The Six-Item Version of the Internet Addiction Test: Its Development, Psychometric Properties, and Measurement Invariance among Women with Eating Disorders and Healthy School and University Students
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study 1
2.1.1. Study Design, Participants, and Procedure
2.1.2. Data Collection Measures
2.1.3. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Study 2
2.2.1. Study Design, Participants, and Procedure
2.2.2. Data Collection Measures
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Study 3
2.3.1. Study Design, Participants, and Procedure
2.3.2. Data Collection Measures
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study 1
3.2. Study 2
3.2.1. Confirmatory Factor Analysis of the Internet Addiction Test
3.2.2. Invariance of the Internet Addiction Test across Eating Disorders
3.2.3. Reliability and Criterion Validity of the Internet Addiction Test
3.3. Study 3
3.3.1. Factor Structure of the Internet Addiction Test
3.3.2. Invariance of the Internet Addiction Test
3.3.3. Reliability and Criterion Validity of the Internet Addiction Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| χ2 | Chi square |
| AN | Anorexia nervosa |
| BFAS | Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale |
| EDs | Eating disorders |
| CFA | Confirmatory factor analysis |
| CFI | Comparative Fit Index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EFA | Exploratory factor analysis |
| IA | Internet addiction |
| IAT | Internet Addiction Test |
| KMO | Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin |
| RMSEA | Root mean square error of approximation |
| SRMR | standardized root-mean-square residual |
| TLI | Tucker–Lewis Index |
References
- Rachubińska, K.; Cybulska, A.M.; Grochans, E. The relationship between loneliness, depression, internet and social media addiction among young Polish women. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimtsiou, Z.; Haidich, A.-B.; Kokkali, S.; Dardavesis, T.; Young, K.S.; Arvanitidou, M. Greek Version of the Internet Addiction Test: A Validation Study. Psychiatr. Q. 2014, 85, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, C.S.; Torsheim, T.; Brunborg, G.S.; Pallesen, S. Development of a Facebook Addiction Scale. Psychol. Rep. 2012, 110, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siste, K.; Hanafi, E.; Sen, L.T.; Christian, H.; Adrian; Siswidiani, L.P.; Limawan, A.P.; Murtani, B.J.; Suwartono, C. The Impact of Physical Distancing and Associated Factors Towards Internet Addiction Among Adults in Indonesia During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Nationwide Web-Based Study. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 580977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafur-Mendoza, A.A.; Acosta-Prado, J.C.; Zárate-Torres, R.A.; Ramírez-Ospina, D.E. Assessing the Psychometric Properties of the Internet Addiction Test in Peruvian University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorel, O.I.; Vintilă, M.; Vlaicu, L.; Bălăuță, D.; Goian, C.; Rusu, A. Romanian Version of the Internet Addiction Test: Psychometric Properties and Cross-Gender Invariance. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2019, 17, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.C.; Isa, S.M.; Hashim, A.H.; Pillai, S.K.; Harbajan Singh, M.K. Validity of the Malay version of the Internet Addiction Test: A study on a group of medical students in Malaysia. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2015, 27, Np2210–Np2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Meng, S.-Q.; Bao, Y.-P.; Cheng, J.-L.; Chang, X.-W.; Ran, M.-S.; Sun, Y.-K.; Kosten, T.; Strang, J.; et al. Internet Addiction Increases in the General Population During COVID-19: Evidence from China. Am. J. Addict. 2021, 4, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenager, T.; Neissner, M.; Koopmann, A.; Reinhard, I.; Georgiadou, E.; Müller, A.; Kiefer, F.; Hillemacher, T. COVID-19 Lockdown Restrictions and Online Media Consumption in Germany. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servidio, R.; Bartolo, M.G.; Palermiti, A.L.; Costabile, A. Fear of COVID-19, depression, anxiety, and their association with Internet addiction disorder in a sample of Italian students. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2021, 4, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yang, F.; Lu, X.; Hao, W. Internet Addiction and Related Psychological Factors Among Children and Adolescents in China During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Epidemic. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, B.; Uzun, B.; Aydin, C.; Tan-Mansukhani, R.; Vallejo, A.; Saldaña-Gutierrez, A.; Nanda Biswas, U.; Essau, C.A. Internet use during COVID-19 lockdown among young people in low- and middle-income countries: Role of psychological wellbeing. Addict. Behav. Rep. 2021, 14, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, M. A ‘components’ model of addiction within a biopsychosocial framework. J. Subst. Use 2005, 10, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Shorter, G.W.; van Rooij, A.