Acute Limb Ischemia after Intake of the Phenylethylamine Derivate NBOMe
Abstract
1. Introduction
Case Presentation
2. Methods
2.1. Routine Medical and Clinical Diagnostics
2.2. NBOMe Sample Analysis
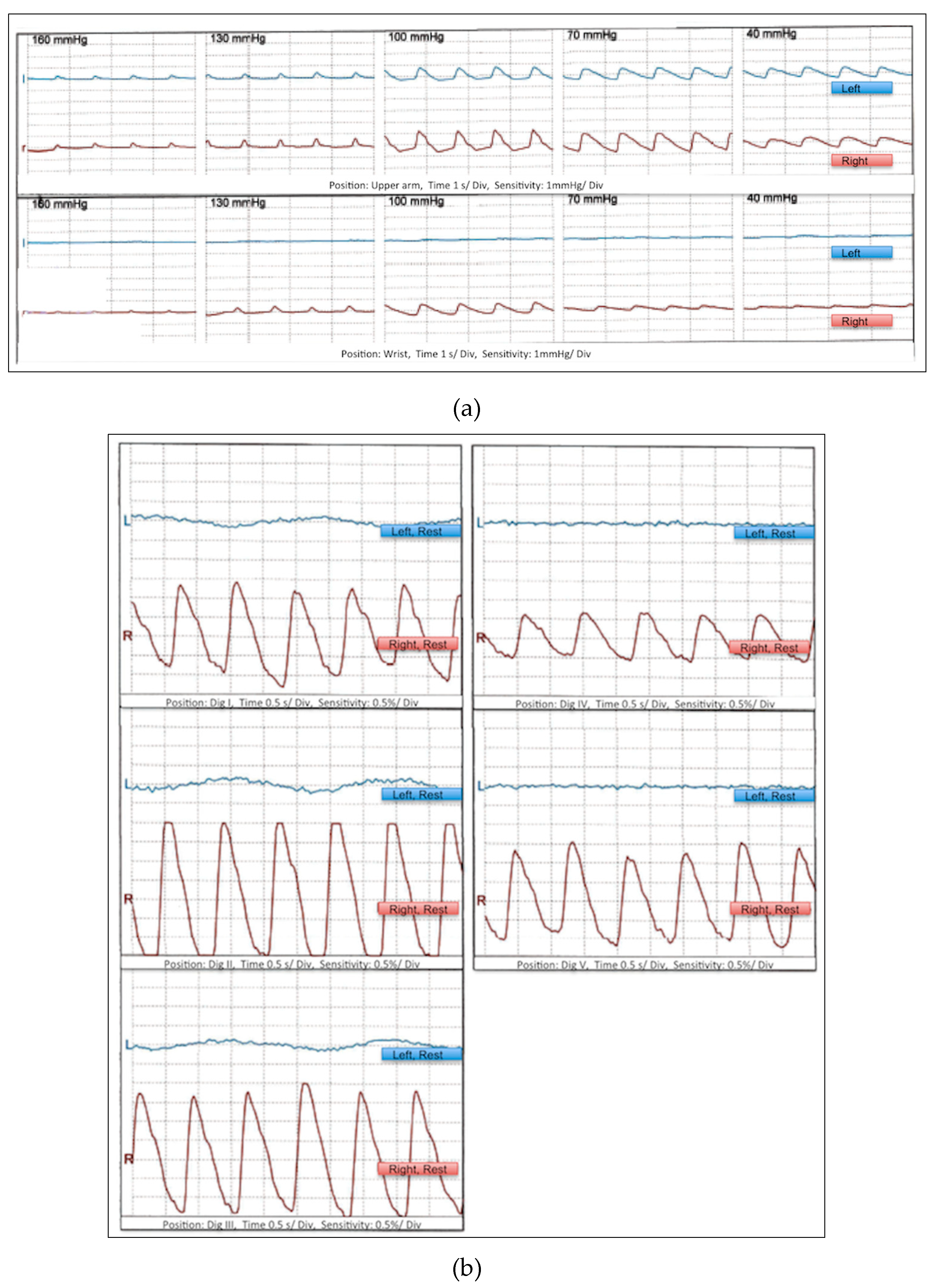
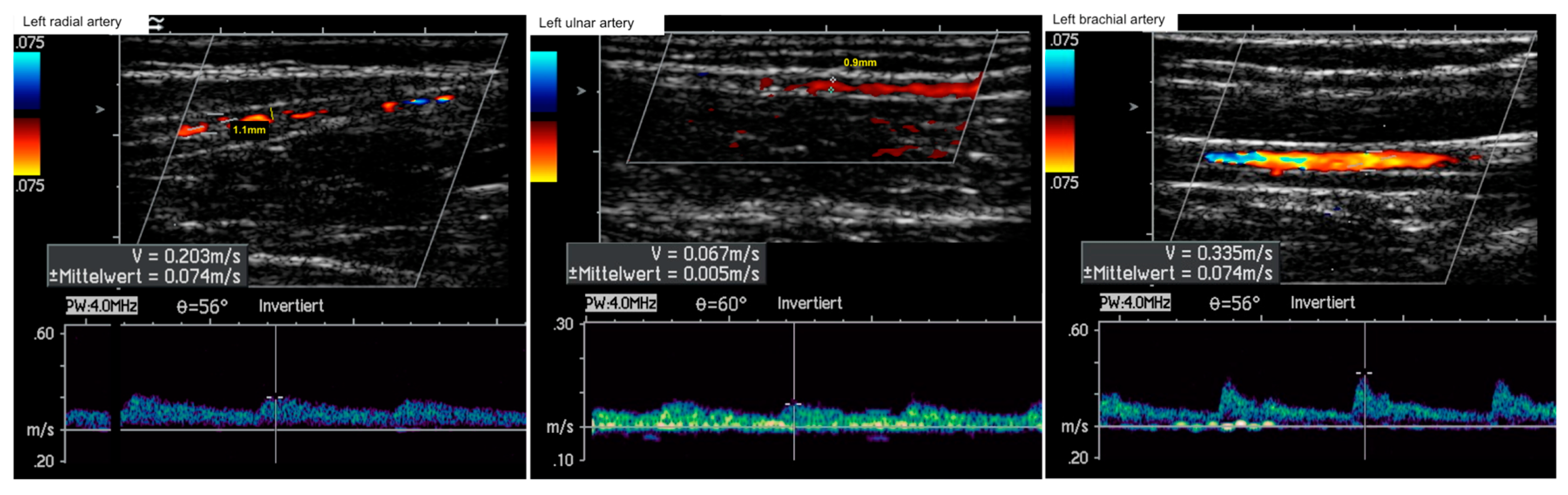
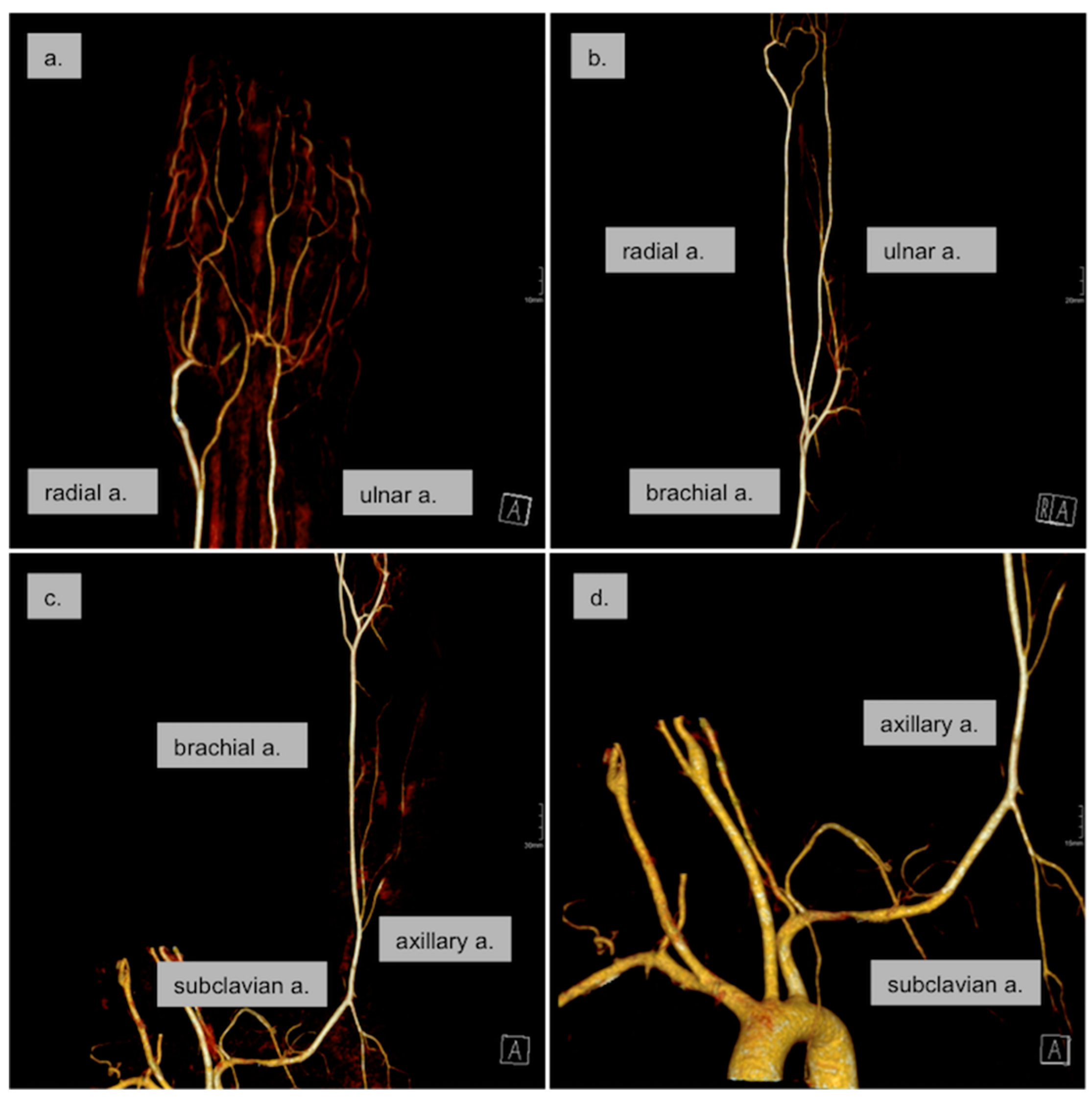
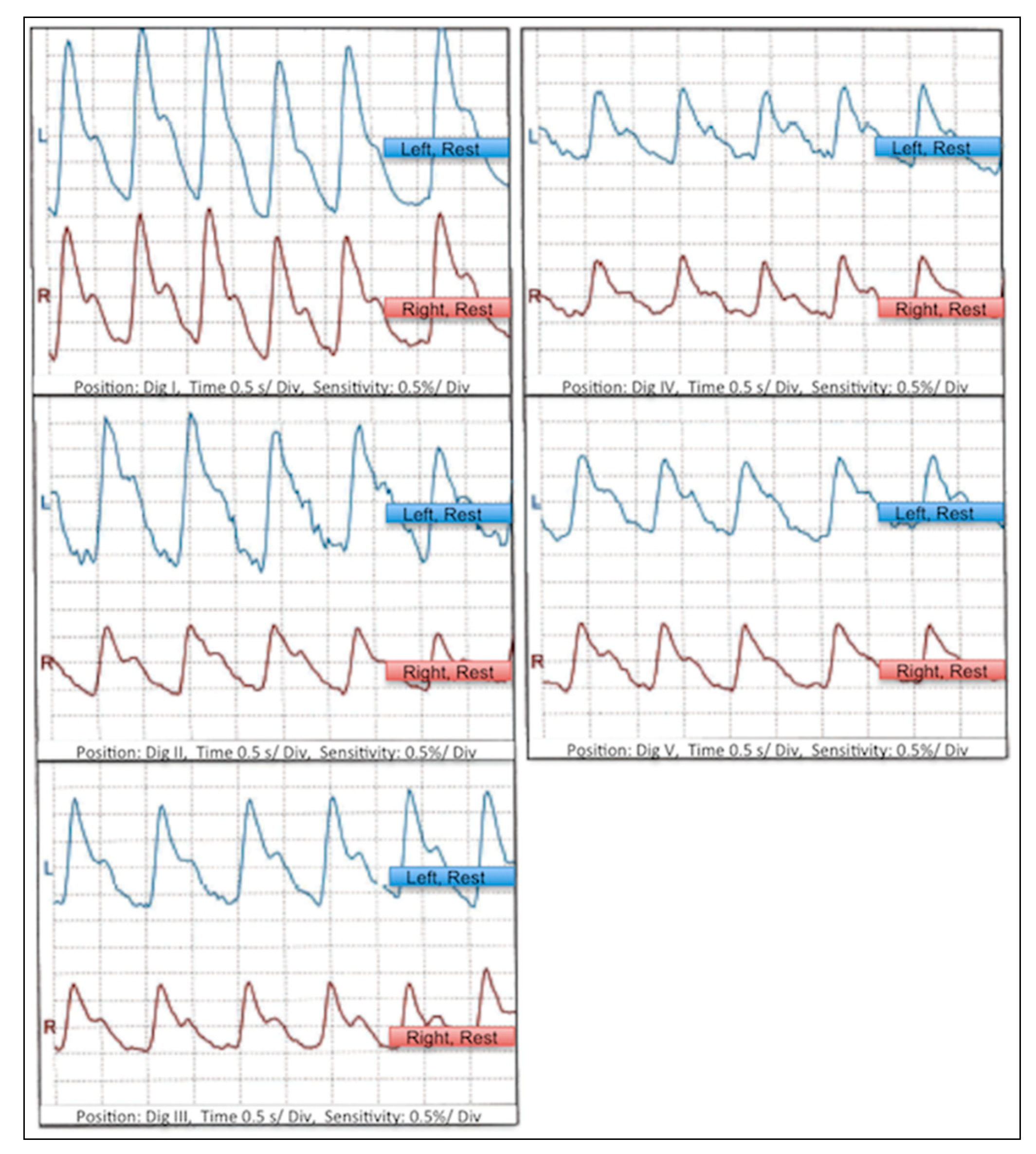
3. Results
3.1. Routine Medical and Clinical Diagnostics
3.2. NBOMe Sample Analysis
- Sample 1: 25I-NBOMe—923 mg/g, 25C-NBOMe—17 mg/g, 25H-NBOMe—16 mg/g and traces of the substance pentylon.
- Sample 2: 25I-NBOMe—914 mg/g, 25C-NBOMe—20 mg/g, 25H-NBOMe—16 mg/g.
- Sample 3: 25I-NBOMe—941 mg/g, 25C-NBOMe—23 mg/g, 25H-NBOMe—20 mg/g.
- Sample 4: 25I-NBOMe—951 mg/g, 25C-NBOMe—22 mg/g, 25H-NBOMe—19 mg/g.
3.3. Therapeutic Measures and Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wohlfarth, A.; Roman, M.; Andersson, M.; Kugelberg, F.C.; Diao, X.; Carlier, J.; Eriksson, C.; Wu, X.; Konradsson, P.; Josefsson, M.; et al. 25C-NBOMe and 25I-NBOMe metabolite studies in human hepatocytes, in vivo mouse and human urine with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 9, 680–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braden, M.R.; Parrish, J.C.; Naylor, J.C.; Nichols, D.E. Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halberstadt, A.L.; Geyer, M.A. Effects of the hallucinogen 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (2C-I) and superpotent N-benzyl derivatives on the head twitch response. Neuropharmacology 2014, 77, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, J.; Dekker, M.A.; Valenti, E.S.; Cruz, F.A.A.; Correa, A.M.; Poklis, J.L.; Poklis, A. Toxicities associated with NBOMe ingestion-a novel class of potent hallucinogens: A review of the literature. Psychosomatics 2015, 56, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersani, F.S.; Corazza, O.; Albano, G.; Valeriani, G.; Santacroce, R.; Bolzan Mariotti Posocco, F.; Cinosi, E.; Simonato, P.; Martinotti, G.; Bersani, G.; et al. 25C-NBOMe: Preliminary data on pharmacology, psychoactive effects, and toxicity of a new potent and dangerous hallucinogenic drug. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 734749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, M.F.; Telving, R.; Rosendal, I.; Eg, M.B.; Hasselstrom, J.B.; Andersen, L.V. A fatal poisoning involving 25C-NBOMe. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 251, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristofic, J.J.; Chmiel, J.D.; Jackson, G.F.; Vorce, S.P.; Holler, J.M.; Robinson, S.L.; Bosy, T.Z. Detection of 25C-NBOMe in Three Related Cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 40, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostermann, K.M.; Luf, A.; Lutsch, N.M.; Dieplinger, R.; Mechtler, T.P.; Metz, T.F.; Schmid, R.; Kasper, D.C. MALDI Orbitrap mass spectrometry for fast and simplified analysis of novel street and designer drugs. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 433, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbir-Gurman, A.; Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Nahir, A.M. Cocaine-Induced raynaud’s phenomenon and ischaemic finger necrosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2001, 20, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, A.; England, J.D.; Krupski, W.C. Cocaine-induced peripheral vascular occlusive disease--a case report. Angiology 1998, 49, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaumann, A.J.; Levy, F.O. 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in the human cardiovascular system. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 674–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadley, K.J. The vascular effects of trace amines and amphetamines. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 125, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigley, F.M.; Flavahan, N.A. Raynaud’s Phenomenon. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dipasquale, S.; Pariante, C.M.; Dazzan, P.; Aguglia, E.; McGuire, P.; Mondelli, V. The dietary pattern of patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinty, E.E.; Baller, J.; Azrin, S.T.; Juliano-Bult, D.; Daumit, G.L. Interventions to Address Medical Conditions and Health-Risk Behaviors Among Persons With Serious Mental Illness: A Comprehensive Review. Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 42, 96–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.J.; Reynolds, G.P.; Barnes, T.R.E.; England, E.; Haddad, P.M.; Heald, A.; Holt, R.I.G.; Lingford-Hughes, A.; Osborn, D.; McGowan, O. BAP guidelines on the management of weight gain, metabolic disturbances and cardiovascular risk associated with psychosis and antipsychotic drug treatment. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 717–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, E.; Yesufu-Udechuku, A.; Taylor, C.; Kendall, T. Management of psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: Summary of updated NICE guidance. BMJ 2014, 348, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speyer, H.; Jakobsen, A.S.; Westergaard, C.; Nørgaard, H.C.B.; Pisinger, C.; Krogh, J.; Hjorthøj, C.; Nordentoft, M.; Gluud, C.; Correll, C.U.; et al. Lifestyle Interventions for Weight Management in People with Serious Mental Illness: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis, Trial Sequential Analysis, and Meta-Regression Analysis Exploring the Mediators and Moderators of Treatment Effects. Psychother. Psychosom. 