Diagnostic Accuracy of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for the Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Highlights
- Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE) has very high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC);
- Transference of the first experimental results of CLE in the oral cavity of humans into an effective and evidence based clinical setting is recommended;
- A conclusive statement can only be made when additional comparable studies with homogeneous methodological strategies will be undertaken.
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Objective and Definition of Reference Standard
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Risk of Bias
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Meta-Analysis
3. Results
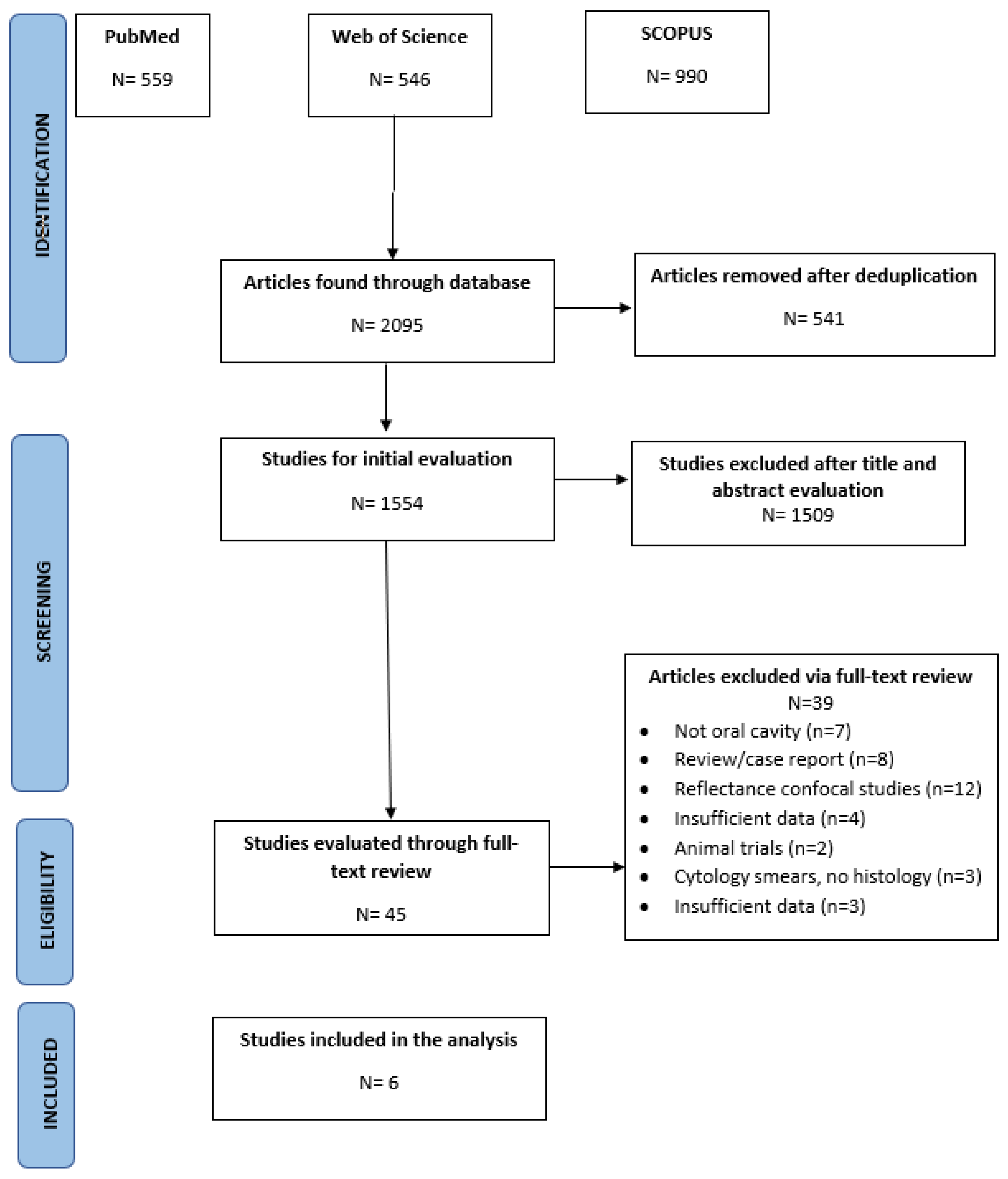
3.1. Literature Search Results
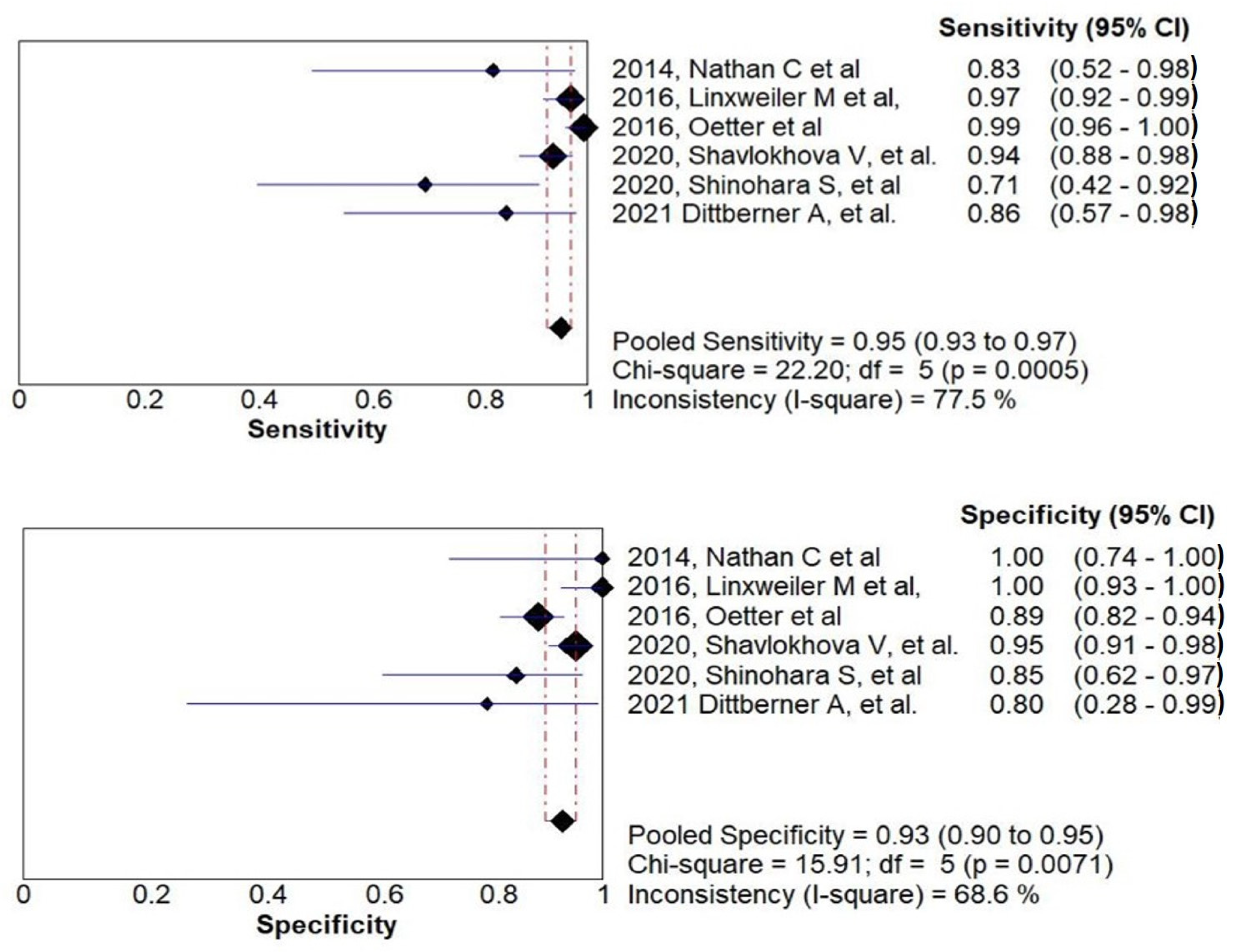
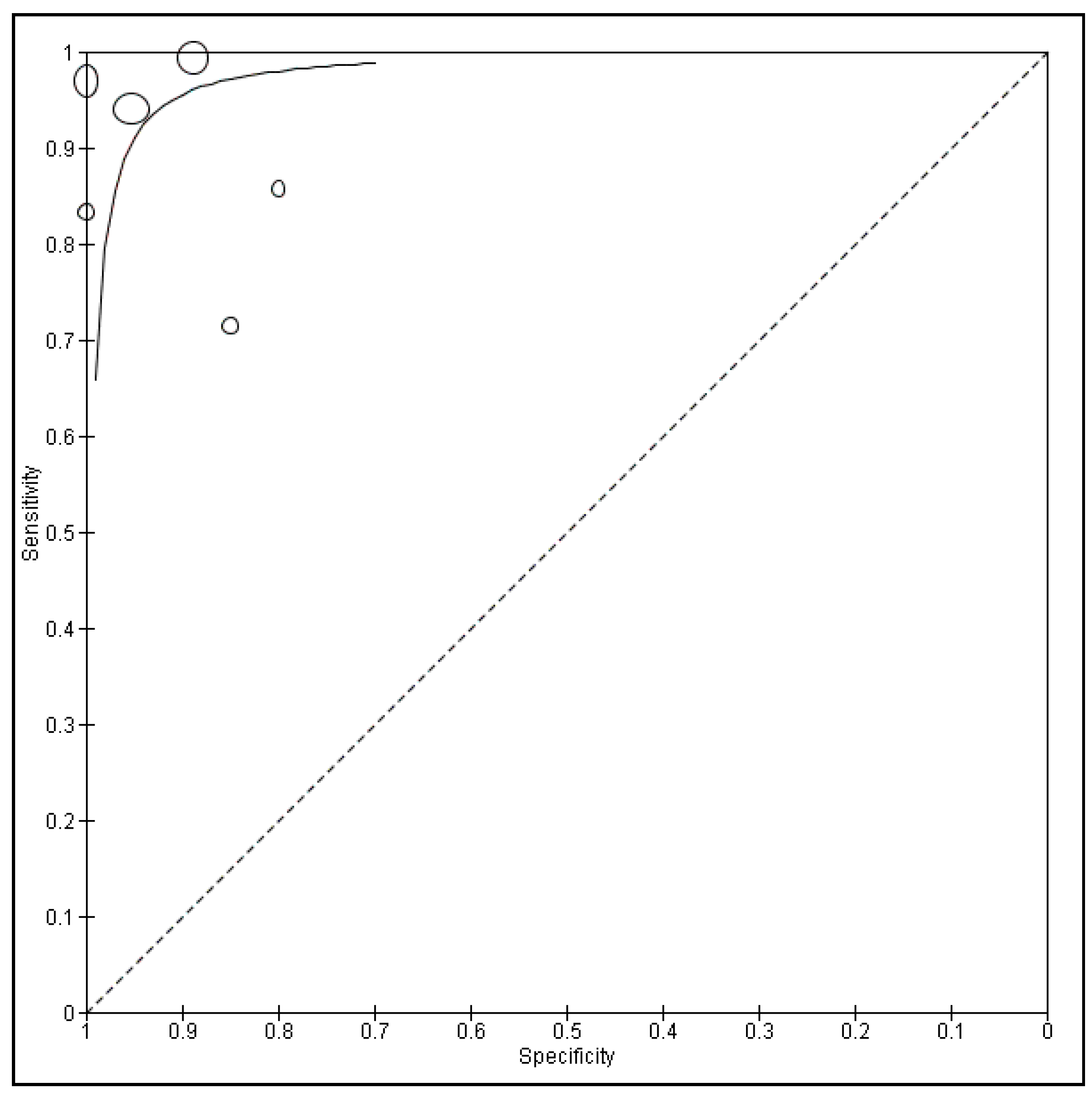
3.2. Diagnostic Accuracy of CLE and Meta-Analysis
3.3. Heterogeneity Analysis
4. Discussion
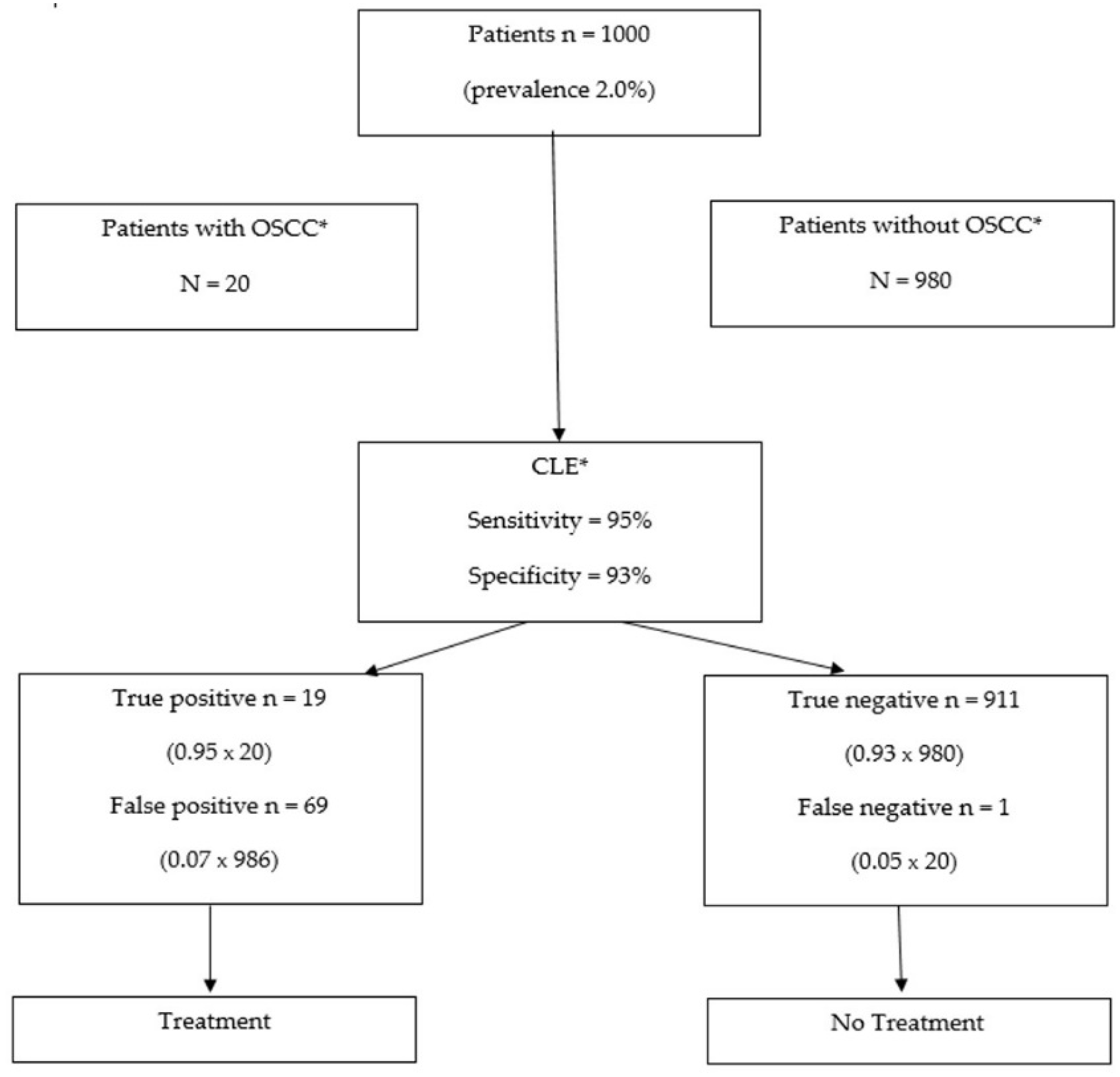
4.1. Clinical Relevance
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
4.3. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.-R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: Globocan 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; Forastiere, A.A. Head and Neck Cancer: Changing Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, K.B.; Gupta, N. Clinicopathological prognostic implicators of oral squamous cell carcinoma: Need to understand and revise. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 5, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciubba, J.J.; Larian, B. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: Early detection and improved 5-year survival in 102 patients. Gen. Dent. 2018, 66, e11–e16. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra, R.; Yadav, S. Oral squamous cell carcinoma: Etiology, pathogenesis and prognostic value of genomic alterations. Indian J. Cancer 2006, 43, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Jagannathan, N. Oral field cancerization: An update on current concepts. Oncol. Rev. 2014, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, D.P.; Southwick, H.W.; Smejkal, W. Field cancerization in oral stratified squamous epithelium. Clinical implications of multicentric origin. Cancer 1953, 6, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardimci, G.; Kutlubay, Z.; Engin, B.; Tuzun, Y. Precancerous lesions of oral mucosa. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Ariyawardana, A. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: A systematic review of observational studies. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; de Mendoza, I.L.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the last 5 years. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa, F.; Mauri, S.; Tradati, N.; Calabrese, L.; Giugliano, G.; Ansarin, M.; Andrle, J.; Zurrida, S.; Orecchia, R.; Scully, C. Surfing prognostic factors in head and neck cancer at the Millennium. Oral Oncol. 1999, 35, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinni, M.L.; Ferlito, A.; Brandwein-Gensler, M.S.; Takes, R.P.; Silver, C.E.; Westra, W.H.; Seethala, R.R.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Corry, J.; Bradford, C.R.; et al. Surgical margins in head and neck cancer: A contemporary review. Head Neck 2012, 35, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cikojević, D.; Glunčić, I.; Pešutić-Pisac, V. Comparison of contact endoscopy and frozen section histopathology in the intra-operative diagnosis of laryngeal pathology. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 122, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, A.; Hijioka, H.; Ishida, T.; Nozoe, E.; Nakamura, N.; Oya, R. Intraoperative frozen section histological analysis of resection samples is useful for the control of primary lesions in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.B.; Annavajjula, S. Surgical Margins and Its Evaluation in Oral Cancer: A Review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, ZE01–ZE05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, E.M.; Aaboubout, Y.; van der Sar, L.C.; Mast, H.; Sewnaik, A.; Hardillo, J.A.; Hove, I.T.; Soares, M.R.N.; Ottevanger, L.; Schut, T.C.B.; et al. Performance of Intraoperative Assessment of Resection Margins in Oral Cancer Surgery: A Review of Literature. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, A.; Maglione, M.; Crispo, A.; Perri, F.; Villano, S.; Pavone, E.; Aversa, C.; Longo, F.; Feroce, F.; Botti, G.; et al. Oral lichen planus and other confounding factors in narrow band imaging (NBI) during routine inspection of oral cavity for early detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective pilot study. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.N.; Matias, M.A.T.; Matias, M.; Farah, C. Diagnostic accuracy of Narrow Band Imaging for the detection of oral potentially malignant disorders. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Xu, H.; He, M.; Han, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Dan, H.; et al. Accuracy of autofluorescence in diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma and oral potentially malignant disorders: A comparative study with aero-digestive lesions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagri-Manjrekar, K.; Chaudhary, M.; Sridharan, G.; Tekade, S.; Gadbail, A.; Khot, K. In vivo autofluorescence of oral squamous cell carcinoma correlated to cell proliferation rate. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pałasz, P.; Adamski, Ł.; Górska-Chrząstek, M.; Starzyńska, A.; Studniarek, M. Contemporary Diagnostic Imaging of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma—A Review of Literature. Pol. J. Radiol. 2017, 82, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.-A.O.; Kaskas, N.M.; Ma, X.; Chaudhery, S.; Lian, T.; Moore-Medlin, T.; Shi, R.; Mehta, V. Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy in the Detection of Head and Neck Precancerous Lesions. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2014, 151, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martirosyan, N.L.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Kalani, M.Y.S.; Turner, J.D.; Belykh, E.; Spetzler, R.F.; Nakaji, P.; Preul, M.C. Prospective evaluation of the utility of intraoperative confocal laser endomicroscopy in patients with brain neoplasms using fluorescein sodium: Experience with 74 cases. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 40, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.B.; Sharma, P.; Lightdale, C. Preliminary accuracy and interobserver agreement for the detection of intraepithelial neoplasia in Barrett’s esophagus with probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Palma, G.D. Confocal laser endomicroscopy in the "in vivo" histological diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 5770–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesslich, R.; Burg, J.; Vieth, M.; Gnaendiger, J.; Enders, M.; Delaney, P.; Polglase, A.; McLaren, W.; Janell, D.; Thomas, S.; et al. Confocal laser endoscopy for diagnosing intraepithelial neoplasias and colorectal cancer in vivo. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, M. Colonoscopic Surveillance in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: State of the Art Reduction of Biopsies. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Quinn, M.; Pyman, J.M.; Delaney, P.M.; McLaren, W.J. Detection of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in vivo using confocal endomicroscopy. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 116, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, K.; Pavlova, I.; Collier, T.; Descour, M.; Follen, M.; Richards-Kortum, R. Confocal microscopy: Imaging cervical precancerous lesions. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 99, S84–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, M.L.; Stephen, L.; Annette, M.; Jean, C.L.R.; Marshall, A.; Calum, E.M. Confocal fluorescence microendoscopy of bronchial epithelium. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 024008. [Google Scholar]
