Measurements of Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter at Belgrade Tunnel; Comparison of BPEAnit, DTT and DCFH Assays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
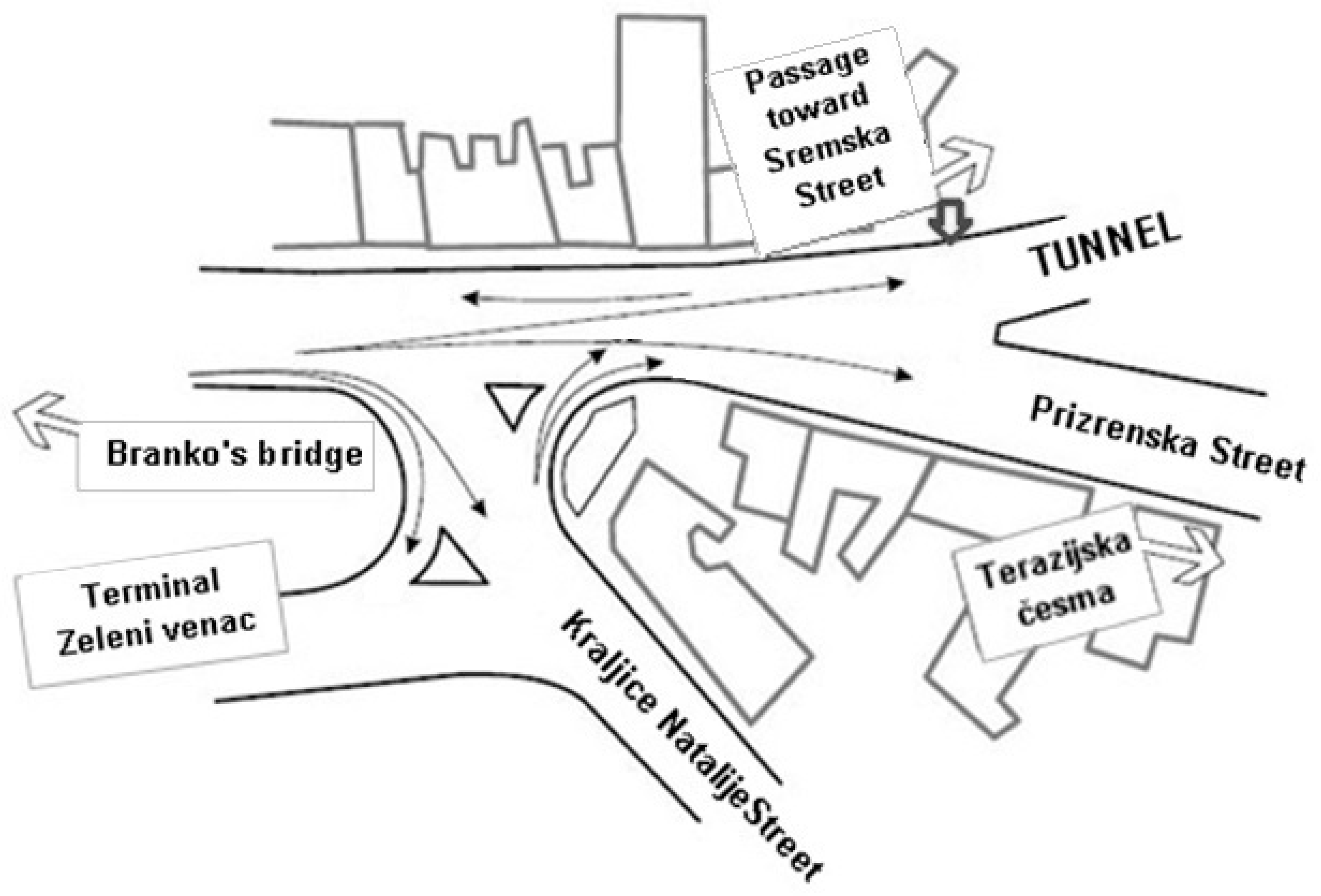
2.1. Sampling Locations
2.2. PM Collection
2.3. PM Mass Contraction
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.4.1. Carbon Analysis
2.4.2. WSOC Analysis
2.5. OP Measurements
2.5.1. DTT Assay
2.5.2. DCFH-DA Assay
2.5.3. The Profluorescent BPEA Nitroxide Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
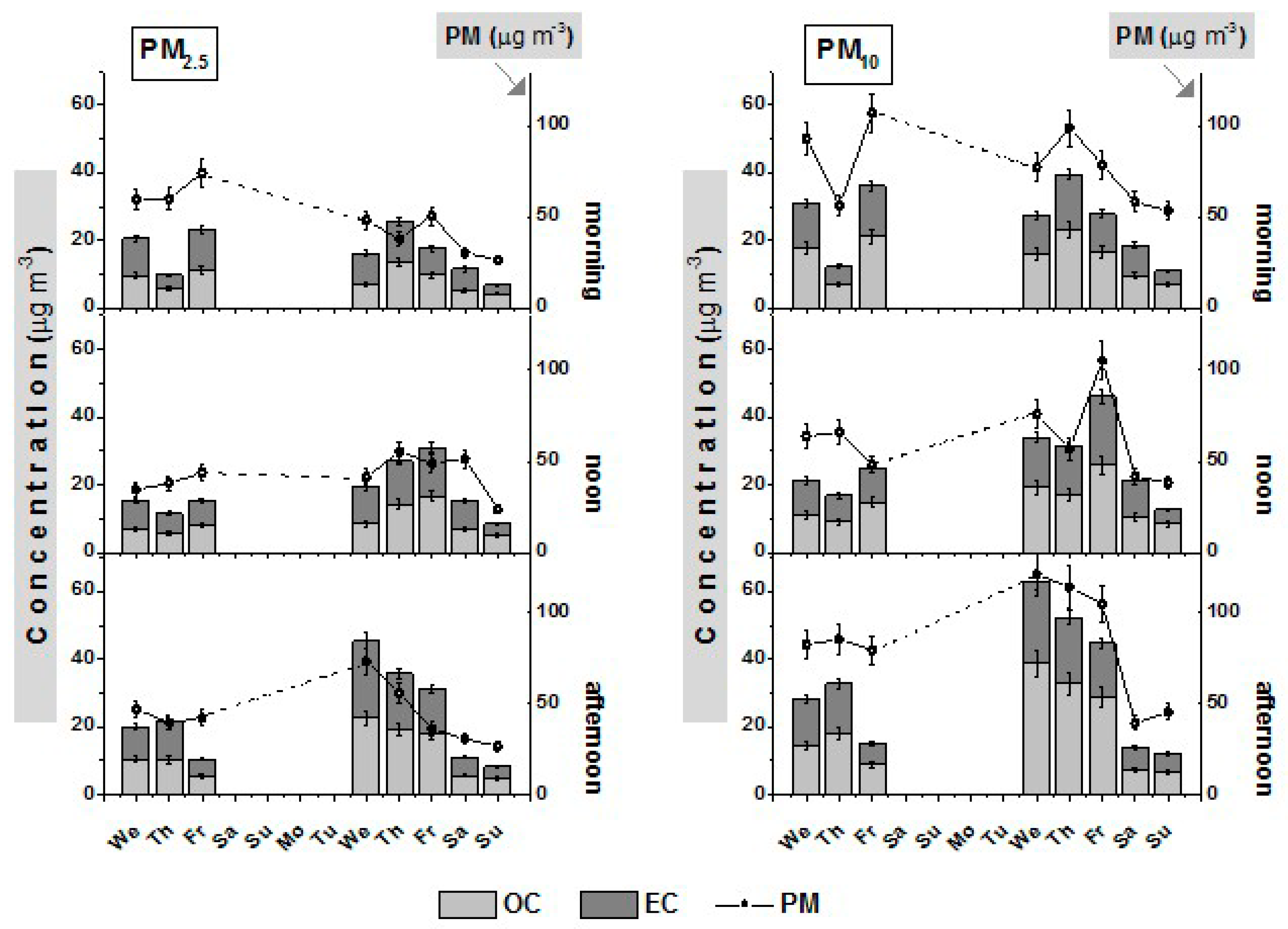
3.1. OC, EC and TC Concentrations
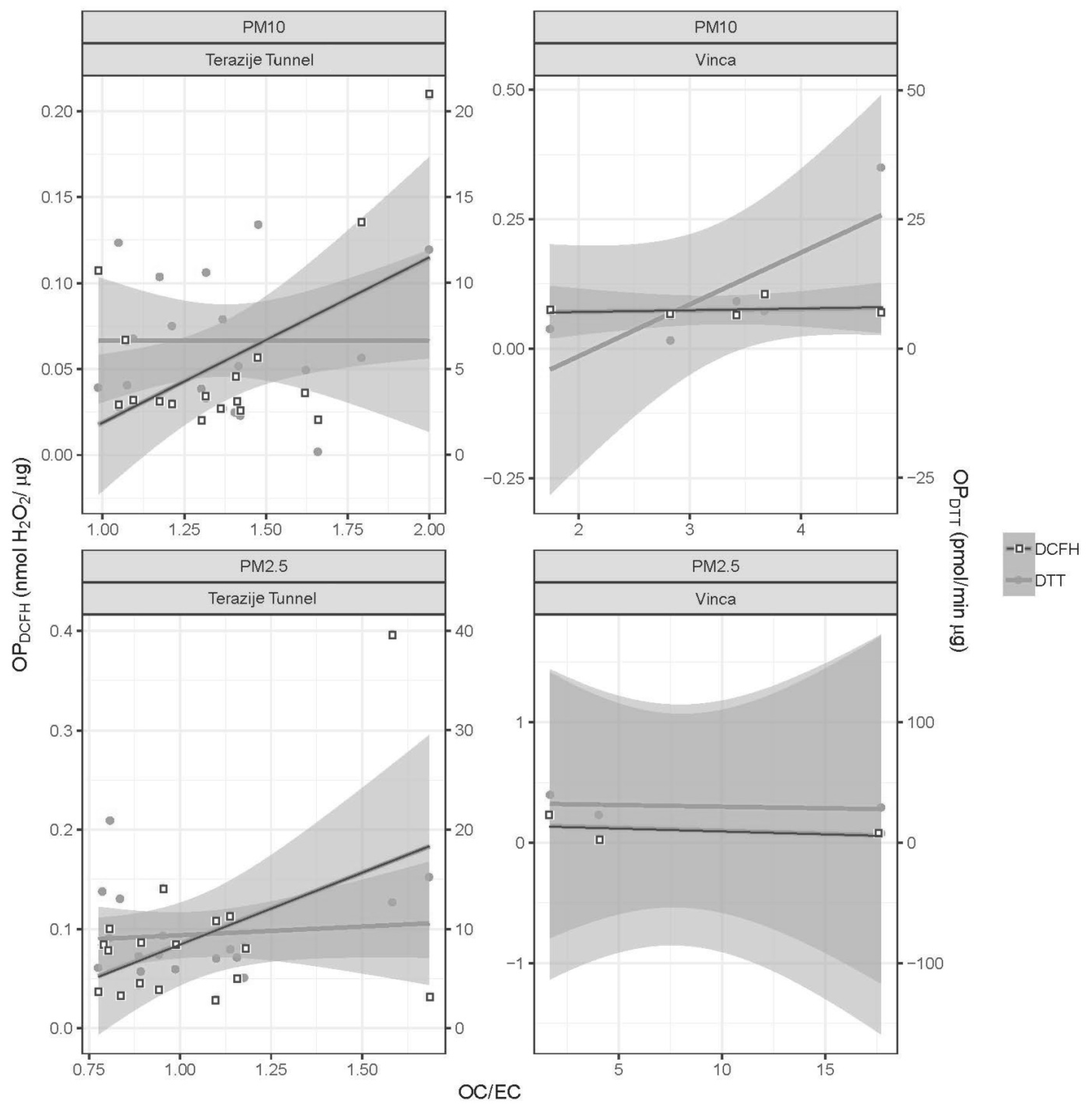
3.2. OPDTT and OPDCFH Measurements and Their Correlation with PM Components (OC, EC and WSOC)
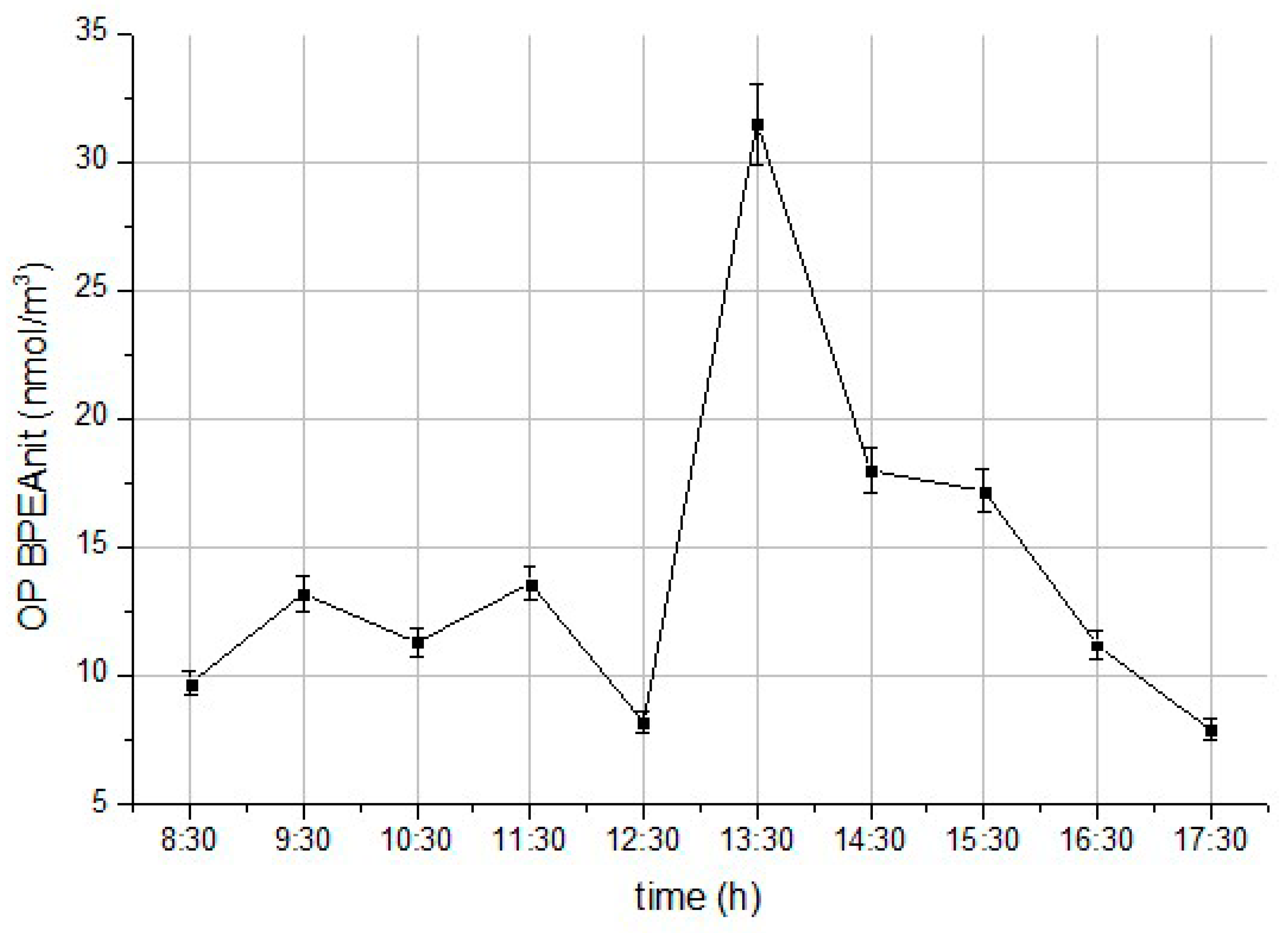
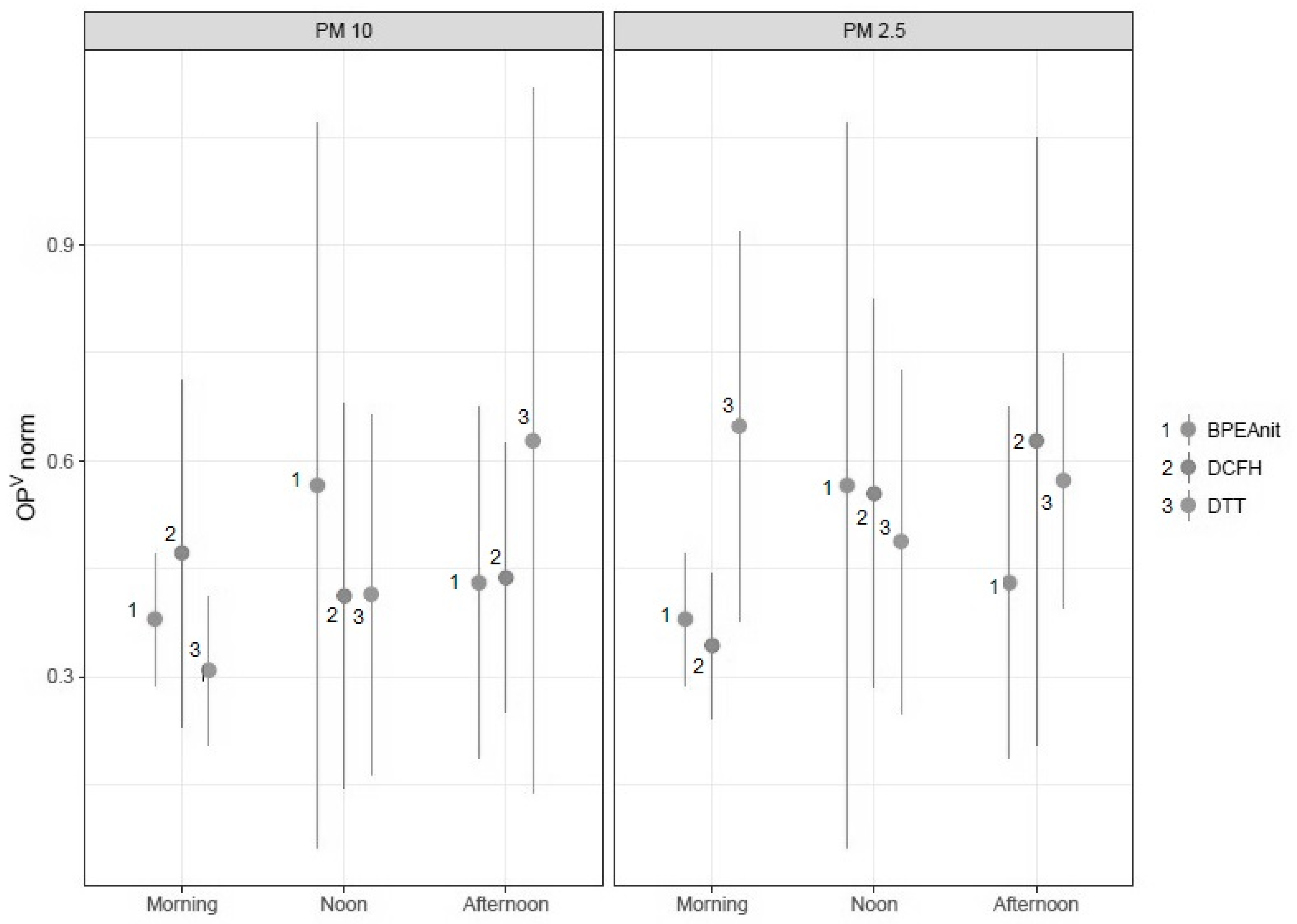
3.3. Diurnal OP Profiles at the Busy Urban Site Measured by BPEAnit
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide: Global Update 2005: Summary of Risk Assessment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Stieb, D.M.; Judek, S.; Burnett, R.T. Meta-analysis of time-series studies of air pollution and mortality: Effects of gases and particles and the influence of cause of death, age, and season. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinwood, A.L.; De Klerk, N.; Rodriguez, C.; Jacoby, P.; Runnion, T.; Rye, P.; Landau, L.; Murray, F.; Feldwick, M.; Spickett, J. The relationship between changes in daily air pollution and hospitalizations in Perth, Australia 1992–1998: A case-crossover study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2006, 16, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, A.C.; Arbour, L. The shared pathoetiological effects of particulate air pollution and the social environment on fetal-placental development. J. Environ. Public Health 2014, 2014, 901017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.C.; Talbott, E.O.; Roberts, J.M.; Catov, J.M.; Bilonick, R.A.; Stone, R.A.; Sharma, R.K.; Ritz, B. Ambient air pollution exposure and blood pressure changes during pregnancy. Environ. Res. 2012, 117, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Stevanovic, S.; Ristovski, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Particle exposure level and potential health risks of domestic Chinese cooking. Build. Environ. 