Approach. Proceedings of the VIII World Congress of Sport Psychology, Lisbon, Portugal, 22–27 June 1993; Serpa, S., Alves, J., Ferreira, V., Ferreira, A., Eds.; International Society of Sport Psychology: Lisbon, Portugal, 1993; pp. 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Hanin, Y.L. Emotions and athletic performance: Individual zones of optimal functioning model. Eur. Yearb. Sport Psychol. 1997, 1, 29–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.H. Motivation and Emotion in Sport: Reversal Theory; Psychology Press: East Sussex, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, R.S. From psychological stress to the emotions: A history of changing outlooks. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 1993, 44, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Males, J.R.; Kerr, J.H. Stress, emotion, and performance in Elite Slalom canoeists. Sport Psychol. 1996, 10, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.G.H.; Gotwals, J.K.; Dunn, J.C. An examination of the domain specificity of perfectionism among intercollegiate student-athletes. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2005, 38, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.D. The perfectionist’s script for self-defeat. Psychol. Today 1980, 14, 34–52. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, R.O.; Marten, P.A.; Lahart, C.; Rosenblate, R. The dimensions of perfectionism. Cognit. Ther. Res. 1990, 14, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, P.L.; Flett, G.L. Perfectionism and stress processes in psychopathology. In Perfectionism and Stress Processes in Psychopathology; Flett, G.L., Hewitt, P.L., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 255–284. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Son, C.N. The effects of cognitive behavioral therapy on anxiety and depression of evaluative concerns perfectionist undergraduate students. Korean J. Clin. Psychol. 2007, 26, 805–826. [Google Scholar]
- Enns, M.W.; Cox, B.J. Perfectionism and depression symptom severity in major depressive disorder. Behav. Res. Ther. 1999, 37, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, K.; Kanda, K. Relationship between neurotic perfectionism, depression, anxiety, and psychosomatic symptoms: A prospective study among Japanese men. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2002, 32, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, H.G.; Hyun, M.H. The mediating effect of cognitive coping strategies on the relationships between perfectionism and anger expression. Korean J. Clin. Psychol. 2009, 28, 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley, D.M.; Blankstein, K.R. Self-Critical Perfectionism, Coping, Hassles, and Current Distress: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Cognit. Ther. Res. 2000, 24, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboonchi, F.; Lundh, L.-G. Perfectionism, anger, somatic health, and positive affect. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2003, 35, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafran, R.; Mansell, W. Perfectionism and psychopathology: A review of research and treatment. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 21, 879–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivula, N.; Hassmén, P.; Fallby, J. Self-esteem and perfectionism in elite athletes: Effects on competitive anxiety and self-confidence. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2002, 32, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M. The relationship of the tendency of perfectionism of university taekwondo athletes and the tendency of achievement goal and stress. Taekwondo J. Kukkiwon. 2014, 5, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, B.H. The effect of perfectionism on university poomsae players’ self-management and perceived performance. Korea J. Sport. 2020, 18, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K. The Effect of the Perfectionist Tendencies of College Judo Players on Perceived Performance. Unpublished Master’s Thesis, Kyonggi University, Suwon, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]

| Variable | Division | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 209 | 100 |
| Nationality | Korean | 61 | 29 |
| Japanese | 148 | 71 | |
| Grade | Freshman | 68 | 32.5 |
| Sophomore | 58 | 27.8 | |
| Junior | 45 | 21.5 | |
| Senior | 38 | 18.2 | |
| Average age (years) | 209 | 20.25 | |
| Position | Pitcher | 139 | 66.5 |
| Fielder | 70 | 33.5 | |
| Period | Baseball career(years) | 209 | 12.1 |
| Pitcher career(years) | 139 | 5.6 |
| Variables | Index | Question | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Background Variables | General characteristics | Gender (1) | 6 |
