Association of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case-Crossover, Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Data Source
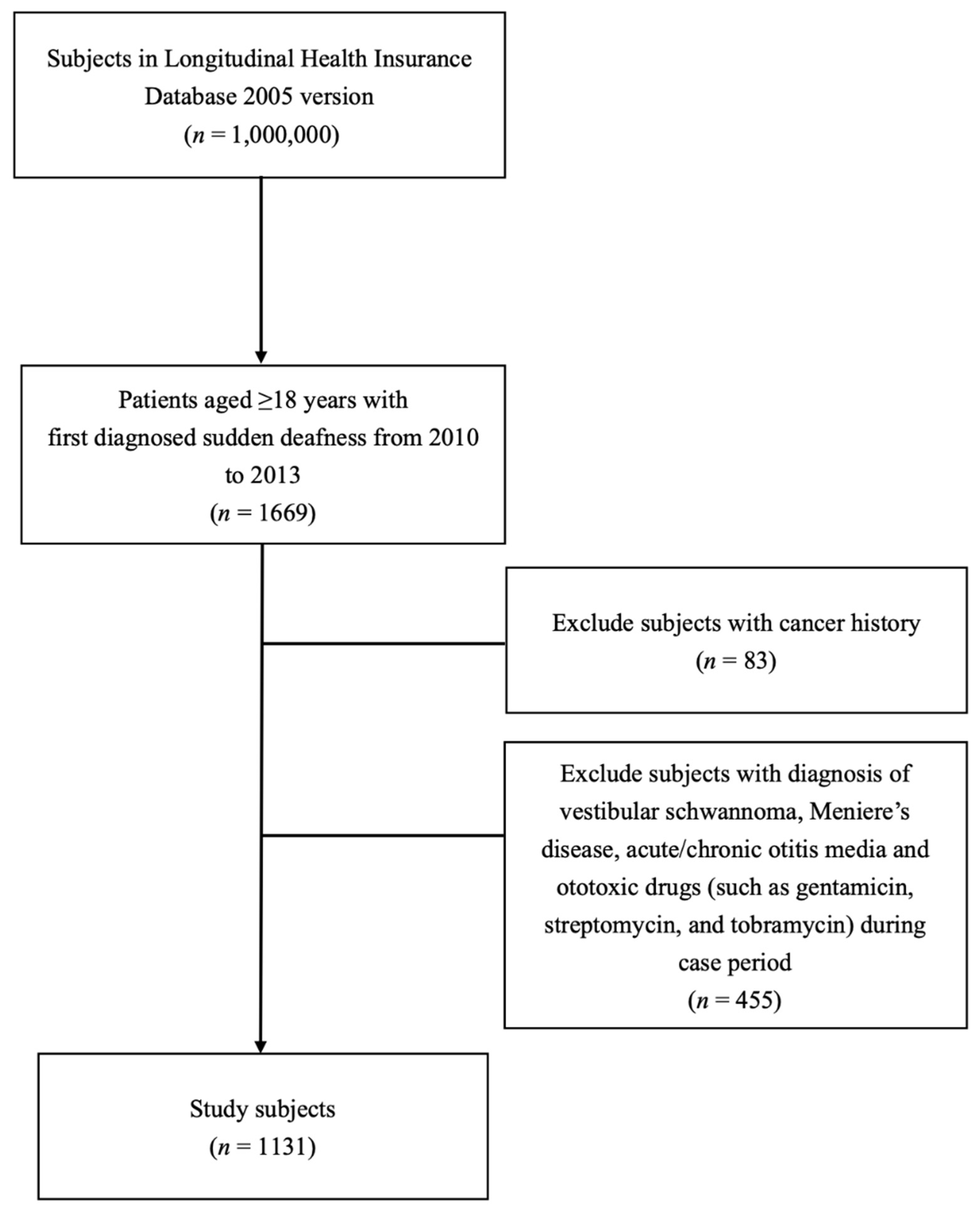
2.2. Patients
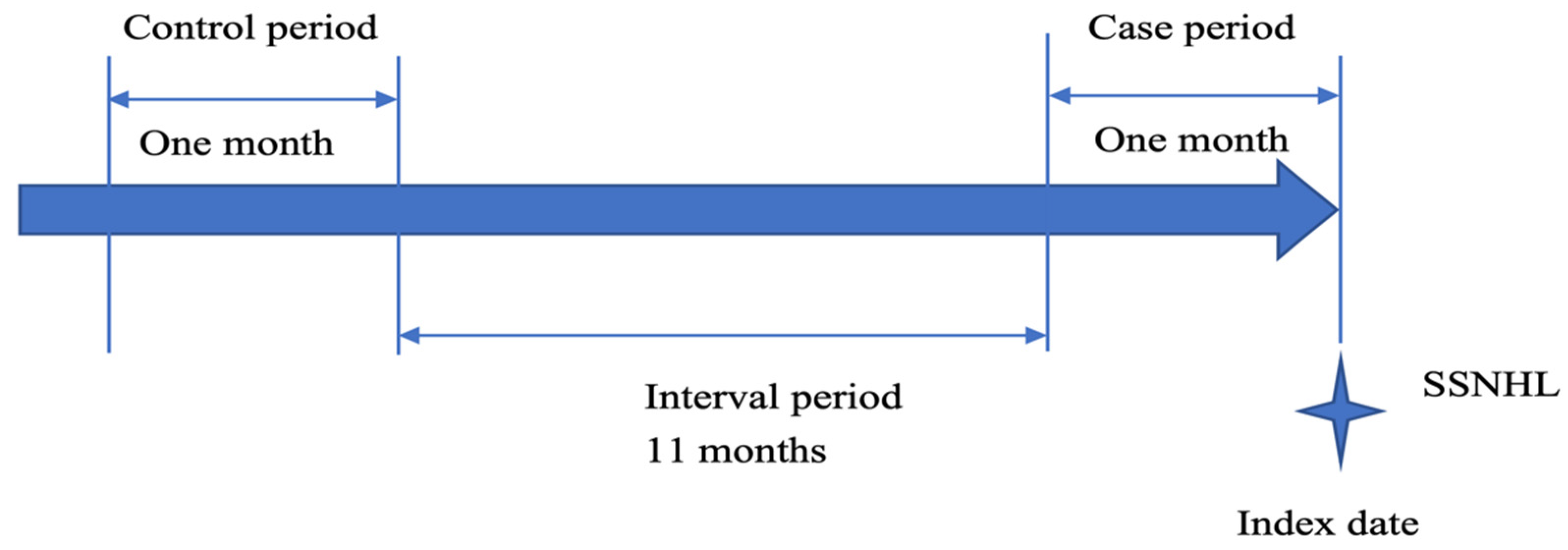
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Definition of Acute URI Exposure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort
3.2. Conditional Logistic Regression Models of Acute URIs and SSNHL Risk
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Varying Exposure Time Window
3.4. Forest Plots of aORs for SSNHL Stratified by Sex and Age
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aOR | adjusted odds ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| cOR | crude odds ratio |
| SSNHL | sudden sensorineural hearing loss |
| URIs | upper respiratory tract infections |
| DDD | defined daily dose |
| SD | standard deviation |
| LHID | longitudinal health insurance database |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database |
| ICD-9-CM | International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification |
References
- Stachler, R.J.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Archer, S.M.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Schwartz, S.R.; Barrs, D.M.; Brown, S.R.; Fife, T.D.; Ford, P.; Ganiats, T.G.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, S1–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.S.; Lin, H.C.; Chao, P.Z. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Evidence from Taiwan. Audiol. Neurootol. 2006, 11, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, T.H.; Harris, J.P. Incidence of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.K.; Lin, J.R.J.; Atashband, S.; Irvine, R.A.; Westerberg, B.D. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-T.; Chang, I.-J.; Hsu, C.-M.; Yang, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Tsai, M.-S.; Chang, G.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Huang, E.I.; Lin, M.-H.; et al. Association between Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Preexisting Thyroid Diseases: A Nationwide Case-Control Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-C.; Lin, C.; Weng, S.-F.; Lin, Y.-S. Higher Risk of Developing Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Patients with Chronic Otitis Media. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.J.; Krall, R.; Westerberg, B.D.; Chadha, N.; Chau, J.K. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk factors for sudden sensorineural hearing loss in adults. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Tanabe, T.; Yanagita, N.; Wakai, K.; Ohno, Y. Risk factors for sudden deafness: A case-control study. Auris Nasus Larynx 1997, 24, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetarpal, U.; Nadol, J.J.B.; Glynn, R.J. Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Postnatal Viral Labyrinthitis: A Statistical Comparison of Temporal Bone Findings. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1990, 99, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dishoeck, H.A.; Bierman, T.A. Sudden perceptive deafness and viral infection; report of the first one hundred patients. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1957, 66, 963–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielides, V.; Nousia, C.-S.; Bartzokas, A.; Lolis, C.J.; Kateri, M.; Skevas, A. Weather conditions and sudden sensorineural hearing loss. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2002, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.B. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment of the common cold. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997, 78, 531–539, quiz 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.B.; Hendley, J.O. Virucidal hand treatments for prevention of rhinovirus infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 805–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Heman-Ackah, S.E.; Shaikh, J.A.; Roehm, P.C. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Su, C.-C.; Shao, S.-C.; Sung, S.-F.; Lin, S.-J.; Kao, Y.-H.Y.; Lai, E.C.-C. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database: Past and future. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.J.; Wu, C.-S.; Kang, J.-H.; Lin, H.-C. Association of Acute Myocardial Infarction with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Audiol. Neurotol. 2013, 18, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.-C.; Hu, L.-Y.; Liu, M.-E.; Yang, A.C.; Shen, C.-C.; Tsai, S.-J. Risk of depressive disorders following sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 197, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclure, M.; Mittleman, M.A. Should we use a case-crossover design? Annu. Rev. Public Health 2000, 21, 193–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclure, M. The Case-Crossover Design: A Method for Studying Transient Effects on the Risk of Acute Events. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 133, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, H.M.; McLean, H.Q.; Chow, B.D. Variability in Antibiotic Prescribing for Upper Respiratory Illnesses by Provider Specialty. J. Pediatr. 2018, 203, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, A.; Alweis, R.; Scheirer, J.; Schamel, S.; Wasser, T.; Levingood, K. Factors affecting adherence to evidence-based guidelines in the treatment of URI, sinusitis, and pharyngitis. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, M.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Peterson, J.; Gold, J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-H.; Yen, Y.-C.; Yang, H.-C.; Liu, S.-H.; Yuan, S.-P.; Wu, L.-L.; Lee, F.-P.; Lin, K.-C.; Lai, M.-T.; Wu, C.-C.; et al. Curative-Intent Aggressive Treatment Improves Survival in Elderly Patients With Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and High Comorbidity Index. Medicine 2016, 95, e3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinan-Altman, S.; Werner, P. Subjective Age and Its Correlates Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. 2019, 88, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolberg, P.; Ayalon, L. Subjective Meanings and Identification with Middle Age. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. 2018, 87, 52–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennell, L.M.; Galligan, C.L.; Fish, E.N. Sex affects immunity. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 38, J282–J291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.D. Clinical practice. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, B.E.; Agrup, C.; Haskard, D.O.; Luxon, L.M. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lancet 2010, 375, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schattner, A.; Halperin, D.; Wolf, D.; Zimhony, O. Enteroviruses and sudden deafness. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2003, 168, 1421–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Umashankar, A.; Prakash, P.; Prabhu, P. Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Post Coronavirus Disease: A Systematic Review of Case Reports. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Imrit, T.S.; Liu, A. Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children: Clinical Characteristics, Etiology, Treatment Outcomes, and Prognostic Factors. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, G.L. The common cold. Prim. Care 1996, 23, 657–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branche, A.R.; Falsey, A.R. Parainfluenza Virus Infection. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 538–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, H.K.; Falsey, A.R. The Diagnosis of Viral Respiratory Disease in Older Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betakova, T.; Kostrabova, A.; Lachova, V.; Turianova, L. Cytokines Induced During Influenza Virus Infection. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 2616–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, D.; McCracken, C.E.; Kopleman, H.B.; Kyu, S.Y.; Lee, F.E.-H.; Lu, X.; Anderson, L.J. Human Rhinovirus Induced Cytokine/Chemokine Responses in Human Airway Epithelial and Immune Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofler, S.; Nickel, T.; Weis, M. Role of cytokines in cardiovascular diseases: A focus on endothelial responses to inflammation. Clin. Sci. 2005, 108, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Rengarajan, T.; Thangavel, J.; Nishigaki, Y.; Sakthisekaran, D.; Sethi, G.; Nishigaki, I. The Vascular Endothelium and Human Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, C.R.; Jick, S.S.; Derby, L.E.; Vasilakis, C.; Jick, H. Acute respiratory-tract infections and risk of first-time acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 1998, 351, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gorp, E.C.M.; Suharti, C.; Cate, H.T.; Dolmans, W.M.V.; Van Der Meer, J.W.M.; Cate, J.W.T.; Brandjes, D.P.M. Review: Infectious Diseases and Coagulation Disorders. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumenina, L.T.; Rayes, J.; Frimat, M.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V. Endothelial cells: Source, barrier, and target of defensive mediators. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvago, P.; Rizzo, S.; Bianco, A.; Martines, F. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Is there a relationship between routine haematological parameters and audiogram shapes? Int. J. Audiol. 2017, 56, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeijenbier, M.; van Wissen, M.; van de Weg, C.; Jong, E.; Gerdes, V.; Meijers, J.; Brandjes, D.; van Gorp, E. Review: Viral infections and mechanisms of thrombosis and bleeding. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 1680–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majoor, C.J.; Van De Pol, M.A.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Molenkamp, R.; Wolthers, K.C.; Van Der Poll, T.; Nieuwland, R.; Johnston, S.L.; Sterk, P.J.; et al. Evaluation of coagulation activation after Rhinovirus infection in patients with asthma and healthy control subjects: An observational study. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, S.M.; Darwish, I.; Lee, W.L. Endothelial activation and dysfunction in the pathogenesis of influenza a virus infection. Virulence 2013, 4, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.M.; Azgomi, M.N. Metabolic syndrome components and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A case–control study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.W.; Lin, Y.S.; Weng, S.F.; Chou, C.W. Risk of developing sudden sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic patients: A population-based cohort study. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lin, S.-W.; Lin, Y.-S.; Weng, S.-F.; Lee, T.-M. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is correlated with an increased risk of acute myocardial infarction: A population-based cohort study. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 2254–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Chao, P.-Z.; Lee, H.-C. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss increases the risk of stroke: A 5-year follow-up study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graydon, K.; Waterworth, C.; Miller, H.; Gunasekera, H. Global burden of hearing impairment and ear disease. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2019, 133, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). GBD Compare Data Visualization. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/ (accessed on 30 December 2019).
