Involving Parents to Help Improve Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviours Through a School-Based Intervention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Challenge Me Intervention
2.2.1. Intervention Development
2.2.2. Implementation
2.3. Study Participants
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Performance of Challenges
2.4.2. Child Characteristics
2.4.3. Family Characteristics
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Child and Family Characteristics
3.2. Performance of Challenges
3.3. Associations between Child and Family Characteristics and Challenges Performed
4. Discussion
Strenghts and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
Appendix A
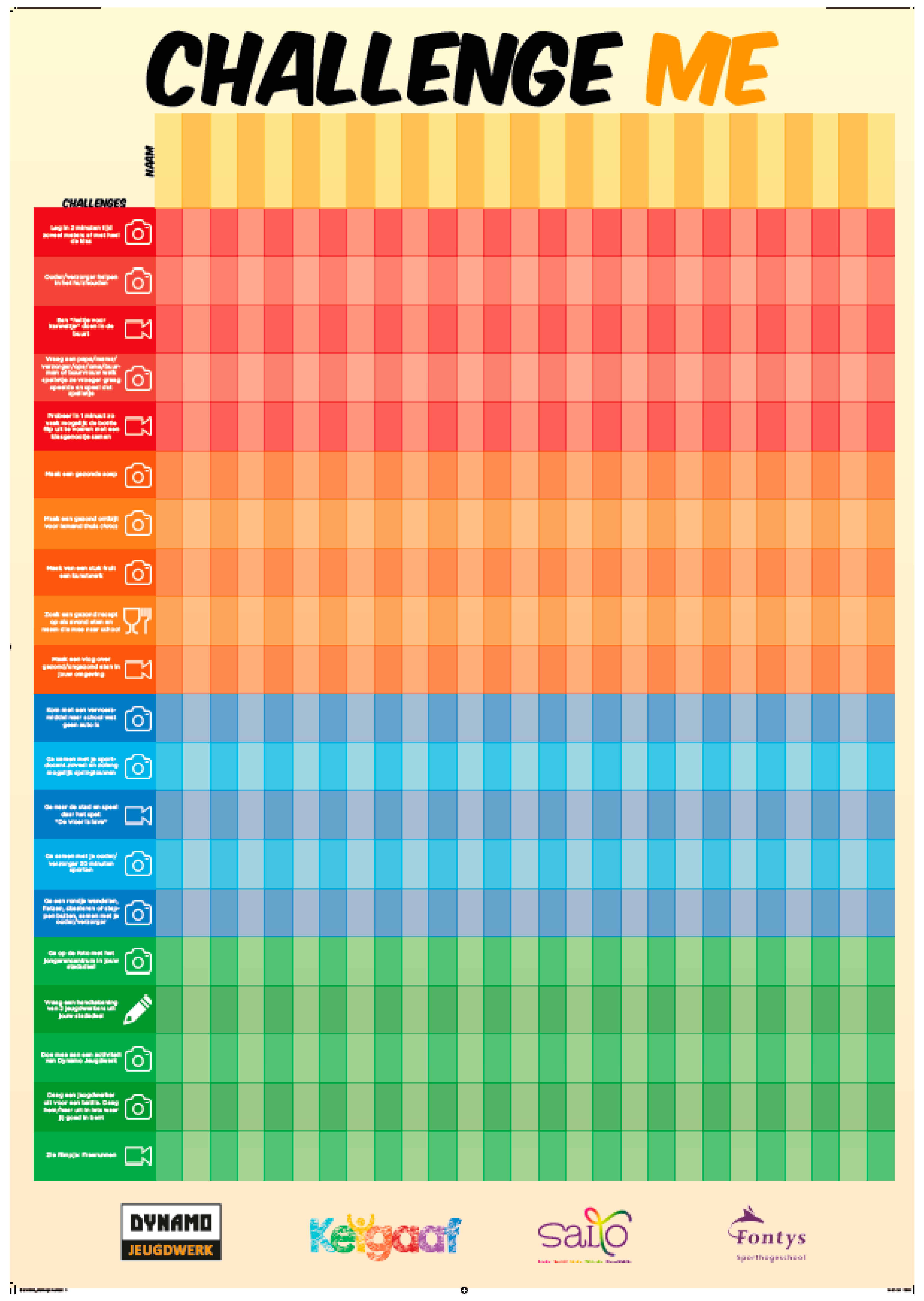
Appendix B
| Category | Challenge | N | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA Child only | Run as far as possible with your entire class, in 2 min. | 171 | 75.7 |
| Try to perform as many bottle flips as possible in 1 min. | 150 | 66.4 | |
| Jump rope as long and often as you can, together with your PE teacher. | 125 | 55.3 | |
| Go to the town-/city centre and play a game of ‘the floor is lava’. | 99 | 43.8 | |
| Participate in an activity of your local youth organisation. | 37 | 16.4 | |
| Challenge a local youth worker for a battle. Challenge him/her in something you are good at. | 69 | 30.5 | |
| Watch instruction video: Free Running | 133 | 58.8 | |
| PA Parental Involvement | Help your parent/guardian with the housekeeping. | 118 | 52.5 |
| Ask your dad/mom/guardian/grandpa/grandma/neighbour what game they liked to play when they were young, and play that game. | 49 | 21.7 | |
| Go exercise for 30 min together with your parent(s)/guardian(s). | 39 | 17.3 | |
| Go walking, rollerblading, or stepping, together with your parent(s)/guardian(s) | 61 | 27.0 | |
| Do a ‘bob for a job’ in your neighbourhood. | 27 | 11.9 | |
| Come to school using a means of transport other than a car. | 176 | 77.9 | |
| Nutrition child only | Find a healthy dinner recipe and bring this with you to school. | 56 | 24.8 |
| Make a vlog about healthy/unhealthy food in your surroundings. | 13 | 5.8 | |
| Nutrition Parental Involvement | Cook a healthy soup. | 69 | 30.5 |
| Make a healthy breakfast for someone in your household. | 54 | 23.9 | |
| Make a work of art out of a piece of fruit. | 78 | 34.5 |
References
- WHO Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Wang, Y.; Lim, H. The global childhood obesity epidemic and the association between socio-economic status and childhood obesity. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2012, 24, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, R.; Bonell, C.; Jones, H.; Campbell, R. Obesity prevention and the Health promoting Schools framework: Essential components and barriers to success. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Netherlands Leefstijl en (Preventief) Gezondheidsonderzoek; Persoonskenmerken. Available online: https://opendata.cbs.nl/statline/#/CBS/nl/dataset/83021NED/table?ts=1592403956183 (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Brown, T.; Moore, T.H.; Hooper, L.; Gao, Y.; Zayegh, A.; Ijaz, S.; Elwenspoek, M.; Foxen, S.C.; Magee, L.; O’Malley, C.; et al. Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, Cd001871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Childhood Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/childhood/en/ (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Black, A.P.; D’Onise, K.; McDermott, R.; Vally, H.; O’Dea, K. How effective are family-based and institutional nutrition interventions in improving children’s diet and health? A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Velde, S.J.; Singh, A.; Chinapaw, M.