Spatial Disparity and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination Development of Economy–Environment–Tourism–Traffic: A Case Study in the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Coupling and Coordinated Development of Economy, Environment, Tourism and Traffic
2.2. Influencing Factors on Coupling and Coordinated Development
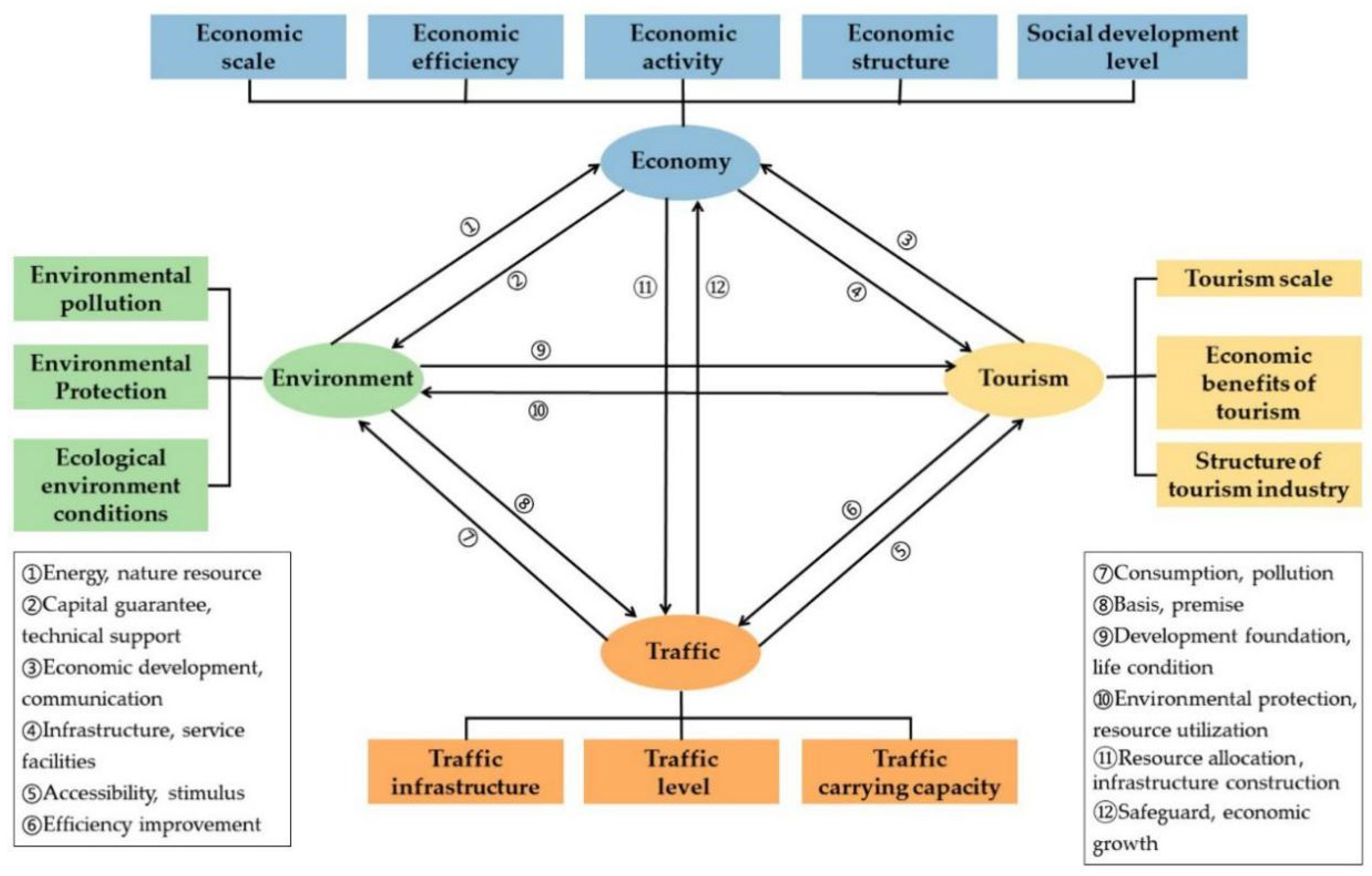
2.3. Analytical Framework of the EETT
3. Materials and Methods
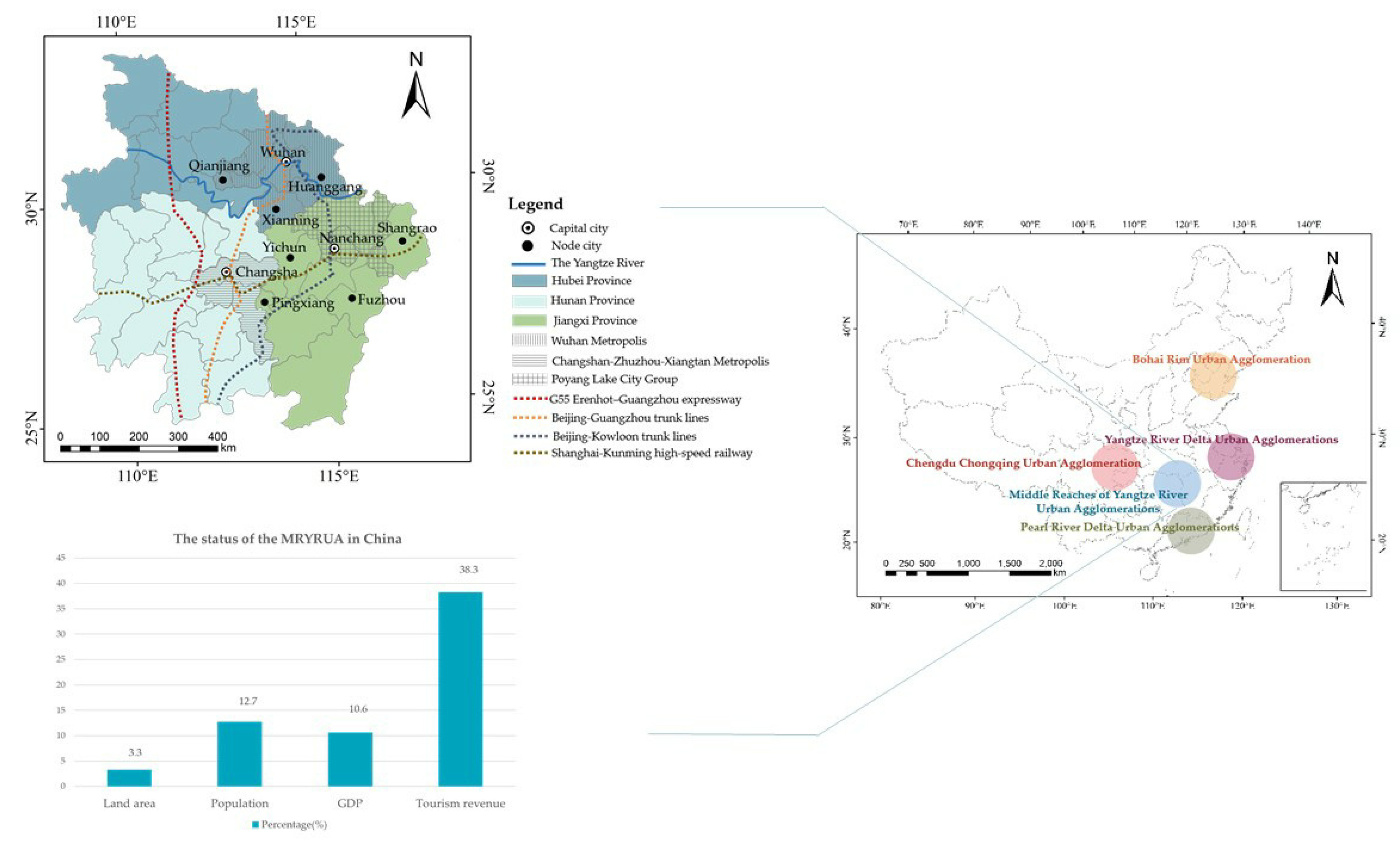
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Sources and Pre-Processing
