Chemical Characterization of Seasonal PM2.5 Samples and Their Cytotoxicity in Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
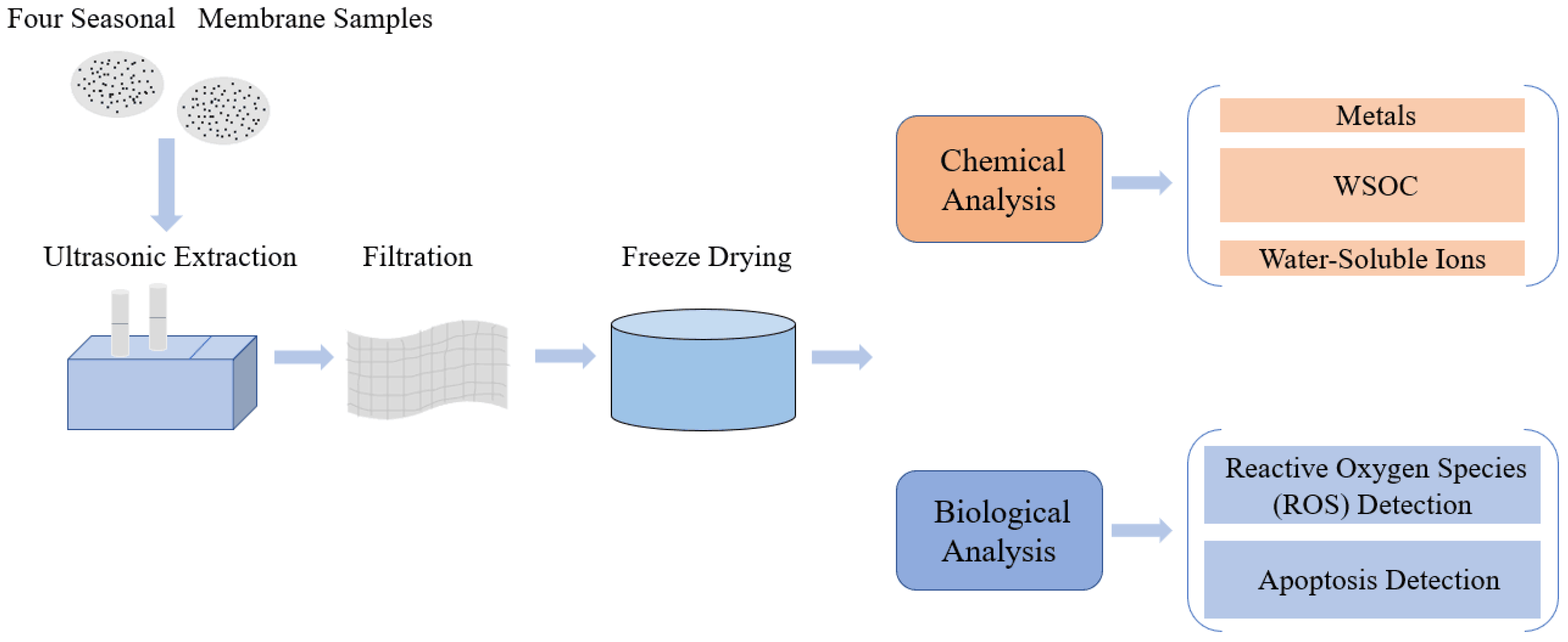
2.2. PM2.5 Collection and Preparation
2.3. PM2.5 Composition Analysis
2.4. Cell Culture and Exposure
2.5. ROS and Apoptosis Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PM2.5 Chemical Characteristics
3.1.1. WSOC
3.1.2. Water-Soluble Ions
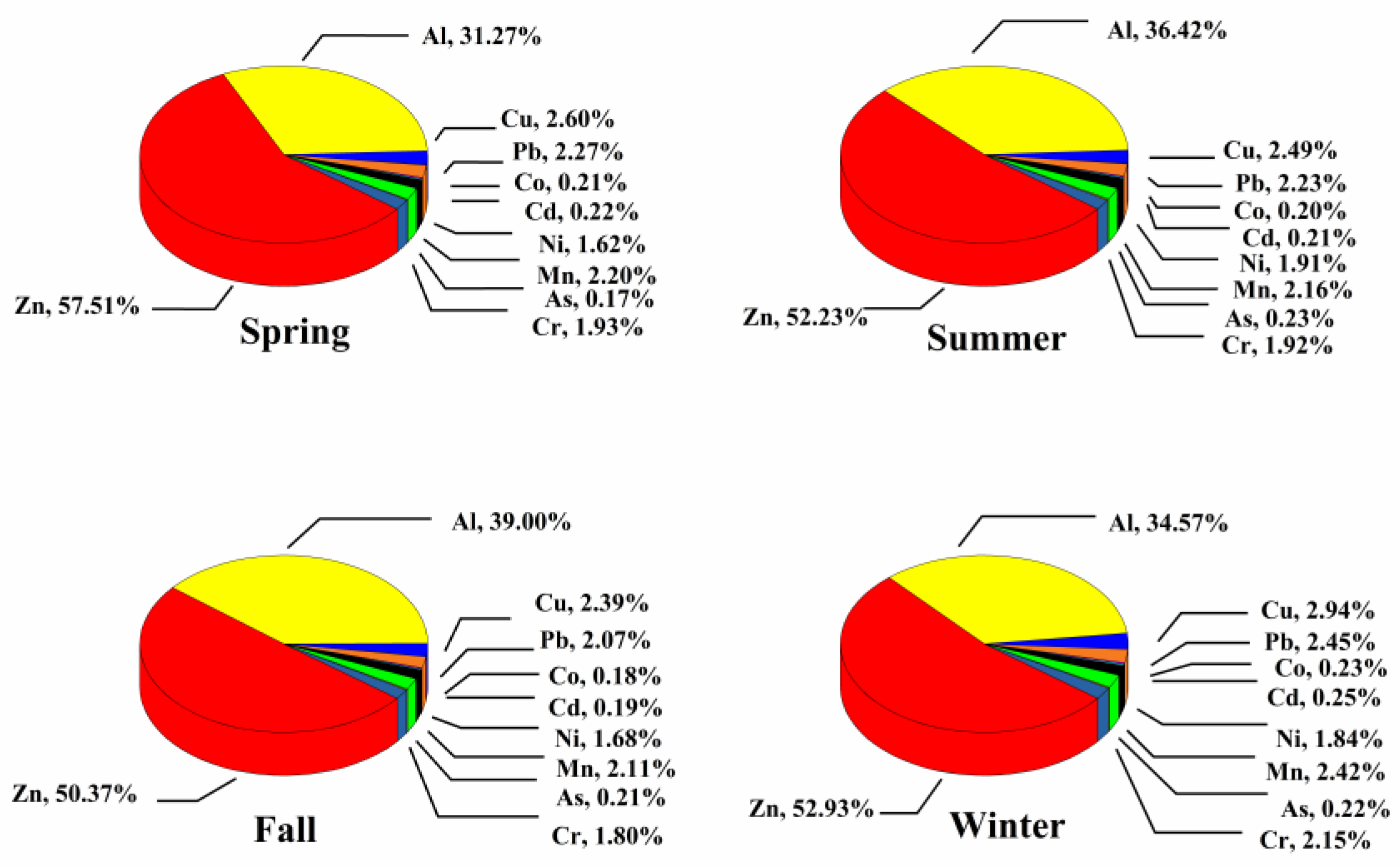
3.1.3. Heavy Metals
3.2. Cytotoxicity of PM2.5
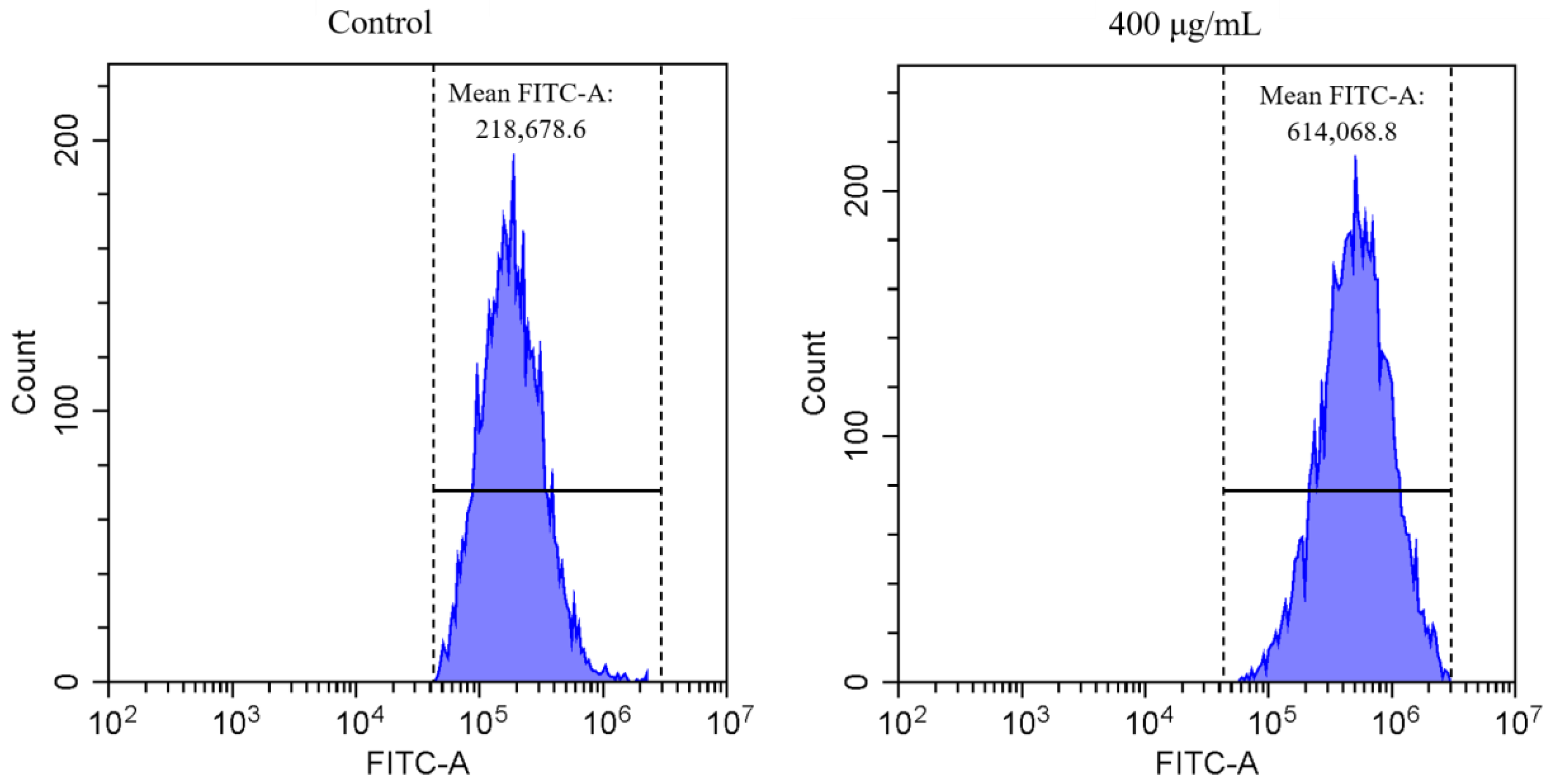
3.2.1. Cellular ROS
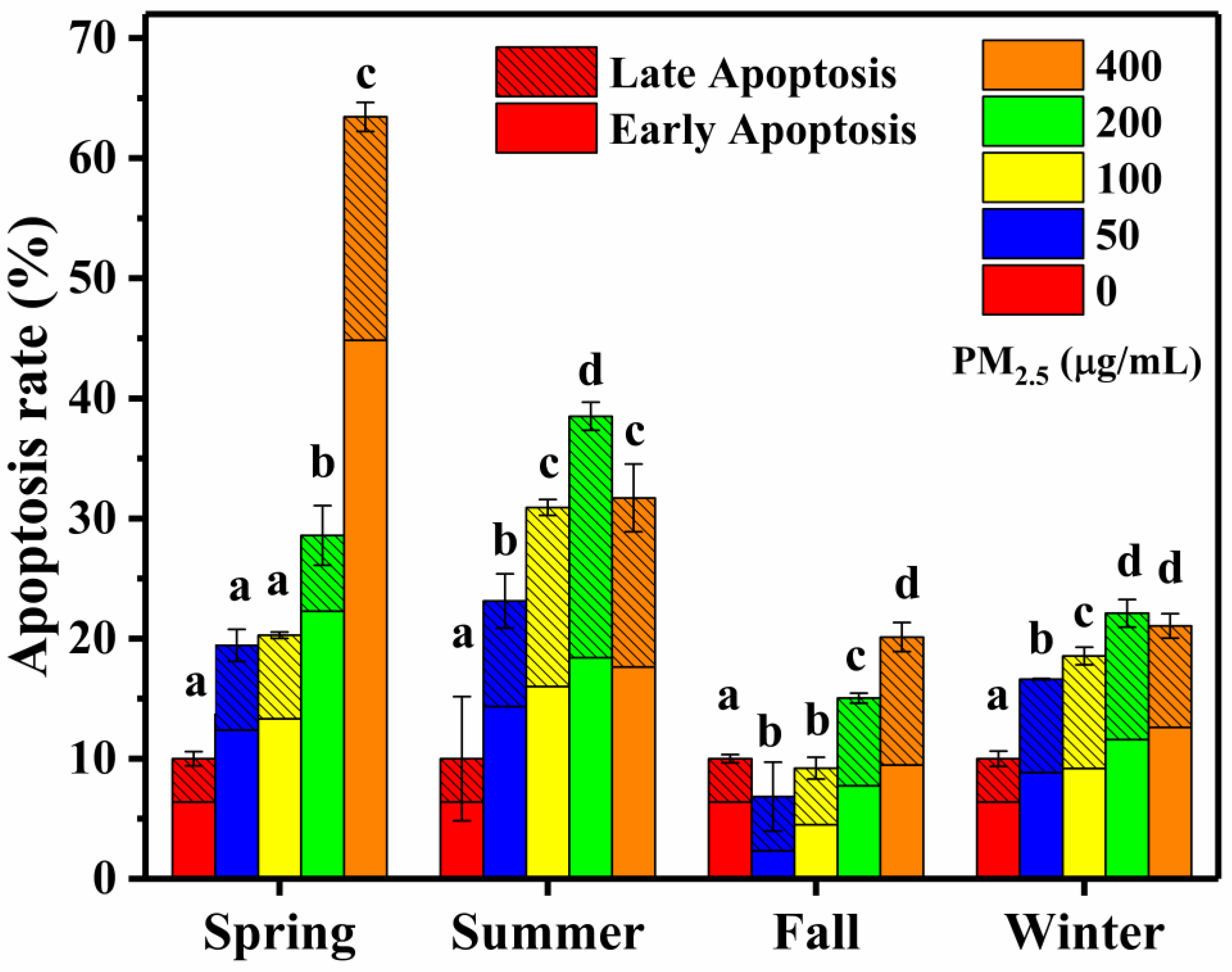
3.2.2. Cell Apoptosis
3.2.3. Correlation between the PM2.5 Components and Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nie, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Ge, P. Characterization of Fine Partiulate Matter and Associated Health Burden in Nanjing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräuner, E.V.; Mortensen, J.; Møller, P.; Bernard, A.; Vinzents, P.; Wåhlin, P.; Glasius, M.; Loft, S. Effects of ambient air particulate exposure on blood-gas barrier permeability and lung function. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A.; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease An Update to the Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Guo, X.; Hong, L.; Xin, F.; Yang, M.; Wei, C. Effects of dust storm PM2.5 on cell proliferation and cell cycle in human lung fibroblasts. Toxicol. Vitro 2007, 21, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Gonzalez-Flecha, B.; Kobzik, L. Reactive oxygen species in pulmonary inflammation by ambient particulates. Free Radical. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Zhang, F.; Qu, F.; Ding, W. Water-insoluble fraction of airborne particulate matter (PM10) induces oxidative stress in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, A.; Yang, J.; Liao, C.; Lu, H.; Chou, S.; Ma, C.; Hsia, T.; Ko, Y.; Chung, J. Benzyl isothiocyanate (bitc) and phenethyl isothiocyanate (peitc)-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species causes cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis via activation of caspase-3, mitochondria dysfunction and nitric oxide (no) in human osteogenic. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurny, K.R. Chemical mixtures in atmospheric aerosols and their correlation to lung diseases and lung cancer occurence in the general population. Toxicol. Lett. 1996, 88, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.M.; Schulte, P.A.; Straif, K.; Hopf, N.B.; Caldwell, J.C.; Carreón, T.; DeMarini, D.M.; Fowler, B.A.; Goldstein, B.D.; Hemminki, K.; et al. Research recommendations for selected IARC-classified agents. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X.; Nie, D.; Wang, M.; Zhou, H.; Chen, M. In vitro toxicity evaluation of heavy metals in urban air particulate matter on human lung epithelial cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Kang, Y.; Wang, W.; Chan, C.; Wang, X.; Wong, M. Potential cytotoxicity of water-soluble fraction of dust and particulate matters and relation to metal(loid)s based on three human cell lines. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, R.B.; Cassee, F. Atmospheric Secondary Inorganic Particulate Matter: The Toxicological Perspective as a Basis for Health Effects Risk Assessment. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 197–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, L. Toxicological and epidemiological studies of cardiovascular effects of ambient air fine particulate matter (PM 2.5) and its chemical components: Coherence and public health implications. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 299–347. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, M.J.; Yan, B.; Chillrud, S.N.; Acosta, L.M.; Divjan, A.; Jacobson, J.S.; Miller, R.L.; Goldstein, I.F.; Perzanowski, M.S. Domestic airborne black carbon levels and 8-isoprostane in exhaled breath condensate among children in new york city. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostro, B.; Roth, L.; Malig, B.; Marty, M. The effects of fine particle components on respiratory hospital admissions in children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltenrich, N. PM2.5 and Kidney Function: Long-Term Exposures May Lead to Modest Declines. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padula, A.M.; Mortimer, K.; Hubbard, A.; Lurmann, F.; Jerrett, M.; Tager, I.B. Exposure to traffic-related air pollution during pregnancy and term low birth weight: Estimation of causal associations in a semiparametric model. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; Belanger, K.; Ebisu, K.; Gent, J.F.; Leaderer, B.F. Relationship between birth weight and exposure to airborne fine particulate potassium and titanium during gestation. Environ. Res. 2012, 117, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.H.; Schauer, J.J.; Antkiewicz, D.S.; Shafer, M.M.; Kadhim, A.K. Ros production and gene expression in alveolar macrophages exposed to PM2.5 from baghdad, iraq: Seasonal trends and impact of chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Chen, L.C.; Gordon, T.; Rom, W.; Tang, M.S. Particulate matter inhibits DNA repair and enhances mutagenesis. Mutat. Res. Fund. Mol. Mech. 2008, 657, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.L.; Thomas, P.S. Current perspectives of oxidative stress and its measurement in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD 2010, 7, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, P.; Finch, A.; Evan, G. Apoptosis in development. Nature 2000, 136, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehling, W.; Khachatryan, L.; Dellinger, B. Hydroxyl radical generation from environmentally persistent free radicals (epfrs) in PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4266–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhin, E.; Holme, J.A.; Gutzkow, K.B.; Arlt, V.M.; Gualtieri, M. Cell cycle alterations induced by urban PM2.5 in bronchial epithelial cells: Characterization of the process and possible mechanisms involved. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Pakbin, P.; Shafer, M.M.; Antkiewicz, D.; Schauer, J.J.; Sioutas, C. Macrophage reactive oxygen species activity of water-soluble and water-insoluble fractions of ambient coarse, PM2.5 and ultrafine particulate matter (pm) in los angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönkkö, T.J.; Jalava, P.I.; Happo, M.S.; Kasurinen, S.; Sippula, O.; Leskinen, A.; Koponen, H.; Kuuspalo, K.; Ruusunen, J.; Väisänen, O.; et al. Emissions and atmospheric processes influence the chemical composition and toxicological properties of urban air particulate matter in Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1290–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Hong, Y.; Pang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L. Seasonally varied cytotoxicity of organic components in PM2.5 from urban and industrial areas of a Chinese megacity. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Nie, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X.; Hu, J.; Ge, P.; Li, W.; Huang, B.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Chemical Characterization of Two Seasonal PM2.5 Samples in Nanjing and Its Toxicological Properties in Three Human Cell Lines. Environments 2019, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Ge, P.; Yuan, Y.; Ge, X. Bioaccessibility and health risk of trace elements in fine participate matter in different simulated body fluids. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 186, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Song, Y.; Ding, Q.; Liao, X.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Tsang, S.; Cai, Z. Water soluble and insoluble components of PM2.5 and their functional cardiotoxicities on neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in vitro. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, D.A.; Ma, Y.; Sullivan, A.; Sierau, B.; Banmann, K.; Weber, R.J. Refinements to the particle-into-liquid sampler (PILS) for ground and airborne measurements of water soluble aerosol composition. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, M. Comparison of water-soluble inorganic ions and trace metals in PM2.5 between online and offline measurements in Beijing during winter. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Song, W.; Hayashi, Y.; Ding, X.; Li, W. In Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Induced by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes in Murine RAW 264.7 Macrophages and Human A549 Lung Cells. Biomed. Environ. Sci. BES 2011, 24, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.K.; Wang, T.; Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C. Characteristics of summertime PM2.5 organic and elemental carbon in four major chinese cities: Implications of high acidity for water-soluble organic carbon (wsoc). Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Tsang, P.K.; Ho, S.S.H.; Zou, C.W.; Zou, S.C.; Cao, J.J.; Xu, H.M. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in PM2.5: Pearl Delta River Region, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Bao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M. Seasonal light absorption properties of water-soluble brown carbon in atmospheric fine particles in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Maggos, T.; Saraga, D.; Petrakakis, M. Organic and elemental carbon associated to PM10 and PM2.5 at urban sites of northern greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 1769–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.Z.; Vasconcellos, P.; Lee, H.; Aurela, M.; Saarnio, K.; Teinilä, K.; Hillamo, R. Composition of PM2.5 and PM10 Collected at Urban Sites in Brazil. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; Ma, S.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, Y.; Su, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Ge, X. Summertime Day-Night Differences of PM2.5 Components (Inorganic Ions, OC, EC, WSOC, WSON, HULIS, and PAHs) in Changzhou, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; Ge, X.; Chen, M. Chemical Characteristics of PM2.5 and Water-Soluble Organic Nitrogen in Yangzhou, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Yin, L. Chemical compositions and extinction coefficients of PM2.5 in peri-urban of Xiamen, China, during June 2009–May 2010. Atmos. Res. 2012, 106, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Chang, X. Analysis of Compositional Variation and Source Characteristics of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 during Several Winter-Haze Pollution Episodes in Shenyang, China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Kong, L.; Cheng, T.; Chen, J.; Du, J.; Li, L.; Xia, X.; Leng, C.; Huang, G. Insights into summertime haze pollution events over Shanghai based on online water-soluble ionic composition of aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5131–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, B.; Huang, X.; Virkkula, A.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Li, C.; et al. The impacts of emission control and regional transport on PM2.5 ions and carbon components in Nanjing during the 2014 Nanjing Youth Olympic Games. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiliro, T.; Bonetta, S.; Alessandria, L.; Gianotti, V.; Carrao, E.; Gilli, G. PM10 in a background urban site: Chemical characteristics and biological effects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 39, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, K.; Iii, D.R.C. Characterization and source identification of trace elements in PM2.5 from mira loma, southern California. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Querol, X.; Amato, F.; Karanasiou, A.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M. Hourly elemental concentrations in PM2.5 aerosols sampled simultaneously at urban background and road site during sapuss—diurnal variations and pmf receptor modelling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4375–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chen, M.D.; Ge, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, B. Seasonal variations and sources of 17 aerosol metal elements in suburban Nanjing, China. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, M.; Mantecca, P.; Corvaja, V.; Longhin, E.; Perrone, M.G.; Bolzacchini, E.; Camatini, M. Winter fine particulate matter from Milan induces morphological and functional alterations in human pulmonary epithelial cells (A549). Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 188, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, M.; Longhin, E.; Mattioli, M.; Mantecca, P.; Tinaglia, V.; Mangano, E.; Proverbio, M.C.; Bestetti, G.; Camatini, M.; Battaglia, C. Gene expression profiling of A549 cells exposed to milan PM2.5. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 209, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Cai, Y. The protection of selenium on ROS mediated-apoptosis by mitochondria dysfunction in cadmium-induced LLC-PK1 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Tian, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Metabolomics analysis reveals heavy metal copper-induced cytotoxicity in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 78445–78456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.; Gualtieri, M.; Ferrero, L.; Porto, C.L.; Udisti, R.; Bolzacchini, E.; Camatini, M. Seasonal variations in chemical composition and in vitro biological effects of fine PM from Milan. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Rui, W.; Bai, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Ding, W. Effects of size-fractionated particulate matter on cellular oxidant radical generation in human bronchial epithelial beas-2b cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, E.Z.; Uski, O.; Nyström, R.; Jalava, P.; Eriksson, A.C.; Genberg, J.; Roldin, P.; Bergvall, C.; Westerholm, R.; Jokiniemi, J.; et al. Influence of ozone initiated processing on the toxicity of aerosol particles from small scale wood combustion. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| R | As | Zn | Pb | Co | Cd | Ni | Mn | Cr | Cu | Al |
| ROS | 0.465 * | 0.863 * | 0.807 * | 0.795 * | 0.794 * | 0.793 * | 0.805 * | 0.797 * | 0.804 * | 0.803 * |
| Apop | 0.295 | 0.675 * | 0.624 * | 0.612 * | 0.612 * | 0.618 * | 0.612 * | 0.611 * | 0.611 * | 0.596 * |
| R | Total Metals | Cl¯ | SO42− | NO3− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | WSOC |
| ROS | 0.773 * | 0.503 * | 0.754 * | 0.708 * | 0.578 * | 0.756 * | 0.824 * | 0.722 * | 0.731 * | 0.737 * |
| Apop | 0.586 * | 0.345 | 0.599 * | 0.514 * | 0.395 | 0.567 * | 0.624 * | 0.574 * | 0.590 * | 0.569 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di, A.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Nie, D.; Ge, X. Chemical Characterization of Seasonal PM2.5 Samples and Their Cytotoxicity in Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124599
Di A, Wu Y, Chen M, Nie D, Ge X. Chemical Characterization of Seasonal PM2.5 Samples and Their Cytotoxicity in Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(12):4599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124599
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi, Ao, Yun Wu, Mindong Chen, Dongyang Nie, and Xinlei Ge. 2020. "Chemical Characterization of Seasonal PM2.5 Samples and Their Cytotoxicity in Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 12: 4599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124599
APA StyleDi, A., Wu, Y., Chen, M., Nie, D., & Ge, X. (2020). Chemical Characterization of Seasonal PM2.5 Samples and Their Cytotoxicity in Human Lung Epithelial Cells (A549). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4599. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124599