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Schoenmakers, T.M. Assessing Internet Addiction Using the Parsimonious Internet Addiction Components Model—A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2014, 12, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Černja, I.; Vejmelka, L.; Rajter, M. Internet addiction test: Croatian preliminary study. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayeed, A.; Hassan, M.N.; Rahman, M.H.; El Hayek, S.; Banna, M.H.A.; Mallick, T.; Hasan, A.-R.; Meem, A.E.; Kundu, S. Facebook addiction associated with internet activity, depression and behavioral factors among university students of Bangladesh: A cross-sectional study. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 118, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atroszko, P.A.; Balcerowska, J.M.; Bereznowski, P.; Biernatowska, A.; Pallesen, S.; Schou Andreassen, C. Facebook addiction among Polish undergraduate students: Validity of measurement and relationship with personality and well-being. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 85, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yeo, K.J.; Guo, F.; Zhao, Z. Factor structure and a multiple indicators multiple cause model of internet addiction test: The effect of socio-demographic and internet use variables. Curr. Psychol. 2020, 39, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Meng, F.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X.Y. Internet addiction among college students in a Chinese population: Prevalence, correlates, and its relationship with suicide attempts. Depress. Anxiety 2020, 37, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Kuang, L.; Wang, W.; Cao, J.; Xiao, M.-N. Abnormal brain activity in adolescents with Internet addiction who attempt suicide: An assessment using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Yen, J.Y.; Yen, C.F.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, C.C. The association between Internet addiction and psychiatric disorder: A review of the literature. Eur. Psychiatry 2012, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Q.; Yao, N.Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z.T. The association between attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and internet addiction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, T.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Cao, R.; Mei, S.; Meng, X. When adolescents face both Internet addiction and mood symptoms: A cross-sectional study of comorbidity and its predictors. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 284, 112795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, G.; Berloffa, S.; Muratori, P.; Paciello, M.; Rossi, M.; Milone, A. Internet addiction disorder in referred adolescents: A clinical study on comorbidity. Addict. Res. Theory 2021, 29, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, A.L.; Bae, S.M.; Kim, J.W. Psychometric Properties of the Internet Addiction Test: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2018, 21, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraci, P.; Craparo, G.; Messina, R.; Severino, S. Internet Addiction Test (IAT): Which is the Best Factorial Solution? J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaha, A.A.; Fawaz, M.; El Yahfoufi, N.; Gebbawi, M.; Abdallah, H.; Baydoun, S.A.; Ghaddar, A.; Eid, A.H. Assessing the Psychometric Properties of the Internet Addiction Test (IAT) Among Lebanese College Students. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wéry, A.; Burnay, J.; Karila, L.; Billieux, J. The Short French Internet Addiction Test Adapted to Online Sexual Activities: Validation and Links With Online Sexual Preferences and Addiction Symptoms. J. Sex Res. 2016, 53, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrault, S.; Durousseau, F.; Ballon, N.; Réveillère, C.; Brunault, P. Smartphone addiction: French validation of the Internet Addiction Test-Smartphone version (IAT-smartphone) and associated psychopathological features. Encephale 2019, 45, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaal, Y.; Billieux, J.; Thorens, G.; Khan, R.; Louati, Y.; Scarlatti, E.; Theintz, F.; Lederrey, J.; Van Der Linden, M.; Zullino, D. French validation of the internet addiction test. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Villa, T.; Molina, A.J.; García-Martín, M.; Llorca, J.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Martín, V. Validation and psychometric analysis of the Internet Addiction Test in Spanish among college students. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korkeila, J.; Kaarlas, S.; Jääskeläinen, M.; Vahlberg, T.; Taiminen, T. Attached to the web—Harmful use of the Internet and its correlates. Eur. Psychiatry 2010, 25, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowski, M.; Altstötter-Gleich, C.; Brand, M. Validation and psychometric properties of a short version of Young’s Internet Addiction Test. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2013, 29, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barke, A.; Nyenhuis, N.; Kröner-Herwig, B. The German version of the internet addiction test: A validation study. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2012, 15, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, G.; Casale, S. Evaluation of the psychometric properties of the Italian Internet Addiction Test. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawi, N.S.; Blachnio, A.; Przepiorka, A. Polish validation of the Internet Addiction Test. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 48, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysan, M.; Kuss, D.J.; Barut, Y.; Ayköse, N.; Güleç, M.; Özdemir, O. Psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the Internet Addiction Test (IAT). Addict. Behav. 2017, 64, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawi, N.S. Arabic validation of the Internet addiction test. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaffe, Y.; Seroussi, D.E. Further Evidence for the Psychometric Properties of Young’s Internet Addiction Test (IAT): A Study on a Sample of Israeli-Arab Male Adolescents. Am. J. Health Behav. 2019, 43, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.P.M.; Chang, M.K. Factor Structure for the Internet Addiction Test: A Confirmatory Approach. 2007. Available online: http://gebrc.nccu.edu.tw/proceedings/APDSI/2007/papers/Final_82.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2021).
- Siste, K.; Suwartono, C.; Nasrun, M.W.; Bardosono, S.; Sekartini, R.; Pandelaki, J.; Sarasvita, R.; Murtani, B.J.; Damayanti, R.; Wiguna, T. Validation study of the Indonesian internet addiction test among adolescents. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyanto, L.; McMurran, M. The psychometric properties of the internet addiction test. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2004, 7, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyanto, L.; Griffiths, M.D.; Brunsden, V. A psychometric comparison of the Internet Addiction Test, the Internet-Related Problem Scale, and self-diagnosis. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2011, 14, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Hendawy, A.O.; Ahmad, O.; Sabbah, H.A.; Smail, L.; Kunugi, H. The Arabic version of the Cohen perceived stress scale: Factorial validity and measurement invariance. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Green, J. Factor structure of the depression anxiety stress Scale-21 (DASS-21): Unidimensionality of the Arabic version among Egyptian drug users. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 2019, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.M.; Mak, K.K.; Cheng, C.; Watanabe, H.; Nomachi, S.; Bahar, N.; Young, K.S.; Ko, H.C.; Kim, D.; Griffiths, M.D. Measurement Invariance of the Internet Addiction Test Among Hong Kong, Japanese, and Malaysian Adolescents. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putnick, D.L.; Bornstein, M.H. Measurement Invariance Conventions and Reporting: The State of the Art and Future Directions for Psychological Research. Dev. Rev. DR 2016, 41, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, N.; Kuljanin, G. Measurement invariance: Review of practice and implications. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2008, 18, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Hori, H.; Kim, Y.; Kunugi, H. Predictors of nutritional status, depression, internet addiction, Facebook addiction, and tobacco smoking among women with eating disorders in Spain. Front. Psychiatry 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, M.T.; Ota, A.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Fujisawa, A.; Morita, M.; Minagawa, A.; Li, Y.; Naito, H.; Yatsuya, H. Validation of the Japanese Version of the Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 (J-YFAS 2.0). Nutrients 2019, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.; Kauffman, B.Y.; Rosenfield, D.; Smits, J.A.J.; Zvolensky, M.J. Emotion dysregulation and body mass index: The explanatory role of emotional eating among adult smokers. Eat. Behav. 2019, 33, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübel, C.; Abdulkadir, M.; Herle, M.; Loos, R.J.F.; Breen, G.; Bulik, C.M.; Micali, N. One size does not fit all. Genomics differentiates among anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jáuregui-Lobera, I.; García-Cruz, P.; Carbonero-Carreño, R.; Magallares, A.; Ruiz-Prieto, I. Psychometric properties of Spanish version of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire-R18 (Tfeq-Sp) and its relationship with some eating- and body image-related variables. Nutrients 2014, 6, 5619–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baenas, I.; Caravaca-Sanz, E.; Granero, R.; Sánchez, I.; Riesco, N.; Testa, G.; Vintró-Alcaraz, C.; Treasure, J.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Fernández-Aranda, F. COVID-19 and eating disorders during confinement: Analysis of factors associated with resilience and aggravation of symptoms. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2020, 28, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipou, A.; Meyer, D.; Neill, E.; Tan, E.J.; Toh, W.L.; Van Rheenen, T.E.; Rossell, S.L. Eating and exercise behaviors in eating disorders and the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia: Initial results from the COLLATE project. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini Usubini, A.; Cattivelli, R.; Varallo, G.; Castelnuovo, G.; Molinari, E.; Giusti, E.M.; Pietrabissa, G.; Manari, T.; Filosa, M.; Franceschini, C.; et al. The Relationship between Psychological Distress during the Second Wave Lockdown of COVID-19 and Emotional Eating in Italian Young Adults: The Mediating Role of Emotional Dysregulation. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Intermittent fasting, dietary modifications, and exercise for the control of gestational diabetes and maternal mood dysregulation: A review and a case report. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleplé, A.; Lalanne, C.; Huas, C.; Mattar, L.; Hanachi, M.; Flament, M.F.; Carchon, I.; Jouen, F.; Berthoz, S.; Godart, N. Nutritional status and anxious and depressive symptoms in anorexia nervosa: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laessle, R.G.; Schweiger, U.; Pirke, K.M. Depression as a correlate of starvation in patients with eating disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 1988, 23, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Skeletal muscle damage in COVID-19: A call for action. Medicina 2021, 57, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Royal jelly as an intelligent anti-aging—a focus on cognitive aging and Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Screening for sarcopenia (physical frailty) in the COVID-19 era. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 5563960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Molina, C.; Martos-Cabrera, M.B.; Membrive-Jiménez, M.J.; Vargas-Roman, K.; Suleiman-Martos, N.; Ortega-Campos, E.; Gómez-Urquiza, J.L. Smartphone addiction, risk factors and its adverse effects in nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Educ. Today 2021, 98, 104741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buneviciene, I.; Bunevicius, A. Prevalence of internet addiction in healthcare professionals: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2021, 67, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinojo-Lucena, F.J.; Aznar-Díaz, I.; Cáceres-Reche, M.P.; Trujillo-Torres, J.M.; Romero-Rodríguez, J.M. Problematic Internet Use as a Predictor of Eating Disorders in Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayhan Kartal, F.; Yabancı Ayhan, N. Relationship between eating disorders and internet and smartphone addiction in college students. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z. The relationship between Internet addiction and bulimia in a sample of Chinese college students: Depression as partial mediator between Internet addiction and bulimia. Eat. Weight Disord. 2013, 18, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Aranda, F.; Pinheiro, A.P.; Thornton, L.M.; Berrettini, W.H.; Crow, S.; Fichter, M.M.; Halmi, K.A.; Kaplan, A.S.; Keel, P.; Mitchell, J.; et al. Impulse control disorders in women with eating disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2008, 157, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratacòs, M.; González, J.R.; Mercader, J.M.; de Cid, R.; Urretavizcaya, M.; Estivill, X. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Val66Met and Psychiatric Disorders: Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies Confirm Association to Substance-Related Disorders, Eating Disorders, and Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Kunugi, H. Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A pandemic that threatens physical and mental health by promoting physical inactivity. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2020, 2, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Ali, E.M.; Mousa, A.A.; Ahmed, M.E.; Hendawy, A.O. Bee honey and exercise for improving physical performance, reducing fatigue, and promoting an active lifestyle during COVID-19. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2021, 3, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panea-Pizarro, I.; López-Espuela, F.; Martos-Sánchez, A.; Domínguez-Martín, A.T.; Beato-Fernández, L.; Moran-García, J.M. Internet addiction and Facebook addiction in Spanish women with eating disorders. Arch. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2020, 34, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, F.; Leung, C.H. The Concurrent Validity of the Internet Addiction Test (IAT) and the Mobile Phone Dependence Questionnaire (MPDQ) [Data set]. PLoS ONE 2018, e1286048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Espuela, F.; Beato-Fernández, L.; Panea Pizarro, I.; Martos-Sánchez, A.; Moran Garcia, J.M.; Domínguez-Martín, A.T. Data for: Internet addiction and Facebook addiction in Spanish women with eating disorders. Mendeley Data 2020, V1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yeo Kee, J.; Guo, F.; Zhao, Z. Factor Structure and a Multiple Indicators Multiple Cause Model of Internet Addiction Test: The Effect of Socio-Demographic and Internet Use Variables, 1st ed.; Harvard Dataverse: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, F.; Leung, C.H. The concurrent validity of the Internet Addiction Test (IAT) and the Mobile Phone Dependence Questionnaire (MPDQ). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, M.A.; Lonzoy, A.J.E.C.; Capa-Luque, W. ¿Hay alguien en línea?: Validez y fiabilidad de la versión en español de la Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale (BFAS) en universitarios. Health Addict. Salud Drog. 2018, 18, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.M.; Hendawy, A.O.; Elhay, E.S.A.; Ali, E.M.; Alkhamees, A.A.; Kunugi, H.; Hassan, N.I. The Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale: Its psychometric properties and invariance among women with eating disorders. BMC Women’s Health 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.M.; Alkhamees, A.A.; Hori, H.; Kim, Y.; Kunugi, H. The Depression Anxiety Stress Scale 21: Development and Validation of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale 8-item in Psychiatric Patients and the General Public for Easier Mental Health Measurement in a Post-COVID-19 World. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumero, A.; Marrero, R.J.; Pérez-Albéniz, A.; Fonseca-Pedrero, E. Adolescents’ Bipolar Experiences and Suicide Risk: Well-being and Mental Health Difficulties as Mediators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.; Coste, J.; Lemetayer, F.; Rat, A.C.; Montel, S.; Recchia, S.; Debouverie, M.; Pouchot, J.; Spitz, E.; Guillemin, F. Item reduction based on rigorous methodological guidelines is necessary to maintain validity when shortening composite measurement scales. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveros, M.P.; Bermúdez-Silva, F.J.; Lopez-Rodriguez, A.B.; Wagner, E.J. The Endocannabinoid System as Pharmacological Target Derived from Its CNS Role in Energy Homeostasis and Reward. Applications in Eating Disorders and Addiction. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 1101–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, A.; Milano, W.; Cauli, O. Changes in the Peripheral Endocannabinoid System as a Risk Factor for the Development of Eating Disorders. Endocr. Meta.b Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, M.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Zaplatic, E.; Bellia, F.; Maccarrone, M.; Cifani, C.; D’Addario, C. Transcriptional regulation of the endocannabinoid system in a rat model of binge-eating behavior reveals a selective modulation of the hypothalamic fatty acid amide hydrolase gene. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourdy, R.; Hertz, A.; Filliol, D.; Andry, V.; Goumon, Y.; Mendoza, J.; Olmstead, M.C.; Befort, K. The endocannabinoid system is modulated in reward and homeostatic brain regions following diet-induced obesity in rats: A cluster analysis approach. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4621–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.; Carter, J.C. Compulsive overeating as an addiction disorder. A review of theory and evidence. Appetite 2009, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Jiang, W.Q.; Lin, Z.G.; Du, Y.S.; Vance, A. Comparison of psychological symptoms and serum levels of neurotransmitters in Shanghai adolescents with and without internet addiction disorder: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCuen-Wurst, C.; Ruggieri, M.; Allison, K.C. Disordered eating and obesity: Associations between binge-eating disorder, night-eating syndrome, and weight-related comorbidities. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1411, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimoradi, Z.; Lin, C.-Y.; Broström, A.; Bülow, P.H.; Bajalan, Z.; Griffiths, M.D.; Ohayon, M.M.; Pakpour, A.H. Internet addiction and sleep problems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2019, 47, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsui, K.; Komada, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Kuriyama, K.; Inoue, Y. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Nocturnal Eating Behavior and Sleep-Related Eating Disorder-Like Behavior in Japanese Young Adults: Results of an Internet Survey Using Munich Parasomnia Screening. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Yager, T.J. Reliability and validity of screening scales: Effect of reducing scale length. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1989, 42, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfvebrand, S.; Birgegård, A.; Norring, C.; Högdahl, L.; von Hausswolff-Juhlin, Y. Psychiatric comorbidity in women and men with eating disorders results from a large clinical database. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 230, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Ahmed, A.H.; Smail, L. Psychological Climacteric Symptoms and Attitudes toward Menopause among Emirati Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Dong, G. Sex difference in the effect of Internet gaming disorder on the brain functions: Evidence from resting-state fMRI. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 698, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
