Design of a Network Optimization Platform for the Multivehicle Transportation of Hazardous Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Data System of Optimization Platform of the Hazardous Materials Transportation Network
2.1. Basic Data Stratification
2.2. Basic Data Composition
3. Key Elements of the Multidestination, Multiterminal, and Multivehicle Transportation Network Optimization for Hazardous Materials
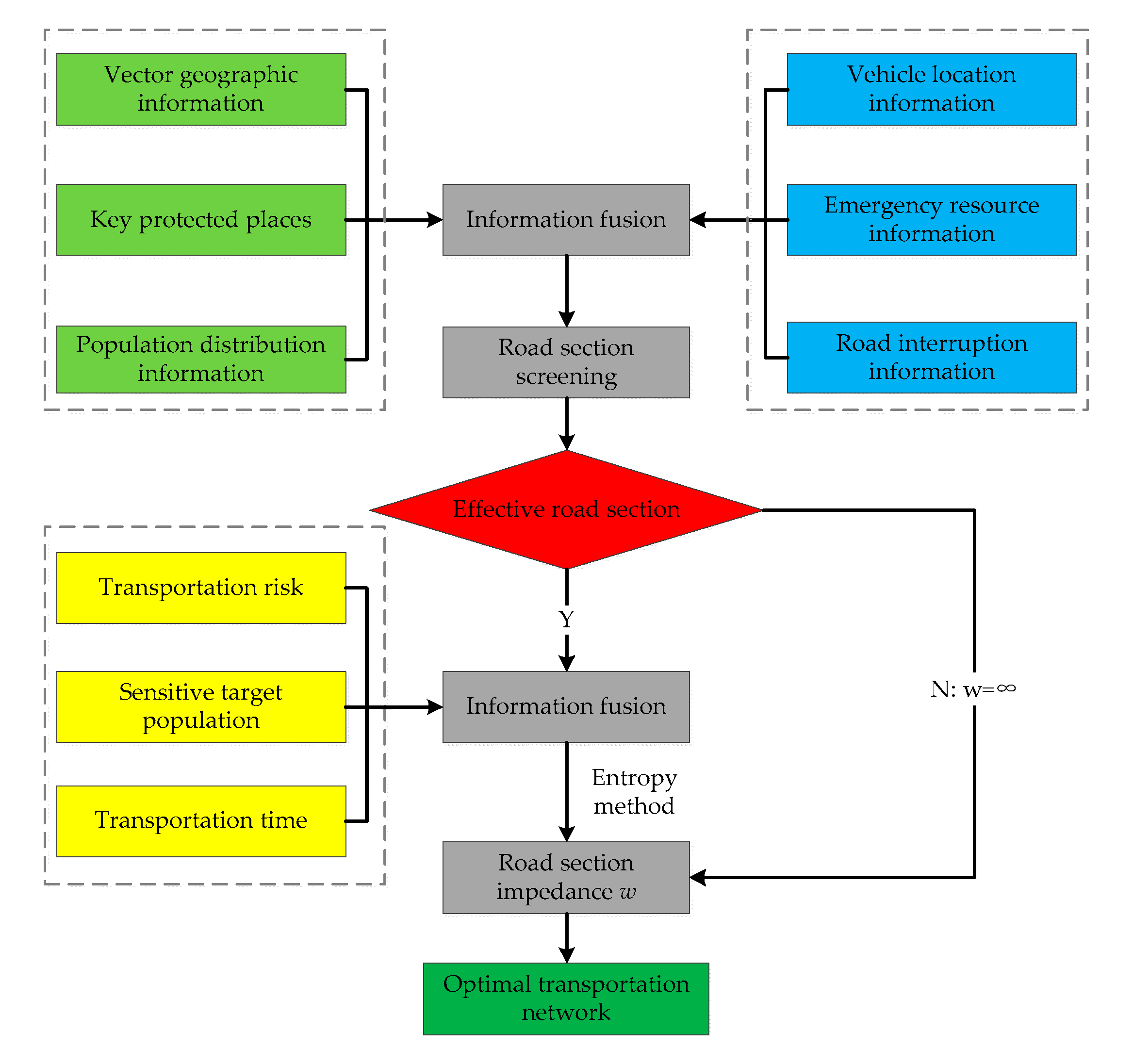
3.1. The Screening of Effective Road Sections
3.2. Key Parameters for Obtaining the Optimal Transport Network Solution
3.3. Optimal Transportation Network Solution Process
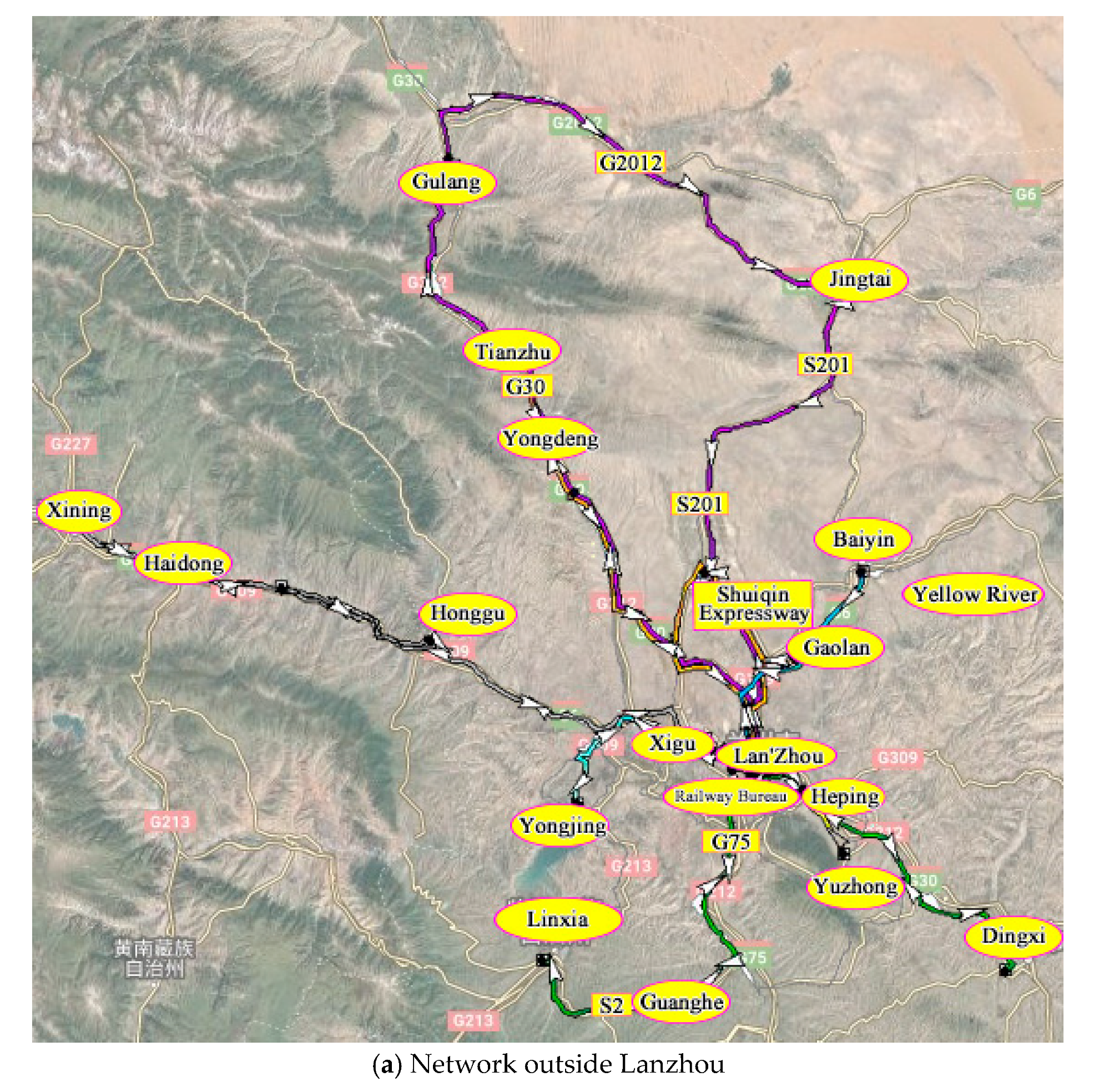
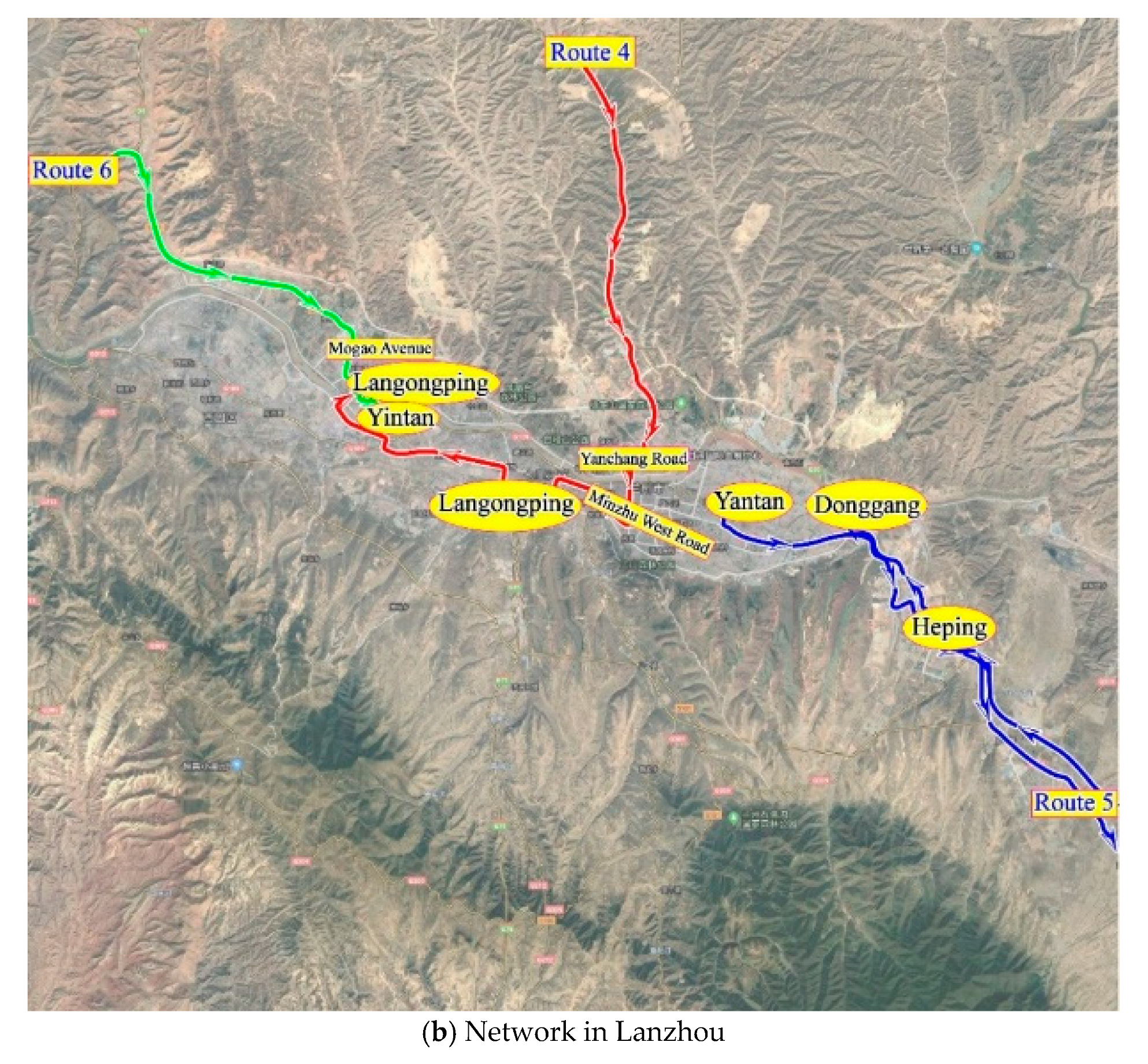
4. Case Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Erkut, E.; Tjandra, S.; Verter, V. Hazardous materials transportation. Handb. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2007, 14, 539–621. [Google Scholar]
- List, G.; Mirchandani, P.; Turnquist, M.; Zografos, K. Modeling and analysis for hazardous materials transportation: Risk analysis, routing/scheduling and facility location. Transp. Sci. 1991, 25, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, C.; Wang, L. Analysis on tank truck accidents involved in road hazardous materials transportation in China. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2014, 15, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Pei, J.; Xu, M.; Huang, X.; Luo, Y. Risk assessment of the areas along the highway due to hazardous material transportation accidents. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Turla, T.; Zhang, Z. Accident-cause-specific risk analysis of rail transport of hazardous materials. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Wang, J.; Yip, T.L.; Gu, Y. An innovative gravity-based approach to assess vulnerability of a Hazmat road transportation network: A case study of Guangzhou, China. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, B.; Lu, F.; Fang, S.; You, Z. Analysis of surface water pollution accidents in China: Characteristics and lessons for risk management. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Dong, S.; Yan, B.; Zhang, M.; Yang, R. An adaptive agent digraph simulation for road traffic safety statue in bridge–tunnel groups. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batta, R.; Chiu, S. Optimal obnoxious paths on a network: Transportation of hazardous materials. Oper. Res. 1988, 36, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkazis, J.; Boffey, T. Optimal location of routes for vehicles transporting hazardous materials. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1995, 86, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zografos, K.; Androutsopoulos, K. A heuristic algorithm for solving hazardous materials distribution problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 152, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zografos, K.; Androutsopoulos, K. A decision support system for integrated hazardous materials routing and emergency response decisions. Transp. Res. Part C: Emerg. Technol. 2008, 16, 684–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Lee, D.; Cheu, R. Multiobjective vehicle routing and scheduling problem with time window constraints in hazardous material transportation. J. Transp. Eng. 2005, 131, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Mazumder, T.; Gupta, A. Pareto frontier analyses based decision making tool for transportation of hazardous waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhananga, R.; Taniguchi, E.; Yamada, T.; Qureshi, A. Bi-objective decision support system for routing and scheduling of hazardous materials. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2014, 48, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Guang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Y. Highway transportation route decision-making of hazardous material in developed transportation network. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2009, 9, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model for hazardous materials transportation routes. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2006, 6, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, B.; Verter, V. Designing a road network for hazardous materials transportation. Transp. Sci. 2004, 38, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, Y.; He, R.; Wu, F.; Qi, B.; Ye, Q. Route optimisation models and algorithms for hazardous materials transportation under different environments. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2013, 5, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C. Network optimisation design of hazmat based on multi-objective genetic algorithm under the uncertain environment. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2018, 12, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hao, W.; He, R.; Moghimi, B. A multiobjective route robust optimization model and algorithm for hazmat transportation. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hao, W.; Pan, F.; Xiang, W. Road screening and distribution route multi-objective robust optimization for hazardous materials based on neural network and genetic algorithm. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderi, A.; Burdett, R. An integrated location and routing approach for transporting hazardous materials in a bi-modal transportation network. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 127, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ramos, F.; Nasini, S.; Guarnaschelli, A. Road network pricing and design for ordinary and hazmat vehicles: Integrated model and specialized local search. Comput. Oper. Res. 2019, 109, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Song, M.; Ma, X. Investigation on the injury severity of drivers in rear-end collisions between cars using a random parameter bivariate ordered probit model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, S. Injury severities of truck drivers in single-and multi-vehicle accidents on rural highways. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2011, 43, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Peng, H.; Ma, X.; Liang, J.; Hao, W.; Pan, X. Examining the safety of trucks under crosswind at bridge-tunnel section: A driving simulator study. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Mao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Dong, S. Risk Assessment in urban large-scale public spaces using Dempster-Shafer theory: An empirical study in Ningbo, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guo, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, M.; Mao, T. Simulation of pedestrian evacuation route choice using social force model in large-scale public space: Comparison of five evacuation strategies. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Mao, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, M. Congestion evaluation of pedestrians in metro stations based on normal-cloud theory. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y. Modeling correlation and heterogeneity in crash rates by collision types using full Bayesian random parameters multivariate Tobit model. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 128, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sayed, T.; Zaki, M.H. Evaluating the safety impacts of powered two wheelers on a shared roadway in China using automated video analysis. J. Transp. Saf. Secur. 2019, 11, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qian, D.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, R. Development of a global positioning system data-based trip-purpose inference method for hazardous materials transportation management. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 24, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Pan, Y.; Xu, J. Fleet Scheduling optimization of hazardous materials transportation: A literature review. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliper Corporation. TransCAD: Transportation Workstation Software Reference Manual Version 2.0. 1990. Available online: https://www.caliper.com/transcad/transcadversions.htm (accessed on 16 September 2019).