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Information Entropy Weight Method and Evaluation of Subsystems
3.3.2. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
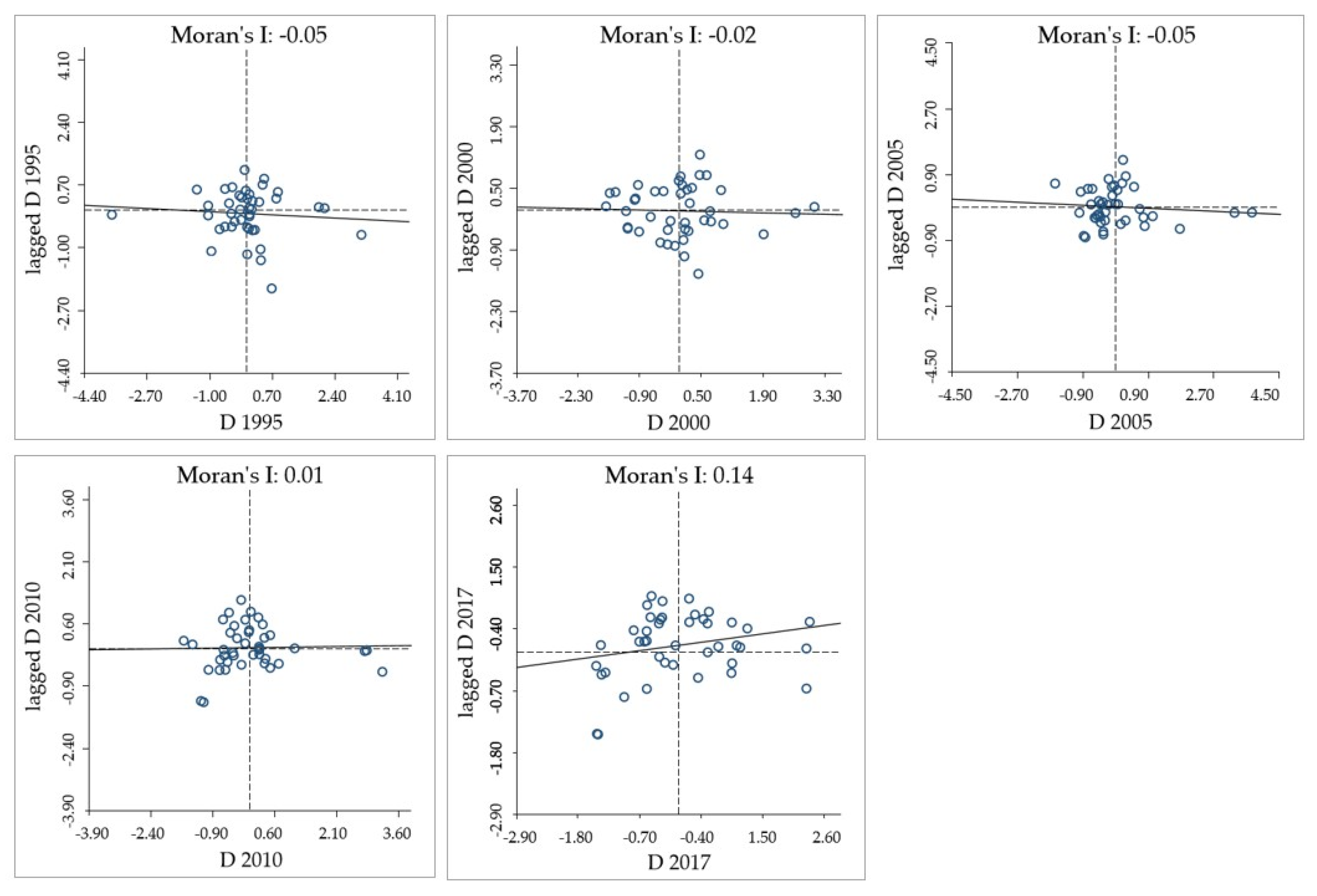
3.3.3. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis Model
3.3.4. Grey Correlation Degree Analysis
3.3.5. Index System
4. Results
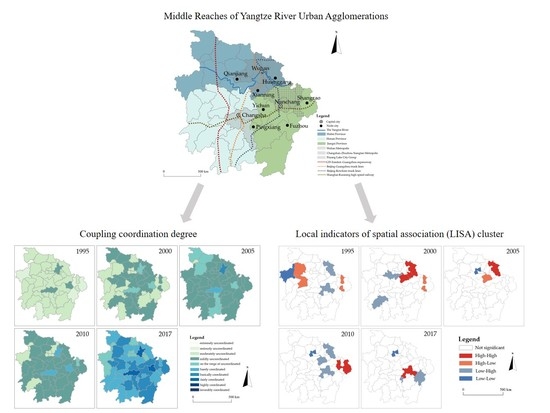
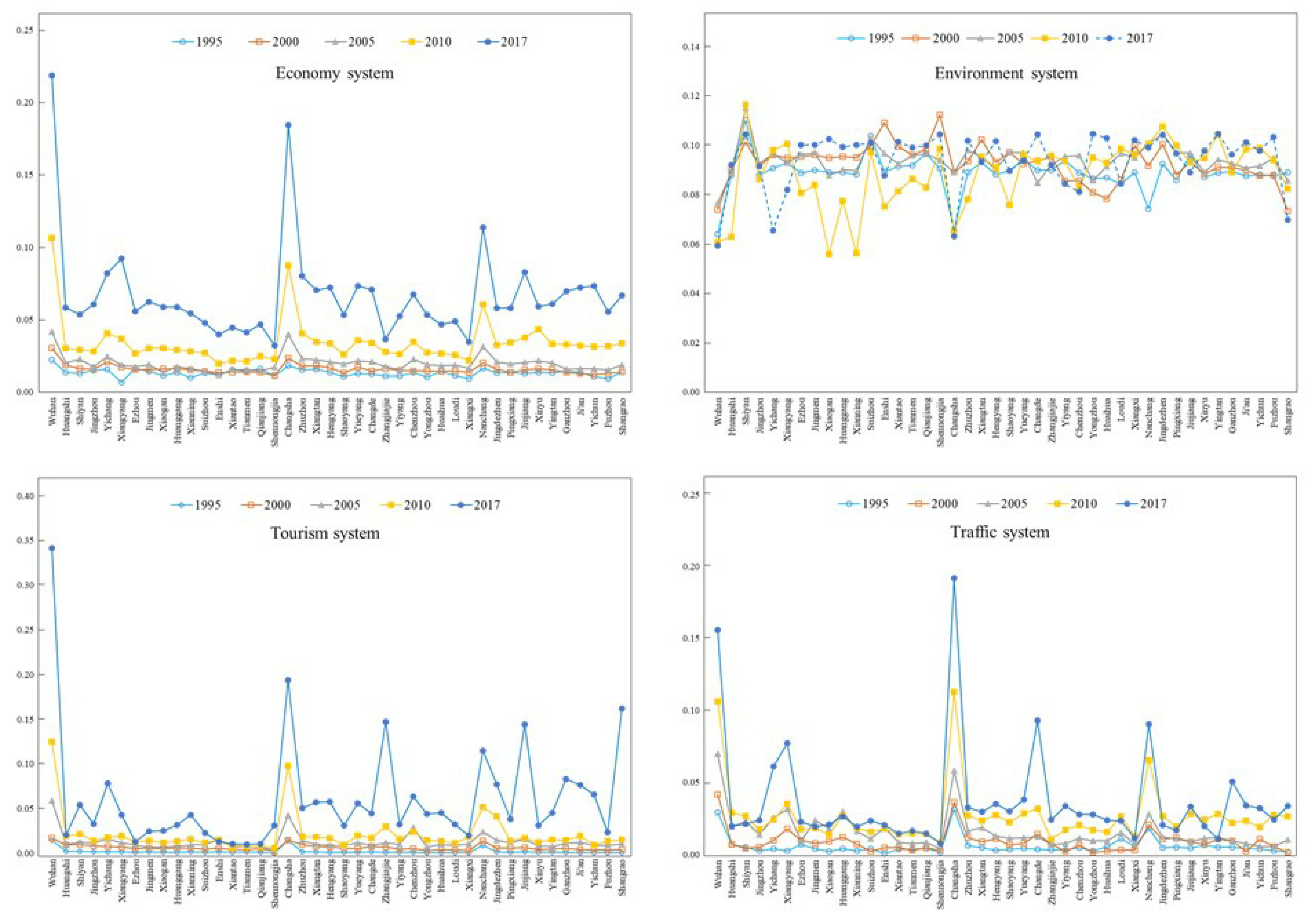
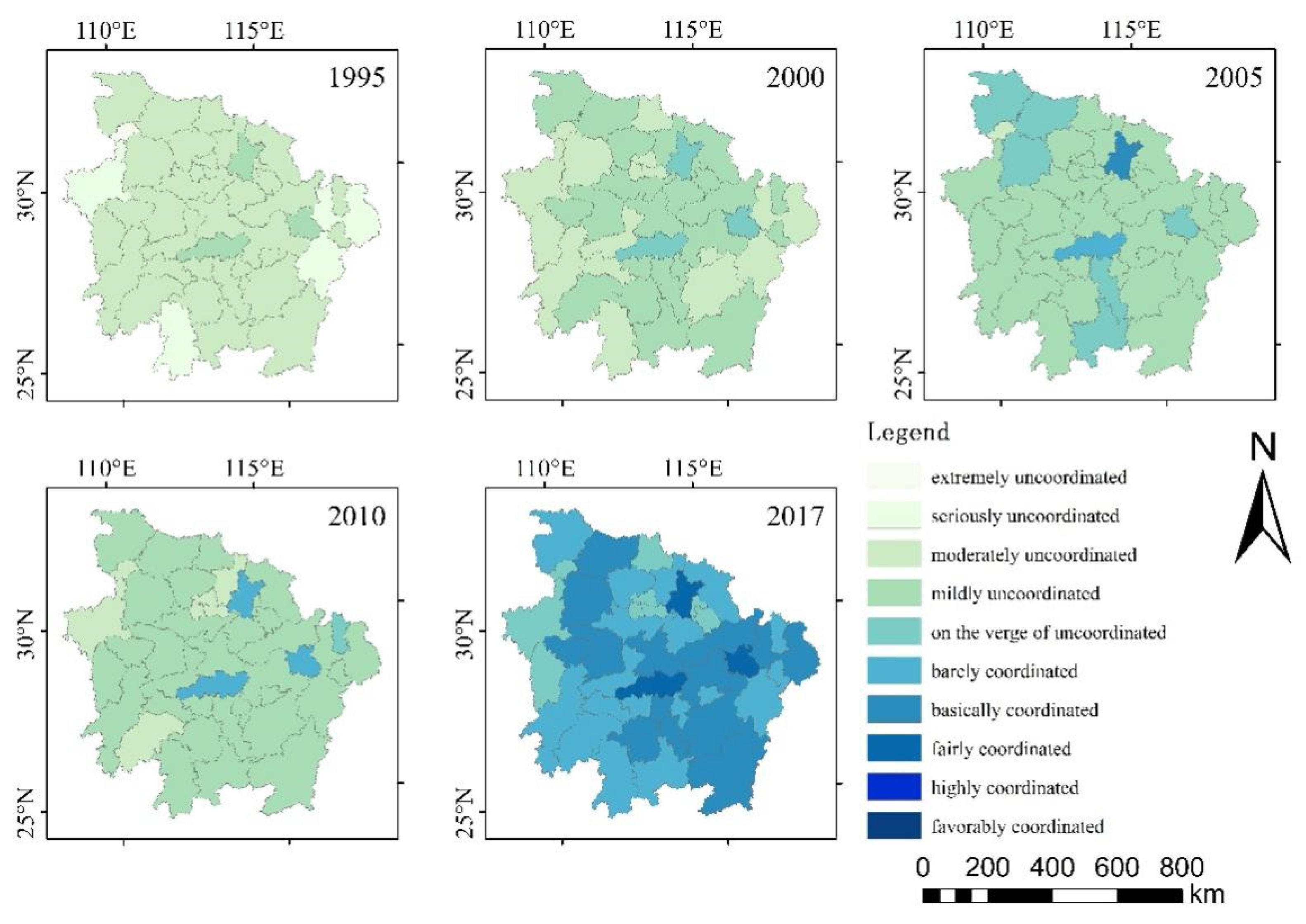
4.1. Coupling Coordination Degree
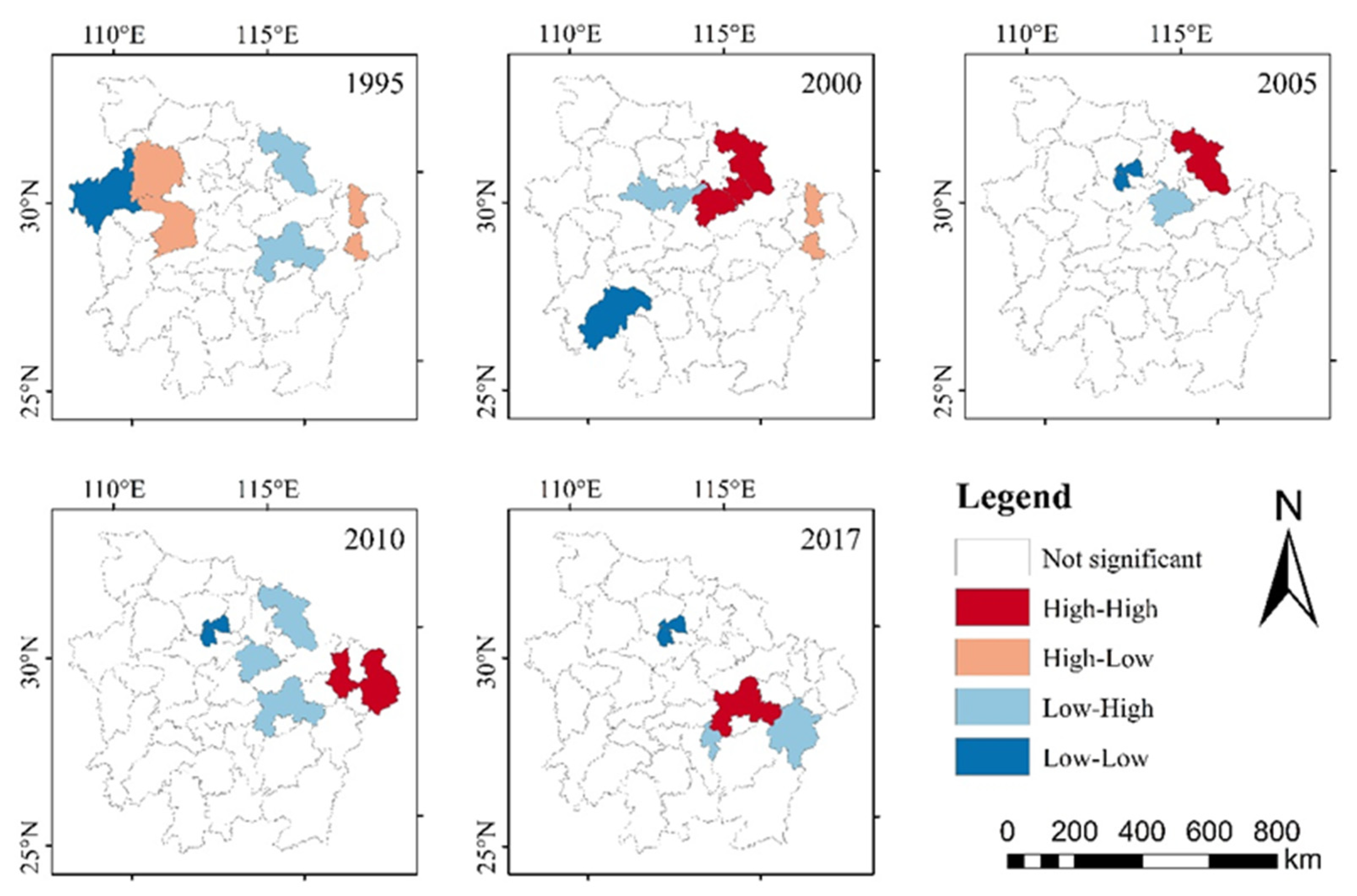
4.2. Spatial Disparity of Coupling Coordination Degree
4.3. Influencing Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. Dynamic Change of Coupling Coordination Degree in MRYRUA
5.2. Spatial Agglomeration of Coupling Coordination Degree
5.3. Identification of Influencing Indicators
5.4. Policy Implications
5.5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The coupling coordination degree of EETT transitioned from the uncoordinated period to the coordinated period; the coupling coordination degree of each city kept increasing, accompanied by a phenomenon where some cities’ degree decreased first and then increased, which was basically consistent with the research results in the previous literature [27,29]. Particularly during the study period, the growth rate of provincial capital cities is greater, which indicates that the concentration of resources, the scale of industry and the radiation of transportation provide an important guarantee for the coordinated development of EETT.
- (2)
- The results of the global–spatial autocorrelation analysis and local–spatial autocorrelation analysis documented that the spatial agglomeration degree in the MRYRUA has shown a positive trend since 2010. “High–High” and “Low–High” agglomeration regions spread from the east to the south; in particular, Qianjiang has consistently been a “Low–Low” agglomeration area, while Yichun changed from “Low–High” to “High–High”. The adjustment of national and regional development strategies plays an important role in the coordinated development of the EETT system, especially the policy adjustment of industrial transformation and upgrading.