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Jan, N.; Kovacs, E.; Bere, E.; Vik, F.N.; Bringolf-Isler, B.; Manios, Y.; et al. Energy balance related behaviour: Personal, home- and friend-related factors among schoolchildren in Europe studied in the ENERGY-project. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, S.E. Expert Committee Recommendations Regarding the Prevention, Assessment, and Treatment of Child and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity: Summary Report. Pediatrics 2007, 120 (Suppl. 4), S164–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Adolescent Obesity and Related Behaviours: Trends and Inequalities in the WHO European Region, 2002–2014. 2017. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/339211/WHO_ObesityReport_2017_v3.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Brug, J.; van Stralen, M.M.; Te Velde, S.J.; Chinapaw, M.J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Lien, N.; Bere, E.; Maskini, V.; Singh, A.S.; Maes, L.; et al. Differences in weight status and energy-balance related behaviors among schoolchildren across Europe: The ENERGY-project. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Population-Based Approaches to Childhood Obesity Prevention; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Verjans-Janssen, S.R.B.; van de Kolk, I.; Van Kann, D.H.H.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Gerards, S.M.P.L. Effectiveness of school-based physical activity and nutrition interventions with direct parental involvement on children’s BMI and energy balance-related behaviors—A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, D.L.; O’Connell, M.; Njike, V.Y.; Yeh, M.C.; Nawaz, H. Strategies for the prevention and control of obesity in the school setting: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2008, 32, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleich, S.N.; Vercammen, K.A.; Zatz, L.Y.; Frelier, J.M.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Peeters, A. Interventions to prevent global childhood overweight and obesity: A systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.K.; Collins, C.; May, C.; Brain, K.; Wong See, D.; Burrows, T. Effectiveness of family-based weight management interventions for children with overweight and obesity: An umbrella review. JBI Database Syst. Rev. Implement. Rep. 2019, 17, 1341–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrie, G.A.; Brindal, E.; Corsini, N.; Gardner, C.; Baird, D.; Golley, R.K. Combined home and school obesity prevention interventions for children: What behavior change strategies and intervention characteristics are associated with effectiveness? Health Educ. Behav. 2012, 39, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golley, R.K.; Hendrie, G.A.; Slater, A.; Corsini, N. Interventions that involve parents to improve children’s weight-related nutrition intake and activity patterns—What nutrition and activity targets and behaviour change techniques are associated with intervention effectiveness? Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hingle, M.D.; O’Connor, T.M.; Dave, J.M.; Baranowski, T. Parental involvement in interventions to improve child dietary intake: A systematic review. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jull, A.; Chen, R. Parent-only vs. parent-child (family-focused) approaches for weight loss in obese and overweight children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2013, 14, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlechter, C.R.; Rosenkranz, R.R.; Guagliano, J.M.; Dzewaltowski, D.A. A systematic review of children’s dietary interventions with parents as change agents: Application of the RE-AIM framework. Prev. Med. 2016, 91, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.L.; Luepter, R.V.; Murray, D.M.; Kurth, C.; Mullis, R.; Crockett, S.; Jacobs, D.R.J. Parent Involvement with Children’s Health Promotion: The Minnesota Home Team. Am. J. Public Health 1988, 78, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lippevelde, W.; Verloigne, M.