Seasonal Impacts of Particulate Matter Levels on Bike Sharing in Seoul, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
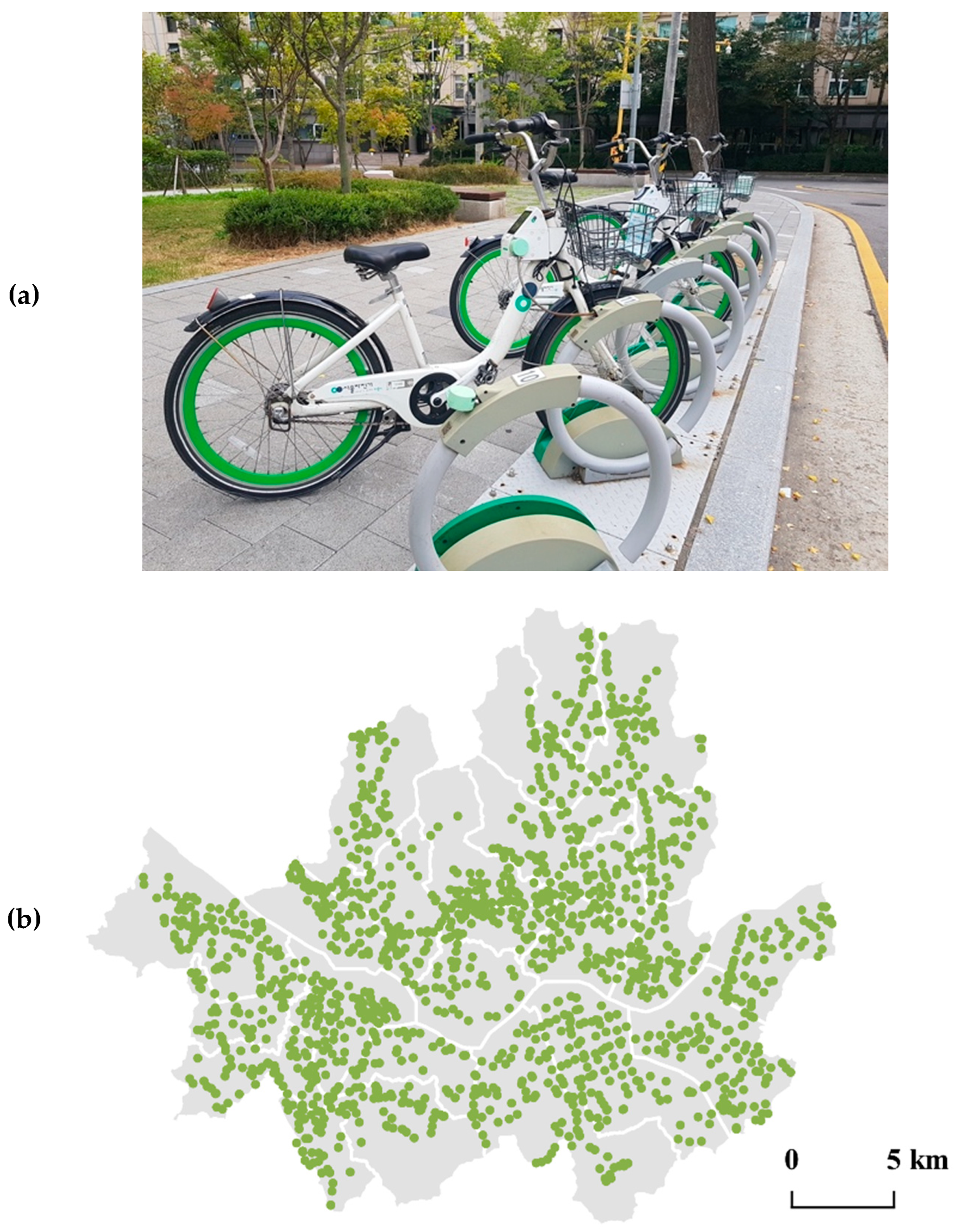
2. Case Context
3. Methods
4. Results and Discussion
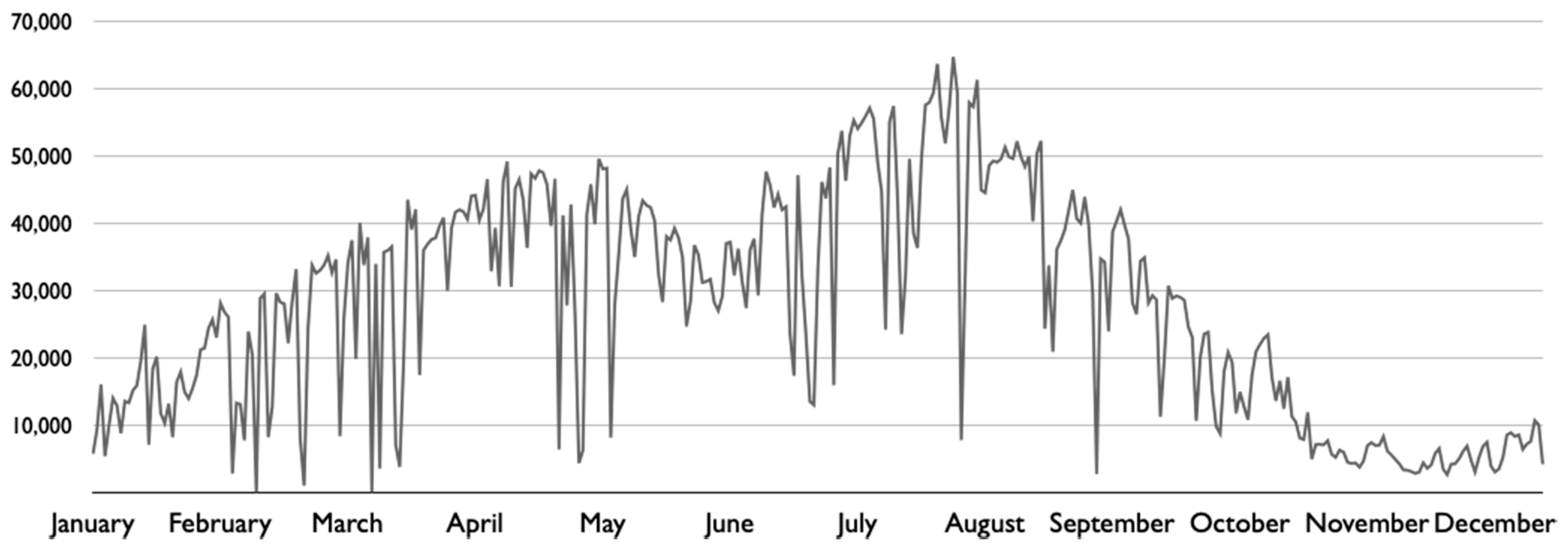
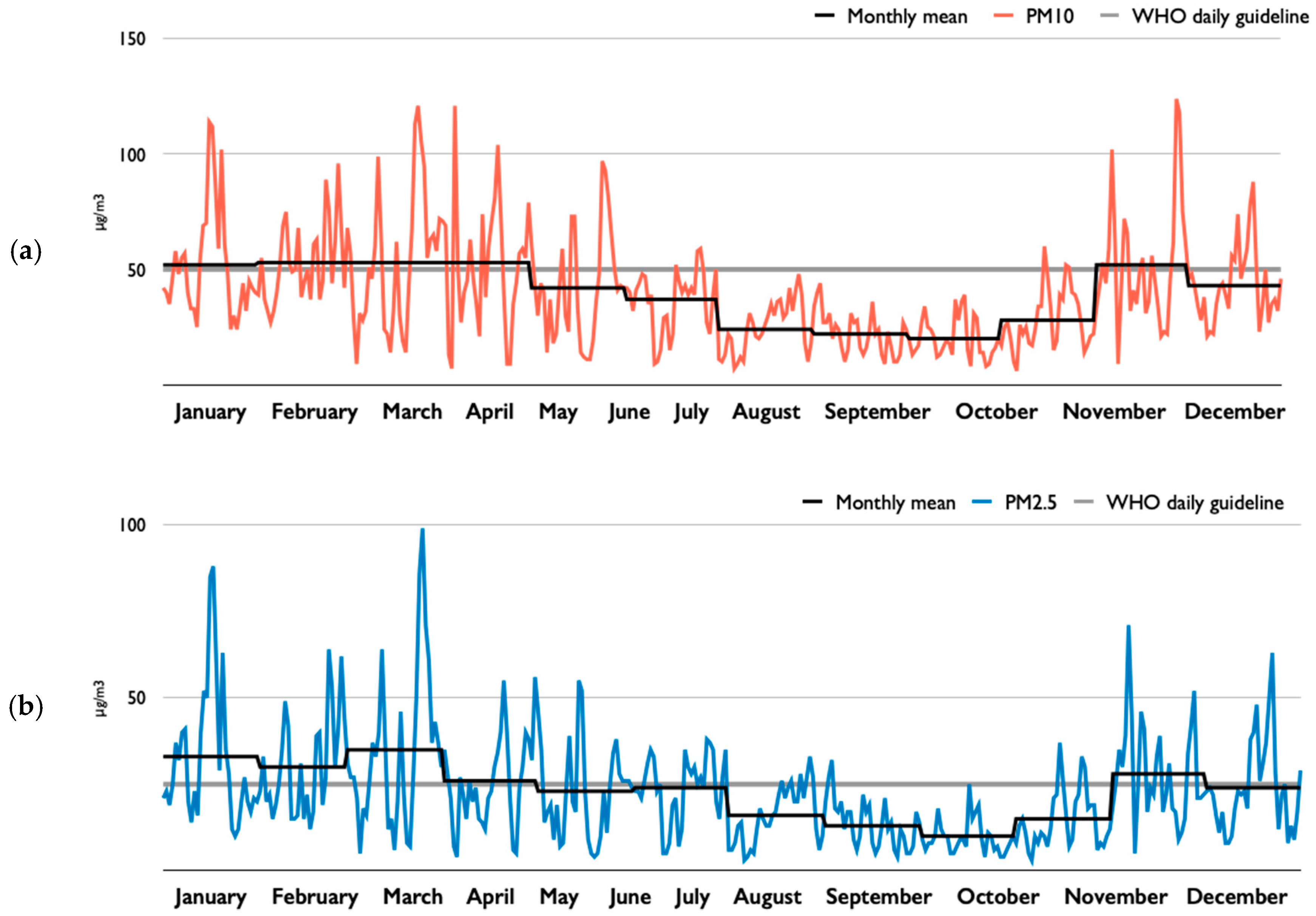
4.1. Results
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM10 level | −0.0031 ** | 0.011 | −0.0033 ** | 0.034 | −0.0026 * | 0.068 |
| (Mean PM10 level) × (Summer) | −0.0041 * | 0.080 | −0.0074 *** | 0.009 | −0.0086 *** | 0.001 |
| (Mean PM10 level) × (Fall) | 0.0125 *** | 0.000 | 0.0117 *** | 0.000 | 0.0101 *** | 0.000 |
| (Mean PM10 level) × (Winter) | −0.0049 *** | 0.002 | −0.0071 *** | 0.000 | −0.0078 *** | 0.000 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0534 *** | 0.000 | 0.0668 *** | 0.000 | 0.0685 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0182 *** | 0.000 | −0.0206 *** | 0.000 | −0.0224 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | 0.0308 | 0.870 | 0.0887 | 0.707 | 0.1488 | 0.504 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.0975 ** | 0.033 | −0.1187 ** | 0.038 | −0.1119 ** | 0.036 |
| Mean humidity | 0.0192 *** | 0.000 | −0.0120 *** | 0.000 | −0.0118 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.1092 ** | 0.049 | −0.0375 | 0.586 | −0.1251 * | 0.051 |
| N | 365 | 365 | 365 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −7760.657 | −13,974.815 | −10,202.575 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 7784.7 | 13,998.8 | 10,266.6 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM2.5 level | −0.0048 ** | 0.015 | −0.0046 * | 0.062 | −0.0034 | 0.141 |
| (Mean PM2.5 level) × (Summer) | −0.0058 * | 0.096 | −0.0108 ** | 0.012 | −0.0126 *** | 0.001 |
| (Mean PM2.5 level) × (Fall) | 0.0228 *** | 0.000 | 0.0213 *** | 0.000 | 0.0186 *** | 0.000 |
| (Mean PM2.5 level) × (Winter) | −0.0067 *** | 0.007 | −0.0098 *** | 0.001 | −0.0109 *** | 0.000 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0551 *** | 0.000 | 0.0688 *** | 0.000 | 0.0706 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0181 *** | 0.000 | −0.0206 *** | 0.000 | −0.0223 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | 0.0344 | 0.857 | 0.0918 | 0.701 | 0.1523 | 0.499 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.1104 ** | 0.019 | −0.1337 ** | 0.023 | −0.1246 ** | 0.023 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0102 *** | 0.000 | −0.0118 *** | 0.000 | −0.0117 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.1126 ** | 0.043 | −0.0349 | 0.615 | −0.1227 * | 0.058 |
| N | 365 | 365 | 365 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −7764.990 | −13,979.984 | −10,208.968 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 7789.0 | 14,004.0 | 10,233.0 | |||
References
- Shaheen, S.A.; Guzman, S.; Zhang, H. Bikesharing in Europe, the Americas, and Asia: Past, Present, and Future. Transp. Res. Rec. 2010, 2143, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMaio, P. Bike-sharing: History, Impacts, Models of Provision, and Future. J. Public Transp. 2009, 12, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Gal, S. The number of Bike-Sharing Programs Worldwide Has Doubled Since 2014—And the Number of Public Bikes Has Increased Almost 20-Fold. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/bike-sharing-programs-doubled-since-2014-public-bikes-charts-2018-7 (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Fishman, E.; Washington, S.; Haworth, N. Bike Share: A Synthesis of the Literature. Transp. Rev. 2013, 33, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucher, J.; Buehler, R. City Cycling; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-262-30499-3. [Google Scholar]
