Efficiency of an Air Cleaner Device in Reducing Aerosol Particulate Matter (PM) in Indoor Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
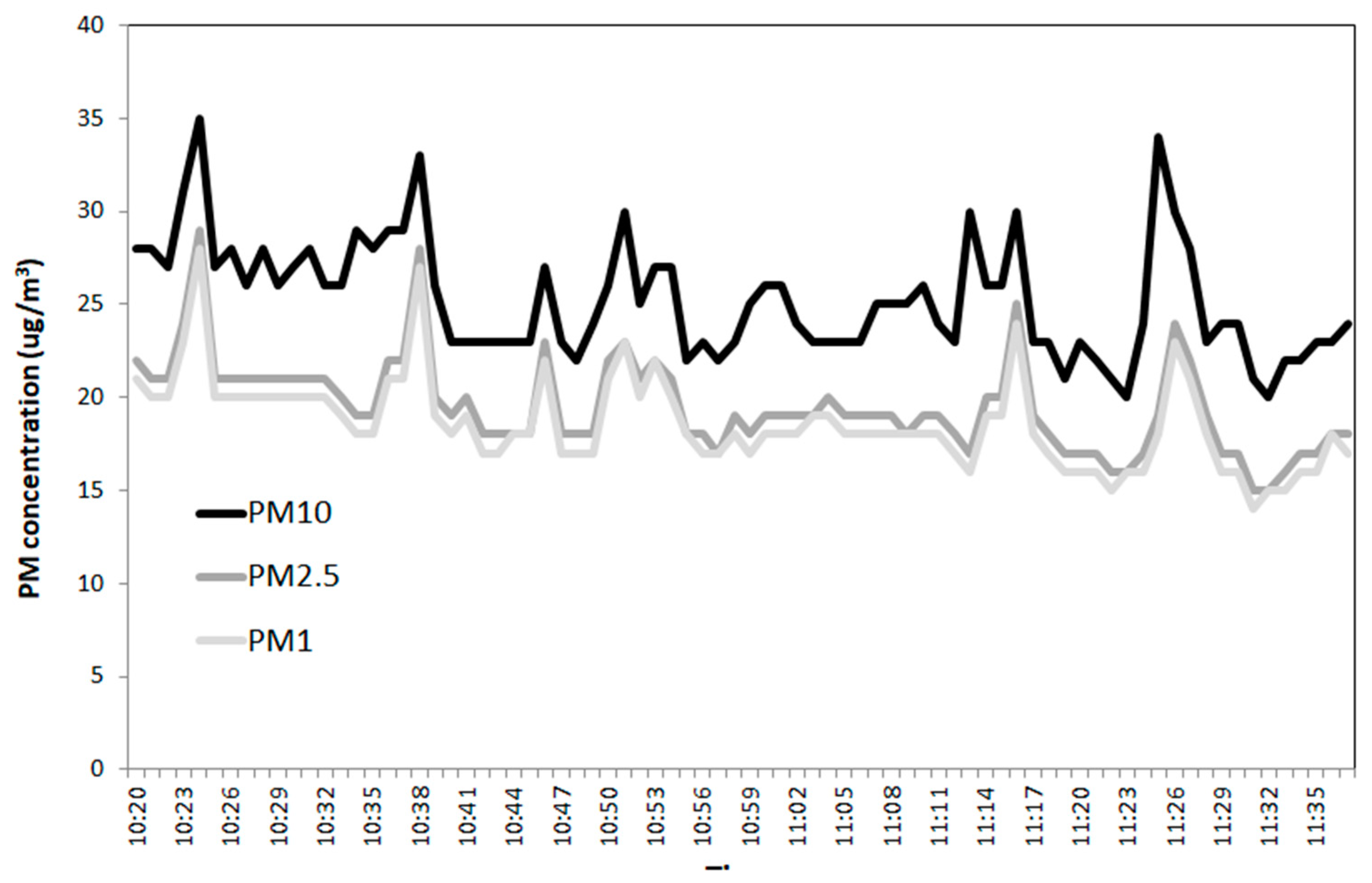
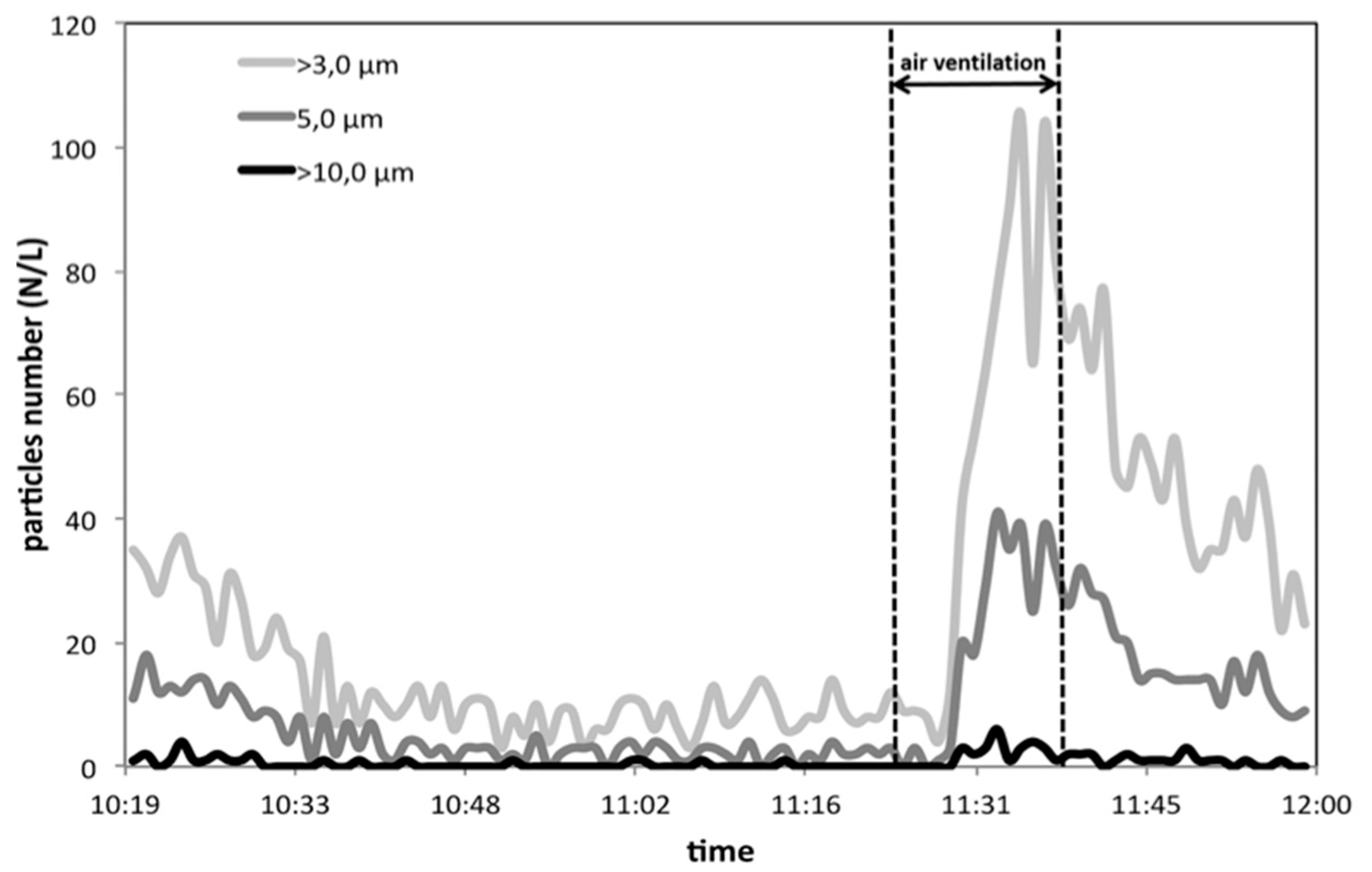
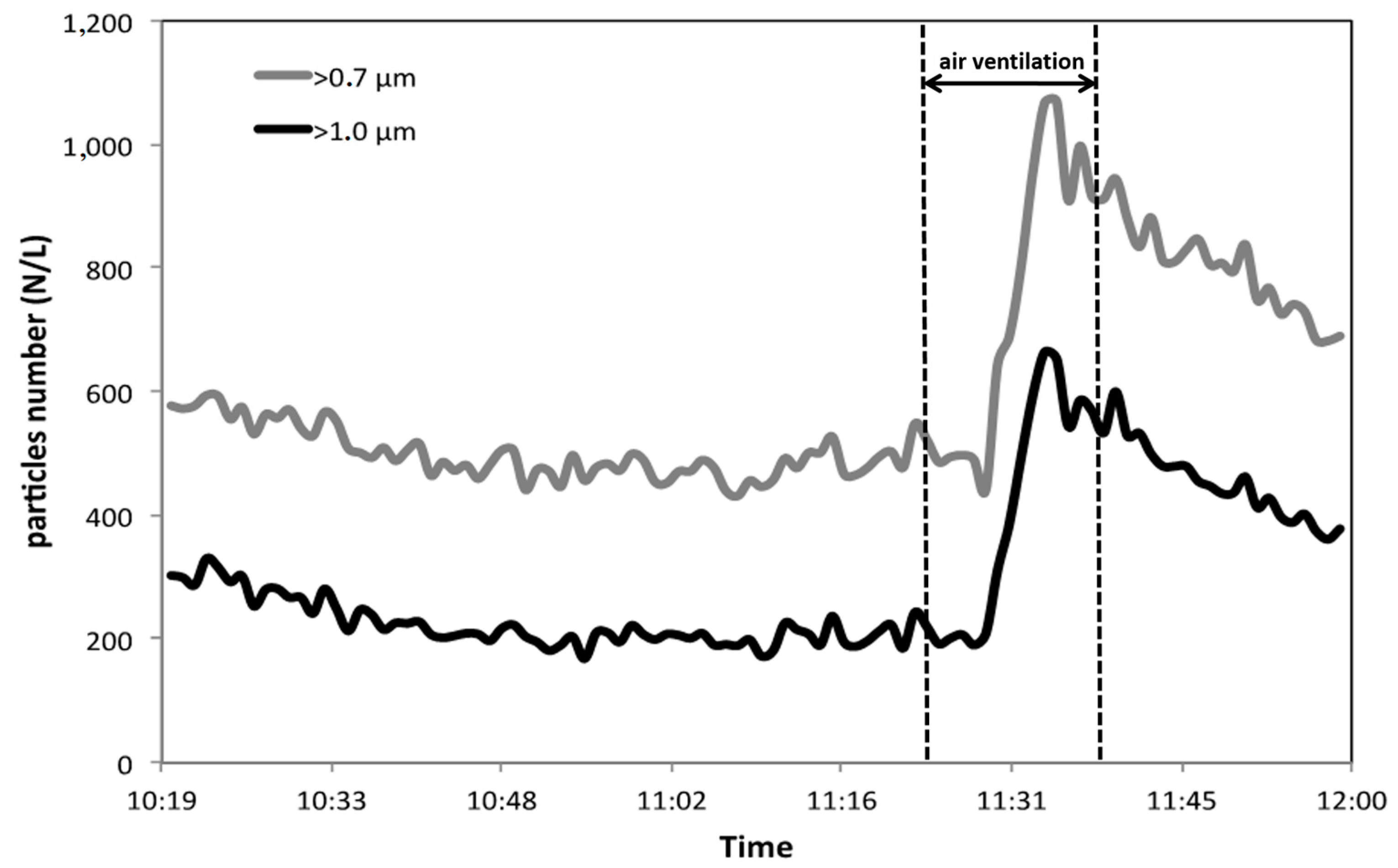
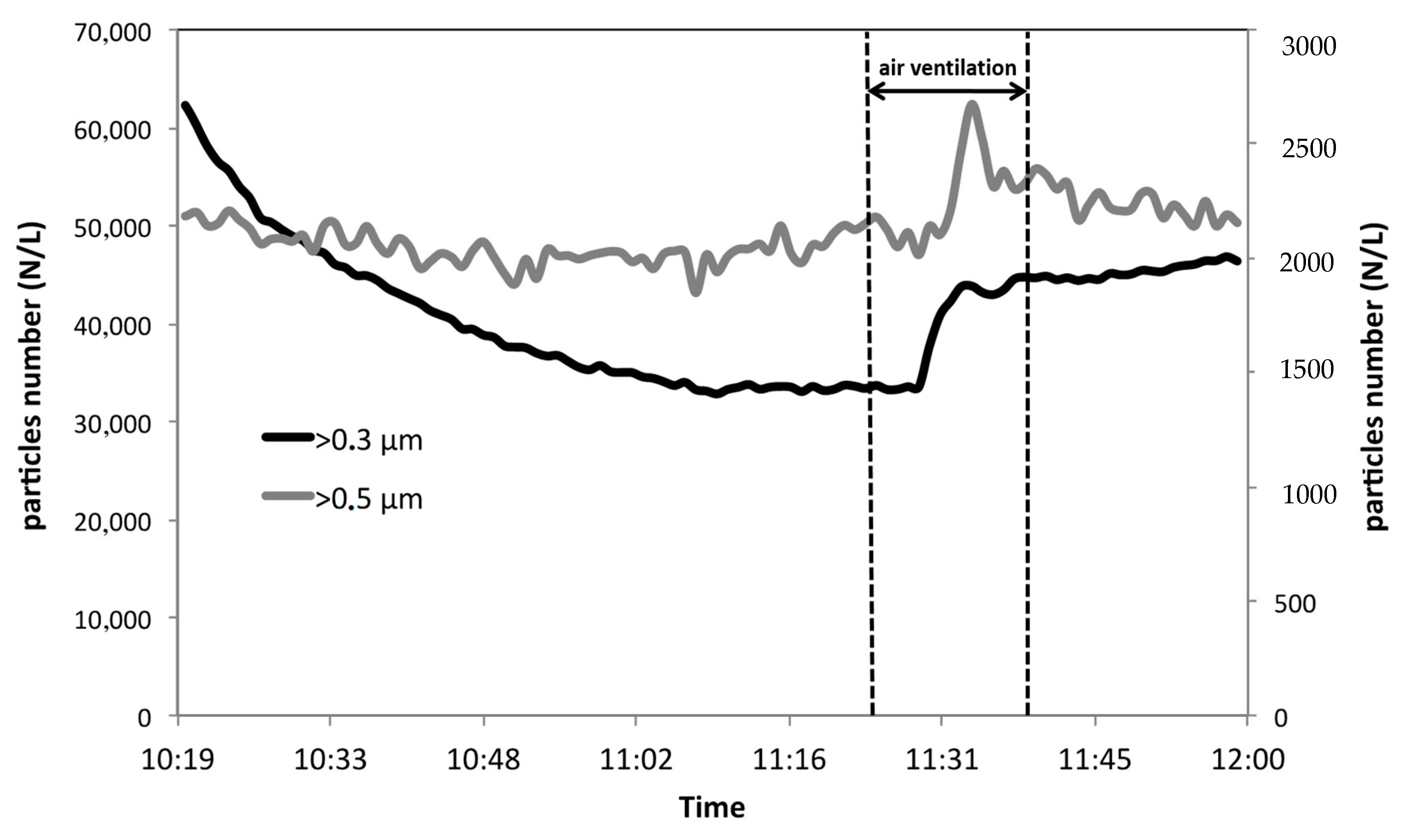
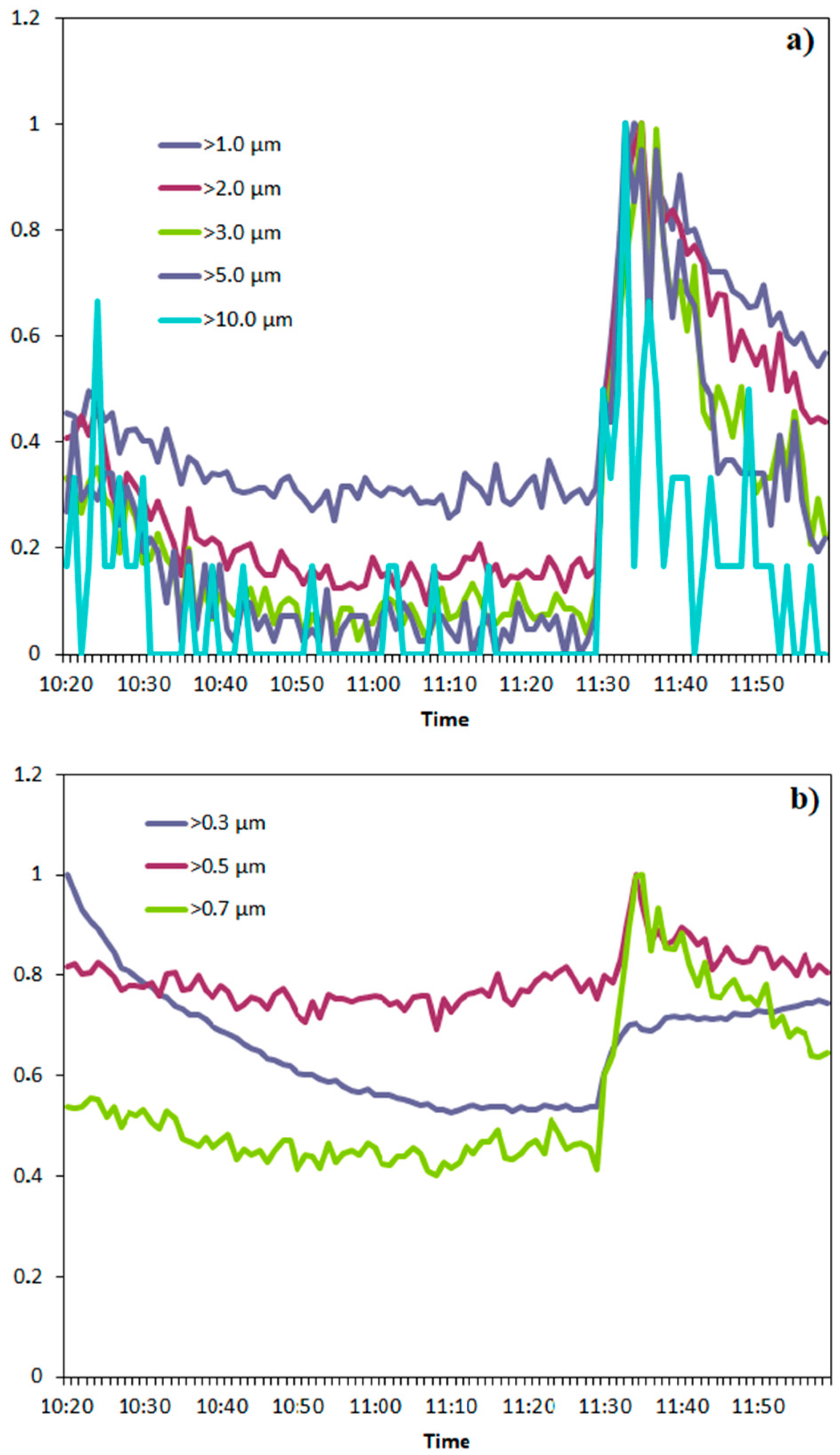
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, L.; Wu, S.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Dong, W.; Shan, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Shima, M.; Deng, F.; et al. The short-term effects of indoor size-fractioned particulate matter and black carbon on cardiac autonomic function in COPD patients. Environ. Int. 2018, 112, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, C.H.; Salehi, S.; Wu, J.; North, M.L.; Kim, J.S.; Chow, C.W.; Evans, G.J. Indoor measurements of air pollutants in residential houses in urban and suburban areas: Indoor versus ambient concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, A.; Matson, U.; Ekberg, L.E. Characterization of indoor sources of fine and ultrafine particles: A study conducted in a full-scale chamber. Indoor Air 2005, 15, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.Y.; Guo, J.J.; Guo, Z.J.; Lan, X. Allergy and Immunology Efficacy of air purifier therapy in allergic rhinitis. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 36, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Johnson, K.; Norris, C.; Shafer, M.M.; Bergin, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Schauer, J.J. The influence of air cleaners on indoor particulate matter components and oxidative potential in residential households in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Env. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, F.; Ashrafi, A.; Kinney, P.; Mills, D. Towards a fuller assessment of benefits to children’s health of reducing air pollution and mitigating climate change due to fossil fuel combustion. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Fermo, P.; Urso, P.; Perrone, M.G.; Piazzalunga, A.; Tarlassi, J.; Carrer, P.; Cavallo, D.M. Particulate-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon sources and determinants in residential homes. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Vecchi, R.; Valli, G.; Ceriani, M. A TGA/FT-IR study for measuring OC and EC in aerosol samples. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daellenbach, K.R.; Bozzetti, C.; Křepelová, A.; Canonaco, F.; Wolf, R.; Zotter, P.; Fermo, P.; Crippa, M.; Slowik, J.G.; Sosedova, Y.; et al. Characterization and source apportionment of organic aerosol using offline aerosol mass spectrometry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daellenbach, K.R.; Stefenelli, G.; Bozzetti, C.; Vlachou, A.; Fermo, P.; Gonzalez, R.; Piazzalunga, A.; Colombi, C.; Canonaco, F.; Hueglin, C.; et al. Long-term chemical analysis and organic aerosol source apportionment at nine sites in central Europe: Source identification and uncertainty assessment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13265–13282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzetti, C.; El Haddad, I.; Salameh, D.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Fermo, P.; Gonzalez, R.; Minguillón, M.C.; Iinuma, Y.; Poulain, L.; Elser, M.; et al. Organic aerosol source apportionment by offline-AMS over a full year in Marseille. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8247–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccia, E.; Massabò, D.; Ariola, V.; Bove, M.C.; Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Prati, P. Size-resolved