- Thiberville, L.; Moreno-Swirc, S.; Vercauteren, T.; Peltier, E.; Cavé, C.; Heckly, G.B. In VivoImaging of the Bronchial Wall Microstructure Using Fibered Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, F.S.; Zirlik, S.; Hildner, K.; Schubert, J.; Vieth, M.; Neurath, M.F. Confocal laser endomicroscopy for diagnosing lung cancer in vivo. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonn, G.A.; Jones, S.-N.E.; Tarin, T.V.; Du, C.B.; Mach, K.E.; Jensen, K.C.; Liao, J.C. Optical Biopsy of Human Bladder Neoplasia With In Vivo Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.C.; Liu, J.-J.; Liao, J.C. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of the urinary tract: The technique. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 2013, e4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snuderl, M.; Wirth, D.; Sheth, S.A.; Bourne, S.K.; Kwon, C.-S.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Curry, W.T.; Frosch, M.P.; Yaroslavsky, A.N. Dye-Enhanced Multimodal Confocal Imaging as a Novel Approach to Intraoperative Diagnosis of Brain Tumors. Brain Pathol. 2013, 23, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampaki, P.; Javed, M.; Daali, S.; Heiroth, H.J.; Igressa, A.; Weber, F. Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Real-time Histomorphological Diagnosis: Our Clinical Experience With 150 Brain and Spinal Tumor Cases. Neurosurgery 2015, 62 (Suppl. S1), 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Wei, L.; Cimino, P.J.; Liu, J.T.C.; Sanai, N. Video-Mosaicked Handheld Dual-Axis Confocal Microscopy of Gliomas: An ex vivo Feasibility Study in Humans. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.M.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; González, S.; Fabian, R.L.; Anderson, R.R. Noninvasive Imaging of Human Oral Mucosa in Vivo by Confocal Reflectance Microscopy. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.L.; Gillenwater, A.; Collier, T.G.; Alizadeh-Naderi, R.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Richards-Kortum, R.R. Confocal microscopy for real-time detection of oral cavity neoplasia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4714–4721. [Google Scholar]