- Ma, J.; Pei, Y. Development and application of TransCAD for urban traffic planning. J. Harbin Univ. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2002, 5, 4–10. [Google Scholar]

| Field Name | Data Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | Identify unique facilities |
| NAME | Character | Facility name |
| Longitude | Integer | Longitude coordinates of facility location |
| Latitude | Integer | Latitude coordinates of facility location |
| OPEN TIME | Integer | The earliest time of vehicle delivery |
| CLOSE TIME | Integer | The latest time the vehicle returns |
| NODE_ID | Integer | The node ID nearest to the facility point in the road network |
| Field Name | Data Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | Identify unique customers |
| NAME | Character | Customer name |
| Longitude | Integer | Longitude coordinates of customer location |
| Latitude | Integer | Latitude coordinates of customer location |
| OPEN TIME | Integer | The earliest time the customer can accept the service |
| CLOSE TIME | Integer | The latest time the customer can accept the service |
| FIXED SERVICE TIME | Integer | Fixed service time |
| TIME PER UNIT | Integer | Unit unloading time |
| DEMAND | Integer | Customer demand volume |
| NODE_ID | Integer | The node ID nearest to the customer point in the road network |
| Vehicle Type | A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle capacity (t) | 12 | 16 | 20 | |
| Field name | Data type | Meaning | ||
| Depot ID | Integer | Depot ID | ||
| Capacity | Float | Vehicle load volume | ||
| Type | Integer | Vehicle type | ||
| Number of vehicles | Integer | Total number of vehicles at facility point | ||
| Cost | Float | The fixed cost of each type vehicle | ||
| ID | Relative Longitude | Relative Latitude | Demand Point Name | Open Time | Close Time | Fixed Service Time (min) | Demand (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 111832980 | 10401159 | Mogao Dadao Intersection | 13:00 | 18:00 | 20 | 1.8 |
| 2 | 111850054 | 10373911 | Yintan | 14:00 | 19:00 | 20 | 2.4 |
| 3 | 112017194 | 10337563 | Yantan | 8:00 | 12:00 | 30 | 3.5 |
| 4 | 111973124 | 10297599 | Lanzhou Railway Bureau | 8:00 | 16:00 | 30 | 3.2 |
| 5 | 111967266 | 10310053 | Minzhu West Rd. Intersection | 10:00 | 14:00 | 20 | 3.0 |
| 6 | 112015917 | 10305978 | Donggang | 10:00 | 18:00 | 30 | 3.3 |
| 7 | 111910421 | 10325543 | Langongping | 14:00 | 18:00 | 20 | 2.0 |
| 8 | 111897059 | 10366829 | Anning District | 10:00 | 18:00 | 20 | 2.3 |
| 9 | 111970885 | 10339850 | Yanchang Rd. Intersection | 11:00 | 15:00 | 20 | 2.1 |
| 10 | 111774002 | 10386268 | Xigu District | 8:00 | 12:00 | 30 | 3.5 |
| 11 | 112085409 | 10626368 | Gaolan County | 10:00 | 16:00 | 20 | 3.5 |
