Knowledge, Practice of Personal Hygiene, School Sanitation, and Risk Factors of Contracting Diarrhea among Rural Students from Five Western Provinces in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Respondents
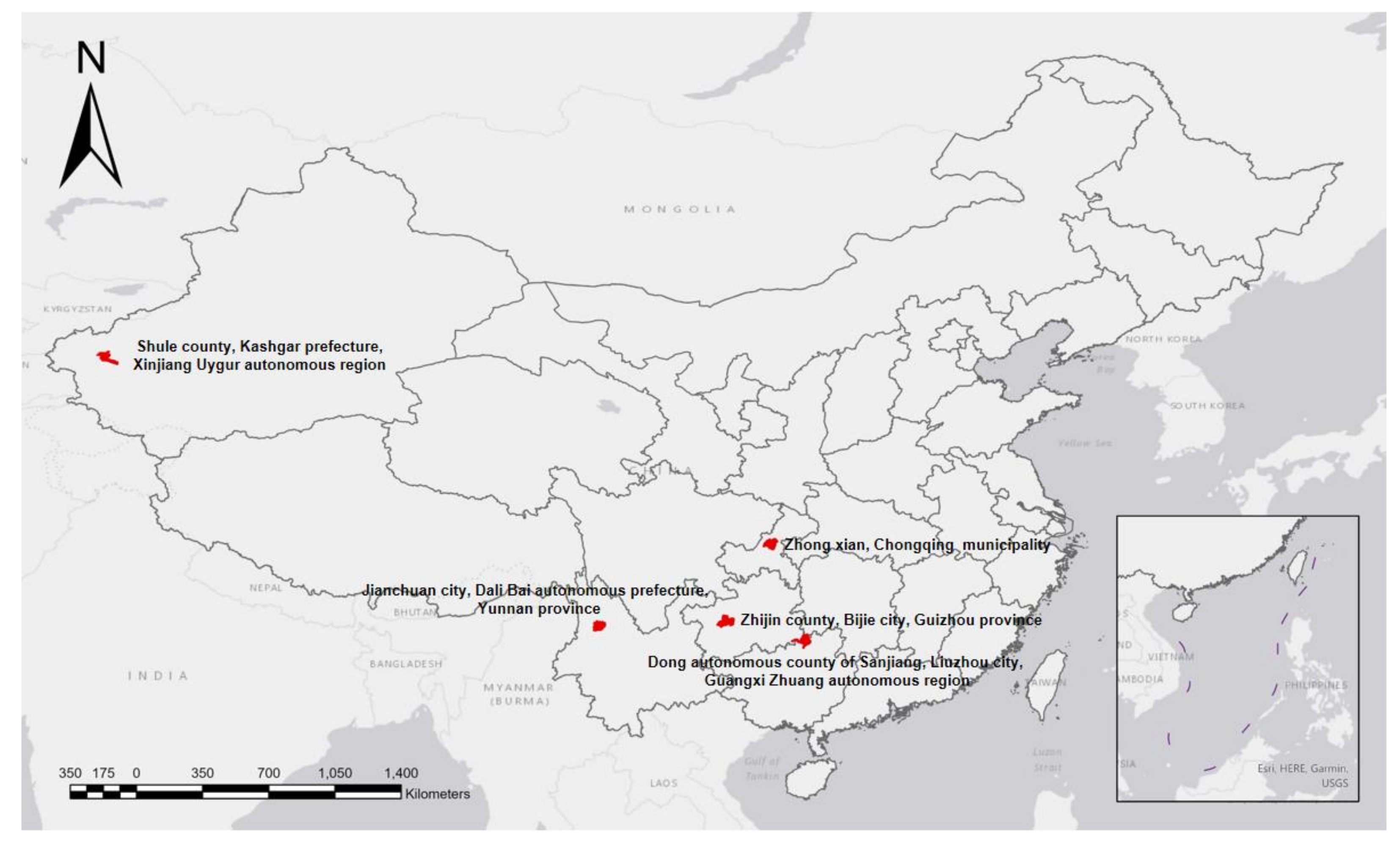
2.2. Survey Method
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Information
3.2. Univariate Logistic Regression Analysis
3.3. Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. The Treatment of Diarrhea: A Manual for Physicians and Other Senior Health Workers; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant, R.L.; Hughes, J.M.; Lima, N.L.; Crane, J. Diarrhea in developed and developing countries: Magnitude, special settings, and etiologies. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12, S41–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkman, D.S.; Lescano, A.G.; Gilman, R.H.; Lopez, S.L.; Black, M.M. Effects of stunting, diarrhoeal disease, and parasitic infection during infancy on cognition in late childhood: A follow-up study. Lancet 2002, 359, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Diarrhoeal Disease Collaborators. Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of diarrhoea in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018, 18, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, C.L.; Black, R.E. Diarrhoea morbidity and mortality in older children, adolescents, and adults. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.H.; Hu, Y. Burden of diarrhoeal diseases in China and World Bank countries at different economic levels from 1990 to 2017. Mod. Bus. Trade Ind. 2020, 41, 80–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.T. Analysis of causes of death and burden of disease in school aged children. In Proceedings of the Healthy China—4th Asia-Pacific International Congress on Health Emergency and Rescue, Shenzhen, China, 31 March 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yan, B.Q. Current situation and management countermeasures of public health emergencies in Chinese schools. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2013, 34, 513–515. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal variations in the incidence of bacillary dysentery and long-term effects associated with meteorological and socioeconomic factors in China from 2013 to 2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Schmidt, A.M.; Elliott, S.J. Socioeconomic factors and bacillary dysentery risk in Jiangsu Province, China: A spatial investigation using Bayesian hierarchical models. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vally, H.; McMichael, C.; Doherty, C.; Li, X.; Guevarra, G.; Tobias, P. The Impact of a School-Based Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Intervention on Knowledge, Practices, and Diarrhoea Rates in the Philippines. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cairncross, S.; Hunt, C.; Boisson, S. Water, sanitation and hygiene for the prevention of diarrhoea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39 (Suppl. 1), i193–i205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curtis, V.; Cairncross, S. Effect of washing hands with soap on diarrhoea risk in the community: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Hunter, P.R.; Freeman, M.C. Impact of drinking water, sanitation and handwashing with soap on childhood diarrheal disease: Updated meta-analysis and meta-regression. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2018, 23, 508–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, W.A.; Mostafa, N.S.; Hakim, S.A. Health Literacy Co-Design in a Low Resource Setting: Harnessing Local Wisdom to Inform Interventions across Fishing Villages in Egypt to Improve Health and Equity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Children’s Fund. Water and Sanitation Project Newsletter. Available online: https://www.unicef.cn/reports/wash-newsletter-2019-01 (accessed on 1 July 2021). (In Chinese).