- Just, T.; Stave, J.; Boltze, C.; Wree, A.; Kramp, B.; Guthoff, R.F.; Pau, H.W. Laser Scanning Microscopy of the Human Larynx Mucosa: A Preliminary, Ex Vivo Study. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaci, M.; Temam, S.; Casiraghi, O.; Vielh, P.; Bosq, J.; Fouret, P.; Laplace-Builhé, C. Characterization of laryngeal carcinoma by confocal endomicroscopy. Head Neck Oncol. 2009, 1, O14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muldoon, T.J.; Roblyer, D.; Williams, M.D.; Stepanek, V.M.; Richards-Kortum, R.; Gillenwater, A. Noninvasive imaging of oral neoplasia with a high-resolution fiber-optic microendoscope. Head Neck 2011, 34, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahati, B.; Stachs, O.; Prall, F. Rigid confocal endoscopy for in vivo imaging of experimental oral squamous intra-epithelial lesions. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2010, 39, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Harris, M.; Kho, K.W.; Thong, P.S.; Hibbs, A.; Olivo, M.; Soo, K.C. Confocal endomicroscopic imaging of normal and neoplastic human tongue tissue using ALA-induced-PPIX fluorescence: A preliminary study. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 12, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, P.S.-P.; Olivo, M.C.; Kho, K.-W.; Zheng, W.; Mancer, K.; Harris, M.R.; Soo, K.-C. Laser confocal endomicroscopy as a novel technique for fluorescence diagnostic imaging of the oral cavity. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 014007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitland, K.C.; Gillenwater, A.M.; Williams, M.D.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Descour, M.R.; Richards-Kortum, R.R. In vivo imaging of oral neoplasia using a miniaturized fiber optic confocal reflectance microscope. Oral Oncol. 2008, 44, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haxel, B.R.; Goetz, M.; Kiesslich, R.; Gosepath, J. Confocal endomicroscopy: A novel application for imaging of oral and oropharyngeal mucosa in human. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2010, 267, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schardt, C.; Adams, M.B.; Owens, T.; Keitz, S.; Fontelo, P. Utilization of the PICO framework to improve searching PubMed for clinical questions. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2007, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeflang, M.M.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Macaskill, P. Cochrane diagnostic test accuracy reviews. Syst. Rev. 2013, 2, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linxweiler, M.; Kadah, B.A.; Bozzato, A. Noninvasive histological imaging of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas using confocal laser endomicroscopy. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2016, 273, 4473–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetter, N.; Knipfer, C.; Rohde, M.; Von Wilmowsky, C.; Maier, A.; Brunner, K.; Adler, W.; Neukam, F.