Correlation between Non-Polio Acute Flaccid Paralysis Rates with Pulse Polio Frequency in India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horsemann, D.M.; Paul, J.R. The incubation period in human poliomyelitis and its implications. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1947, 135, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.; Hlady, W.G.; Andrus, J.K.; Sarkar, S.; Fitzsimmons, J.; Abeykoon, P. Poliomyelitis surveillance: The model used in India for polio eradication. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tangermann, R.H.; Lamoureux, C.; Tallis, G.; Goel, A. The critical role of acute flaccid paralysis surveillance in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative. Int. Health 2017, 9, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Rehman, A. One year surveillance data of acute flaccid paralysis at Bahwal Victoria Hospital Bahawalpur Pakistan. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 23, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Pediatric Society. Surveillance Canadian Pediatric Surveillance Programme Acute Flaccid Paralysis. Available online: http://www.cps.ca/english/Surveillance/CPSP/Studies/acute.htm (accessed on 25 May 2018).
- Marx, A.; Glass, J.D.; Sutter, R.W. Differential diagnosis of acute flaccid paralysis and its role in poliomyelitis surveillance. Epidemiol. Rev. 2000, 2, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO-Recommended Surveillance Standard of Poliomyelitis. Available online: http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/burden/vpd/surveillance_type/active/poliomyelitis_standards/en/ (accessed on 25 May 2018).
- Pan American Health Organisation and World Health Organisations. Polio Weekly Bulletin. Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&view=article&id=295&Itemid=3626&lang=en (accessed on 25 May 2018).