- (3)
- Of the natural factors, “vegetation index”, “average temperature” and “annual average precipitation” are the most significant influencing factors. Regarding the human factors, “land used for urban construction as a percentage of urban area”, “natural population growth rate” and “number of operating buses per square meter of road” have a great impact on the coupling coordination degree. The identification results of human factors are consistent with relevant literature [30,39,43], and moreover, this study comprehensively considers the combined effects of natural and human factors, where the influence of natural factors on the coupling coordination degree is higher than that of human factors.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, S.Y.; Gao, M.; Kim, H.; Shah, K.J.; Pei, S.L.; Chiang, P.C. Advances and challenges in sustainable tourism toward a green economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katircioglu, S.T.; Feridun, M.; Kilinc, C. Estimating tourism-induced energy consumption and CO2 emissions: The case of Cyprus. Renew. Sustain. Energy Environ. 2014, 29, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavarda, A.; Dau, G.; Felipe Scavarda, L.; Duarte Azevedo, B.; Luis Korzenowski, A. Social and ecological approaches in urban interfaces: A sharing economy management framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 134407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, B.H.; Habibullah, M.S.; Baharom, A.H.; Saari, M.D. Are Shadow Economy and Tourism Related? International Evidence. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2016, 35, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Chi, Y.; Zou, D.; Fu, C.; Huang, Q.; Ni, M. Energy–environment–economy assessment of waste management systems from a life cycle perspective: Model development and case study. Appl. Energy 2014, 114, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbo, J.M.; Graham, D.J. Quantifying the impacts of air transportation on economic productivity: A quasi-experimental causal analysis. Econ. Transp. 2020, 24, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramati, S.R.; Shahbaz, M.; Alam, M.S. Does tourism degrade environmental quality? A comparative study of Eastern and Western European Union. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drius, M.; Bongiorni, L.; Depellegrin, D.; Menegon, S.; Pugnetti, A.; Stifter, S. Tackling challenges for Mediterranean sustainable coastal tourism: An ecosystem service perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-L.; Wu, K.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lim, M.K.; Bui, T.-D.; Chen, C.-C. Assessing sustainable tourism in Vietnam: A hierarchical structure approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, J. Traditions of sustainability in tourism studies. Ann. Tour. Res. 2006, 33, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Antunes, C.H. A multi-objective multi-sectoral economy–energy–environment model: Application to Portugal. Energy 2011, 36, 2856–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Yin, Q.; Zheng, M.; Gao, P. Transport and regional economic integration: Evidence from the Chang-Zhu-Tan region in China. Transp. Policy 2019, 79, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, J. Land use transitions and the associated impacts on ecosystem services in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China based on the geo-informatic Tupu method. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ye, X.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, Q.; Dong, W. Analyzing requisition–compensation balance of farmland policy in China through telecoupling: A case study in the middle reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations. Land Use Policy 2019, 83, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chi, G.; Li, J. The spatial association of ecosystem services with land use and land cover change at the county level in China, 1995-2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Zhong, M.; Pan, S. Coupling Analysis of Ecosystem Services Value and Economic Development in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: A Case Study in Hunan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Chen, Q.; Lu, F.; Wu, Q.; Wang, W. Spatial-temporal disparities, saving potential and influential factors of industrial land use efficiency: A case study in urban agglomeration in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chi, G.; Li, J. The spatial aspect of ecosystem services balance and its determinants. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Chen, X.; Xue, Y.; Li, R.; Zeng, W. An integrated approach to investigate the relationship of coupling coordination between social economy and water environment on urban scale-A case study of Kunming. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K.; Peters, S.; van Wee, B. Transportation technologies, sharing economy, and teleactivities: Implications for built environment and travel. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 92, 102716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.-O. The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B. The Mediation Effect of Outdoor Recreation Participation on Environmental Attitude-Behavior Correspondence. J. Environ. Educ. 2010, 41, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.; Cai, L.P. Environmental and energy-related challenges to sustainable tourism in the United States and China. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2012, 19, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacitignola, D.; Petrosillo, I.; Cataldi, M.; Zurlini, G. Modelling socio-ecological tourism-based systems for sustainability. Ecol. Model. 2007, 206, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosillo, I.; Zurlini, G.; Grato, E.; Zaccarelli, N. Indicating fragility of socio-ecological tourism-based systems. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, M.A.; Ghadikolaei, A.S.; Govindan, K.; Akbari, V. Analysis of the sharing economy effect on sustainability in the transportation sector using Fuzzy cognitive mapping. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-s.; Loo, B.P.Y.; Vickerman, R. High-speed rail networks, economic integration and regional specialisation in China and Europe. Travel Behav. Soc. 2015, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Cheng, X.; Mu, R.; Zuo, J. Coordinated development of energy, economy and environment subsystems—A case study. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z. An integrated approach to evaluating the coupling coordination between tourism and the environment. Tour. Manag. 2015, 46, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariminia, S.; Ahmad, S.S.; Hashim, R.; Ismail, Z. Environmental Consequences of Antarctic Tourism from a Global Perspective. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 105, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Bao, W.; Liu, Y. Coupling coordination analysis of rural production-living-ecological space in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassanino, M.; Sacco, D.; Zavattaro, L.; Grignani, C. Nutrient balance as a sustainability indicator of different agro-environments in Italy. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Yang, Y.; Tian, G.; Zhuang, Q. Comprehensive evaluation of disassembly performance based on the ultimate cross-efficiency and extension-gray correlation degree. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canh, N.P.; Thanh, S.D. Domestic tourism spending and economic vulnerability. Ann. Tour Res. 2020, 85, 103063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Jiao, S.; Zhang, X.; Xie, F.; Ran, J.; Jin, R.; Xu, S. Seeking sustainable development policies at the municipal level based on the triad of city, economy and environment: Evidence from Hunan province, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, N. The spatial and temporal evolution of coordinated ecological and socioeconomic development in the provinces along the Silk Road Economic Belt in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.M.; Huynh, T.L.D.; Nasir, M.A. Environmental consequences of population, affluence and technological progress for European countries: A Malthusian view. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint Akadiri, S.; Adewale Alola, A.; Olasehinde-Williams, G.; Udom Etokakpan, M. The role of electricity consumption, globalization and economic growth in carbon dioxide emissions and its implications for environmental sustainability targets. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuxi, Z.; Linsheng, Z. Identifying conflicts tendency between nature-based tourism development and ecological protection in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chang, C.-P. Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tour. Manag. 2008, 29, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvan, E.; Dolnicar, S. Measuring environmentally sustainable tourist behaviour. Ann. Tour. Res. 2016, 59, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, F.; Hu, N.; Liang, L. Evaluation of the coordination between eco-environment and socioeconomy under the “Ecological County Strategy” in western China: A case study of Meixian. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyeiwaah, E.; McKercher, B.; Suntikul, W. Identifying core indicators of sustainable tourism: A path forward? Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2017, 24, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Cao, Z.C.; Zhang, S.L.; Liang, S.M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ji, T.B.; Shi, Q. Coordination Investigation of the Economic, Social and Environmental Benefits of Urban Public Transport Infrastructure in 13 Cities, Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.M.; Fang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Z. Tourism, Transportation and Low-Carbon City System Coupling Coordination Degree: A Case Study in Chongqing Municipality, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Weng, G.M.; Li, C.H.; Li, J.P. Coupling Coordination and Influencing Factors among Tourism Carbon Emission, Tourism Economic and Tourism Innovation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepal, R.; Indra al Irsyad, M.; Nepal, S.K. Tourist arrivals, energy consumption and pollutant emissions in a developing economy–implications for sustainable tourism. Tour. Manag. 2019, 72, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervi, L. Travellers’ virtual communities: A success story. Univ. Rev. Cienc. Soc. Hum. 2019, 30, 97–125. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.R.; Shen, J.; Miao, L. Carbon Emissions Trading and Sustainable Development in China: Empirical Analysis Based on the Coupling Coordination Degree Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Ye, G.; Wong, S.-W. Improved coupling analysis on the coordination between socio-economy and carbon emission. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Pinheiro, F.; Brito, M.C. The effects of environmental transport policies on the environment, economy and employment in Portugal. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Song, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Xie, Q. Coupling coordination between carbon emissions and the eco-environment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Li, W.; Pang, M.; Xue, B.; Miao, H. Quantifying the Economy-Environment Interactions in Tourism: Case of Gansu Province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chi, G.; Li, J. Ecosystem Services and Their Driving Forces in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, J.; Chu, Y.; Liang, J. Impacts of Landscape Patterns on Ecosystem Services Value: A Multiscale Buffer Gradient Analysis Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tang, Y.K.; Chen, Y.Z.; Shang, L.W.; Ji, X.M.; Yao, M.C.; Wang, P. The Coupling and Coordinated Development from Urban Land Using Benefits and Urbanization Level: Case Study from Fujian Province (China). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.W. Integrated Evaluation of Coupling Coordination for Land Use Change and Ecological Security: A Case Study in Wuhan City of Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.X.; Lin, K.X.; Ding, Y.; Dong, X.L.; Sun, H.J.; Hu, B.B. Research on the Coupling Coordination Relationships between Urban Function Mixing Degree and Urbanization Development Level Based on Information Entropy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Shi, K.F.; Yang, Q.Y. A Multiscale Evaluation of the Coupling Relationship between Urban Land and Carbon Emissions: A Case Study of Chongqing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Long, R.; Chen, H.; Li, Q. Coupling coordination degree and spatial dynamic evolution of a regional green competitiveness system–A case study from China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Da, B. Examining the coordination between urbanization and eco-environment using coupling and spatial analyses: A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Z.; Lan, X.; Zhang, H.; Fan, M. The Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Dilemmas of Sustainable Urbanization in China: A New Perspective Based on the Concept of Five-in-One. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakizadeh, M. Spatial analysis of total dissolved solids in Dezful Aquifer: Comparison between universal and fixed rank kriging. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 221, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Sahakyan, L.; Zhang, C.; Saghatelyan, A. The application of Local Moran’s I to identify spatial clusters and hot spots of Pb, Mo and Ti in urban soils of Yerevan. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 104, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Peng, B.; Xu, L.; Andrews, A.; Elahi, E. Analysis of regional energy economic efficiency and its influencing factors: A case study of Yangtze river urban agglomeration. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 41, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins-Desbiolles, F. Sustainable tourism: Sustaining tourism or something more? Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2018, 25, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghir, G.M.; Mostéfa, B.; Abbes, S.M.; Zakarya, G.Y. Tourism Spending-Economic Growth Causality in 49 Countries: A Dynamic Panel Data Approach. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 23, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Lu, Z. Study on the interaction and relation of society, economy and environment based on PCA–VAR model: As a case study of the Bohai Rim region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Fernández, J.I.; Cárdenas-García, P.J.; Espinosa-Pulido, J.A. Does environmental sustainability contribute to tourism growth? An analysis at the country level. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-g.; Niu, Y.; Qian, J. Evolution and optimization of China’s urban tourism spatial structure: A high speed rail perspective. Tour. Manag. 2018, 64, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, K.Z. Spatial-Temporal Coupling Analysis of the Coordination between Urbanization and Water Ecosystem in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, V.; Monni, S. Environment, human development and economic growth. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 64, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, S.; Mbarek, M.B.; Atiq-ur-Rehman, M. Long-run causal relationship between economic growth, transport energy consumption and environmental quality in Asian countries: Evidence from heterogeneous panel methods. Energy 2020, 192, 116628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhou, C.; Qin, C. No difference in effect of high-speed rail on regional economic growth based on match effect perspective? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 106, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Range | (0, 0.1) | (0.1, 0.2) | (0.2, 0.3) | (0.3, 0.4) | (0.4, 0.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| category | extremely uncoordinated | seriously uncoordinated | moderately uncoordinated | mildly uncoordinated | on the verge of uncoordinated |
| Range | (0.5, 0.6) | (0.6, 0.7) | (0.7, 0.8) | (0.8, 0.9) | (0.9, 1) |
| category | barely coordinated | basically coordinated | fairly coordinated | favorably coordinated | highly coordinated |
| Subsystem | First-Class Index | Second-Class Index | Direction | Weights | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economy | Economic scale | GDP | + | 0.034 | [45,46,47] |
| GDP per capita | + | 0.021 | [45,46,47] | ||
| Regional fiscal revenue | + | 0.048 | [47,48,49] | ||
| Fixed-asset investment | + | 0.044 | [47,48,50] | ||
| Economic efficiency | Output-to-input ratio | + | 0.021 | [46,47,48,51] | |
| Economic activity | GDP growth rate | + | 0.001 | [45,46,47] | |
| Total retail sales of consumer goods | + | 0.037 | [47,48,51] | ||
| Economic structure | The ratio of the added value of the primary industry to GDP | − | 0.007 | [45,46,47] | |
| The ratio of the added value of the secondary industry to GDP | − | 0.001 | [45,46,47] | ||
| The ratio of the added value of the tertiary industry to GDP | + | 0.001 | [45,46,47] | ||
| Social development level | Per capita disposable income of urban residents | + | 0.010 | [46,47,51] | |
| Per capita disposable income of rural residents | + | 0.015 | [47,48] | ||
| Urban population unemployment rate | − | 0.008 | [48,52] | ||
| Environment | Environmental pollution | Total discharge of industrial wastewater | − | 0.020 | [48,50,53] |
| Total emission by industries | − | 0.038 | [48,50,54] | ||
| Total amount of industrial solid waste | − | 0.028 | [47,49] | ||
| Environmental protection | Urban sewage treatment rate | + | 0.013 | [46,48,50] | |
| Life garbage treatment rate | + | 0.004 | [48,50,51] | ||
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | + | 0.003 | [46,50] | ||
| Ecological environment conditions | Per capita green area | + | 0.023 | [47,48] | |
| Built-up area green coverage rate | + | 0.002 | [47,49,54] | ||
| Tourism | Tourism scale | Number of total tourists | + | 0.046 | [31,45,52] |
| Number of domestic tourists | + | 0.046 | [45,55] | ||
| Number of international tourists | + | 0.061 | [45,52,54] | ||
| Economic benefits of tourism | Total tourism revenue | + | 0.058 | [31,55,56] | |
| Domestic tourism revenue | + | 0.059 | [31,56] | ||
| International tourism revenue | + | 0.071 | [52,54,56] | ||
| Structure of tourism industry | Number of travel agencies | + | 0.016 | [45,55] | |
| Number of star-rated hotels | + | 0.013 | [45,52,56] | ||
| Number of tourist enterprises | + | 0.011 | [52,54] | ||
| Traffic | Traffic infrastructure | Urban per capita road area | + | 0.017 | [18,45] |
| Traffic level | Per capita freight volume | + | 0.010 | [17,18,19] | |
| Per capita passenger volume | + | 0.015 | [17,19,45] | ||
| Traffic carrying capacity | Number of civilian cars | + | 0.034 | [18,19,45] | |
| Number of passenger cars | + | 0.042 | [17,18,45] | ||
| Number of other cars | + | 0.022 | [18,45] | ||
| Take-offs and landings of aircrafts | + | 0.100 | [19,45] |
| Factors | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | f6 | f7 | f8 | f9 | f10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grey correlation degree | 0.82 | 0.53 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.84 | 0.61 | 0.48 |
| Average degree | 0.70 | 0.62 | ||||||||
| Sorting | 2 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 5 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Bi, Y.; Li, J. Spatial Disparity and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination Development of Economy–Environment–Tourism–Traffic: A Case Study in the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157947
Chen Q, Bi Y, Li J. Spatial Disparity and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination Development of Economy–Environment–Tourism–Traffic: A Case Study in the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(15):7947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157947
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qian, Yuzhe Bi, and Jiangfeng Li. 2021. "Spatial Disparity and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination Development of Economy–Environment–Tourism–Traffic: A Case Study in the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 15: 7947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157947
APA StyleChen, Q., Bi, Y., & Li, J. (2021). Spatial Disparity and Influencing Factors of Coupling Coordination Development of Economy–Environment–Tourism–Traffic: A Case Study in the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(15), 7947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157947