- De Chardon, C.M. The contradictions of bike-share benefits, purposes and outcomes. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 121, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.L. Bike Lanes Are White Lanes: Bicycle Advocacy and Urban Planning; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, Canada, 2016; ISBN 978-0-8032-8822-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie, F.; Goodman, A. Inequalities in usage of a public bicycle sharing scheme: Socio-demographic predictors of uptake and usage of the London (UK) cycle hire scheme. Prev. Med. 2012, 55, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosford, K.; Winters, M. Who Are Public Bicycle Share Programs Serving? An Evaluation of the Equity of Spatial Access to Bicycle Share Service Areas in Canadian Cities. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audikana, A.; Ravalet, E.; Baranger, V.; Kaufmann, V. Implementing bikesharing systems in small cities: Evidence from the Swiss experience. Transp. Policy 2017, 55, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurdak, R. The Impact of Cost and Network Topology on Urban Mobility: A Study of Public Bicycle Usage in 2 U.S. Cities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.A.; Martin, E.W.; Cohen, A.P.; Finson, R.S. Public Bikesharing in North America: Early Operator and User Understanding; Mineta Transportation Institute: San Jose, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fishman, E.; Washington, S.; Haworth, N. Barriers and facilitators to public bicycle scheme use: A qualitative approach. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2012, 15, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basch, C.H.; Zagnit, E.A.; Rajan, S.; Ethan, D.; Basch, C.E. Helmet Use Among Cyclists in New York City. J. Community Health 2014, 39, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mi, Z. Environmental benefits of bike sharing: A big data-based analysis. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Lövenheim, B.; Schantz, P.; Wahlgren, L.; Almström, P.; Markstedt, A.; Strömgren, M.; Forsberg, B.; Sommar, J.N. Impacts on air pollution and health by changing commuting from car to bicycle. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, G.; Macmillan, A.; Woodward, A. Moving urban trips from cars to bicycles: Impact on health and emissions. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2011, 35, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, S.A.; Cohen, A.P.; Martin, E.W. Public Bikesharing in North America: Early Operator Understanding and Emerging Trends. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2387, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, X. Bike-sharing systems and congestion: Evidence from US cities. J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 65, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T.L.; Wichman, C.J. Bicycle infrastructure and traffic congestion: Evidence from DC’s Capital Bikeshare. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 87, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, I.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Rojas-Rueda, D. Health impacts of bike sharing systems in Europe. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, C.; Becker, S.; Gomolinsky, U.; Klein, T.; Thiel, A. Health, Medical Risk Factors, and Bicycle Use in Everyday Life in the Over-50 Population. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2008, 16, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Rueda, D.; de Nazelle, A.; Tainio, M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. The health risks and benefits of cycling in urban environments compared with car use: Health impact assessment study. BMJ 2011, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, J.; Tainio, M.; Cheshire, J.; O’Brien, O.; Goodman, A. Health effects of the London bicycle sharing system: Health impact modelling study. BMJ 2014, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, E.; Schepers, P. Global bike share: What the data tells us about road safety. J. Saf. Res. 2016, 56, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, C.; Brereton, F.; Bailey, S. The economic contribution of public bike-share to the sustainability and efficient functioning of cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 28, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.Y.; He, L.Y. Bike Sharing and the Economy, the Environment, and Health-Related Externalities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.; Kietzmann, J. Ride On! Mobility Business Models for the Sharing Economy. Organ. Environ. 