- Trinies, V.; Garn, J.V.; Chang, H.H.; Freeman, M.C. The impact of a school-based water, sanitation, and hygiene program on absenteeism, diarrhea, and respiratory infection: A matched-control trial in Mali. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weaver, E.R.; Agius, P.A.; Veale, H. Water, sanitation, and hygiene facilities and hygiene practices associated with diarrhea and vomiting in monastic schools, Myanmar. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Ghamdi, M.A.; Bentham, G.; Hunter, P.R. Environmental risk factors for diarrhea among male schoolchildren in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia. J. Water Health 2009, 7, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shine, S.; Muhamud, S.; Adanew, S.; Demelash, A.; Abate, M. Prevalence and associated factors of diarrhea among under-five children in Debre Berhan town, Ethiopia 2018: A cross-sectional study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komarulzaman, A.; Smits, J.; de Jong, E. Clean water, sanitation and diarrhea in Indonesia: Effects of household and community factors. Glob. Public Health 2017, 12, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmud, M.A.; Spigt, M.; Bezabih, A.M.; Pavon, I.L.; Dinant, G.J.; Velasco, R.B. Efficacy of handwashing with soap and nail clipping on intestinal parasitic infections in school-aged children: A factorial cluster randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwin, P.; Azage, M. Geographical variations and factors associated with childhood diarrhea in Tanzania: A national population based survey 2015–2016. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2019, 29, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, L.Q.; Pu, S.C.; Tang, S.D.; Yi, J.R.; Mei, L.J. Analysis on health literacy and its influencing factors among residents in 86 poverty-stricken counties and districts in Yunnan Province. Chin. J. Health Educ. 2020, 1, 13–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Kan, B.; Xu, W. Epidemic status and surveillance of infectious diarrhea in yunnan province. Parasitoses Infect. Dis. 2014, 12, 179–183. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.; Colford, J.M. Effects of Boiling Drinking Water on Diarrhea and Pathogen-Specific Infections in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 1362–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arslan, M.; Xu, B.; El-Din, M.G. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via fecal-oral and aerosols-borne routes: Environmental dynamics and implications for wastewater management in underprivileged societies. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144013/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK144013.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Mbakaya, B.C.; Lee, P.H.; Lee, R.L. Hand hygiene intervention strategies to reduce diarrhea and respiratory infections among schoolchildren in developing countries: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ping, L.I.; Rong-Qing, M.A.; Wang, X.J. Epidemiological investigation on an outbreak of infectious diarrhea in a school of Zhenba County of Shanxi Province. Occup. Health 2009, 25, 35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.X.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, L.X. Intestinal parasite co-infection among pulmonary tuberculosis cases without human immunodeficiency virus infection in a rural county in China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeman, M.C.; Greene, L.E.; Dreibelbis, R. Assessing the impact of a school-based water treatment, hygiene and sanitation programme on pupil absence in Nyanza Province, Kenya: A cluster-randomized trial. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2012, 17, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, L.M.P.P.; Poore, M.R. School toilets: Facilitating hand hygiene? A review of primary school hygiene facilities in a developed country. J. Public Health 2012, 34, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, R.G.; Sharp, D.S.; Hughes, M.C. Environmental influences on helminthiasis and nutritional status among Pacific schoolchildren. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2004, 14, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasper, C.; Le, T.T.; Bartram, J. Water and sanitation in schools: A systematic review of the health and educational outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2772–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lundblad, B.; Hellström, A.L. Perceptions of school toilets as a cause for irregular toilet habits among schoolchildren aged 6 to 16 years. J. Sch. Health 2005, 75, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon, S.L.B.; Hellstrom, A.L. Children’s experiences of school toilets present a risk to their physical and psychological health. Child Care Health Dev. 2003, 29, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Demographics | Number of Subjects (% Subject Population) or Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 9.9 ± 0.3 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 1151 (49.40) |
| Female | 1179 (50.60) |
| Ethnic group | |
| Han people | 841 (36.09 |
| Ethnic minority | 1489 (63.91) |
| Boarding | |
| Yes | 433 (18.58) |
| No | 1897 (81.42) |
| Region | |
| Chongqing municipality | 538 (23.09) |
| Guizhou province | 465 (19.96) |
| Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region | 461 (19.79) |
| Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region | 456 (19.57) |
| Yunnan province | 410 (17.60) |
| Item | Category | Univariate Logistic Regression Analysis | Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Respondents | Number of Students Who Contracted Diarrhea | Diarrhea Rate (%) | χ2 Value | p Value | β Value | SE | Wald χ2 Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | ||
| Basic Inform-ation | Sex | 0.184 | 0.668 | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| Male | 1151 | 376 | 32.67 | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| Female | 1179 | 395 | 33.50 | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| Ethnic group | 48.909 | 0 | |||||||||
| Han people | 841 | 202 | 24.02 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Ethnic minority | 1489 | 569 | 38.21 | 0.040 | 0.150 | 0.071 | 1.04 (0.78, 1.40) | 0.790 | |||
| Boarding | 1.472 | 0.225 | – | – | – | – | – | ||||
| Yes | 433 | 154 | 35.57 | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| No | 1897 | 617 | 32.53 | – | – | – | – | – | |||
| Region | 96.815 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Chongqing municipality | 538 | 88 | 16.36 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Guizhou province | 465 | 156 | 33.55 | 0.357 | 0.187 | 3.627 | 1.43 (0.99, 2.06) | 0.057 | |||
| Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region | 461 | 175 | 37.96 | 0.249 | 0.222 | 1.262 | 1.28 (0.83, 1.98) | 0.261 | |||
| Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region | 456 | 177 | 38.82 | 0.153 | 0.232 | 0.432 | 1.17 (0.74, 1.84) | 0.511 | |||
| Yunnan province | 410 | 175 | 42.68 | 0.717 | 0.217 | 10.887 | 2.05 (1.34, 3.14) | 0.001 * | |||
| Hygiene know-ledge | Drinking untreated water is harmful to health. | 29.504 | 0.000 | ||||||||
| Aware | 1887 | 576 | 30.52 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 443 | 195 | 44.02 | 0.032 | 0.127 | 0.064 | 1.03 (0.81, 1.33) | 0.801 | |||