| Nationality (1) | |||
| Grade (1) | |||
| Position (1) | |||
| Period (2) | |||
| Independent Variables | Mood states | Confusion (4) | 11 |
| Tension (3) | |||
| Vigor (4) | |||
| Mediating Variables | Perfectionism | Other-oriented (5) | 12 |
| Socially prescribed (4) | |||
| Self-oriented (3) | |||
| Dependent Variables | Choking | Anxiety-related thinking (3) | 10 |
| Self-focusing and motor control (3) | |||
| Cognitive, emotional, and perceptual confusion (4) | |||
| Total | 39 | ||
| Variables | Item | λ | S.E. | C.R.(t) | p | SC | AVE | C.R. | ɑ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
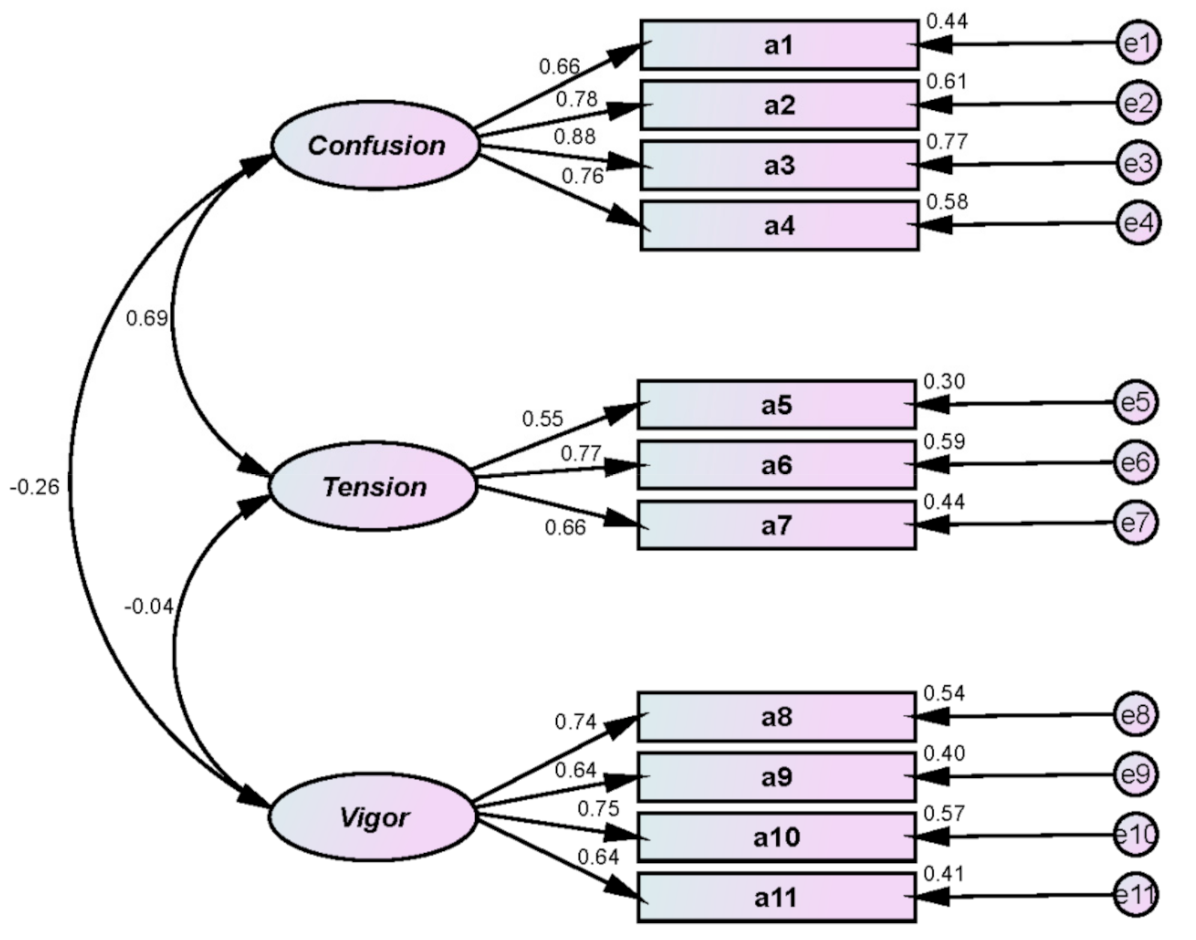
| Mood states | confusion | a1. distracted | 1.000 | 0.660 | 0.578 | 0.938 | 0.877 | |||
| a2. woozy | 1.122 | 0.118 | 9.537 | 0.001 | 0.780 | |||||
| a3. perplexed | 1.435 | 0.139 | 10.302 | 0.001 | 0.880 | |||||
| a4. uncertain | 1.134 | 0.122 | 9.330 | 0.001 | 0.758 | |||||
| tension | a5. nervous | 1.000 | 0.548 | 0.618 | 0.829 | 0.894 | ||||
| a6. agitated | 1.445 | 0.219 | 6.607 | 0.001 | 0.767 | |||||
| a7. restless | 1.344 | 0.212 | 6.330 | 0.001 | 0.664 | |||||
| vigor | a8. energetic | 1.000 | 0.736 | 0.550 | 0.829 | 0.874 | ||||
| a9. active | 0.978 | 0.125 | 7.821 | 0.001 | 0.636 | |||||
| a10. lively | 1.047 | 0.120 | 8.755 | 0.001 | 0.753 | |||||
| a11. cheerful | 0.975 | 0.124 | 7.838 | 0.001 | 0.638 | |||||
| χ2 = 95.788, df = 41, p = 0.001, SRMR = 0.066, IFI = 0.935, TLI = 0.912, CFI = 0.934, RMSEA = 0.080 | ||||||||||
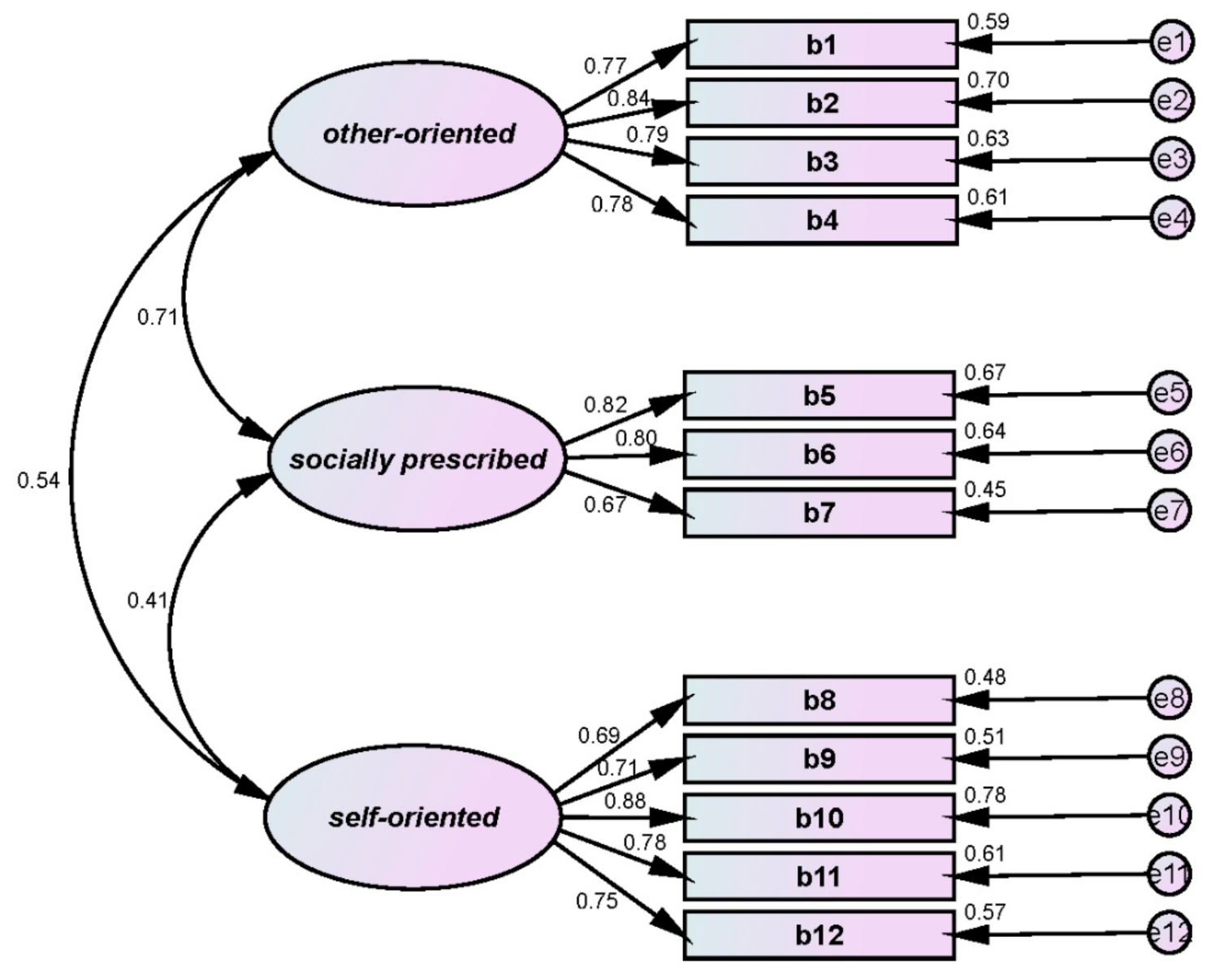
| Perfectionism | other-oriented | b1. People around me expect more than what I am capable of | 1.000 | 0.765 | 0.555 | 0.833 | 0.872 | |||
| b2. People around me expect me to be perfect | 1.203 | 0.098 | 12.237 | 0.001 | 0.839 | |||||
| b3. My family expect me to be perfect | 1.244 | 0.108 | 11.563 | 0.001 | 0.795 | |||||
| b4. People around me expect too much from me | 1.104 | 0.097 | 11.418 | 0.001 | 0.783 | |||||
| socially prescribed | b5. People around me will like me when I excel in sports and everything | 1.000 | 0.819 | 0.559 | 0.792 | 0.812 | ||||
| b6. People around me would think of me as a nice person only if I am successful | 1.020 | 0.092 | 11.086 | 0.001 | 0.802 | |||||