2014, 27, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Won, D.H.; Ko, E.J. The multiple impacts of the neighbourhood environment on the use of public bicycles by residents: An empirical study of Changwon in Korea. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2015, 19, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, J.; Brady, J.F.; Mills, A.F.; Machemehl, R.B. Effects of On-Street Bicycle Facility Configuration on Bicyclist and Motorist Behavior. Transp. Res. Rec. 2010, 2190, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Palomares, J.C.; Gutiérrez, J.; Latorre, M. Optimizing the location of stations in bike-sharing programs: A GIS approach. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Greg, L.; Schoner, J.E.; Harrison, A. Modeling Bike Share Station Activity: Effects of Nearby Businesses and Jobs on Trips to and from Stations. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2016, 142, 04015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frade, I.; Ribeiro, A. Bike-sharing stations: A maximal covering location approach. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2015, 82, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, K.; Noland, R.B. The impact of weather conditions on bikeshare trips in Washington, DC. Transportation 2014, 41, 1205–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Assi, W.; Salah Mahmoud, M.; Nurul Habib, K. Effects of built environment and weather on bike sharing demand: A station level analysis of commercial bike sharing in Toronto. Transportation 2017, 44, 589–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, J.; Li, T.; Rohde, D.; Charles-Edwards, E.; Mateo-Babiano, D. Spatio-temporal patterns of a Public Bicycle Sharing Program: The effect of weather and calendar events. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 41, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, B.; O’Mahony, M.; Brazil, W.; Weldon, P. Examining usage patterns of a bike-sharing scheme in a medium sized city. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 100, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K. Investigation on the effects of weather and calendar events on bike-sharing according to the trip patterns of bike rentals of stations. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 66, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, K. The bicycle as a feedering mode: Experiences from three European countries. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2004, 9, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nankervis, M. The effect of weather and climate on bicycle commuting. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 1999, 33, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Magnusson, R. Potential of transferring car trips to bicycle during winter. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2003, 37, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, B.S.; Dana, G.S.; Sears, J.; Aultman-Hall, L. Weather factor impacts on commuting to work by bicycle. Prev. Med. 2012, 54, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Macdonald, E. Does Wind Discourage Sustainable Transportation Mode Choice? Findings from San Francisco, California, USA. Sustainability 2016, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNaughton, P.; Melly, S.; Vallarino, J.; Adamkiewicz, G.; Spengler, J.D. Impact of bicycle route type on exposure to traffic-related air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lan, B.; Shirai, J.; Austin, E.; Yang, C.; Seto, E. Exposures to Air Pollution and Noise from Multi-Modal Commuting in a Chinese City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apparicio, P.; Carrier, M.; Gelb, J.; Séguin, A.M.; Kingham, S. Cyclists’ exposure to air pollution and road traffic noise in central city neighbourhoods of Montreal. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 57, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kamargianni, M. Providing quantified evidence to policy makers for promoting bike-sharing in heavily air-polluted cities: A mode choice model and policy simulation for Taiyuan-China. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 111, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kamargianni, M. Air Pollution and Seasonality Effects on Mode Choice in China. Transp. Res. Rec. 2017, 2634, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. How’s Life? 2020: Measuring Well-Being; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, G.; Chow, J.Y.J. Unlimited-ride bike-share pass pricing revenue management for casual riders using only public data. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citi Bike System Data. Available online: http://www.citibikenyc.com/system-data (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Transport for London Santander Cycles Achieves a Record Breaking Year. Available online: https://tfl.gov.uk/info-for/media/press-releases/2018/december/santander-cycles-achieves-a-record-breaking-year (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- World Health Organization WHO Global Ambient Air Quality Database (Update 2018). Available online: http://www.who.int/airpollution/data/cities/en/ (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- Martinelli, N.; Olivieri, O.; Girelli, D. Air particulate matter and cardiovascular disease: A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polichetti, G.; Cocco, S.; Spinali, A.; Trimarco, V.; Nunziata, A. Effects of particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5 and PM1) on the cardiovascular system. Toxicology 2009, 261, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, G.; Zhou, J.; Jin, X.; Wang, W.; Pan, X. The spatial characteristics of ambient particulate matter and daily mortality in the urban area of Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.C.; Cassidy, A.; Christiani, D.C. A Systematic Review of Occupational Exposure to Particulate Matter and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1773–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, F.; Gao, Q.; Wu, L.; Tao, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Hospital Emergency Room Visits for Respiratory Disease in Urban Areas in Beijing, China, in 2013. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fang, B.; Wang, C.; Xia, T.; Bottai, M.; Fang, F.; Cao, Y. Comparison of Frequentist and Bayesian Generalized Additive Models for Assessing the Association between Daily Exposure to Fine Particles and Respiratory Mortality: A Simulation Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkhama, E.; Ndhlovu, M.; Dvonch, J.T.; Lynam, M.; Mentz, G.; Siziya, S.; Voyi, K. Effects of Airborne Particulate Matter on Respiratory Health in a Community near a Cement Factory in Chilanga, Zambia: Results from a Panel Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Dailey, A.B.; Kan, H.; Xu, X. The effect of atmospheric particulate matter on survival of breast cancer among US females. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Song, F.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Z.; Trevathan, E.; Mao, H.; Han, B.; Vaughn, M.; et al. Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and lung cancer mortality: A 12-year cohort study in Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scungio, M.; Stabile, L.; Rizza, V.; Pacitto, A.; Russi, A.; Buonanno, G. Lung cancer risk assessment due to traffic-generated particles exposure in urban street canyons: A numerical modelling approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Hu, W.; Wei, F.; Korn, L.; Chapman, R.S.; Zhang, J.J. Ambient particulate matter and lung function growth in Chinese children. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, C.; Che, Z.; Cao, J. Maternal exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and pregnancy outcomes: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3383–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranft, U.; Schikowski, T.; Sugiri, D.; Krutmann, J.; Krämer, U. Long-term exposure to traffic-related particulate matter impairs cognitive function in the elderly. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.H.; de Hartog, J.J.; Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B.; Lanki, T.; Timonen, K.L.; Pekkanen, J. Personal Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter in Elderly Subjects: Relation between Personal, Indoor, and Outdoor Concentrations. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. The Economic Consequences of Outdoor Air Pollution; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment. Ministry of Environment Comprehensive Plan for Managing Particulate Matter (2020–2024); Ministry of Environment: Sejong, South Korea, 2019.
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.U.; Jin, C.S.; Hong, S.; Park, R.; Son, S.W.; Bae, C.; Bae, M.; Song, C.K.; et al. Recent increase of surface particulate matter concentrations in the Seoul Metropolitan Area, Korea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Yoon, E.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.K. The Effects of Risk Perceptions Related to Particulate Matter on Outdoor Activity Satisfaction in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashqar, H.I.; Elhenawy, M.; Rakha, H.A. Modeling bike counts in a bike-sharing system considering the effect of weather conditions. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2019, 7, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, N.; Monsere, C.M.; Dill, J. Influence of Bike Lane Buffer Types on Perceived Comfort and Safety of Bicyclists and Potential Bicyclists. Transp. Res. Rec. 2015, 2520, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, L. Effects of plant leaf surface and different pollution levels on PM2.5 adsorption capacity. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 34, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yan, H.; Liu, M.; Kang, L.; Yu, J.; Yang, R. Relationship between PM2.5 adsorption and leaf surface morphology in ten urban tree species in Shenyang, China. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
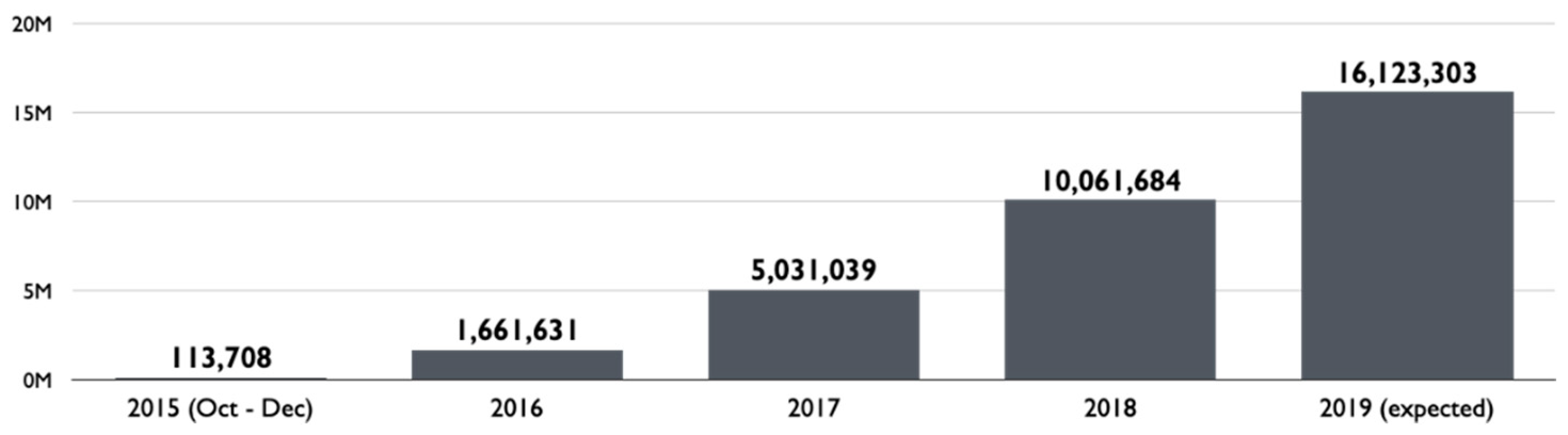
| Variable | Unit | Data Source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variables | Total number of trips | - | Seoul Open Data Plaza |
| Total traveled distances | meter | ||
| Total traveled times | minute | ||
| Independent variables | Mean PM10 level | μg/m3 | Seoul Metropolitan Government Air Quality Information |
| Mean PM2.5 level | μg/m3 | ||
| Control variables | Mean temperature | °C | Korea Meteorological Administration |
| Precipitation | mm | ||
| Heavy rain b | 1: precipitation ≥ 15; 0: precipitation < 15 | ||
| Mean wind speed | m/s | ||
| Mean humidity | % | ||
| Weekday b | 1: weekday; 0: Saturday, Sunday, and public holidays | ||
| Season | Variable | Mean or Frequency | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All seasons | Total number of trips | 27,560 | 16,575 | 1036 | 64,644 |
| Total traveled distances (million meters) | 125 | 86 | 3 | 390 | |
| Total traveled times (thousand minutes) | 757 | 544 | 19 | 2486 | |
| Mean PM10 level (μg/m3) | 39.7 | 23.1 | 6 | 124 | |
| Mean PM2.5 level (μg/m3) | 22.8 | 15.3 | 3 | 99 | |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 13.0 | 11.5 | −14.8 | 33.7 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | 3.5 | 12.0 | 0 | 97 | |
| Heavy rain 1 | 23 | - | - | - | |
| Mean wind speed (m/s) | 1.7 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 4.1 | |
| Mean humidity (%) | 57.5 | 15.1 | 23 | 97 | |
| Weekday 1 | 261 | - | - | - | |
| Spring | Total number of trips | 22,883 | 11,550 | 1036 | 43,468 |
| Total traveled distances (million meters) | 107 | 62 | 3 | 252 | |
| Total traveled times (thousand minutes) | 682 | 419 | 19 | 1800 | |
| Mean PM10 level (μg/m3) | 48.7 | 27.6 | 7 | 121 | |
| Mean PM2.5 level (μg/m3) | 27.5 | 17.9 | 4 | 99 | |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 13.1 | 5.7 | −0.7 | 23.2 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | 4.5 | 12.7 | 0 | 83 | |
| Heavy rain 1 | 8 | - | - | - | |