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Brug, J.; Bjelland, M.; Lien, N.; Maes, L. Does parental involvement make a difference in school-based nutrition and physical activity interventions? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Public Health 2012, 57, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axford, N.; Lehtonen, M.; Kaoukji, D.; Tobin, K.; Berry, V. Engaging parents in parenting programs: Lessons from research and practice. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2012, 34, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostbye, T.; Krause, K.M.; Stroo, M.; Lovelady, C.A.; Evenson, K.R.; Peterson, B.L.; Bastian, L.A.; Swamy, G.K.; West, D.G.; Brouwer, R.J.; et al. Parent-focused change to prevent obesity in preschoolers: Results from the KAN-DO study. Prev. Med. 2012, 55, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raat, H.; Wijtzes, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Moll, H.A.; Hofman, A.; Mackenbach, J.P. The health impact of social disadvantage in early childhood; the Generation R study. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rossem, L.; Hafkamp-de Groen, E.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Mackenbach, J.P.; Raat, H. The role of early life factors in the development of ethnic differences in growth and overweight in preschool children: A prospective birth cohort. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodenburg, G.; Oenema, A.; Pasma, M.; Kremers, S.P.J.; van de Mheen, D. Clustering of food and activity preferences in primary school children. Appetite 2013, 60, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niermann, C.; Krapf, F.; Renner, B.; Reiner, M.; Woll, A. Family health climate scale (FHC-scale): Development and validation. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, T.S.; Horn, J.L. Family Influences on Children’s Sport and Physical Activity Participation, Behavior, and Psychosocial Responses. In Handbook of Sport Psychology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 685–711. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ansem, W.J.; van Lenthe, F.J.; Schrijvers, C.T.; Rodenburg, G.; van de Mheen, D. Socio-economic inequalities in children’s snack consumption and sugar-sweetened beverage consumption: The contribution of home environmental factors. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijtzes, A.I.; Jansen, W.; Bouthoorn, S.H.; Pot, N.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Raat, H. Social inequalities in young children’s sports participation and outdoor play. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijtzes, A.I.; Jansen, W.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; van Lenthe, F.J.; Raat, H. Social Inequalities in Young Children’s Meal Skipping Behaviors: The Generation R Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verjans-Janssen, S.R.B.; Van Kann, D.H.H.; Gerards, S.M.P.L.; Vos, S.B.; Jansen, M.W.J.; Kremers, S.P.J. Study protocol of the quasi-experimental evaluation of “KEIGAAF”: A context-based physical activity and nutrition intervention for primary school children. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sociaal Cultureel Planbureau Statusontwikkeling van Wijken in Nederland 1998–2010. Available online: https://www.scp.nl/Publicaties/Alle_publicaties/Publicaties_2012/Statusontwikkeling_van_wijken_in_Nederland_1998_2010 (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- Central Committee on Research involving Human Subjects Consent. Available online: https://english.ccmo.nl/investigators/types-of-research/research-with-subjects-under-the-age-of-16-years/consent (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Huntington, S.P. The Clash of Civilizations and the Remaking of World Order; Simon & Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Voedingscentrum Vruchtensap. Available online: https://www.voedingscentrum.nl/encyclopedie/vruchtensap.aspx?query=fruitsap (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Schonbeck, Y.; Talma, H.; van Dommelen, P.; Bakker, B.; Buitendijk, S.E.; Hirasing, R.A.; van Buuren, S. Increase in prevalence of overweight in Dutch children and adolescents: A comparison of nationwide growth studies in 1980, 1997 and 2009. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics, International Standard Classification of Education: ISCED 2011; UIS: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2012; p. 85.
- Gerards, S.M.; Niermann, C.; Gevers, D.W.; Eussen, N.; Kremers, S.P. Context matters! The relationship between mother-reported family nutrition climate, general parenting, food parenting practices and children’s BMI. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Martin, A.; Janssen, X.; Wilson, M.G.; Gibson, A.M.; Hughes, A.; Reilly, J.J. Longitudinal changes in moderate-to-vigorous-intensity physical activity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.A.; Parkinson, K.N.; Adamson, A.J.; Pearce, M.S.; Reilly, J.K.; Hughes, A.R.; Janssen, X.; Basterfield, L.; Reilly, J.J. Timing of the decline in physical activity in childhood and adolescence: Gateshead Millennium Cohort Study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labree, W.; Lotters, F.; van de Mheen, D.; Rutten, F.; Rivera Chavarria, A.; Neve, M.; Rodenburg, G.; Machielsen, H.; Koopmans, G.; Foets, M. Physical activity differences between children from migrant and native origin. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, C.B.; McMurray, R.G.; Harrell, J.S.; Deng, S. Changes in common activities of 3rd through 10th graders: The CHIC study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVeigh, J.A.; Norris, S.A.; de Wet, T. The relationship between socio-economic status and physical activity patterns in South African children. Acta Paediatr. 2004, 93, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, L.A.; Etelson, D.; Brand, D.A. Parents’ perceptions of neighborhood safety and children’s physical activity. Prev. Med. 2006, 43, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.S.; Zhou, C.; Sallis, J.F.; Cain, K.L.; Frank, L.D.; Saelens, B.E. Home environment relationships with children’s physical activity, sedentary time, and screen time by socioeconomic status. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, J.F.; Prochaska, J.J.; Taylor, W.C. A review of correlates of physical activity of children and adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddoch, C.J.; Bo Andersen, L.; Wedderkopp, N.; Harro, M.; Klasson-Heggebo, L.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cooper, A.R.; Ekelund, U. Physical activity levels and patterns of 9- and 15-yr-old European children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansdottir, G.; Vilhjalmsson, R. Sociodemographic differences in patterns of sedentary and physically active behavior in older children and adolescents. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resaland, G.K.; Aadland, E.; Andersen, J.R.; Bartholomew, J.B.; Anderssen, S.A.; Moe, V.F. Physical activity preferences of 10-year-old children and identified activities with positive and negative associations to cardiorespiratory fitness. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willeboordse, M.; van de Kant, K.D.; van der Velden, C.A.; van Schayck, C.P.; Dompeling, E. Associations between asthma, overweight and physical activity in children: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselma, M.; Chinapaw, M.; Altenburg, T. Not Only Adults Can Make Good Decisions, We as Children Can Do That as Well. Evaluating the Process of the Youth-Led Participatory Action Research ‘Kids in Action’. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Child-Only | Parental Involvement | |