-W.; Neumann, H.; Stelzle, F. Development and validation of a classification and scoring system for the diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinomas through confocal laser endomicroscopy. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavlokhova, V.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Sandhu, S.; Pilz, M.; Vollmer, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Engel, M.; Freudlsperger, C. Detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma with ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy: Sensitivity and specificity compared to histopathology. J. Biophoton. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, S.; Funabiki, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Takebayashi, S.; Hamaguchi, K.; Hara, S.; Yamashita, D.; Imai, Y.; Mizoguchi, A. Real-time imaging of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas using confocal micro-endoscopy and applicable dye: A preliminary study. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittberner, A.; Ziadat, R.; Hoffmann, F.; Pertzborn, D.; Gassler, N.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Fluorescein-Guided Panendoscopy for Head and Neck Cancer Using Handheld Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy: A Pilot Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, T.P.A.; Moons, K.G.M.; Riley, R.D. Detecting small-study effects and funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analysis of survival data: A comparison of new and existing tests. Res. Synth. Methods 2018, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelski, B.; Hanenkamp, U.; Goetz, M.; Kiesslich, R.; Gosepath, J. Systematic intraoperative application of confocal endomicroscopy for early detection and resection of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A preliminary report. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Just, T.; Pau, H.W. Intra-operative application of confocal endomicroscopy using a rigid endoscope. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2013, 127, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumerman, H.; Freedman, P.; Kerpel, S. Oral epithelial dysplasia and the development of invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1995, 79, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaoutakis, D.; Bishop, J.; Westra, W.; Califano, J.A. Recurrence patterns and management of oral cavity premalignant lesions. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.; Hossain, S.; Rahman, Q.B.; Molla, M.R. A study on histological grading of oral squamous cell carcinoma and its co-relationship with regional metastasis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2011, 15, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Triantafyllou, A.; de Bree, R.; Strojan, P.; Rinaldo, A.; Hernandez-Prera, J.C.; Suárez, C.; Kowalski, L.P.; Ferlito, A.; et al. Staging and grading of oral squamous cell carcinoma: An update. Oral Oncol. 2020, 107, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, H.; Shaban, M.; Rajpoot, N.; Khurram, S.A. Artificial Intelligence-based methods in head and neck cancer diagnosis: An overview. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year | Author | Country | Site Distribution | Examination Setting | Ni. of Reviewers | CLE * Device | Fluorescent Agent Used | Total Patients | Total Sites | Patient Gender (%) and Age (Mean/Median) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Dittberner A, et al. | Germany | Oropharynx (52.9%), oral cavity (35.3%), and hypopharynx (11.8%). | In vivo | 2 | CONVIVO, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany | Fluorescein | 13 | 30 | Mean age—1.9 years M—69% F—31% | Conventional histopathology |
| 2020 | Shinohara S, et al. | Japan | Hypopharynx (30%), larynx (10%) lower gingiva (20%), tongue (20%), oropharynx (20%) | Ex vivo | NS* | FIGH-300S or FIGH 350S, Fujikura or HDIG, Sumita | Acriflavine | 10 | 10 | Mean age—67.7 years M—80% F—20% | Conventional histopathology |
| 2020 | Shavlokhova V, et al. | Germany | Lip (7%), palate (18%), tongue (37%), buccal mucosa (15%), floor of the mouth (23%) | Ex vivo | 3 | Vivascope 2500 Multilaser, Lucid Inc., Rochester, NY*, USA* | Acridine Orange | 70 | 70 | Mean age—68.7 years M—52.2% F—47.8% | Conventional histopathology |
| 2016 | Oetter et al. | Germany | NS | In vivo | 6 | Cellvizio, Mauna Kea Technologies, Paris, France | Fluorescein Alcon | NS | 95 | NS | Conventional histopathology |
| 2016 | Linxweiler M et al. | Germany | Tonsil cancer (26%), tongue base cancer (24%), hypopharyngeal cancer (15%), tongue cancer (10%), cancer of the soft palate (8%), cancer of the pharyngeal wall (7%), cancer of the floor of the mouth (6%), cancer of the buccal mucosa (3%) | Ex vivo | 12 | Cellvizio system (Mauna Kea Technologies, Paris, France | Acriflavine hydrochloride | 99 | 185 | NS | Conventional histopathology |
| 2014 | Nathan C et al. | USA * | Tongue (66.6%), tonsil (4.7%), vocal cord (14.2%), epiglottis (4.7%), floor of mouth (4.7%), retromolar triangle (4.7%) | In vivo | 4 | CellVizio; Mauna Kea Technologies, Paris, France | Fluorescein Alcon | 21 | 21 | Mean Age—64.2 years M—47.6% F—52.3% | Conventional histopathology |
| Author, Year, [Reference] | Laser Confocal Endoscopy Microscopic Criteria |