| Mean wind speed (m/s) | 1.9 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 4.1 | |
| Mean humidity (%) | 59.2 | 16.3 | 23 | 97 | |
| Weekday 1 | 64 | - | - | - | |
| Summer | Total number of trips | 36,352 | 10,248 | 4357 | 49,519 |
| Total traveled distances (million meters) | 169 | 54 | 18 | 275 | |
| Total traveled times (thousand minutes) | 1018 | 370 | 102 | 1784 | |
| Mean PM10 level (μg/m3) | 27.8 | 12.8 | 7 | 59 | |
| Mean PM2.5 level (μg/m3) | 17.8 | 9.4 | 3 | 38 | |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 26.6 | 3.7 | 20.2 | 33.7 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | 6.1 | 17.1 | 0 | 61 | |
| Heavy rain 1 | 10 | - | - | - | |
| Mean wind speed (m/s) | 1.6 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 2.6 | |
| Mean humidity (%) | 65.1 | 12.8 | 39 | 95 | |
| Weekday 1 | 66 | - | - | - | |
| Fall | Total number of trips | 42,004 | 13,130 | 2728 | 64,644 |
| Total traveled distances (million meters) | 194 | 80 | 8 | 390 | |
| Total traveled times (thousand minutes) | 1153 | 543 | 44 | 2486 | |
| Mean PM10 level (μg/m3) | 33.3 | 22.1 | 6 | 124 | |
| Mean PM2.5 level (μg/m3) | 17.5 | 12.6 | 3 | 71 | |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 14.1 | 6.4 | 1.9 | 25.5 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | 2.8 | 10.2 | 0 | 64 | |
| Heavy rain 1 | 4 | - | - | - | |
| Mean wind speed (m/s) | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 3.2 | |
| Mean humidity (%) | 59.2 | 12.4 | 27 | 94 | |
| Weekday 1 | 65 | - | - | - | |
| Winter | Total number of trips | 9256 | 6107 | 2640 | 24,620 |
| Total traveled distances (million meters) | 32 | 22 | 8 | 99 | |
| Total traveled times (thousand minutes) | 182 | 122 | 46 | 575 | |
| Mean PM10 level (μg/m3) | 49.2 | 19.9 | 21 | 114 | |
| Mean PM2.5 level (μg/m3) | 28.7 | 16.5 | 8 | 88 | |
| Mean temperature (°C) | −2.1 | 5.5 | −14.8 | 11.5 | |
| Precipitation (mm) | 0.6 | 2.9 | 0 | 25 | |
| Heavy rain 1 | 1 | - | - | - | |
| Mean wind speed (m/s) | 1.9 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 3.8 | |
| Mean humidity (%) | 46.3 | 12.1 | 26 | 87 | |
| Weekday 1 | 64 | - | - | - |
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM10 level | −0.0034 ** | 0.011 | −0.0043 ** | 0.007 | −0.0041 ** | 0.007 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0527 *** | 0.000 | 0.0663 *** | 0.000 | 0.0686 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0192 *** | 0.000 | −0.0215 *** | 0.000 | −0.0231 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | −0.1121 | 0.613 | −0.0531 | 0.842 | 0.0252 | 0.20 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.2036 *** | 0.000 | −0.2213 *** | 0.000 | −0.2001 *** | 0.000 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0075 *** | 0.004 | −0.0094 *** | 0.003 | −0.0097 *** | 0.001 |
| Weekday | 0.1157 | 0.071 | −0.0376 | 0.626 | −0.1341 | 0.065 |
| N | 365 | 365 | 365 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −7871.343 | −14,064.148 | −10,298.510 | |||
| AIC | 7889.3 | 14,082 | 10,317 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM2.5 level | −0.0080 *** | 0.000 | −0.0094 *** | 0.000 | −0.0087 *** | 0.000 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0512 *** | 0.000 | 0.0647 *** | 0.000 | 0.0672 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0203 *** | 0.000 | −0.0227 *** | 0.000 | −0.0243 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | −0.1283 | 0.558 | −0.0684 | 0.795 | 0.0133 | 0.957 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.2278 *** | 0.000 | −0.2479 *** | 0.000 | −0.2250 *** | 0.000 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0055 * | 0.035 | −0.0073 ** | 0.022 | −0.0076 ** | 0.010 |
| Weekday | 0.1037 | 0.102 | −0.0525 | 0.492 | −0.1484 * | 0.039 |
| N | 365 | 365 | 365 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −7862.803 | −14,056.852 | −10,291.406 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 7880.8 | 14,075 | 10,309 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM10 level | −0.0016 | 0.146 | −0.0029 * | 0.028 | −0.0027 * | 0.043 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0766 *** | 0.000 | 0.0878 *** | 0.000 | 0.0904 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0332 *** | 0.000 | −0.0399 *** | 0.000 | −0.0388 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | 0.2009 | 0.264 | 0.3107 | 0.142 | 0.2927 | 0.187 |