- Kennedy, R.H.; Danielson, M.A.; Mulder, D.W.; Kurland, L.T. Guillain-Barre syndrome: A 42-year epidemiologic and clinical study. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 1978, 53, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcala, H. The differential diagnosis of poliomyelitis and other flaccid paralysis. Biol. Med. Infant Mex. 1993, 50, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram, R. World Bank. A Polio-Free India Is One of the Biggest Achievements in Global Health May 29, 2014. Available online: http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2014/05/29/polio-free-india-biggest-achievements-global-health (accessed on 30 May 2018).
- Vashisht, N.; Puliyel, J. Polio programme: Let us declare victory and move on Indian. J. Med. Ethics 2012, 9, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puliyel, J.; Sathyamala, C.; Banerji, D. Protective efficacy of a monovalent oral type 1 poliovirus vaccine. Lancet 2007, 370, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassly, N.C.; Wenger, J.; Bahl, S.; Sutter, R.W.; Aylward, R.B. Protective efficacy of a monovalent oral type 1 poliovirus vaccine Authors reply. Lancet 2007, 370, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puliyel, J.M.; Gupta, M.A.; Mathew, J.L. Polio eradication and the future for other programmes: Situation analysis for strategic planning in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2007, 125, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sathyamala, C. Polio eradication programme in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2007, 125, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naranjo, C.A.; Busto, U.; Sellers, E.M.; Sandor, P.; Ruiz, I.; Roberts, E.A.; Janecek, E.; Domecq, C.; Greenblatt, D.J. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 30, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnunen, E.; Farkkila, M.; Hovi, T.; Juntunen, J.; Weckstrom, P. Incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome during a nationwide oral poliovirus vaccine campaign. Neurology 1989, 39, 1034–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhari, M.; Rantala, H.; Niemela, M. Cluster of childhood Guillain-Barré cases after an oral poliovaccine campaign (letter). Lancet 1989, 2, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anlar, O.; Tombul, T.; Arslan, S.; Akdeniz, H.; Caksen, H.; Gundem, A.; Akbayram, S. Report of five children with Guillain-Barré syndrome following a nationwide oral polio vaccine campaign in Turkey. Neurol. India 2003, 51, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Vaccine Safety Committee. Adverse Events Associated with Childhood Vaccines Evidence Bearing on Causality; Stratton, K.R., Howe, C.J., Johnston, R.B., Jr., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1994; ISBN-10 0-309-04895-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vashisht, N.; Puliyel, J.; Sreenivas, V. Trends in non-polio acute flaccid paralysis incidence in India 2000–2013. F1000 Res. (Poster) 2018, 7, 202, doi:10.7490/f1000research.1115276.1. Pediatrics 2015, 135 (Suppl. S1), S16–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
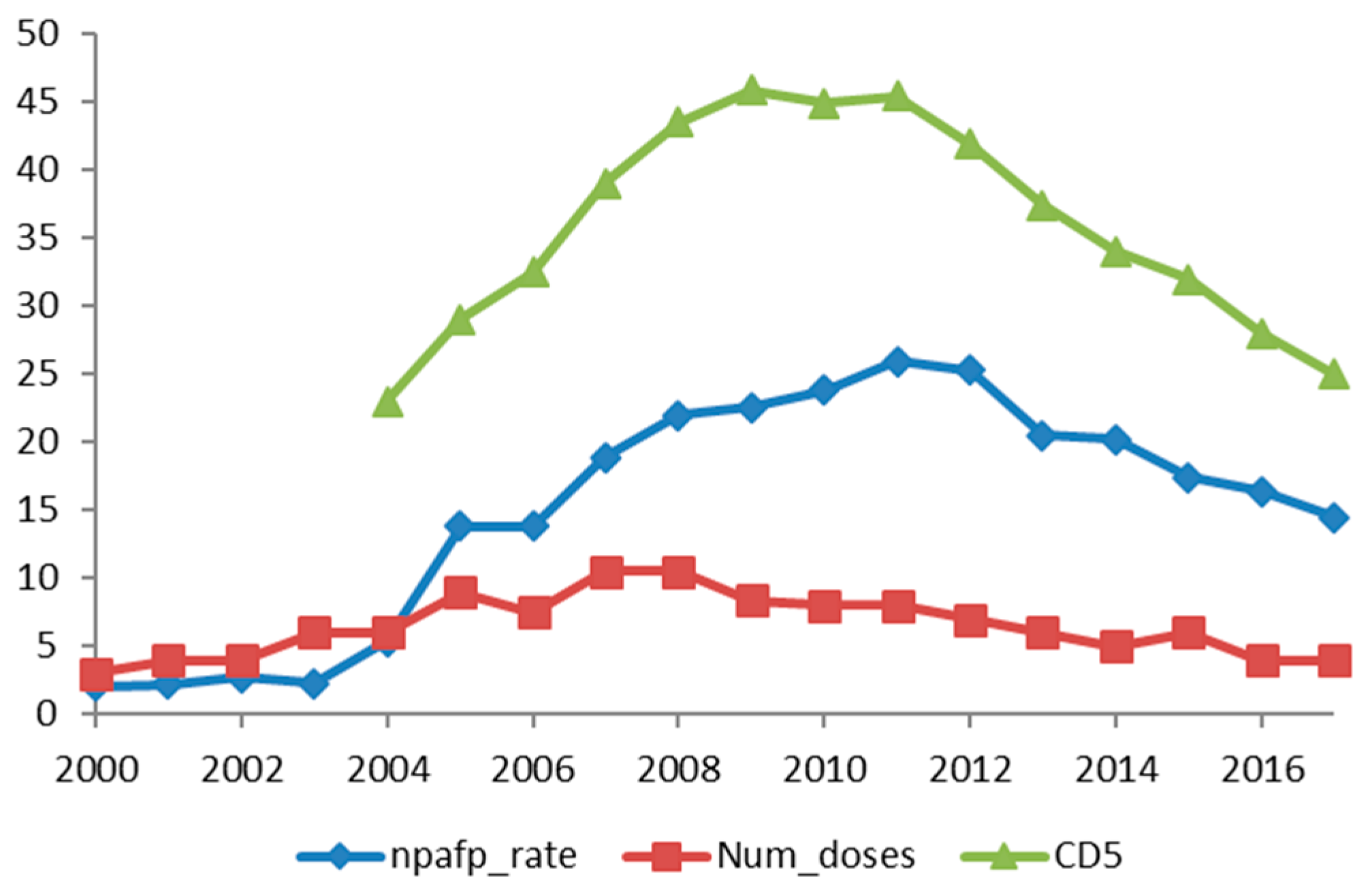
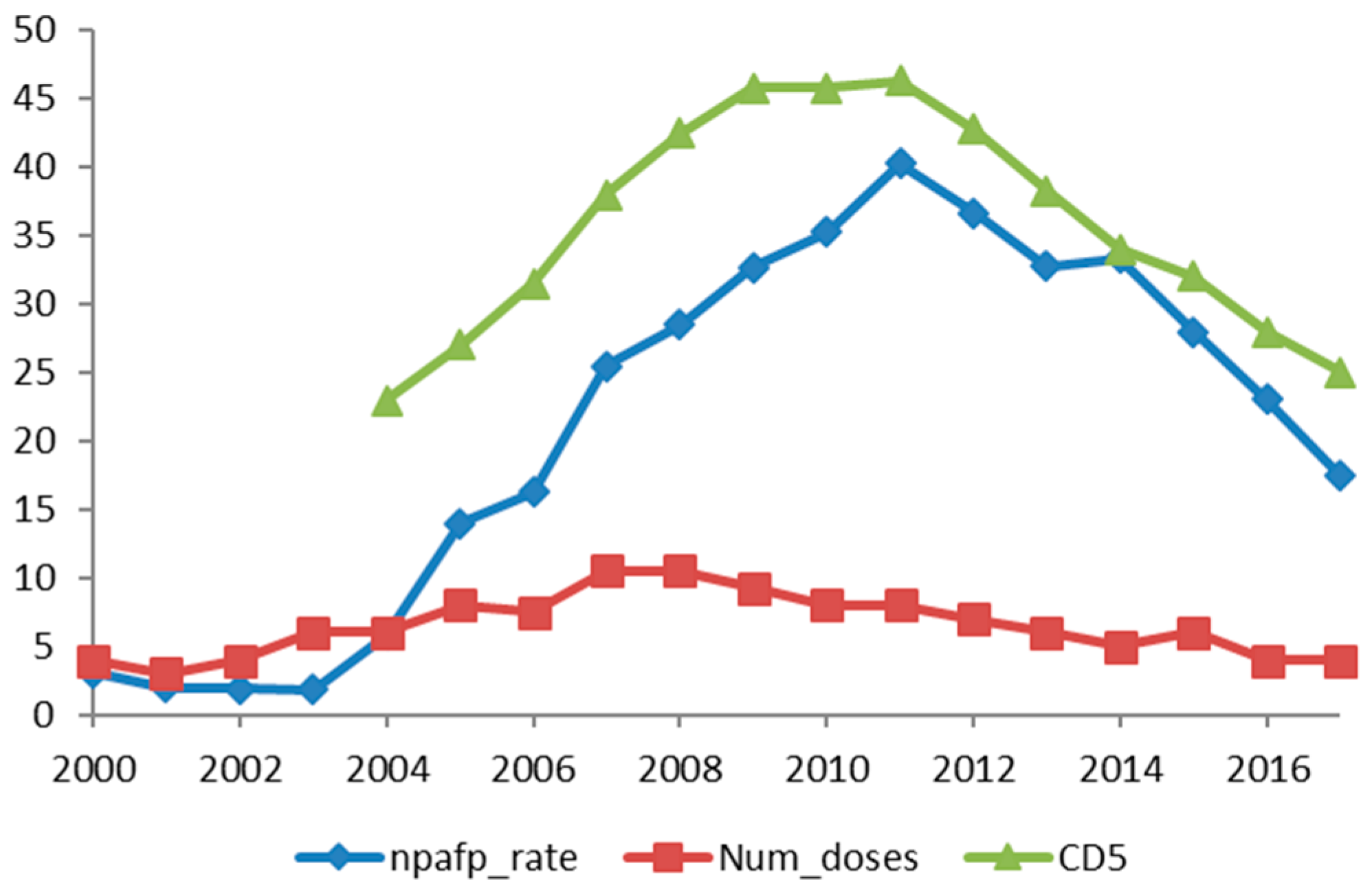
| Serial No. | Number of Years of Cumulative Doses | NPAFP Rate Regression Coefficient R | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 Year | 0.52 | p < 0.001 |
| 2 | 2 Years | 0.60 | p < 0.001 |
| 3 | 3 Years | 0.67 | p < 0.001 |
| 4 | 4 Years | 0.72 | p < 0.001 |
| 5 | 5 Years | 0.76 | p < 0.001 |
| 6 | 6 Years | 0.75 | p < 0.001 |
| Year | AFP Rate | NPAFP Rate | AFP | NPAFP | Expected NPAFP | Excess NPAFP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2.16 | 1.94 | 7260 | 7485 | −225 | |
| 2001 | 1.91 | 1.75 | 7510 | 6858 | 7838 | −980 |
| 2002 | 2.45 | 1.87 | 9713 | 7404 | 7919 | −515 |
| October 2003 | 2.11 | 1.67 | 6850 | 5417 | 6487 | −1070 |
| 2004 | 3.24 | 3.11 | 13,274 | 12,765 | 8209 | 4556 |