| Diarrhea can be transmitted through contaminated water. | 0.959 | 0.328 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Aware | 973 | 311 | 31.96 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Unaware | 1357 | 460 | 33.90 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Dirty hands can transmit diseases. | 20.287 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Aware | 2081 | 657 | 31.57 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 249 | 114 | 45.78 | 0.113 | 0.155 | 0.539 | 1.12 (0.83, 1.52) | 0.463 | |||
| The correct way to wash hands. | 19.036 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Aware | 2197 | 704 | 32.04 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 133 | 67 | 50.38 | 0.148 | 0.208 | 0.507 | 1.16 (0.77, 1.74) | 0.476 | |||
| Hand washing can prevent diseases like diarrhea, dysentery, hepatitis A, and roundworm disease. | 13.944 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Aware | 2171 | 697 | 32.11 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 159 | 74 | 46.54 | 0.097 | 0.199 | 0.238 | 1.1 (0.75, 1.63) | 0.626 | |||
| Feces can transmit diseases like roundworm disease, hookworm disease, diarrhea, and dysentery. | 8.060 | 0.005 | |||||||||
| Aware | 1974 | 630 | 31.91 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 356 | 141 | 39.61 | −0.093 | 0.141 | 0.434 | 0.91 (0.69, 1.20) | 0.510 | |||
| Diarrhea can be prevented by washing fruits before eating them raw and not drinking untreated water. | 26.466 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Aware | 1605 | 477 | 29.72 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 725 | 294 | 40.55 | 0.276 | 0.105 | 6.939 | 1.32 (1.07, 1.62) | 0.008 * | |||
| Diarrhea can be prevented by washing hands before meals and after going to the toilet. | 41.238 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Aware | 1876 | 563 | 30.01 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 454 | 208 | 45.81 | 0.432 | 0.119 | 13.096 | 1.54 (1.22, 1.95) | 0 * | |||
| Open defecation may pollute water sources, damage environmental sanitation, and breed mosquitoes and flies. | 8.310 | 0.004 | |||||||||
| Aware | 2241 | 729 | 32.53 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Unaware | 89 | 42 | 47.19 | −0.017 | 0.254 | 0.005 | 0.98 (0.60, 1.62) | 0.946 | |||
| Hygiene practices | I never drink untreated water at school. | 143.404 | 0.000 | ||||||||
| Yes | 1464 | 353 | 24.11 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 866 | 418 | 48.27 | 0.451 | 0.115 | 15.344 | 1.57 (1.25, 1.97) | 0 * | |||
| I never drink untreated water at home. | 131.024 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 1459 | 357 | 24.47 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 871 | 414 | 47.53 | 0.432 | 0.115 | 14.111 | 1.54 (1.23, 1.93) | 0 * | |||
| I wash vegetables and fruits every time before eating them raw. | 47.016 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 2075 | 638 | 30.75 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 255 | 133 | 52.16 | 0.293 | 0.158 | 3.419 | 1.34 (0.98, 1.83) | 0.064 | |||
| I wash hands before every meal. | 56.449 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 1972 | 591 | 29.97 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 358 | 180 | 50.28 | 0.358 | 0.147 | 5.962 | 1.43 (1.07, 1.91) | 0.015 * | |||
| I wash hands after every visit to the toilet at school. | 27.914 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 2067 | 646 | 31.25 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 263 | 125 | 47.53 | 0.061 | 0.167 | 0.135 | 1.06 (0.77, 1.47) | 0.713 | |||
| I wash hands after every visit to the toilet at home. | 34.800 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 2078 | 646 | 31.09 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 252 | 125 | 49.60 | −0.068 | 0.174 | 0.153 | 0.93 (0.66, 1.31) | 0.696 | |||
| I wash hands with running water and soap/hand sanitizer at school. | |||||||||||
| Yes | 1583 | 471 | 29.75 | 24.826 | 0.000 | 1.00 | |||||
| No | 747 | 300 | 40.16 | 0.014 | 0.117 | 0.015 | 1.01 (0.81, 1.28) | 0.903 | |||