| b7. People around me would think of me as competent only if I don’t make a mistake | 0.817 | 0.086 | 9.450 | 0.001 | 0.670 | |||||
| self-oriented | b8. I try to be as perfect as possible | 1.000 | 0.691 | 0.535 | 0.851 | 0.873 | ||||
| b9. It is important for me to be perfect in everything | 1.004 | 0.107 | 9.359 | 0.001 | 0.711 | |||||
| b10. I want myself to be perfect | 1.447 | 0.129 | 11.229 | 0.001 | 0.884 | |||||
| b11. I have a strong desire to become perfect | 1.393 | 0.136 | 10.216 | 0.001 | 0.783 | |||||
| b12. My goal is to be perfect in everything | 1.404 | 0.142 | 9.853 | 0.001 | 0.752 | |||||
| χ2 = 126.008, df = 50, p = 0.001, SRMR = 0.060, IFI = 0.944, TLI = 0.926, CFI = 0.944, RMSEA = 0.085 | ||||||||||
| Choking | anxiety-related thinking | c1. I was concerned about how other people think of me | 1.000 | 0.765 | 0.682 | 0.865 | 0.870 | |||
| c2. I couldn’t shake off a mistake and kept thinking of it | 1.062 | 0.087 | 12.155 | 0.001 | 0.818 | |||||
| c3. I was worried about and afraid of disappointing other people | 1.265 | 0.096 | 13.235 | 0.001 | 0.909 | |||||
| self-focusing and motor control | c4. My decision-making ability was worse than normal due to high pressure | 1.000 | 0.853 | 0.707 | 0.879 | 0.896 | ||||
| c5. I moved impatiently | 1.034 | 0.064 | 16.122 | 0.001 | 0.893 | |||||
| c6. My movement was stiff and not soft | 0.983 | 0.066 | 14.902 | 0.001 | 0.842 | |||||
| cognitive, emotional, and perceptual confusion | c7. I felt as if all people watched only me | 1.000 | 0.713 | 0.595 | 0.854 | 0.874 | ||||
| c8. I became more conscious of the surrounding environment than usual | 1.067 | 0.096 | 11.139 | 0.001 | 0.824 | |||||
| c9. I thought that things around me and the environment were against me | 1.144 | 0.106 | 10.798 | 0.001 | 0.797 | |||||
| c10. I was engulfed by the atmosphere | 1.096 | 0.096 | 11.461 | 0.001 | 0.851 | |||||
| χ2 = 93.005, df = 32, p = 0.001, SRMR = 0.047, IFI = 0.957, TLI = 0.939, CFI = 0.957, RMSEA = 0.096 | ||||||||||
| Variables | Subfactors | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mood states | confusion (1) | 1 | ||||||||
| tension (2) | 0.519 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| vigor (3) | −0.216 ** | −0.012 | 1 | |||||||
| Perfectionism | other-oriented (4) | 0.406 ** | 0.216 ** | 0.002 | 1 | |||||
| socially prescribed (5) | 0.387 ** | 0.096 | −0.016 | 0.597 ** | 1 | |||||