|---|---|---|
| PA | Run as far as possible with your entire class, in 2 min. Try to perform as many bottle flips as possible in 1 min. Jump rope as long and often as you can, together with your PE teacher. Go to the town-/city centre and play a game of ‘the floor is lava’. Participate in an activity of your local youth organisation. Challenge a local youth worker for a battle. Challenge him/her in something you are good at. Watch instruction video: Free running. | Help your parent/guardian with the housekeeping. Ask your dad/mom/guardian/grandpa/grandma/neighbour what game they liked to play when they were young, and play that game. Go exercise for 30 min together with your parent(s)/guardian(s). Go walking, rollerblading, or stepping, together with your parent(s)/guardian(s). Do a ‘bob for a job’ in your neighbourhood. Come to school using a means of transport other than a car. |
| Nutrition | Find a healthy dinner recipe and bring this with you to school. Make a vlog about healthy/unhealthy food in your surroundings. | Cook a healthy soup. Make a healthy breakfast for someone in your household. Make a work of art out of a piece of fruit. |
| N | % | Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Child characteristics | |||||
| Age | 10.9 | 1.0 | |||
| BMI z | 0.09 | 1.1 | |||
| Gender | Boy | 100 | 44.2 | ||
| Girl | 126 | 55.8 | |||
| Ethnicity | Western | 141 | 62.7 | ||
| non-Western | 84 | 37.3 | |||
| Sports membership | Member | 173 | 77.9 | ||
| non-member | 49 | 22.1 | |||
| Preference PA (0–28) | Active | 15.7 | 3.3 | ||
| Preference nutrition (0–14) | Healthy | 6.2 | 2.8 | ||
| Family characteristics | |||||
| Filled in by | Mother | 141 | 82.9 | ||
| Father | 26 | 15.3 | |||
| Other | 3 | 1.8 | |||
| Family situation | Parent with partner | 157 | 84.4 | ||
| Single parent | 29 | 15.6 | |||
| Residential status score | −0.9 | 0.8 | |||
| Siblings | 0 | 24 | 10.9 | ||
| 1 | 105 | 47.7 | |||
| 2 | 48 | 21.8 | |||
| 3 | 28 | 12.7 | |||
| 4–7 | 15 | 6.9 | |||
| Parental level of education | Low | 92 | 50.0 | ||
| Low/High mixed | 37 | 20.1 | |||
| High | 55 | 29.9 | |||
| FHC-PA (1–4) | 2.8 | 0.4 | |||
| FHC nutrition (1–4) | 3.1 | 0.4 | |||
| 0 Challenges Performed (0%) | At Least One Challenge Performed (1–99%) | All Challenges Performed (100%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | N | % | N | % | N | % |
| PA | 2 | 0.9 | 224 | 99.1 | 0 | 0 |
| PA child-only (7 challenges) | 17 | 7.5 | 205 | 90.7 | 4 | 1.8 |
| PA parental involvement (6 challenges) | 22 | 9.7 | 200 | 88.5 | 4 | 1.8 |
| Nutrition | 85 | 37.6 | 139 | 61.5 | 2 | 0.9 |
| Nutrition child-only (2 challenges) | 162 | 71.7 | 59 | 26.1 | 5 | 2.2 |
| Nutrition parental involvement (3 challenges) | 100 | 44.2 | 111 | 49.2 | 15 | 6.6 |
| PA | PA Child-Only | PA Parental Involvement | Nutrition | Nutrition Child-Only | Nutrition Parental Involvement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Reference | β | β | β | β | Β | β |
| Age | −0.153 * | −0.227 * | 0.016 | −0.154 * | −0.063 | −0.165 * | |
| BMI z | −0.010 | −0.064 | 0.065 | 0.048 | 0.036 | 0.042 | |
| Gender | Boys | 0.047 | 0.052 | 0.018 | 0.098 | 0.009 | 0.122 |
| Ethnicity | Western | −0.151 * | −0.102 | −0.146 * | −0.078 | −0.050 | −0.074 |
| Sports membership | Non-member | 0.226 * | 0.221 * | 0.128 | 0.110 | 0.112 | 0.082 |