| I wash hands with running water and soap/hand sanitizer at home. | 28.771 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 1793 | 542 | 30.23 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 537 | 229 | 42.64 | 0.040 | 0.121 | 0.111 | 1.04 (0.82, 1.32) | 0.739 | |||
| I like health classes. | 24.991 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 2174 | 691 | 31.78 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 156 | 80 | 51.28 | 0.128 | 0.195 | 0.433 | 1.14 (0.78, 1.67) | 0.511 | |||
| My hands are clean. | 24.465 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 1848 | 566 | 30.63 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 482 | 205 | 42.53 | 0.042 | 0.122 | 0.121 | 1.04 (0.82, 1.33) | 0.728 | |||
| I have long fingernails. | 6.786 | 0.009 | |||||||||
| No | 1789 | 567 | 31.69 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Yes | 541 | 204 | 37.71 | 0.117 | 0.118 | 0.985 | 1.12 (0.89, 1.42) | 0.321 | |||
| School sanitation | School has hand washing facilities. | 23.919 | 0.000 | ||||||||
| Yes | 2153 | 683 | 31.72 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 177 | 88 | 49.72 | 0.150 | 0.187 | 0.648 | 1.16 (0.81, 1.68) | 0.421 | |||
| School has drinking water facilities. | 22.259 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 2133 | 676 | 31.69 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 197 | 95 | 48.22 | 0.351 | 0.171 | 4.239 | 1.42 (1.02, 1.99) | 0.040 * | |||
| School toilets are clean. | 34.117 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 1726 | 513 | 29.72 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 604 | 258 | 42.72 | 0.110 | 0.129 | 0.727 | 1.12 (0.87, 1.44) | 0.394 | |||
| I have to queue for toilets. | 1.839 | 0.175 | |||||||||
| No | 1537 | 494 | 32.14 | ||||||||
| Yes | 793 | 277 | 34.93 | ||||||||
| Toilets smell bad. | 94.187 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| No | 969 | 212 | 21.88 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Yes | 1361 | 559 | 41.07 | 0.404 | 0.120 | 11.341 | 1.5 (1.18, 1.89) | 0.001 * | |||
| There are flies in the toilets. | 96.381 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| No | 1101 | 253 | 22.98 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Yes | 1229 | 518 | 42.15 | 0.290 | 0.113 | 6.550 | 1.34 (1.07, 1.67) | 0.010 * | |||
| The toilets are safe. | 14.923 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Yes | 2244 | 726 | 32.35 | 1.00 | |||||||
| No | 86 | 45 | 52.33 | 0.260 | 0.245 | 1.131 | 1.30 (0.8, 2.10) | 0.288 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, Y.-E.; Fu, Y.-Z.; Yao, W. Knowledge, Practice of Personal Hygiene, School Sanitation, and Risk Factors of Contracting Diarrhea among Rural Students from Five Western Provinces in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189505
Cha Y-E, Fu Y-Z, Yao W. Knowledge, Practice of Personal Hygiene, School Sanitation, and Risk Factors of Contracting Diarrhea among Rural Students from Five Western Provinces in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(18):9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189505
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Yu-E, Yuan-Zheng Fu, and Wei Yao. 2021. "Knowledge, Practice of Personal Hygiene, School Sanitation, and Risk Factors of Contracting Diarrhea among Rural Students from Five Western Provinces in China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 18: 9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189505
APA StyleCha, Y.-E., Fu, Y.-Z., & Yao, W. (2021). Knowledge, Practice of Personal Hygiene, School Sanitation, and Risk Factors of Contracting Diarrhea among Rural Students from Five Western Provinces in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(18), 9505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189505