2017, 123, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borm, P.J.; Kelly, F.; Kunzli, N.; Schins, R.P.; Donaldson, K. Oxidant generation by particulate matter: From biologically effective dose to a promising, novel metric. Occup. Environ. Med. 2007, 64, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.T.; Brook, J.; Dann, T.; Delocla, C.; Philips, O.; Cakmak, S.; Vincent, R.; Goldberg, M.S.; Krewski, D. Association between particulate- and gas-phase components of urban air pollution and daily mortality in eight Canadian cities. Inhalation Toxicol. 2000, 12 (Suppl. 4), 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mates, J.M. Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology 2000, 153, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Whiteman, M. Measuring reactive species and oxidative damage in vivo and in cell culture: How should you do it and what do the results mean? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.T.; Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Zeng, L.; Weber, R.J.; Tolbert, P.E.; Abrams, J.Y.; Sarnat, S.E.; Klein, M.; Mulholland, J.A.; et al. Review of Acellular Assays of Ambient Particulate Matter Oxidative Potential: Methods and Relationships with Composition, Sources, and Health Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4003–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellack, B.; Nickel, C.; Albrecht, C.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Boland, S.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Wohlleben, W.; Schins, R.P.F. Analytical methods to assess the oxidative potential of nanoparticles: A review. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1920–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, S.; Ristovski, Z.D.; Miljevic, B.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Bottle, S.E. Application of Profluorescent Nitroxides for Measurements of Oxidative Capacity of Combustion Generated Particles. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2012, 18, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ayres, J.G.; Borm, P.; Cassee, F.R.; Castranova, V.; Donaldson, K.; Ghio, A.; Harrison, R.M.; Hider, R.; Kelly, F.; Kooter, I.M.; et al. Evaluating the toxicity of airborne particulate matter and nanoparticles by measuring oxidative stress potential-a workshop report and consensus statement. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 20, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrier, J.G.; Anastasio, C. On dithiothreitol (DTT) as a measure of oxidative potential for ambient particles: Evidence for the importance of soluble transition metals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 11317–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Froines, J.R.; Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C. Relationship between redox activity and chemical speciation of size-fractionated particulate matter. Part. Fibre Toxicol 2007, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Verma, V.; Schauer, J.J.; Cassee, F.R.; Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C. Oxidative potential of semi-volatile and non volatile particulate matter (PM) from heavy-duty vehicles retrofitted with emission control technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3905–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachari, P.; Hopke, P.K. Development and Laboratory Testing of an Automated Monitor for the Measurement of Atmospheric Particle-Bound Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein as a fluorescent probe for reactive oxygen species measurement: Forty years of application and controversy. Free Radic. Res. Commun. 2010, 44, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Joseph, J.A. Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, S.; Miljevic, B.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Bottle, S.E.; Ristovski, Z.D.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E. The Use of a Nitroxide Probe in DMSO to Capture Free Radicals in Particulate Pollution. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5908–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, S.; Vaughan, A.; Hedayat, F.; Salimi, F.; Rahman, M.M.; Zare, A.; Brown, R.A.; Brown, R.J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Oxidative potential of gas phase combustion emissions—An underestimated and potentially harmful component of air pollution from combustion processes. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 158, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.S.; Siegel, J.A.; Kinney, K.A. Technical Note: Particulate reactive oxygen species concentrations and their association with environmental conditions in an urban, subtropical climate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6777–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, N.A.; Yang, A.; Strak, M.; Steenhof, M.; Hellack, B.