Association between Club Sports Participation and Physical Fitness across 6- to 14-Year-Old Austrian Youth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.2. Physical Fitness and Sports Participation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
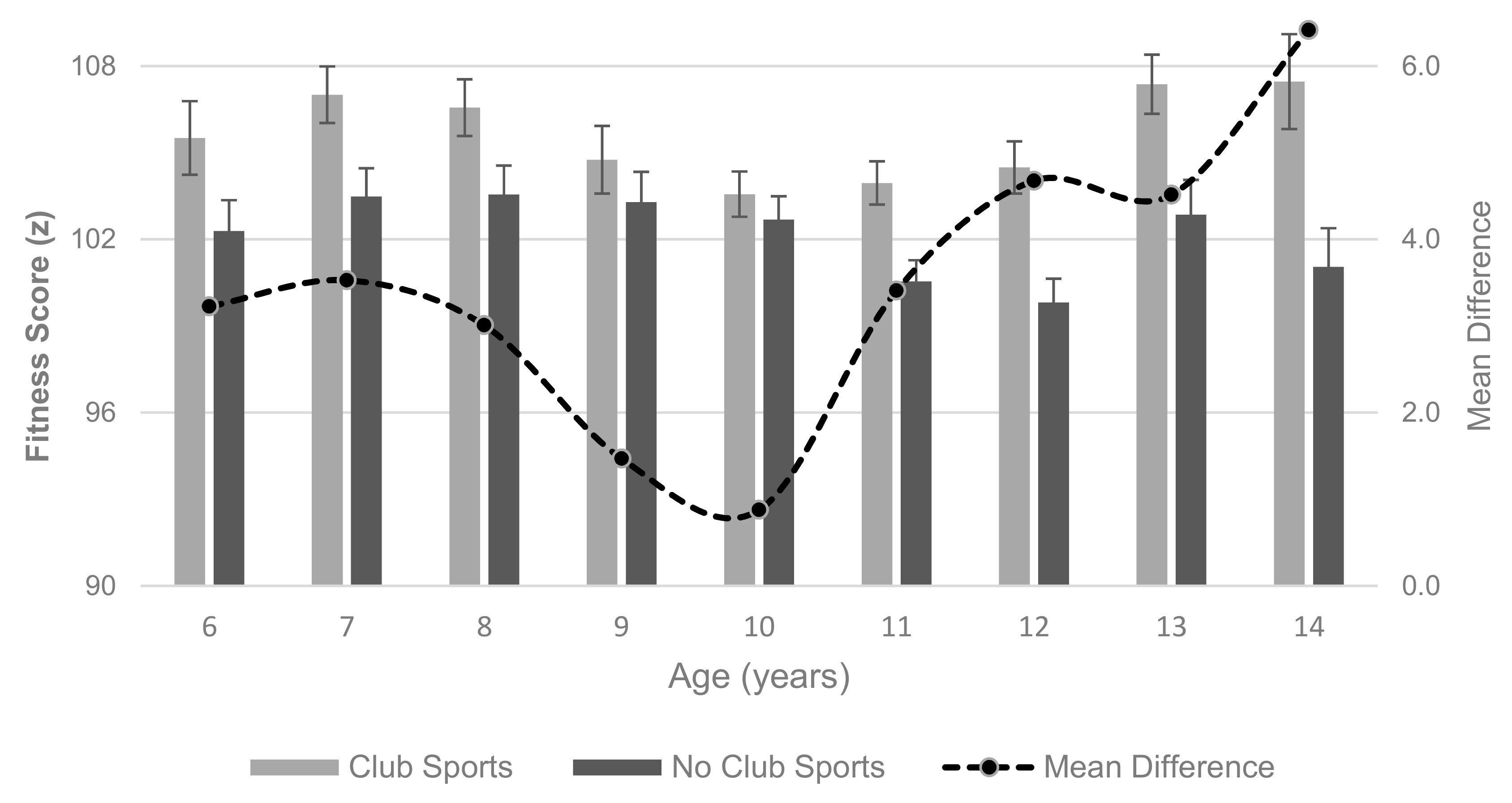
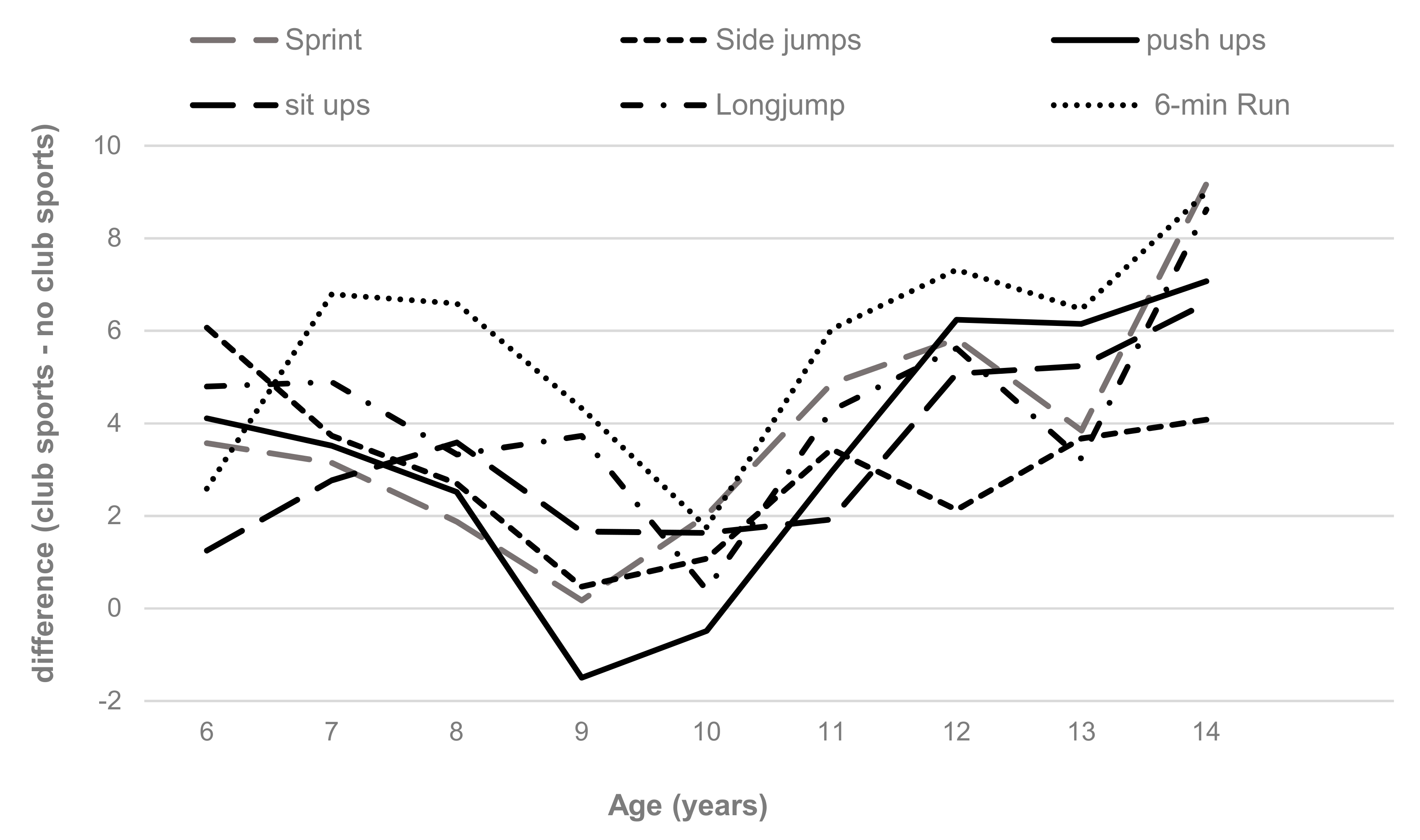
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trost, S.; Blair, S.; Khan, K. Physical inactivity remains the greatest public health problem of the 21st century: Evidence, improved methods and solutions using the ‘7 insvestments that work’ as a framework. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Saltin, B. Exercise as medicine—Evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Health Behavior in School-Aged Children (HBSC) Study: International Report from the 2013/2014 Survey; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Barnes, J.D.; González, S.A.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Onywera, V.O.; Reilly, J.J.; Tomkinson, G.R. Global Matrix 2.0: Report Card Grades on the Physical Activity of Children and Youth Comparing 38 Countries. J. Phys. Act. Health 2016, 13, S343–S366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hecke, L.; Loyen, A.; Verloigne, M.; Van der Ploeg, H.P.; Lakerveld, J.; Brug, J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Ekelund, U.; Donnelly, A.; Hendriksen, I.; et al. Variation in population levels of physical activity in European children and adolescents according to cross-European studies: A systematic literature review within DEDIPAC. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, R. Tracking of physical activity and physical fitness across the lifespan. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1996, 67, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.E.; Williams, D.R. Inflammatory factors, physical activity, and physical fitness in young people. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2008, 18, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenson, G.S.; Srnivasan, S.R.; Group, B.H.S. Cardiovascular risk factors in youth with implications for aging: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Neurobiol. Aging 2005, 26, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollman, J.; Norton, K.; Norton, L. Evidence for secular trends in children’s physical activity behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, W.B.; Malina, R.M.; Blimkie, C.J.; Daniels, S.R.; Dishman, R.K.; Gutin, B.; Hergenroeder, A.C.; Must, A.; Nixon, P.A.; Pivarnik, J.M.; et al. Evidence based physical activity for school-age youth. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; King, N.A.; Armstrong, T.P. The contribution of physical activity and sedentary behaviours to the growth and development of children and adolescents: Implications for overweight and obesity. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser-Jovy, S.; Scheu, A.; Greier, K. Media use, sports activities, and motor fitness in childhood and adolescence. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2017, 129, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, S.J.; Marshall, S.J.; Gorely, T.; Cameron, N. Temporal and environmental patterns of sedentary and active behaviors during adolescents’ leisure time. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2009, 16, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkinson, G.R.; Olds, T.S. Secular changes in pediatric aerobic fitness test performance: The global picture. Med. Sport Sci. 2007, 50, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Runhaar, J.; Collard, D.C.; Singh, A.S.; Kemper, H.C.; van Mechelen, W.; Chinapaw, M. Motor fitness in Dutch youth: Differences over a 26-year period (1980–2006). J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, B.J.; Blizzard, L.; Tomkinson, G.R.; Lycett, K.; Wake, M.; Burgner, D.; Ranganathan, S.; Juonala, M.; Dwyer, T.; Venn, A.J.; et al. The great leap backward: Changes in the jumping performance of Australian children aged 11-12-years between 1985 and 2015. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjöström, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintjens, S.; Menting, M.D.; Daams, J.G.; van Poppel, M.N.M.; Roseboom, T.J.; Gemke, R.J.B.J. Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Childhood and Adolescence Affects Future Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2577–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Santos, D.A.; Hillman, C.H.; Sardinha, L.B. How does academic achievement relate to cardiorespiratory fitness, slef-reported physical activity and objectively reported physical activity: A systematic review in children and adolescents aged 6–18 years. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.M.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Physical activity and fitness in an international growth standard for preadolescent and adolescent children. Food Nutr. Bull. 2006, 27, S295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R. Children and adoelscents in the sport culture: The overwhelming majority to the select few. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2009, 7, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Ekelund, U.; Sardinha, L. Associations between organized sports participation and objectively measured physical activity, sedentary time and weight status in youth. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickel, E.E.; Eisenmann, J.C. Contribution of youth sport to total daily physical activity among 6- to 12-yr-old boys. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, L.; Misigoj-Duracovic, M.; Devrnja, A.; Podnar, H.; Petric, V.; Soric, M. Tracking of physical activity, sport participation, and sedentary behaviors over four years of high school. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, L.L.; O’Hara, B.J.; Rogers, K.; St. George, A.; Bauman, A. Contribution of organized and nonorganized activity to children’s motor skills and fitness. J. Sch. Health 2014, 84, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.J.; Møller, N.C.; Andersen, L.B.; Wedderkopp, N. Organized Sport Participation Is Associated with Higher Levels of Overall Health-Related Physical Activity in Children (CHAMPS Study-DK). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Pope, Z.; Gao, Z. The Role of Youth Sports in Promoting Children’s Physical Activity and Preventing Pediatric Obesity: A Systematic Review. Behav. Med. 2018, 44, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokko, S.; Martin, L.; Geidne, S.; Van Hoye, A.; Lane, A.; Meganck, J.; Scheerder, J.; Seghers, J.; Villberg, J.; Kudlacek, M.; et al. Does sports club participation contribute to physical activity among children and adolescents? A comparison across six European countries. Scand. J. Public Health 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riso, E.M.; Toplaan, L.; Viira, P.; Vaiksaar, S.; Jürimäe, J. Physical fitness and physical activity of 6–7-year-old children according to weight status and sports participation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallal, P.C.; Wells, J.C.; Reichert, F.F.; Anselmi, L.; Victora, C.G. Early determinants of physical activity in adolescence: Prospective birth cohort study. BMJ 2006, 332, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, M.R.; Araújo, C.L.; Cozzensa da Silva, M.; Hallal, P.C. Tracking of physical activity from adolescence to adulthood: A population-based study. Rev. Saude Publica 2007, 41, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammelin, T.; Näyhä, S.; Hills, A.P.; Järvelin, M.R. Adolescent participation in sports and adult physical activity. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 24, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola, T.; Kalaja, S.; Liukkonen, J.; Jutila, A.; Virtanen, P.; Watt, A. Relations among physical activity patterns, lifestyle activities, and fundamental movement skills for Finnish students in grade 7. Percept. Mot. Skills 2009, 108, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.; Carolina Reyes, A.; Moura-Dos-Santos, M.A.; Pereira, S.; Natacha Gomes, T.; Tani, G.; Vasconcelos, O.; Chaves, R.N.; Garganta, R.; Barreira, T.V.; et al. A multi-level analysis of individual- and school-level correlates of physical fitness in children. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2018, 45, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.; Queiroz, D.; Silva, J.; Feitoza, A.; Cattuzzo, M. Relationship between organized physical activity and motor competence in teenagers. Am. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2017, 5, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.J.; Larouch, R.; Tremblay, M.S. The association between physical fitness and health in a nationally representative sample of Canadian children and youth aged 6 to 17 years. Health Promot. Chronic. Dis. Prev. Can. 2019, 39, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Wabitsch, M.; Kunze, D.; Geller, F.; Geiß, H.C.; Hesse, V.; von Hippel, A.; Jaeger, U.; Johnsen, D.; Korte, W.; et al. Perzentile für den Body-mass-Index für das Kindes-und Jugendalter unter Heranziehung verschiedener deutscher Stichproben. Mon. Kinderheilkd. 