| self-oriented (6) | 0.054 | 0.072 | 0.008 | 0.464 ** | 0.345 ** | 1 | ||||
| Choking | anxiety-related thinking (7) | 0.101 | 0.272 ** | −0.019 | 0.304 ** | 0.021 | 0.183 ** | 1 | ||
| self-focusing and motor control (8) | 0.087 | 0.191 ** | 0.032 | 0.202 ** | 0.088 | 0.131 | 0.600 ** | 1 | ||
| cognitive, emotional, and perceptual confusion (9) | 0.117 | 0.230 ** | 0.047 | 0.296 ** | 0.098 | 0.259 ** | 0.620 ** | 0.638 ** | 1 |
| H | Path | Estimate | S.E. | C.R(t) | Sig. | Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Mood states | → | Perfectionism | 0.111 | 0.054 | 20.059 | 0.039 | Accept |
| H2 | Mood states | → | Choking | −0.031 | 0.032 | −0.971 | 0.332 | Reject |
| H3 | Perfectionism | → | Choking | 0.538 | 0.141 | 30.808 | 0.001 | Accept |
| Fit Index | χ2(df) = 56.195(23)/p = 0.001, SRMR = 0.071, IFI = 0.940, TLI = 0.904, CFI = 0.939, RMSEA = 0.083 | |||||||
| Path | Bootstrap Estimates 95% Confidence Interval | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indirect Effect | Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Mood states | → | Perfectionism | → | Choking | 0.001 | 0.040 | 0.234 | |||
| Model | χ2 | df | p | SRMR | IFI | TLI | CFI | RMSEA | ||
| Complete mediation | 57.290 | 24 | 0.001 | 0.066 | 0.940 | 0.908 | 0.938 | 0.082 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.-J.; Irie, K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lim, S.-M. Perfectionism, Mood States, and Choking in Asian University Baseball Players under Pressure during a Game. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312856
Yoon S-J, Irie K, Lee J-H, Lim S-M. Perfectionism, Mood States, and Choking in Asian University Baseball Players under Pressure during a Game. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312856
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Sang-Jin, Kazunori Irie, Jun-Ho Lee, and Sea-Mi Lim. 2021. "Perfectionism, Mood States, and Choking in Asian University Baseball Players under Pressure during a Game" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312856
APA StyleYoon, S.-J., Irie, K., Lee, J.-H., & Lim, S.-M. (2021). Perfectionism, Mood States, and Choking in Asian University Baseball Players under Pressure during a Game. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12856. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312856