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Kuhlbusch, T.; Kelly, F.; Harrison, R.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Oxidative potential of particulate matter collected at sites with different source characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudway, I.S.; Stenfors, N.; Duggan, S.T.; Roxborough, H.; Zielinski, H.; Marklund, S.L.; Blomberg, A.; Frew, A.J.; Sandstrom, T.; Kelly, F.J. An in vitro and in vivo investigation of the effects of diesel exhaust on human airway lining fluid antioxidants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 423, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Su, S.; Jin, W.; Wang, B.; Li, N.; Shen, H.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Characteristics and cellular effects of ambient particulate matter from Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 191, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljevic, B.; Hedayat, F.; Stevanovic, S.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Bottle, S.E.; Ristovski, Z.D. To Sonicate or Not to Sonicate PM Filters: Reactive Oxygen Species Generation Upon Ultrasonic Irradiation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenhof, M.; Gosens, I.; Strak, M.; Godri, K.J.; Hoek, G.; Cassee, F.R.; Mudway, I.S.; Kelly, F.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Lebret, E.; et al. In vitro toxicity of particulate matter (PM) collected at different sites in the Netherlands is associated with PM composition, size fraction and oxidative potential—The RAPTES project. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.-F.; Wang, C.-S. Experimental determination of reactive oxygen species in Taipei aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, S.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Balasubramanian, R. Contrasting reactive oxygen species and transition metal concentrations in combustion aerosols. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachari, P.; Hopke, P.K.; Brune, W.H.; Ren, X.; Lesher, R.; Mao, J.; Mitchell, M. Characterization of Wintertime Reactive Oxygen Species Concentrations in Flushing, New York. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simonetti, G.; Conte, E.; Perrino, C.; Canepari, S. Oxidative potential of size-segregated PM in an urban and an industrial area of Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calas, A.; Uzu, G.; Kelly, F.J.; Houdier, S.; Martins, J.M.F.; Thomas, F.; Molton, F.; Charron, A.; Dunster, C.; Oliete, A.; et al. Comparison between five acellular oxidative potential measurement assays performed with detailed chemistry on PM10 samples from the city of Chamonix (France). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7863–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, S.J.; Wragg, F.P.H.; Nutter, J.; Kalberer, M. Comparison of on-line and off-line methods to quantify reactive oxygen species (ROS) in atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, M.E.; Cary, R.A. Elemental Carbon-Based Method for Monitoring Occupational Exposures to Particulate Diesel Exhaust. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1996, 25, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, H.J.; Saarikoski, S.K.; Aurela, M.A.; Saarnio, K.M.; Hillamo, R.E.J. Water-soluble organic carbon in urban aerosol: Concentrations, size distributions and contribution to particulate matter. Boreal Environ. Res. 2008, 13, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, A.K.; Sioutas, C.; Miguel, A.H.; Kumagai, Y.; Schmitz, D.A.; Singh, M.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Froines, J.R. Redox activity of airborne particulate matter at different sites in the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyer, P.; Worek, F.; Kiderlen, D.; Sinko, G.; Stuglin, A.; Simeon-Rudolf, V.; Reiner, E. Molar absorption coefficients for the reduced Ellman reagent: Reassessment. Anal. Biochem. 2003, 312, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, D.A.; Ma, Y.; Sullivan, A.; Sierau, B.; Baumann, K.; Weber, R.J. Refinements to the particle-into-liquid sampler (PILS) for ground and airborne measurements of water soluble aerosol composition. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1243–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanovic, S.; Miljevic, B.; Surawski, N.C.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Bottle, S.E.; Brown, R.; Ristovski, Z.D. Influence of Oxygenated Organic Aerosols (OOAs) on the Oxidative Potential of Diesel and Biodiesel Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7655–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sioutas, C.; Cho, A.; Schmitz, D.; Misra, C.; Sempf, J.; Wang, M.; Oberley, T.; Froines, J.; Nel, A. Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Polidori, A.