2001, 149, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bös, K.; Schlenker, L.; Büsch, D.; Lämmle, L.; Müller, H.; Oberger, J.; Seidl, I.; Tittlbach, S. Deutscher Motorik-Test 6-18 (DMT6-18) [German Motor Abilities Test 6-18 (DMT6-18)]; Czwalina: Hamburg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Drenowatz, C.; Greier, K. Cross-sectional and longitudinal association of sports participation, media consumption and motor competence in youth. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.M.; Bouchard, C.; Bar-Or, O. Growth, Maturation, and Physical Activity, 2nd ed.; Human Kinectics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, M.N.; Nielsen, C.M.; Ørntoft, C.Ø.; Randers, M.B.; Manniche, V.; Hansen, L.; Hansen, P.R.; Bangsbo, J.; Krustrup, P. Physical Fitness and Body Composition in 8-10-Year-Old Danish Children Are Associated With Sports Club Participation. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 3425–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, R.M.; Telford, R.D.; Cochrane, T.; Cunningham, R.B.; Olive, L.S.; Davey, R. The influence of sport club participation on physical activity, fitness and body fat during childhood and adolescence: The LOOK Longitudinal Study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahner, L.; Muehlbauer, T.; Schmid, M.; Meyer, U.; Puder, J.J.; Kriemler, S. Association of sports club participation with fitness and fatness in children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, I.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Perez-Gomez, J.; Jimenez-Ramirez, J.; Serrano-Sanchez, J.A.; Dorado, C.; Calbet, J.A. Influence of extracurricular sports activities on body composition and physical fitness in boys: A 3-year longitudinal study. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krustrup, P.; Hansen, P.R.; Nielsen, C.M.; Larsen, M.N.; Randers, M.B.; Manniche, V.; Hansen, L.; Dvorak, J.; Bangsbo, J. Structural and functional cardiac adaptations to a 10-week school-based football intervention for 9-10-year-old children. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faude, O.; Kerper, O.; Multhaupt, M.; Winter, C.; Beziel, K.; Junge, A.; Meyer, T. Football to tackle overweight in children. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriemler, S.; Meyer, U.; Martin, E.; van Sluijs, E.M.; Andersen, L.B.; Martin, B.W. Effect of school-based interventions on physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents: A review of reviews and systematic update. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbins, M.; Husson, H.; DeCorby, K.; LaRocca, R.L. School-based physical activity programs for promoting physical activity and fitness in children and adolescents aged 6 to 18. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, R. The economics of physical activity: Societal trends and rationales for interventions. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2004, 27, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, J.; Bulten, R.; King-Dowling, S.; Arbour-Nicitopoulos, K. A Longitudinal Study of the Effect of Organized Physical Activity on Free Active Play. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 1772–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørntoft, C.; Larsen, M.N.; Madsen, M.; Sandager, L.; Lundager, I.; Møller, A.; Hansen, L.; Madsen, E.E.; Elbe, A.M.; Ottesen, L.; et al. Physical Fitness and Body Composition in 10-12-Year-Old Danish Children in Relation to Leisure-Time Club-Based Sporting Activities. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9807569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenegger, V.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Kriemler, S.; Nydegger, A.; Zahner, L.; Niederer, I.; Bürgi, F.; Puder, J.J. Differences in aerobic fitness and lifestyle characteristics in preschoolers according to their weight status and sports club participation. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirard, J.R.; Pfeiffer, K.A.; Dowda, M.; Pate, R.R. Race differences in activity, fitness, and BMI in female eighth graders categorized by sports participation status. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2008, 20, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koorts, H.; Timperio, A.; Arundell, L.; Parker, K.; Abbott, G.; Salmon, J. Is sport enough? Contribution of sport to overall moderate- to vigorous-intensity physical activity among adolescents. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.B.; Sardinha, L.B.; Froberg, K.; Riddoch, C.J.; Page, A.S.; Anderssen, S.A. Fitness, fatness and clustering of cardiovascular risk factors in children from Denmark, Estonia and Portugal: The European Youth Heart Study. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2008, 3, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, E.L.; Baker, J.S.; Buchan, D.S.; Stratton, G.; Fairclough, S.J.; Foweather, L.; Gobbi, R.; Graves, L.E.; Hopkins, N.; Boddy, L.M. Cardiorespiratory fitness predicts clustered cardiometabolic risk in 10-11.9-year-olds. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2013, 172, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gobbi, R.; Davies, I.G.; Fairclough, S.J.; Mackintosh, K.A.; Warburton, G.L.; Stratton, G.; George, K.P.; Hackett, A.F.; Boddy, L.M. Clustered cardiometabolic risk, cardiorespiratory fitness and physical activity in 10-11 year-old children. The CHANGE! Project Baseline. Arch. Exerc. Health Dis. 2012, 3, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Health and Social Care. Start Active, Stay Active: A Report on Physical Activity for Health from the Four Home Countries’ Chief Medical Officers; Department of Health: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, T.F.; Stovitz, S.D.; Thomas, M.; LaVoi, N.M.; Bauer, K.W.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Do youth sports prevent pediatric obesity? A systematic review and commentary. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2011, 10, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, I.; Vicente-Rodríguez, G.; Jimenez-Ramirez, J.; Dorado, C.; Serrano-Sanchez, J.A.; Calbet, J.A. Regular participation in sports is associated with enhanced physical fitness and lower fat mass in prepubertal boys. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, A.E. Updating the evidence that physical activity is good for health: An epidemiological review 2000–2003. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2004, 7, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliaferro, L.A.; Rienzo, B.A.; Donovan, K.A. Relationships between youth sport participation and selected health risk behaviors from 1999 to 2007. J. Sch. Health 2010, 80, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eime, R.M.; Young, J.A.; Harvey, J.T.; Charity, M.J.; Payne, W.R. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for children and adolescents: Informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimech, A.; Seiler, R. Extra-curricular sport participation: A potential buffer against social anxiety symptoms in primary school children. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2011, 12, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, N.; Kingsley, B.; Tink, L.; Scherer, J. Benefits and challenges assocaited with sport participation by children and parents from low-income families. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2011, 12, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring-Dimitriou, S.; Krustrup, P.; Coelho-E-Silva, M.J.; Mota, J.; Seabra, A.; Rego, C.; Mazur, A.; Vlachopapadopoulou, E.; Caroli, M.; Frelut, M.L.; et al. Could sport be part of pediatric obesity prevention and treatment? Expert conclusions from the 28th European Childhood Obesity Group Congress. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age Group (N, % Male) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI PCT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 years (N = 254, 55.9%) | 121.8 ± 6.1 | 24.1 ± 4.7 | 56.1 ± 28.3 |
| 7 years (N = 354, 52.3%) | 126.5 ± 5.8 | 26.5 ± 5.1 | 55.5 ± 27.9 |
| 8 years (N = 347, 52.7%) | 131.5 ± 6.7 | 29.8 ± 6.4 | 56.7 ± 29.6 |
| 9 years (N = 279, 52.3%) | 137.2 ± 6.7 | 33.8 ± 7.8 | 58.8 ± 29.7 |
| 10 years (N = 542, 55.7%) | 144.2 ± 7.5 | 37.9 ± 9.1 | 55.5 ± 30.7 |
| 11 years (N = 620, 55.5%) | 149.0 ± 7.9 | 42.2 ± 11.0 | 55.8 ± 30.3 |
| 12 years (N = 459, 57.7%) | 156.5 ± 7.3 | 49.3 ± 12.5 | 59.8 ± 30.5 |
| 13 years (N = 280, 57.2%) | 161.4 ± 7.9 | 54.1 ± 12.9 | 61.1 ± 29.1 |
| 14 years (N = 158, 55.7%) | 164.5 ± 8.3 | 58.2 ± 12.8 | 61.9 ± 28.6 |
| 6 Years | 7 Years | 8 Years | 9 Years | 10 Years | 11 Years | 12 Years | 13 Years | 14 Years | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sprint (sec) | Club | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 3.6 ± 0.3 |
| No Club | 5.0 ± 0.6 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 4.2 ± 0.4 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.4 | |