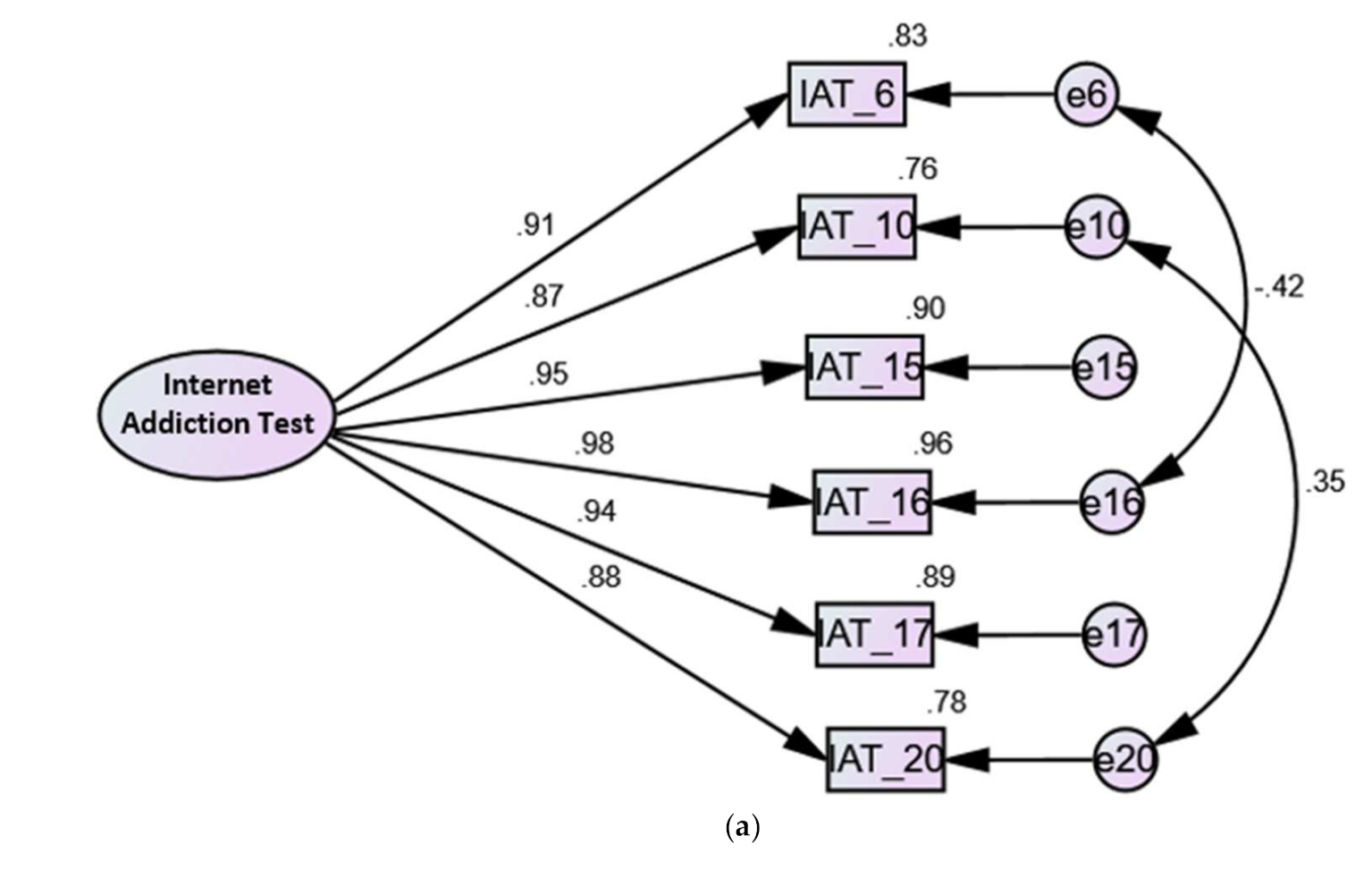
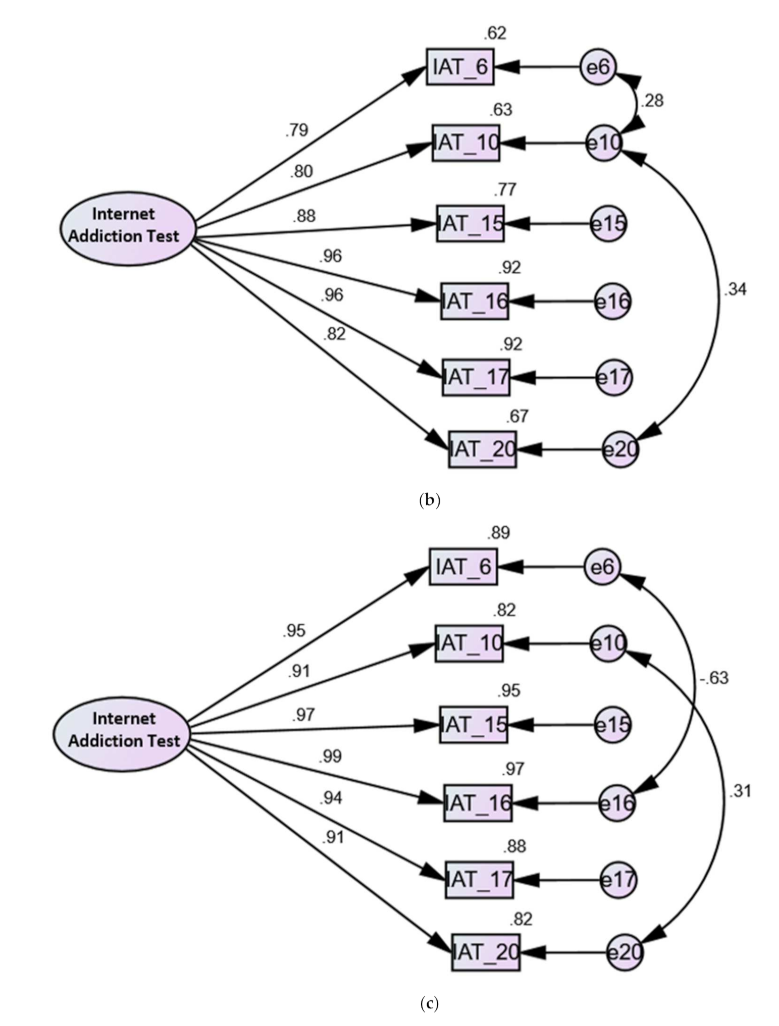
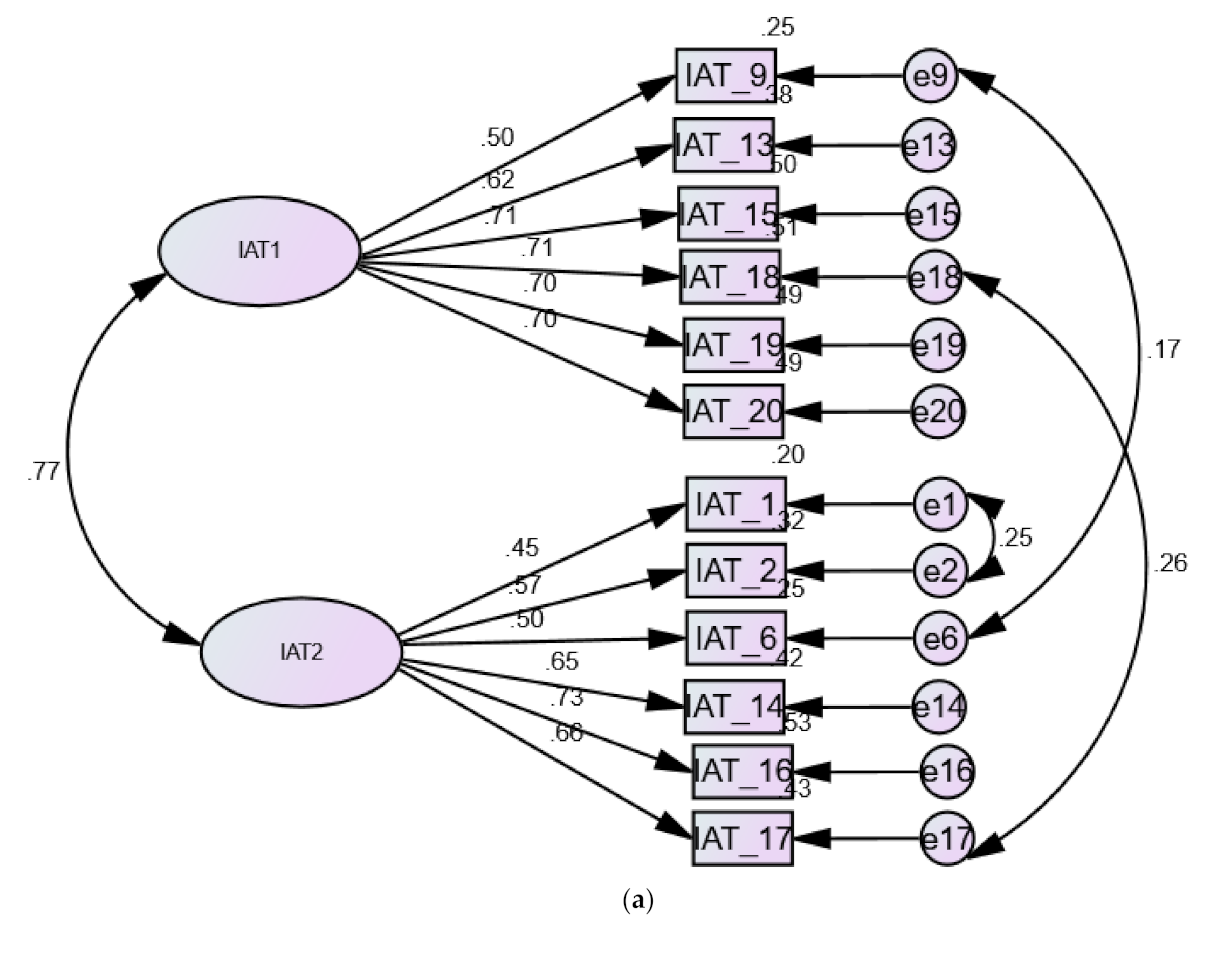

| Factors | Items Comprising Factors in Each Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 Model 2, Model 3 ○, Model 4 ○ | Model 5, Model 6, Model 7 ○, Model 8 ○ (Fernández-Villa et al., 2015) | Model 9, Model 10, Model 11 ○, Model 15 ○◭ (Barke, et al., 2012) | Model 12, Model 13, Model 14 ○ (Widyanto, et al., 2011) | Model 16, Model 17 (Pawlikowski, et al, 2013) | Model 18, Model 19 | |
| Internet addiction | 1–20 | 6, 10, 15, 16, 17, 20 | ||||
| Emotional investment | 3, 4, 9, 10,11,12, 13, 14, 15, 19, 20 | |||||
| Performance and time management | 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 16, 17, 18 | |||||
| Emotional and cognitive preoccupation | 3, 4, 5, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15, 18, 19, 20 | |||||
| Loss of control and interference with daily life | 1, 2, 6, 7, 8, 10, 14, 16, 17 | |||||
| Emotional/psychological conflict | 3, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 17, 18, 19 | |||||
| Time management | 1, 2, 6, 7, 16 | |||||
| Mood modification | 4, 12, 13, 14, 15, 20 | |||||
| Craving/social problems | 9, 13, 15, 18, 19, 20 | |||||
| Loss of control/Time management | 1, 2, 6, 14, 16, 17 | |||||
| Participants’ Characteristics | All Students (N = 1119) | Males (N = 629) | Females (N = 490) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | |
| Age mean (SD) in years | 21.1 (1.6) | 21.0 (1.7) | 21.2 (1.6) |
| Nationality | |||
| Malay Chinese Others | 723 (64.6) 321 (28.7) 75 (6.7) | 402 (63.9) 180 (28.6) 47 (7.5) | 321 (65.6) 141 (28.8) 28 (5.7) |
| Academic major | |||
| Art, humanities and social science Science Engineering Others | 136 (12.2) 377 (33.7) 523 (46.7) 83 (7.4) | 53 (8.4) 150 (23.8) 393 (62.5) 33 (5.5) | 83 (16.9) 227 (46.3) 130 (26.5) 50 (10.2) |
| Academic grade | |||
| Freshman Sophomore Junior Senior | 278 (24.8) 266 (23.8) 309 (27.6) 266 (23.8) | 168 (26.7) 167 (26.6) 161 (25.6) 133 (21.1) | 110 (22.4) 99 (20.2) 148 (30.2) 133 (27.1) |
| Common internet use activities | |||
| Gaming Social networking General use Others | 132 (11.8) 812 (72.6) 133 (11.9) 42 (3.8) | 121 (19.2) 412 (65.5) 69 (11.0) 27 (4.3) | 11 (2.2) 400 (81.6) 64 (13.1) 15 (3.1) |
| Time spent online | 6.5 (4.9) | 6.7 (5.1) | 6.3 (4.6) |
| Perceived effect on study | 3.4 (1.0) | 3.3 (1.0) | 3.5 (1.0) |
| Years of internet use experience | 7.6 (3.0) | 7.6 (2.9) | 7.6 (3.0) |
| 20-item IAT mean (SD) | 48.1 (15.1) | 49.4 (15.4) | 46.3 (14.5) |
| 12-item IAT mean (SD) | 27.7 (10.0) | 29.9 (10.2) | 27.5 (9.7) |
| Six-item IAT mean (SD) | 14.0 (5.4) | 14.5 (5.5) | 13.4 (5.2) |
| Items | Extracted Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | ||
| 1 | Do you find that you stay online longer than you intended? | 0.208 | 0.612 | 0.062 | 0.192 |
| 2 | Do you neglect household chores to spend more time online? | 0.224 | 0.527 | 0.150 | −0.002 |
| 3 | Do you prefer excitement of the Internet to intimacy with your partner? | 0.448 | 0.284 | 0.288 | 0.041 |
| 4 | Do you form new relationships with fellow online users? | 0.234 | 0.131 | 0.527 | −0.091 |
| 5 | Do others in your life complain to you about the amount of time you spend online? | 0.226 | 0.373 | 0.143 | 0.183 |
| 6 | Does your work suffer (e.g., postponing things, not meeting deadlines, etc.) because of the amount of time you spend online? | 0.045 | 0.099 | 0.531 | 0.182 |
| 7 | Do you check your E-mail before something else that you need to do? | 0.045 | 0.168 | 0.175 | 0.074 |
| 8 | Does your job performance or productivity suffer because of the Internet? | 0.148 | 0.420 | 0.233 | 0.402 |
| 9 | Do you become defensive or secretive when anyone asks you what you do online? | 0.270 | 0.115 | 0.162 | 0.254 |
| 10 | Do you block disturbing thoughts about your life with soothing thoughts of the Internet? | 0.174 | 0.044 | 0.481 | 0.189 |
| 11 | Do you find yourself anticipating when you go online again? | 0.572 | 0.328 | 0.078 | 0.146 |
| 12 | Do you fear that life without the Internet would be boring, empty and joyless? | 0.523 | 0.118 | 0.243 | 0.098 |
| 13 | Do you snap, yell, or act annoyed if someone bothers you while you are online? | 0.403 | 0.232 | 0.113 | 0.272 |
| 14 | Do you lose sleep due to late night log-ins? | 0.443 | 0.329 | 0.272 | 0.157 |
| 15 | Do you feel preoccupied with the Internet when off-line or fantasise about being online? | 0.628 | 0.196 | 0.190 | 0.148 |
| 16 | Do you find yourself saying “Just a few more minutes” when online? | 0.578 | 0.532 | 0.012 | 0.180 |
| 17 | Do you try to cut down the amount of time you spend online and fail? | 0.361 | 0.329 | 0.162 | 0.381 |
| 18 | Do you try to hide how long you’ve been online? | 0.384 | 0.195 | 0.139 | 0.451 |
| 19 | Do you choose to spend mor e time online over going out with others? | 0.614 | 0.189 | 0.092 | 0.185 |