| 12 | 111827008 | 10864803 | Lanzhou New District | 8:00 | 14:00 | 20 | 4.2 |
| 13 | 112279239 | 10868423 | Baiyin | 8:00 | 18:00 | 30 | 6.6 |
| 14 | 112085409 | 10256862 | Heping Village | 10:00 | 15:00 | 20 | 2.4 |
| 15 | 112227743 | 10077823 | Yuzhong County | 14:00 | 18:00 | 20 | 3.1 |
| 16 | 112686557 | 9754533 | Dingxi | 8:00 | 18:00 | 30 | 6.4 |
| 17 | 111373082 | 9782756 | Linxia | 10:00 | 18:00 | 30 | 4.5 |
| 18 | 111693257 | 9665655 | Guanghe County | 13:00 | 18:00 | 20 | 3.0 |
| 19 | 111470477 | 10219942 | Yongjing County | 10:00 | 16:00 | 20 | 3.2 |
| 20 | 111051917 | 10670978 | Honggu District | 10:00 | 18:00 | 20 | 3.1 |
| 21 | 110627221 | 10825869 | Haidong | 10:00 | 18:00 | 30 | 4.0 |
| 22 | 110019508 | 11005135 | Xi’ning | 8:00 | 21:00 | 30 | 6.2 |
| 23 | 111458170 | 11081151 | Yongdeng County | 8:00 | 14:00 | 20 | 3.5 |
| 24 | 111332813 | 11400164 | Tianzhu County | 13:00 | 17:00 | 20 | 2.7 |
| 25 | 111117539 | 12000757 | Gulang County | 10:00 | 16:00 | 20 | 3.3 |
| 26 | 112233577 | 11655669 | Jingtai County | 10:00 | 16:00 | 20 | 3.0 |
| Distribution Center | Vehicle Type | Route | Loading/Capacity | Customer Name | Arrival−Departure Time | Delivery Volume (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | A | 1 | 9.8/12.0 | F1 | 6:34 AM | |
| Yongdeng County | 8:00 am−10:05 am | 3.5 | ||||
| Gulang County | 11:32 am−1:31 pm | 3.3 | ||||
| Jingtai County | 3:29 pm−5:19 pm | 3 | ||||
| F1 | 8:36 PM | |||||
| C | 2 | 17.1/20.0 | F1 | 6:33 AM | ||
| Dingxi | 8:00 am−10:38 am | 6.4 | ||||
| Railway Bureau of Lanzhou | 12:08 pm−1:42 pm | 3.2 | ||||
| Guanghe County | 2:58 pm−4:48 pm | 3 | ||||
| Linxia | 5:27 pm−7:27 pm | 4.5 | ||||
| F1 | 9:33 PM | |||||
| A | 3 | 10.4/12.0 | F1 | 9:17 AM | ||
| Gaolan County | 10:00 am−12:05 pm | 3.5 | ||||
| Lanzhou New District | 12:47 pm−3:13 pm | 4.2 | ||||
| Tianzhu County | 4:51 pm−6:32 pm | 2.7 | ||||
| F1 | 8:26 PM | |||||
| B | 4 | 16.0/16.0 | F1 | 6:55 AM | ||
| Baiyin | 8:00 am−10:42 am | 6.6 | ||||
| Yanchang Road | 11:42 am−1:05 pm | 2.1 | ||||
| Minzhu West Road | 1:12 pm−3:02 pm | 3 | ||||
| Langongping | 3:13 pm−4:33 pm | 2 | ||||
| Anning | 4:44 pm−6:13 pm | 2.3 | ||||
| F1 | 6:38 PM | |||||
| B | 5 | 12.3/16.0 | F1 | 10:02 AM | ||
| Yantan | 10:05 am−11:45 am | 3.5 | ||||
| Heping Town | 12:01 pm−1:33 pm | 2.4 | ||||
| Yuzhong County | 2:00 pm−3:53 pm | 3.1 | ||||
| Donggang | 4:36 pm−6:12 pm | 3.3 | ||||
| F1 | 6:21 PM | |||||
| F2 | C | 6 | 17.5/20.0 | F2 | 5:11 AM | |
| Xining | 8:00 am−10:34 am | 6.2 | ||||
| Haidong | 11:28 am−1:18 pm | 4 | ||||
| Honggu District | 2:16 pm−4:09 pm | 3.1 | ||||
| Mogao Avenue | 5:30 pm−6:44 pm | 1.8 | ||||
| Yintan | 6:51 pm−8:23 pm | 2.4 | ||||
| F2 | 8:39 PM | |||||
| A | 7 | 6.7/12.0 | F2 | 8:54 AM | ||
| Yongjing County | 10:00 am−11:56 am | 3.2 | ||||