| Mean wind speed | 0.0191 | 0.719 | −0.0197 | 0.752 | −0.0202 | 0.757 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0108 *** | 0.000 | −0.0128 *** | 0.000 | −0.0124 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.0648 | 0.309 | −0.1177 | 0.116 | −0.2431 *** | 0.002 |
| N | 90 | 90 | 90 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1793.18 | −3334.478 | −2430.358 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1811.2 | 3352.5 | 2448.4 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM2.5 level | −0.0025 | 0.128 | −0.0043 * | 0.030 | −0.0041 * | 0.048 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0757 *** | 0.000 | 0.0862 *** | 0.000 | 0.0889 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0335 *** | 0.000 | −0.0403 *** | 0.000 | −0.0392 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | 0.2059 | 0.251 | 0.3227 | 0.127 | 0.3061 | 0.167 |
| Mean wind speed | 0.0014 | 0.979 | −0.0498 | 0.428 | −0.0492 | 0.455 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0104 *** | 0.000 | −0.0121 *** | 0.000 | −0.0118 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.0608 | 0.339 | −0.1243 | 0.098 | −0.2500 *** | 0.002 |
| N | 90 | 90 | 90 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1793.002 | −3334.58 | −2430.548 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1811.0 | 3352.6 | 2448.5 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM10 level | 0.0009 | 0.633 | 0.0002 | 0.928 | 0.0006 | 0.792 |
| Mean temperature | −0.0260 *** | 0 | −0.0332 *** | 0 | −0.0454 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0178 *** | 0 | −0.0197 *** | 0 | −0.0212 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | 0.0245 | 0.859 | −0.0055 | 0.973 | −0.0004 | 0.998 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.0187 | 0.748 | −0.0187 | 0.782 | −0.0267 | 0.693 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0077 *** | 0.002 | −0.0087 *** | 0.002 | −0.0105 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.1384 ** | 0.011 | 0.0190 | 0.763 | −0.0486 | 0.441 |
| N | 92 | 92 | 92 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1904.752 | −3483.012 | −2539.546 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1922.8 | 3501 | 2557.5 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM2.5 level | 0.0007 | 0.789 | −0.0003 | 0.925 | 0.0002 | 0.944 |
| Mean temperature | −0.0262 *** | 0 | −0.0333 *** | 0 | −0.0456 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0178 *** | 0 | −0.0197 *** | 0 | −0.0213 *** | 0.000 |
| Heavy rain | 0.0217 | 0.875 | −0.0089 | 0.956 | −0.0038 | 0.981 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.0167 | 0.773 | −0.0170 | 0.801 | −0.0246 | 0.715 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0077 *** | 0.001 | −0.0087 *** | 0.002 | −0.0105 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.1394 ** | 0.010 | 0.0201 | 0.749 | −0.0474 | 0.452 |
| N | 92 | 92 | 92 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1904.901 | −3483.011 | −2539.607 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1922.9 | 3501 | 2557.6 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM10 level | −0.0003 | 0.853 | −0.0017 | 0.315 | −0.0020 | 0.281 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0367 *** | 0 | 0.0531 *** | 0 | 0.0597 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0074 | 0.399 | −0.0003 | 0.979 | 0.0042 | 0.717 |
| Heavy rain | −0.5192 | 0.198 | −0.8230 | 0.090 | −0.9827 | 0.062 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.0383 | 0.500 | −0.0621 | 0.364 | −0.0754 | 0.308 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0122 *** | 0 | −0.0169 *** | 0 | −0.0189 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.0485 | 0.401 | −0.0784 | 0.265 | −0.1729 ** | 0.023 |