| Side Jump (reps) | Club | 24.3 ± 5.5 | 28.5 ± 6.9 | 33.8 ± 7.1 | 35.1 ± 7.6 | 36.4 ± 6.5 | 40.4 ± 7.7 | 43.6 ± 7.7 | 48.6 ± 7.4 | 48.8 ± 5.6 |
| No Club | 21.7 ± 6.2 | 25.7 ± 6.0 | 31.4 ± 7.3 | 34.6 ± 7.3 | 35.6 ± 6.5 | 37.8 ± 7.4 | 41.2 ± 6.7 | 44.4 ± 7.0 | 44.3 ± 5.9 | |
| Long Jump (cm) | Club | 116.5 ± 17.4 | 124.9 ± 18.0 | 131.1 ± 19.7 | 137.2 ± 19.7 | 144.6 ± 21.0 | 156.2 ± 21.5 | 164.5 ± 26.5 | 171.0 ± 25.8 | 184.8 ± 27.4 |
| No Club | 107.1 ± 18.3 | 114.9 ± 18.9 | 123.3 ± 18.9 | 128.6 ± 21.5 | 144.2 ± 22.7 | 146.2 ± 22.5 | 141.1 ± 22.5 | 164.1 ± 30.9 | 159.2 ± 29.9 | |
| Push-Ups (reps) | Club | 12.2 ± 4.1 | 14.3 ± 4.6 | 15.9 ± 4.2 | 14.8 ± 4.4 | 14.7 ± 6.5 | 15.6 ± 5.9 | 16.5 ± 5.9 | 19.3 ± 4.2 | 19.7 ± 4.6 |
| No Club | 10.7 ± 3.9 | 12.7 ± 4.3 | 14.9 ± 4.8 | 15.3 ± 4.2 | 14.9 ± 6.2 | 14.4 ± 6.0 | 14.1 ± 5.6 | 17.1 ± 5.2 | 16.5 ± 3.4 | |
| Sit Ups (reps) | Club | 14.6 ± 5.7 | 18.2 ± 5.0 | 21.2 ± 4.9 | 21.6 ± 5.4 | 21.8 ± 6.2 | 22.8 ± 6.3 | 24.5 ± 5.9 | 27.5 ± 6.3 | 28.1 ± 5.7 |
| No Club | 13.4 ± 5.7 | 16.2 ± 5.6 | 18.5 ± 5.3 | 20.5 ± 5.3 | 20.9 ± 6.3 | 21.4 ± 6.4 | 21.2 ± 5.4 | 24.8 ± 6.2 | 24.4 ± 5.1 | |
| 6-Min Run (m) | Club | 877 ± 138 | 950 ± 132 | 963 ± 133 | 956 ± 163 | 987 ± 161 | 1056 ± 158 | 1084 ± 185 | 1092 ± 178 | 1107 ± 167 |
| No Club | 831 ± 149 | 855 ± 130 | 871 ± 136 | 890 ± 124 | 968 ± 154 | 959 ± 157 | 962 ± 177 | 991 ± 172 | 943 ± 165 | |
| Ba-lance (steps) | Club | 25.5 ± 9.3 | 31.1 ± 9.2 | 34.3 ± 9.7 | 36.0 ± 8.4 | 37.8 ± 9.1 | 38.6 ± 8.4 | 39.9 ± 7.9 | 41.3 ± 7.8 | 41.9 ± 7.2 |
| No Club | 25.0 ± 9.7 | 28.4 ± 10.0 | 31.3 ± 9.1 | 35.8 ± 9.0 | 35.7 ± 9.8 | 36.6 ± 8.8 | 36.8 ± 8.8 | 37.1 ± 9.6 | 37.0 ± 8.2 | |
| Stand & Reach (cm)* | Club | 1.7 ± 4.7 | 1.5 ± 6.0 | 0.6 ± 7.5 | –0.1 ± 6.5 | –0.7 ± 7.5 | –0.7 ± 7.7 | 0.2 ± 8.4 | 2.7 ± 9.3 | 4.0 ± 8.9 |
| No Club | 1.2 ± 6.2 | 1.8 ± 6.1 | 0.3 ± 6.7 | –1.3 ± 7.4 | –1.3 ± 6.9 | –1.4 ± 7.2 | –1.3 ± 8.8 | 1.4 ± 9.5 | 1.6 ± 9.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drenowatz, C.; Greier, K.; Ruedl, G.; Kopp, M. Association between Club Sports Participation and Physical Fitness across 6- to 14-Year-Old Austrian Youth. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183392
Drenowatz C, Greier K, Ruedl G, Kopp M. Association between Club Sports Participation and Physical Fitness across 6- to 14-Year-Old Austrian Youth. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(18):3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183392
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrenowatz, Clemens, Klaus Greier, Gerhard Ruedl, and Martin Kopp. 2019. "Association between Club Sports Participation and Physical Fitness across 6- to 14-Year-Old Austrian Youth" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 18: 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183392
APA StyleDrenowatz, C., Greier, K., Ruedl, G., & Kopp, M. (2019). Association between Club Sports Participation and Physical Fitness across 6- to 14-Year-Old Austrian Youth. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(18), 3392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16183392