| Xigu | 12:54 pm−2:34 pm | 3.5 | ||||
| F2 | 2:41 PM |
| Distribution Center | Vehicle Type | Route | Loading/Capacity | Customer Name | Arrival–Departure Time | Delivery Volume (t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | B | 1 | 12.7/16.0 | F1 | 7:46 am | |
| Lanzhou Railway Bureau | 8:00 am−9:34 am | 3.2 | ||||
| Linxia | 11:26 am−1:26 pm | 4.5 | ||||
| Guanghe County | 2:05 pm−3:55 pm | 3 | ||||
| Langongping | 5:00 pm−6:20 pm | 2 | ||||
| F1 | 6:41 pm | |||||
| C | 2 | 17.3/20.0 | F1 | 6:34 am | ||
| Dingxi | 8:00 am−10:38 am | 6.4 | ||||
| Heping Village | 11:47 am−1:19 pm | 2.4 | ||||
| Yanchang Rd. Intersection | 1:37 pm−3:00 pm | 2.1 | ||||
| Donggang | 3:11 pm−4:47 pm | 3.3 | ||||
| Yuzhong County | 5:28 pm−7:21 pm | 3.1 | ||||
| F1 | 8:03 pm | |||||
| B | 3 | 13.1/16.0 | F1 | 6:55 am | ||
| Baiyin | 8:00 am−10:42 am | 6.6 | ||||
| Gaolan County | 11:13 am−1:18 pm | 3.5 | ||||
| Minzhu West Rd. Intersection | 2:00 pm−3:50 pm | 3 | ||||
| F1 | 4:02 pm | |||||
| A | 4 | 7.7/12.0 | F1 | 7:00 am | ||
| Lanzhou New District | 8:00 am−10:26 am | 4.2 | ||||
| Yantan | 11:23 am−1:03 pm | 3.5 | ||||
| F1 | 1:05 pm | |||||
| F2 | A | 5 | 9.0/12.0 | F2 | 6:43 am | |
| Jingtai County | 10:00 am−11:50 am | 3 | ||||
| Gulang County | 1:48 pm−3:47 pm | 3.3 | ||||
| Tianzhu County | 4:51 pm−6:32 pm | 2.7 | ||||
| F2 | 8:18 pm | |||||
| C | 6 | 17.5/20.0 | F2 | 5:15 am | ||
| Xi’ning | 8:00 am−10:34 am | 6.2 | ||||
| Haidong | 11:26 am−1:16 pm | 4 | ||||
| Honggu | 2:04 pm−3:57 pm | 3.1 | ||||
| Mogao Avenue | 5:19 pm−6:33 pm | 1.8 | ||||
| Yintan | 6:39 pm−8:11 pm | 2.4 | ||||
| F2 | 8:26 pm | |||||
| B | 7 | 12.5/16.0 | F2 | 7:16 am | ||
| Xigu | 7:22 am−9:02 am | 3.5 | ||||
| Yongjing County | 10:00 am−11:56 am | 3.2 | ||||
| Yongdeng County | 1:40 pm−3:45 pm | 3.5 | ||||
| An’ning | 5:06 pm−6:35 pm | 2.3 | ||||
| F2 | 6:54 pm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, S.; Zhou, J.; Ma, C. Design of a Network Optimization Platform for the Multivehicle Transportation of Hazardous Materials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031104
Dong S, Zhou J, Ma C. Design of a Network Optimization Platform for the Multivehicle Transportation of Hazardous Materials. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031104
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Sheng, Jibiao Zhou, and Changxi Ma. 2020. "Design of a Network Optimization Platform for the Multivehicle Transportation of Hazardous Materials" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031104
APA StyleDong, S., Zhou, J., & Ma, C. (2020). Design of a Network Optimization Platform for the Multivehicle Transportation of Hazardous Materials. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031104