| 20 | Do you feel depressed, moody, or nervous when you are offline, which goes away once you are back online? | 0.538 | 0.127 | 0.305 | 0.413 |
| Model | Invariance Levels | χ2 | Df | p | Δχ2 | Δdf | p(Δχ2) | CFI | ΔCFI | TLI | ΔTLI | RMSEA | ΔRMSEA | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 2 | Configural | 759.986 | 332 | 0.001 | 0.897 | 0.882 | 0.103 | 0.0461 | ||||||
| Metric | 775.256 | 351 | 0.001 | 15.270 | 19 | 0.705 | 0.898 | −0.001 | 0.890 | −0.008 | 0.100 | 0.003 | 0.0481 | |
| Strong | 785.181 | 352 | 0.001 | 9.925 | 1 | 0.002 | 0.896 | 0.002 | 0.888 | 0.002 | 0.101 | −0.001 | 0.0974 | |
| Strict | 812.099 | 376 | 0.001 | 26.918 | 24 | 0.308 | 0.895 | 0.001 | 0.894 | −0.006 | 0.098 | 0.003 | 0.1038 | |
| Model 4 | Configural | 690.297 | 300 | 0.001 | 0.899 | 0.885 | 0.104 | 0.0438 | ||||||
| Metric | 707.016 | 318 | 0.001 | 16.719 | 18 | 0.453 | 0.900 | −0.001 | 0.892 | −0.007 | 0.101 | 0.003 | 0.0467 | |
| Strong | 717.577 | 319 | 0.001 | 10.561 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.897 | 0.003 | 0.890 | 0.002 | 0.102 | −0.001 | 0.0940 | |
| Strict | 740.32 | 340 | 0.001 | 22.743 | 21 | 0.358 | 0.897 | 0.000 | 0.896 | −0.006 | 0.099 | 0.003 | 0.0992 | |
| Model 6 | Configural | 713.298 | 328 | 0.001 | 0.907 | 0.893 | 0.099 | 0.0456 | ||||||
| Metric | 724.393 | 346 | 0.001 | 11.095 | 18 | 0.890 | 0.909 | −0.002 | 0.900 | −0.007 | 0.095 | 0.004 | 0.0471 | |
| Strong | 737.242 | 349 | 0.001 | 12.849 | 3 | 0.005 | 0.907 | 0.002 | 0.898 | 0.002 | 0.096 | −0.001 | 0.0974 | |
| Strict | 764.561 | 374 | 0.001 | 27.319 | 25 | 0.340 | 0.906 | 0.001 | 0.905 | −0.007 | 0.093 | 0.003 | 0.1038 | |
| Model 8 | Configural | 587.141 | 292 | 0.001 | 0.924 | 0.911 | 0.091 | 0.0412 | ||||||
| Metric | 597.180 | 309 | 0.001 | 10.039 | 17 | 0.902 | 0.926 | −0.002 | 0.918 | −0.007 | 0.088 | 0.003 | 0.0430 | |
| Strong | 610.667 | 312 | 0.001 | 13.487 | 3 | 0.004 | 0.923 | 0.003 | 0.916 | 0.002 | 0.089 | −0.001 | 0.0942 | |
| Strict | 634.998 | 336 | 0.001 | 24.330 | 24 | 0.443 | 0.923 | 0.000 | 0.921 | −0.005 | 0.086 | 0.003 | 0.0994 | |
| Model 11 | Configural | 596.787 | 292 | 0.001 | 0.921 | 0.908 | 0.093 | 0.0412 | ||||||
| Metric | 610.115 | 309 | 0.001 | 13.329 | 17 | 0.714 | 0.922 | −0.001 | 0.914 | −0.006 | 0.090 | 0.003 | 0.0427 | |
| Strong | 623.974 | 312 | 0.001 | 13.858 | 3 | 0.003 | 0.919 | 0.003 | 0.912 | 0.002 | 0.091 | −0.001 | 0.0950 | |
| Strict | 648.061 | 336 | 0.001 | 24.087 | 24 | 0.457 | 0.919 | 0.000 | 0.918 | −0.006 | 0.088 | 0.003 | 0.1000 | |
| Model 17 | Configural | 207.656 | 98 | 0.001 | 0.952 | 0.936 | 0.096 | 0.0433 | ||||||
| Metric | 217.050 | 108 | 0.001 | 9.394 | 10 | 0.495 | 0.953 | −0.001 | 0.942 | −0.006 | 0.091 | 0.005 | 0.0430 | |
| Strong | 232.192 | 111 | 0.001 | 15.142 | 3 | 0.002 | 0.947 | 0.006 | 0.938 | 0.004 | 0.095 | −0.004 | 0.0892 | |
| Strict | 251.243 | 127 | 0.001 | 19.051 | 16 | 0.266 | 0.946 | 0.001 | 0.944 | −0.006 | 0.090 | 0.005 | 0.0946 | |
| Model 19 | Configural | 20.234 | 14 | 0.123 | 0.994 | 0.986 | 0.061 | 0.0289 | ||||||
| Metric | 23.825 | 19 | 0.203 | 3.591 | 5 | 0.610 | 0.995 | −0.001 | 0.992 | −0.006 | 0.046 | 0.015 | 0.0319 | |
| Strong | 36.294 | 20 | 0.014 | 12.470 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.984 | 0.011 | 0.975 | 0.017 | 0.082 | −0.036 | 0.0749 | |
| Strict | 52.669 | 28 | 0.003 | 16.374 | 8 | 0.037 | 0.975 | 0.009 | 0.973 | 0.002 | 0.085 | −0.003 | 0.0780 |
| Criteria | Whole Sample (N = 123) | Anorexia Nervosa (N = 59) | Other Eating Disorders (N = 64) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 Items | 12 Items | Six Items | 20 Items | 12 Items | Six Items | 20 Items | 12 Items | Six Items | |
| Coefficient alpha | 0.989 | 0.983 | 0.972 | 0.981 | 0.971 | 0.950 | 0.992 | 0.988 | 0.980 |
| Range of corrected item-total correlations | 0.837–0.937 | 0.831–0.943 | 0.883–0.946 | 0.718–0.898 | 0.728–0.896 | 0.816–0.897 | 0.891–0.957 | 0.878–0.965 | 0.904–0.980 |
| Range of Cronbach’s alpha if-item-deleted | All values = 0.989 | 0.981–0.983 | 0.963–0.970 | 0.980–0.982 | 0.968–0.971 | 0.936–0.944 | All values = 0.992 | 0.986–0.988 | 0.973–0.979 |
| Correlation with the Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale | 0.906 | 0.883 | 0.878 | 0.856 | 0.824 | 0.823 | 0.908 | 0.888 | 0.881 |
| Correlation with the original Internet Addiction Test | -- | 0.983 | 0.973 | -- | 0.977 | 0.972 | -- | 0.984 | 0.970 |
| Shapiro–Wilk W | 0.827 | 0.811 | 0.807 | 0.859 | 0.830 | 0.842 | 0.820 | 0.815 | 0.799 |
| Models | χ2 | p | df | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | RMSEA 90% CI | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 16 (C); 2F 12 items | 478.247 | 0.001 | 53 | 0.903 | 0.879 | 0.085 | 0.078 to 0.092 | 0.0560 |
| Model 17 (E); 2F 12 items | 329.008 | 0.001 | 50 | 0.936 | 0.916 | 0.071 | 0.063 to 0.078 | 0.0458 |
| Model 18 (C); 1F six items | 160.494 | 0.001 | 9 | 0.899 | 0.832 | 0.123 | 0.106 to 0.140 | 0.0506 |
| Model 19 (E); 1F six items | 35.038 | 0.001 | 7 | 0.981 | 0.960 | 0.060 | 0.041 to 0.080 | 0.0241 |
| Groups | Invariance Levels | χ2 | df | P | Δχ2 | Δdf | p(Δχ2) | CFI | ΔCFI | TLI | ΔTLI | RMSEA | ΔRMSEA | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All EDs | Configural | 369.624 | 100 | 0.001 | 0.939 | 0.920 | 0.066 | 0.0202 | ||||||