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Cassee, F.R.; Sioutas, C. Physicochemical and Toxicological Profiles of Particulate Matter in Los Angeles during the October 2007 Southern California Wildfires. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentin, M.; Pagnoni, A.; Sarti, E.; Pietrogrande, M.C. Urban PM2.5 oxidative potential: Importance of chemical species and comparison of two spectrophotometric cell-free assays. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, M.G.; Zhou, J.; Malandrino, M.; Sangiorgi, G.; Rizzi, C.; Ferrero, L.; Dommen, J.; Bolzacchini, E. PM chemical composition and oxidative potential of the soluble fraction of particles at two sites in the urban area of Milan, Northern Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadi, F.; Hasheminassab, S.; Wang, D.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Delfino, R.J.; Sioutas, C. The relative importance of tailpipe and non-tailpipe emissions on the oxidative potential of ambient particles in Los Angeles, CA. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 189, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Xu, L.; Peltier, R.E.; Russell, A.G.; Ng, N.L.; Weber, R.J. Organic Aerosols Associated with the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Water-Soluble PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4646–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagai, M.; Saito, H.; Ichinose, T.; Kodama, M.; Mori, Y. Biological effects of diesel exhaust particles. I. In vitro production of superoxide and in vivo toxicity in mouse. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1993, 14, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Fang, T.; Verma, V.; Zeng, L.; Weber, R.J. A method for measuring total aerosol oxidative potential (OP) with the dithiothreitol (DTT) assay and comparisons between an urban and roadside site of water-soluble and total OP. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2821–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Rico-Martinez, R.; Kotra, N.; King, L.; Liu, J.; Snell, T.W.; Weber, R.J. Contribution of Water-Soluble and Insoluble Components and Their Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Subfractions to the Reactive Oxygen Species-Generating Potential of Fine Ambient Aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11384–11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Jedynska, A.; Hellack, B.; Kooter, I.; Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Cassee, F.R.; Janssen, N.A.H. Measurement of the oxidative potential of PM2.5 and its constituents: The effect of extraction solvent and filter type. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 83, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, A.; Daher, N.; Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Manoli, E.; Karagkiozidou, O.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Shafer, M.M.; et al. Increased Biomass Burning Due to the Economic Crisis in Greece and Its Adverse Impact on Wintertime Air Quality in Thessaloniki. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13313–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q.; Yu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tao, S. Oxidative potential of ambient PM2.5 in the coastal cities of the Bohai Sea, northern China: Seasonal variation and source apportionment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Guo, H.; King, L.; Bates, J.T.; Peltier, R.E.; Edgerton, E.; Russell, A.G.; Weber, R.J. Reactive oxygen species associated with water-soluble PM2.5 in the southeastern United States: Spatiotemporal trends and source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12915–12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreeland, H.; Weber, R.; Bergin, M.; Greenwald, R.; Golan, R.; Russell, A.G.; Verma, V.; Sarnat, J.A. Oxidative potential of PM2.5 during Atlanta rush hour: Measurements of in-vehicle dithiothreitol (DTT) activity. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljevic, B.; Fairfull-Smith, K.E.; Bottle, S.E.; Ristovski, Z.D. The application of profluorescent nitroxides to detect reactive oxygen species derived from combustion-generated particulate matter: Cigarette smoke—A case study. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2224–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayat, F.; Stevanovic, S.; Milic, A.; Miljevic, B.; Nabi, M.N.; Zare, A.; Bottle, S.E.; Brown, R.J.; Ristovski, Z.D. Influence of oxygen content of the certain types of biodiesels on particulate oxidative potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545–546, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.E.; Weber, R.J. Development and testing of an online method to measure ambient fine particulate reactive oxygen species (ROS) based on the 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin (DCFH) assay. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Kreisberg, N.; Hering, S. An online monitor of the oxidative capacity of aerosols (o-MOCA). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Oxidative Potential | PM2.5 | PM10 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Average ± std | Min | Max | Average ± std | |