- Conlin, A.E.; Parnes, L.S. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: I. A systematic review. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlin, A.E.; Parnes, L.S. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: II. A Meta-analysis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wei, B.P.C.; Stathopoulos, D.; O’Leary, S. Steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD003998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mort, D.J.; Bronstein, A.M. Sudden deafness. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.-L.; Kao, Y.-H.Y.; Lin, S.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lai, M.L. Validation of the national health insurance research database with ischemic stroke cases in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2011, 20, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-L.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, P.-S.; Li, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-J.; Yang, Y.-H.K. Validation of Acute Myocardial Infarction Cases in the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Lai, M.-L. Validating the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke in a National Health Insurance claims database. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Warren-Gash, C.; Smeeth, L.; Chen, P.-C. Data resource profile: The National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). Epidemiol. Health 2018, 40, e2018062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Case Period | Control Period | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at first SSNHL diagnosis (years), N (%) | |||
| 18–39 | 261 (23.1%) | ||
| 40–64 | 622 (55.0%) | ||
| ≥65 | 248 (21.9%) | ||
| Sex | |||
| Female | 515 (45.5%) | ||
| Male | 616 (54.5%) | ||
| Disease | |||
| Hypertension | 396 (35.0%) | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 219 (19.4%) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 323 (28.6%) | ||
| End-stage renal disease | 12 (1.1%) | ||
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 104 (9.2%) | ||
| Hyperthyroidism/hypothyroidism | 65 (5.7%) | ||
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | |||
| 0 | 1043 (92.2%) | ||
| 1–2 | 69 (6.1%) | ||
| ≥3 | 19 (1.68%) | ||
| Medication dosage, DDD (mean ± SD) | |||
| Statins | 2.0 ± 7.9 | 1.8 ± 7.8 | 0.167 |
| Antiplatelet | (3.6 ± 12.1) | (3.2 ± 11.5) | 0.424 |
| NSAIDs | (3.1 ± 8.0) | (2.7 ± 8.2) | 0.506 |
| Furosemide | (0.9 ± 10.1) | (0.7 ± 3.8) | 0.233 |
| Case Period (n) a | Control Period (n) b | cOR (95% CI) | aOR (95% CI) c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute URIs | 139 | 90 | 1.54 (1.18–2.01) | 1.57 (1.20–2.05) |
| Exposure Time Window | Case Period 1–30 Days Control Period 365–395 Days | Case Period 1–60 Days Control Period 365–425 Days | Case Period 1–90 Days Control Period 365–455 Days | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cOR (95%CI) aOR (95%CI) a | cOR (95%CI) aOR (95%CI) a | cOR (95%CI) aOR (95%CI) a | ||||
| Acute URIs | 1.54 (1.18–2.01) | 1.57 (1.20–2.05) | 1.36 (1.08–1.70) | 1.36 (1.09–1.71) | 1.26 (1.01–1.56) | 1.25 (1.01–1.56) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-Y.; Kuo, P.-H.; Wu, S.-Y. Association of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case-Crossover, Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010745
Lin C-Y, Kuo P-H, Wu S-Y. Association of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case-Crossover, Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(20):10745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010745
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chuan-Yi, Po-Hsiu Kuo, and Szu-Yuan Wu. 2021. "Association of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case-Crossover, Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 20: 10745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010745
APA StyleLin, C.-Y., Kuo, P.-H., & Wu, S.-Y. (2021). Association of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infections with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case-Crossover, Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(20), 10745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182010745