| Metric | 406.460 | 110 | 0.001 | 36.836 | 10 | 0.001 | 0.933 | 0.006 | 0.920 | 0.000 | 0.066 | 0.000 | 0.0259 | |
| Strong | 532.650 | 113 | 0.001 | 126.189 | 3 | 0.001 | 0.906 | 0.027 | 0.890 | 0.030 | 0.078 | −0.012 | 0.1598 | |
| Strict | 978.087 | 128 | 0.001 | 445.438 | 15 | 0.001 | 0.809 | 0.097 | 0.803 | 0.087 | 0.104 | 0.026 | 0.3331 | |
| AN | Configural | 318.615 | 100 | 0.001 | 0.925 | 0.901 | 0.063 | 0.0406 | ||||||
| Metric | 344.099 | 110 | 0.001 | 25.483 | 10 | 0.005 | 0.920 | 0.005 | 0.904 | −0.003 | 0.062 | 0.001 | 0.0669 | |
| Strong | 374.675 | 113 | 0.001 | 30.576 | 3 | 0.001 | 0.911 | 0.009 | 0.896 | 0.008 | 0.065 | −0.003 | 0.1704 | |
| Strict | 604.347 | 128 | 0.001 | 229.672 | 15 | 0.001 | 0.837 | 0.074 | 0.832 | 0.064 | 0.082 | −0.023 | 0.3300 | |
| Other EDs | Configural | 324.543 | 100 | 0.001 | 0.936 | 0.916 | 0.064 | 0.0211 | ||||||
| Metric | 356.586 | 110 | 0.001 | 32.043 | 10 | 0.001 | 0.930 | 0.006 | 0.916 | 0.000 | 0.064 | 0.000 | 0.0270 | |
| Strong | 478.600 | 113 | 0.001 | 122.014 | 3 | 0.001 | 0.896 | 0.034 | 0.879 | 0.037 | 0.077 | −0.013 | 0.2125 | |
| Strict | 729.810 | 128 | 0.001 | 251.210 | 15 | 0.001 | 0.829 | 0.067 | 0.824 | 0.055 | 0.092 | 0.015 | 0.3945 |
| Groups | Invariance Levels | χ2 | df | P | Δχ2 | Δdf | p(Δχ2) | CFI | ΔCFI | TLI | ΔTLI | RMSEA | ΔRMSEA | SRMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All EDs | Configural | 43.378 | 14 | 0.001 | 0.983 | 0.963 | 0.059 | 0.0170 | ||||||
| Metric | 53.515 | 19 | 0.001 | 10.137 | 5 | 0.071 | 0.979 | 0.004 | 0.968 | −0.005 | 0.055 | 0.004 | 0.0194 | |
| Strong | 123.389 | 20 | 0.001 | 69.874 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.938 | 0.041 | 0.908 | 0.040 | 0.092 | −0.037 | 0.1184 | |
| Strict | 406.563 | 28 | 0.001 | 283.174 | 8 | 0.001 | 0.775 | 0.163 | 0.758 | 0.150 | 0.149 | 0.057 | 0.3245 | |
| AN | Configural | 34.186 | 14 | 0.002 | 0.980 | 0.957 | 0.051 | 0.0316 | ||||||
| Metric | 42.937 | 19 | 0.001 | 8.751 | 5 | 0.119 | 0.976 | 0.004 | 0.963 | −0.006 | 0.048 | 0.003 | 0.0467 | |
| Strong | 51.143 | 20 | 0.001 | 8.206 | 1 | 0.004 | 0.969 | 0.007 | 0.954 | 0.009 | 0.053 | −0.005 | 0.1154 | |
| Strict | 212.966 | 28 | 0.001 | 161.823 | 8 | 0.001 | 0.817 | 0.152 | 0.804 | 0.150 | 0.110 | 0.057 | 0.3329 | |
| Other EDs | Configural | 39.297 | 14 | 0.001 | 0.980 | 0.957 | 0.057 | 0.0136 | ||||||
| Metric | 48.712 | 19 | 0.001 | 9.415 | 5 | 0.094 | 0.977 | 0.003 | 0.963 | −0.006 | 0.053 | 0.004 | 0.0162 | |
| Strong | 126.688 | 20 | 0.001 | 77.975 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.916 | 0.061 | 0.874 | 0.089 | 0.098 | −0.045 | 0.1556 | |
| Strict | 279.151 | 28 | 0.001 | 152.464 | 8 | 0.001 | 0.803 | 0.113 | 0.789 | 0.085 | 0.127 | 0.029 | 0.3778 |
| Criteria | 20 Item | 12 Items | Six Items |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient alpha | 0.899 | 0.865 | 0.768 |
| Range of corrected item-total correlations | 0.207–0.643 | 0.354–0.664 | 0.429–0.573 |
| Range of Cronbach’s alpha if-item-deleted | 0.891–0.902 | 0.846–0.860 | 0.717–0.754 |
| Correlation with time spent online | 0.227 | 0.218 | 0.206 |
| Correlation with years of internet use experience | 0.134 ** | 0.102 ** | 0.103 ** |
| Correlation with perceived effect of internet use on academic performance | −0.078 * | −0.107 ** | −0.106 ** |
| Correlation with the original Internet Addiction Test | -- | 0.959 | 0.923 |
| Shapiro–Wilk W | 0.987 | 0.988 | 0.986 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, A.M.; Hendawy, A.O.; Almarwani, A.M.; Alzahrani, N.; Ibrahim, N.; Alkhamees, A.A.; Kunugi, H. The Six-Item Version of the Internet Addiction Test: Its Development, Psychometric Properties, and Measurement Invariance among Women with Eating Disorders and Healthy School and University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312341
Ali AM, Hendawy AO, Almarwani AM, Alzahrani N, Ibrahim N, Alkhamees AA, Kunugi H. The Six-Item Version of the Internet Addiction Test: Its Development, Psychometric Properties, and Measurement Invariance among Women with Eating Disorders and Healthy School and University Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312341
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Amira Mohammed, Amin Omar Hendawy, Abdulaziz Mofdy Almarwani, Naif Alzahrani, Nashwa Ibrahim, Abdulmajeed A. Alkhamees, and Hiroshi Kunugi. 2021. "The Six-Item Version of the Internet Addiction Test: Its Development, Psychometric Properties, and Measurement Invariance among Women with Eating Disorders and Healthy School and University Students" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312341
APA StyleAli, A. M., Hendawy, A. O., Almarwani, A. M., Alzahrani, N., Ibrahim, N., Alkhamees, A. A., & Kunugi, H. (2021). The Six-Item Version of the Internet Addiction Test: Its Development, Psychometric Properties, and Measurement Invariance among Women with Eating Disorders and Healthy School and University Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312341