| OPDTT pmol DTT (min·µg)−1 | 5.06 | 20.90 | 9.43 ± 4.27 | 0.18 | 13.39 | 6.66 ± 3.90 |
| OPDCFH nmol H2O2 eq·µg−1 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.09 ± 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.05 ± 0.05 |
| OPDTT pmol DTT (min·m3)−1 | 153.03 | 638.17 | 365.67 ± 149.74 | 20.99 | 1059.72 | 457.82 ± 290.81 |
| OPDCFH nmol H2O2 eq·m−3 | 0.62 | 6.38 | 3.14 ± 1.65 | 0.83 | 7.25 | 3.20 ± 1.60 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jovanovic, M.V.; Savic, J.Z.; Salimi, F.; Stevanovic, S.; Brown, R.A.; Jovasevic-Stojanovic, M.; Manojlovic, D.; Bartonova, A.; Bottle, S.; Ristovski, Z.D. Measurements of Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter at Belgrade Tunnel; Comparison of BPEAnit, DTT and DCFH Assays. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16244906
Jovanovic MV, Savic JZ, Salimi F, Stevanovic S, Brown RA, Jovasevic-Stojanovic M, Manojlovic D, Bartonova A, Bottle S, Ristovski ZD. Measurements of Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter at Belgrade Tunnel; Comparison of BPEAnit, DTT and DCFH Assays. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(24):4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16244906
Chicago/Turabian StyleJovanovic, Maja V., Jasmina Z. Savic, Farhad Salimi, Svetlana Stevanovic, Reece A. Brown, Milena Jovasevic-Stojanovic, Dragan Manojlovic, Alena Bartonova, Steven Bottle, and Zoran D. Ristovski. 2019. "Measurements of Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter at Belgrade Tunnel; Comparison of BPEAnit, DTT and DCFH Assays" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 24: 4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16244906
APA StyleJovanovic, M. V., Savic, J. Z., Salimi, F., Stevanovic, S., Brown, R. A., Jovasevic-Stojanovic, M., Manojlovic, D., Bartonova, A., Bottle, S., & Ristovski, Z. D. (2019). Measurements of Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter at Belgrade Tunnel; Comparison of BPEAnit, DTT and DCFH Assays. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(24), 4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16244906