| N | 91 | 91 | 91 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1930.961 | −3493.132 | −2571.092 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1949 | 3511.1 | 2589.1 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM2.5 level | 0.0026 | 0.362 | 0.0005 | 0.883 | 0.0005 | 0.900 |
| Mean temperature | 0.0398 *** | 0 | 0.0567 *** | 0 | 0.0638 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.0045 | 0.617 | 0.0026 | 0.811 | 0.0075 | 0.527 |
| Heavy rain | −0.5932 | 0.142 | −0.8990 | 0.067 | −1.0728 * | 0.043 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.0222 | 0.703 | −0.0477 | 0.499 | −0.0599 | 0.433 |
| Mean humidity | 0.0140 *** | 0 | −0.0182 *** | 0 | −0.0204 *** | 0.000 |
| Weekday | 0.0519 | 0.372 | −0.0777 | 0.272 | −0.1718 ** | 0.025 |
| N | 91 | 91 | 91 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1930.163 | −3483.008 | −2572.10 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1948.2 | 3501 | 2557.6 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM10 level | −0.0152 *** | 0 | −0.0165 *** | 0 | −0.0152 *** | 0.000 |
| Mean temperature | 0.1110 *** | 0 | 0.1330 ** | 0 | 0.1285 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.1240 ** | 0.013 | −0.1337 ** | 0.005 | −0.1318 *** | 0.003 |
| Heavy rain | 1.9941 | 0.101 | 2.1959 | 0.060 | 2.0818 | 0.051 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.0304 | 0.650. | −0.0403 | 0.529 | −0.0314 | 0.591 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0062 | 0.298 | −0.0094 | 0.103 | −0.0080 | 0.125 |
| Weekday | 0.2774 ** | 0.005 | 0.1680 | 0.077 | 0.1607 | 0.064 |
| N | 90 | 90 | 90 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1712.240 | −3162.796 | −2222.028 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1730.2 | 3180.8 | 2240 | |||
| Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | Coeff. | p | |
| Mean PM2.5 level | −0.0174 *** | 0 | −0.0191 *** | 0 | −0.0175 *** | 0.000 |
| Mean temperature | 0.1012 *** | 0 | 0.1224 *** | 0 | 0.1187 *** | 0.000 |
| Precipitation | −0.1212 ** | 0.019 | −0.1314 ** | 0.008 | −0.1290 *** | 0.005 |
| Heavy rain | 1.9035 | 0.128 | 2.1141 | 0.079 | 1.9939 | 0.070 |
| Mean wind speed | −0.0747 | 0.289 | −0.0893 | 0.188 | −0.0761 | 0.219 |
| Mean humidity | −0.0041 | 0.530 | −0.0069 | 0.270 | −0.0059 | 0.303 |
| Weekday | 0.2790 ** | 0.006 | 0.1691 | 0.083 | 0.1618 | 0.069 |
| N | 90 | 90 | 90 | |||
| 2 Log Likelihood | −1715.924 | −3167.469 | −2226.91 | |||
| Akaike information criterion | 1733.9 | 3185.5 | 2244.9 | |||
| Season | PM | Total Number of Trips | Total Traveled Distances | Total Traveled Times |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All seasons | Mean PM10 level | −0.0034 ** | −0.0043 *** | −0.0041 *** |
| Mean PM2.5 level | −0.0080 *** | −0.0094 *** | −0.0087 *** | |
| Spring | Mean PM10 level | −0.0016 | −0.0029 * | −0.0027 * |
| Mean PM2.5 level | −0.0025 | −0.0043 * | −0.0041 * | |
| Summer | Mean PM10 level | 0.0009 | 0.0002 | 0.0006 |
| Mean PM2.5 level | 0.0007 | −0.0003 | 0.0002 | |
| Fall | Mean PM10 level | −0.0003 | −0.0017 | −0.0020 |
| Mean PM2.5 level | 0.0026 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | |
| Winter | Mean PM10 level | −0.0152 *** | −0.0165 *** | −0.0152 *** |
| Mean PM2.5 level | −0.0174 *** | −0.0191 *** | −0.0175 *** |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H. Seasonal Impacts of Particulate Matter Levels on Bike Sharing in Seoul, South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113999
Kim H. Seasonal Impacts of Particulate Matter Levels on Bike Sharing in Seoul, South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(11):3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113999
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyungkyoo. 2020. "Seasonal Impacts of Particulate Matter Levels on Bike Sharing in Seoul, South Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 11: 3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113999
APA StyleKim, H. (2020). Seasonal Impacts of Particulate Matter Levels on Bike Sharing in Seoul, South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(11), 3999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113999