2019, 88, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wadowski, P.P.; Giurgea, G.-A.; Schlager, O.; Luf, A.; Gremmel, T.; Hobl, E.-L.; Unterhumer, S.; Löffler-Stastka, H.; Koppensteiner, R. Acute Limb Ischemia after Intake of the Phenylethylamine Derivate NBOMe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245071
Wadowski PP, Giurgea G-A, Schlager O, Luf A, Gremmel T, Hobl E-L, Unterhumer S, Löffler-Stastka H, Koppensteiner R. Acute Limb Ischemia after Intake of the Phenylethylamine Derivate NBOMe. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(24):5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245071
Chicago/Turabian StyleWadowski, Patricia P., Georgiana-Aura Giurgea, Oliver Schlager, Anton Luf, Thomas Gremmel, Eva-Luise Hobl, Sylvia Unterhumer, Henriette Löffler-Stastka, and Renate Koppensteiner. 2019. "Acute Limb Ischemia after Intake of the Phenylethylamine Derivate NBOMe" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 24: 5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245071
APA StyleWadowski, P. P., Giurgea, G.-A., Schlager, O., Luf, A., Gremmel, T., Hobl, E.-L., Unterhumer, S., Löffler-Stastka, H., & Koppensteiner, R. (2019). Acute Limb Ischemia after Intake of the Phenylethylamine Derivate NBOMe. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(24), 5071. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245071