| Preference active activities | 0.091 | 0.073 | 0.073 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Preference healthy nutrition | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0.000 | −0.055 | 0.030 | |
| Residential status score | 0.046 | 0.079 | −0.019 | 0.008 | −0.041 | 0.032 | |
| Siblings | 0.142 * | 0.046 | 0.200 * | 0.065 | 0.040 | 0.063 | |
| Parental educational level | (both) Low educated | ||||||
| Mixed | 0.095 | 0.091 | 0.054 | 0.167 | 0.147 | 0.139 | |
| (both) high educated | 0.054 | 0.125 | −0.065 | 0.125 | 0.130 | 0.094 | |
| FHC-PA | −0.021 | 0.038 | −0.083 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| FHC nutrition | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0.007 | 0.036 | −0.010 |
| PA | PA Child-Only | PA Parental Involvement | Nutrition | Nutrition Child-Only | Nutrition Parental Involvement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Reference | β | β | β | β | β | β |
| Age | −0.136 * | −0.208 * | 0.019 | −0.131 | −0.052 | −0.142 * | |
| BMI z | −0.008 | −0.065 | 0.069 | 0.050 | 0.040 | 0.044 | |
| Gender | Boys | 0.030 | 0.047 | −0.004 | 0.115 | 0.040 | 0.127 |
| Ethnicity | Western | −0.119 | −0.056 | −0.148 * | −0.052 | −0.030 | −0.052 |
| Sports membership | Non-member | 0.182 * | 0.180 * | 0.101 | 0.109 | 0.103 | 0.085 |
| Preference active activities | 0.095 | 0.070 | 0.084 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Preference healthy nutrition | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | −0.032 | −0.064 | −0.007 |
| PA | PA Child-Only | PA Parental Involvement | Nutrition | Nutrition Child-Only | Nutrition Parental Involvement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Reference | β | β | β | β | β | β |
| Residential status score | 0.082 | 0.175 * | −0.063 | −0.063 | −0.097 | −0.029 | |
| Siblings | 0.140 | −0.002 | 0.247 * | 0.091 | −0.030 | 0.138 | |
| Parental educational level | (both) Low educated | ||||||
| Mixed | 0.075 | 0.036 | 0.090 | 0.214 * | 0.205 * | 0.169 | |
| (both) high educated | −0.067 | −0.020 | −0.094 | 0.133 | 0.142 | 0.097 | |
| FHC-PA | −0.002 | 0.047 | −0.059 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| FHC nutrition | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | −0.038 | −0.028 | −0.035 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verhees, A.H.; Verjans-Janssen, S.R.B.; Van Kann, D.H.H.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Vos, S.B.; Gerards, S.M.P.L. Involving Parents to Help Improve Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviours Through a School-Based Intervention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134838
Verhees AH, Verjans-Janssen SRB, Van Kann DHH, Kremers SPJ, Vos SB, Gerards SMPL. Involving Parents to Help Improve Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviours Through a School-Based Intervention. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(13):4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134838
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerhees, Anke H., Sacha R.B. Verjans-Janssen, Dave H.H. Van Kann, Stef P.J. Kremers, Steven B. Vos, and Sanne M.P.L. Gerards. 2020. "Involving Parents to Help Improve Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviours Through a School-Based Intervention" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 13: 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134838
APA StyleVerhees, A. H., Verjans-Janssen, S. R. B., Van Kann, D. H. H., Kremers, S. P. J., Vos, S. B., & Gerards, S. M. P. L. (2020). Involving Parents to Help Improve Children’s Energy Balance-Related Behaviours Through a School-Based Intervention. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(13), 4838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134838