| 2005 | 6.54 | 6.43 | 27,049 | 26,586 | 8269 | 18,317 |
| 2006 | 7.63 | 7.35 | 32,194 | 31,024 | 8442 | 22,582 |
| 2007 | 9.71 | 9.32 | 41,534 | 39,831 | 8547 | 31,284 |
| 2008 | 10.5 | 9.93 | 45,586 | 43,103 | 8681 | 34,422 |
| 2008 | 11.64 | 11.33 | 50,412 | 49,082 | 8664 | 40,418 |
| 2010 | 12.7 | 12.65 | 55,785 | 55,548 | 8782 | 46,766 |
| 2011 | 13.55 | 13.35 | 60,750 | 59,849 | 8966 | 50,883 |
| 2012 | 13.97 | 13.61 | 61,038 | 59,462 | 8738 | 50,724 |
| 2013 | 12.51 | 12.48 | 54,645 | 54,511 | 8736 | 45,775 |
| 2014 | 12.48 | 12.48 | 53,933 | 53,910 | 8639 | 45,271 |
| 2015 | 10.78 | 10.77 | 46,970 | 46,957 | 8720 | 38,237 |
| 2016 | 10.61 | 10.16 | 46,524 | 44,571 | 8774 | 35,797 |
| 2017 | 8.97 | 8.72 | 39,339 | 38,232 | 8769 | 29,463 |
| Totals | 653,106 | 642,370 | 150,666 | 49,1704 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhiman, R.; Prakash, S.C.; Sreenivas, V.; Puliyel, J. Correlation between Non-Polio Acute Flaccid Paralysis Rates with Pulse Polio Frequency in India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081755
Dhiman R, Prakash SC, Sreenivas V, Puliyel J. Correlation between Non-Polio Acute Flaccid Paralysis Rates with Pulse Polio Frequency in India. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(8):1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081755
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhiman, Rachana, Sandeep C. Prakash, V. Sreenivas, and Jacob Puliyel. 2018. "Correlation between Non-Polio Acute Flaccid Paralysis Rates with Pulse Polio Frequency in India" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 8: 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081755
APA StyleDhiman, R., Prakash, S. C., Sreenivas, V., & Puliyel, J. (2018). Correlation between Non-Polio Acute Flaccid Paralysis Rates with Pulse Polio Frequency in India. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(8), 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081755