comprehensive characterization of airborne particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassura, I.; Venturini, E.; Marchetti, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; Bernardi, E.; Fermo, P.; Passarini, F. Markers and influence of open biomass burning on atmospheric particulate size and composition during a major bonfire event. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, M.C.; Brotto, P.; Calzolai, G.; Cassola, F.; Cavalli, F.; Fermo, P.; Hjorth, J.; Massabò, D.; Nava, S.; Piazzalunga, A.; et al. PM10 source apportionment applying PMF and chemical tracer analysis to ship-borne measurements in the Western Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Morisaki, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.; Hu, M.; Shima, M.; et al. Characteristics of air pollutants inside and outside a primary school classroom in Beijing and respiratory health impact on children. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonniaux, E.; Mailleux, A.C. House Dust Mites Avoidance and Allergic Children: A Prospective Study of a New Strategy. J. Allergy Ther. 2014, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinoi, A.; Donateo, A.; Conte, M.; Contini, D.; Belosi, F. Comparison of atmospheric particle concentration measurements using different optical detectors: Potentiality and limits for air quality applications. Measurement 2017, 106, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuraimi, M.S.; Vuotari, M.; Nilsson, G.; Magee, R.; Kemery, B.; Alliston, C. Impact of dust loading on long term portable air cleaner performance. Build. Environ. 2017, 112, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Thompson, D.; Chang, D.; Chen, S.; Pui, D.Y.H. Separation and Purification Technology Filtration efficiency and loading characteristics of PM 2.5 through commercial electret filter media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, C.; Cuccia, E.; Dal Santo, U. Progetto Supersiti: La stazione di Milano Via Pascal. Available online: https://www.arpalombardia.it/sites/DocumentCenter/Documents/Aria%20-%20Progetto%20Superstiti/RMM_Milano_20181231.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2019).
- Cho, Y.S.; Lee, J.T.; Jung, C.H.; Chun, Y.S.; Kim, Y.S. Relationship between particulate matter measured by optical particle counter and mortality in Seoul, Korea, during 2001. J. Environ. Health 2008, 71, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lonati, G.; Crippa, M.; Gianelle, V.; Van Dingenen, R. Daily patterns of the multi-modal structure of the particle number size distribution in Milan, Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fermo, P.; Comite, V.; Falciola, L.; Guglielmi, V.; Miani, A. Efficiency of an Air Cleaner Device in Reducing Aerosol Particulate Matter (PM) in Indoor Environments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010018
Fermo P, Comite V, Falciola L, Guglielmi V, Miani A. Efficiency of an Air Cleaner Device in Reducing Aerosol Particulate Matter (PM) in Indoor Environments. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleFermo, Paola, Valeria Comite, Luigi Falciola, Vittoria Guglielmi, and Alessandro Miani. 2020. "Efficiency of an Air Cleaner Device in Reducing Aerosol Particulate Matter (PM) in Indoor Environments" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010018
APA StyleFermo, P., Comite, V., Falciola, L., Guglielmi, V., & Miani, A. (2020). Efficiency of an Air Cleaner Device in Reducing Aerosol Particulate Matter (PM) in Indoor Environments. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010018