|---|---|
| Dittberner, A, 2021 [59] | Chronic inflammation, dysplasia-free normal tissue, none to severe artefact classification, tissue architecture, cell morphology, fluorescence leakage, and the vessels. |
| Shinohara S, et al., 2020 [58] | Uniformity of nuclear size and shapes, cell density, nuclei and cytoplasm of cells |
| Shavlokhova V, 2021 [57] | Disturbed polarity of the basal cells, basal cell hyperplasia, irregular epithelial stratification or disturbed maturational sequence, cellular pleomorphism/anisocytosis, nuclear hyperchromatism, prominent nucleoli, intraepithelial keratinization, increase in nuclear cytoplasmic ratio |
| Oetter et al., 2016 [56] | Homogeneity, intercellular gaps, cell morphology, fluorescein leakage, vessel morphology |
| Linxweiler M et al., 2019 [55] | Variable cellular morphology, lack of cytoplasmic membranes, and a hazy, moth-eaten appearance. |
| Nathan C et al., 2014 [25] | Normal or non-dysplasia, dysplasia, or cancer. |
| Studies | Domain 1 Patient Selection | Domain 2 Index Test(s) | Domain 3 Reference Standard | Domain 4 Flow & Timing | Total Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | Risk of Bias | ||
| Dittberner A, et al. | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | 0 |
| Shinohara S, et al | Low | Unclear | High | Low | High | High | Low | 7 |
| Shavlokhova V, et al | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | High | 3 |
| Oetter N, et al | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | 3 |
| Linxweiler M, et al | Low | High | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | 3 |
| Nathan C, et al | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Unclear | High | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sethi, S.; Ju, X.; Logan, R.M.; Sambrook, P.; McLaughlin, R.A.; Jamieson, L.M. Diagnostic Accuracy of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for the Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312390
Sethi S, Ju X, Logan RM, Sambrook P, McLaughlin RA, Jamieson LM. Diagnostic Accuracy of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for the Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312390
Chicago/Turabian StyleSethi, Sneha, Xiangqun Ju, Richard M. Logan, Paul Sambrook, Robert A. McLaughlin, and Lisa M. Jamieson. 2021. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for the Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312390
APA StyleSethi, S., Ju, X., Logan, R. M., Sambrook, P., McLaughlin, R. A., & Jamieson, L. M. (2021). Diagnostic Accuracy of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for the Diagnosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312390








